Introduction
Tooth agenesis (TA), the absence of teeth due to developmental failure, is one of the most common developmental malformations, with significant aesthetic, masticatory, and psychological consequences. More than 300 genes are involved in various phases of tooth development. Mutations in these genes can disrupt the interaction between surface-located epithelial cells and the underlying mesenchyme during embryonic development, leading to alterations in the initiation, formation, and differentiation of skin appendages. To date, EDA signaling pathways have been shown to play a crucial role in embryonic ectodermal development [
1].
The ectoderm dysplasia A (EDA) gene, located on chromosome Xq12-13.1, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily [
2]. In 1996, Kere identified that the total length of the human
EDA gene is 425kb, consisting of 12 exons, with EDA1 composing 391 amino acids. EDA is differentially expressed in specific regions and stages of tooth development, and regulates its transcriptional activity by activating the EDA-NF-κB signaling pathway [
3]. Mues and Shen demonstrated that EDA1 variants in non-syndromic tooth agenesis (NSTA) reduce the binding ability of their specific receptor (EDAR), while syndromic mutations in EDA1 associated with syndromic tooth agenesis (STA) completely lose this binding ability [
4], resulting in a reduction or loss of the transcriptional activity of the downstream signaling molecule Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) [
5], consequently decreasing the proliferation capacity of odontogenic cells. However, overexpression of EDA1 can promote cell proliferation in the dental lamina, facilitate the development of additional substrates, and enhance the transcriptional activity of NF-κB [
6].
In the human embryo, EDA1 expression is not limited to the ectodermal tissues but is also detected in the developing neuroectoderm, thymus, and bone [
7]. Park found that osteopetrosis-like changes in the calvarial bone of Eda1-deficient mice and the impact of EDA1 deficiency on osteoclastic differentiation in vitro, suggesting that diminished expression of osteoclastic activity-associated co-enzymes may lead to disturbed bone homeostasis in Tabby calvariae postnatally [
8]. Tabby mice exibit a striking kink in the tail and medaka (afl
-/-) [
9], which has a nonsense mutation in its
EDA1 gene, show a lack of elongation in fin rays [
10]. This indicates that the EDA/EDAR signaling event precedes osteoblast differentiation. During tooth embryo development in Tabby mouse, the tooth bud develops abnormally, becoming smaller in size [
11], the number of teeth decreases after birth, and the number of tooth cusps is reduced, leading to undersized teeth [
1].
Numerous studies have shown that the effects of EDA1/EDAR are largely mediated by NF-κB [
12,
13], although the exact mechanisms by which EDA1 regulates the development of ectodermal structures are still under investigation. The specific ways in which EDA1 regulates the development of dental stem cells into teeth remain to be further studied. Our study utilizes the characteristics of dental pulp stem cells to investigate the effects of EDA1 on proliferation, migration, and mineralization during tooth development, as well as its regulatory mechanisms. This research provides new insights into the pathogenesis of congenital tooth loss.
Materials and Methods
1. Construction of EDA expression vectors
Mammalian expression vectors for secreted FLAG-tagged forms of wild-type EDA1, EDA1 with the HED-causing variant H252L were kindly provided by Professor Pascal Schneider (Department of Biochemistry, University of Lausanne, Switzerland). Variants of EDA1 associated with non-syndromic tooth agenesis (A259E, S374R) were generously provided by Professor Hailan Feng (Department of Prosthodontics, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, China) [
14].
2. hDPSCs cell culture and transient plasmid transfection
Human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs) were generously donated by the Oral Stem Cell Bank (Beijing Taisheng Biotechnology Co., LTD, Beijing, China). hDPSCs were cultured in high-glucose DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 ℃ and incubated in a 5% CO2 incubator. After 12 hours, the serum was removed. The hDPSCs were then spread in 6-well cell culture plates at a density of 2×105 cells per well and incubated for 24 hours. Plasmids of each group (Wt, STA-H252L, NSTA-A259E, NSTA-S374R, PCR3/NC) were transfected with Lipofectam 3000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA).
3. Proliferation
3.1 Cell counting kit 8 (CCK8) assay
The proliferation of hDPSCs was investigated using the CCK8 (Beyotime Biotechnology, Shanghai, China). Briefly, 3 hours after transfection, the cells (6 × 103/well) were seeded into a 96-well plate (Corning). Five parallel wells were set up in each group, with a control group receiving only 200 μl medium. At 0, 12, 24, 48, 72 and 96 hours, hDPSCs were incubated with CCK8 reagents at 37 ℃ for 3 hours. Absorbance at 450 nm was measured using a microplate reader (BioTek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA).
3.2 Flow cytometry analysis
Forty-eight hours after transfection, hDPSCs were digested with 0.25% trypsin solution and washed twice with precold PBS buffer; The cells were then fixed with 70% ethanol at 4 ℃ for 24 h. The cells were suspended in 200 μl PBS, mixed with 1 ml propidium iodide(PI) solution, and stained at 4 ℃ for 30 minutes. Flow cytometry was used to detect the data, and Muticycle AV analysis software was employed for fitting analysis. The experiment was repeated for 3 times.
4. Migration assay
4.1 Wound-healing migration assay
The cells were plated on Petri dishes and cultured for at least 12 h after transfection. A wound was created by dragging a sterile blue pipette tip along the center of the plate. Detached cells were washed out twice. Images of the cell monolayers were taken at the indicated time using the phase-contrast microscope with a digital camera. The wound width was calculated by measuring the mean distance between the wound margins in randomly selected fields, directly on photographs. Migration was quantified by calculating the wound area at time points t0 (time of wound), t24 (24 hours after wound) t48 (48 hours after wound) and t72 (72 hours after wound). Normalization was achieved using the formula [area (t0) – area (t24 or 48 or 72)]/ area(t0)×100%.
