Submitted:
06 August 2024
Posted:
07 August 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Experimental Procedures
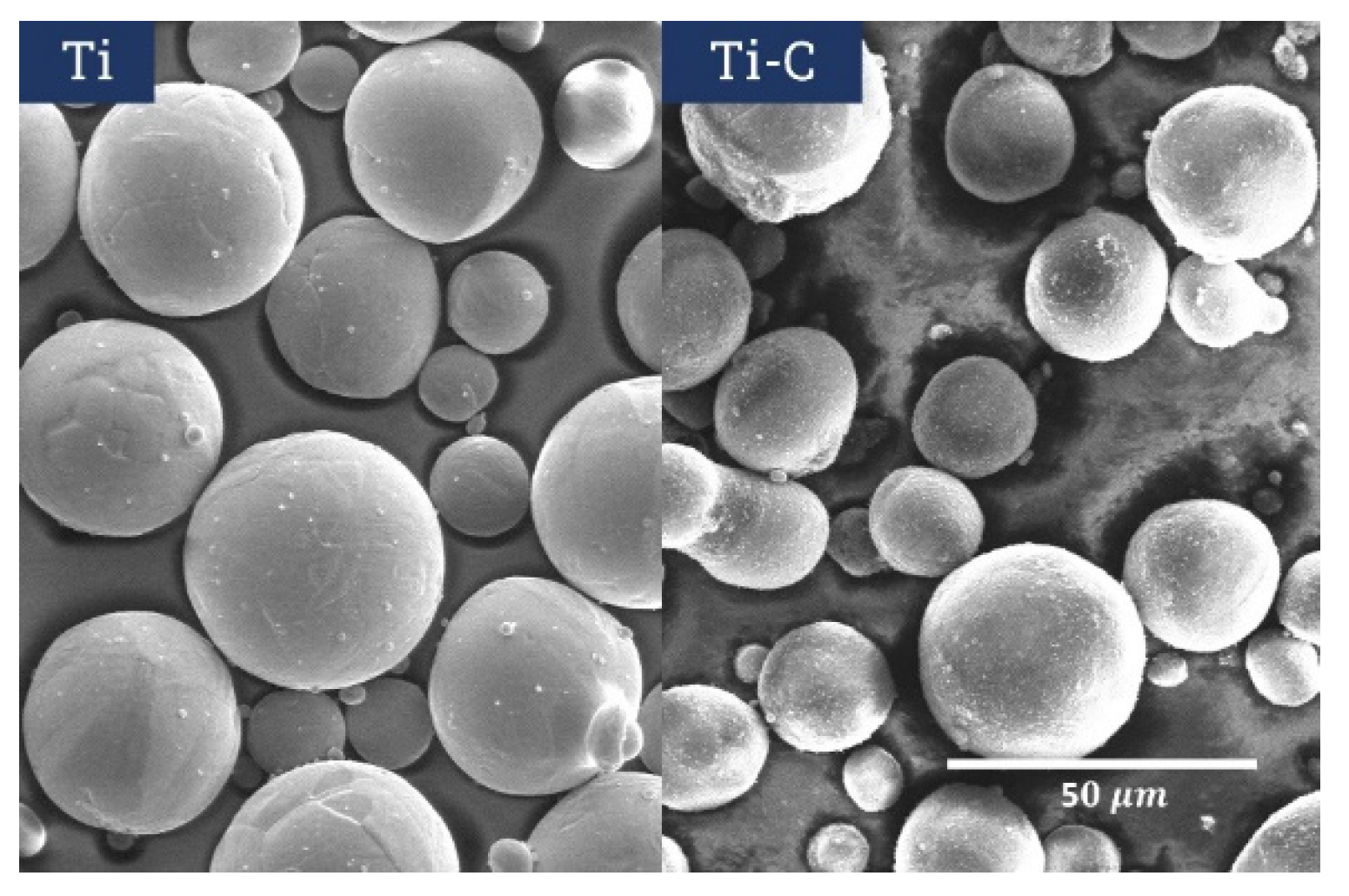
Powder Preparation
Laser Powder Bed Fusion Processing
Heat-Treatment
Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization
Results and Discussion
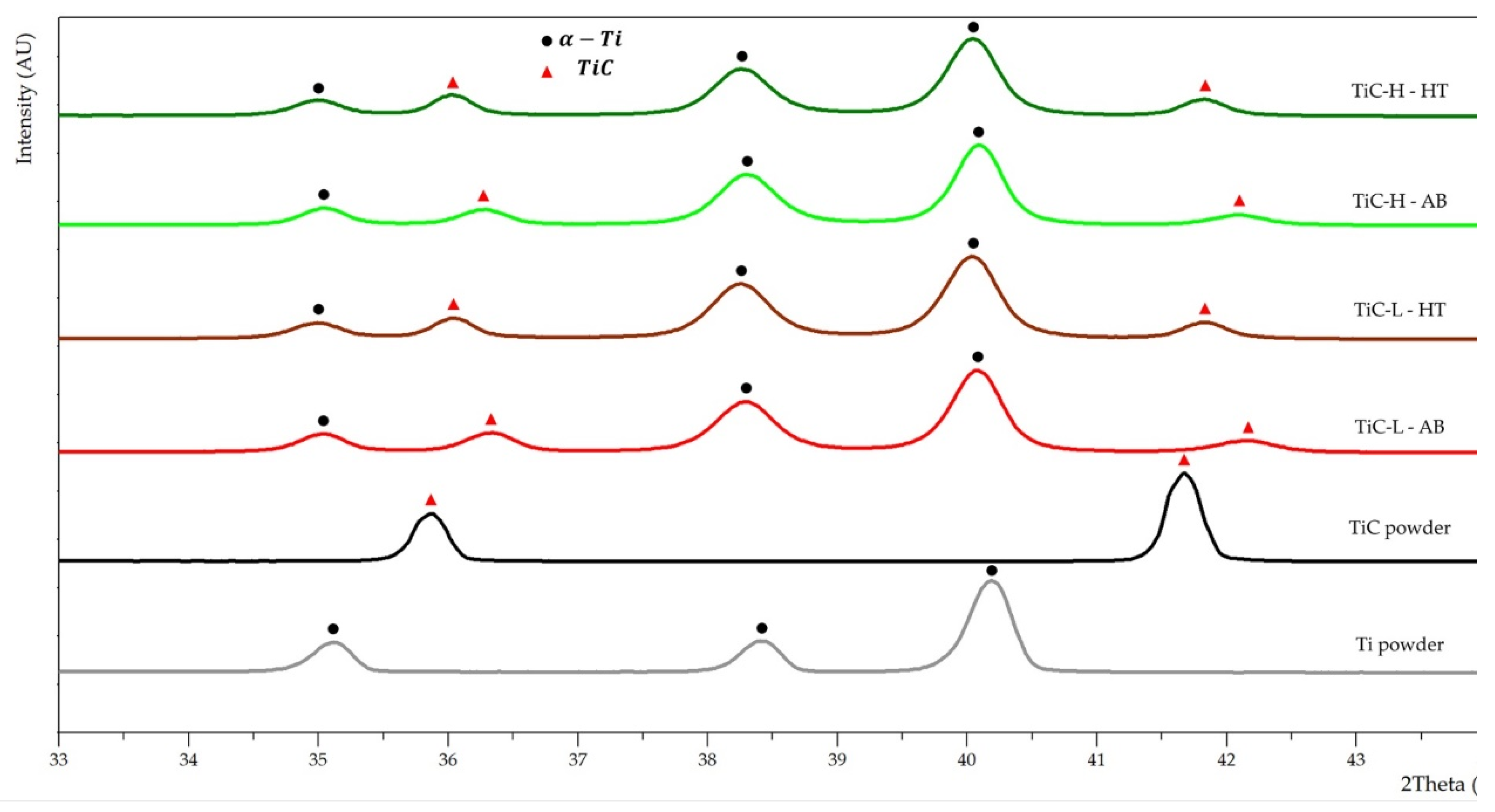
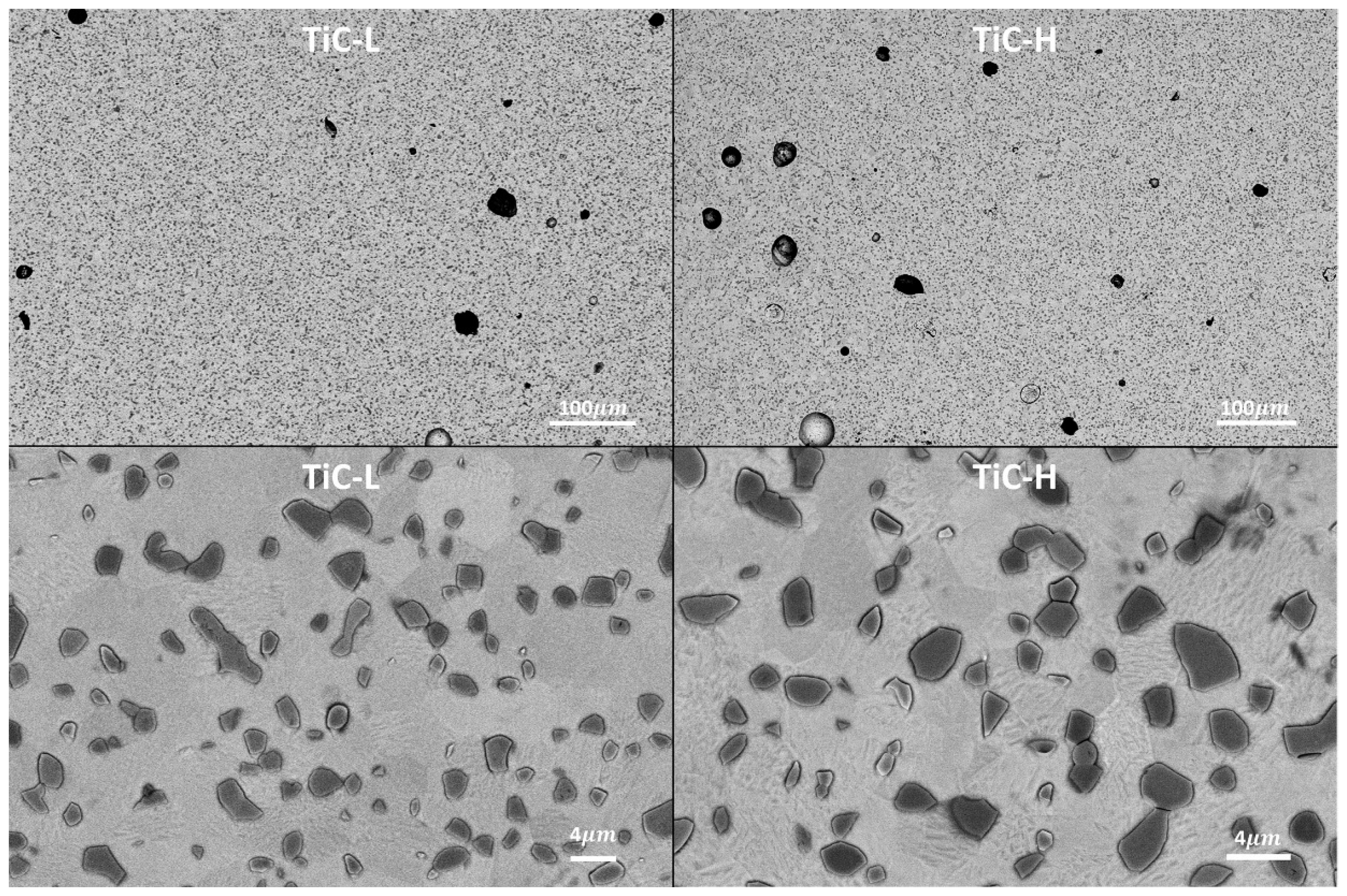
As-Built Microstructure
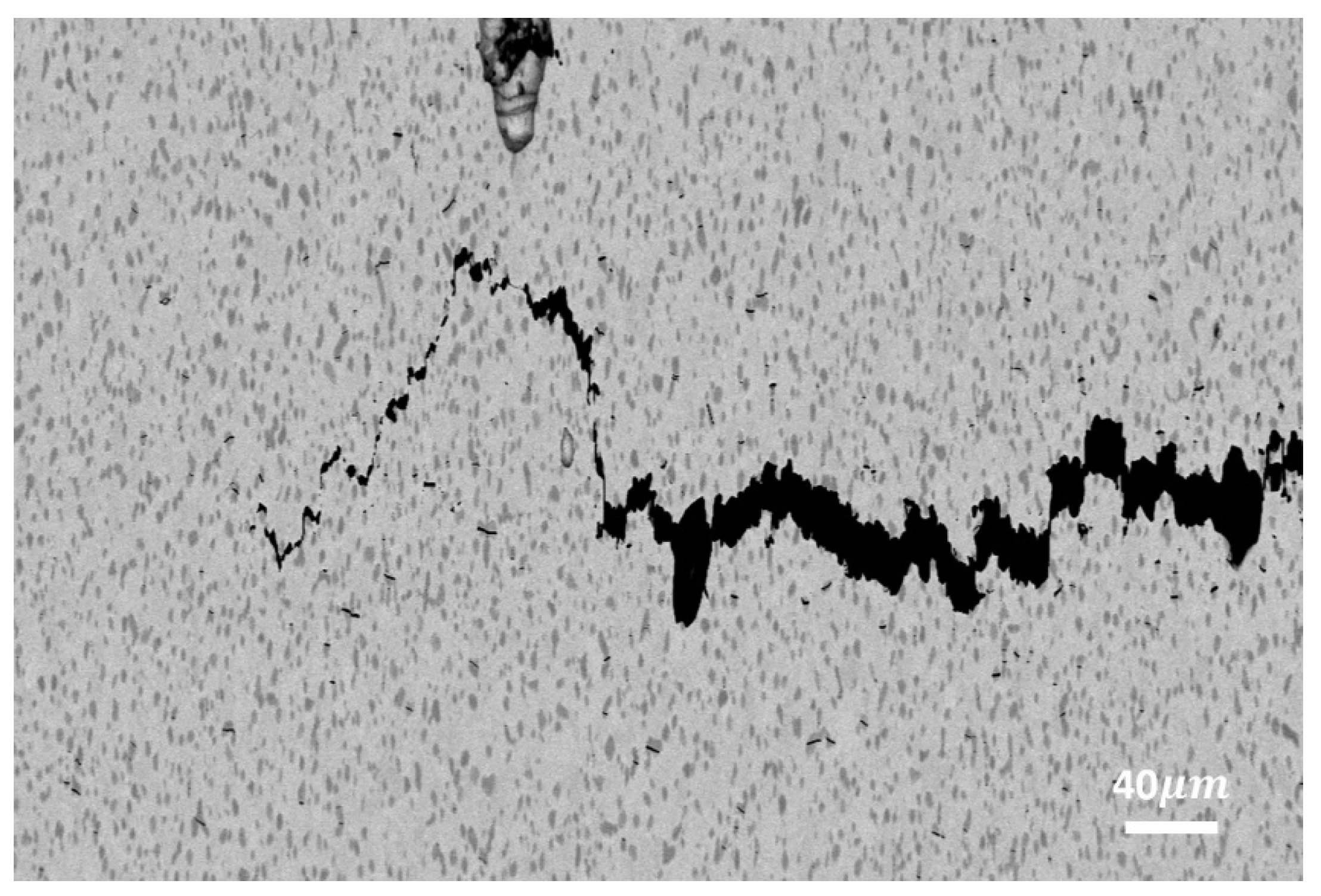
Heat-Treated Microstructure
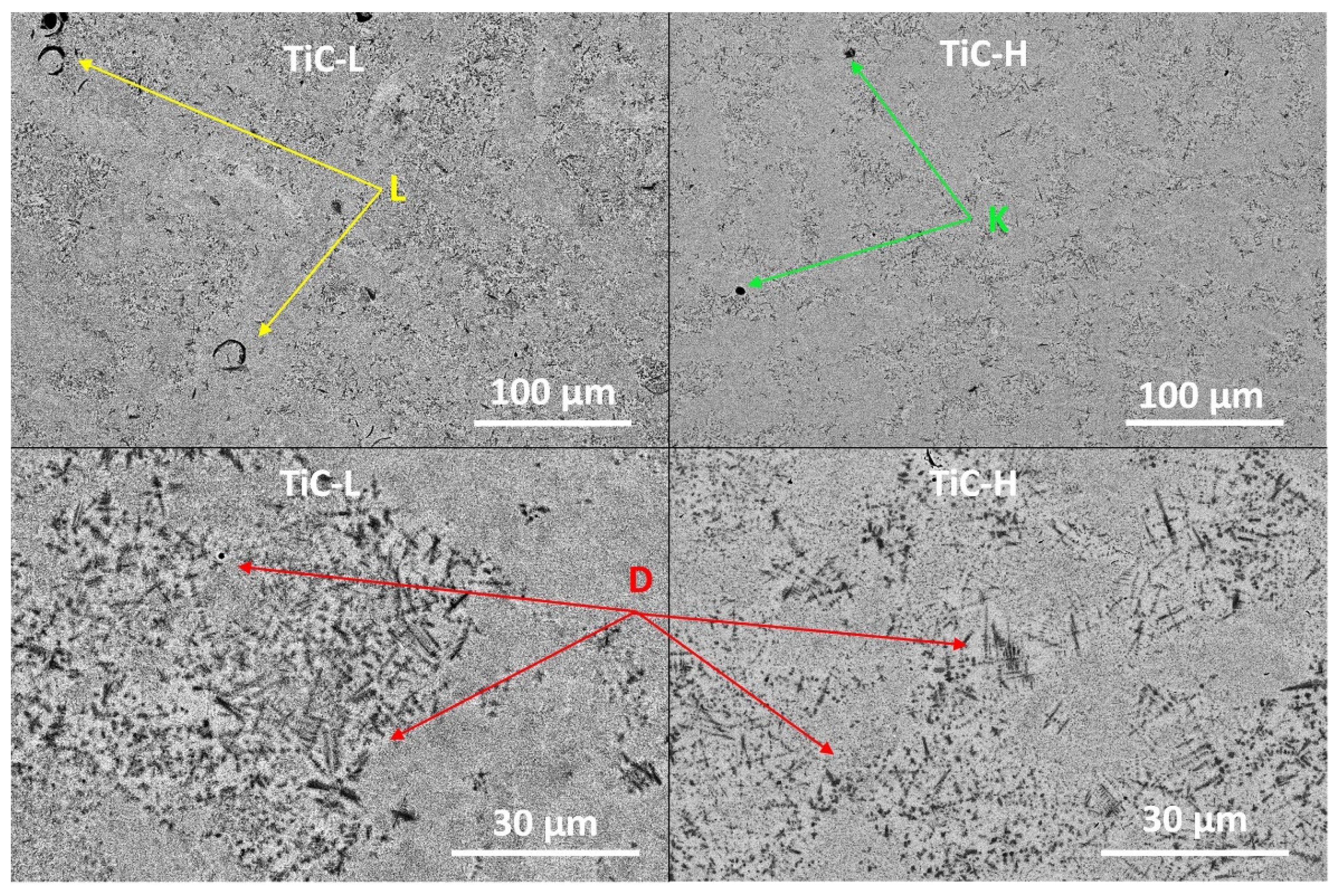
Density Characterization
| XCT measurement | Image analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Sample density [%] | Hatching density [%] | Hatching density [%] |
| TiC-L | 99.8 | 99.8 | 99.2 |
| TiC-H | 99.9 | 99.9 | 98.9 |
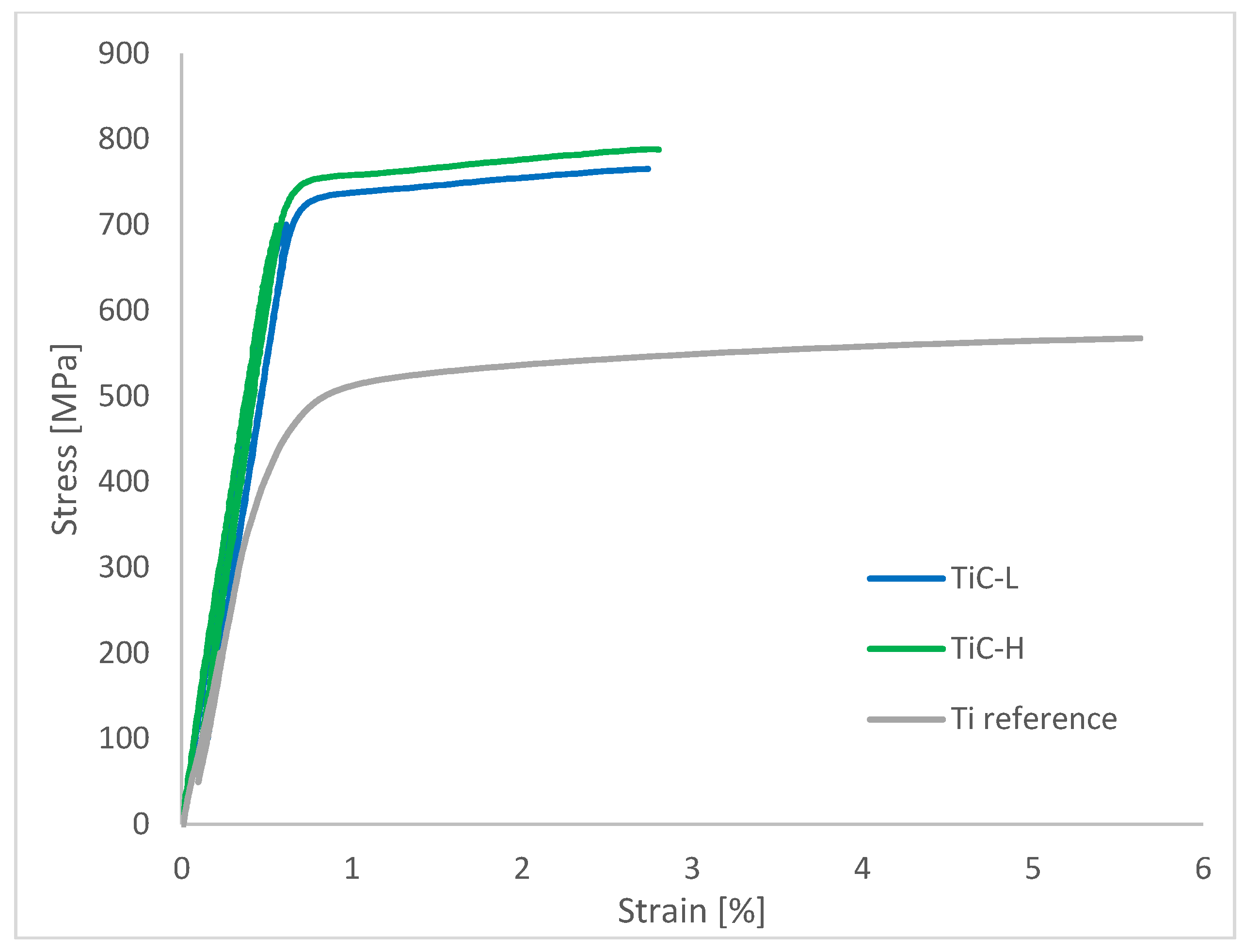
Mechanical Properties in Heat Treated Conditions
Conclusions
- A density >99% and >98% was achieved in TiC-L and TiC-H, respectively. Porosities with a size above 20 µm accounted for <0.2% of the volume in both cases.
- A uniform TiC dendritic structure before heat treatment was transformed into equiaxed grains following the heat treatment. The average Ti and TiC grain sizes remained below 1.4 µm and 3.1 µm, for the two levels of energy density.
- Both TiC-H and TiC-L exhibited significantly improved mechanical properties. Compared to the Ti reference, the Young’s moduli increased by 27% and 22%, the yield strength by 44% and 41%, and the ultimate tensile strength by 34% and 30%. The