Submitted:
06 August 2024
Posted:
08 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
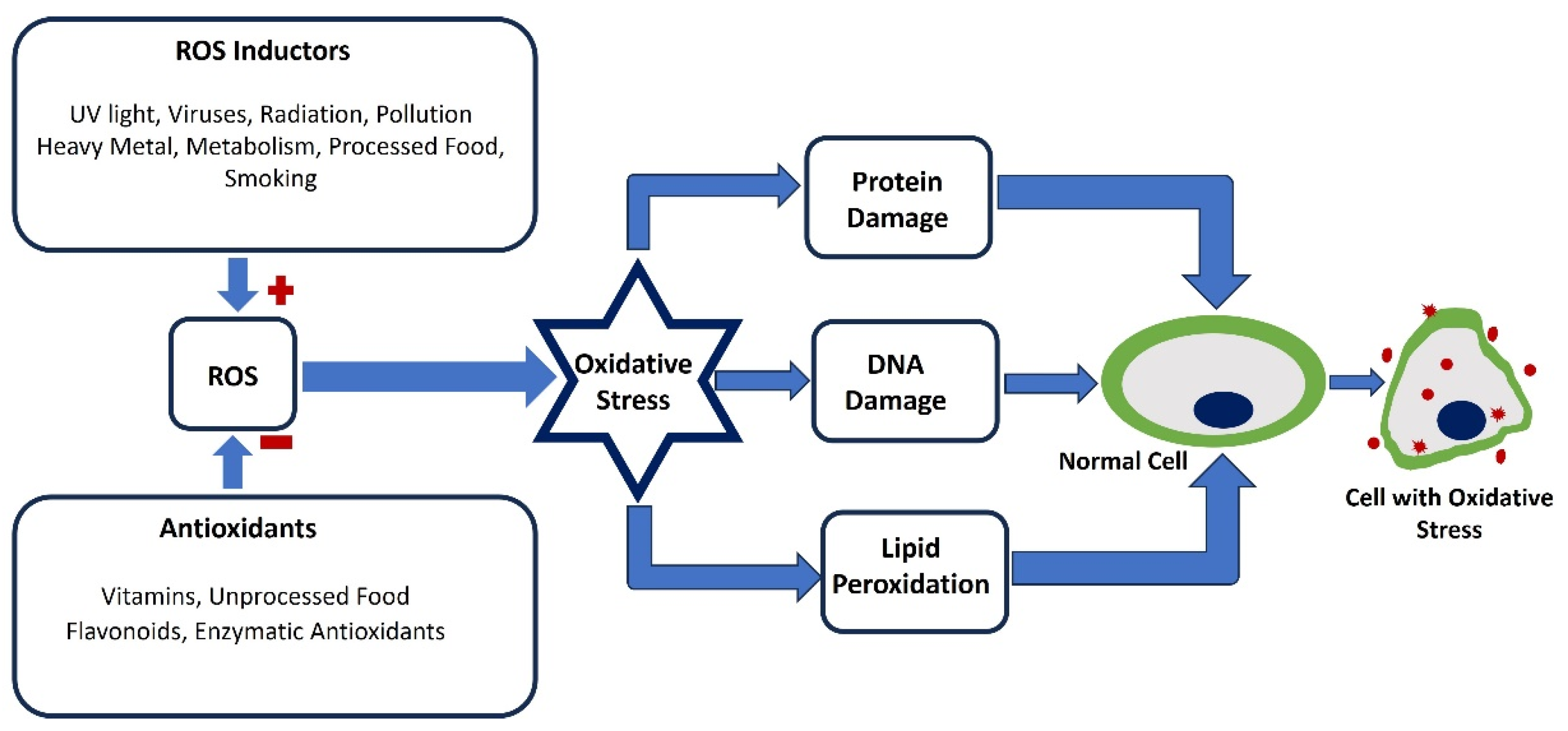
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Ion channel biophysics and oxidative stress
Voltage-Dependent Ca2+ Channels
Sodium (Na+) Channels:
Potassium (K+) Channels
Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Channels
Orai Ion Channels
P2X2 Receptors
4. Interstitial cells of Cajal and oxidative stress
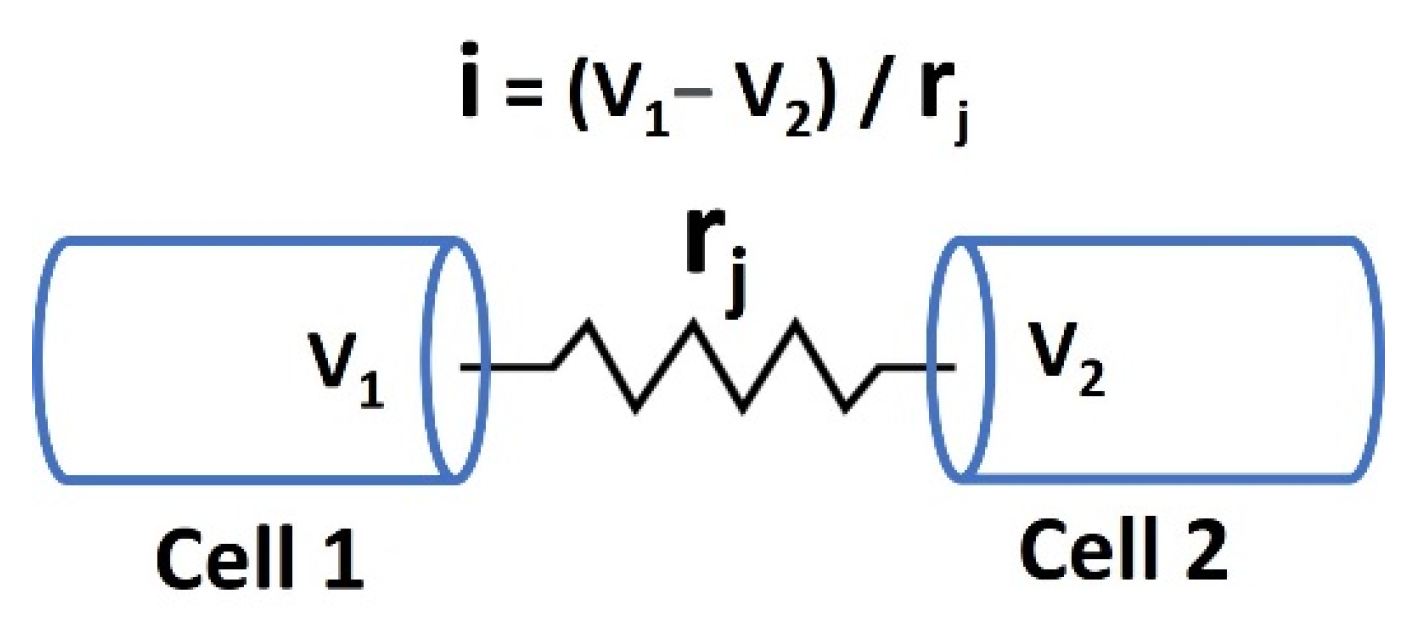
5. Gap junction and oxidative stress
6. Calcium dynamics and oxidative stress
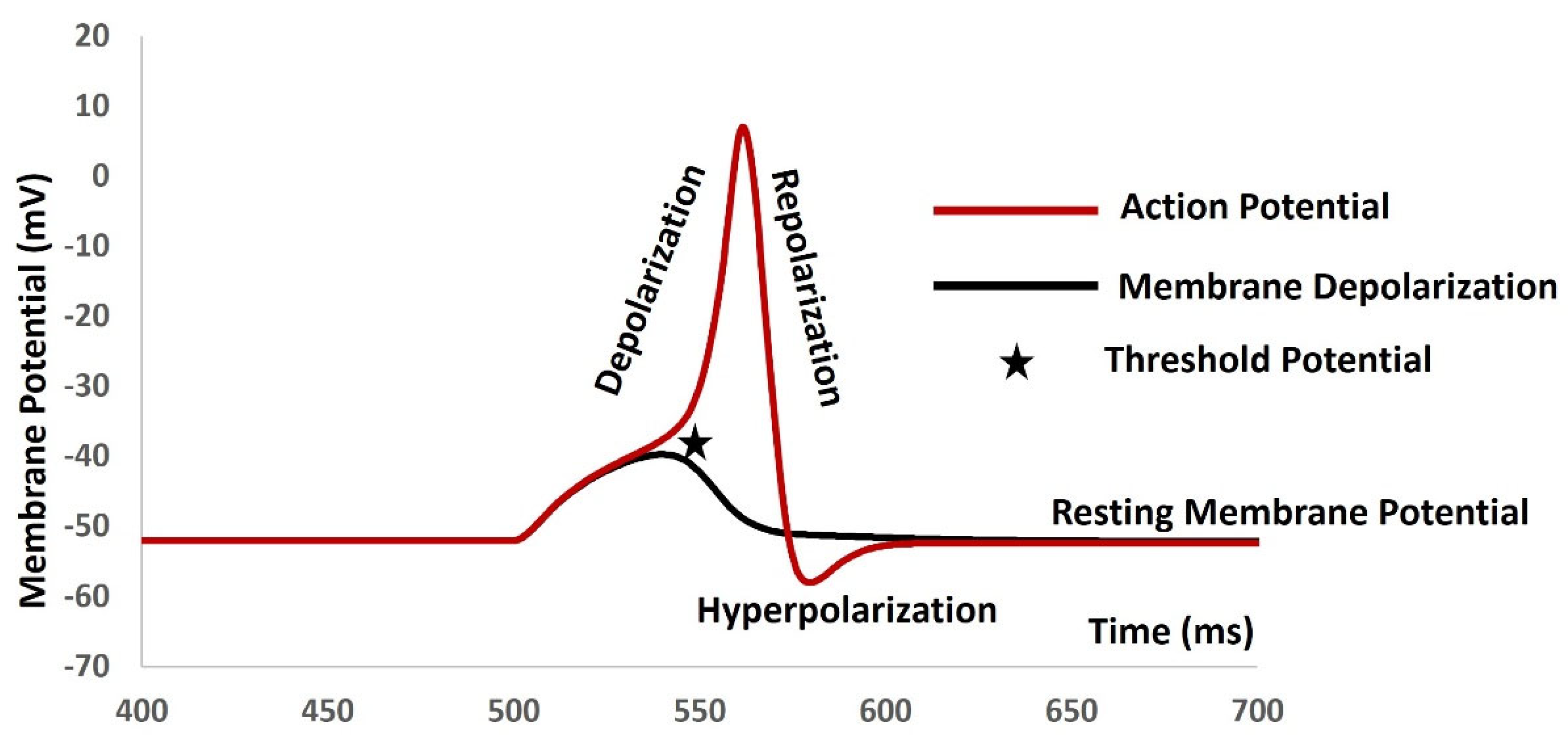
7. The model of oxidative stress impact on AP
- Endo/Sarcoplasmic Ca²⁺ is sourced from the endoplasmic/sarcoplasmic reticulum (ER/SR), an intracellular reservoir. Ca²⁺ ions are