4.2 Transwell assay
Transfected 293T cells were simultaneously spread with hDPSCs at 1×105/ml on the upper layer of 24-well Transwell cells using 200 μl of cell suspension. Forty-eight hours after transfection, the Transwell culture chamber was taken out and lightly washed twice with PBS. The cells were then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 30 minutes, stained with 0.1% crystal violet for 1 hour, and washed three times with double-distilled water. Neutral gum was used to seal the slides. Photographs were taken and cell counting were performed under an inverted microscope at high power (×40). Five fields were randomly selected for photography and counting of migrated cells.
5. Odontogenic differentiation
5.1 Alizarin red staining assay
Transfected hDPSCs were plated in 12-well plates and cultured for 21 days. The cells were then fixed with 4 % PFA for 1 hour and washed with PBS. Next, the cells were stained with 40 mmol/L alizarin red solution (pH 4.2) for 10 minutes under gentle agitation. After decoloration and air-drying, the culture plates were evaluated by light microscopy using an inverted microscope. The color intensity of each image was analyzed using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, USA) [
15]. The color intensity of cells is directly proportional to the odontoblastic activity of hDPSCs.
5.2 Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) assay
Transfected hDPSCs were seeded in a 12-well plate and cultured for 7 and 14 days, respectively. After cultivation, cells were stained with 200 μL of 0.2% lysis buffer solution containing 10 μl Triton X-100 in 5 mL MgCl2 for the Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) assay, following the manufacturer’s protocol outlined in the ALP analysis kit (DGKC, Pars Azmun, Iran). Photographs of the stained 12-well plates were taken using an inverted microscope, and the results were analyzed semi-quantitatively using Image Pro Plus 6.0 software.
6. RNA sequencing
hDPSCs transfected with wild-type EDA1 and variants were seeded in a 6-well plate and cultured for 48 hours, with three samples in each group. Samples were sent to iGeneTech (iGeneTech Bioscience Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) for transcriptome sequencing. Paired-end libraries were prepared using the ABclonal mRNA-seq Lib Prep Kit (ABclonal, China), following the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR products were purified using the AMPure XP system, and library quality was assessed on an Agilent Bioanalyzer 4150 system. Finally, the libraries were sequenced on an Illumina Novaseq 6000 (or MGISEQ-T7) to generate 150 bp paired-end reads. Data from the Illumina (or BGI) platform were utilized for bioinformatics analysis. All the analyses were performed using an in-house pipeline from Shanghai Applied Protein Technology. Differential expression analysis was performed using DESeq2 (
http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/DESeq2.html). Genes with | log 2 FC | > 1 and an adjusted p-value (Padj) < 0.05 were considered to be significantly differentially expressed.
7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Total RNA was extracted from hDPSCs transfected with EDA1 variants using TRIzol™ reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific) following a standard RNA isolation protocol. cDNA was synthesized using the Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus Reverse Transcriptase system (Promega GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Quantitative real-time PCR (RT-PCR was performed using
Applied Biosystems™ 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), with primer sequences and thermal cycling conditions available upon request. The gene encoding the 18S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) served as a housekeeping gene for normalization. All measurements were performed in quintuplicate and averaged. Relative gene expression levels were calculated using the delta-delta Ct method. The specific primers used for genes are shown in
Table 1:
Results
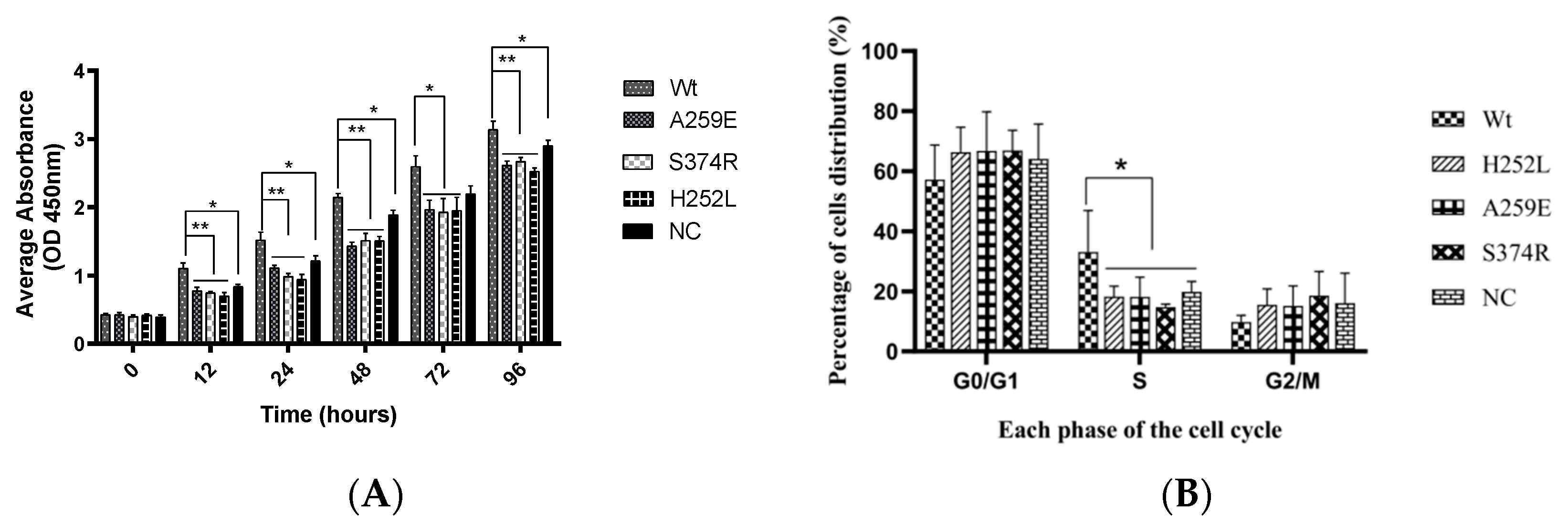
1. Wild-type EDA1 promotes DNA replication in the S phase of hDPSCs, thereby enhancing cell proliferation, while EDA1 variants lost this ability.
