1. Introduction
Humans are constantly exposed to electromagnetic fields originating from both natural and artificial sources. Extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields (ELF-EMF), ranging from 3 Hz to 300 Hz, and produced by power lines, railways, and electrical devices, have been the subject of extensive biomedical research. However, the information available remains fragmentary, incomplete, and occasionally contradictory, leaving uncertainty about whether exposure to ELF-EMF is beneficial or harmful to human body [
1].
Numerous studies have suggested potential genotoxic, carcinogenic, and neurological effects of ELF-EMF [
2,
3], but recent investigations have also reported anti-neoplastic [
4,
5] or therapeutic effects on various organs and body systems including the mechanisms of repair in bone, cartilage, and skeletal muscle [
6,
7,
8]. This heterogeneity of results could be primarily attributed to variable models and different frequencies, intensities, and exposure times of ELF-EMF.
To fully comprehend the effects of electromagnetic fields on skeletal muscle and other body systems, both in vitro and in vivo models are required. In vitro models provide a controlled environment (including specific wavelengths, frequencies, and magnetic field intensities) to examine the direct effects of ELF-EMF on cells, allowing a focused understanding on the cellular mechanisms involved.
Our previous in vitro investigations provided new insights into the mechanisms underlying the biological effects of ELF-EMF on skeletal muscle. We demonstrated that short exposures (5-30 minutes) to ELF-EMF (0.1-1.0 mT, 50 Hz) on skeletal muscle cells modulate their redox status and Ca
2+ handling and that these effects are abolished by the administration of an antioxidant molecule [
9]. Many others in vitro studies revealed that the mechanisms underlying the interaction between ELF-EMF and cells involve the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [
10,
11,
12]. If ROS generation and accumulation in the cells can be considered the primum movens of effects induced by ELF-EMF exposure, the modification of intracellular Ca
2+ levels could be one of the most important mechanisms by which ROS exert their multiple effects on cellular processes including differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis [
13].
Indeed, we observed that long exposures (24-48-72 hours) to ELF-EMF promoted skeletal muscle differentiation in C2C12 cells, through increasing gap junctional intercellular communication and facilitating direct cell-cell transfer of ions such as Ca
2+ and other small molecules [
14].
A recent study found that exposure to ELF-EMF at 2.0 mT magnetic flux density can activate C2C12 cells and upregulate the transcription factor PAX7, which is crucial for the activation and proliferation of satellite cells. Meanwhile, exposure to 1.5 mT ELF-EMF can upregulate the expression of MyoD and myogenin. The authors suggest that ELF-EMF therapy that uses different magnetic flux densities may be more effective in promoting muscle repair in clinical practice [
15].
Nevertheless, in vitro models have limitations as they simplify the natural environment and overlook the complex interactions between various cell types, tissues, and organs found in living organisms. Animal models can provide a more integrated understanding of the physiological consequences of electromagnetic field exposure on skeletal muscle since they allow the observation of long-term effects and the exploration of complex interactions between different organs and tissues.
Some in vivo studies have confirmed that the action of ELF-EMF occurs through the production of ROS [
16,
17].
Lai et al. reported that exposure of rats to a 60-Hz magnetic field induced DNA single and double bond breaks in nervous cells [
18,
19]. The use of free radical scavengers prevented DNA damage, thus supporting the hypothesis of an active role of free radicals in EMF-induced processes. In a similar study conducted by Gao and colleagues, natural antioxidants, catechin and epicatechin, showed an ability to protect animals’ brains from oxidative stress induced by ELF- EMF at 50 Hz [
20].
Moreover, Gunes and collaborators [
21] observed that muscle mechanical activity of diaphragm was not affected in rats exposed to sinusoidal ELF-EMF (50 Hz frequency, 1.5 mT magnetic flux density) from neonatal to adult period (chronic exposure).
While studies have been conducted on the effects of ELF-EMF on various tissues and functions, there is still limited research on the potential consequences of ELF-EMF on skeletal muscle function. Considering our previous in vitro results and those from other authors, the aim of this work is to study the ELF-EMF impact on skeletal muscle. The experimental plane was designed using C57BL/6 sedentary adult mice exposed to 0.1 or 1 mT ELF-EMF (50 Hz) for 1h/die up to 5 weeks. During the experimental period, control (Sham group) and exposed animals were fed a standard diet or a N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) enriched diet.
Understanding the mechanisms underlying the effects induced by ELF-EMF on skeletal muscle can provide valuable insights into the potential therapeutic applications of electromagnetic fields.
3. Discussion
Our previous studies investigated the biological effects of ELF-EMF on muscle cells, revealing that short-term exposure modulates oxidative stress and influences intracellular Ca
2+ signaling pathways, crucial for muscle differentiation. Long-term exposure to ELF-EMF enhances the myogenic process, by increasing gap junction intercellular communication activity, suggesting potential therapeutic applications of ELF-EMF in muscle repair and regeneration [
9,
14]. Building upon these findings, the present pilot study aimed to investigate the possible impact of ELF-EMF on the skeletal muscle of sedentary adult mice. The experimental design involved three groups of mice: a Sham group (control group) and two groups exposed to ELF-EMF at intensities of 0.1 mT or 1.0 mT. These field intensities were chosen to explore a range of biological responses covering both the levels commonly encountered in daily environments and higher intensities typically used in experimental studies and clinical applications of ELF-EMF [
7,
22,
23]. Exposures were administered for 1 hour per day, 5 days a week, over periods of either 1 week or 5 weeks, simulating protocols commonly used in magnetotherapy during rehabilitation protocols [
7,
24]. This approach allowed the assessment of both short-term and long-term effects of ELF-EMF on skeletal muscle physiology. Importantly, the mice were fed a diet with or without antioxidant supplementation, using N-acetylcysteine (NAC). This aspect of the study aimed to investigate whether antioxidant supplementation could modulate the potential oxidative stress and changes induced by ELF-EMF exposure.
