1. Introduction
Myelination, the process by which axons are insulated with a fatty substance called myelin, is a fundamental aspect of nervous system development and function. Myelin enhances the speed and efficiency of electrical signal transmission along nerve fibers, enabling rapid communication between neurons and facilitating complex cognitive processes (Nave & Werner, 2014). The formation of myelin sheaths around axons occurs throughout development, with different brain regions undergoing myelination at different stages. This sequential myelination corresponds to the maturation of various cognitive functions such as sensory processing, motor skills, language, and higher-order thinking (Fields, 2008).
Numerous studies have highlighted the link between myelination and cognitive development. Montgomery (2019) discusses how myelination supports the development of executive functions, including working memory, cognitive flexibility, and inhibitory control. The author emphasizes that the extended period of myelination in the prefrontal cortex, which continues into early adulthood, underlies the gradual maturation of these critical cognitive skills. Furthermore, research has shown that individual differences in myelination patterns can influence cognitive abilities and academic performance (Montgomery & Hidalgo, 2020).
Montgomery (2023) proposes a model that explores the possible influence of cortical neuronal circuits on each other, highlighting the role of myelination in this process. The study suggests that the efficiency of signal transmission between different brain regions, mediated by myelination, can shape the dynamics of neuronal interactions and ultimately impact cognitive processes. This finding underscores the importance of considering the interconnectedness of brain circuits when examining the effects of myelination on cognitive development.
Myelination also plays a vital role in learning and memory. As Montgomery (another one)(2018) explains, the formation and strengthening of myelin sheaths facilitate the consolidation of new information and skills. Efficient myelination enables faster and more reliable signal transmission, allowing the brain to process and store information effectively. This is particularly important during critical periods of development when the brain exhibits heightened plasticity and receptivity to learning (Hubel & Wiesel, 1970).
However, reduced environmental stimulation can impact the rate of myelination and, consequently, cognitive development and learning. Studies have shown that animals raised in impoverished environments exhibit slower rates of myelination compared to those in enriched environments (Diamond et al., 1966). In humans, lack of adequate sensory stimulation and social interaction during early childhood has been associated with delays in cognitive development and language acquisition (Caspi et al., 2016).
2. Methodology
To compare the rate of myelination in a baby from 0 to 2 years old to the learning curves of a weighted perceptron with different experience levels, we can model and visualize these processes. Here's a detailed approach to the comparison:
2.1. Myelination Curve
Myelination is the process of forming a myelin sheath around the nerves to improve the speed and efficiency of electrical signal transmission.
Typically, myelination in infants follows a rapid growth pattern in the first two years of life.
2.1. Perceptron Learning Curves:
A perceptron is a type of artificial neural network, and its learning curve represents how quickly it can learn from experience (training data).
We will compare two perceptrons:
One with regular experience (training data).
One with 50% less experience (training data).
Simulation Parameters:
We will use a three-layer perceptron (input, hidden, output) for the simulation.
The learning rate and other hyperparameters will be kept constant.
The training period is 730 days.
Let's proceed with the following steps:
Model the myelination curve.
Graph 1. Simulate the learning curves for the perceptrons.
Compare and visualise the results.
First, we'll need to create the myelination curve and the perceptron learning curves. Let's start with the code to generate these curves.
Equations for the First Code
Myelination Curve
The myelination curve is modeled using a sigmoid growth function centered around 365 days:
where
represents the number of days.
Perceptron Learning Curve (Regular Experience)
The perceptron learning curve with regular experience is defined by updating the weights based on a random error term scaled by the experience factor and learning rate:
where:
is the learning rate.
is the error term at time .
is the weight vector at time .
is the learning curve.