In this study, cell proliferation of hDPSCs was assessed using CCK-8 (
Figure 1A). Wt-EDA1 significantly promoted hDPSCs proliferation at all observation time points, compared to NAST-EDA1 (A259E, S374R) and STA-EDA1 (H252L) groups (p<0.01). There was also a statistically significant difference between the Wt-EDA1 group and the control group (p<0.05). However, there was no significant difference between EDA1 variants and the control group.
The cell cycle of hDPSCs transfected with EDA1 variants was analyzed by flow cytometry. The proportion of S-phase hDPSCs was obviously higher in the Wt-EDA1 group compared to the control group and all varians (
p<0.05). No significant differences were observed between variants and the control group. The proportion of G0/G1 phase cells decreased in Wt-EDA1 group, and there was no dramatically difference compared with the control group and all variants (
p>0.05). Similarly, there was almost no difference in the distribution of cells in the G2/M phase among all groups (
p>0.05) (
Table 2,
Figure 1B).
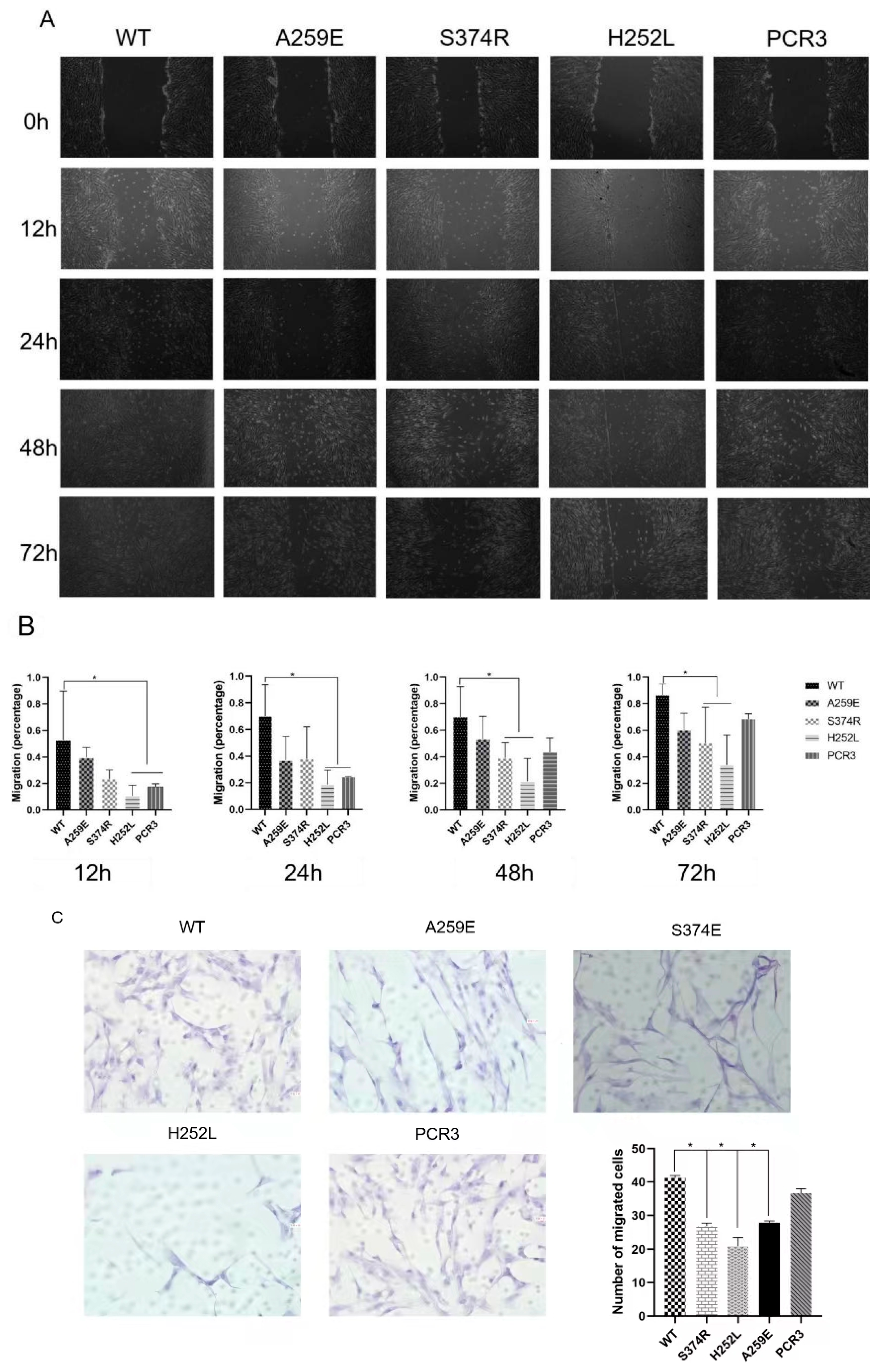
2. EDA1 variants downregulates the migration of hDPSCs cells
Scratch experiments on hDPSCs transfected with wild-type and EDA1 variants (
Figure 2A,B) revealed that the scratch area was smallest in the wild-type EDA1 group at various time points. Specifically, at 12 hours and 24 hours scratching, the scratch area in the wild-type group was significantly decreased indicating increased migration rate compared to control group and variants and the syndrome mutation group (H252L) (
p<0.05). At 48 hours and 72 hours, the migration rate of hDPSCs in variants was lower than that of the wild-type group. However, compared to the nonsyndromic mutation group (S374R) and the syndrome mutation group (H252L), the scratch area of the wild-type group was significantly reduced, and the migration rate was significantly increased (
p<0.05). At each time point, there was no significant difference in the cell migration rate between variants and the control group.