fracture strain, 2.8% for TiC-H and 2.3% for TiC-L, was remarkably high considering 20 vol% reinforcement content. The superior mechanical properties of TiC-H are attributed to the absence of lack of fusion defects, resulting in the highest Young’s modulus, yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and fracture strain.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Declaration of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
References
- T. Saito, ‘A cost-effective P/M titanium matrix composite for automobile use’, Adv Perform Mater, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 121–144, Jun. 1995. [CrossRef]
- K. Soorya Prakash, P. M. Gopal, D. Anburose, and V. Kavimani, ‘Mechanical, corrosion and wear characteristics of powder metallurgy processed Ti-6Al-4V/B4C metal matrix composites’, Ain Shams Engineering Journal, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 1489–1496, Dec. 2018. [CrossRef]
- C. Mohanraj, K. M. N. Kumar, K. PraveenKumar, and S. Mukesh, ‘Development of AA6082 based metal matrix composite using Sic,Ti,Ni,Cr by conventional casting technique’, Materials Today: Proceedings, p. S2214785320333022, May 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Kouzeli and D. C. Dunand, ‘Effect of temperature and strain rate on the compressive flow of aluminum composites containing submicron alumina particles’, Metall Mater Trans A, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 287–292, Jan. 2004. [CrossRef]
