Submitted:
06 August 2024
Posted:
07 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
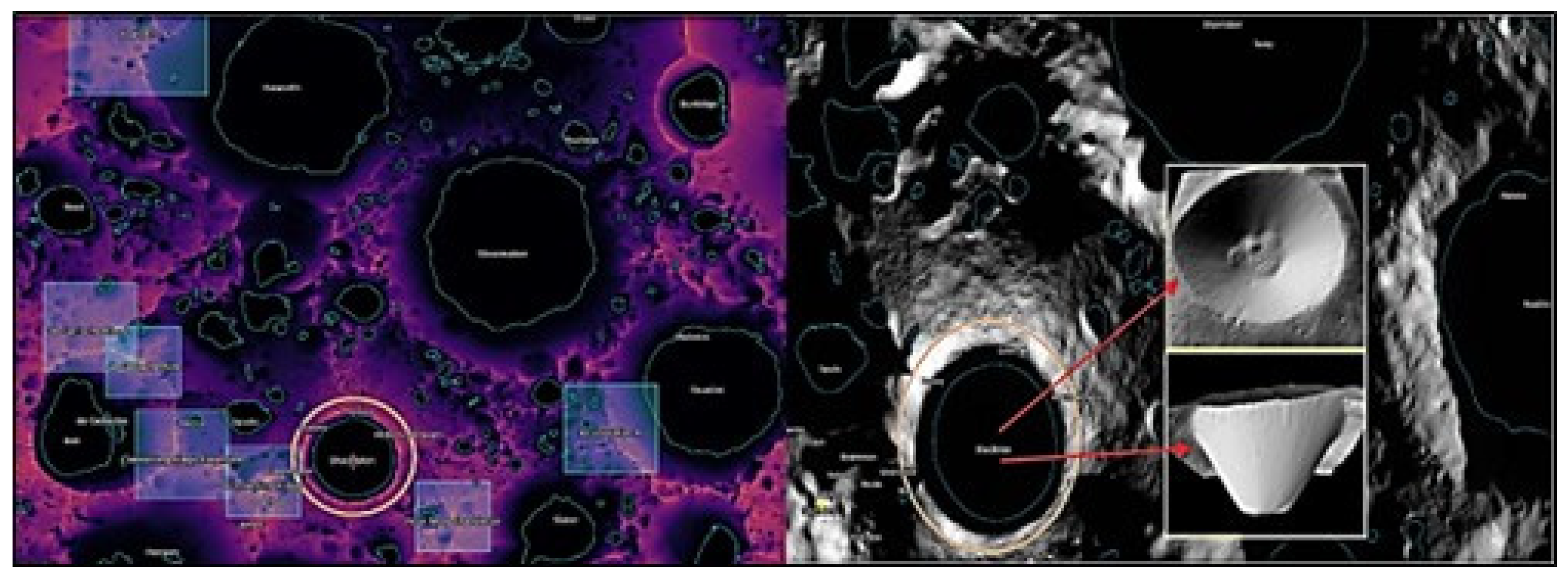
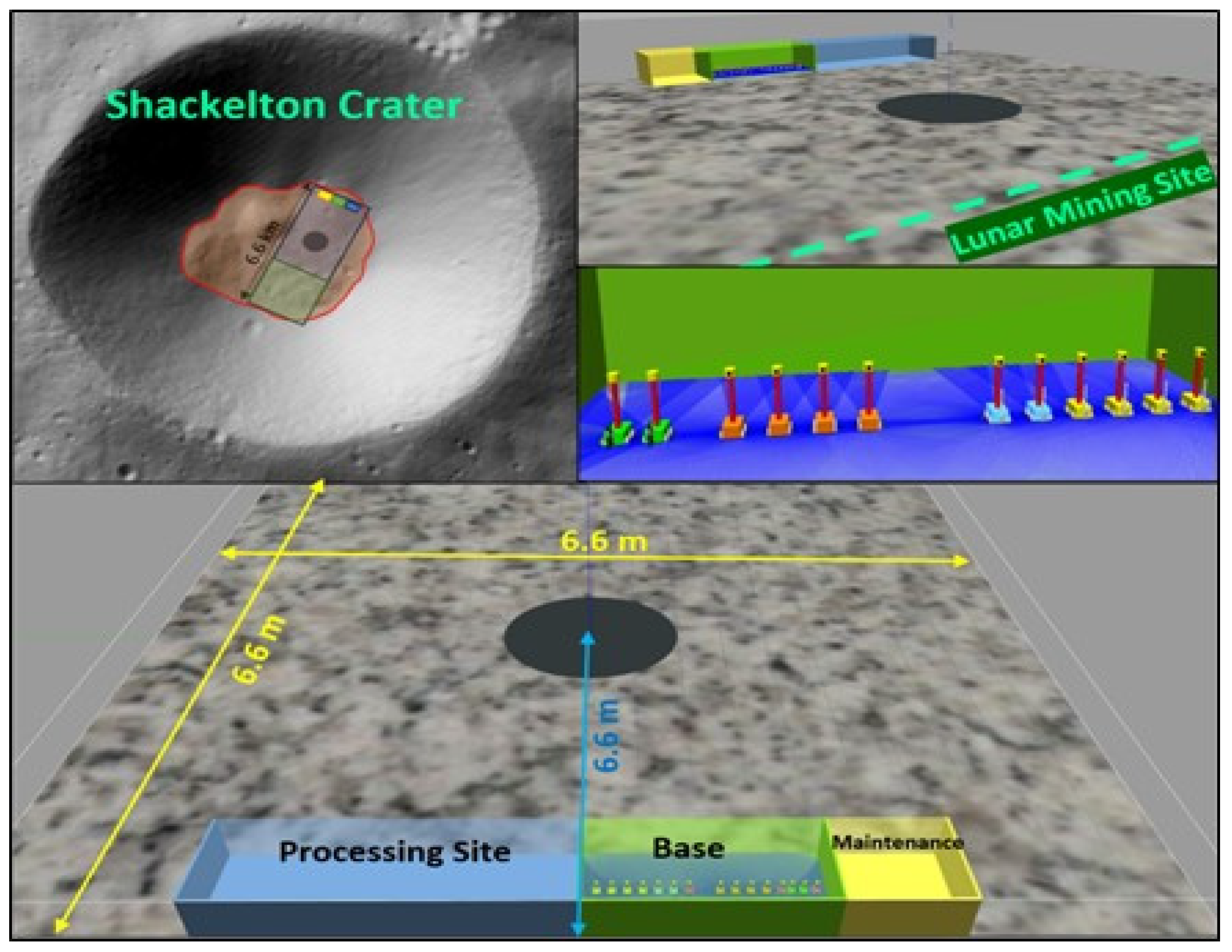
2.1. Mining Site Selection