On mice in all tested conditions, the first parameters monitored in vivo were the body weight and muscle strength, both related to skeletal muscle status considering that this tissue represents a very high percentage of the body mass. Consistent with previous studies [
25,
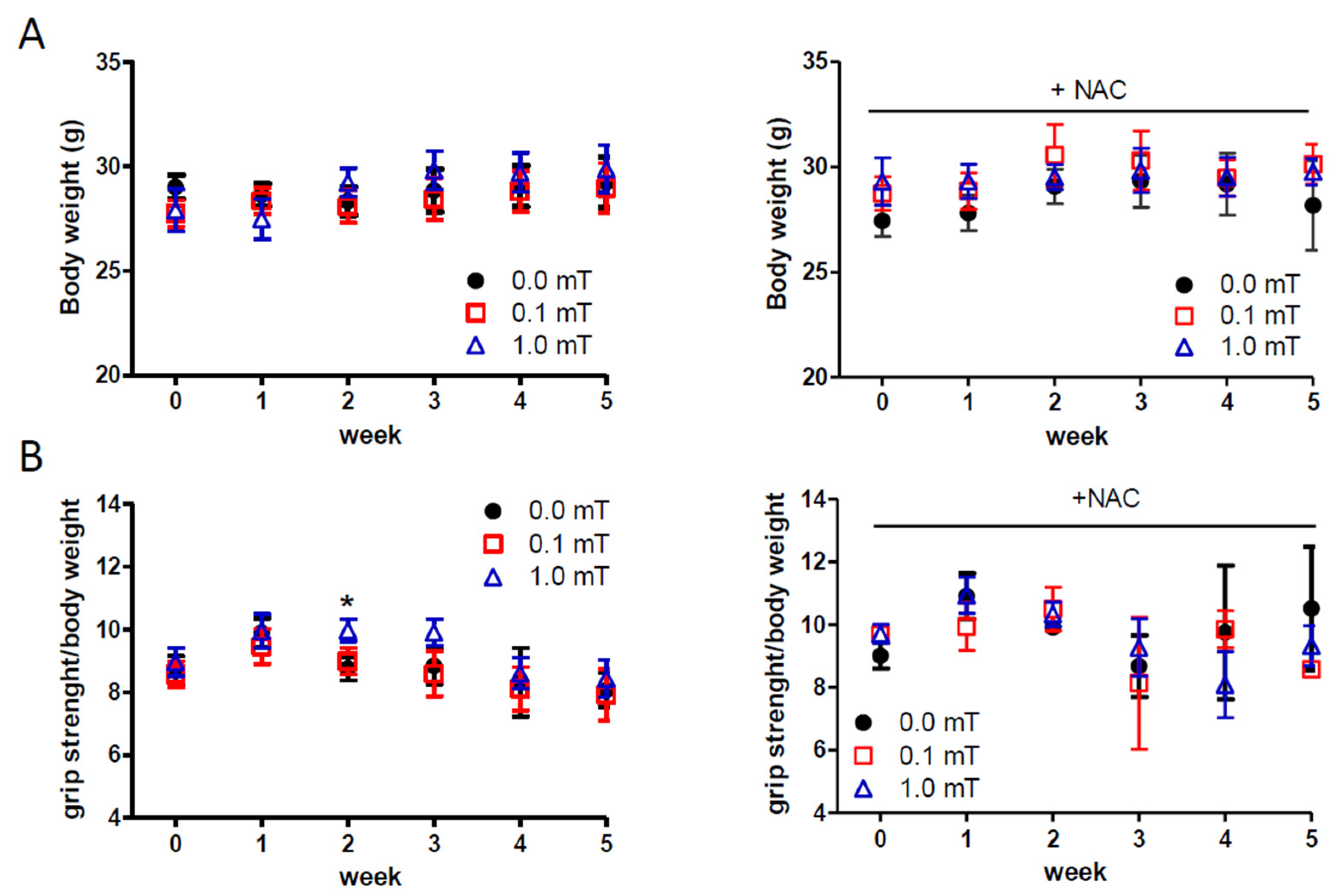
26], our findings indicated no significant changes in body weight in all tested samples. The lack of significant changes in body weight suggests that ELF-EMF exposure does not induce systemic metabolic alterations that could affect body mass. However, a transient significant change in muscle strength was observed in mice exposed to 1.0 mT ELF-EMF. This transient variation could be linked only to an initial boost in muscle fiber recruitment and activation, which might not yet translate to long-term changes in an enhanced muscle mass or overall body weight.
Skeletal muscle homeostasis and regeneration are regulated by a complex network of signaling pathways, involving the key role of satellite cells. In response to different stimuli (electrical, mechanical etc), these quiescent cells rapidly become mitotically active and proliferate generating myoblasts; then differentiate and fuse to regenerate the new muscle fibers [
27,
28,
29]. These processes are regulated by a sequential expression pattern of different transcription factors such as Pax7 essential for satellite cell development, MyoD and myogenin for myogenic commitment, and finally of specific proteins as MyH and α-actinin for muscle differentiation. Our data showed that ELF-EMF exposures increased the expression of one of the key markers of satellite cell activation, suggesting a role of ELF-EMF in modulating muscle remodeling and in enhancing satellite cells’ proliferative capacity, which is crucial for muscle repair and regeneration. The increase in Pax7 expression levels after ELF-EMF exposure was not dependent on NAC supplementation and the NAC itself induced this increase. These effects were persistent up to the 5-weeks’ experimental period. This result is in accordance with other Authors that observed stimulation of cell proliferation triggered by ELF-EMF exposure, in different cellular models [
30,
31]. In addition, the modulation of MyH expression levels, a terminal marker of muscle differentiation, indicated that ELF-EMF and/or NAC may influence different stages of muscle differentiation. L’Honoré et al. [
32] demonstrated that NAC increased the proliferative capacity of satellite cells in primary cultures while inhibited differentiation. In our experimental model NAC promoted satellite cells’ activation and inhibited final muscle differentiation supported by the significant reduction in MyH in Sham group and in 0.1 mT ELF-EMF group after 1-week treatment. Conversely, after 5-weeks of treatment, ELF-EMF exposure showed a pro-differentiation effect, inducing an increase of MyH expression levels in mice muscle samples, not related to NAC supplementation, even if NAC alone appeared to simulate the effects of ELF-EMF. However, no additive effect was observed with ELF-EMF exposure in muscles from mice that were fed with a NAC-enriched diet. The different response of NAC underscores the complexity of antioxidant interactions with muscle regeneration pathways and highlights the importance of temporal factors in therapeutic strategies involving antioxidants. However, the lack of an additive effect suggests that both stimuli (ELF-EMF and NAC) are likely influencing the same pathways or mechanisms. NAC could be stronger, as continually present in the diet, and fully activate the pathway on its own, or the pathway may have a maximum response limit that is reached with NAC and leaves no space for an additional effect from ELF-EMF exposure. Further investigation into the specific pathways and their regulatory mechanisms would be necessary to fully understand the interactions between these stimuli.
Although, at cellular level, ROS have been proposed to mediate the effects of ELF-EMF [
9,
33,
34], several studies have reported controversial results in in vivo investigations [
1]. However, it is now widely established by the scientific literature, that ROS play a dual role in the physiology of skeletal muscle. At low concentrations, ROS can modulate cellular proliferation, differentiation, and muscle contraction; so, they increase muscle force and enhance adaptation to exercise. Whereas at a high concentration, ROS lead to a decline in muscle performance [
35,
36]. Since ROS levels depend on the dynamic balance between ROS generation and removal, this study evaluated whether ELF-EMF exposure affected ROS production or elimination processes.