- T. M. T. Gofrey, P. S. Goodwin, and C. M. Ward-Close, ‘Titanium Particulate Metal Matrix Composites—Reinforcement, Production Methods, and Mechanical Properties’, Adv. Eng. Mater., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 85–91, Mar. 2000. [CrossRef]
- C. Cai et al., ‘In-situ TiB/Ti-6Al-4V composites with a tailored architecture produced by hot isostatic pressing: Microstructure evolution, enhanced tensile properties and strengthening mechanisms’, Composites Part B: Engineering, vol. 164, pp. 546–558, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Lagos, I. Agote, G. Atxaga, O. Adarraga, and L. Pambaguian, ‘Fabrication and characterisation of Titanium Matrix Composites obtained using a combination of Self propagating High temperature Synthesis and Spark Plasma Sintering’, Materials Science and Engineering: A, vol. 655, pp. 44–49, Feb. 2016. [CrossRef]
- J. Shi and Y. Wang, ‘Development of metal matrix composites by laser-assisted additive manufacturing technologies: a review’, J Mater Sci, vol. 55, no. 23, pp. 9883–9917, Aug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Hu and W. Cong, ‘A review on laser deposition-additive manufacturing of ceramics and ceramic reinforced metal matrix composites’, Ceramics International, vol. 44, no. 17, pp. 20599–20612, Dec. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Mahmood, A. C. Popescu, and I. N. Mihailescu, ‘Metal Matrix Composites Synthesized by Laser-Melting Deposition: A Review’, Materials, vol. 13, no. 11, p. 2593, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- W. H. Yu, S. L. Sing, C. K. Chua, C. N. Kuo, and X. L. Tian, ‘Particle-reinforced metal matrix nanocomposites fabricated by selective laser melting: A state of the art review’, Progress in Materials Science, vol. 104, pp. 330–379, Jul. 2019. [CrossRef]
- H. Attar, S. Ehtemam-Haghighi, D. Kent, and M. S. Dargusch, ‘Recent developments and opportunities in additive manufacturing of titanium-based matrix composites: A review’, International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, vol. 133, pp. 85–102, Oct. 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Dadbakhsh, R. Mertens, L. Hao, J. Van Humbeeck, and J. Kruth, ‘Selective Laser Melting to Manufacture “In Situ” Metal Matrix Composites: A Review’, Adv. Eng. Mater., vol. 21, no. 3, p. 1801244, Mar. 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. Gu, Y.-C. Hagedorn, W. Meiners, K. Wissenbach, and R. Poprawe, ‘Selective Laser Melting of in-situ TiC/Ti5Si3 composites with novel reinforcement architecture and elevated performance’, Surface and Coatings Technology, vol. 205, no. 10, pp. 3285–3292, Feb. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Y. Pan et al., ‘Microstructure and tribological properties of titanium matrix composites reinforced with in situ synthesized TiC particles’, Materials Characterization, vol. 170, p. 110633, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Xi et al., ‘Interfacial structure and wear properties of selective