1. Introduction
"Lipid mediators" are chemical messengers, which are produced locally through specific biosynthetic pathways in response to either neural cell activation or neuronal injury. Lipid mediators are lipophilic molecules, which produce their effect either by binding to their receptors or by inducing inflammation and oxidative stress [
1]. They not only play important roles in internal and external communication, but also modulate cellular growth, differentiation, adhesion, and migration [
2]. In membranes lipids are organized in bilayers with the amine-containing phospholipids enriched on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane (PM), while the choline-containing phospholipids and sphingolipids enriched on the outer surface. The two lipid bilayers of membranes are held together by hydrophobic, coulombic and van der Waal forces and hydrogen bonding [
2]. This organization of lipid bilayer is spontaneous, meaning it is a natural process, which does not require energy. The distribution of phospholipids and sphingolipids in two leaflets of lipid bilayer is asymmetric. Phospholipids and sphingolipids contribute to the lipid asymmetry, whereas cholesterol and sphingolipids form lipid microdomains or lipid rafts that float within the membranes along with proteins. A large number of signaling molecules are concentrated within lipid rafts, which function as signaling centers capable of facilitating efficient and specific signal transduction pathways [
3]. The interactions of an agonist with its receptors on neural membrane surface results in the enhancement of phospholipid, sphingolipid, and cholesterol metabolism. This process not only increases the activities of phospholipid, sphingolipid, and cholesterol metabolizing enzymes and increase levels of lipid mediators, but also modulate many physicochemical properties of neural membranes such as fluidity, lateral pressure profile, bilayer thickness, permeability, and activity of ion channels [
4]. Thus, lipid metabolism in brain is a tightly regulated process. Any alteration/dysregulation of lipid metabolism may impact brain health and functions. In brain, the function of signal transduction network is to convey extracellular signals from the neural cell surface to the nucleus, where lipid mediators mediate biological responses at the gene level [
5]. The dysregulation of lipid mediator metabolism has been linked to neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptotic cell death in neurological disorders [
6].
2. ARA-Derived Lipid Mediators
In phospholipids, arachidonic acid (ARA, 20:4n-6) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; 22:6n-3) are located at the sn-2 position of glycerol moiety [
7]. Majority of ARA is enriched in phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho), whereas phosphatidylethanolamine (PtdEtn) and ethanolamine plasmelogen (PlsEtn) contain both ARA and DHA. Phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) is enriched in DHA [
7]. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) liberates ARA from phospholipids whereas DHA is released by the action of Ca2+-independent PLA2 [
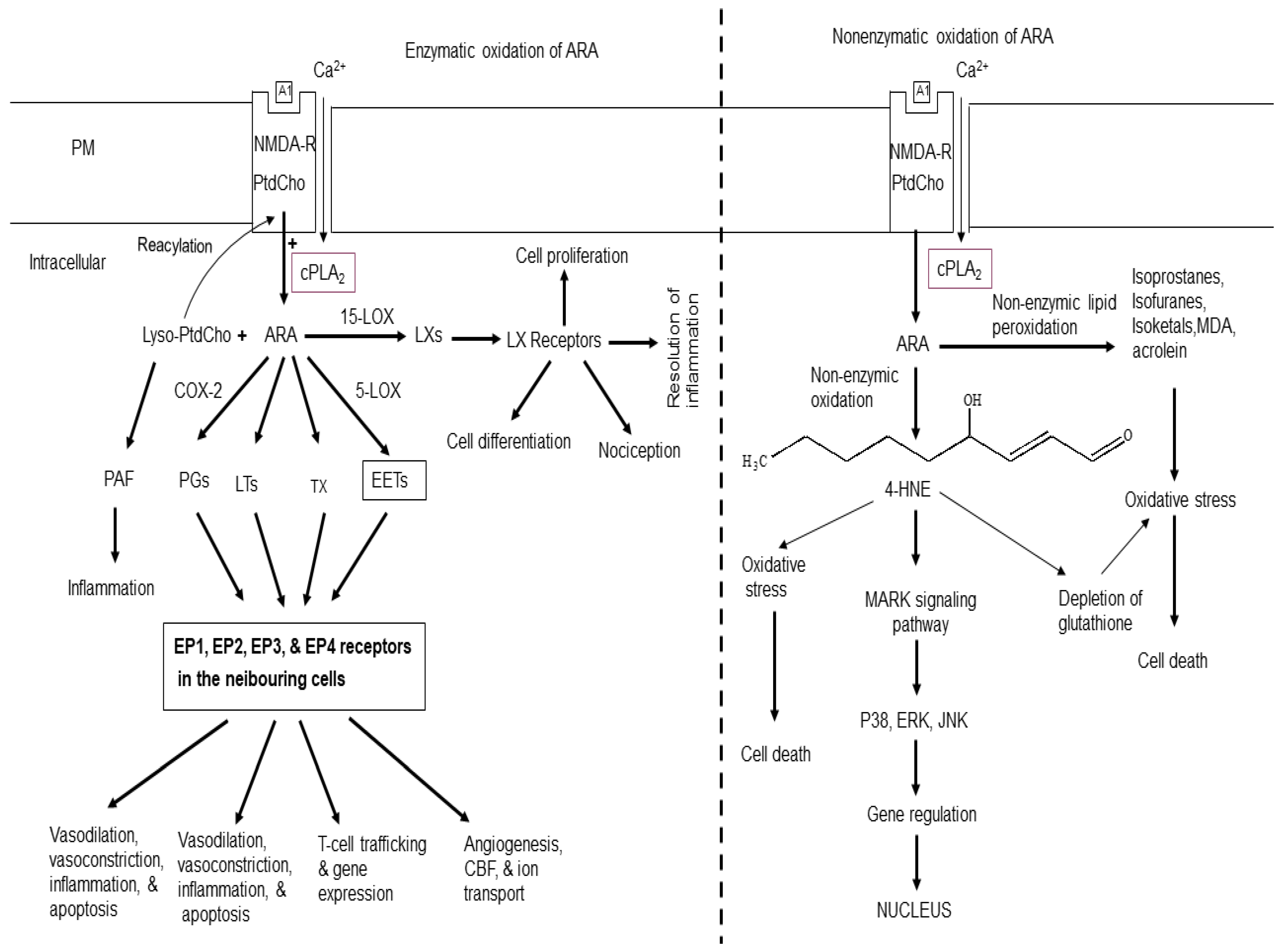
2] (
Figure 1). Under physiological conditions, some ARA is oxidized by cyclooxygenases (COXs)and lipoxygenases (LOXs). These enzymes transform ARA into proinflammatory prostaglandins (PGs), leukotrienes (LTs), thromboxane (TX), and an anti-inflammatory lipoxins [
2,
8,
9] (
Figure 1). The other products of PLA2-catalyzed reaction is lysophospholipid. This metabolite is immediate precursor of platelet-activating factor, a potent inflammatory mediator. It produces it effects by binding to platelet-activating factor receptors [
4,
7]. Accumulation of lysophospholipids is controlled by either through reacylation to native phospholipids [
7] or by their metabolism into water-soluble glycerophosphodiesters such as glycerophosphocholine by lysophospholipases [
2].
PGs are potent autocrine and paracrine lipid mediators, which play important role in physiologic and pathophysiologic responses in the brain. Among 12 PGs, the most potent are PGD2, PGE2, and PGF2. PGE2 mediate their signaling through four distinct G protein-coupled receptors, EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4, which are encoded by different genes and differ in their responses to various agonists and antagonists and differentially expressed on neuronal and glial cells throughout the brain (
Figure 1). In addition, brain also contains the PGF receptor (FP), the PGI receptor (IP), and the TxA receptor (TP) [
10,
11,
12]. These lipid mediators play important roles in neurotransmitter release, sleep, vasodilation and vasoconstriction of cerebral vessels [
4,
7].
