Submitted:
06 August 2024
Posted:
07 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- What are the volume and dynamics of the research on using IoT and Big Data in preventive medicine?
- How is the research geographically distributed?
- Which are the core and most prolific information sources that first inform the scientific community and second enable the community to present its research results?
- Which funding bodies are the most productive?
- What are the most prolific research themes, concepts, and future directions?
- How did the research themes envolve historically?
- What are the possible research gaps?
2. Materials and Methods
- Research publications were harvested from the Scopus bibliographic database using the search string TITLE-ABS-KEY (( "internet of things" OR iot OR big-data) AND prevent*) AND (LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA,"MEDI") OR LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA,"HEAL") OR LIMIT-TO (SUBJAREA,"NURS")).
- Descriptive bibliometric analysis was performed using Scopus’s built-in functionality and the Bibliometrics software [16].
- Author keywords were used as meaningful units of information in content analysis. First, bibliometric mapping was performed using VOSViewer [6]. Next, using content analysis on the most popular authors' keywords, the node size, links, and proximity between author keywords in individual clusters and their borders presented in the bibliometric map were analyzed from the medical and computer science viewpoints to form categories, identify concepts and name the research theme.
- Next, the representative themes and subcategories' author keywords/terms were applied to form search strings to locate relevant publications associated with describing categories and themes' scope.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive and Production Bibliometrics
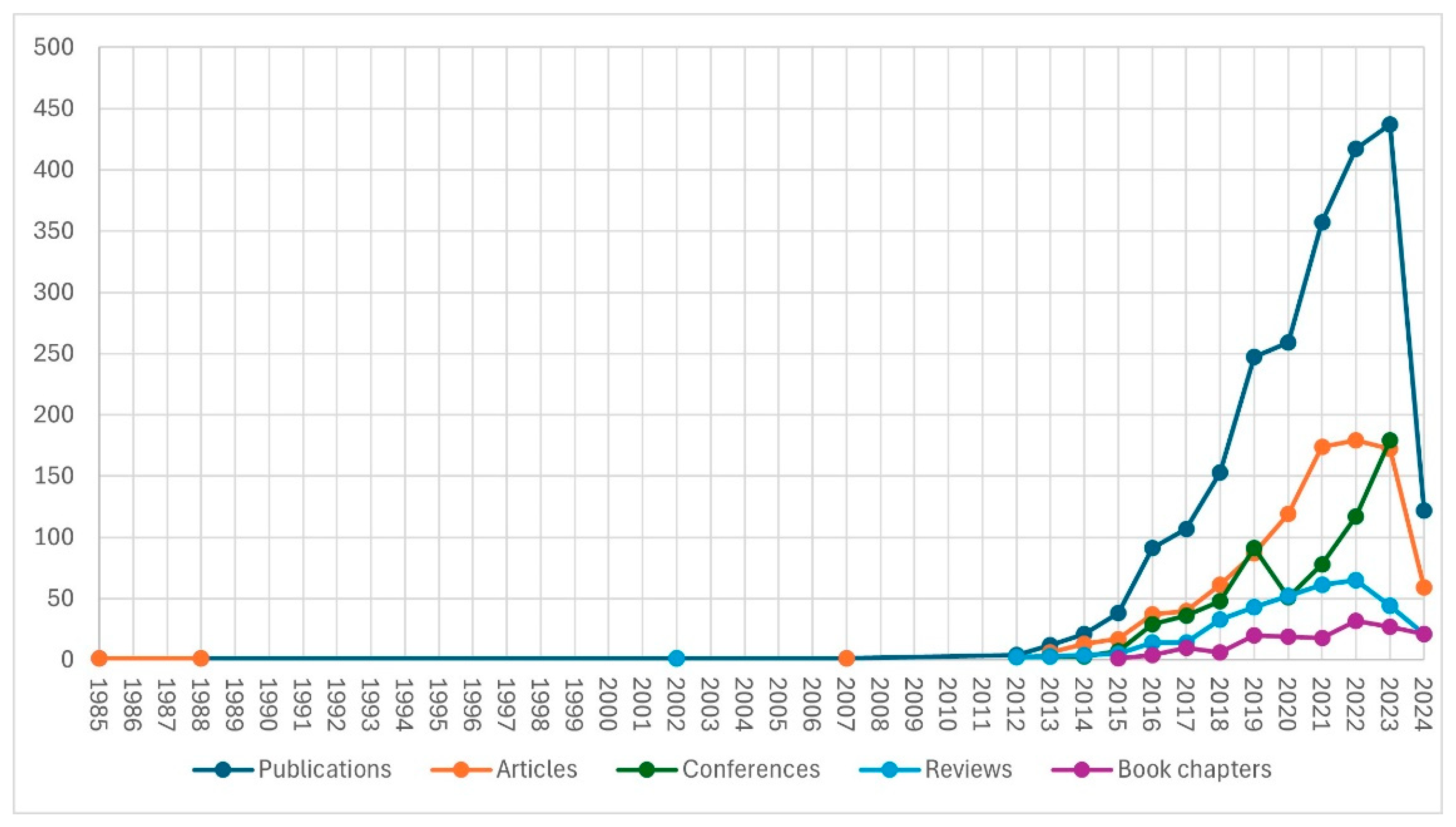
3.1.1. Volume of Research
3.1.2. The Dynamics of the Research Literature Production
3.1.3. Prolific Information Sources
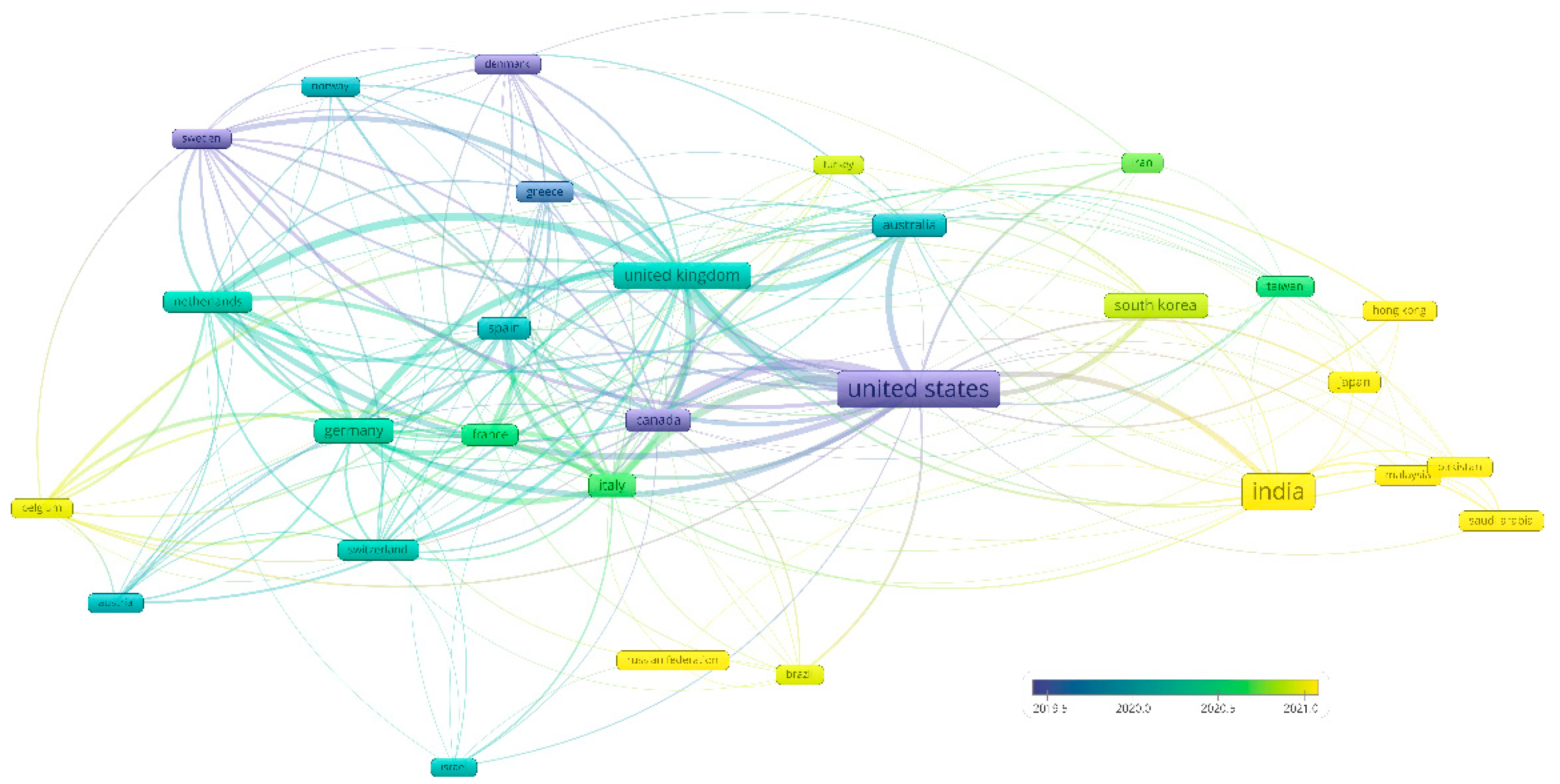
3.1.4. Geographical Distribution of Research
3.1.5. Most Prolific Funding Bodies
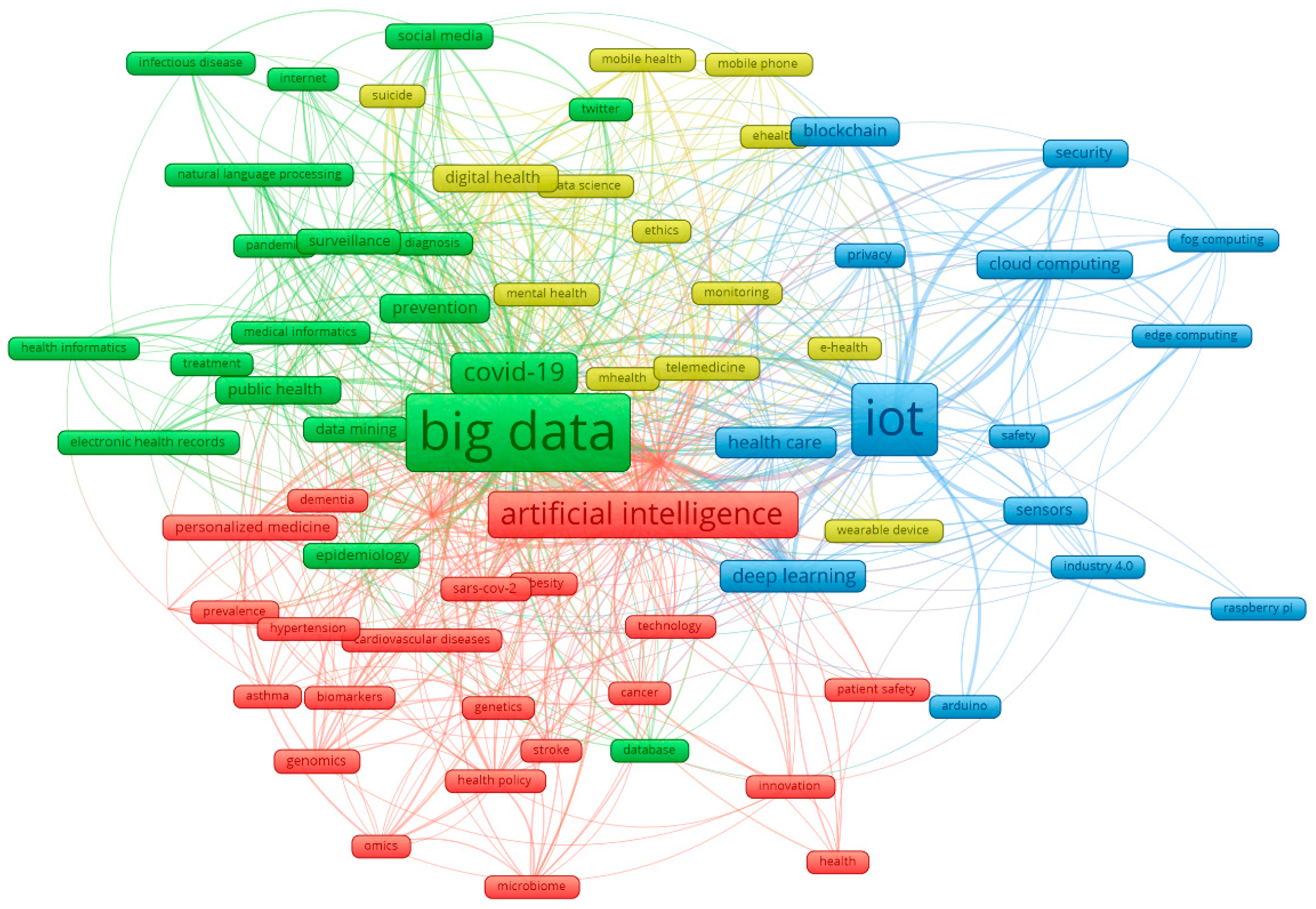
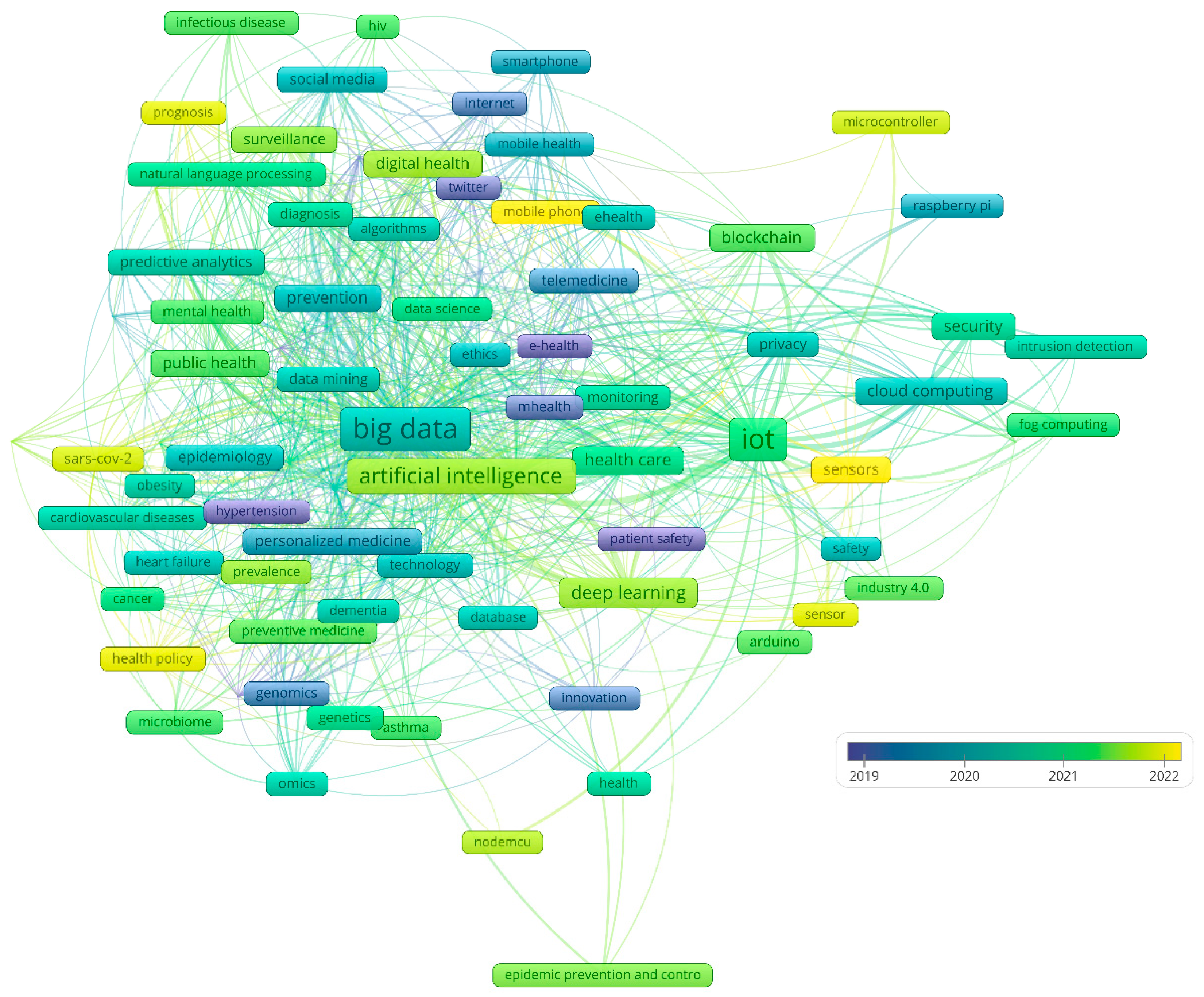
3.2. Most Prolific Research Themes
3.3. Timeline of the Recent Research and Seminal Publications
3.4. Hot Topics and Future Research Directions
3.5. Research Gaps and Challenges
- Cyber security threats and managing trust: Healthcare data poses excellent security and privacy risks, but adding IoT and big data significantly increases the risk of exposure [131].
- Regulatory challenges: Clinical-grade medical devices need approval and clearance from various regulators, which can present new challenges for the regulatory and legislative bodies [132].