Our data show no significant changes in NOX2 and NOX4 expression or activity, that are considered one of major sources of ROS in striated muscles [
37]. However, it is noteworthy that there is an increase, although not significant, in NOX2 expression, particularly after exposure to 0.1mT ELF-EMF, observed as early as 1-week treatment and persistent up to 5 weeks. NOX2 is predominantly located in the sarcolemma and transverse tubules, while NOX4 is also expressed in the sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria [
38,
39]. NOX4 is constitutively active, contributing to the baseline production of ROS in myocytes. In contrast, NOX2 activation is induced by specific stimuli, such us mechanical or contractile stress. Moreover, a growing body of evidence suggest that NOX2 is directly involved in mechano-transduction in response to mechanical stimuli [
37]. Therefore, we speculate that the observed slight increase in NOX2 expression could represent a sensible target to the presence of physical agent such as ELF-EMF, leading to an increase in ROS production.
To further understand the implications of these findings, we evaluated the activation of antioxidant enzymes, which is indicative of ROS balance. This analysis is crucial to determine whether the observed trends in NOX2 expression correlate with compensatory mechanisms aimed at mitigating oxidative stress. The redox status of skeletal muscle was evaluated by analyzing the protein expression of antioxidant enzymes (SOD1, SOD2, catalase), of the total antioxidant capacity (that includes enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidative factors) and of the transcription factor NRF2 that regulates the expression of genes involved in antioxidant response.
Interestingly, after 1-week treatment, an increase in total antioxidant capacity of skeletal muscle from mice exposed to ELF-EMF was observed not related to the presence of NAC in the diet, and accompanied by an increase in catalase expression levels and a decrease of its activity. These last effects were reduced by the presence of NAC in the diet.
Taken together these results highlights an involvement of the oxidative metabolism in the ELF-EMF induced effects and a possible adaptive mechanism to manage increased ROS production in response to ELF-EMF exposure. Indeed, the down-regulation of catalase activity despite its increased expression could indicate a potential post-translational modification required as homeostatic response. The presence of NAC seemed to counteract these effects, indicating its protective role against ELF-EMF-induced oxidative stress. NAC’s role as an antioxidant was also underscored by its ability to reduce elevated levels of lipid oxidation in response to 1mT ELF-EMF 1-week exposure, the only condition in which it is possible to observe oxidative induced damage to lipids.
After 5 weeks of exposure, there were no significant differences in the antioxidant parameters even if a trend of increase in the total antioxidant capacity persisted. The results after 5 weeks of treatment indicated a potential adaptation to prolonged ELF-EMF exposure. This suggests that the skeletal muscle can achieve a new homeostatic balance following prolonged exposure.
Remarkably, among the markers of oxidative-induced damage to macromolecules, the protein carbonyls appeared significantly increased in samples exposed to ELF-EMF starting from 1-week exposure, and NAC supplementation induced only a partial reduction of this effect, indicating that NAC can only mitigate oxidative damage induced by ELF-EMF. One possible explanation for this could be the different mechanisms through which NAC interacts with lipid and protein oxidation processes. NAC is known to replenish intracellular levels of reduced glutathione, an essential non-enzymatic antioxidant that plays a significant role in maintaining cellular redox balance [
40]. Studies on animal models have consistently shown that this antioxidant is associated with improvements in fatigue resistance [
41,
42] and has a beneficial effect on muscle regeneration and function [
43]. However, it is important to highlight that several groups have found that NAC can provide protective benefits to skeletal muscle without significantly affecting biomarkers of protein and lipid oxidative damage [
42]. In mdx mice, NAC administration successfully mitigated exercise-induced myonecrosis but did not prevent alterations in the levels of oxidative modifications to lipids and proteins within skeletal muscle [
44]. These observations emphasize the notion that NAC may exert multifaceted positive effects on skeletal muscle, implying involvement of alternative mechanisms beyond direct modulation of oxidative states in macromolecules.
4. Materials and Methods
Exposure System
ELF-EMF (50 Hz and 0.1 or 1.0 mT) were generated by a solenoid (length: 300 mm and diameter: 124 mm; Oersted Technology Corp., Troutdale, OR, USA). The coil is made of copper (Ø: 1.25 mm); and the wire is made by a single layer, precisely winded to preserve field homogeneity. The coil carrier (length: 350 mm) is non-magnetic, with maximal thermal and mechanical stability, suitable for long term (up to a few days) operations. The power supply (Elgar Electronics, San Diego, CA, USA) is connected to the solenoid through a highly reliable cable.
Animals and Experimental Plan
The study was conducted on male C57BL/6 mice at the age of 12 weeks. The care and use of the mice strictly followed “The Guiding Principles for the Care and Use of Animals”, in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, with the European Community Council (86/609/CEE) and the Italian Government law on the protection of animals for experimental procedures in research laboratory (92/116). The mice were housed in the animal facility of the Center Advanced Studies Technologies (CAST) of the University G.d’Annunzio of Chieti-Pescara (Chieti, Italy).
All procedures were also approved by the local University Committee on Animal Resources, Comitato Etico Inter-ateneo per la Sperimentazione Animale - CEISA (prot. n. 03/2011/CEISA/PROG/11).
Mice were randomly divided into three groups (n= 24/group,
Table 1): one Sham group and two ELF-EMF exposed groups. All animals were placed inside the solenoid, for 1 hour/day for 5 day/week up to 1 week or 5 weeks, and the solenoid was turned off during sham controls exposure and operated at 0.1 or 1.0 mT during ELF-EMF exposure for the exposed groups (
Figure 1). During the experimentation, both exposed and sham mice were fed a diet supplemented with or without N-acetylcysteine (NAC, Merck Life Science S.r.l., Milan, Italy). NAC was administered through ad libitum access to drinking water containing 1% weight/volume (1% w/v) NAC following the protocol described by Michelucci et al. [
45]. At the end of the experimentation period (1 week or 5 weeks), after body weight and grip test measurements, Sham and ELF-EMF exposed mice were sacrificed and muscle tissue was collected from the hind limbs of each mouse. Then, muscle tissues were rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C for subsequent biochemical analyses.
Body Weight and Grip Strength Test
Body weight and grip strength measurements were performed as previously described [
46]. Briefly, the mice were weighed before the grip strength test. Grip strength was evaluated using a force transducer (ShimpoFgv0.5×; Metrotec Group, San Sebastian, Spain), by lifting the mouse and allowing it to grasp a grid with its paws. Peak force values were normalized to total body mass measured before grip strength test.
Chemicals and Materials
Unless otherwise indicated, cell culture media, sera, antibiotics, and cell culture dishware were obtained from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Monza, Italy); reagents and standards from Merck Life Science (Milan, Italy).