Lipoxygenases (5-LOX, 12-LOX, and 15-LOX) are non-heme, iron-containing dioxygenases that insert molecular oxygen into ARA [
9,
13]. Five LTs, namely leukotriene A4 (LTA4), leukotriene B4 (LTB4), leukotriene C4 (LTC4), leukotriene D4 (LTD4), and leukotriene E4 (LTE4) are synthesized from ARA in various body tissue. LTA4 and LTB4 (non-cysteinyl leukotrienes) are structurally different from the cysteinyl leukotrienes (Cys-LT) as they lack the cysteine moiety, which is present in the Cys-LT (LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4) [
13,
14]. These leukotrienes can interact with BLT1 and BLT2 receptors [
15]. whereas LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4 are the ligands for majorly of cysteinyl leukotrienes type 1 (CysLT1R) and type 2 receptor (CysLT2R) [
16].
Thromboxanes (TXs) are synthesized from ARA by the sequential action of three enzymes – cPLA2, COX-2, and TXA2 synthase (TXAS) [
17]. TXs are not only potent hypertensive agents, but also play an important role in platelet aggregation. Among thromboxanes, TXA2 interacts with thromboxane receptor (TP) [
18], which are linked with G protein linked receptors. Levels of thromboxane are elevated in cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, and inflammatory visceral diseases [
19]. Irreversible inhibition of TXA2 with low-dose aspirin is currently used as an antiplatelet therapy for the prevention of primary and secondary vascular thrombotic events. TXA2 also plays an important role in vasoconstriction, adhesion molecule expression, inflammation, cell migration, proliferation, and hypertrophy [
19,
20].
Figure 1.
Enzymatic and non-enzymatic metabolism of arachidonic acid. Plasma membrane (PM); N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA-R); glutamate (Glu); phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho); lysophosphatidylcholine (Lyso-PtdCho); cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2); arachidonic acid (ARA); cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2); 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX); 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX); platelet activating factor (PAF); epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EETs), prostaglandins (PGs); leukotrienes (LTs); thromboxane (TX); lipoxins (LXs); 4-hydroxy 2-nonenal (4-HNE); cerebral blood flow (CBF); A1 (Glu); mitogen-activated protein kinase (P38); serine/threonine protein kinase (ERK).
Figure 1.
Enzymatic and non-enzymatic metabolism of arachidonic acid. Plasma membrane (PM); N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA-R); glutamate (Glu); phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho); lysophosphatidylcholine (Lyso-PtdCho); cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2); arachidonic acid (ARA); cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2); 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX); 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX); platelet activating factor (PAF); epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EETs), prostaglandins (PGs); leukotrienes (LTs); thromboxane (TX); lipoxins (LXs); 4-hydroxy 2-nonenal (4-HNE); cerebral blood flow (CBF); A1 (Glu); mitogen-activated protein kinase (P38); serine/threonine protein kinase (ERK).
LXs are classified into two groups: native LXs and aspirin-triggered lipoxins (ATLs). LXs include lipoxin A4 and lipoxin B4. ATLs include aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 (15-epi-LXA4, ATLA4) and aspirin-triggered lipoxin B4 (15-epi-LXB4, ATLB4). Compared to native LXs, ATLs are more resistant to metabolic inactivation and have an enhanced ability to evoke bioactions. LXs are involved in the resolution of inflammation and stimulation of non-phlogistic phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by microglial cells [
9]. In addition, LXs also produce antioxidative, antiapoptotic, and autophagy-moderating effects [
21,
22,
23,
24].
3. Non-Enzymatic Oxidation of ARA
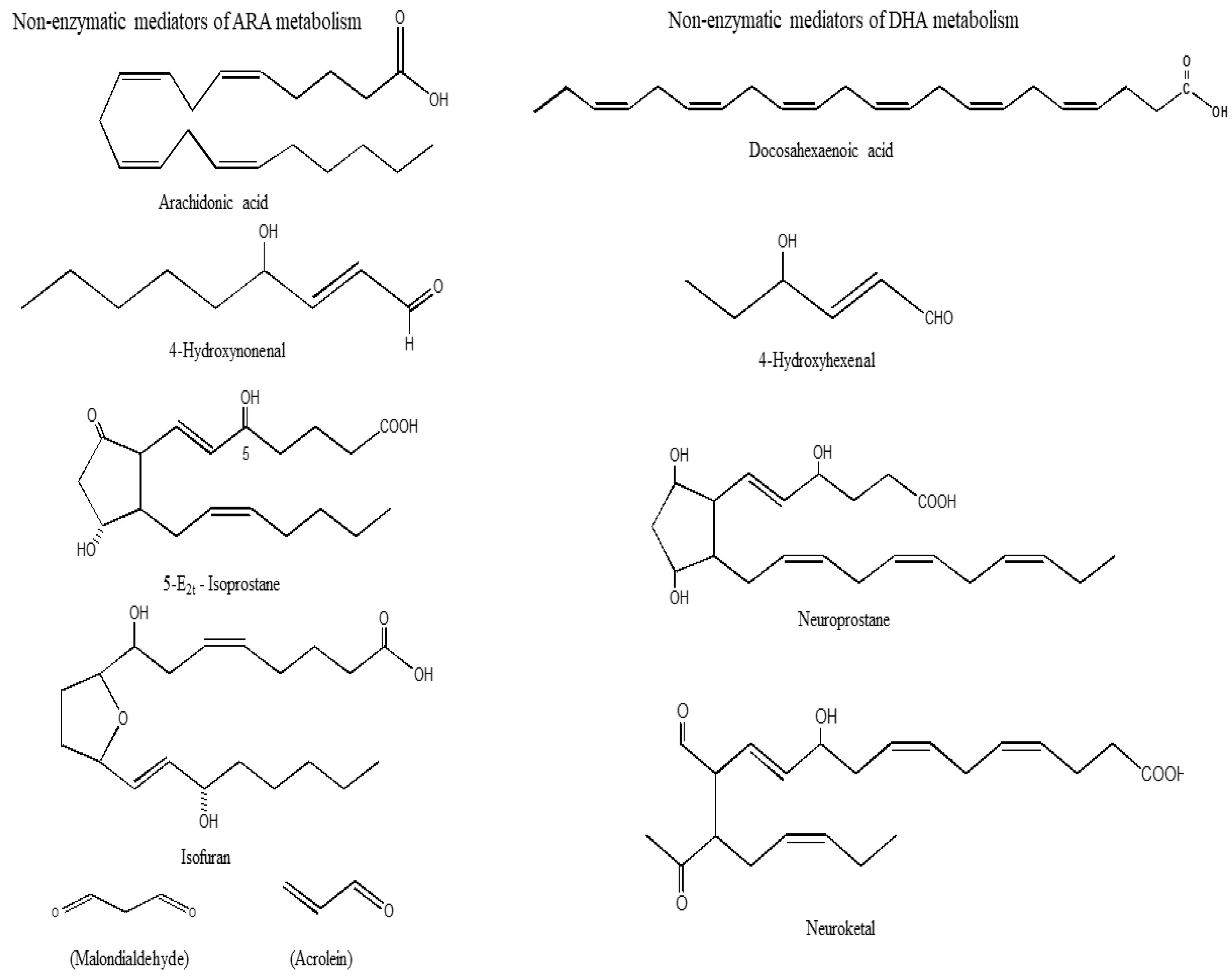
Non-enzymatic oxidation of ARA results in generation of various metabolites, such as 4-hydroxy 2-nonenal (4-HNE), reactive oxygen species (ROS), isoprostane (IsoP), isoketals (IsoK), and isofurans (IsoF) malondialdehyde (MDA), acrolein (Ac) [
4,
7] (
Figure 1). Among these mediators, 4-HNE is a nine carbon α, β-unsaturated aldehyde containing three functional groups. It is prone to be attacked by nucleophile, such as thiol or amino groups in proteins. It is highly toxic and an important biomarker for oxidative stress [
25,
26]. 4-HNE differentially modulates cell death, growth and differentiation. The detoxification of 4-HNE involves conjugation with glutathione. Lower intracellular concentrations (< 2 µM) of 4-HNE produces beneficial effects in cells by promoting cell survival and proliferation [
26]. However, at higher concentrations 4-HNE (10 to 60 μM) produces genotoxic effects by producing sister chromatid exchange, micronuclei formation and DNA fragmentation. Furthermore, 4- HNE at (> 100 μM) inhibits enzymes of glycolysis, mitochondrial respiration, DNA metabolism, and protein synthesis [
26]. In addition, 4-HNE also inhibits many enzymes such as MAP kinase, caspases, ATPase, and enzymes of cell cycle [
27,
28]. 4-HNE also regulates transcription factors that are responsible for redox homeostasis (Ref-1, Nrf2, p53, NFκB, and Hsf1). Levels of 4-HNE are increased in stroke, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and prion disease [
29,
30,
31].