transported from this storage site to the sarcoplasm via Ca²⁺ channels, which are regulated by intracellular agents. Ca²⁺ is replenished in the ER/SR by a pump powered by ATP. An increase in the Ca2+ concentration near the ER/SR triggers further release of Ca2+ which is called the calcium-induced calcium release (CICR). ROS can influence various factors affecting the filling or release of Ca²⁺ in/from the ER/SR. Additionally, Ca²⁺ modulates the release of ATP and ROS from mitochondria, and the ROS released can negatively impact the Endo/Sarcoplasmic Ca²⁺ dynamics. The red arrow indicates this negative feedback loop from mitochondria to the Endo/Sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- There is a potential increase in the concentration of a diffusible second messenger, which links the surface membrane to the release of intracellular Ca2+. This process primarily involves the activation of purinergic receptors (P2X) or M3 muscarinic receptors. Upon activation, these receptors initiate a series of membrane-bound processes that lead to the production of inositol trisphosphate (IP3). IP3, in turn, can influence Ca2+ dynamics as previously described. Changes in the sensitivity or effectiveness of this mechanism can significantly impact the release of intracellular Ca2+. ATP may bind to the purinergic receptor (P2X/M), opening a non-specific cation channel that allows the influx of positive ions (X+), leading to an increase in membrane potential. This depolarization, modulated by ROS, can open L-type Ca2+ channels, facilitate Ca2+ influx, and trigger APs.