laser melted Ti/(TiC+TiN) composites with high content of reinforcements’, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, vol. 870, p. 159436, Jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Bai, P. Huo, Z. Zhao, W. Du, Z. Zhang, and L. Wang, ‘Microstructure evolution and corrosion mechanism of in situ synthesized TiC/TC4 alloy nanocomposites fabricated by laser powder bed fusion’, Ceramics International, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 2752–2764, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Dadbakhsh, ‘Heat treatment possibilities for an in situ βTi-TiC composite made by laser powder bed fusion’, Additive Manufacturing, vol. 36, p. 101577, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Dadbakhsh, R. Mertens, K. Vanmeensel, G. Ji, and J.-P. Kruth, ‘In situ transformations during SLM of an ultra-strong TiC reinforced Ti composite’, Scientific Reports, vol. 10, no. 1, Art. no. 1, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. Zhang, Z. Guo, F. Yang, H. Wang, Y. Shao, and B. Lu, ‘In situ formation of low interstitials Ti-TiC composites by gas-solid reaction’, Journal of Alloys and Compounds, vol. 769, pp. 37–44, Nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- E. Fereiduni, A. Ghasemi, and M. Elbestawi, ‘Unique opportunities for microstructure engineering via trace B4C addition to Ti-6Al-4V through laser powder bed fusion process: As-built and heat-treated scenarios’, Additive Manufacturing, vol. 50, p. 102557, Feb. 