4. Other Non-Enzymatic Metabolites of ARA Metabolism
Non-enzymatic oxidation of ARA produces isoprostane (IsoP), isoketals (IsoK), and isofurans (IsoF) malondialdehyde (MDA), acrolein (Ac), (
Figure 2) and reactive oxygen species (ROS). Among above lipid mediators, IsoPs are not only potent vasoconstrictors [
32,
33], but also contribute to cell proliferation, mitogenesis, and monocytic adhesion. These processes may be closely related to the onset of inflammation and atherosclerosis in the body [
34,
35,
36].
The formation of IsoK also occurs through the rearrangement of H2-IsoP endoperoxides (
Figure 2). IsoK are highly reactive γ-ketoaldehydes that form pyrrole adducts with the ε-amino group of lysine residues on protein in tissues and biological fluids [
37]. IsoKs inhibit the activity of proteasomes in glial cells with an IC50 of 330 nM and induce cell death with an IC50 of 670 nM). Intra-hemispheric injections of 15-E2-IsoK disrupt the blood brain barrier.
Lipid peroxidation of unsaturated lipids produces lipid hydroperoxides (LOOH) [
38]. Malondialdehyde (MDA) is the principal product of lipid peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (
Figure 2). This aldehyde is a highly toxic and is considered as a biomarker for lipid peroxidation [
39]. Its interaction with DNA and proteins has often been referred to as potentially mutagenic and atherogenic [
39]. Acrolein is another metabolite of lipid peroxidation. It is a simplest α, β-unsaturated aldehyde which can form Michael adducts with thiol groups of cysteines that affect the activity of many proteins. Acrolein can readily enter the cell where it causes glutathione depletion and thus can break the cellular redox balance and subsequently lead to oxidative stress [
40]. Acrolein promotes apoptosis and adducts accumulate in several pathological conditions [
41].
The non-enzymic oxidation of ARA also produces reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are the primary effector molecules of oxidative stress. ROS are produced under physiological states as well as in pathological conditions (AD, PD, ALS, and HD). The non-enzymic oxidation of ARA also produces reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are the primary effector molecules of oxidative stress and inflammation. At low levels, ROS act as signaling molecules and regulate fundamental processes such as cell growth and adaptation responses [
41,
42]. However, high levels of ROS produce oxidative stress. This process impairs molecular signaling pathways, alters enzyme activities, and damages cellular lipids, proteins, or DNA leading to metabolic alterations in pathological conditions such as AD, PD, ALS, and HD [
43,
44].
5. DHA-Derived Lipid Mediators
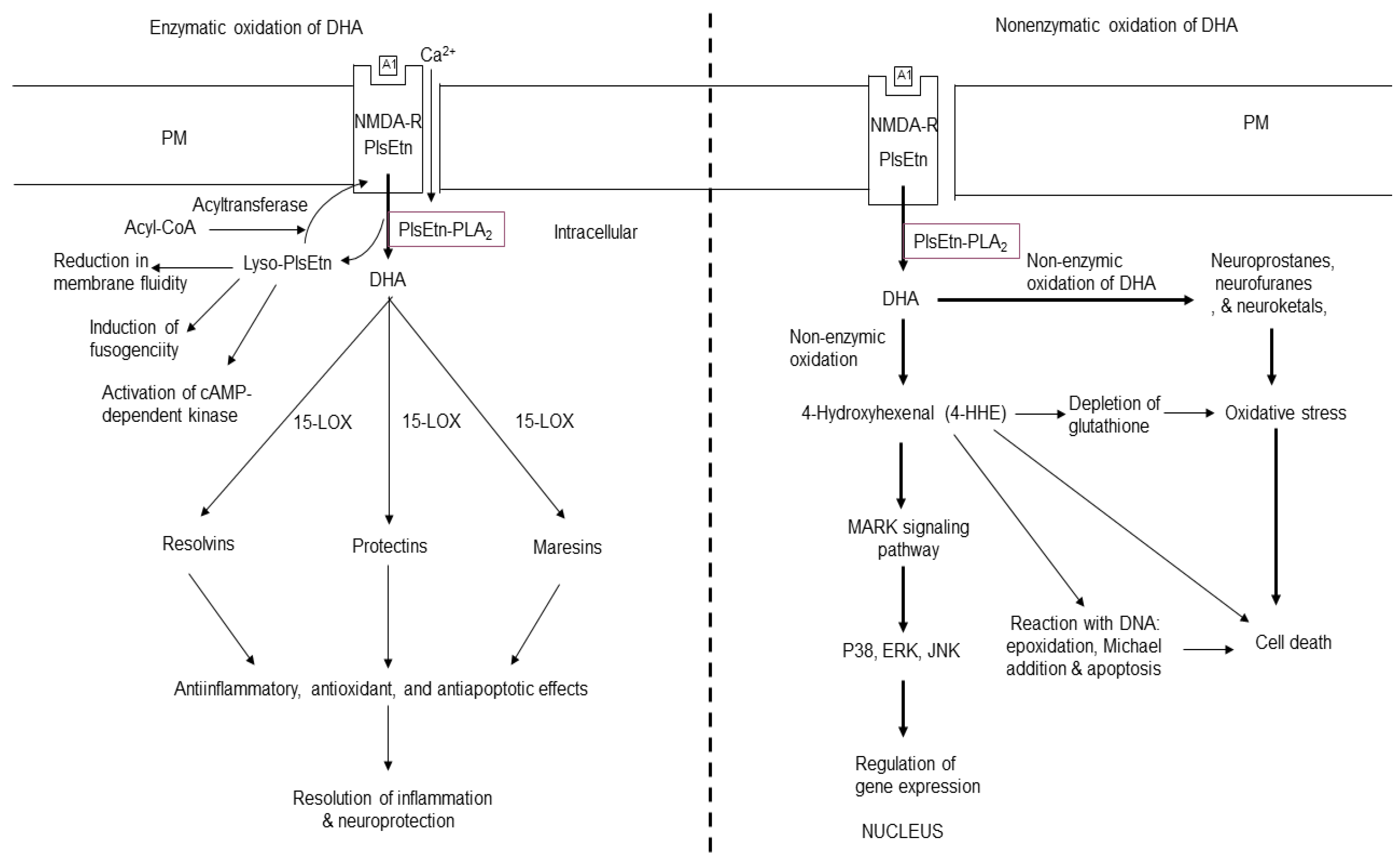
Free DHA is enzymatically metabolized into resolvins (RVs), protectin D1 (PD1), and maresins (MaRs) (
Figure 3). These mediators induce anti-inflammatory and pro-resolutionary effects [
45]. In the presence of aspirin, the action of COX-2 on DHA produces aspirin-triggered forms of RVs that not only produce potent anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects, but also regulate leukocytes trafficking [
46,
47]. RVs also reduce cytokine expression in isolated microglial cells [
48].