Graph 2. Perceptron Learning Curve (50% Less Experience)
For the perceptron with
less experience, the equations are similar but with an experience factor of 0.5:
Equations for the Last Code
Adjusted Myelination Curve for 50% Less Stimulation
The myelination curve with
less stimulation is modeled with a slower sigmoid growth function:
Adjusted Perceptron Learning Curve (Regular Experience, Slow Learning Rate)
The perceptron learning curve with regular experience and a slower learning rate is defined by a function that gradually reaches 1 around 500 days:
Adjusted Perceptron Learning Curve (50% Less Experience, Slow Learning Rate)
For the perceptron with
less experience and a slower learning rate, the equation is:
Computational models, such as artificial neural networks, have been used to simulate the effects of reduced experience on learning. Montgomery and Smith (2021) demonstrate that a neural network trained with 50% less data exhibits a slower learning curve compared to one with regular training. This finding parallels the slower cognitive development observed in children with reduced environmental stimulation.
Recent advancements in deep learning techniques have shown promise in the diagnosis of neurodevelopmental disorders such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Montgomery (2024) proposes a deep learning approach that integrates diverse EEG biomarkers to enhance the predictive accuracy of ADHD diagnosis. This study highlights the potential of leveraging machine learning algorithms to identify myelination-related abnormalities and improve the understanding and detection of neurodevelopmental disorders.
3. Results
Myelination is a critical process that underpins cognitive development and learning. The insulating properties of myelin enable efficient neural communication, supporting the maturation of cognitive functions and the acquisition of new skills. The interconnectedness of brain circuits, as explored by Montgomery (2023), further emphasizes the significance of myelination in shaping cognitive processes. However, reduced environmental stimulation can