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. Han et al., ‘Microstructure and mechanical properties of (TiB+TiC)/Ti composites fabricated in situ via selective laser melting of Ti and B4C powders’, Additive Manufacturing, vol. 36, p. 101466, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- D. Gu, Y.-C. Hagedorn, W. Meiners, K. Wissenbach, and R. Poprawe, ‘Nanocrystalline TiC reinforced Ti matrix bulk-form nanocomposites by Selective Laser Melting (SLM): Densification, growth mechanism and wear behavior’, Composites Science and Technology, vol. 71, no. 13, pp. 1612–1620, Sep. 2011. [CrossRef]
- D. Gu, G. Meng, C. Li, W. Meiners, and R. Poprawe, ‘Selective laser melting of TiC/Ti bulk nanocomposites: Influence of nanoscale reinforcement’, Scripta Materialia, vol. 67, no. 2, pp. 185–188, Jul. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Q. Yan, B. Chen, and J. S. Li, ‘Super-high-strength graphene/titanium composites fabricated by selective laser melting’, Carbon, vol. 174, pp. 451–462, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- D. K. Das and M. M. Ghosh, ‘On Mechanical Properties of Graphene Sheet Estimated Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations’, Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, vol. 26, no. 9, pp. 4522–4532, Sep. 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Guemmaz, A. Mosser, R. Ahujab, and B. Johansson, ‘Elastic properties of sub-stoichiometric titanium carbides Comparison of FP-LMTO calculations and experimental results’, Solid State Communications, vol. 110, no. 6, p. 5, Apr. 1999. [CrossRef]
