Submitted:
01 August 2024
Posted:
05 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Statistical Risk of Familial Pancreatic Cancer
Genes Associated with Familial Pancreatic Cancer
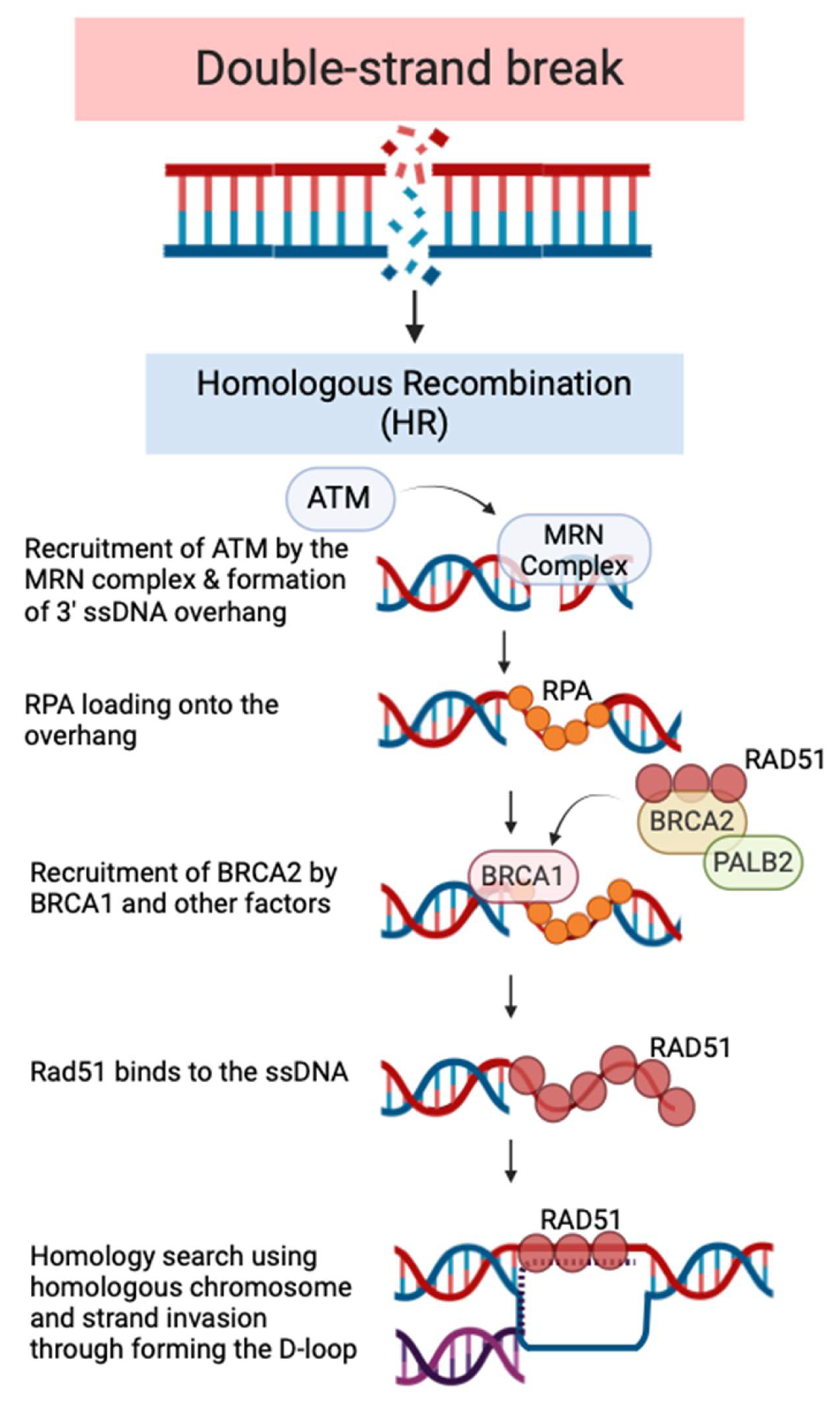
Double-Stranded Breaks (DSB) and Homologous Recombination (HR) Pathway
FPC and PARP Inhibitors
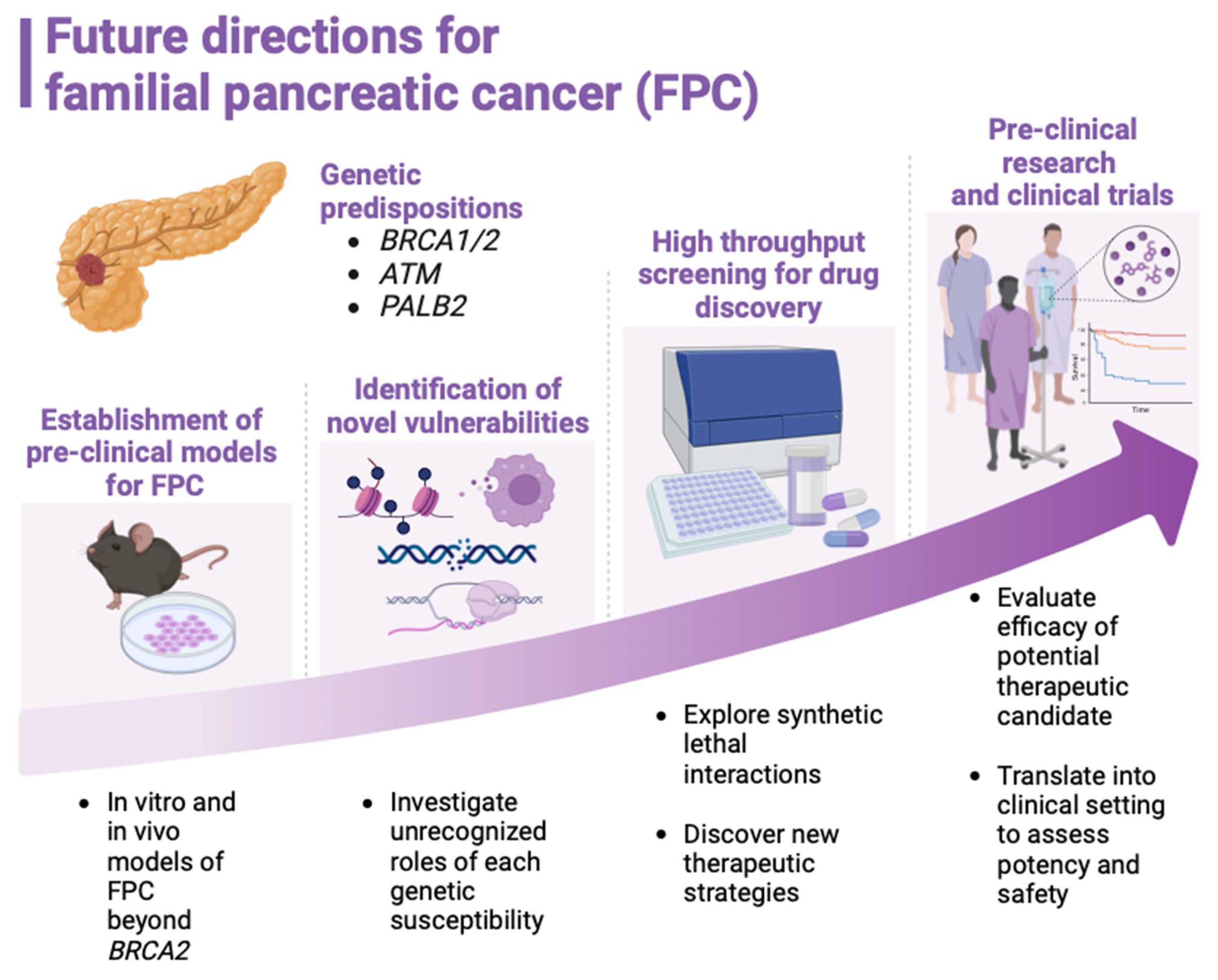
Pre-clinical Models of FPC
Current Status of Basic Research on FPC
Conclusion
Acknowledgment
References
- Tempero, M.A. NCCN Guidelines Updates: Pancreatic Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2019, 17, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, X.Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Wu, X.L.; Zhou, C.H.; Yan, J.Y.; Hu, B.Y.; et al. The Molecular Biology of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Translational Challenges and Clinical Perspectives. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.C.; Rajbhandari, N.; Liu, C.; Sakamoto, K.; Zhang, Q.; Triplett, A.A.; Batra, S.K.; Opavsky, R.; Felsher, D.W.; DiMaio, D.J.; et al. Dormant Cancer Cells Contribute to Residual Disease in a Model of Reversible Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosens, L.A.A.; Hackeng, W.M.; Offerhaus, J.; Hruban, R.H.; Wood, L.D. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Pathology: Changing “Landscape. ” J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 6, 358–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarski, R. The Role of BRCA Testing in Hereditary Pancreatic and Prostate Cancer Families. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. B. 2019, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, G.M. Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.P.; Brune, K.A.; Petersen, G.M.; Goggins, M.; Tersmette, A.C.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Griffin, C.; Cameron, J.L.; Yeo, C.J.; Kern, S.; et al. Prospective Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Familial Pancreatic Cancer Kindreds. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 2634–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, R.R.; Rabe, K.G.; Olswold, C.; De Andrade, M.; Petersen, G.M. Risk of Malignancy in First-Degree Relatives of Patients with Pancreatic Carcinoma. Cancer 2005, 104, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tersmette, A.C.; Petersen, G.M.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Falatko, F.C.; Brune, K.A.; Goggins, M.; Rozenblum, E.; Wilentz, R.E.; Yeo, C.J.; Cameron, J.L.; et al. Increased Risk of Incident Pancreatic Cancer among First-Degree Relatives of Patients with Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 738–744. [Google Scholar]