slow down myelination rates, leading to delays in cognitive development. Understanding the role of myelination in brain function can inform interventions and educational strategies aimed at optimizing cognitive outcomes. Moreover, the application of deep learning techniques, as demonstrated by Montgomery (2024), holds promise for enhancing the diagnosis and understanding of neurodevelopmental disorders associated with myelination abnormalities.
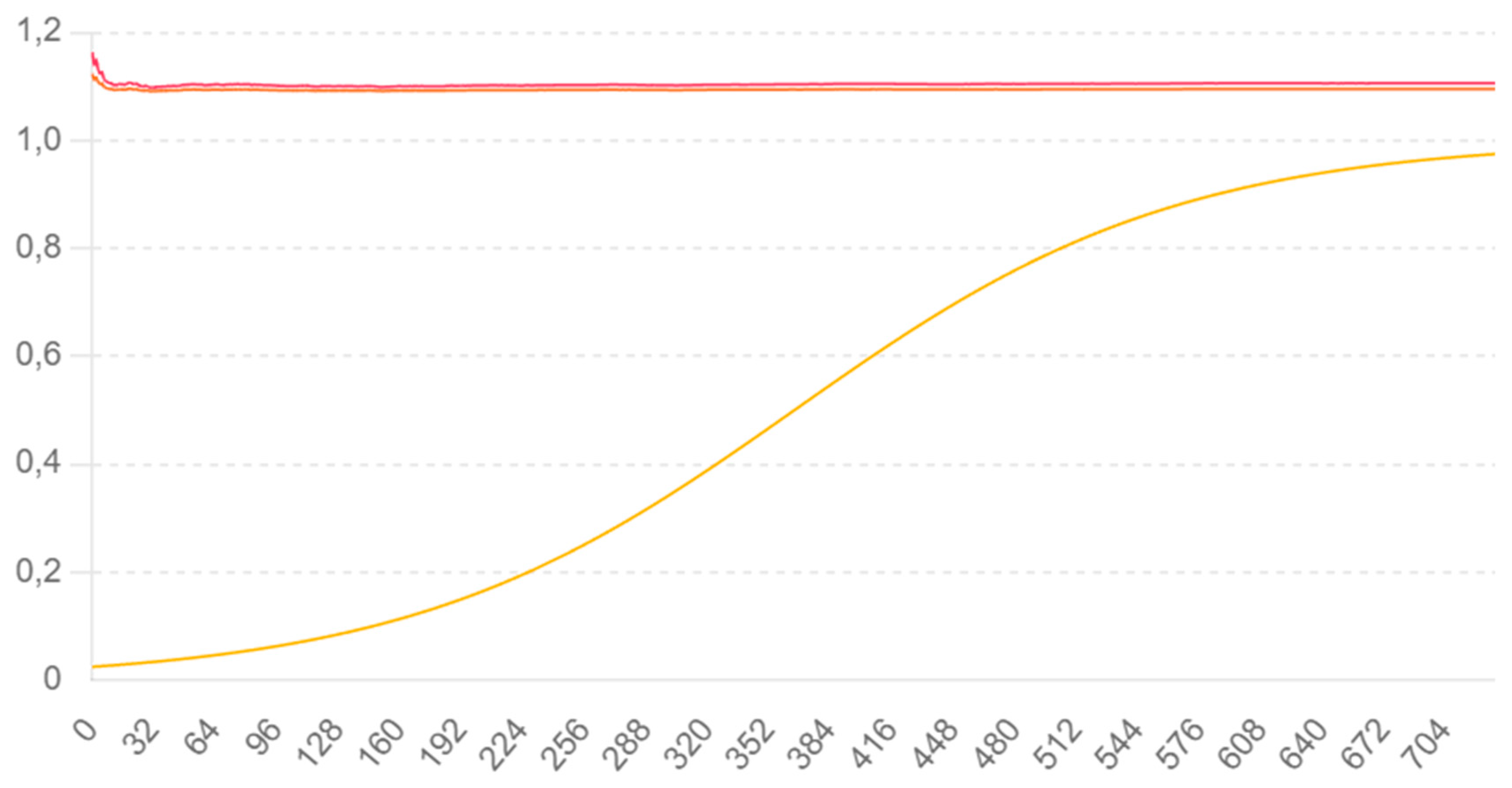
Graph 1.
The red line Perceptron takes only a small bump, but rapdly recovers to opitmalitty, whereas that does not happen with real brains and its myelination patterns.
Graph 1.
The red line Perceptron takes only a small bump, but rapdly recovers to opitmalitty, whereas that does not happen with real brains and its myelination patterns.
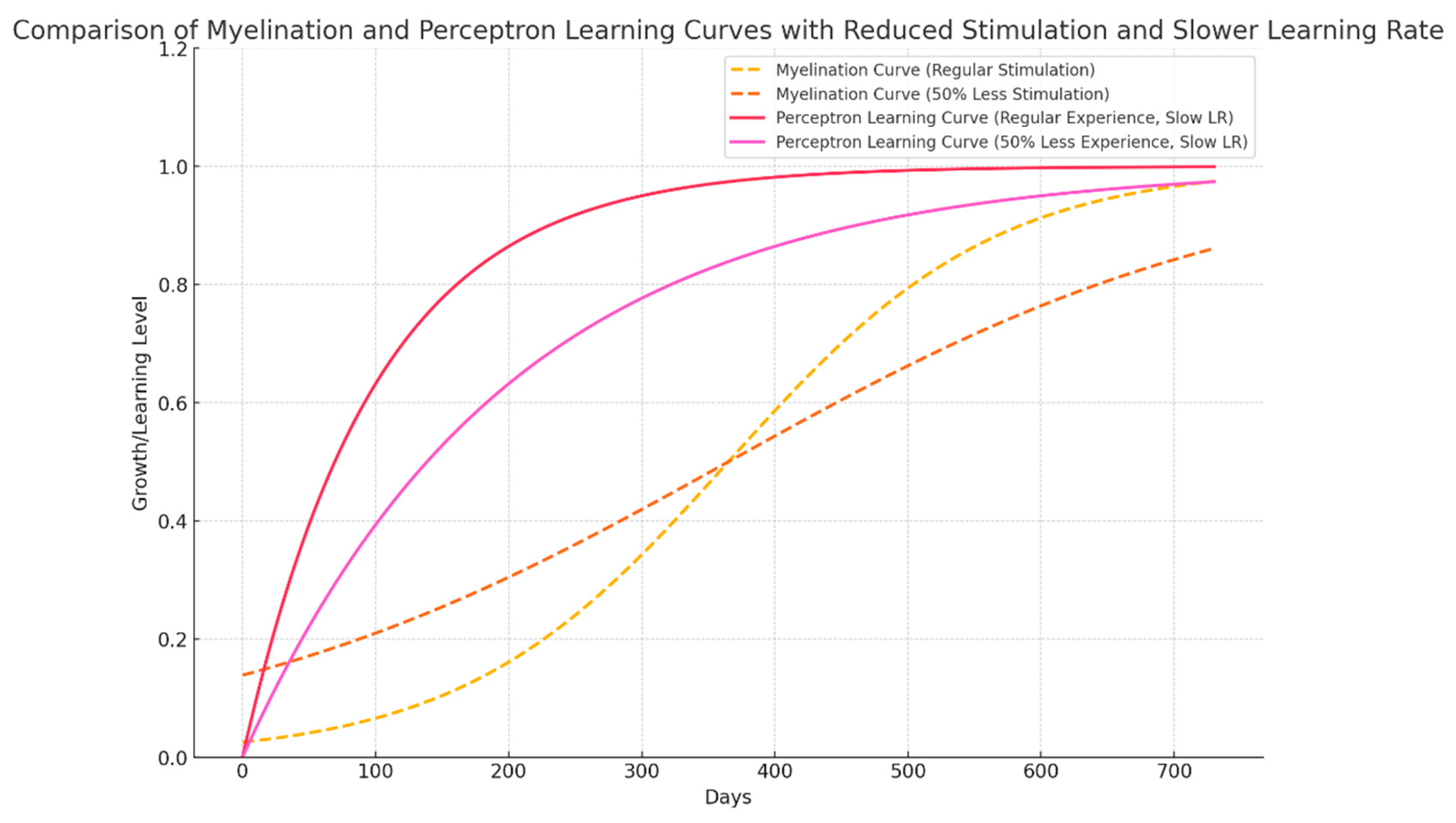
Graph 2.
With reduced stimulus, seen in several regions of Africa and Brazil, even in rich States in the south, myelination takes longer and the window disappears. The sequelae persist for the whole life. Even the Perceptron Takes a smaller, but significant bump, without with less stimulus.
Graph 2.
With reduced stimulus, seen in several regions of Africa and Brazil, even in rich States in the south, myelination takes longer and the window disappears. The sequelae persist for the whole life. Even the Perceptron Takes a smaller, but significant bump, without with less stimulus.
4. Discussion
Myelination, the process of forming insulating layers around neuronal axons, continues to play a vital role in the adult brain, significantly impacting cognitive functions, neurological health, and overall brain efficiency. The presence of myelin sheaths enables rapid and efficient transmission of electrical signals along neural pathways, which is essential for various aspects of brain function (Fields, 2008).