2.2. Water-Ice Extraction Process
2.3. Constraints and Assumption
2.4. Virtual Lunar Environment Development
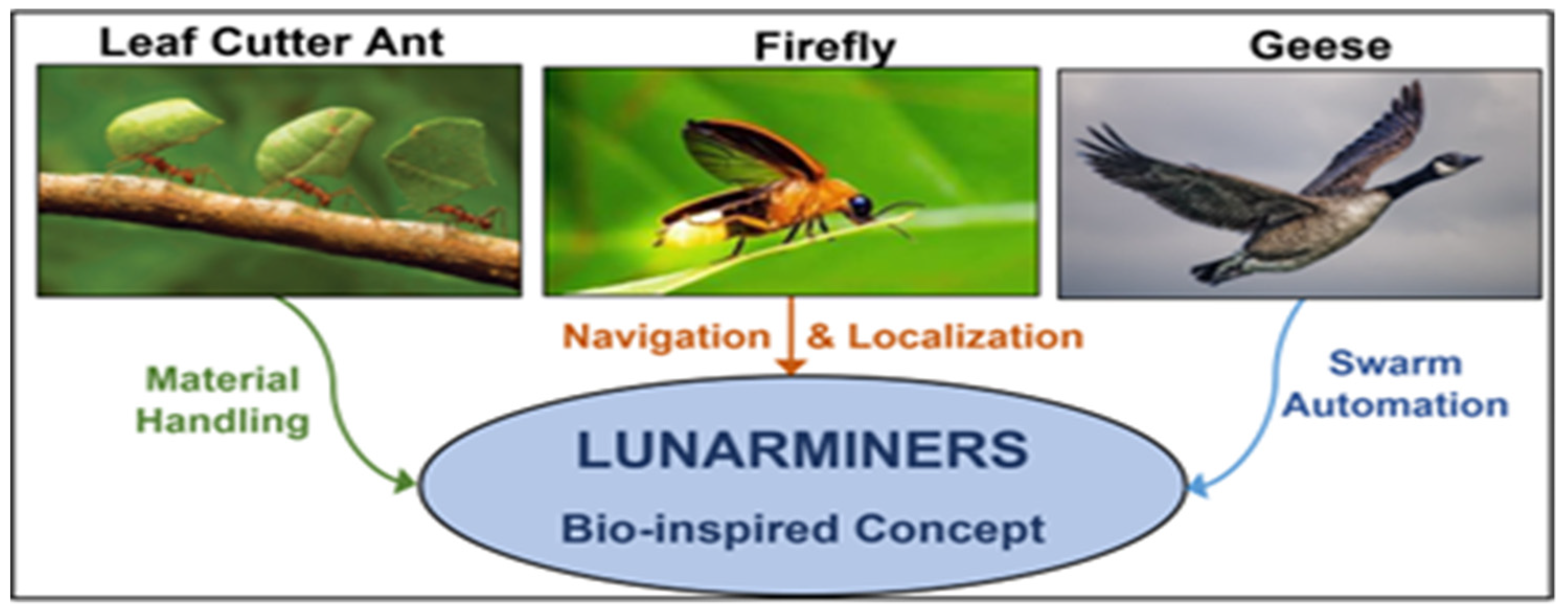
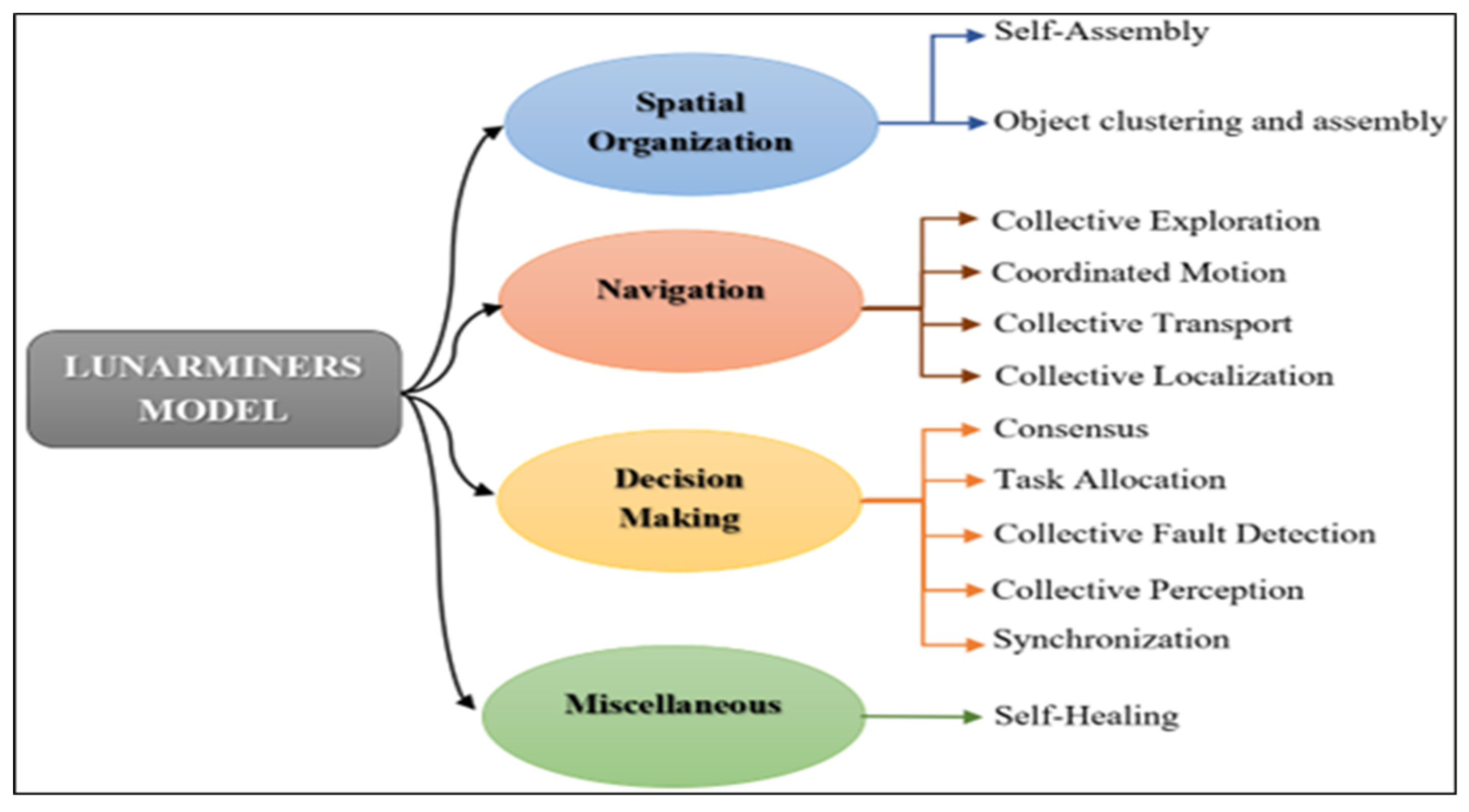