- Permuth-Wey, J.; Egan, K.M. Family History Is a Significant Risk Factor for Pancreatic Cancer: Results from a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Fam. Cancer 2009, 8, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFaul, C.D.; Greenhalf, W.; Earl, J.; Howes, N.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Kress, R.; Sina-Frey, M.; Rieder, H.; Hahn, S.; Bartsch, D.K. Anticipation in Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Gut 2006, 55, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.P. Genetic Susceptibility to Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2012, 51, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, K.M.; Brune, K.A.; Griffin, C.; Sollenberger, J.E.; Petersen, G.M.; Bansal, R.; Hruban, R.H.; Kern, S.E. Evaluation of Candidate Genes MAP2K4, MADH4, ACVR1B, and BRCA2 in Familial Pancreatic Cancer: Deleterious BRCA2 Mutations in 17%. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 3789–3793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hahn, S.A.; Greenhalf, B.; Ellis, I.; Sina-Frey, M.; Rieder, H.; Korte, B.; Gerdes, B.; Kress, R.; Ziegler, A.; Raeburn, J.A.; et al. BRCA2 Germline Mutations in Familial Pancreatic Carcinoma. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moynahan, M.E.; Pierce, A.J.; Jasin, M. BRCA2 Is Required for Homology-Directed Repair of Chromosomal Breaks. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Miki, Y. Role of BRCA1 and BRCA2 as Regulators of DNA Repair, Transcription, and Cell Cycle in Response to DNA Damage. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.M.; Pierce, A.J.; Oh, J.; Pastink, A.; Jasin, M. Genetic Steps of Mammalian Homologous Repair with Distinct Mutagenic Consequences. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 9305–9316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakem, R. DNA-Damage Repair; the Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. EMBO J. 2008, 27, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narod, S.A.; Foulkes, W.D. BRCA1 and BRCA2: 1994 and Beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, A.; O’Hara, C.; Khan, S.; Shack, L.; Woodward, E.; Maher, E.R.; Lalloo, F.; Evans, D.G.R. Risk of Cancer Other than Breast or Ovarian in Individuals with BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations. Fam. Cancer 2012, 11, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, Z.K.; Salo-Mullen, E.; Patil, S.M.; Pietanza, M.C.; Vijai, J.; Saloustros, E.; Hansen, N.A.L.; Kauff, N.D.; Kurtz, R.C.; Kelsen, D.P.; et al. Prevalence of BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations in Ashkenazi Jewish Families with Breast and Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer 2012, 118, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, D.B.; Rabe, K.G.; Gallinger, S.; Syngal, S.; Schwartz, A.G.; Goggins, M.G.; Hruban, R.H.; Cote, M.L.; McWilliams, R.R.; Roberts, N.J.; et al. BRCA1, BRCA2, PALB2, and CDKN2A Mutations in Familial Pancreatic Cancer: A PACGENE Study. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, N.J.; Norris, A.L.; Petersen, G.M.; Bondy, M.L.; Brand, R.; Gallinger, S.; Kurtz, R.C.; Olson, S.H.; Rustgi, A.K.; Schwartz, A.G.