DHA and its oxygenated derivatives are endogenous ligands for retinoid X receptors (RXRs) and PPAR receptors [
49,
50,
51,
52] in different cell types including neurons and astrocytes [
53,
54,
55]. Converging evidence suggests that DHA and its metabolites modulate the expression a number of genes, which control inflammation, cell survival, DNA binding, transcriptional regulation, transport, cell adhesion, cell proliferation, and raft formation [
56,
57].
6. Non-Enzymatic Oxidation of DHA
The non-enzymic oxidation of DHA generates 4-hydroxyhexanal (4-HHE), neuroprostane (NP), neuroketal (NK), and neurofuran (NF) (
Figure 2) [
58]. DHA is highly enriched in neurons, so the generation of these metabolites have been used as an important index of neuronal protection/ damage. Generation of 4-HHE from DHA results in stimulation of Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. This process results in cardioprotective effects of DHA. In contrast, ARA produces 4-HNE, a lipid mediator, which produces oxidative stress [
59]. NPs have 22 carbons and 4 double bonds and analogous to IsoP. The synthesis of NPs from DHA also produces peroxyl radicals, which may contribute to alterations in neural membrane fluidity and permeability leading to neuronal dysfunction [
58].
7. Sphingolipid-Derived Lipid Mediators
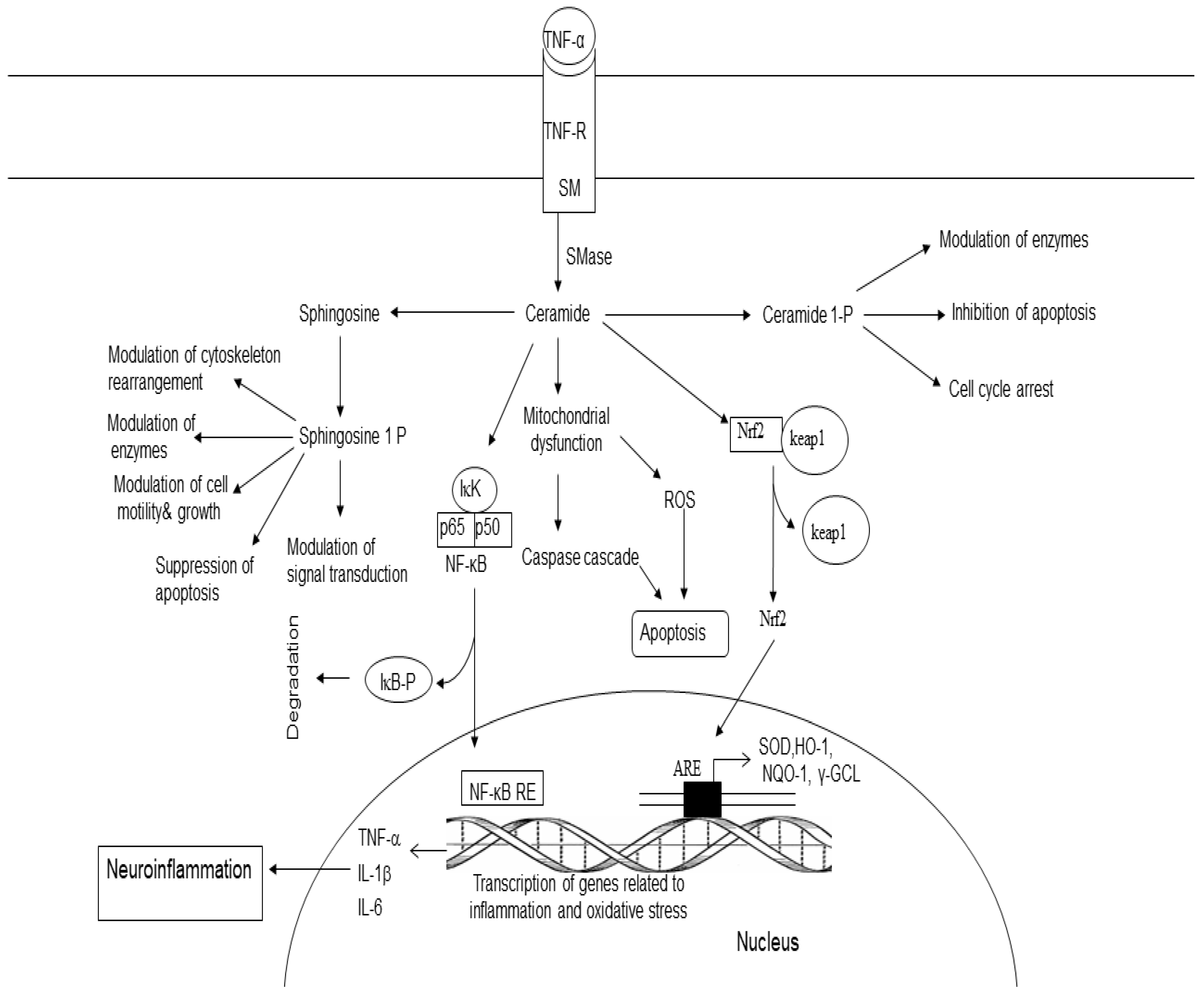
Sphingomyelin (SM) is a major sphingolipid of myelin sheaths of neurons and lipid rafts in neural cell membranes. SM is hydrolyzed by sphingomyelinase (SMase), an enzyme that produces ceramide (Cer) and choline (
Figure 4). Three SMases are known to occur in the brain namely acid SMase (acid SMase), neutral SMase (nSMase), and alkaline SMase [
60,
61]. Ceramide consists of a sphingosine backbone attached to fatty acid (palmitic (C16) and stearic (C18) non-hydroxy fatty acids) by an amide bond. In the brain, ceramide synthesis not only occurs through the de novo synthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum, but also by SMases [
60,
61,
62]. From the endoplasmic reticulum, ceramide is transported by ceramide transport protein (CERT) to the Golgi apparatus, where it is required for the synthesis of sphingomyelin (CerPCho or SM) [
63,
64] (
Figure 4). Ceramide functions as a second messenger in a variety of cellular events, including proliferation, differentiation, growth arrest, inflammation, stress responses, synaptic activity, and apoptosis [
65,
66,
67,
68,
69]. Ceramide is phosphorylated into ceramide1 phosphate (C 1-P) by ceramide kinase (
Figure 4) [
70]. C1-P activates cPLA2, an enzyme, which hydrolyzes PtdCho and generates lyso-PtdCho and ARA, a fatty acid, which is converted into proinflammatory PGs, LTs, and TXs. Ceramide also activates serine/threonine protein kinases and phosphatases [
71,
72]. The cross-talk between sphingolipids metabolites and transcription factors (NF-κB and FOXOs) may be important for immune regulation and cell survival/death [
73]. Stimulation of the atypical protein kinase zeta (PKCζ) by ceramide results in suppression of mitogenesis [
74,
75]. In contrast, C 1-P stimulates cell migration, proliferation, angiogenesis, cell survival, and metabolism [
76].