- Interoperability of data and Standardization issues: To obtain meaningful and clinically relevant decisions from data collected from the various IoMT devices, all IoMT devices and big data algorithms must be interoperable [133].
- High infrastructure costs: IoT and big data software/hardware systems require a high initial investment that might act as a barrier to IoMT [134].
- Strain on Existing Networks: Many current health institutions' networks are neither secure nor robust enough to operate the new IoMT/big data platforms [135]
- Scale: While IoMT/big data is becoming increasingly popular in preventive medicine, ensuring future growth scalability and broader adoption might be problematic [136].
3.6. Study Strengths and Limitations
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.; Chai, Y.; Khan, F.; Jan, S.R.U.; Verma, S.; Menon, V.G.; Kavita; Li, X. A Comprehensive Survey on Machine Learning-Based Big Data Analytics for IoT-Enabled Smart Healthcare System. Mobile Netw Appl 2021, 26, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Verma, S.; Bansal, A. IOT Big Data Analytics in Healthcare: Benefits and Challenges. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Signal Processing, Computing and Control (ISPCC); October 2021; pp. 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.F.; Rafique, W.; Rasool, R.U.; Alhumam, A.; Anwar, Z.; Qadir, J. Leveraging 6G, Extended Reality, and IoT Big Data Analytics for Healthcare: A Review. Computer Science Review 2023, 48, 100558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Integration of IoT, Big Data, and Cloud Computing Technologies | 1 | T. Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.1201/9781003298335-1/integration-iot-big-data-cloud-computing-technologies-sita-rani-pankaj-bhambri-aman-kataria (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Pulimamidi, R. To Enhance Customer (or Patient) Experience Based on IoT Analytical Study through Technology (IT) Transformation for E-Healthcare. Measurement: Sensors 2024, 33, 101087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, K.; Yang, D.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, X. Biomedical Big Data Technologies, Applications, and Challenges for Precision Medicine: A Review. Global Challenges 2024, 8, 2300163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, I.; Din, S.; Farooq, S.; Díez, I. de la T.; Breñosa, J.; Espinosa, J.C.M.; Ashraf, I. Design and Development of Patient Health Tracking, Monitoring and Big Data Storage Using Internet of Things and Real Time Cloud Computing. PLOS ONE 2024, 19, e0298582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putra, K.T.; Arrayyan, A.Z.; Hayati, N.; Firdaus; Damarjati, C. ; Bakar, A.; Chen, H.-C. A Review on the Application of Internet of Medical Things in Wearable Personal Health Monitoring: A Cloud-Edge Artificial Intelligence Approach. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 21437–21452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Duan, J.; Li, B.; Fu, S.; Yin, W.; Yang, Z.; Qu, Z. Global Quantitative Analysis and Visualization of Big Data and Medical Devices Based on Bibliometrics. Expert Systems with Applications 2024, 254, 124398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-S.; Danh, H.-C.; Ma, Q.-P.; Mesicek, J.; Hajnys, J.; Pagac, M.; Petru, J. A Bibliometrics Analysis of Medical Internet of Things for Modern Healthcare. Electronics 2023, 12, 4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshi, A.; Shah, A.; Shafi, S.; Qadri, M.H. Big Data in Healthcare - A Comprehensive Bibliometric Analysis of Current Research Trends. Scalable Computing: Practice and Experience 2023, 24, 531–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P. Synthetic Knowledge Synthesis in Hospital Libraries. Journal of Hospital Librarianship 2023, 0, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Železnik, U.; Kokol, P.; Starc, J.; Železnik, D.; Završnik, J.; Vošner, H.B. Research Trends in Motivation and Weight Loss: A Bibliometric-Based Review. Healthcare 2023, 11, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markoulli, M.P.; Lee, C.I.S.G.; Byington, E.; Felps, W.A. Mapping Human Resource Management: Reviewing the Field and Charting Future Directions. Human Resource Management Review 2017, 27, 367–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.D. Triangulation: A Method to Increase Validity, Reliability, and Legitimation in Clinical Research. Journal of Emergency Nursing 2019, 45, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-Tool for Comprehensive Science Mapping Analysis. Journal of Informetrics 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haunschild, R.; Bornmann, L. Reference Publication Year Spectroscopy (RPYS) in Practice: A Software Tutorial. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 7253–7271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P.; Vošner, H.B.; Završnik, J. Knowledge Development in Artificial Intelligence Use in Paediatrics. Knowledge 2022, 2, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P.; Završnik, J.; Vošner, H.B. Bibliographic-Based Identification of Hot Future Research Topics: An Opportunity for Hospital Librarianship. Journal of Hospital Librarianship 2018, 18, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Nasir, A.; Khan, K.I. An Assessment of the Quality of the Search Strategy: A Case of Bibliometric Studies Published in Business and Economics. Scientometrics 2023, 128, 4855–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Wang, S.; Niu, D.; Yang, C.; Bai, H.; Lei, T.; Liu, H. A Bibliometric Analysis of the Research Landscape on Vascular Normalization in Cancer. Heliyon 2024, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- G20. Wikipedia 2024.