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing Defines the Genetic Heterogeneity of Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, N.J.; Jiao, Y.; Yu, J.; Kopelovich, L.; Petersen, G.M.; Bondy, M.L.; Gallinger, S.; Schwartz, A.G.; Syngal, S.; Cote, M.L.; et al. ATM Mutations in Patients with Hereditary Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivas, U.S.; Tan, B.W.Q.; Vellayappan, B.A.; Jeyasekharan, A.D. ROS and the DNA Damage Response in Cancer. Redox Biol. 2019, 25, 101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pâques, F.; Haber, J.E. Multiple Pathways of Recombination Induced by Double-Strand Breaks in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 349–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murnane, J.P. Telomeres and Chromosome Instability. DNA Repair (Amst). 2006, 5, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastav, M.; De Haro, L.P.; Nickoloff, J.A. Regulation of DNA Double-Strand Break Repair Pathway Choice. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickoloff, J.A. Recombination: Mechanisms and Roles in Tumorigenesis. Encycl. Cancer 2002, 4, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas, P.; Jackason, S.P. Human CtIP Mediates Cell Cycle Control of DNA End Resection and Double Strand Break Repair. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 9558–9565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groelly, F.J.; Fawkes, M.; Dagg, R.A.; Blackford, A.N.; Tarsounas, M. Targeting DNA Damage Response Pathways in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; McCorvie, T.J.; Yates, L.A.; Zhang, X. Structural Basis of Homologous Recombination. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Paulus, B.F.; Wold, M.S. Interactions of Human Replication Protein A with Oligonucleotides. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 14197–14206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Heyer, W.D. Homologous Recombination in DNA Repair and DNA Damage Tolerance. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasin, M.; Rothstein, R. Repair of Strand Breaks by Homologous Recombination. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, H.; McCabe, H.; Lord, C.J.; Tutt, A.H.J.; Johnson, D.A.; Richardson, T.B.; Santarosa, M.; Dillon, K.J.; Hickson, I.; Knights, C.; et al. Targeting the DNA Repair Defect in BRCA Mutant Cells as a Therapeutic Strategy. Nature 2005, 434, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Kanji, Z.S.; Epelbaum, R.; Devaud, N.; Dagan, E.; Holter, S.; Aderka, D.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Kaufman, B.; Gershoni-Baruch, R.; et al. Overall Survival and Clinical Characteristics of Pancreatic Cancer in BRCA Mutation Carriers. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underhill, C.; Toulmonde, M.; Bonnefoi, H. A Review of PARP Inhibitors: From Bench to Bedside. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Macarulla, T.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.-O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.