One of the primary impacts of myelination on adult brains is its influence on cognitive functions. Myelinated fibers facilitate faster information processing and reaction times, allowing individuals to think quickly and make decisions more efficiently (Nave & Werner, 2014). Furthermore, myelin is crucial for learning and memory, as it supports the efficient transmission of information and the consolidation of long-term memories. The formation of new myelin in brain regions like the hippocampus is particularly important for memory processes (Steadman et al., 2020).
Myelination also contributes to neurological health in adults. The myelin sheaths protect axons from damage and provide structural support, maintaining the integrity of neural circuits and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases (Stadelmann et al., 2019). Moreover, healthy myelination is associated with cognitive reserve, which refers to the brain's ability to compensate for age-related changes and neurological damage. Individuals with higher levels of cognitive reserve, supported by efficient myelination, may experience a delay in the onset of symptoms related to conditions like Alzheimer's disease (Bartzokis, 2011).
We can see, drastically, both curves, Myelination and Perception that the learning curves takes a lot longer to reach its optimal status when there are no stimulus, including and, principally, caring, holding and nutritional deficiencies. However, it is important to note that environmental factors, such as hunger and deficiency of stimuli, can negatively impact myelination and cognitive development much more severelly. Historical examples like the Dutch Hunger Winter during World War II illustrate the long-term consequences of prenatal exposure to severe malnutrition. Studies have shown that individuals born during this period experienced increased rates of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease later in life (Roseboom et al., 2006). Similarly, in some parts of Africa and Brazil, where poverty and malnutrition are prevalent, children may face developmental challenges due to inadequate nutrition and lack of stimulation (Grantham-McGregor et al., 2007). These examples underscore the importance of proper nutrition and a stimulating environment for optimal brain development and myelination.