Western Blotting Analysis
Proteins were extracted from hind limb muscles of the mice, quantified and separated using a protocol previously described by Caprara et al. [
46]. Equal amounts of proteins were loaded on electrophoresis gels for Western blotting analysis. After blotting, the membranes were blocked with EveryBlot Blocking Buffer (Bio-rad) for 15 min at room temperature before incubation with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C. After washing, the membranes were incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated appropriate secondary antibodies (1:10,000 in blocking buffer) for 1 h at room temperature. The signals were detected using an ECL kit (AmershamTM Cytiva, Marlborough, MA, USA) and analyzed with an image acquisition system (Uvitec mod Alliance 9.7, Uvitec, Cambridge, UK). Primary antibodies used in this study included: mouse monoclonal antibody anti-PAX7 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., SantaCruz, CA, USA, cod. sc-81648, 1:1000 dilution); mouse monoclonal antibody anti-MyoD (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc, cod. sc-377460, 1:1000 dilution); mouse monoclonal antibody anti-MyoG (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc, cod. sc-12732, 1:1000 dilution); mouse monoclonal antibody anti-α-actinin (Merck Life Science S.r.l, cod A7732, dil 1:1000); mouse monoclonal antibody anti-MYH (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc, sc-376157, dil 1:1000); rabbit polyclonal antibody anti-SOD1 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cod. PA527240, 1:1000 dilution,); mouse monoclonal antibody anti-SOD2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cod. MA5-31514, 1:1000 dilution); rabbit monoclonal antibody anti-catalase (Cell Signaling Technology, Pero, Italy, cod. 14097, 1:1000 dilution); rabbit monoclonal antibody anti-NRF2 (Merck Life Science S.r.l, cd SAB4501984, 1:500 dilution); rabbit polyclonal antibody anti-pNRF2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cod PA567520, dil 1:1000); mouse monoclonal antibody anti-NOX2 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc., cod. sc-130543, 1:500 dilution); rabbit monoclonal antibody anti-NOX4 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cod. MA5-32090, 1:500 dilution); mouse monoclonal antibody anti-4HNE (Merck Life Science S.r.l., cod. SAB5202472, 1:1000 dilution); polyclonal rabbit antibody anti-3-nitrotyrosine (Merck Life Science S.r.l., cod. 4511, 1:1000 dilution). A mouse monoclonal antibody anti-β-tubulin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cod MA5-16308, 1: 1000 dilution) or a mouse monoclonal antibody anti-GAPDH antibody (Merck Life Science S.r.l., cod. CB1001, 1:10000 dilution) were used as loading controls.
Total Antioxidant Status
Total antioxidant capacity in skeletal muscle was measured by a colorimetric assay using a commercial kit (TEAC assay, Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor USA). Total hind limb muscles were homogenized in cold buffer (5 mM potassium phosphate, pH 7.4, 0.9% NaCl, 0.1% glucose) and centrifuged (10,000x g, 15 min at 4°C). Cytosolic proteins (50 µg), determined by Bio-Rad protein assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories Srl, Milan, Italy), were processed following the manufacturer’s instructions. Reaction mixtures were read at 750 nm using a microplate reader (Synergy H1 multimode, Biotek, Bad Friedrichshall, Germany). Results were expressed as Trolox equivalents by reference to a linear calibration curve computed from pure Trolox-containing reactions (range 0–0.33 mM).
Catalase Assay
The catalase activity was assessed with a spectrophotometric method using commercial kit (Sigma-Aldrich, Merck Life Science S.r.l.). Briefly, hind-limb muscles were homogenized in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, containing 0.1% Triton X-100 and protease inhibitors (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The homogenates were centrifuged at 10,000× g for 10 min at 4°C, and supernatants were collected for the enzymatic assay performed following the manufacturer’s instructions. The catalase present in the sample reacts with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to produce water and oxygen. The unconverted H2O2 reacts with probe to produce a product that can be measured colorimetrically at 570 nm. The catalase assay was initiated by mixing 5 μl of supernatant with 50 mM H2O2 in a total volume of 25μl (reaction mix). The reaction was carried out at room temperature for 5 min and stopped with 15 mm sodium azide. The residual H2O2 was measured colorimetrically, after incubation with Color Reagent for 15 min at room temperature. The reaction produced a red quinoneimine dye that absorbs at 520 nm. The concentration of H2O2 in the samples was determined using a standard curve. Results were expressed as the ratio between the concentration of remaining H2O2 and protein content of every sample.
NOXs Activity
The NOXs activity was evaluated through a colorimetric assay using a commercial kit (Abcam, Cambridge, UK). Total hind limb muscles were homogenized in sodium phosphate pH 7.0, containing protease inhibitors, and then centrifuged at 10,000× g for 10 min at 4°C. Supernatants were collected and processed following the manufacturer’s instructions. The assay started by mixing each sample (50 μg) with NADH OXIDASE Enzyme mix, Substrate I, Substrate II and Probe (Reaction Mix) in a total volume of 100 μl. The assay was performed recording the absorbance at 600 nm in kinetic mode for 30 min at 25 °C using a microplate reader (Synergy H1 multimode, Biotek, Bad Friedrichshall, Germany). The oxidation of NADH by NOX and the reduction of a colored substrate leading to a colorless product was determined using a standard curve.
Protein Carbonyl Measurement
The total protein carbonyls, biomarkers of protein oxidative stress, were measured using a commercial kit based on a colorimetric assay (Protein Carbonyl Assay Kit, cat. 10005020, Cayman Chemical) as previously described [
9].
Statistical Analyses
The data, if not otherwise reported, are expressed as Means ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M.) of 6 independent experiments, each of which regarded the exposure of a mouse at 0.0, 0.1 or 1.0 mT for time periods and conditions described in the paragraph “Animals and experimental plan”. Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t-test with Prism5 software (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). p-Values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
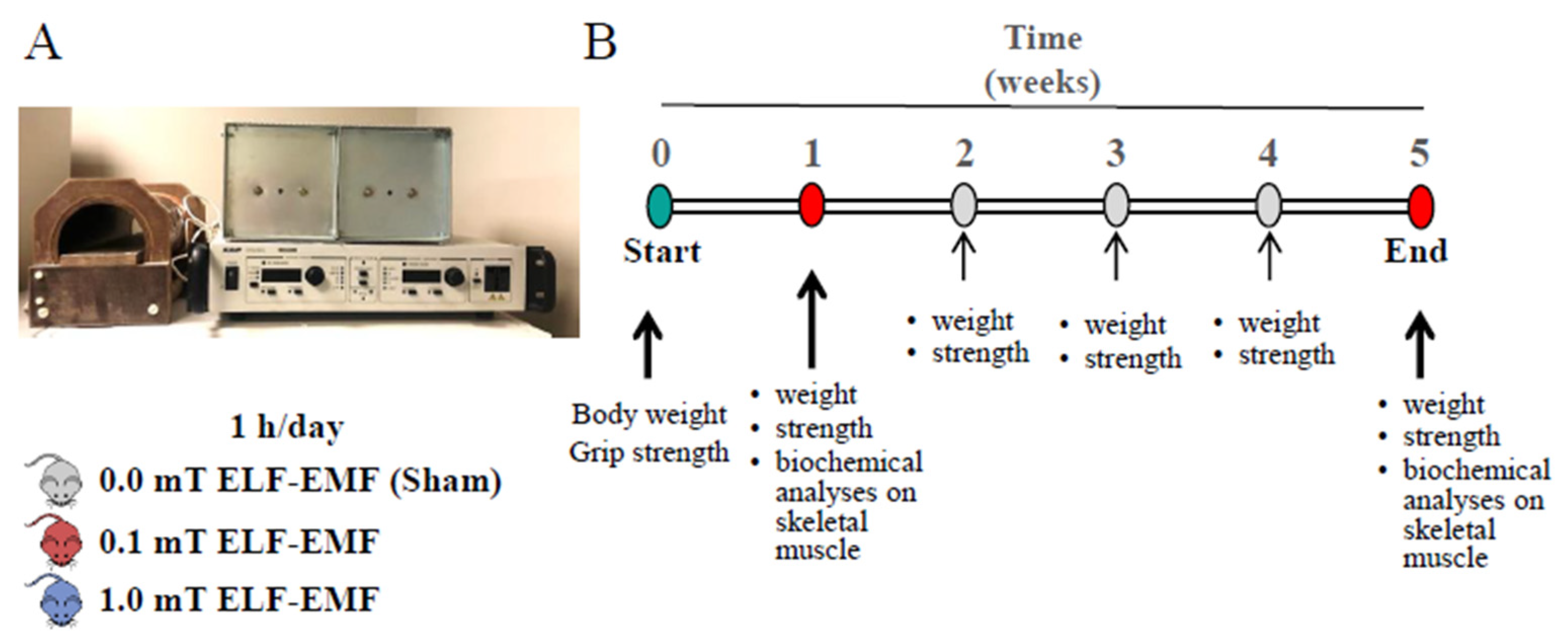
Figure 1.