HEK293T cells transfected with wild-type and variants of EDA1 were cultured in the lower chamber, while hDPSCs cells were co-cultured in the upper chamber. The number of hDPSCs passing through the pores was detected at 48 hours. It was observed that the highest number of hDPSCs passed through the pore was the most in the wild-type group, with a significant difference compared to the variants (
p<0.05). The number of migrated hDPSCs in the variants was lower than that in the control group, and higher in the wild-type EDA1 group compared to the control group. However, there was no statistical significance in the number of migrated hDPSCs between the wild-type EDA1 group and the mutant EDA1 groups compared to the control group (
p>0.05) (
Figure 2C).
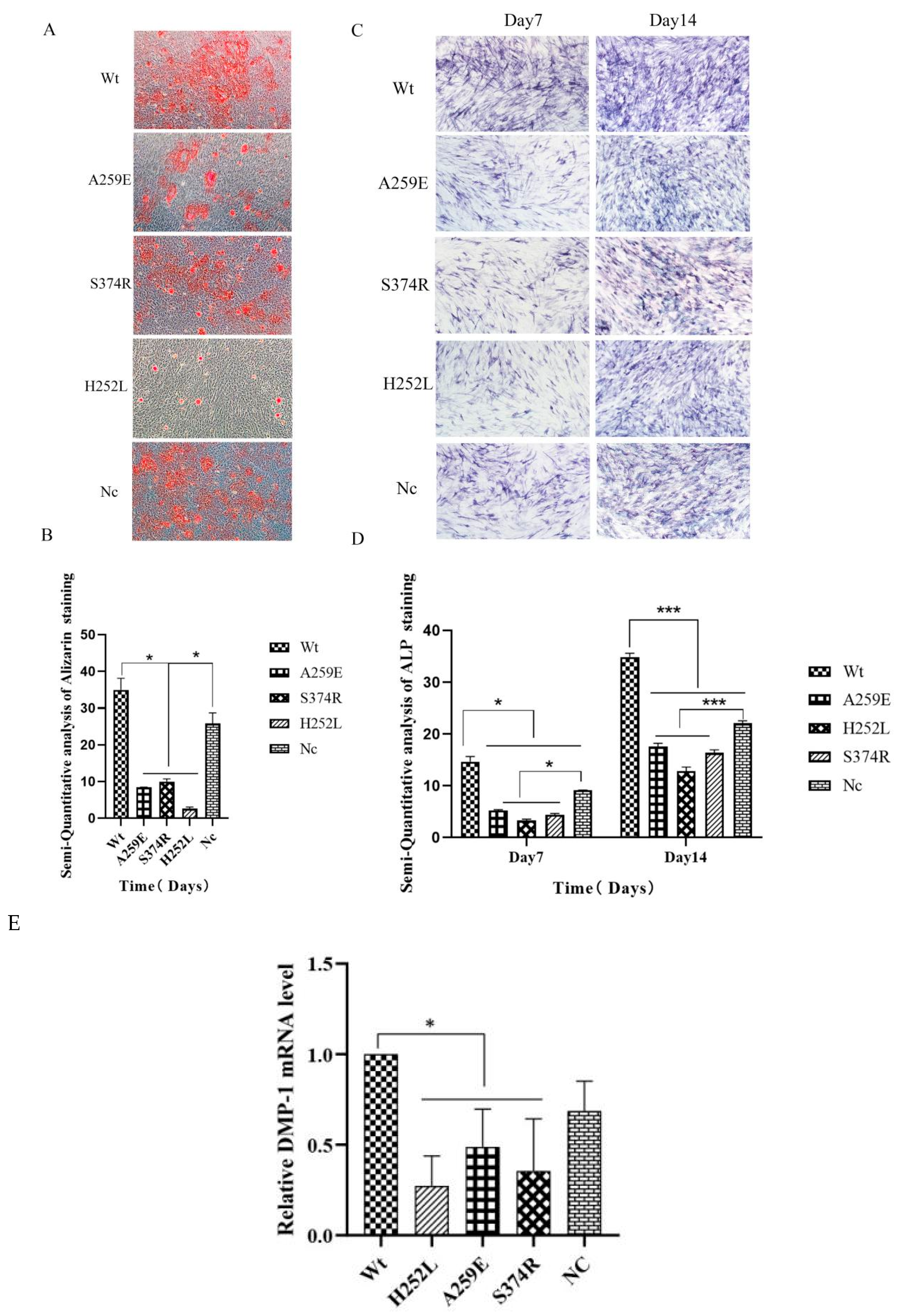
3. Wild-type EDA1 promotes odontogenic differentiation of hDPSCs
In this study, alizarin red staining and ALP staining were used to assess the effect of EDA1 on the mineralization ability of hDPSCs. The results from alizarin red staining showed that on the 21st day of odontogenic differentiation induction, the overexpression of wild-type (Wt) EDA1 upregulated the mineralization ability of hDPSCs. The Wt group showed the highest deposition of calcification, while EDA1 variants caused reduced calcification in hDPSCs. Using Image Pro Plus 6.0 software for semi-quantitative analysis of the staining results, it was observed that the calcium deposition in both non-syndromic and syndromic variants of EDA1 was dramatically lower than that in Wt and NC groups (
p<0.05). This suggests that EDA1 variants inhibit the mineralization of hDPSCs. Additionally, there was no statistically significant difference in calcium deposition between the groups with non-syndromic and syndromic EDA1 mutations (
Figure 3A,B).