- The membrane potential can be transmitted from cell 2 to cell 1 through gap junctions, as some excitable cells function as a syncytium. Moreover, the activation of pacemaking interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) can also induce an increase in membrane potential. ROS can modulate both gap junction and ICC internal mechanisms, and the resulting depolarization can trigger APs.
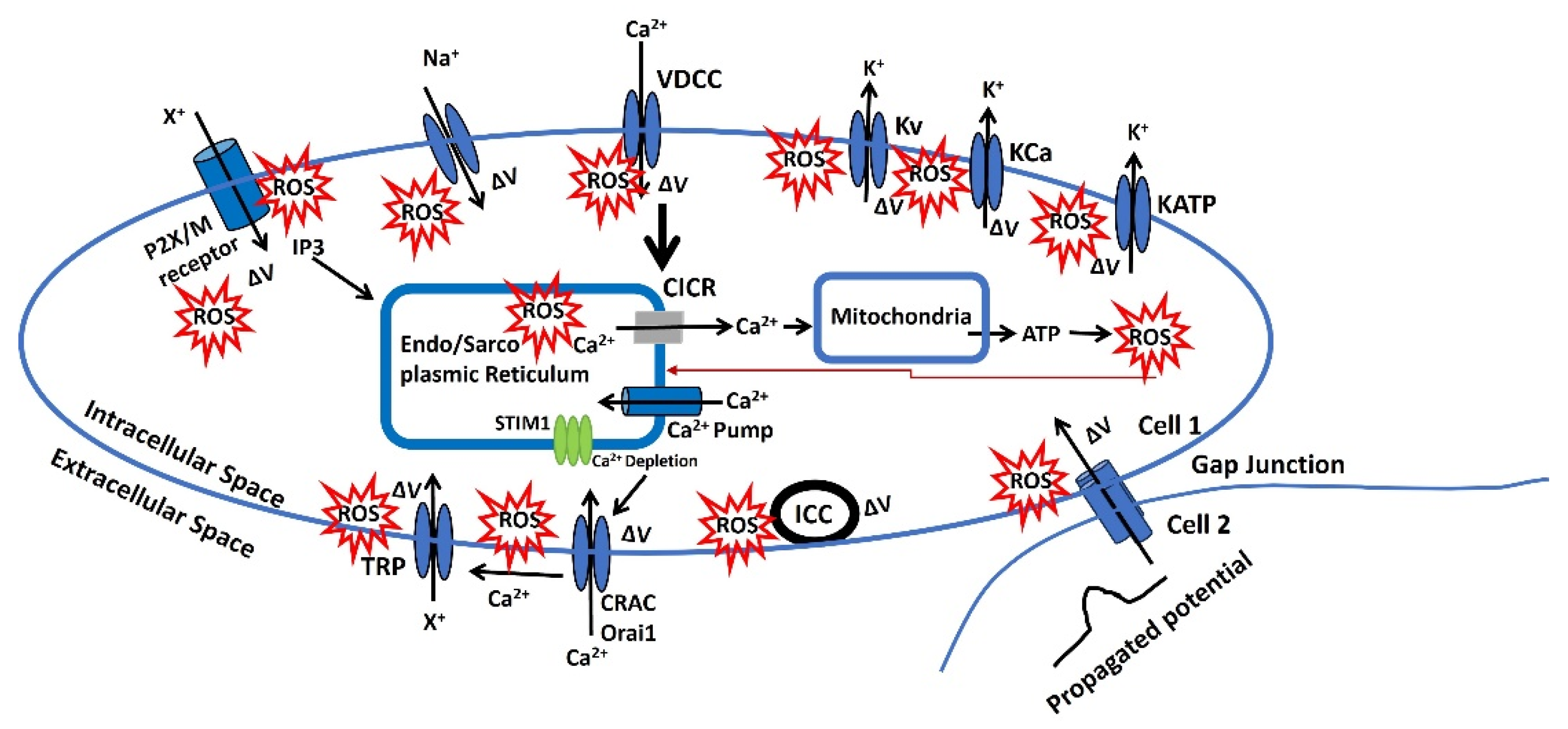
- 4.