2.4. Swarm Robotic Development.
3. Proposed LUNARMINERS Concept
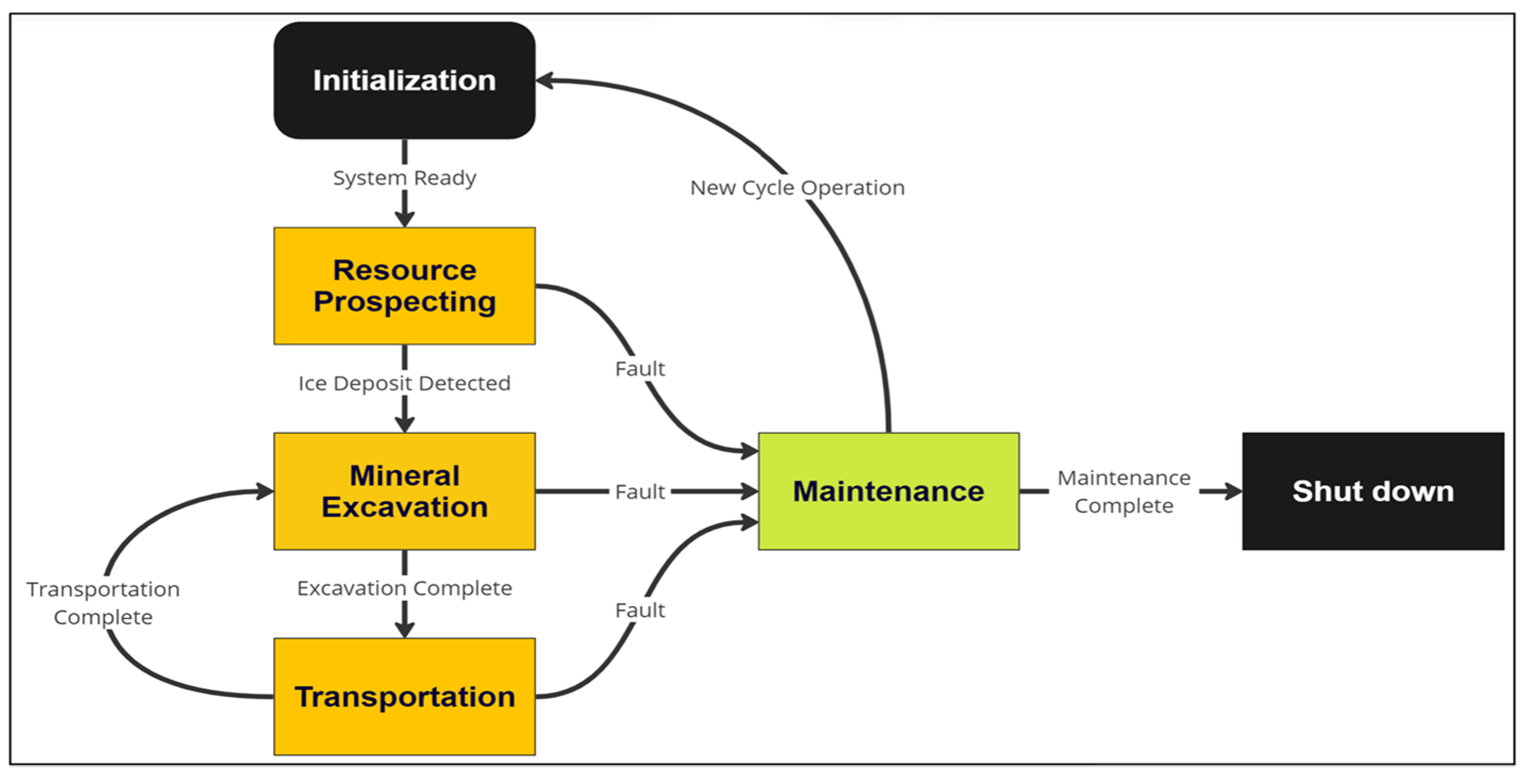
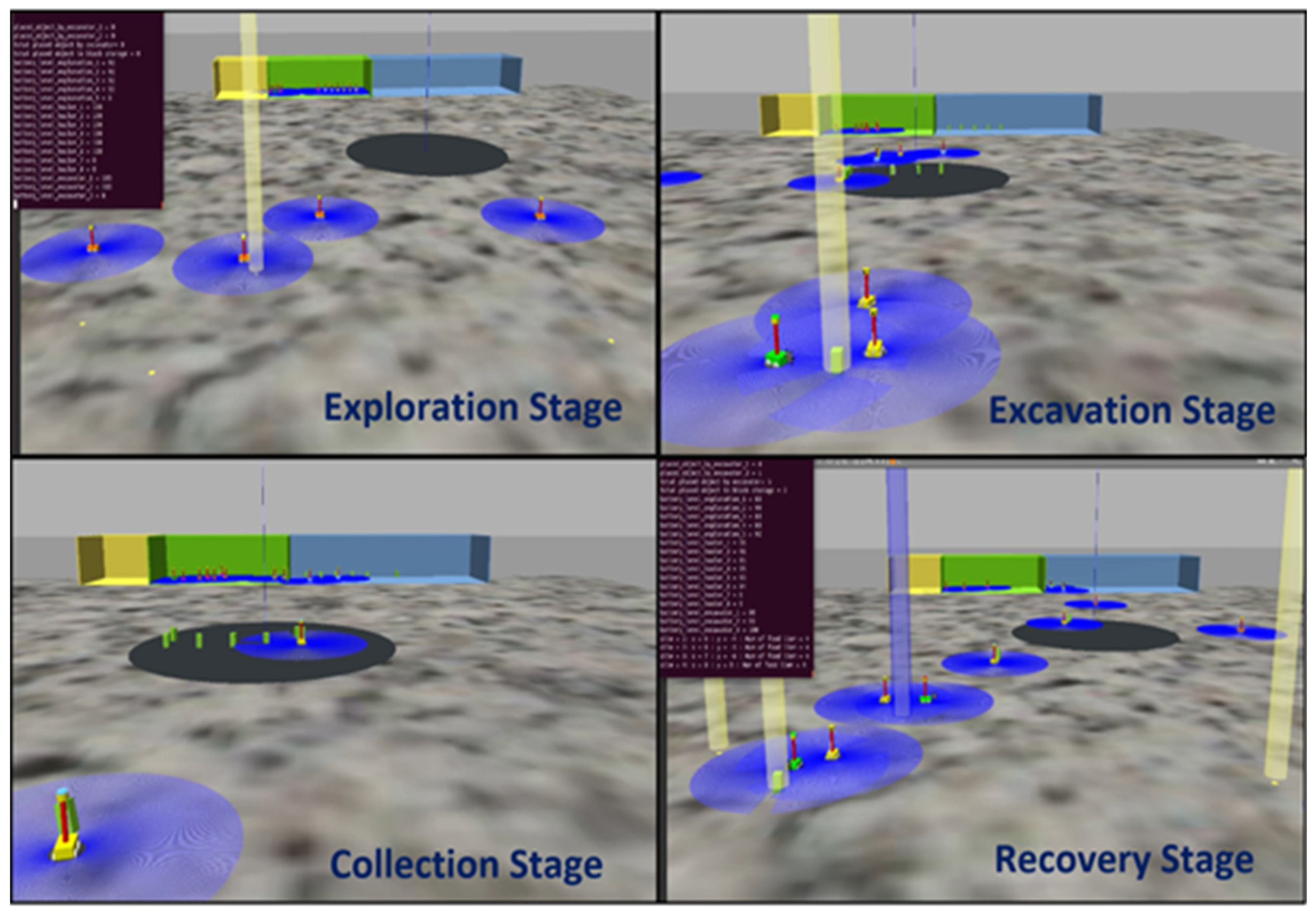
3.1. LUNARMINERS Mining Lifecycle
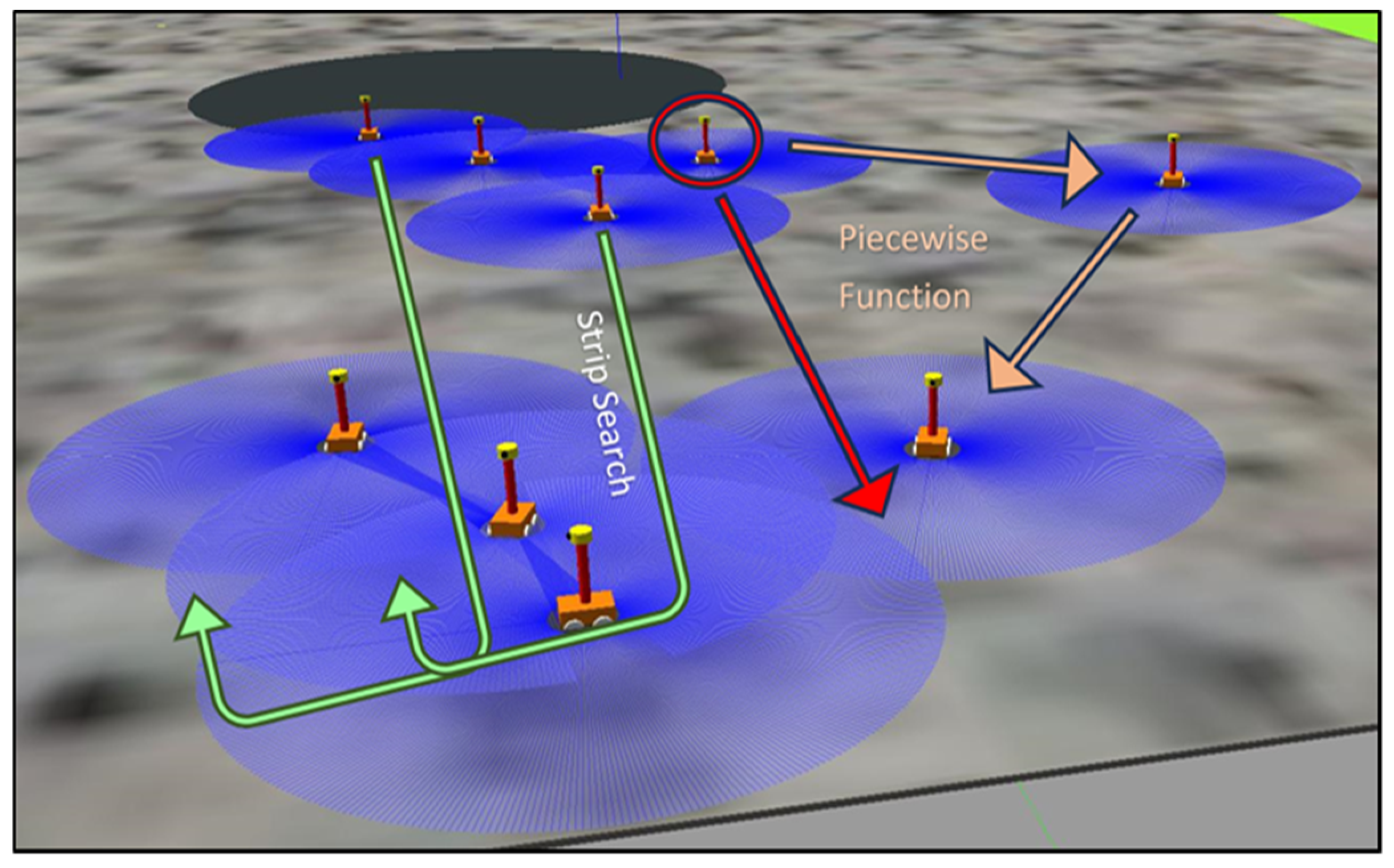