The set-up and the experimental plan configuration. (A) Experimental set-up: horizontal solenoid with power supply. The mice were placed inside the solenoid for 1h/day for 5 days/week up to 1 week or 5 weeks. The solenoid worked at 0.0 mT for sham controls, at 0.1 or 1.0 mT for mice exposed to ELF-EMF. (B) Timeline of the experimental plan. During the experimentation, the mice were fed with a diet with or without NAC and their weight and strength recorded weekly. After 1 or 5 weeks also biochemical analyses were performed.
Figure 1.
The set-up and the experimental plan configuration. (A) Experimental set-up: horizontal solenoid with power supply. The mice were placed inside the solenoid for 1h/day for 5 days/week up to 1 week or 5 weeks. The solenoid worked at 0.0 mT for sham controls, at 0.1 or 1.0 mT for mice exposed to ELF-EMF. (B) Timeline of the experimental plan. During the experimentation, the mice were fed with a diet with or without NAC and their weight and strength recorded weekly. After 1 or 5 weeks also biochemical analyses were performed.
Figure 2.
In vivo mice measurements. (A) Body weight and (B) Muscle strength measurements in mice that experienced 0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF up to 5 weeks, during which the mice were fed a diet supplemented without (left panels) or with (right panels) 1% NAC in drinking water. Body weights (g) and muscle strengths (expressed as ratio between grip strength and body weight of each mouse) were measured weekly. All data are expressed as means ± SEM from 6 mice/group.
Figure 2.
In vivo mice measurements. (A) Body weight and (B) Muscle strength measurements in mice that experienced 0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF up to 5 weeks, during which the mice were fed a diet supplemented without (left panels) or with (right panels) 1% NAC in drinking water. Body weights (g) and muscle strengths (expressed as ratio between grip strength and body weight of each mouse) were measured weekly. All data are expressed as means ± SEM from 6 mice/group.
Figure 3.
Expression levels of muscle regeneration markers. (A-D) Representative immunoblots of Pax7, MyoD, myogenin (MyoG), MyH, and α-actinin with the corresponding densitometric analyses in skeletal muscles from mice groups after 1-week exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) and that were fed a diet without or with (+ NAC) NAC supplementation. (E-H) Representative immunoblots of Pax7, MyoD, myogenin (MyoG), MyH, and α-actinin with the corresponding densitometric analyses in skeletal muscles from mice groups after 5-weeks’ exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) and that were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. Densitometry analyses were calculated as the ratio between the OD × mm2 of each band and the OD × mm2 of the corresponding loading control band (GAPDH for Pax7, MyoD, MyoG and α-actinin, or β-tubulin for MyH). All data are expressed as means ± SEM from 6 independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05 versus 0.0 mT without NAC supplementation. and §p < 0.05 versus 0.0 mT with NAC supplementation.
Figure 3.
Expression levels of muscle regeneration markers. (A-D) Representative immunoblots of Pax7, MyoD, myogenin (MyoG), MyH, and α-actinin with the corresponding densitometric analyses in skeletal muscles from mice groups after 1-week exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) and that were fed a diet without or with (+ NAC) NAC supplementation. (E-H) Representative immunoblots of Pax7, MyoD, myogenin (MyoG), MyH, and α-actinin with the corresponding densitometric analyses in skeletal muscles from mice groups after 5-weeks’ exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) and that were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. Densitometry analyses were calculated as the ratio between the OD × mm2 of each band and the OD × mm2 of the corresponding loading control band (GAPDH for Pax7, MyoD, MyoG and α-actinin, or β-tubulin for MyH). All data are expressed as means ± SEM from 6 independent experiments. ∗p < 0.05 versus 0.0 mT without NAC supplementation. and §p < 0.05 versus 0.0 mT with NAC supplementation.