- The voltage-gated and Ca2+-activated K+ ion channels (Kv, KCa, and KATP) shown in Figure 3 facilitate the flow of K+ from the intracellular to the extracellular space, leading to hyperpolarization. However, the modulating effects of ROS compromise these ion channel mechanisms, resulting in abnormal AP generation. Conversely, VDCC (L-type, T-type, and P/Q type) and voltage-gated Na+ channels allow the influx of Ca2+ and Na+ ions, depolarizing the membrane. ROS also affects these ion channels, contributing to abnormal AP generation.
- 5.
- CRAC channels are activated by intracellular depletion mediated by STIM1 and STIM2, allowing an influx of Ca2+ that depolarizes the membrane. Ca2+, along with other stimuli, can also activate various TRP ion channels, permitting the influx of cations (X+) and further depolarizing the membrane to generate APs. Additionally, ROS influences these ion channels, leading to abnormal AP generation.
- 8.
- Techniques for studying oxidative stress effects on membrane potentials
- a.
- Experimental techniques
- ∙
- Patch-Clamp Electrophysiology: The patch-clamp technique is a powerful method to study ion channel activity and membrane potential in real time [147]. By isolating a small patch of membrane, researchers can measure the ionic currents that flow through individual ion channels or across the entire cell membrane. This technique allows the investigation of how oxidative stress, often induced by reactive oxygen species (ROS), affects ion channel function and AP generation. For example, researchers can compare the ion channel activity in cells treated with ROS to those in untreated cells to determine the impact of oxidative stress.
- ∙
- Fluorescence Imaging and Voltage-Sensitive Dyes: Fluorescent dyes that are sensitive to changes in membrane potential can be used to visualize and measure membrane potential dynamics in live cells [148]. These dyes, such as Di-8-ANEPPS, emit fluorescence in response to voltage changes across the membrane, allowing researchers to monitor how oxidative stress affects membrane potential. Additionally, fluorescent indicators like Fura-2 can be used to measure intracellular calcium levels, providing insights into calcium-dependent processes affected by oxidative stress.
- ∙
- Redox-Selective Probes: To specifically measure oxidative stress levels, redox-sensitive fluorescent probes like roGFP (reduction-oxidation sensitive green fluorescent protein) can be employed [149]. These probes allow for the real-time monitoring of the cellular redox state and ROS levels. When combined with electrophysiological measurements, these probes help elucidate the correlation between oxidative stress and changes in membrane potential or ion channel activity.
- ∙
- Western Blot and Immunoprecipitation: Protein expression and post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, of ion channels can be assessed using western blotting [150]. Immunoprecipitation techniques can help identify protein-protein interactions that may be altered under oxidative stress. These biochemical techniques provide information on how oxidative stress may lead to modifications of ion channel proteins, thus affecting their function.
- b.
- Computational Techniques
- ∙
- Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations: MD simulations are computational methods used to study the behavior of biomolecules at the atomic level [151]. By simulating ion channels in different redox states, researchers can observe how oxidative stress affects the structure, dynamics, and function of these channels. MD simulations help in understanding the conformational changes that occur in ion channels under oxidative conditions and predict how these changes impact ion flow and membrane potential.
- ∙
- Computational Electrophysiology: This approach involves using mathematical models to simulate the electrical behavior of cells and tissues [152]. By incorporating data on oxidative stress, such as altered ion channel conductance or gating properties, computational models can predict the impact on membrane potential and AP generation. These simulations can help identify potential therapeutic targets for mitigating the effects of oxidative stress on neuronal and cardiac function.