- Kokol, P. Discrepancies among Scopus and Web of Science, Coverage of Funding Information in Medical Journal Articles: A Follow-up Study. Journal of the Medical Library Association 2023, 111, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Završnik, J.; Kokol, P.; Žlahtič, B.; Blažun Vošner, H. Artificial Intelligence and Pediatrics: Synthetic Knowledge Synthesis. Electronics 2024, 13, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokol, P. The Use of AI in Software Engineering: A Synthetic Knowledge Synthesis of the Recent Research Literature. Information 2024, 15, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellner, M.D.B. Which Countries Are Spending the Most on Preventive Care? Available online: https://www.healthcarebusinessinternational.com/which-countries-are-spending-the-most-on-preventive-care/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Meng, Q. Strengthening Public Health Systems in China. The Lancet Public Health 2022, 7, e987–e988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muharremi, G.; Meçani, R.; Muka, T. The Buzz Surrounding Precision Medicine: The Imperative of Incorporating It into Evidence-Based Medical Practice. Journal of Personalized Medicine 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Okazaki, K.; Ohira, T.; Maeda, M.; Sakai, A.; Nakano, H.; Hayashi, F.; Nagao, M.; Harigane, M.; Takahashi, A.; et al. Suboptimal Diabetic Control and Psychological Burden after the Triple Disaster in Japan: The Fukushima Health Management Survey. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, K.; Gjorgov, N.; Bajraktarov, S. Predictive, Preventive, and Personalized Approach in Sleep Medicine. Advances in Predictive, Preventive and Personalised Medicine 2023, 17, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.K.; Erion, K.; Florez, J.C.; Hattersley, A.T.; Hivert, M.-F.; Lee, C.G.; McCarthy, M.I.; Nolan, J.J.; Norris, J.M.; Pearson, E.R.; et al. Precision Medicine in Diabetes: A Consensus Report from the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1617–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoitsis, G.; Papakonstantinou, M.; Karvounis, M.; Manouselis, N. The Role of Big Data and Artificial Intelligence in Food Risk Assessment and Prediction. In Present Knowledge in Food Safety: A Risk-Based Approach through the Food Chain; 2022; pp. 1032–1044. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Du, Z.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y. Accurate Prediction of Stroke for Hypertensive Patients Based on Medical Big Data and Machine Learning Algorithms: Retrospective Study. JMIR Medical Informatics 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilne, B.; Ķibilds, J.; Siksna, I.; Lazda, I.; Valciņa, O.; Krūmiņa, A. Could Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning and Inclusion of Diet-Gut Microbiome Interactions Improve Disease Risk Prediction? Case Study: Coronary Artery Disease. Frontiers in Microbiology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burugadda, V.R.; Dutt, V. ; Mamta; Vyas, N. Personalized Cardiovascular Disease Risk Prediction Using Random Forest: An Optimized Approach.; 2023; pp. 226–232. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xia, Z.; Zhu, R.; Gong, H.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Diabetes Risk Prediction Model Based on Community Follow-up Data Using Machine Learning. Preventive Medicine Reports 2023, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cen, X.; Wang, F.; Huang, X.; Jovic, D.; Dubee, F.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. Towards Precision Medicine: Omics Approach for COVID-19. Biosafety and Health 2023, 5, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, S.M. Electronic Health Record–Enabled Big-Data Approaches to Nephrotoxin-Associated Acute Kidney Injury Risk Prediction. Pharmacotherapy 2018, 38, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, T.A.; Ammerman, B.A.; Jacobucci, R. The Use of Machine Learning in the Study of Suicidal and Non-Suicidal Self-Injurious Thoughts and Behaviors: A Systematic Review. Journal of Affective Disorders 2019, 245, 869–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniz-Garcia, A.; Fabelo, H.; Rodriguez-Almeida, A.J.; Zamora-Zamorano, G.; Castro-Fernandez, M.; del Pino Alberiche Ruano, M.; Solvoll, T.; Granja, C.; Schopf, T.R.; Callico, G.M.; et al. Quality, Usability, and Effectiveness of mHealth Apps and the Role of Artificial Intelligence: Current Scenario and Challenges. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2023, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Urtnasan, E.; Hwang, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, S.B.; Youk, H. Concept and Proof of the Lifelog Bigdata Platform for Digital Healthcare and Precision Medicine on the Cloud. Yonsei Medical Journal 2022, 63, S84–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, M.; Wojtusciszyn, A.; Favre, L.; Boughorbel, S.; Shan, J.; Letaief, K.B.; Pitteloud, N.; Chouchane, L. Precision Medicine in the Era of Artificial Intelligence: Implications in Chronic Disease Management. Journal of Translational Medicine 2020, 18, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaoui, W.; Retal, S.; El Bhiri, B.; Kharmoum, N.; Ziti, S. Towards Revolutionizing Precision Healthcare: A Systematic Literature Review of Artificial Intelligence Methods in Precision Medicine. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked 2024, 46, 101475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrifa-Yamoah, E.; Adua, E.; Peprah-Yamoah, E.; Anto, E.O.; Opoku-Yamoah, V.; Acheampong, E.; Macartney, M.J.; Hashmi, R. Pathways to Chronic Disease Detection and Prediction: Mapping the Potential of Machine Learning to the Pathophysiological Processes While Navigating Ethical Challenges. Chronic Diseases and Translational Medicine n/a. [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.; Bertozzi, G.; Di Fazio, N.; Aquila, I.; Di Fazio, A.; Maiese, A.; Volonnino, G.; Frati, P.; La Russa, R. Risk Management and Patient Safety in the Artificial Intelligence Era: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2024, 12, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalis, V.D. The Integration of Artificial Intelligence into Clinical Practice. Applied Biosciences 2024, 3, 14–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, M.H.; Handiyani, H.; Nuraini, T.; Hariyati, R.T.S.; Sutrisno, S. A Systematic Review of Artificial Intelligence-Powered (AI-Powered) Chatbot Intervention for Managing Chronic Illness. Ann Med 2024, 56, 2302980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storeng, K.T.; de Bengy Puyvallée, A. The Smartphone Pandemic: How Big Tech and Public Health Authorities Partner in the Digital Response to Covid-19. Global Public Health 2021, 16, 1482–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, A.; Bouaziz, B.; Trabelsi, K.; Glenn, J.M.; Zmijewski, P.; Müller, P.; Chtourou, H.; Jmaiel, M.; Chamari, K.; Driss, T.; et al. Applying Digital Technology to Promote Active and Healthy Confinement Lifestyle during Pandemics in the Elderly. Biology of Sport 2021, 38, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Wu, H.; Zhou, D.