-Y.; et al. Maintenance Olaparib for Germline BRCA -Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shroff, R.T.; Hendifar, A.; McWilliams, R.R.; Geva, R.; Epelbaum, R.; Rolfe, L.; Goble, S.; Lin, K.K.; Biankin, A. V.; Giordano, H.; et al. Rucaparib Monotherapy in Patients With Pancreatic Cancer and a Known Deleterious BRCA Mutation. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, J.; Huang, S.Y.N.; Renaud, A.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, J.; Takeda, S.; Morris, J.; Teicher, B.; Doroshow, J.H.; Pommier, Y. Stereospecific PARP Trapping by BMN 673 and Comparison with Olaparib and Rucaparib. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Rehman, F.L.; Feng, Y.; Boshuizen, J.; Bajrami, I.; Elliott, R.; Wang, B.; Lord, C.J.; Post, L.E.; Ashworth, A. BMN673, a Novel and Highly Potent PARP1/2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Human Cancers with DNA Repair Deficiency. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5003–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bono, J.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Mina, L.; Chugh, R.; Glaspy, J.; Rafii, S.; Kaye, S.; Sachdev, J.; Heymach, J.; Smith, D.C.; et al. Phase I, Dose-Escalation, Two-Part Trial of the PARP Inhibitor Talazoparib in Patients with Advanced Germline BRCA1/2 Mutations and Selected Sporadic Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.A.; Im, S.-A.; Schram, A.M.; Sharp, A.; Balmana, J.; Baird, R.D.; Brown, J.S.; Schwaederle, M.; Pilling, E.A.; Moorthy, G.; et al. Abstract CT007: PETRA: First in Class, First in Human Trial of the next Generation PARP1-Selective Inhibitor AZD5305 in Patients (Pts) with BRCA1/2, PALB2 or RAD51C/D Mutations. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, CT007–CT007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, E.M.; Lee, J.W.; Zalupski, M.; Capanu, M.; Park, J.; Golan, T.; Tahover, E.; Lowery, M.A.; Chou, J.F.; Sahai, V.; et al. Randomized, Multicenter, Phase II Trial of Gemcitabine and Cisplatin with or without Veliparib in Patients with Pancreas Adenocarcinoma and a Germline BRCA/ PALB2 Mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, N.A.; Burchard, P.R.; Dunne, R.F.; Linehan, D.C. Immunologic Strategies in Pancreatic Cancer: Making Cold Tumors Hot. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2789–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhari, A.B.; Chan, G.K.; Gamper, A.M. Targeting the DNA Damage Response for Cancer Therapy by Inhibiting the Kinase Wee1. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.P.; Moser, S.C.; Ganesan, S.; Jonkers, J. Understanding and Overcoming Resistance to PARP Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.L.; Brough, R.; Lord, C.J.; Natrajan, R.; Vatcheva, R.; Levine, D.A.; Boyd, J.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Ashworth, A. Resistance to Therapy Caused by Intragenic Deletion in BRCA2. Nature 2008, 451, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, W.; Swisher, E.M.; Karlan, B.Y.; Agarwal, M.K.; Higgins, J.; Friedman, C.; Villegas, E.; Jacquemont, C.; Farrugia, D.J.; Couch, F.J.; et al. Secondary Mutations as a Mechanism of Cisplatin Resistance in BRCA2-Mutated Cancers. Nature 2008, 451, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, K.K.; Swisher, E.M.; Taniguchi, T. Secondary Mutations of BRCA1/2 and Drug Resistance. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.J.; Yablonovitch, A.; Till, J.E.; Yen, J.; Kiedrowski, L.A.; Hood, R.; O’Hara, M.H.; Teitelbaum, U.; Karasic, T.B.; Schneider, C.; et al. The Clinical Implications of Reversions in Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer and Pathogenic Variants in BRCA1, BRCA2, or PALB2 after Progression on Rucaparib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 5207–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigelt, B.; Comino-Méndez, I.; De Bruijn, I.; Tian, L.; Meisel, J.L.; García-Murillas, I.; Fribbens, C.; Cutts, R.; Martelotto, L.G.; Ng, C.K.Y.; et al. Diverse BRCA1 and BRCA2 Reversion Mutations in Circulating Cell-Free DNA of Therapy-Resistant Breast or Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6708–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrashova, O.; Topp, M.; Nesic, K.; Lieschke, E.; Ho, G.Y.; Harrell, M.I.; Zapparoli, G. V.; Hadley, A.; Holian, R.; Boehm, E.; et al. Methylation of All BRCA1 Copies Predicts Response to the PARP Inhibitor Rucaparib in Ovarian Carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C. Il; Boj, S.F.; Clevers, H.; Tuveson, D.A. Preclinical Models of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoof, J.; Harrold, E.; Mariottino, S.; Lowery, M.A.; Walsh, N. DNA Damage Repair Deficiency in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Preclinical Models and Clinical Perspectives. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casolino, R.; Corbo, V.; Beer, P.; Hwang, C. Il; Paiella, S.; Silvestri, V.; Ottini, L.; Biankin, A. V. Germline Aberrations in Pancreatic Cancer: Implications for Clinical Care. Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiriac, H.; Belleau, P.; Engle, D.D.; Plenker, D.; Deschênes, A.; Somerville, T.D.D.; Froeling, F.E.M.; Burkhart, R.A.; Denroche, R.E.; Jang, G.H.; et al. Organoid Profiling Identifies Common Responders to Chemotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1112–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, I.; Borgida, A.; Cao, P.; Cheung, M.; Pintilie, M.; Bianco, T.; Holter, S.; Ibrahimov, E.; Kumareswaran, R.; Bristow, R.G.; et al. BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Sensitize to Chemotherapy in Patient-Derived Pancreatic Cancer Xenografts. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, C.K.; Booij, T.H.; Grob, L.; Simmler, P.; Toussaint, N.C.; Keller, D.; Taube, D.; Ludwig, V.; Goryachkin, A.; Pauli, C.; et al. Drug Screening and Genome Editing in Human Pancreatic Cancer Organoids Identifies Drug-Gene Interactions and Candidates for off-Label Therapy. Cell Genomics 2022, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Stossel, C.; Atias, D.; Buzhor, E.; Halperin, S.; Cohen, K.; Raitses-Gurevich, M.; Glick, Y.; Raskin, S.; Yehuda, D.; et al. Recapitulating the Clinical Scenario of BRCA-Associated Pancreatic Cancer in Pre-Clinical Models. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Komar, C.A.; Bengsch, F.; Graham, K.; Beatty, G.L. Genetically Engineered Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer: The KPC Model (LSL-KrasG12D/+;LSL-Trp53R172H/+;Pdx-1-Cre), Its Variants, and Their Application in Immuno-Oncology Drug Discovery. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2016, 2016, 14–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariston Gabriel, A.N.; Jiao, Q.; Yvette, U.; Yang, X.; Al-Ameri, S.A.; Du, L.; Wang, Y. shan; Wang, C. Differences between KC and KPC Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Mice Models, in Terms of Their Modeling Biology and Their Clinical Relevance. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, G.; Karikari, C.; Dal Molin, M.; Duringer, S.; Volkmann, P.; Bartsch, D.K.; Bisht, S.; Koorstra, J.B.; Brossart, P.; Maitra, A.; et al. Inactivation of Brca2 Cooperates with Trp53R172H to Induce Invasive Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas in Mice: A Mouse Model of Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Cassidy, L.D.; Pisupati, V.; Jonasson, J.G.; Bjarnason, H.; Eyfjord, J.E.; Karreth, F.A.; Lim, M.; Barber, L.M.; Clatworthy, S.A.; et al. Germline Brca2 Heterozygosity Promotes KrasG12D -Driven Carcinogenesis in a Murine Model of Familial Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, M.; Ohashi, A.; Mondal, G.; Mills, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Sundsbak, R.; Shapiro, V.; Muders, M.H.; Smyrk, T.; et al. Inactivation of Brca2 Promotes Trp53-Associated but Inhibits KrasG12D-Dependent Pancreatic Cancer Development in Mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.; Perkhofer, L.; Liebau, S.; Lin, Q.; Lechel, A.; Feld, F.M.; Hessmann, E.; Gaedcke, J.; Güthle, M.; Zenke, M.; et al. Loss of ATM Accelerates Pancreatic Cancer Formation and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosos, Y.; Escobar, D.; Chiang, M.Y.; Roys, K.; Valentine, V.; Valentine, M.B.; Rehg, J.E.; Sahai, V.; Begley, L.A.; Ye, J.; et al. ATM-Deficiency Increases Genomic Instability and Metastatic Potential in a Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Shakya, R.; Koivisto, C.; Pitarresi, J.R.; Szabolcs, M.; Kladney, R.; Hadjis, A.; MacE, T.A.; Ludwig, T. Murine Models for Familial Pancreatic Cancer: Histopathology, Latency and Drug Sensitivity among Cancers of Palb2, Brca1 and Brca2 Mutant Mouse Strains. PLoS One 2019, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.L.; Shakya, R.; Lipsyc, M.D.; Mitchel, E.B.; Kumar, S.; Hwang, C.; Deng, L.; Devoe, C.; Chabot, J.A.; Szabolcs, M.; et al. High Prevalence of BRCA1 and BRCA2 Germline Mutations with Loss of Heterozygosity in a Series of Resected Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma and Other Neoplastic Lesions. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3396–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, H.E.; Schultz, N.; Thomas, H.D.; Parker, K.M.; Flower, D.; Lopez, E.; Kyle, S.; Meuth, M.; Curtin, N.J.; Helleday, T. Specific Killing of BRCA2-Deficient Tumours with Inhibitors of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase; 2005.