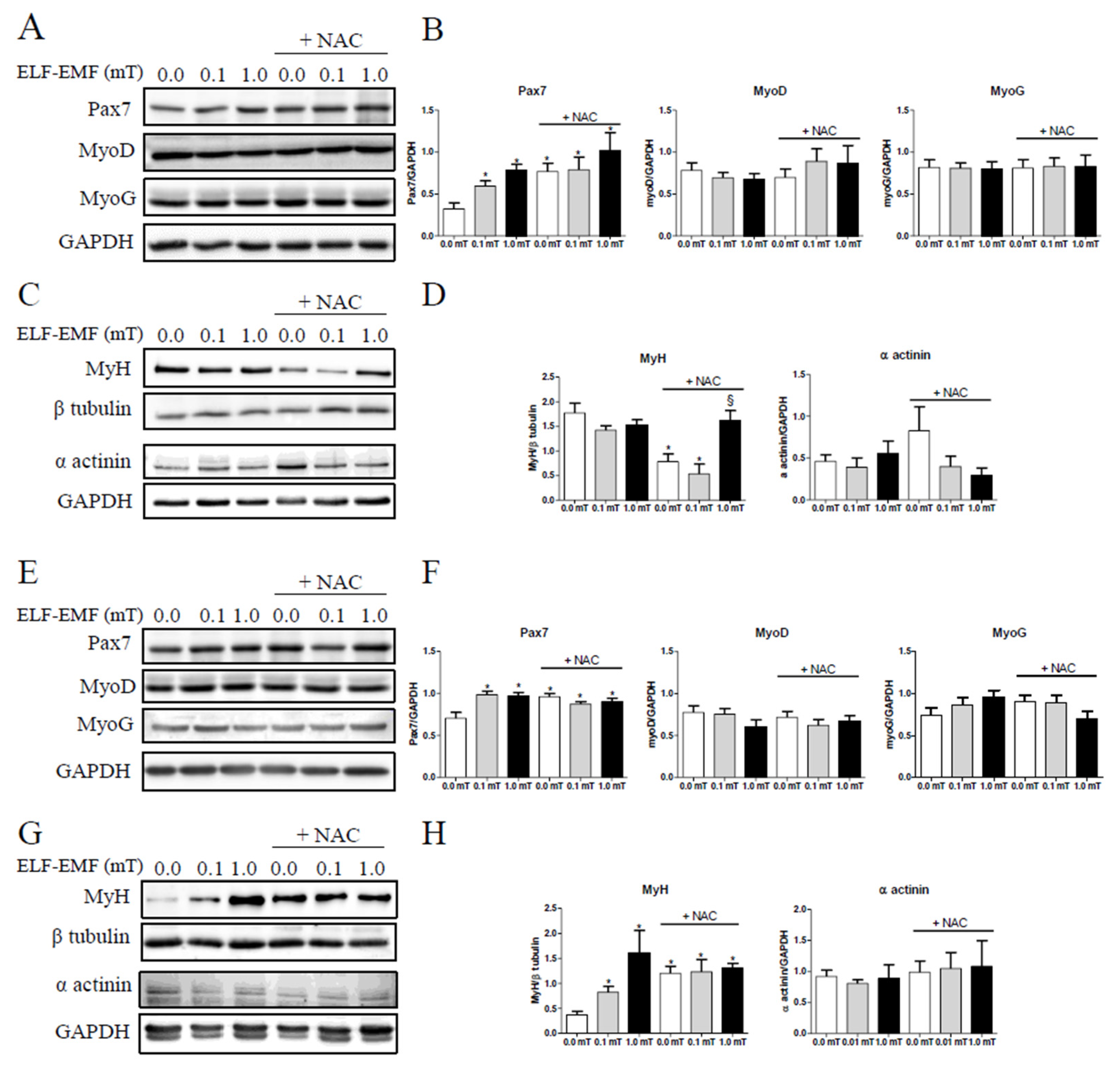
Figure 4.
Expression levels of muscle regeneration markers. (A) and (B) Representative immunoblots of NOX2 and NOX4 (Top panels) and the corresponding densitometric analyses (Bottom groups) in skeletal muscle from mice groups after 1-week exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. (C) NOX enzymatic activity in the same skeletal muscle samples tested in A and B. (D) and (E) Representative immunoblots of NOX2 and NOX4 (Top panels) and the corresponding densitometric analyses (Botton panels) in skeletal muscle from mice groups after 5-week exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. (F) NOX enzymatic activity in the same skeletal samples tested in D and E. Densitometry analyses (A, B, D, and E) were calculated as the ratio between the OD × mm2 of each band and the OD × mm2 of the corresponding loading control band (GAPDH). All data are expressed as means ± SEM from 6 independent experiments.
Figure 4.
Expression levels of muscle regeneration markers. (A) and (B) Representative immunoblots of NOX2 and NOX4 (Top panels) and the corresponding densitometric analyses (Bottom groups) in skeletal muscle from mice groups after 1-week exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. (C) NOX enzymatic activity in the same skeletal muscle samples tested in A and B. (D) and (E) Representative immunoblots of NOX2 and NOX4 (Top panels) and the corresponding densitometric analyses (Botton panels) in skeletal muscle from mice groups after 5-week exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. (F) NOX enzymatic activity in the same skeletal samples tested in D and E. Densitometry analyses (A, B, D, and E) were calculated as the ratio between the OD × mm2 of each band and the OD × mm2 of the corresponding loading control band (GAPDH). All data are expressed as means ± SEM from 6 independent experiments.
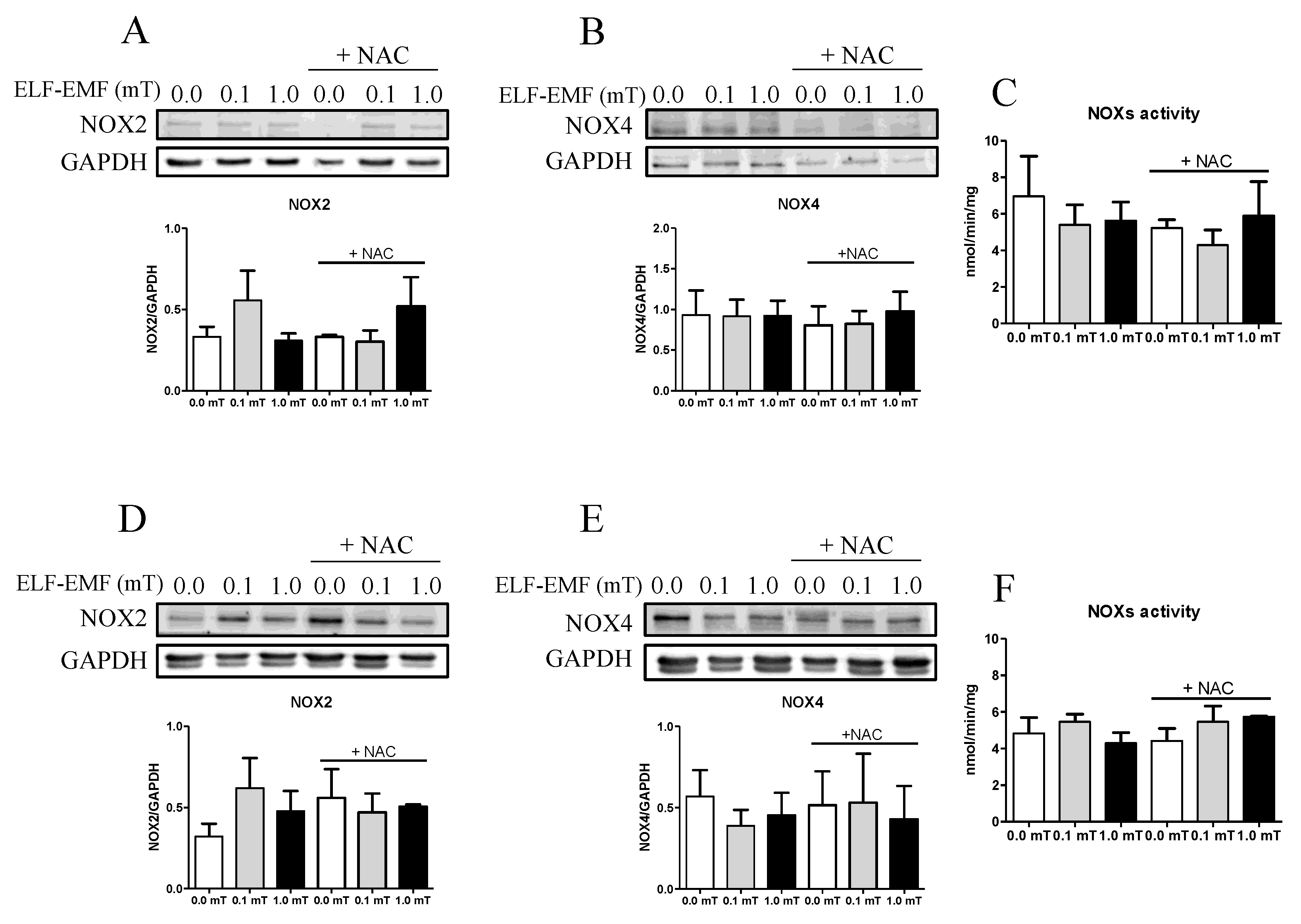
Figure 5.