- ∙
- Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship (QSAR) Models: QSAR models use statistical methods to relate the chemical structure of molecules to their biological activity [153]. By analyzing a series of ion channel modulators or antioxidants, QSAR models can predict which compounds are likely to protect against oxidative stress-induced alterations in ion channel function. This technique is useful for drug discovery and development.
- ∙
- Bioinformatics and Network Analysis: High-throughput data from omics studies (genomics, proteomics, transcriptomics) can be analyzed using bioinformatics tools to identify pathways and networks affected by oxidative stress [154]. Network analysis can reveal key regulatory nodes and interactions between ion channels and other cellular components, providing a holistic view of how oxidative stress impacts cellular electrophysiology.
- c.
- Integrative Approaches
- 9.
- Clinical Implications and Future Directions
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Oxidative stress contributes to neuronal damage and death in diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Aberrant ion channel activity due to oxidative modifications can disrupt neuronal signaling, leading to cognitive decline and motor dysfunction. Understanding these mechanisms can guide the development of targeted antioxidants or ion channel modulators to preserve neuronal function.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: In conditions such as ischemia-reperfusion injury and heart failure, oxidative stress alters ion channel function, affecting cardiac excitability and contractility. Therapeutic strategies that protect ion channels from oxidative damage or restore their normal function could improve outcomes in patients with heart disease.
- Diabetes: Oxidative stress plays a role in diabetic complications by affecting ion channels in various tissues, including the pancreas, nerves, and blood vessels. Interventions aimed at reducing oxidative stress or correcting ion channel dysfunction could mitigate these complications.
- Cancer: Some cancer cells exploit oxidative stress to drive proliferation and survival. Ion channels are involved in cancer cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Targeting ion channel modifications induced by oxidative stress could provide new avenues for cancer therapy.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: Development of more sensitive and specific fluorescent probes and imaging techniques to measure real-time changes in membrane potential, ROS levels, and ion channel activity in live cells and tissues. This will enhance our understanding of the spatial and temporal dynamics of oxidative stress.
- High-Throughput Screening: Implementing high-throughput screening methods to identify compounds that can protect against oxidative stress-induced ion channel dysfunction. This approach can accelerate the discovery of new therapeutic agents.
- Integrative Multi-Omics Approaches: Combining genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics with electrophysiological data to construct comprehensive models of how oxidative stress impacts ion channel function and cellular excitability. This holistic view can uncover new regulatory mechanisms and potential drug targets.
- Personalized Medicine: Investigating individual variability in oxidative stress responses and ion channel function to develop personalized therapeutic strategies. Genetic and epigenetic factors that influence susceptibility to oxidative stress and ion channel modifications should be identified.
- Animal Models and Clinical Trials: Utilizing animal models to study the in vivo relevance of findings from cellular and molecular studies. Translating these findings into clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of targeted therapies in mitigating the effects of oxidative stress in human diseases.
- Novel Therapeutics: Developing novel antioxidants, ion channel modulators, and gene therapies to specifically address the ion channel dysfunctions caused by oxidative stress. Combination therapies that target multiple pathways involved in oxidative stress responses could prove particularly effective.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Veschetti, L.; Treccani, M.; De Tomi, E.; Malerba, G. Genomic Instability Evolutionary Footprints on Human Health: Driving Forces or Side Effects? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmaninejad, A.; Ilkhani, K.; Marzban, H.; Navashenaq, J.G.; Rahimirad, S.; Radnia, F.; Yousefi, M.; Bahmanpour, Z.; Azhdari, S.; Sahebkar, A. Genomic Instability in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potentials. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 3161–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, D.; Daura, X.; Zagrovic, B. Effect of Oxidative Damage on the Stability and Dimerization of Superoxide Dismutase 1. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlo, D.; Mollinari, C.; Racaniello, M.; Garaci, E.; Cardinale, A. DNA Double Strand Breaks: A Common Theme in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016, 13, 1208–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziąbowska-Grabias, K.; Sztanke, M.; Zając, P.; Celejewski, M.; Kurek, K.; Szkutnicki, S.; Korga, P.; Bulikowski, W.; Sztanke, K. Antioxidant Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-G.; Zhu, X.; Nunomura, A.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A. Amyloid Beta: The Alternate Hypothesis. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2006, 3, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Seung-Jae. "α-Synuclein aggregation: a link between mitochondrial defects and Parkinson's disease?." Antioxidants and Redox Signaling 5, no. 3 (2003): 337-348.