The degradation ceramide by ceramidase results in the synthesis of sphingosine, which is then phosphorylated by ATP in the presence of sphingosine kinases (SphKs). This reaction results in the synthesis of sphingosine 1 phosphate (S1P) [
77]. This metabolite promotes inflammation, cell proliferation, cell survival, and angiogenesis. It also contributes to neuritogenesis and immune function [
78,
79]. S1P can be converted back to sphingosine by S1P phosphatases (SPPase) or can be irreversibly broken down by sphingosine phosphate lyase (SPL) [
78,
79]. Collective evidence suggests that sphingolipid metabolites regulate diverse processes including cell survival, oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and proliferation.
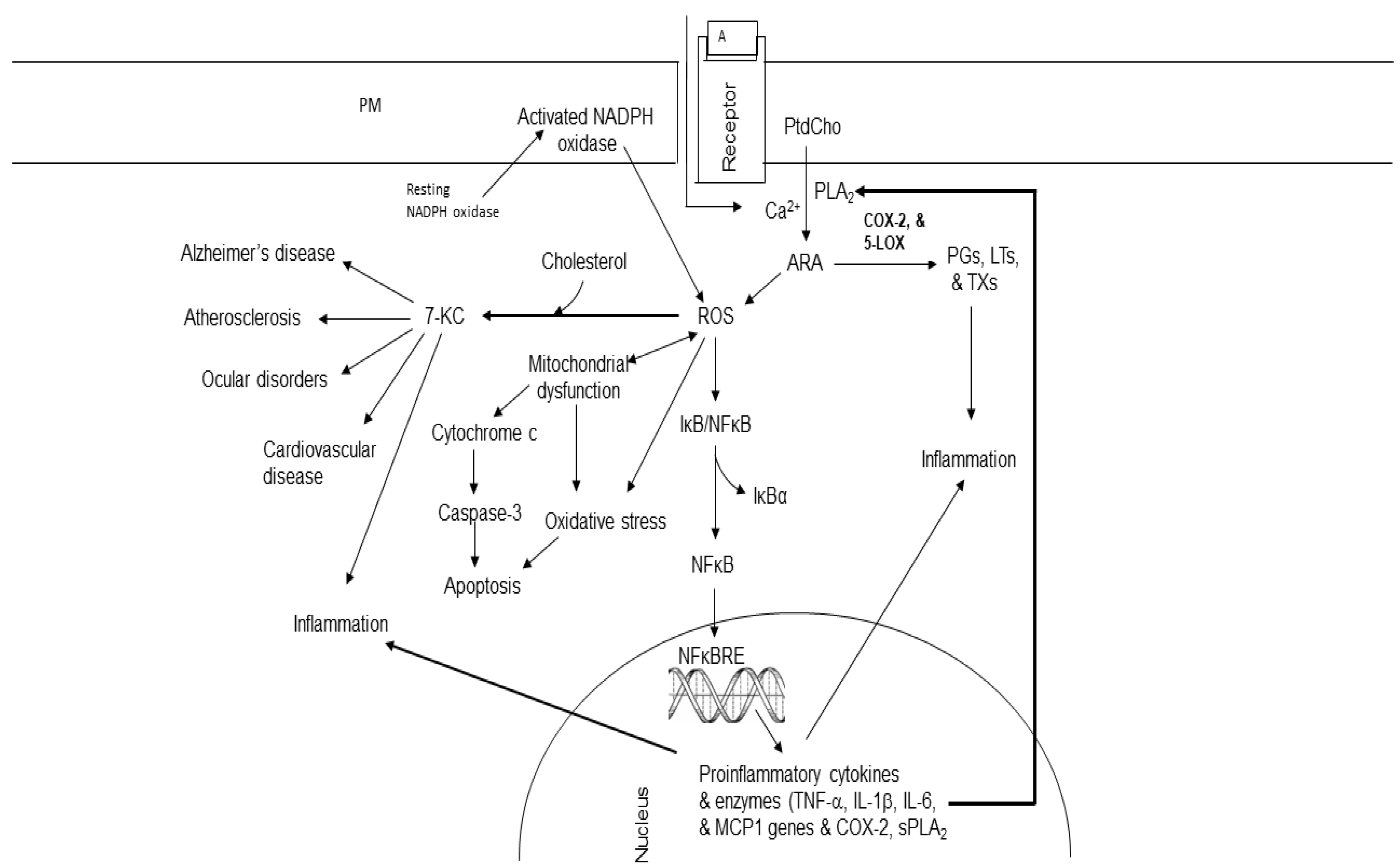
8. Cholesterol-Derived Lipid Mediators
Among various body tissues, brain is the richest source of cholesterol in the body. Two pools of cholesterol are present in the brain. One pool, which is metabolically stable accounts for ∼70% of the total cholesterol. This pool is present in myelin membranes of white matter [
80]. The second pool, which represent ∼30% of total cholesterol is associated with the plasma and subcellular membranes of neurons and glial cells of gray matter. This is metabolically active and contribute to the formation of lipid rafts. Free cholesterol cannot cross BBB. However, some cholesterol oxidation products (27-hydroxycholesterol, 24S-hydroxycholesterol, and 7-ketocholesterol) may diffuse into the brain [
81].
Hydroxycholesterol are not only important regulators of cholesterol metabolism and lipid homeostasis, but also play important role in immune function, and membrane fluidity regulation. In liver the activation of some nuclear receptors, such as liver X receptor α (LXRα) and RAR-related orphan receptors by hydroxycholesterols results in the regulation of various physiological processes in multiple tissues (
Figure 5) [
82]. These cholesterol metabolites not only produce strong pro-apoptotic and pro-inflammatory effects [
83,
84], but also impact on the renin–angiotensin system [
85,
86]. Among cholesterol metabolites, 27-Hydroxycholesterol depletes glutathione, promotes generation of ROS, and induces inflammation and apoptosis [
87]. 7-Ketocholesterol (7-KC) is formed during ROS attack on the carbon 7 of cholesterol (
Figure 5). Increased levels of 7-KC have been found in the tissues, plasma and/or cerebrospinal fluid of patients with major age-related diseases (cardiovascular diseases, eye diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases) [
88]. 7-KC not only promotes increase in Ca2+, but also activates cPLA2 an enzyme that releases ARA. This ARA interacts with 7-KC and in the presence of Acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) to form 7KC-ARA complex [
89]. It is suggested that 7-KC damages vascular endothelial cells by inducing inflammatory responses. This process elevates the risk of cardiovascular diseases, AD, and age-related macular degeneration. In addition, unesterified 7-KC not only disrupts membrane fluidity, but also promotes inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. In retina, 7- KC increases retinal microglial cell migration and angiogenicity. These processes may be involved in age-related macular degeneration [
90,
91,
92].