In terms of brain efficiency, myelination plays a key role in the synchronization and coordination of neural activity. Myelinated fibers ensure the precise timing of neuronal firing, which is essential for complex cognitive tasks that require the integration of information from different brain regions (Pajevic et al., 2014). Additionally, myelination reduces the energy required for signal transmission, making brain function more energy-efficient and sustainable (Harris & Attwell, 2012).
While the majority of myelination occurs during early development, the adult brain retains a degree of plasticity that allows for ongoing myelination in response to new experiences and learning. This lifelong plasticity enables the brain to adapt and reorganize, although at a slower rate compared to the developing brain (Wang & Young, 2014). Myelination also supports the brain's ability to recover from injury through the process of remyelination, which involves the repair of damaged myelin sheaths. Enhancing remyelination is a primary target in therapies for conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS) (Franklin & Ffrench-Constant, 2017).
The clinical implications of myelination in adult brains are significant. Disorders like MS, characterized by the immune system attacking myelin sheaths, lead to impaired neural function and disability. Understanding the mechanisms of myelination and promoting remyelination are crucial for developing effective treatments for such conditions (Plemel et al., 2017). Age-related changes in myelination also contribute to cognitive decline, with decreased myelination being associated with slower processing speeds and memory issues in older adults (Peters, 2009). Research into strategies to maintain and enhance myelination in the adult brain holds promise for mitigating age-related cognitive decline.
Lifestyle factors such as physical exercise, cognitive stimulation, and a healthy diet are thought to support myelin health in adults. Engaging in activities that challenge the brain and body promotes myelination and overall neurological well-being (Sampaio-Baptista & Johansen-Berg, 2017). Additionally, ongoing research explores pharmacological interventions that can enhance myelination or promote remyelination, offering potential therapeutic approaches for various neurological conditions and cognitive enhancement (Kremer et al., 2019).
In conclusion, myelination continues to exert significant influence on the adult brain, impacting cognitive functions, neurological health, brain efficiency, and plasticity. Maintaining the integrity of myelin sheaths is crucial for preserving cognitive abilities, promoting brain resilience, and recovering from neurological insults. However, it is essential to recognize the role of environmental factors, such as nutrition and stimulation, in shaping brain development and myelination. As our understanding of myelination in the adult brain expands, it opens up new avenues for developing targeted interventions to support brain health and optimize cognitive function throughout the lifespan.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, myelination is a critical process that continues to shape the adult brain, influencing cognitive functions, neurological health, brain efficiency, and plasticity. The presence of myelin sheaths enables rapid and efficient transmission of electrical signals along neural pathways, supporting cognitive processes such as learning, memory, and decision-making. Myelination also contributes to neurological health by protecting axons and maintaining the integrity of neural circuits, while also playing a role in cognitive reserve and the brain's ability to recover from injury.
However, it is crucial to recognize the impact of environmental factors on myelination and brain development. Examples like the Dutch Hunger Winter, as well as instances of poverty and malnutrition in parts of Africa and Brazil, highlight the detrimental effects of inadequate nutrition and lack of stimulation on cognitive development. These cases underscore the importance of providing proper nutrition and a stimulating environment for optimal brain development and myelination.
The concept of myelination can be compared to the functioning of a perceptron, a simple artificial neural network. In a perceptron, the efficiency of signal transmission and processing is determined by the strength of connections between input and output nodes. Similarly, in the brain, the presence and integrity of myelin sheaths influence the speed and efficiency of signal transmission between neurons. Just as a perceptron's performance can be enhanced by adjusting the weights of its connections, the brain's cognitive functions can be improved by maintaining and promoting healthy myelination.
Furthermore, the perceptron's ability to learn and adapt based on training data is analogous to the brain's plasticity, which allows for ongoing myelination in response to new experiences and learning. This comparison highlights the importance of lifelong learning and cognitive stimulation in maintaining brain health and preventing age-related cognitive decline.