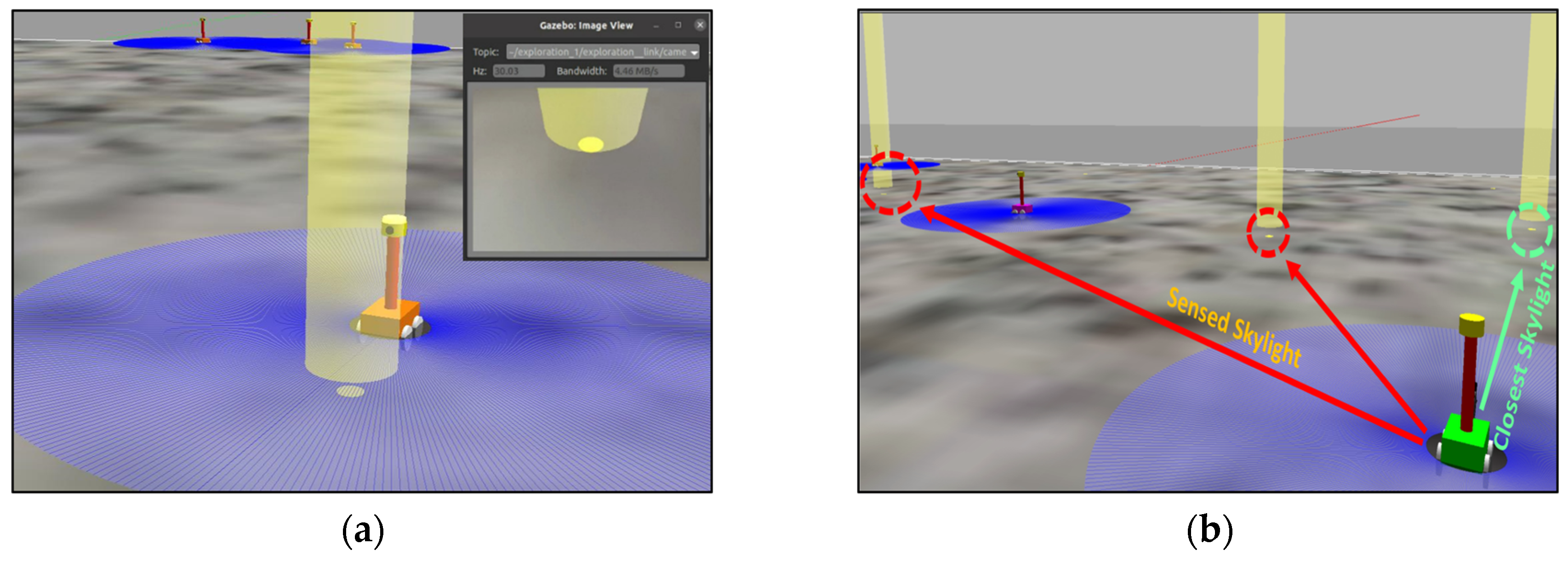
3.1.1. Resource Prospecting and Localization
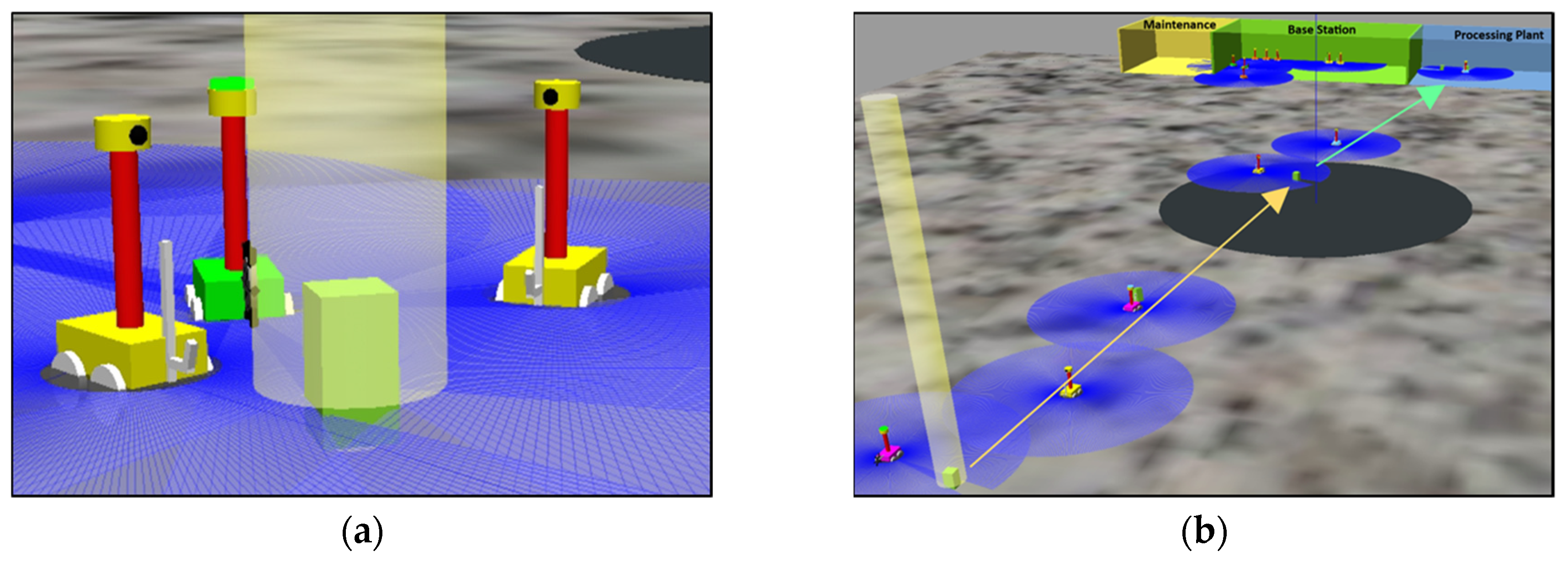
3.1.2. Mineral Excavation and Transportation