The results of ALP staining were consistent with those of alizarine red staining (
Figure 3C,D). On day 7 and 14 of odongenetic differentiation, the expression of ALP in hDPSCs decreased in the non-syndromic and syndromic mutants of EDA1, whereas wild-type EDA1 promoted ALP expression in hDPSCs. It was found that on the 7th day of odontogenic differentiation, compared with Wt and NC groups, the expression of ALP significantly decreased in the non-syndromic and syndromic mutant groups (
p<0.05). On the 14th day of odontogenic differentiation, ALP expression in the non-syndromic and syndromic mutant EDA1 groups further decreased compared to the Wt and NC group, with a statistically significant difference (
p<0.001). There was no statistically significant between the Wt and NC groups. All variants inhibited the expression of ALP in hDPSCs, but there was no statistically difference in ALP expression among the different variants.
The expression level of
DMP-1 mRNA in hDPSCs during odontogenic differentiation was detected by qPCR. The results showed that compared with the Wt group, EDA1 variants down-regulated
DMP-1 mRNA expression, with the difference being statistically significant (
p < 0.05). However, there was no significant difference in the expression of
DMP-1 mRNA among the variants.(
Figure 3E).
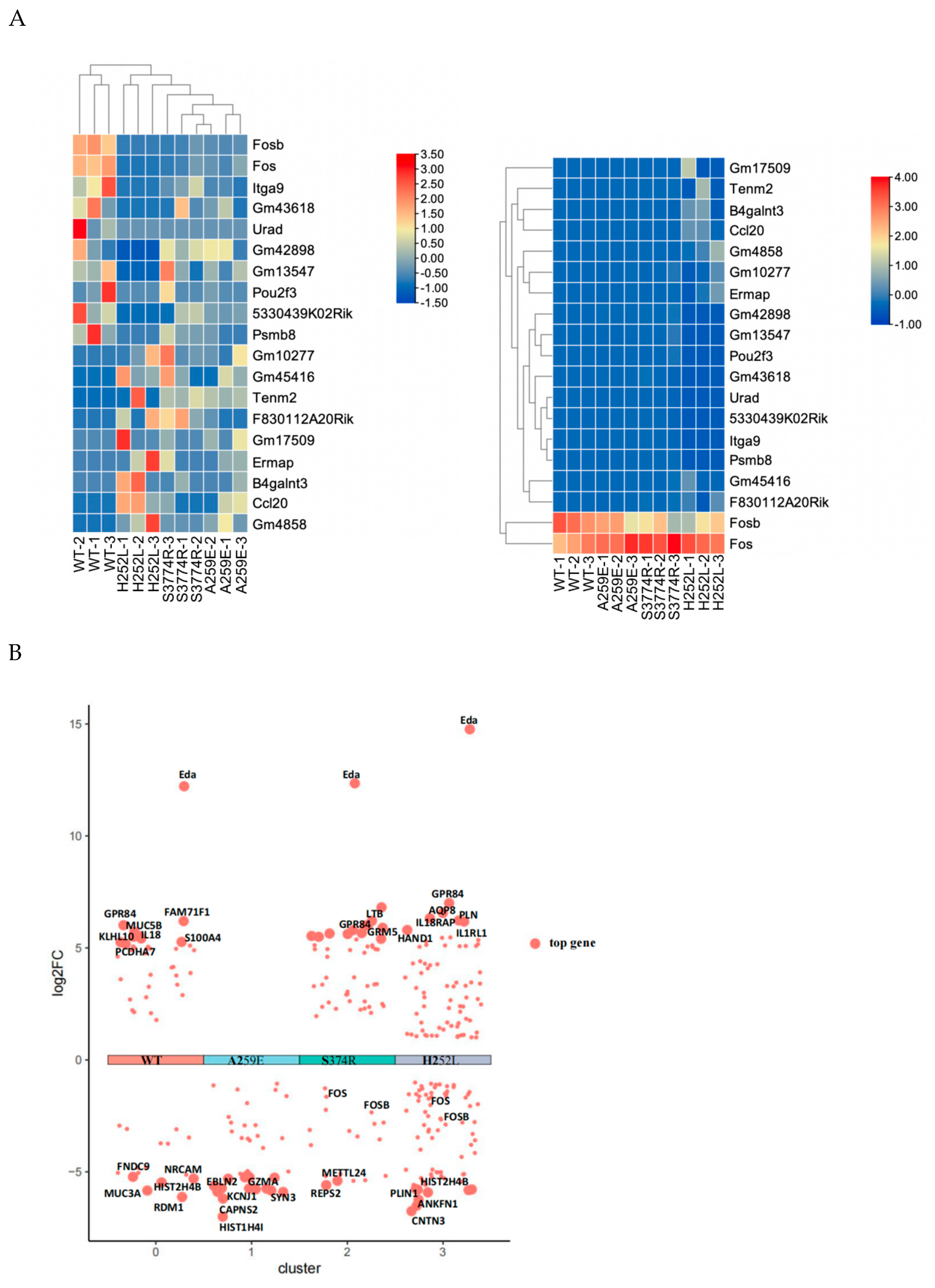
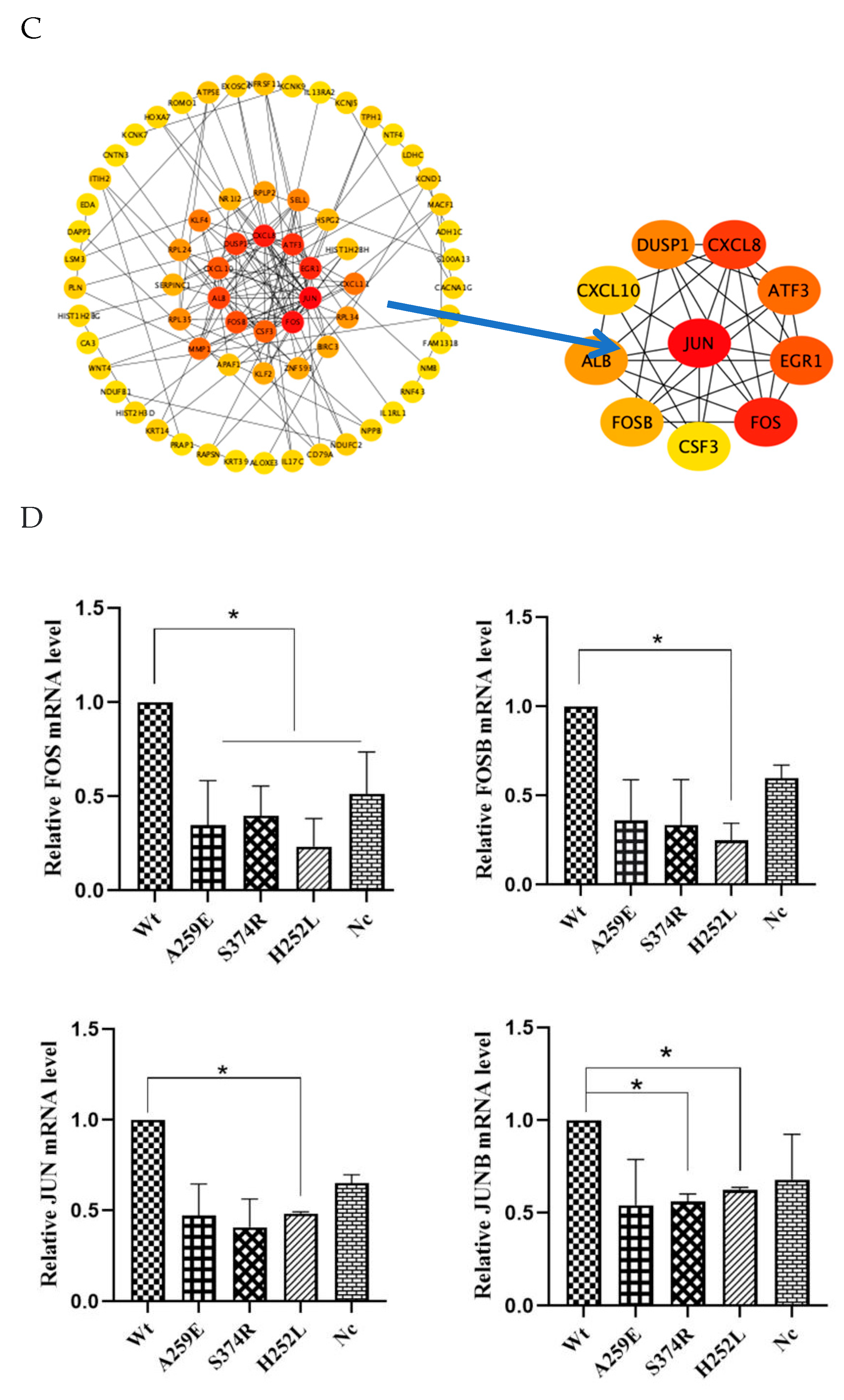
4. RNA-sequencing revealed differential expression of AP-1, and further found that EDA1 variants fail to the promote c-FOS mRNA expression in hDPSCs
The transcriptome data of the all variants were compared with those of the wild-tyoe group. Differential gene expression analysis identified common differentially expressed genes accorss each group:
c-FOS,
FOSB,
JUN,
JUNB. The data were visualized in a “volcano plot”, where the horizontal axis represents the fold change in gene expression between different samples (log2 Fold Change), and the vertical axis denotes the significance level of gene expression differences (-log10 (p-value)). Elevated expression levels are depicted by red dots, decreased expression levels by green dots, and no significant change by black dots. Volcano plot analysis showed that, compared with the NSTA-S374R group, the expression levels of
FOSB and
c-FOS genes in the wild group were significantly increased (
p<0.05). Similarly, compared with the STA-H252L, the expression levels of
FOSB,
c-FOS and
JUN genes in the wild group were obviously increased (
p<0.05) (
Figure 4A,B). The key hub genes identified were
c-FOS,
FOSB,
JUN and
JNB (
Figure 4C).