- Lorey, M.B.; Öörni, K.; Kovanen, P.T. Modified Lipoproteins Induce Arterial Wall Inflammation During Atherogenesis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 841545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holvoet, P.; Collen, D. Oxidized lipoproteins in atherosclerosis and thrombosis. FASEB J. 1994, 8, 1279–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, Timothy, Patrick KY Goon, and Gregory YH Lip. "Endothelial progenitor cells, endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and oxidative stress in hypertension." Antioxidants & redox signaling 10, no. 6 (2008): 1079-1088.
- De Meyer, Guido RY, and Arnold G. Herman. "Nitric oxide and vascular endothelial dysfunction." In Nitric oxide, pp. 547-567. Academic press, 2000.
- Gelderman, K.A.; Hultqvist, M.; Olsson, L.M.; Bauer, K.; Pizzolla, A.; Olofsson, P.; Holmdahl, R. Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Disease Development and Therapeutic Strategies. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1541–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi-Barr, S.; Lux, C.d.G.; Mahmoud, E.; Almutairi, A. Exploiting Oxidative Microenvironments in the Body as Triggers for Drug Delivery Systems. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 730–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, Miranda J., Ahuva Nissim, Annie R. Knight, Matthew Whiteman, Richard Haigh, and Paul G. Winyard. "Oxidative stress in autoimmune rheumatic diseases." Free Radical Biology and Medicine 125 (2018): 3-14.
- Cernea, S.; Dobreanu, M. Diabetes and beta cell function: from mechanisms to evaluation and clinical implications. Biochem. Medica 2013, 23, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, Ileana, Cristian Lindner, Ivan Schneider, Erik Diaz, MIguel A. Morales, and Armando Rojas. "The Multifaceted Actions of Polyphenols in the Management of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus." (2023).
- Giacco, F.; Brownlee, M. Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Complications. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firuzi, O.; Miri, R.; Tavakkoli, M.; Saso, L. Antioxidant Therapy: Current Status and Future Prospects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 3871–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Marquez, M.E.; Siller-Lopez, F. Current Antioxidant Molecular Therapies for Oxidative Stress-Related Ailments. Curr. Gene Ther. 2008, 8, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preedy, Victor R., and Vinood Patel, eds. Aging: oxidative stress and dietary antioxidants. Academic Press, 2020.
- Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Martínez-Villaluenga, C. Current Advances for Development of Functional Foods Modulating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress; Elsevier: Amsterdam, NX, Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Król, Elżbieta, H. Dziubinska, and K. Trebacz. "What do plants need action potentials for." Action Potential: Biophysical and Cellular Context, Initiation, Phases and Propagation. DuBois ML.(ed) (2010): 1-26.
- Varró, A.; Tomek, J.; Nagy, N.; Virág, L.; Passini, E.; Rodriguez, B.; Baczkó, I. Cardiac transmembrane ion channels and action potentials: cellular physiology and arrhythmogenic behavior. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1083–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, C. , and K. Shanmugam. "Computational Modeling of Sodium Ion Channel-Based Glucose Sensing Biophysics to Study Cardiac Atrial Cell Electrophysiology." (2024).
- MAHAPATRA, CHITARANJAN, and Kirubanandan Shanmugam. "Computational Modeling of Sodium Ion Channel-Based Glucose Sensing Biophysics to Study Abnormal Electrical Activities in Cardiac Atrial Cell." (2024).
- Rybak, Ilya A., and Jessica Ausborn. "Vertebrate pattern generation: overview." Encyclopedia of Computational Neuroscience (2022): 130-140.