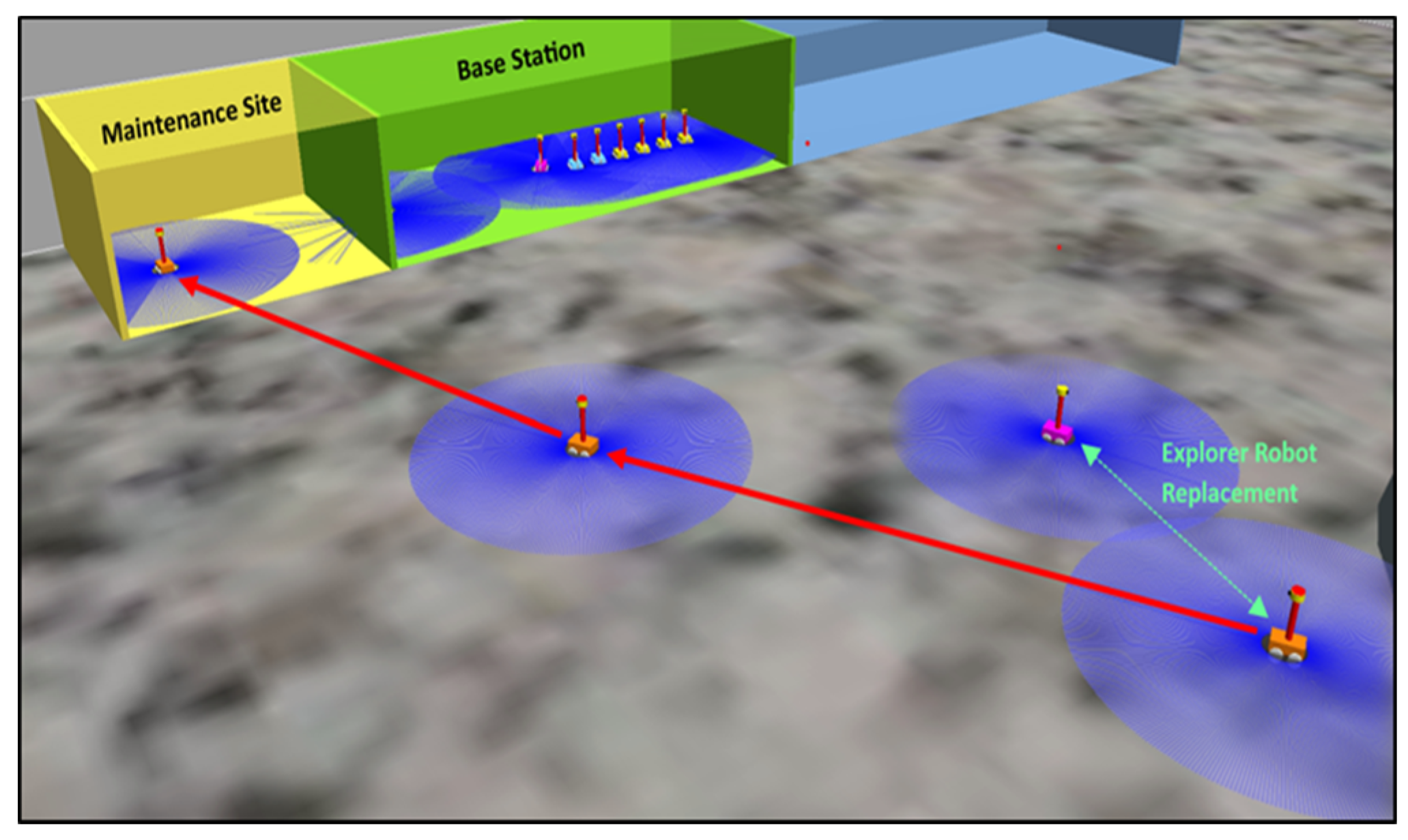
3.1.3. Maintenance and sustainability
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Mining Perfromance
4.2. Simulation Settings
4.3. Overall Perfromance Analysis
4.4. Nature-Behaviour Calssification
5. Conclusion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crawford, I.A., 2015. Lunar resources: A review. Progress in Physical Geography, 39(2), pp.137-167.