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, H.; Tong, Z.; Lou, S.; Liu, Z. Application of Big Data and Artificial Intelligence in COVID-19 Prevention, Diagnosis, Treatment and Management Decisions in China. Journal of Medical Systems 2021, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, S.; Zhang, X.; Xing, Y.; Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Hou, Z. Applications of Social Media and Digital Technologies in COVID-19 Vaccination: Scoping Review. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2023, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, W.; Lv, C. Modern Technologies and Solutions to Enhance Surveillance and Response Systems for Emerging Zoonotic Diseases. Science in One Health 2024, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piovani, D.; Bonovas, S. Real World—Big Data Analytics in Healthcare. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodman, R.; Mangoni, A.A. Artificial Intelligence and the Medicine of the Future. Practical Issues in Geriatrics 2023, Part F1182, 175–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Novillo-Ortiz, D.; Azzopardi-Muscat, N.; Kostkova, P. Digital Data Sources and Their Impact on People’s Health: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews. Frontiers in Public Health 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh, A.; Mohammadzadeh, Z.; Fathifar, Z.; Jahangiri-Mirshekarlou, S.; Rezaei-Hachesu, P. A Framework for Information Technology-Based Management against COVID-19 in Iran. BMC Public Health 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lai, S.; Rai, A.A.; Hassan, A.; Mushtaq, R.T. Exploring the Potential of Big Data Analytics in Urban Epidemiology Control: A Comprehensive Study Using CiteSpace. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ser, S.E.; Shear, K.; Snigurska, U.A.; Prosperi, M.; Wu, Y.; Magoc, T.; Bjarnadottir, R.I.; Lucero, R.J. Clinical Prediction Models for Hospital-Induced Delirium Using Structured and Unstructured Electronic Health Record Data: Protocol for a Development and Validation Study. JMIR Research Protocols 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostkova, P.; Saigí-Rubió, F.; Eguia, H.; Borbolla, D.; Verschuuren, M.; Hamilton, C.; Azzopardi-Muscat, N.; Novillo-Ortiz, D. Data and Digital Solutions to Support Surveillance Strategies in the Context of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Frontiers in Digital Health 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.S.; Safa, N.T.; Sultana, S.; Salam, S.; Karamehic-Muratovic, A.; Overgaard, H.J. Role of Artificial Intelligence-Internet of Things (AI-IoT) Based Emerging Technologies in the Public Health Response to Infectious Diseases in Bangladesh. Parasite Epidemiology and Control 2022, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, T.; Han, X.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Ma, L.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Lai, S.; Li, W.; et al. Influenza Epidemic Trend Surveillance and Prediction Based on Search Engine Data: Deep Learning Model Study. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2023, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadarzynski, T.; Miles, O.; Cowie, A.; Ridge, D. Acceptability of Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Led Chatbot Services in Healthcare: A Mixed-Methods Study. Digit Health 2019, 5, 2055207619871808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenyi, A.O.; Okolo, C.A.; Olorunsogo, T.; Babawarun, O.; Adenyi, A.O.; Okolo, C.A.; Olorunsogo, T.; Babawarun, O. Leveraging Big Data and Analytics for Enhanced Public Health Decision-Making: A Global Review. GSC Advanced Research and Reviews 2024, 18, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbehadji, I.E.; Awuzie, B.O.; Ngowi, A.B.; Millham, R.C. Review of Big Data Analytics, Artificial Intelligence and Nature-Inspired Computing Models towards Accurate Detection of COVID-19 Pandemic Cases and Contact Tracing. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17, 5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kung, L.; Byrd, T.A. Big Data Analytics: Understanding Its Capabilities and Potential Benefits for Healthcare Organizations. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2018, 126, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Ji, H.; Yan, J.; Qi, X. Application of Big Data and Artificial Intelligence in Epidemic Surveillance and Containment. Intell Med 2023, 3, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, M.; Gregg, M. Field Epidemiology; Third Edition, Third Edition.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, New York, 2008; ISBN 978-0-19-531380-2. [Google Scholar]
- Tula, S.T.; Ofodile, O.C.; Okoye, C.C.; Nifise, A.O.A.; Odeyemi, O. ENTREPRENEURIAL ECOSYSTEMS IN THE USA: A COMPARATIVE REVIEW WITH EUROPEAN MODELS. International Journal of Management & Entrepreneurship Research 2024, 6, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karcher, N.R.; Barch, D.M. The ABCD Study: Understanding the Development of Risk for Mental and Physical Health Outcomes. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donelle, L.; Comer, L.; Hiebert, B.; Hall, J.; Shelley, J.J.; Smith, M.J.; Kothari, A.; Burkell, J.; Stranges, S.; Cooke, T.; et al. Use of Digital Technologies for Public Health Surveillance during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Scoping Review. Digit Health 2023, 9, 20552076231173220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsubuga, P.; White, M.E.; Thacker, S.B.; Anderson, M.A.; Blount, S.B.; Broome, C.V.; Chiller, T.M.; Espitia, V.; Imtiaz, R.; Sosin, D.; et al. Public Health Surveillance: A Tool for Targeting and Monitoring Interventions. In Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries; Jamison, D.T., Breman, J.G., Measham, A.R., Alleyne, G., Claeson, M., Evans, D.B., Jha, P., Mills, A., Musgrove, P., Eds.; The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank: Washington (DC), 2006 ISBN 978-0-8213-6179-5.