- M. Kouzeli, L. Weber, C. S. Marchi, and A. Mortensen, ‘Influence of Damage on the Tensile Behaviour of Pure Aluminium Reinforced with 40 vol. pct Alumina Particles’, Acta Materialia, vol. 49, no. 18, pp. 3699–3709, Oct. 2001. [CrossRef]
- T.-C. Lin et al., ‘Aluminum with dispersed nanoparticles by laser additive manufacturing’, Nat Commun, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 4124, Sep. 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. H. Abboud and D. R. F. West, ‘In situ production of Ti-TiC composites by laser melting’, J Mater Sci Lett, vol. 11, no. 24, pp. 1675–1677, 1992. [CrossRef]
- J. Andrieux, B. Gardiola, and O. Dezellus, ‘Synthesis of Ti matrix composites reinforced with TiC particles: in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction and modeling’, J Mater Sci, vol. 53, no. 13, pp. 9533–9544, Jul. 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Roger, ‘Synthesis of Ti matrix composites reinforced with TiC particles: thermodynamic equilibrium and change in microstructure’, J Mater Sci, vol. 52, pp. 4129–4141, Dec. 2016. [CrossRef]
- E28 Committee, ‘Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials’. ASTM International. [CrossRef]
- Y. Lin, R. H. Zee, and B. A. Chin, ‘In situ formation of three-dimensional TiC reinforcements in Ti-TiC composites’, MTA, vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 859–865, Apr. 1991. [CrossRef]