- Van Der Wijngaart, H.; Hoes, L.R.; Van Berge Henegouwen, J.M.; Van Der Velden, D.L.; Zeverijn, L.J.; Roepman, P.; Van Werkhoven, E.; De Leng, W.W.J.; Jansen, A.M.L.; Mehra, N.; et al. Patients with Biallelic BRCA1/2 Inactivation Respond to Olaparib Treatment across Histologic Tumor Types. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 6106–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stossel, C.; Raitses-Gurevich, M.; Atias, D.; Beller, T.; Gorman, Y.G.; Halperin, S.; Peer, E.; Denroche, R.E.; Zhang, A.; Notta, F.; et al. Spectrum of Response to Platinum and PARP Inhibitors in Germline BRCA–Associated Pancreatic Cancer in the Clinical and Preclinical Setting. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 1826–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddell, N.; Pajic, M.; Patch, A.M.; Chang, D.K.; Kassahn, K.S.; Bailey, P.; Johns, A.L.; Miller, D.; Nones, K.; Quek, K.; et al. Whole Genomes Redefine the Mutational Landscape of Pancreatic Cancer. Nature 2015, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.C.H.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Kamiyama, H.; Jimeno, A.; et al. Core Signaling Pathways in Human Pancreatic Cancers Revealed by Global Genomic Analyses. Science (80-. ). 2008, 321, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biankin, A. V.; Waddell, N.; Kassahn, K.S.; Gingras, M.C.; Muthuswamy, L.B.; Johns, A.L.; Miller, D.K.; Wilson, P.J.; Patch, A.M.; Wu, J.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer Genomes Reveal Aberrations in Axon Guidance Pathway Genes. Nature 2012, 491, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, A.L.; Roberts, N.J.; Jones, S.; Wheelan, S.J.; Papadopoulos, N.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W.; Hruban, R.H.; Klein, A.P.; Eshleman, J.R. Familial and Sporadic Pancreatic Cancer Share the Same Molecular Pathogenesis. Fam. Cancer 2015, 14, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartupee, C.; Nagalo, B.M.; Chabu, C.Y.; Tesfay, M.Z.; Coleman-Barnett, J.; West, J.T.; Moaven, O. Pancreatic Cancer Tumor Microenvironment Is a Major Therapeutic Barrier and Target. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaashua, L.; Ben-Shmuel, A.; Pevsner-Fischer, M.; Friedman, G.; Levi-Galibov, O.; Nandakumar, S.; Barki, D.; Nevo, R.; Brown, L.E.; Zhang, W.; et al. BRCA Mutational Status Shapes the Stromal Microenvironment of Pancreatic Cancer Linking Clusterin Expression in Cancer Associated Fibroblasts with HSF1 Signaling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, G.; Wang, A.