9. Involvement of Lipid Mediators in Neurological Disorders
In the brain tissue phospholipid, sphingolipid-, and cholesterol are not merely structural components, but important molecules, which play crucial for the maintenance of membrane fluidity, permeability, and membrane functionality modulating neurotransmitter release and receptor activity. These lipids also play significant roles in synaptic function, aiding in the formation and maintenance of synapses, as well as in synaptic plasticity, which is essential for learning and memory. Cholesterol, for example, is a key component of the myelin sheath, facilitating rapid signal transmission along neuronal axons [
2,
4]. Receptor-mediated degradation of neural membrane phospholipid, sphingolipid-, and cholesterol by phospholipase A
2, cyclooxygenase, lipoxygenase, acyltransferase, sphingomyelinase, and cytochrome P450 results in the generation of enzymic and non-enzymic lipid mediators of phospholipid metabolism. Enzymically-derived lipid mediators promote neuroinflammation. In contrast, increase in non-enzymic lipid mediators of phospholipid metabolism results in elevated production of ROS causing onset of oxidative stress. Both these processes are closely interrelated and are responsible for the pathogenesis of different neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory disorders [
4,
6]. In brain, the metabolism of phospholipid, sphingolipid, and cholesterol-derived lipid mediator is interrelated and interconnected process [
5]. Thus, many cellular stimuli (neurotransmitters, cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors) modulate more than one enzyme of phospholipid, sphingolipid, and cholesterol metabolism at the same time [
5].
Treatment of cells with exogenous sphingolipids results in siphoning of cholesterol from to the plasma membrane suggesting perturbations in sphingolipid levels are coupled with changes in cholesterol metabolism [
93]. It has been reported that 25-hydroxycholesterol produces a significant increase in SM synthesis, which is dependent on oxysterol binding protein (OSBP), ceramide transport protein (CERT), and their shared binding partner VAP [
93]. The precise mechanism of this process is not fully understood, but OSBP appears to activate CERT by promoting its recruitment to membranes and its binding to vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein (VAP). Under physiological conditions, the homeostasis among enzymes of phospholipid, sphingolipid, cholesterol metabolism is based not only on optimal levels of lipid mediators, but also on the complexity and interconnectedness of signal transduction processes involved in their metabolism. However, in neurological disorders, such as stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis marked increase in levels of lipid mediators may disturb the cellular homeostasis. In addition, this process may also prevent the cross-talk among phospholipid, sphingolipid, and cholesterol-derived lipid mediators. This may result in lack of communication among neurons, astroglia, and microglia. Furthermore, the increase in lipid mediator levels may also promote the progression of neurological disorders by controlling oligomerization of aggregate pathogenic proteins (Aβ, α-Syn, mutated huntingtin, and mutated Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase1) associated with the pathogenesis of each disease. These processes may not only threaten the integrity of neural cell lipid homeostasis, but also facilitate neurodegeneration in neurological disorders [
2,
6,
7]. In addition, the dysregulation of the balance among phospholipids, sphingolipids and cholesterol may results in “lipo-toxicity” associated with the pathophysiology of common metabolic and neurological diseases, typically characterized by not only with increased ceramide/sphingosine pools, but also with induction of inflammation and oxidative stress. Lipo-toxicity is closely associated with cell death involving inflammation and oxidative stress [
94,
95]. The severity of the lipo-toxic insult can be modulated by the specific cellular genetic vulnerability to the toxicity induced by phospholipid and sphingolipid metabolites.
10. Conclusion
Lipid mediators are important endogenous metabolites derived from enzymic degradation of membrane lipids by PLA2, COXs, LOXs, acyltransferases, and SMases, respectively. Enzymatic oxidation of ARA produces proinflammatory PGs, LTs, and TXs. The non-enzymatic metabolites of ARA include 4-HNE, IsoP, IsoK, IsoF, MDA, Ac, and ROS. The later interacts with NF-κB and promotes inflammation. In contrast, enzymatic oxidation of DHA generates anti-inflammatory lipid mediators (RVs, PDs, and MaR). These mediators directly or indirectly suppress the activity of NF-κB and inflammation. Sphingolipids derived metabolites are ceramide, C 1-P, sphingosine, S1P. These mediators are essential for cellular signaling. Their synthesis contributes to inflammation, cell migration, and apoptosis. Cholesterol-derived mediators (hydroxycholesterols and 7-KC) are involved in neural cell differentiation, exocytosis, inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Levels of lipid mediators are markedly increased in neurological disorders.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, writing and ending -AAF & TF. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not Applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not Applicable
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Murakami, M. Lipid mediators in life science. Exp Anim. 2011, 60, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, A.A.; Horrocks, L.A. Glycerophospholipids in Brain. 2007, Springer Science + Business Media.
- Allen, J.A.; Halverson-Tamboli, R.A.; Rasenick, M.M. Lipid raft microdomains and neurotransmitter signalling. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, A.A. Hot Topics in Neural Membrane Lipidology. 2009. New York: Springer.
- Tracey, T.J.; Steyn, F.J.; Wolvetang, E.J.; Ngo, S.T. Neuronal Lipid Metabolism: Multiple Pathways Driving Functional Outcomes in Health and Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, A.A. Neurochemical aspects of Neurotraumatic and Neurodegeneration Disease. Springer, 2010, New York.
- Farooqui, A.A.; Horrocks, L.A.; Farooqui, T. Glycerophospholipids in brain: their metabolism, incorporation into membranes, functions, and involvement in neurological disorders. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2000, 106, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqui, A.A.; Horrocks, L.A.; Farooqui, T. Modulation of inflammation in brain: a matter of fat. J. Neurochem. 2007, 101, 577–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillis, J.W.; Horrocks, L.A.; Farooqui, A.A. Cyclooxygenases, lipoxygenases, epoxygenases in CNS: their role and involvement in neurological disorders. Brain Res. Rev. 2006, 52, 201–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, A.A. Cytochrome P450 epoxygenase pathway of polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism. BioChim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 185, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narumiya, S. Prostanoids in immunity: roles revealed by mice deficient in their receptors. Life Sci. 2003, 74, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, K.; Sugimoto, Y.; Ichikawa, A. Prostanoid receptor subtypes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002, 68, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmark, O.; Samuelsson, B. 5-Lipoxygenase: mechanisms of regulation. J. Lipid. Res 2009, 50, S40–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H.; Banthiya, S.; van Leyen, K. Mammalian lipoxygenases and their biological relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2015, 1851, 308–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeggstrom, J.Z.; Funk, C.D. Lipoxygenase and leukotriene pathways: Biochemistry, biology, and roles in disease. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5866–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokomizo, T. Two distinct leukotriene B4 receptors, BLT1 and BLT2. J. Biochem. 2015, 157, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, E.M. Thromboxane and thromboxane receptors in cardiovascular disease. Clin. Lipidol. 2010, 5, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Ushikubi, F.; Yokota, Y.; Kageyama, R.; Nakanishi, S.; Narumiya, S. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a human thromboxane A2 receptor. Nature. 1991, 349, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katugampola, S.D.; Davenport, A.P. Thromboxane receptor density is increased in human cardiovascular disease with evidence for inhibition at therapeutic concentrations by the AT1 receptor antagonist losartan. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, T.; Kawakami, M.; Hidaka, T.; Makino, T.; Kashiwagi, A.; Maegawa, H. Stimulation with thromboxane A2 (TXA2) receptor agonist enhances ICAM-1, VCAM-1 or ELAM-1 expression by human vascular endothelial cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 112, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhai, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, F.; et al. Aspirin-triggered Lipoxin A₄ Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Intracellular ROS in BV2 Microglia Cells by Inhibiting the Function of NADPH Oxidase. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Li, Y.H.; Xu, J.S.; Guo, G.Q.; Chen, D.L.; Bo, Y. Lipoxin A4 Analog Attenuates Morphine Antinociceptive Tolerance, Withdrawal-Induced Hyperalgesia, and Glial Reaction and Cytokine Expression in the Spinal Cord of Rat. Neuroscience 2012, 208, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Jin, W.; Xiao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, T.; Fan, M.; et al. Lipoxin A4 Methyl Ester Alleviates Vascular Cognition Impairment by Regulating the Expression of Proteins Related to Autophagy and ER Stress in the Rat hippocampus. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2015, 20, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, P.; Rosales-Mendoza, C.E.; Terrón, V.; Toledano, V.; Cuadrado, A.; López-Collazo, E.; Bannenborg, G.; Martin-Sanz, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Fernandez-Velasco, M.; Bosca, L. Activation of Autophagy in Macrophages by Pro-resolving Lipid Mediators. Autophagy 2015, 11, 1729–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenico, F.D.; Tramutola, A.; Butterfield, D.A. Majorly Role of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and other selected age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Free. Rad. Biol. Med. 2017, 111, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoeb, M.; Ansari, N.H.; Srivastava, S.K.; Ramana, K. 4-hydroxynonenal in the pathogenesis and progression of human diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadoya, A.; Miyake, H.; Ohyashiki, T. Contribution of lipid dynamics on the inhibition of bovine brain synaptosomal Na+ K+-ATPase activity induced by 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.; Sharma, R.; Vatsyayan, R.; Yadav, S.; Singhal, S.S.; Rauniyar, N.; Prokai, L.; Awasthi, S.; Awasthi, Y.S. Mechanisms of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal induced pro-and anti-apoptotic signaling. Biochemistry. 2010, 49, 6263–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selley, M.L.; Close, D.R.; Stern, S.E. The effect of increased concentrations of homocysteine on the concentration of (E)-4-hydroxy-2-nonenal in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2002, 23, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dexter, D.T.; Carter, C.J.; Wells, F.R.; Javoy-Agid, F.; Agid, Y.; Lees, A.; Jenner, P.; Marsden, C.D. Basal lipid peroxidation in substantia nigra is increased in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1989, 52, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, W.A.; Fu, W.; Keller, J.N.; Markesbery, W.R.; Appel, S.; Smith, R.G.; Kasarskis, E.; Mattson, M.P. Protein modification by the lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal in the spinal cords of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Ann. Neurol. 1998, 44, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S. Isoprostanes: novel bioactive products of lipid peroxidation. Free. Radic. Res. 2004, 38, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.D.; Tapper, A.R.; Zackert, W.E.; Yang, J.; Sanchez, S.C.; Montine, T.J.; Roberts, L.J., II. Formation of novel isoprostane -like compounds from docosahexaenoic acid. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1999, 469, 343–347. [Google Scholar]
- Fam, S.S.; Morrow, J.D. The isoprostane: unique products of arachidonic acid oxidation-a review. Curr Med Chem. 2003, 10, 1723–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, J.D.; Awad, J.A.; Boss, H.J.; Blair, I.A.; Robert, L.J. II. Non-cyclooxygenase-derived prostanoids (F2-isoprostanes) are formed in situ on phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992, 89, 10721–10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cracowski, J.L. Isoprostanes: an emerging role in vascular physiology and disease? Chem. Phys. Lipids 2004, 128, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, S.S.; Amarnath, V.; Robert, L.J. II. Isoketal: highly reactive gamma-ketoaldehyde formed from the H-2-isoprostane pathway. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2004, 128, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, A.; Munoz, M.F.; Arguelles, S. Lipid Peroxidation: Production, Metabolism, and Signaling Mechanisms of Malondialdehyde and 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esterbauer, H.; Lang, J.; Zadravec, S.; Slater, T.F. Detection of malonaldehyde by high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods in Enzymology. 1984, 105, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uemura, T.; Watanabe, K.; Ishibashi, M.; Saiki, R.; Kuni, K.; Nishimura, K.; Toida, T.; Kashiwagi, K.; Igarashi, K. Aggravation of brain infarction through an increase in acrolein production and a decrease in glutathione with aging. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.I.; Lynn, B.C.; Markesbery, W.R.; Lovell, M.A. Increased levels of 4-hydroxynonenal and acrolein, neurotoxic markers of lipid peroxidation, in the brain in Mild Cognitive Impairment and early Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging. 2006, 27, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.J. ; Liu, Z-g. Crosstalk of reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Juan, C.A.; Perez de la Lastra, P.; Plou, F.J.; Perez-Lerez-Lebena, E. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int J Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative Stress. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 715–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serhan, C.N.; and Petasis, N.A. Resolvins and Protectins in Inflammation-Resolution. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5922–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Arita, M.; Hong, S.; Gotlinger, K. Resolvins, docosatrienes, and neuroprotectins, novel omega-3-derived mediators, and their endogenous aspirin-triggered epimers. Lipids. 2004, 39, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Hong, S.; Gronert, K.; Colgan, S.P.; Devchand, P.R.; Mirick, G.; Moussignac, R.L. Resolvins: a family of bioactive products of omega-3 fatty acid transformation circuits initiated by aspirin treatment that counter pro-inflammation signals. J Exp Med. 2002, 196, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lu, Y.; Yang, R.; Gotlinger, K.H.; Petasis, N.A.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin D1, protectin D1, and related docosahexaenoic acid-derived products: analysis via electrospray/low energy tandem mass spectrometry based on spectra and fragmentation mechanisms. J. Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2007, 18, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, A.; Di Nunzio, M.; Danesi, F.; Biagi, P.L. Polyunsaturated fatty acids: from diet to binding to PPARs and other nuclear receptors. Genes. Nutr. 2006, 1, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyall, S.C.; Michael, G.J.; Michael-Titus, A.T. Omega-3 fatty acids reverse age-related decreases in nuclear receptors and increase neurogenesis in old rats. J Neurosci Res. 2010, 88, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Calon, F.; Julien, C.; Winkler, J.W.; Petasis, N.A.; Lukiw, W.J.; et al. Docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 induces neuronal survival via secretase- and PPARγ-mediated mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease models. PLoS One. 2011, 6, e15816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Yamamoto, K. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma and oxidized docosahexaenoic acids as new class of ligand. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008, 377, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras-Sandoval, D.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Pérez-Rojas, J.M. Role of docosahexaenoic acid in the modulation of glial cells in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2016, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, L.; Cimini, A.; Moreno, S.; Ragnelli, A.M.; Paola, C.M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and related transcription factors in differentiating astrocyte cultures. Neuroscience. 2005, 131, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, A.; Benedetti, E.; Cristiano, L.; Sebastiani, P.; D'Amico, M.A.; D'Angelo, B.; et al. Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and retinoic acid receptors (RXRs) in rat cortical neurons. Neuroscience. 2005, 130, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleshin, S.; Grabeklis, S.; Hanck, T.; Sergeeva, M.; Reiser, G. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma positively controls and PPARalpha negatively controls cyclooxygenase-2 expression in rat brain astrocytes through a convergence on PPARbeta/delta via mutual control of PPAR expression levels. Mol Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M.; Ohira, T.; Sun, Y.P.; Elangovan, S.; Chiang, N.; Serhan, C.N. Resolvin E1 selectively interacts with leukotriene B4 receptor BLT1 and ChemR23 to regulate inflammation. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3912–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqui, A.A. n-3 Fatty acid-derived lipid mediators in the brain; New weapons against oxidative stress and inflammation. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikado, A.; Nishio, Y.; Morino, K.; Ugi, S.; Kondo, H.; et al. Low concentration of 4-hydroxy hexenal increases heme oxygenase-1 expression through activation of Nrf2 and antioxidative activity in vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010, 402, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.W.; Idkowiak-Baldys, J.; Simbari, F.; Canals, D.; Roddy, P.; Riner, C.D.; et al. A novel mechanism of lysosomal acid sphingomyelinase maturation: requirement for carboxyl-terminal proteolytic processing. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 3777–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesini, N.; Hannun, Y.A. Acid and neutral sphingomyelinases: roles and mechanisms of regulation. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futerman, A.H.; Riezman, H. The ins and outs of sphingolipid synthesis. Trends. Cell Biol. 2005, 15, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanada, K.; Kumagai, K.; Yasuda, S.; Miura, Y.; Kawano, M.; Fukasawa, M.; Nishijima, M. Molecular machinery for non-vesicular trafficking of ceramide. Nature. 2003, 426, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.Y.; Herr, D.R.; Farooqui, T.; Ling, E.A.; Farooqui, A.A. Role of sphingomyelinases in neurological disorders. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets. 2015, 19, 1725–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. The ceramide-centric universe of lipid-mediated cell regulation: stress encounters of the lipid kind. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25847–25850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.F.; Nikolova-Karakashian, M.; Zhou, D.H.; Cheng, G.J.; Schuchman, E.H.; Mattson, M.P. Pivotal role for acidic sphingomyelinase in cerebral ischemia-induced ceramide and cytokine production, and neuronal apoptosis. J. Mol. Neurosci 2000, 15, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Alwani, M.; Wu, B.X.J.; Obeid, L.M.; Hannun, Y.A. Bioactive sphingolipids in the modulation of the inflammatory response. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 112, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haughey, N.J.; Bandaru, V.V.R.; Bae, M.; Mattson, M.P. Roles for dysfunctional sphingolipid metabolism in Alzheimer's disease neuropathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys Acta - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids 2010, 1801, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mencarelli, C.; Martinez-Martinez, P. ; Ceramide function in the brain: when a slight tilt is enough. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 2013, 70, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettus, B.J.; Bielawska, A.; Subramanian, P.; Wijesinghe, D.S.; Maceyka, M.; Leslie, C.C.; et al. Ceramide 1-phosphate is a direct activator of cytosolic phospholipase A2. J. Biol.Chem. 2004, 279, 11320–11326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canals, D.; Roddy, P.; Hannun, Y.A. Protein phosphatase 1α mediates ceramide-induced ERM protein dephosphorylation: a novel mechanism independent of phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-biphosphate (PIP2) and myosin/ERM phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 10145–10155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddoughi, S.A.; Gencer, S.; Peterson, Y.K.; Ward, K.E.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Oaks, J.; Bielawski, J.; et al. Sphingosine analogue drug FTY720 targets I2PP2A/ SET and mediates lung tumour suppression via activation of PP2A-RIPK1-dependent necroptosis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czubowicz, K.; Jesko, H.; Wencel, P.; Lukiw, W.J.; Strosznajder, R.P. The Role of Ceramide and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 5436–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, T.E.; Houck, K.L.; O'Neill, S.M.; Nagarajan, M.; Stover, T.C.; Pomianowski, P.T.; et al. Ceramide recruits and activates protein kinase C ζ (PKC ζ) within structured membrane microdomains. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 12450–12457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanshu, D.K.; Kamlekar, R.K.; Wijesinghe, D.S.; Zou, X.; Zhai, X.; Mishra, S.K.; Molotkovsky, J.G.; Malinina, L.; Hinchcliffe, E.H.; Chalfant, C.E.; Brown, R.E.; Patel, D.J. Non-vesicular trafficking by a ceramide-1-phosphate transfer protein regulates eicosanoids. Nature. 2013, 500, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novgorodov, S.A.; Riley, C.L.; Yu, J.; Keffler, J.A.; Clarke, C.J.; Van Laer, A.O.; Baicu, C.F.; Zile, M.R.; Gudz, T.I. Lactosylceramide contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetes. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Muñoz, A. Ceramide 1-phosphate/ceramide, a switch between life and death. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006, 1758, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, S.; Milstien, S. Exogenous and intracellularly generated sphingosine 1-phosphate can regulate cellular processes by divergent pathways. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003, 31, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, S.E.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Autocrine and paracrine roles of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 18, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, A.N. Brain sterol metabolism. Adv. Lipid Res. 1965, 3, 171–196. [Google Scholar]
- Björkhem, I.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Leoni, V.; Meaney, S. Oxysterols and neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Aspects Med. 2009, 30, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Nelson, E.R. Oxysterol and nuclear receptors. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2019, 484, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, P.; Guglielmotto, M.; Testa, G.; Monteleone, D.; Zerbinati, C.; Gargiulo, S. Up-regulation of β-amyloidogenesis in neuron-like human cells by both 24- and 27-hydroxycholesterol: protective effect of N-acetyl-cysteine. Aging Cell. 2014, 13, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, P.; Testa, G.; Gargiulo, S.; Staurenghi, E.; Poli, G.; Leonarduzzi, G. Oxidized cholesterol as the driving force behind the development of Alzheimer's disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2015, 7, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, L.; Akterin, S.; Gil-Bea, F.J.; Spulber, S.; Rahman, A.; Björkhem, I.; Schultzberg, M.; Flores-Morales, A.; Cedazo-Mínguez, A. Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein in rodent brain is down-regulated by high fat diet in vivo and by 27-hydroxycholesterol in vitro. Brain Pathol. 2009, 19, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, L.; Ismail, M.A.; Gil-Bea, F.J.; Schüle, R.; Schöls, L.; Heverin, M.; Ronnie Folkesson, R.; Björkhem, I.; Cedazo-Mínguez, A. Side chain-oxidized oxysterols regulate the brain renin-angiotensin system through a liver X receptor-dependent mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 25574–25585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, B.; Prasanthi, J.R.P.; Marwarha, G.; Singh, B.B.; Ghribi, O. The oxysterol 27-hydroxycholesterol increases β-amyloid and oxidative stress in retinal pigment epithelial cells. BMC Ophthalmol. 2010, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejux, A.; Abed-Vieillard, D.; Hajji, K.; Zarrouk, A.; Mackrill, J.J.; Ghosh, S.; Nury, T.; Yammine, A.; Zaibi, M.; Mihoubi, W.; Bouchab, H.; Nasser, B.; Grosjean, Y.; Lizard, G. 7-Ketocholesterol and 7β-hydroxycholesterol: In vitro and animal models used to characterize their activities and to identify molecules preventing their toxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 173, 113648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, N.E. Acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase promotes oxidized LDL/oxysterol-induced apoptosis in macrophages. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indaram, M.; Ma, W.; Zhao, L.; Fariss, R.N.; Rodriguez, I.R.; Wong, W.T. 7-Ketocholesterol increases retinal microglial migration, activation, and angiogenicity: a potential pathogenic mechanism underlying age-related macular degeneration. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariente, A.; Peláez, R.; Pérez-Sala, Á.; Larráyoz, I.M. Inflammatory and cell death mechanisms induced by 7-ketocholesterol in the retina. Implications for age-related macular degeneration. Exp Eye Res 2019, 187, 107746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgway, N.D. 25-Hydroxycholesterol stimulates sphingomyelin synthesis in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Lipid Res. 1995, 36, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, V.; Jefferson, J.R.; Singh, R.D.; Wheatley, C.L.; Marks, D.L.; Pagano, R.E. Sphingolipid storage induces accumulation of intracellular cholesterol by stimulating SREBP-1 cleavage. J. Biol Chem. 2003, 278, 20961–20970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, A.; Igarashi, Y. Cross Talk between sphingolipids and glycerophospholipids in establishment of plasma membrane asymmetry. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2004, 15, 4949–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, A. Sphingosine 1-phosphate is a key metabolite linking sphingolipids to glycerophospholipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).