- B. Wysocki et al., ‘Microstructure and mechanical properties investigation of CP titanium processed by selective laser melting (SLM)’, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, vol. 241, pp. 13–23, Mar. 2017. [CrossRef]
- H. Attar, S. Ehtemam-Haghighi, D. Kent, X. Wu, and M. S. Dargusch, ‘Comparative study of commercially pure titanium produced by laser engineered net shaping, selective laser melting and casting processes’, Materials Science and Engineering: A, vol. 705, pp. 385–393, Sep. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Z. Hashin and S. Shtrikman, ‘A variational approach to the theory of the elastic behaviour of multiphase materials’, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 127–140, Mar. 1963. [CrossRef]
- K. Vasanthakumar and S. R. Bakshi, “Effect of C/Ti ratio on densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of TiCx prepared by reactive spark plasma sintering,” Ceramics International, vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 484–494, Jan. 2018. [CrossRef]

| Set | Laser processing parameters | ||
| VED [J/mm3] | h [µm] | t [µm] | |
| TiC-H | 146 | 40 | 30 |
| TiC-L | 125 | 40 | 30 |
| TiC-L | TiC-H | Ti | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E300 [GPa] | 143±1 | 149±6 | 117±7 |
| E700 [GPa] | 141±1 | 149±7 | - |
| YS [MPa] | 720±2 | 737±13 | 512±6 |
| UTS [MPa] | 750±13 | 770±17 | 576±4 |
| e [%] | 2.3±0.4 | 2.8±0.6 | 29.3±3.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