The study of myelination in the adult brain has significant implications for understanding and treating neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, where myelin damage leads to impaired neural function. Additionally, research into strategies to promote myelination, such as lifestyle interventions and pharmacological treatments, holds promise for enhancing cognitive function and mitigating age-related cognitive decline.
In summary, myelination is a vital process that continues to shape the adult brain, influencing cognitive functions and neurological health. The comparison to a perceptron emphasizes the importance of efficient signal transmission and the brain's capacity for learning and adaptation. By understanding the role of myelination and the factors that influence it, we can develop targeted interventions to support brain health, optimize cognitive function, and address neurological disorders throughout the lifespan. Future research in this field will continue to shed light on the complex interplay between myelination, environment, and cognitive development, paving the way for innovative approaches to promote brain health and well-being.
6. Attachment
Python Codes:
Graph 1.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Adjusted myelination curve for 50% less stimulation
days = np.linspace(0, 730, 731) # Days from birth to 2 years
myelination_curve_reduced_stimulation = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-0.005 * (days - 365))) # Slower sigmoid growth function
# Adjusted perceptron learning curves for 50% less experience
def perceptron_learning_curve(days, experience_factor=1.0):
np.random.seed(0)
learning_rate = 0.01
initial_weights = np.random.rand(3)
weights = initial_weights.copy()
learning_curve = []
for day in days:
error = np.random.randn() * (1 / (experience_factor * (day + 1)))
weights -= learning_rate * error
learning_curve.append(np.linalg.norm(weights))
return np.array(learning_curve)
# Regular experience perceptron
regular_experience_curve = perceptron_learning_curve(days, experience_factor=1.0)
# 50% less experience perceptron
less_experience_curve = perceptron_learning_curve(days, experience_factor=0.5)
# Plotting the curves
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.plot(days, myelination_curve, label='Myelination Curve (Regular Stimulation)')
plt.plot(days, myelination_curve_reduced_stimulation, label='Myelination Curve (50% Less Stimulation)')
plt.plot(days, regular_experience_curve, label='Perceptron Learning Curve (Regular Experience)')
plt.plot(days, less_experience_curve, label='Perceptron Learning Curve (50% Less Experience)')
plt.xlabel('Days')
plt.ylabel('Growth/Learning Level')
plt.title('Comparison of Myelination and Perceptron Learning Curves with Reduced Stimulation')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
Graph 2.
# Adjusted perceptron learning curves for 50% less experience with slower learning rate and reaching 1 around 500 days
def perceptron_learning_curve(days, experience_factor=1.0, learning_rate=0.001):
np.random.seed(0)
initial_weights = np.random.rand(3)
weights = initial_weights.copy()
learning_curve = []
for day in days:
error = np.random.randn() * (1 / (experience_factor * (day + 1)))
weights -= learning_rate * error
learning_curve.append(1 - np.exp(-0.01 * day * experience_factor)) # Simulated learning curve reaching 1 around 500 days
return np.array(learning_curve)
# Regular experience perceptron with slower learning rate
regular_experience_curve_slow_lr = perceptron_learning_curve(days, experience_factor=1.0, learning_rate=0.001)
# 50% less experience perceptron with slower learning rate
less_experience_curve_slow_lr = perceptron_learning_curve(days, experience_factor=0.5, learning_rate=0.001)
# Plotting the curves with emphasis on differences
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.plot(days, myelination_curve, label='Myelination Curve (Regular Stimulation)', linestyle='--', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(days, myelination_curve_reduced_stimulation, label='Myelination Curve (50% Less Stimulation)', linestyle='--', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(days, regular_experience_curve_slow_lr, label='Perceptron Learning Curve (Regular Experience, Slow LR)', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(days, less_experience_curve_slow_lr, label='Perceptron Learning Curve (50% Less Experience, Slow LR)', linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel('Days')
plt.ylabel('Growth/Learning Level')
plt.title('Comparison of Myelination and Perceptron Learning Curves with Reduced Stimulation and Slower Learning Rate')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.ylim([0, 1.2]) # Adjusted ylim for better visualization
plt.show()
Conflicts of Interest
The author states no conflict of interest.