Pro-oxidant enzymes expression levels and activity. (A) and (D) Representative immunoblots of pNRF2, SOD1, SOD2, and catalase (Left panels) and the corresponding densitometric analyses (Right panels) in skeletal muscle from mice groups after 1-week (A) or 5-weeks (D) exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. Densitometry analyses were calculated as the ratio between OD × mm2 of each band and OD × mm2 of the corresponding loading control band (NRF2 for pNRF2, or GAPDH for SOD1, SOD2, and catalase). (B) and (E) Total antioxidant status measured by TEAC assay (see Material and Methods section) in skeletal muscle from mice groups after 1-week (B) or 5-weeks (E) exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. (C) and (F) Catalase enzymatic activity in the same samples of panel (B) and (E), respectively. All data are expressed as means ± SEM from 6 independent experiments. *p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 versus 0.0 mT without NAC supplementation; #p <0.05 versus 0.0 mT with NAC supplementation.
Figure 5.
Pro-oxidant enzymes expression levels and activity. (A) and (D) Representative immunoblots of pNRF2, SOD1, SOD2, and catalase (Left panels) and the corresponding densitometric analyses (Right panels) in skeletal muscle from mice groups after 1-week (A) or 5-weeks (D) exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. Densitometry analyses were calculated as the ratio between OD × mm2 of each band and OD × mm2 of the corresponding loading control band (NRF2 for pNRF2, or GAPDH for SOD1, SOD2, and catalase). (B) and (E) Total antioxidant status measured by TEAC assay (see Material and Methods section) in skeletal muscle from mice groups after 1-week (B) or 5-weeks (E) exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. (C) and (F) Catalase enzymatic activity in the same samples of panel (B) and (E), respectively. All data are expressed as means ± SEM from 6 independent experiments. *p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01 versus 0.0 mT without NAC supplementation; #p <0.05 versus 0.0 mT with NAC supplementation.
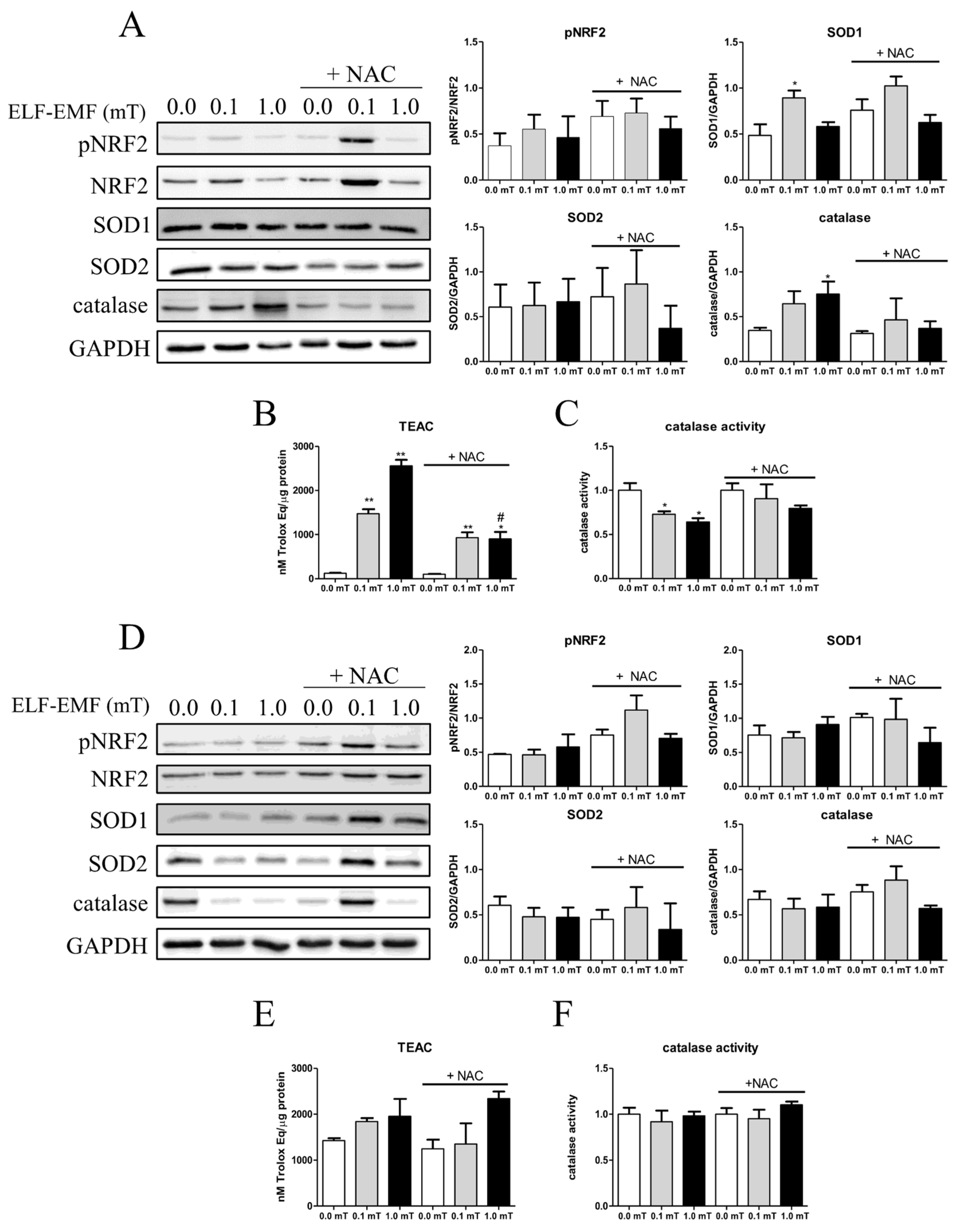
Figure 6.