- Harland, D.M. and Harvey, B., 2007. Space Exploration 2008. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Ellis, T., 2018. Reds in space: American perceptions of the Soviet space programme from Apollo to Mir 1967-1991 (Doctoral dissertation, University of Southampton).
- Colaprete, A., Schultz, P., Heldmann, J., Wooden, D., Shirley, M., Ennico, K., Hermalyn, B., Marshall, W., Ricco, A., Elphic, R.C. and Goldstein, D., 2010. Detection of water in the LCROSS ejecta plume. science, 330(6003), pp.463-468.
- Sanders, G.B., Romig, K.A., Larson, W.E., Johnson, R., Rapp, D., Johnson, K.R., Sacksteder, K., Linne, D., Curreri, P., Duke, M. and Blair, B., 2005, September. Results from the NASA capability roadmap team for in-situ resource utilization (ISRU). In International Lunar Conference 2005 (No. KSC-2005-116).
- Bezruchko, K.A., 2022. Review of potential sources for obtaining energy carriers and mineral raw materials in outer space.
- Heiken, G., Vaniman, D. and French, B.M. eds., 1991. Lunar sourcebook: A user's guide to the Moon (No. 1259). Cup Archive.
- Liu, H., 2014. An overview of the space robotics progress in China. System (ConeXpress ORS), 14, p.15.
- Arvidson, R.E., Ashley, J.W., Bell III, J.F., Chojnacki, M., Cohen, J., Economou, T.E., Farrand, W.H., Fergason, R., Fleischer, I., Geissler, P. and Gellert, R., 2011. Opportunity Mars Rover mission: Overview and selected results from Purgatory ripple to traverses to Endeavour crater. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 116(E7).
- Wilcox, B. and Nguyen, T., 1998. Sojourner on mars and lessons learned for future planetary rovers (No. 981695). SAE Technical Paper.
- Rankin, A., Patel, N., Graser, E., Wang, J.K.F. and Rink, K., 2022, March. Assessing Mars Curiosity rover wheel damage. In 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference (AERO) (pp. 1-19). IEEE.
- Dunbar, B., n.d. Advanced Space Transportation Program Fact sheet, NASA. NASA. Available at: https://www.nasa.gov/centers/marshall/news/background/facts/astp.html. (Accessed: 18 July 2024).
- Satish, H., Radziszewski, P. and Ouellet, J., 2005. Design issues and challenges in lunar/Martian mining applications. Mining Technology, 114(2), pp.107-117.
- Cui, Q., Wang, T., Gu, G., Zhang, R., Zhao, T., Huang, Z., Wang, G. and Chen, F., Ultraviolet and Thermal Dual-Curing Assisted Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing of Lunar Regolith Simulant for In-Site Construction on the Moon. Available at SSRN 4481462.
- Petersen, K.H., Napp, N., Stuart-Smith, R., Rus, D. and Kovac, M., 2019. A review of collective robotic construction. Science Robotics, 4(28), p.eaau8479.
- Beni, G. and Wang, J., 1989. Swarm intelligence in cellular robotic. In Systems Proceedings of NATO Advanced Workshop on Robots and Biological Systems (Vol. 102).
- Şahin, E., 2004, July. Swarm robotics: From sources of inspiration to domains of application. In International workshop on swarm robotics (pp. 10-20). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
- Landis, M.E., Hayne, P.O., Williams, J.P., Greenhagen, B.T. and Paige, D.A., 2022. Spatial distribution and thermal diversity of surface volatile cold traps at the lunar poles. The Planetary Science Journal, 3(2), p.39.
- Spudis, P.D., Bussey, B., Plescia, J., Josset, J.L. and Beauvivre, S., 2008. Geology of Shackleton Crater and the south pole of the Moon. Geophysical research letters, 35(14).
- Haruyama, J., Ohtake, M., Matsunaga, T., Morota, T., Honda, C., Yokota, Y., Pieters, C.M., Hara, S., Hioki, K., Saiki, K. and Miyamoto, H., 2008. Lack of exposed ice inside lunar south pole Shackleton crater. Science, 322(5903), pp.938-939.
- Vasavada, A.R., Paige, D.A. and Wood, S.E., 1999. Near-surface temperatures on Mercury and the Moon and the stability of polar ice deposits. Icarus, 141(2), pp.179-193.
- Halim, S.H., Barrett, N., Boazman, S.J., Gawronska, A.J., Gilmour, C.M., McCanaan, K., Satyakumar, A.V., Shah, J. and Kring, D.A., 2021. Numerical modeling of the formation of Shackleton crater at the lunar south pole. Icarus, 354, p.113992.
- Gertsch, L., Gustafson, R. and Gertsch, R., 2006, January. Effect of water ice content on excavatability of lunar regolith. In AIP conference proceedings (Vol. 813, No. 1, pp. 1093-1100). American Institute of Physics.
- McKay, D.S., Heiken, G., Basu, A., Blanford, G., Simon, S., Reedy, R., French, B.M. and Papike, J., 1991. The lunar regolith. Lunar sourcebook, 567, pp.285-356.
- Ambrose, W. A., 2013, The significance of lunar water ice and other mineral resources for rocket propellants and human settlement of the Moon, in W. A. Ambrose, J. F. Reilly II, and D. C. Peters, eds., Energy resources for human settlement in the solar system and Earth's future in space: AAPG Memoir 101, p. 7–31.