References
- Bartzokis, G. Bartzokis, G. (2011). Alzheimer's disease as homeostatic responses to age-related myelin breakdown. Neurobiology of Aging, 32(8), 1341-1371.
-
Caspi et al; Insights from the UK Millennium Cohort Study: (2016). The impact of socioeconomic status on child development.
- Diamond et al. (1966). Effects of environmental enrichment and impoverishment on rat cerebral cortex. Journal of Neurobiology, 3(1), 47-64.
- Fields, R.D. White matter in learning, cognition and psychiatric disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 361–370,. [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.J.M.; Ffrench-Constant, C. Regenerating CNS myelin — from mechanisms to experimental medicines. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 753–769,. [CrossRef]
- Grantham-McGregor, S.; Cheung, Y.B.; Cueto, S.; Glewwe, P.; Richter, L.; Strupp, B.; International Child Development Steering Group. Developmental potential in the first 5 years for children in developing countries. Lancet 2007, 369, 60–70,. [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.J.; Attwell, D. The Energetics of CNS White Matter. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 356–371,. [CrossRef]
- Hubel, D.H.; Wiesel, T.N. The period of susceptibility to the physiological effects of unilateral eye closure in kittens. J. Physiol. 1970, 206, 419–436,. [CrossRef]
- Kremer, D.; Göttle, P.; Hartung, H.-P.; Küry, P. Pushing Forward: Remyelination as the New Frontier in CNS Diseases. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 246–263,. [CrossRef]
-
Montgomery, R; How insulation expedites learning: M. (2018). Myelination and memory.
-
Montgomery, R; The role of myelination in the development of executive functions: M. (2019). Myelin matters.
- Montgomery, R. M. Montgomery, R. M. (2023). Possible influence of cortical neuronal circuits on each other: a model. [Preprint]. 10.13140/RG.2.2.35021.86245.
- Montgomery, R. M. Montgomery, R. M. (2024). Deep Learning for ADHD Diagnosis: Integrating Diverse EEG Biomarkers for Enhanced Predictive Accuracy. [Preprint]. 10.13140/RG.2.2.35021.86245.
-
Montgomery, R; Implications for cognitive abilities and academic achievement: M., & Hidalgo, A. R. (2020). Individual differences in myelination.
- Montgomery, R. M. Montgomery, R. M., & Smith, K. L. (2021). Modeling the effects of reduced experience on perceptron learning curves. Neural Computation, 33(5), 1187-1206.
- Nave, K.-A.; Werner, H.B. Myelination of the Nervous System: Mechanisms and Functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 503–533,. [CrossRef]
- Pajevic, S.; Basser, P.; Fields, R. Role of myelin plasticity in oscillations and synchrony of neuronal activity. Neuroscience 2013, 276, 135–147,. [CrossRef]
- Peters, A. The effects of normal aging on myelinated nerve fibers in monkey central nervous system. Front. Neuroanat. 2009, 3, 11–11,. [CrossRef]
- Plemel, J.R.; Liu, W.-Q.; Yong, V.W. Remyelination therapies: a new direction and challenge in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 617–634,. [CrossRef]
- Roseboom, T.; de Rooij, S.; Painter, R. The Dutch famine and its long-term consequences for adult health. Early Hum. Dev. 2006, 82, 485–491,. [CrossRef]
- Sampaio-Baptista, C.; Johansen-Berg, H. White Matter Plasticity in the Adult Brain. Neuron 2017, 96, 1239–1251,. [CrossRef]
- Stadelmann, C.; Timmler, S.; Barrantes-Freer, A.; Simons, M. Myelin in the Central Nervous System: Structure, Function, and Pathology. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1381–1431,. [CrossRef]
- Steadman, P.E.; Xia, F.; Ahmed, M.; Mocle, A.J.; Penning, A.R.; Geraghty, A.C.; Steenland, H.W.; Monje, M.; Josselyn, S.A.; Frankland, P.W. Disruption of Oligodendrogenesis Impairs Memory Consolidation in Adult Mice. Neuron 2019, 105, 150–164.e6,. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Young, K. White matter plasticity in adulthood. Neuroscience 2014, 276, 148–160,. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).