Differentially expressed genes (
c-FOS,
FOSB,
JUN,
JUNB) were verified by qPCR. Compared with Wt-EDA1, the expression of
c-FOS mRNA in NSTA-EDA1, STA-EDA1 and Nc groups decreased significantly (p<0.05). However, there was no significant difference in
c-FOS mRNA between the Nc group and the EDA1 variants. Compared with Wt group, only the STA-EDA1 group showed a significant decrease in
FOSB mRNA level (p<0.05), with no difference observed compared with the Nc group. Compared with Wt and Nc groups,
FOSB mRNA levels in NSTA-EDA1 variants were also down-regulated, but the difference was not statistically significant (p>0.05). There was no significant difference in
FOSB mRNA expression level in the Nc group compared with Wt and EDA1 variant groups (p>0.05). The results for
JUN mRNA and
JUNB mRNA expression in the abovementioned groups were consistent with those for
FOSB mRNA (
Figure 4D).
Discussion
The development of teeth is regulated by intricate cell and tissue interactions and genetic networks, involving the same signaling pathways active in all development stages and especially that of ectodermal organs. These pathways, such as Wnt/β-catenin, TGF-β/BMP, SHH and Eda/Edar/NF-κB interact in a complex regulatory network and play key roles in regulating the development of dental embryos [
16,
17]. Disturbances in the homeostasis of these signaling molecules during development can change the number of teeth and tooth morphology [
1,
18,
19]. The EDA signaling pathway is known to be plays a crucial role in tooth development and skin appendages [
20].
Overexpression of
EDA1 increases the size of placodes [
6], while the absence of EDA/Edar signaling leads to a rudimentary pre-placode formation [
21]. Interestingly, ectopic tooth and mammary placodes, and consequently supernumerary organs are induced in mice overexpressing
EDA1 [
6,
22]. These studies show that EDA1 determines the number of teeth and the morphological development of teeth. However, how EDA1 regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal signaling network to determine the fate of tooth development remains a mystery.
The first morphological sign of embryonic development is a localized thickening in the surface epithelium that subsequently invaginates into the underlying mesenchyme to form a placode. During initial morphogenesis, Eda/Edar signaling, which regulates the function of the epithelial signaling centers, is associated with epithelial mesenchymal interactions [
23]. The expression of EDA1 was observed in the dental epithelium of mice 12 days after the initiation of embryonic development. By day 14, EDA1 expression became localized in both the cervical region of cap tooth embryos within the oral epithelium and the outer enamel epithelium. Transfection of
EDA1 variants to human umbilical vein endothelial cells showed that the proliferative activity of the mutants was significantly decreased [
24]. Our research team previously found that overexpression of
EDA1 in ameloblastoid cell lines in vitro promoted the transformation of G0/G1 phase cells into S phase, resulting in cell proliferation, while the syndromic mutant EDA1 lost its ability to promote cell proliferation [
25]. It was speculated that the loss of syndromic variant of EDA1 protein binding to its specific receptor leads to reduced transcription activity of NF-kB in the downstream signaling pathway [
14], losing its ability to induce site-specific proliferation of odontogenic epithelial cells, potentially affecting site-specific development of the tooth embryo. In vivo, in the absence of Edar/NF-κB signalling, placodes in downless and Tabby mice start to develop, but rapidly abort. EDA plays a critical role in promoting BM-MSC differentiation into sweat glands. Furthermore, the expression of downstream genes of NF-κB (
Shh and cyclin
D1) was also enhanced [
26].
In the human embryo, EDA1 expression is not limited to the ectodermal tissues but is also detected in the developing neuroectoderm, thymus, and bone [
7]. The expression of Eda/Edar in hair follicles, teeth and sweat glands is found not only in the epidermis but also in adjacent dermal mesenchymal cells. However, studies on the effect of EDA1 on dental mesenchyme are few and need further investigation. In the present study, we found that wild-type EDA1 promoted DNA replication in the S phase of hDPSCs, thereby promoting cell proliferation. In construct, EDA1 variants lost their ability to promote hDPSCs proliferation, consistent with the effect of EDA1 on odontogenic epithelial proliferation. It is suggested that EDA1 variant leads the decrease of NF-κB activity in tooth germ epithelium and mesenchymal cells, which reduces the proliferation activity of dental epithelial and mesenchymal cells, thus affecting the development of tooth germ. Moreover, we found that EDA1 plays an important role in the migration of dental pulp stem cells. Overexpression of EDA1 upregulated the migration of dental pulp stem cells, while EDA1 down regulated cell migration in both non-syndromic and syndromic variants in vitro. This finding aligns with Iida’s evidence that Edar-expressing cells migrate toward fin ray elongation, stimulating mesenchymal proliferation, followed by mesenchymal condensation and differentiation into mesenchymal cells into osteoprogenitor cells in the proximal region. In afl larvae, the onset of fin ray formation is marked by the expression of Edar in the epithelial cells. However, NF-κB is not activated because of loss of binding of Eda to Edar. Consequently, the Edar-expressing cells are unable to migrate and remain at the starting point. This restriction leads to mesenchymal condensation and differentiation into osteoprogenitor cells, resulting in the formation of short and thin fin rays [
10].