- Paschall, S.C., Brady, T., Cohanim, B.E. and Sostaric, R., 2008, March. A self contained method for safe & precise lunar landing. In 2008 IEEE Aerospace Conference (pp. 1-12). IEEE.
- Act-react QuickMap, (n.d.). LROC QuickMap. (Accessed: 18 July 2024).
- Mueller, R.P., Cox, R.E., Ebert, T., Smith, J.D., Schuler, J.M. and Nick, A.J., 2013, March. Regolith advanced surface systems operations robot (RASSOR). In 2013 IEEE Aerospace Conference (pp. 1-12). IEEE.
- Mueller, R.P., Smith, J.D., Schuler, J.M., Nick, A.J., Gelino, N.J., Leucht, K.W., Townsend, I.I. and Dokos, A.G., 2016, April. Design of an excavation robot: regolith advanced surface systems operations robot (RASSOR) 2.0. In 15th Biennial ASCE Conference on Engineering, Science, Construction, and Operations in Challenging Environments (pp. 163-174). Reston, VA: American Society of Civil Engineers.
- Hugo, A. (2020) ESA molten salt electrolysis plant to study oxygen extraction from regolith, The Space Resource. Available at: https://www.thespaceresource.com/news/2020/1/esa-molten-salt-electrolysis-plant-to-study-oxygen-extraction-from-regolith (Accessed: 18 July 2024).
- Ewert, M. and Stromgren, C., 2019, July. Astronaut mass balance for long duration missions. 49th International Conference on Environmental Systems.
- Brambilla, M., Ferrante, E., Birattari, M. and Dorigo, M., 2013. Swarm robotics: a review from the swarm engineering perspective. Swarm Intelligence, 7(1), pp.1-41.
- Ghanem, M. and Sobh, Z.K., 2021. Crime Scene Searching: An Exploration of Forensic Evidence. Crime Scene Management within Forensic science, pp.37-50.
- Di Pietro, V., Govoni, P., Chan, K.H., Oliveira, R.C., Wenseleers, T. and van den Berg, P., 2022. Evolution of self-organised division of labour driven by stigmergy in leaf-cutter ants. Scientific Reports, 12(1), p.21971.
- Tan, J., Melkoumian, N., Harvey, D., Akmeliawati, R. Classifying Nature-Inspired Swarm Algorithms for Sustainable Autonomous Mining. Insights Min Sci technol.2024; 4(3):555636. DOI: 10.19080/IMST.2024.04.5556236.
- Thomson, B.J., Bussey, D.B.J., Neish, C.D., Cahill, J.T.S., Heggy, E., Kirk, R.L., Patterson, G.W., Raney, R.K., Spudis, P.D., Thompson, T.W. and Ustinov, E.A., 2012. An upper limit for ice in Shackleton crater as revealed by LRO Mini-RF orbital radar. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(14).
- Wagner, R.V., Robinson, M.S., Speyerer, E.J. and Mahanti, P., 2013, March. Topography of 20-km Diameter Craters on the Moon. In Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (Vol. 44, p. 2924).
- Pugacheva, S.G., Feoktistova, E.A. and Shevchenko, V.V., 2016. On the nature of the impactor that formed the Shackleton crater on the Moon. Earth, Moon, and Planets, 118(1), pp.27-50.
- Cole, J.D., Lim, S., Sargeant, H.M., Sheridan, S., Anand, M. and Morse, A., 2023. Water extraction from icy lunar simulants using low power microwave heating. Acta Astronautica, 209, pp.95-103.
- Schlüter, L. and Cowley, A., 2020. Review of techniques for In-Situ oxygen extraction on the moon. Planetary and Space Science, 181, p.104753.
- Cannon, K.M., Mueller, R.P., Deutsch, A.N., Van Susante, P., Tarnas, J.D., Colaprete, A.C., Sowers, G., Dreyer, C.B., Li, S., Sercel, J. and Dove, A.R., 2020, May. The Snow Badger mission concept: Trenching for ice with humans and robots. In Lunar Surface Science Workshop (Vol. 2241, p. 5108).
- Rabagliati, L., Devecchi, M., Lovagnini, A., Pino, P. and Thirion, G., 2021. Regolith Mining in Shackleton Crater on the Moon: Propellant, Building Materials and Vital Resources Production for a Long Duration Manned Mission. International Journal of Astronautics and Aeronautical Engineering, 6(1).
- Metzger, P.T., Sapkota, D., Fox, J. and Bennett, N., 2021. Aqua Factorem: Ultra Low Energy Lunar Water Extraction (No. Grant Number 80NSSC 20K1022).
- Hurley, D.M., Lawrence, D.J., Bussey, D.B.J., Vondrak, R.R., Elphic, R.C. and Gladstone, G.R., 2012. Two-dimensional distribution of volatiles in the lunar regolith from space weathering simulations. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(9).
- Li, S., Lucey, P.G., Milliken, R.E., Hayne, P.O., Fisher, E., Williams, J.P., Hurley, D.M. and Elphic, R.C., 2018. Direct evidence of surface exposed water ice in the lunar polar regions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(36), pp.8907-8912.
- Sowers, G.F., 2016. A cislunar transportation system fueled by lunar resources. Space Policy, 37, pp.103-109.
| Mining Lifecyle | Nature-inspired Algorithms | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACO | PSO | ABC | FA | BA | GWO | SSA | GOA | KH | |
| Mine Exploration & Assessment | |||||||||
| Mine Planning & Design | |||||||||
| Mine Operation & Construction | |||||||||
| Mine Closure & Rehabilitation | |||||||||
| Mining Lifecyle | Nature-inspired Algorithms | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ant – Transportation |
Firefly – Navigation |
Geese – Automation |
|
| Mine Exploration & Assessment | |||
| Mine Planning & Design | |||
| Mine Operation & Construction | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