- Renugadevi, N.; Saravanan, S.; Naga Sudha, C.M.; Tripathi, P. IoT-Enabled Applications and Other Techniques to Combat COVID-19. EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing 2021, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, I.A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Ujjan, R.M.A. Industry 4.0: Use of Digitalization in Healthcare. In Advances in Computational Intelligence for the Healthcare Industry 4.0; 2024; pp. 174–193. [CrossRef]
- Parihar, A.; Prajapati, J.B.; Prajapati, B.G.; Trambadiya, B.; Thakkar, A.; Engineer, P. Role of IOT in Healthcare: Applications, Security & Privacy Concerns. Intelligent Pharmacy 2024. [CrossRef]
- Chandy, A. A REVIEW ON IOT BASED MEDICAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY FOR HEALTHCARE APPLICATIONS. Journal of Innovative Image Processing 2019, 1, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodnia, V.; Slinowsky, M.; Etemad, A. Deep Multitask Learning for Pervasive BMI Estimation and Identity Recognition in Smart Beds. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 2023, 14, 5463–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, A.J.; Zamora-Izquierdo, M.A.; Skarmeta, A.F. Interconnection Framework for mHealth and Remote Monitoring Based on the Internet of Things. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2013, 31, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anurag; Moosavi, S.R.; Rahmani, A.-M.; Westerlund, T.; Yang, G.; Liljeberg, P.; Tenhunen, H. Pervasive Health Monitoring Based on Internet of Things: Two Case Studies. In Proceedings of the 2014 4th International Conference on Wireless Mobile Communication and Healthcare - Transforming Healthcare Through Innovations in Mobile and Wireless Technologies (MOBIHEALTH); November 2014; pp. 275–278. [CrossRef]
- Asif-Ur-Rahman, Md.; Afsana, F.; Mahmud, M.; Kaiser, M.S.; Ahmed, M.R.; Kaiwartya, O.; James-Taylor, A. Toward a Heterogeneous Mist, Fog, and Cloud-Based Framework for the Internet of Healthcare Things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2019, 6, 4049–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, Z.; Heidari, A.; Navimipour, N.J.; Esmaeilpour, M.; Yazdani, Y. The Deep Learning Applications in IoT-Based Bio- and Medical Informatics: A Systematic Literature Review. Neural Comput & Applic 2024, 36, 5757–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, L.; Yin, G.; Li, L.; Zhao, H. A Survey on Security and Privacy Issues in Internet-of-Things. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2017, 4, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayo-Monton, J.-L.; Martinez-Millana, A.; Han, W.; Fernandez-Llatas, C.; Sun, Y.; Traver, V. Wearable Sensors Integrated with Internet of Things for Advancing eHealth Care. Sensors (Basel) 2018, 18, 1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Pathirana, P.N.; Ding, M.; Seneviratne, A. Integration of Blockchain and Cloud of Things: Architecture, Applications and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2020, 22, 2521–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellouze, F.; Fersi, G.; Jmaiel, M. Blockchain for Internet of Medical Things: A Technical Review. In; 2020; pp. 259–267 ISBN 978-3-030-51516-4. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, V.; Kolhe, A.; Kulkarni, J. Intelligent Software Engineering: The Significance of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Enhancing Software Development Lifecycle Processes. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Systems Design and Applications; Abraham, A., Gandhi, N., Hanne, T., Hong, T.-P., Nogueira Rios, T., Ding, W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghdam, Z.N.; Rahmani, A.M.; Hosseinzadeh, M. The Role of the Internet of Things in Healthcare: Future Trends and Challenges. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2021, 199, 105903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejeb, A.; Rejeb, K.; Treiblmaier, H.; Appolloni, A.; Alghamdi, S.; Alhasawi, Y.; Iranmanesh, M. The Internet of Things (IoT) in Healthcare: Taking Stock and Moving Forward. Internet of Things 2023, 22, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, G.; Adeli, H. Machine Learning Techniques for Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease, Mild Cognitive Disorder, and Other Types of Dementia. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2022, 72, 103293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubeis, G. iHealth: The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data in Mental Healthcare. Internet Interventions 2022, 28, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haowei, G.; Ting, W. Analysis of Community Mental Health Services in the Context of Big Data. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Big Data and Social Sciences (ICBDSS); August 2020; pp. 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyrard, A.; Mohammadi, S.; Gaur, M.; Kung, A. IoT-Based Preventive Mental Health Using Knowledge Graphs and Standards for Better Well-Being 2024. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Student Mental Health Risk Prediction Based on Apriori Algorithm in the Context of Big Data. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Electrical Drives, Power Electronics & Engineering (EDPEE); February 2024; pp. 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, S.; Ghimire, A.; Adhikari, S.; Bhoi, A.K.; Barsocchi, P. Chapter 3 - Cognitive Internet of Things (IoT) and Computational Intelligence for Mental Well-Being. In Cognitive and Soft Computing Techniques for the Analysis of Healthcare Data; Bhoi, A.K., de Albuquerque, V.H.C., Srinivasu, P.N., Marques, G., Eds.; Intelligent Data-Centric Systems; Academic Press, 2022; pp. 59–77 ISBN 978-0-323-85751-2. [CrossRef]
- Naik, N.; Hameed, B.M.Z.; Sooriyaperakasam, N.; Vinayahalingam, S.; Patil, V.; Smriti, K.; Saxena, J.; Shah, M.; Ibrahim, S.; Singh, A.; et al. Transforming Healthcare through a Digital Revolution: A Review of Digital Healthcare Technologies and Solutions. Frontiers in Digital Health 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Fan, L.; Nallanathan, A. Scoring Aided Federated Learning on Long-Tailed Data for Wireless IoMT Based Healthcare System. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2024, 28, 3341–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Li, S.; Chen, Y. Digital Health in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Chronic Diseases and Translational Medicine 2023, 9, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshini, S.; Swain, S.C.; Mohanty, S.N.; Dulla, N. IoT-Based Safety Measures and Healthcare Services for Transgender Welfare and Sustainability. In Reconnoitering the Landscape of Edge Intelligence in Healthcare; 2024; pp. 115–137.