Expression of protein and lipid oxidative markers in skeletal muscles. (A) and (B) Representative immunoblots of the expression levels of 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT), and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), respectively. The skeletal muscle samples were from mice groups after 1-week exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. (C) and (D) Densitometric analyses of Western blots of samples shown in (A) and (B), respectively. (E) and (F) Representative immunoblots of the expression levels of 3-NT and 4-HNE, respectively. The skeletal muscle samples were from mice groups after 5-weeks exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. (G) and (H) Densitometric analyses of Western blots of samples shown in (E) and (F), respectively. (I) and (J) Protein carbonyl content in skeletal muscle samples from mice groups after 1-week (I) or 5-weeks (J) exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. The densitometric analyses were calculated as the ratio between the OD × mm2 of each band and the OD × mm2 of the corresponding GAPDH band, which was used as loading control. All data are expressed as means ± SEM from 6 independent experiments. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 versus 0.0 mT without NAC supplementation. #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 versus 0.0 mT with NAC supplementation.
Figure 6.
Expression of protein and lipid oxidative markers in skeletal muscles. (A) and (B) Representative immunoblots of the expression levels of 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT), and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), respectively. The skeletal muscle samples were from mice groups after 1-week exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. (C) and (D) Densitometric analyses of Western blots of samples shown in (A) and (B), respectively. (E) and (F) Representative immunoblots of the expression levels of 3-NT and 4-HNE, respectively. The skeletal muscle samples were from mice groups after 5-weeks exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. (G) and (H) Densitometric analyses of Western blots of samples shown in (E) and (F), respectively. (I) and (J) Protein carbonyl content in skeletal muscle samples from mice groups after 1-week (I) or 5-weeks (J) exposure (0.0, 0.1, or 1.0 mT ELF-EMF) during which they were fed a diet without or with (+NAC) NAC supplementation. The densitometric analyses were calculated as the ratio between the OD × mm2 of each band and the OD × mm2 of the corresponding GAPDH band, which was used as loading control. All data are expressed as means ± SEM from 6 independent experiments. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 versus 0.0 mT without NAC supplementation. #p < 0.05 and ##p < 0.01 versus 0.0 mT with NAC supplementation.
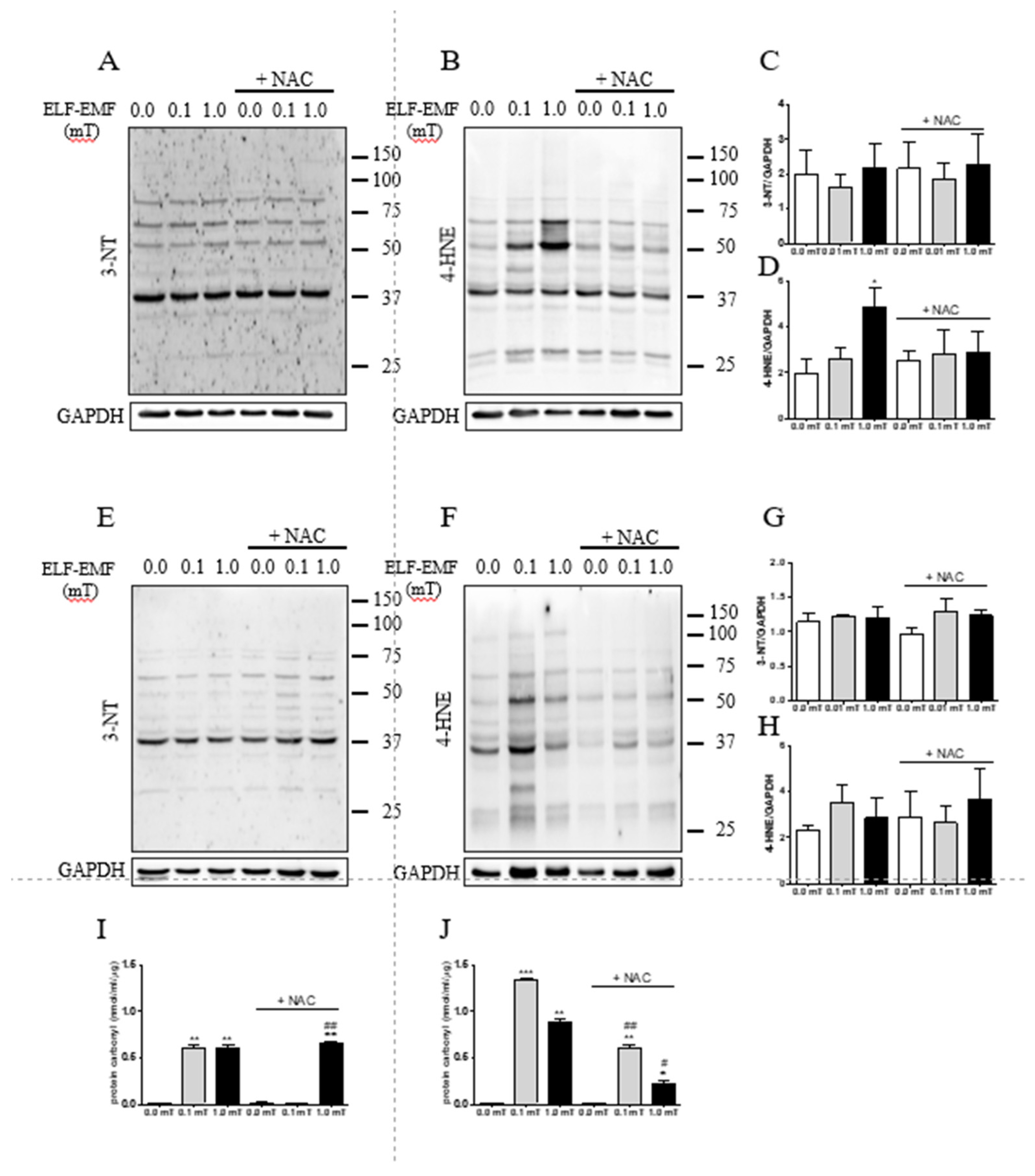
Table 1.
Sperimental groups.
Table 1.
Sperimental groups.
| Group |
Exposure
Intensity |
Exposure
Time |
Antioxidant supplementation |
Number of mice |
Sham
n= 24 |
0.0 mT |
1 week |
w/o 1% NAC |
6 |
| with 1% NAC |
6 |
| 5 weeks |
w/o 1% NAC |
6 |
| with 1% NAC |
6 |
ELF-EMF
n= 48 |
0.1 mT |
1 week |
w/o 1% NAC |
6 |
| with 1% NAC |
6 |
| 5 weeks |
w/o 1% NAC |
6 |
| with 1% NAC |
6 |
| 1.0 mT |
1 week |
w/o 1% NAC |
6 |
| with 1% NAC |
6 |
| 5 weeks |
w/o 1% NAC |
6 |
| with 1% NAC |
6 |