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Werba, G.; Weissinger, D.; Zhao, E.; Dhara, S.; Hernandez, R.E.; Ackermann, A.; et al. POLQ Inhibition Elicits an Immune Response in Homologous Recombination-Deficient Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma via CGAS/STING Signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Archasappawat, S.; Ji, K.; Pena, J.; Fernandez-Vega, V.; Gangaraju, R.; Beesabathuni, N.S.; Kim, M.J.; Tian, Q.; Shah, P.S.; et al. A New Vulnerability to BET Inhibition Due to Enhanced Autophagy in BRCA2 Deficient Pancreatic Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, M.J.; Edelman, E.J.; Heidorn, S.J.; Greenman, C.D.; Dastur, A.; Lau, K.W.; Greninger, P.; Thompson, I.R.; Luo, X.; Soares, J.; et al. Systematic Identification of Genomic Markers of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer Cells. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, J.; Lu, W.; Dai, Y.; Hockings, J.; Zhou, Y.; Nussinov, R.; Eng, C.; Cheng, F. Individualized Genetic Network Analysis Reveals New Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in 6,700 Cancer Genomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, B.; Akar, U.; Gutierrez-Barrera, A.M.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Ozpolat, B. The PARP Inhibitor AZD2281 (Olaparib) Induces Autophagy/Mitophagy in BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutant Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, B.; Dai, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Qian, G.; Yu, T. Knockdown of BRCA2 Enhances Cisplatin and Cisplatin-Induced Autophagy in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, J.J.; Chen, J.; Geller, B.; Jäger, N.; Lipchik, A.M.; Wang, G.; Kurian, A.W.; Ford, J.M.; Snyder, M.P. Chromatin Remodeling in Response to BRCA2-Crisis. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 2182–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKay, R.P.; Xu, Q.; Weinberger, P.M. R-Loop Physiology and Pathology: A Brief Review. DNA Cell Biol. 2020, 39, 1914–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivji, M.K.K.; Renaudin, X.; Williams, Ç.H.; Venkitaraman, A.R. BRCA2 Regulates Transcription Elongation by RNA Polymerase II to Prevent R-Loop Accumulation. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, G.; Gómez-González, B.; Silva, S.; Pérez-Calero, C.; Beaurepere, R.; Barroso, S.; Martineau, S.; Martin, C.; Ehlén, Å.; Martínez, J.S.; et al. BRCA2 Promotes DNA-RNA Hybrid Resolution by DDX5 Helicase at DNA Breaks to Facilitate Their Repair‡. EMBO J. 2021, 40, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Prevalence of deleterious mutations | Associated malignancies and disorders | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | FPC patients | SPC patients | |
| BRCA1 | 1.2% | 0.0% | Breast, ovary, prostate, esophagus, stomach, uveal |
| BRCA2 | 3.7% | 3.0% | Breast, ovary, prostate, esophagus, stomach, uveal, melanoma |
| PALB2 | 0.6% | 0.5% | Fanconi anemia, breast, prostate, stomach, esophagus |
| CDKN2A | 2.5% | 0.0% | Melanoma |
| Total | 8.0% | 3.5% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