- Guo, R.-X.; Tian, X.; Bazoukis, G.; Tse, G.; Hong, S.; Chen, K.-Y.; Liu, T. Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiac Arrhythmia. PACE - Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology 2024, 47, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokinen, A.; Stolt, M.; Suhonen, R. Ethical Issues Related to eHealth: An Integrative Review. Nurs Ethics 2021, 28, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petretto, D.R.; Carrogu, G.P.; Gaviano, L.; Berti, R.; Pinna, M.; Petretto, A.D.; Pili, R. Telemedicine, e-Health, and Digital Health Equity: A Scoping Review. [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, B. REVISITING HEALTH INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ETHICAL, LEGAL, and SOCIAL ISSUES and EVALUATION: TELEHEALTH/TELEMEDICINE and COVID-19. International Journal of Medical Informatics 2020, 143, 104239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawad, L.A. Security and Privacy in Digital Healthcare Systems: Challenges and Mitigation Strategies. Abhigyan 2024, 42, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, Y.; Rowan, W.; Lynch, L.; Heavin, C. Privacy by Design: Informed Consent and Internet of Things for Smart Health. Procedia Computer Science 2017, 113, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bente, B.E.; Van Dongen, A.; Verdaasdonk, R.; van Gemert-Pijnen, L. eHealth Implementation in Europe: A Scoping Review on Legal, Ethical, Financial, and Technological Aspects. Front. Digit. Health 2024, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Clarke, J.; Neves, A.L.; Ashrafian, H.; Darzi, A. Electronic Health Records, Interoperability and Patient Safety in Health Systems of High-Income Countries: A Systematic Review Protocol. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e044941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbers, T.; Takes, R.P.; Honings, J.; Smeele, L.E.; Kool, R.B.; van den Broek, G.B. Development and Validation of Automated Electronic Health Record Data Reuse for a Multidisciplinary Quality Dashboard. Digit Health 2023, 9, 20552076231191007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaramurthy, M.P. IoT on Healthcare Using Clinical Decision Support System. In Diagnostic Applications of Health Intelligence and Surveillance Systems; IGI Global, 2021; pp. 259–280 ISBN 978-1-79986-527-8. [CrossRef]
- Vahdati, M.; Gholizadeh HamlAbadi, K.; Saghiri, A.M. IoT-Based Healthcare Monitoring Using Blockchain.; Namasudra, S., Deka, G.C., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2021; Vol. 83, pp. 141–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Glenn, T.; Monteith, S.; Bauer, R.; Whybrow, P.C.; Geddes, J. Ethical Perspectives on Recommending Digital Technology for Patients with Mental Illness. International Journal of Bipolar Disorders 2017, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Daele, T.; Karekla, M.; Kassianos, A.P.; Compare, A.; Haddouk, L.; Salgado, J.; Ebert, D.D.; Trebbi, G.; Bernaerts, S.; Van Assche, E.; et al. Recommendations for Policy and Practice of Telepsychotherapy and E-Mental Health in Europe and Beyond. Journal of Psychotherapy Integration 2020, 30, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Garg, L.; Guizani, M.; Hu, X. Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Wearable Intenet of Things for Mental Health Detection. International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering 2024. [CrossRef]
- Health, T.L.G. Mental Health Matters. The Lancet Global Health 2020, 8, e1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibniz, G.W. Directiones Ad Rem Medicam Pertinentes. Stud Leibinitiana 1971, 8, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Winslow, C.E. THE UNTILLED FIELDS OF PUBLIC HEALTH. Science 1920, 51, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.B. Observation and Experiment. N Engl J Med 1953, 248, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermack, W.O.; McKendrick, A.G.; Walker, G.T. A Contribution to the Mathematical Theory of Epidemics. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Containing Papers of a Mathematical and Physical Character 1927, 115, 700–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, J.; Mohebbi, M.H.; Patel, R.S.; Brammer, L.; Smolinski, M.S.; Brilliant, L. Detecting Influenza Epidemics Using Search Engine Query Data. Nature 2009, 457, 1012–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, X.; Wu, W.; Shen, L.; Liao, W.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, J. Industrial Internet of Things and Unsupervised Deep Learning Enabled Real-Time Occupational Safety Monitoring in Cold Storage Warehouse. Safety Science 2022, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G.; Iliescu, F.S.; Mihaescu, G.; Cucu, A.I.; Ionescu, O.N.; Popescu, M.; Simion, M.; Burlibasa, L.; Tica, M.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; et al. Advances in the Rapid Diagnostic of Viral Respiratory Tract Infections. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, K.H.; Erdenbayar, U.; Hwang, S.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.B.; Park, J.W.; et al. Internet of Medical Things-Based Real-Time Digital Health Service for Precision Medicine: Empirical Studies Using MEDBIZ Platform. Digital Health 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouedi, O.; Sacco, A.; Piamrat, K.; Marchetto, G. Handling Privacy-Sensitive Medical Data With Federated Learning: Challenges and Future Directions. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2023, 27, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Ning, J. An Access Control Scheme with Privacy-Preserving Authentication and Flexible Revocation for Smart Healthcare. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2024, 28, 3269–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visco, V.; Izzo, C.; Mancusi, C.; Rispoli, A.; Tedeschi, M.; Virtuoso, N.; Giano, A.; Gioia, R.; Melfi, A.; Serio, B.; et al. Artificial Intelligence in Hypertension Management: An Ace up Your Sleeve. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, M.; Yang, J.; Sohn, J.; Lee, J.-H. Digital Healthcare for Dementia and Cognitive Impairment: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2023, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkalainen, H.; Kainulainen, S.; Islind, A.S.; Óskarsdóttir, M.; Strassberger, C.; Nikkonen, S.; Töyräs, J.; Kulkas, A.; Grote, L.; Hedner, J.; et al. Review and Perspective on Sleep-Disordered Breathing Research and Translation to Clinics. Sleep Medicine Reviews 2024, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kessel, R.; Kyriopoulos, I.; Wong, B.L.H.; Mossialos, E. The Effect of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Digital Health–Seeking Behavior: Big Data Interrupted Time-Series Analysis of Google Trends. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2023, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dindorf, C.; Bartaguiz, E.; Gassmann, F.; Fröhlich, M. Conceptual Structure and Current Trends in Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning Research in Sports: A Bibliometric Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachakonda, S.; Moorthy, S.; Jain, A.; Bukharev, A.; Bucur, A.; Manni, F.; Quiterio, T.M.; Joosten, L.; Mendez, N.I. Privacy Enhancing and Scalable Federated Learning to Accelerate AI Implementation in Cross-Silo and IoMT Environments. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2023, 27, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Sindhwani, N.; Anand, R.; Dahiya, A. Role of IoT in Smart Homes and Smart Cities: Challenges, Benefits, and Applications. EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing 2023, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saleh, A.A.; Sheikh, A.M.; Albreem, M.A.M.; Honnurvali, M.S. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): Opportunities and Challenges. Wireless Netw 2024. [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.T.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Neal Joshua, E.S. Chapter 19 - An Extensive Discussion on Utilization of Data Security and Big Data Models for Resolving Healthcare Problems. In Multi-Chaos, Fractal and Multi-Fractional Artificial Intelligence of Different Complex Systems; Karaca, Y., Baleanu, D., Zhang, Y.-D., Gervasi, O., Moonis, M., Eds.; Academic Press, 2022; pp. 311–324 ISBN 978-0-323-90032-4. [CrossRef]