In the study variants of EDA1 inhibit ALP activity and the formation of calcified nodules, thereby reducing the ability of hDPSCs to differentiate into dentin in vitro. This reduction may be related to the small tooth morphology though the underlining mechanism requires further investigation. Additionally, Tabby mice have also been reported to show spontaneous tail vertebral fractures linked to epiphyseal and subepiphyseal dysplasia. Schweikl found that Tabby calvarial bone and Tabby bone marrow-derived osteoclasts showed significantly reduced activity of osteoclastic co-enzymes including cathepsin K, Mmp9, Trap, and Tcirg1 (V-type proton ATPase a3 subunit) compared to wild-type calvariae in vivo or osteoclasts in vitro. This reduction indicates diminished nuclear Nfatc1 and bone-resorbing enzymes, likely underling osteopetrosis-like changes in Eda1-deficient murine calvariae [
8]. Taken together, these studies suggest that EDA1 regulates the osteogenic differentiation of dentin and bone. EDA1 binds to its specific receptor EDAR, which ultimately activates NF-κB, a major regulator of skeletal development and osteoclastic differentiation [
27,
28]. The activation of NF-κB requires the RANKL-RANK-TRAF6 complex. Impairment of this pathway in Tabby mice might interfere with the EDA1-TRAF6-RANK molecular interaction, and consequently, osteoclastic differentiation [
29].
The EDAR has been found to be expressed in osteoclasts [
9]. NF-κB plays a critical role in the maturation of osteoclasts [
30]. As TNF can synergize with minute amounts of RANKL to promote osteoclastogenesis, it is plausible that EDA1 might also synergize with RANKL, a hypothesis that warrants further investigation. In osteoclastic differentiation, the RANKL/RANK binding activates and/or induces the expression of key transcription factors, such as NF-κB, Nfatc1, cellular oncogene fos (c-Fos), microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (Mitf), and purinerich box-1 (PU.1), all of which are essential for osteoclastogenesis both in vitro and in vivo [
31].
Genome-wide expression profiling of whole skin RNA from embryonic and adult mice has identified numerous EDA target genes [
32]. In a complementary study, Esibizione profiled the gene expression patterns of cultured primary keratinocytes from wild-type and Tabby mice, revealing several candidate EDA target genes, including
Tbx1,
Bmp7 and
Jag1, using microarray [
33].
During tooth development, EDA1 activates NF-κB transcription through the EDA-NF-KB signaling pathway, which enters the nucleus to regulate downstream target genes, thereby influencing the proliferation, migration and mineralization of tooth germ cells. Identifying the specific genes regulated by NF-κB after its nuclear entry, and how they affect tooth germ development, remains a significant focus in dental development research. In the study, human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs) were transfected with variants of nonsydromic EDA1, syndromic EDA1 and wild-type plasmids. RNA-sequencing was used to screen the expression of downstream differential gene. Our finding showed the biological behaviors, such as cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation, was consistent with previous studies, indicating that wild-type EDA1 promotes cell proliferation, migration, osteoclast differentiation and other biological behaviors.
Hub genes such as c-FOS, FOSB, JUN and JUNB were identified by RNA-seq, and q-PCR verification revealed that the syndromic EDA1variant significantly reduced the transcription level of AP-1 in dental pulp stem cells. Interestingly, the non-syndromic EDA1 variants primarily affected the transcription level of c-FOS. Therefore, it is speculate that different downstream signaling molecules are activated by the EDA1 variants. The syndromic variant not only affects tooth development, but also impacts the development of other organs, including bone structure, whereas the nonsydromic variant affects tooth development.
The proteins of Activator protein-1 (AP-1) family are involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, inflammation, immune response, and other physiological and disease-related functions. Studies have elucidated that AP-1 family members are expressed during various stages of tooth development and play a role in regulating the expression of tooth development-related proteins, such as DSPP, DMP-1, Amelotin [
34,
35,
36]. The c-Fos protein is a major component of the AP-1 transcription factor complex, which includes members of the Jun family. It has been proposed that c-Fos is important for signal transduction, cell proliferation and differentiation. Stable expression of c-Fos in mice has been observed in developing bones and teeth, haematopoietic cells, germ cells and the central nervous system. All homozygous c-Fos knock out (KO) mice and rats are toothless, indicating that c-Fos is crucial for the occurrence and development of tooth germ [
37,
38]. Homozygous c-Fos KO rats also show bone development abnormalities resulting from a deficiency of osteoclasts, similar to those seen in c-Fos KO mice. Thus, c-Fos is essential for inducing osteoclast differentiation from progenitor cells [
39].
Enamel and dentin are part of human mineralization, similar to bone. XLHED patients and Tabby mice exhibit smaller tooth size, abnormal cusp morphology, and other mineralization abnormalities. In the study, alizarin red staining revealed that EDA1 regulates the odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells in vitro. Variants of EDA1 led to a reduction in mineralized nodules by dental pulp stem cells, particularly with syndromic EDA1 variants. However, the mechanism by which EDA1 affects tooth mineralization remains unclear. RNA-sequencing revealed differential expression of AP-1, further q-PCR verification showed that EDA1 variants fail to the promote c-FOS mRNA expression in hDPSCs.
Therefore, we speculated that EDA1 variants fail to the promote c-FOS mRNA expression in hDPSCs, thereby inhibiting odontogenic differentiation and losing the ability to enhance the proliferation of hDPSCs, thus affecting tooth development.