- Big Data and ICT Solutions in the European Union and China: A Comparative Analysis of Policies in Personalized Medicine - Francesco Andrea Causio, Ilda Hoxhaj, Flavia Beccia, Marzia Di Marcantonio, Timo Strohäker, Chiara Cadeddu, Walter Ricciardi, Stefania Boccia, 2022. Available online: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/20552076221129060 (accessed on 10 July 2024). [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, L. Research Progress in Biomedical Big Data. In Progress in China Epidemiology: Volume 1; Ye, D.-Q., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 391–400. ISBN 978-981-19219-9-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfell, O.J.; Davidson, K.; Woods, L.; Sullivan, C.; Cocoros, N.M.; Klompas, M.; Zambarano, B.; Eakin, E.; Littlewood, R.; Burton-Jones, A. Precision Public Health for Non-Communicable Diseases: An Emerging Strategic Roadmap and Multinational Use Cases. Front. Public Health 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Awan, F.M.; Naz, A.; deAndrés-Galiana, E.J.; Alvarez, O.; Cernea, A.; Fernández-Brillet, L.; Fernández-Martínez, J.L.; Kloczkowski, A. Innovations in Genomics and Big Data Analytics for Personalized Medicine and Health Care: A Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnegar, A. Point-of-Care Devices in Healthcare: A Public Health Perspective. In Current and Future Trends in Health and Medical Informatics; Daimi, K., Alsadoon, A., Seabra Dos Reis, S., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, 2023; pp. 75–92. ISBN 978-3-031-42112-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Source Title | Number of publications | H-Index in Scopus | Scopus SJR | Quarter |
| Eai Springer Innovations In Communication And Computing | 55 | 26 | 0.15 | Q4 |
| International Journal Of Environmental Research And Public Health | 54 | 198 | 0.81 | Q2 |
| Journal Of Medical Internet Research | 36 | 197 | 2.02 | Q1 |
| Studies In Health Technology And Informatics | 28 | 67 | 0.29 | Q3 |
| Frontiers In Public Health | 27 | 101 | 0.90 | Q1 |
| Journal Of Healthcare Engineering | 24 | 57 | 0.51 | Q2 |
| Safety Science | 20 | 154 | 1.28 | Q1 |
| Accident Analysis And Prevention | 17 | 188 | 1.90 | Q1 |
| BMC Public Health | 12 | 197 | 1.25 | Q1 |
| BMJ Open | 12 | 160 | 0.97 | Q1 |
| Authors | Title | Publication year | Source title | Cited by | SJR 2023 | Core journal |
| Tomczak K. et al. | The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of knowledge | 2015 | Wspolczesna Onkologia | 1452 | 0.532 (Q2) | Yes |
| Peeri N.C. et al. | The SARS, MERS, and novel coronavirus (COVID-19) epidemics are the newest and biggest global health threats. What lessons have we learned? | 2021 | International Journal of Epidemiology | 987 | 2.663 (Q1) | Yes |
| Vaishya R.; et al. | Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications for the COVID-19 pandemic | 2020 | Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews | 927 | 1.313 (Q1) | Yes |
| Dimitrov D.V. | Medical internet of things and big data in healthcare | 2016 | Healthcare Informatics Research | 645 | 1.628 Q1) | Yes |
| Brisimi T.S. et al. | Federated learning of predictive models from federated Electronic Health Records | 2018 | International Journal of Medical Informatics | 552 | 1,493 (Q1) | Yes |
| Cluster color (number of keywords) | Representative author keywords (ICT viewpoint in upper cell / medical viewpoint in lower cell) | Concepts (ICT viewpoint in upper cell / medical viewpoint in lower cell) |
Theme (ICT viewpoint in upper cell / medical viewpoint in lower cell) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red (n=26) | Artificial intelligence (n=206), Machine learning (n=205), Precision medicine (n=64), Personalised medicine (n=32), Risk prediction (n=31), Health policy (n=17), | -The use of artificial intelligence and Omics in personalized and precision medicine according to health policies; -The use of machine learning in risk prediction; -The role of personalized medicine in chronic disease management |
The role of artificial intelligence in personal, precision, and preventive medicine |
| Artificial intelligence (n=206), Personalised medicine (n=32), Sars-cov2 (n=23), Cardiovascular diseases (n=20), Genetics (n=17), Genomics (n=19), Obesity (n=15), Asthma (n=15), Cancer (n=12), Dementia (n=11), | -Use of AI in the genetics and genomics of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, dementia, obesity, asthma -Investigating an individual's risk for the most common chronic diseases -Use of AI in Sars-Cov2 management |
The role of AI in personalized medicine (genetics, genomics) in the field of the most common diseases of the modern population (cardiovascular diseases, dementia, obesity, asthma, sars-cov2, cancer) | |
| Green (n=20) | Big data (n=494), Covid-19 (n=153), Prevention (n=52), Social media (n=33), Public health (n=43), Predictive analytics (n=33), Epidemiology (n=32) | -Big data mining of social media and electronic health records used in epidemiology, predictive analysis, and prevention; -Big data analysis in public health surveillance |
The role of big data in public health |
| Big data (n=494), Covid-19 (n=153), Prevention (n=52), Public health (n=43), Surveillance (n=29) | -Use of big data and databases in the field of public health -Use of databases in epidemiology -Planning and researching prevention and survival in covid19 |
The role of big data and databases in public health, especially in the field of prevention, epidemiology, and surveillance | |
| Blue (n=14) | IoT (n=439), Deep learning (n=83), Health care (n=63), Cloud computing (n=49), Blokchain (n=48) | -IoT, Cloud Computing and deep learning, blockchain in secure and safe healthcare | The role of IoT, Cloud Computing, deep learning, and blockchain in secure and safe healthcare |
| IoT (n=439), Deep Learning (n=83), Health care (n=63), Security (n=49), Sensors (n=38), Privacy (n=24) | -Application of deep learning and IoT in healthcare -Security and privacy of IoT and deep learning -Sensitivity of the sensors for the acquisition of IoT -Importance of sensors for deep learning |
The role of IoT and deep learning in the security and privacy of health care | |
| Yellow (n=13) | Digital health (n=39), Telemedicine (n=39), Mobile health (n=30), Monitoring (n=17), suicide (n=16) | -Mobile health and wearable devices in monitoring mental health; -Digital health use in telemedicine |
The role of digital health in monitoring and Telemedicine |
| Telemedicine (n=39), Digital Health (n=39), Monitoring (n=26), Mental health (n=15), eHealth (n=14), Ethics (n=12), | -Ethical aspects of digital health and telemedicine -Data monitoring for eHealth -Ethical aspects of monitoring an individual's mental health |
The role of ethics in telemedicine and digital health |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