- Iaizzo, Paul A. "Introduction to neurophysiology." Neural engineering (2020): 1-64.
- Mahapatra, C.; Kumar, R. Biophysical Mechanisms of Vaginal Smooth Muscle Contraction: The Role of the Membrane Potential and Ion Channels. Pathophysiology 2024, 31, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezanilla, Francisco. "Voltage-gated ion channels." Biological Membrane Ion Channels: Dynamics, Structure, and Applications (2007): 81-118.
- Catterall, William A. "Voltage gated sodium and calcium channels: Discovery, structure, function, and Pharmacology." Channels 17, no. 1 (2023): 2281714.
- Pongs, O. Molecular biology of voltage-dependent potassium channels. Physiol. Rev. 1992, 72, S69–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, C. , and A. Pradhan. "Nifedipine is identified as a potential pharmacological modulator in Parkinson's disease by an in silico electrophysiological study." Parkinsonism & Related Disorders 122 (2024).
- Mahapatra, C.; Samuilik, I. A Mathematical Model of Spontaneous Action Potential Based on Stochastics Synaptic Noise Dynamics in Non-Neural Cells. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, Chitaranjan, Keith Brain, and Rohit Manchanda. "Biophysically Realistic Modles of Detrusor Ion Channels: role in shaping spike and excitavility." In Urinary Bladder Physiology: Computational Insights. Publ Narosa Publishing House, 2024.
- Mahapatra, Chitaranjan. "Computational Study of Action Potential Generation in Urethral Smooth Muscle Cell." In Computational Advances in Bio and Medical Sciences: 10th International Conference, ICCABS 2020, Virtual Event, -12, 2020, Revised Selected Papers 10, pp. 26-32. Springer International Publishing, 2021. 10 December.
- Mahapatra, Chitaranjan, and Rohit Manchanda. "Computational studies on ureter smooth muscle: Modeling ion channels and their role in generating electrical activity." In Proceedings of the 2019 Summer Simulation Conference, pp. 1-6. 2019.
- Mahapatra, Chitaranjan, and Rohit Manchanda. "Modeling Vas Deferens Smooth Muscle Electrophysiology: Role of Ion Channels in Generating Electrical Activity." In Soft Computing for Problem Solving: SocProS 2017, Volume 2, pp. 655-663. Springer Singapore, 2019.
- Rajagopal, S.; Ponnusamy, M. Calcium Signaling: From Physiology to Diseases; Springer Nature: Dordrecht, GX, Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dulla, C.G.; Coulter, D.A.; Ziburkus, J. From Molecular Circuit Dysfunction to Disease. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, Chitaranjan, and Rohit Manchanda. "Modulating Properties of Hyperpolarization-Activated Cation Current in Urinary Bladder Smooth Muscle Excitability: A Simulation Study." In Recent Findings in Intelligent Computing Techniques: Proceedings of the 5th ICACNI 2017, Volume 1, pp. 261-266. Springer Singapore, 2019.
- Mahapatra, C.; Brain, K.L.; Manchanda, R. Computational Study of Hodgkin-Huxley Type Calcium-Dependent Potassium Current in Urinary Bladder Over Activity. 2018 IEEE 8th International Conference on Computational Advances in Bio and Medical Sciences (ICCABS). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, United StatesDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 1–4.
- Mahapatra, C. , and R. Manchanda. "Contribution of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in the subthalamic nucleus neurons towards Parkinson's disease." In MOVEMENT DISORDERS, vol. 33, pp. S146-S146. 111 RIVER ST, HOBOKEN 07030-5774, NJ USA: WILEY, 2018.
- Mahapatra, C.; Brain, K.L.; Manchanda, R. A biophysically constrained computational model of the action potential of mouse urinary bladder smooth muscle. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0200712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bers, Donald M. "Cardiac excitation–contraction coupling." Nature 415, no. 6868 (2002): 198-205.
- Forsberg, A.M.; Bergström, J.; Lindholm, B.; Hultman, E. Resting Membrane Potential of Skeletal Muscle Calculated from Plasma and Muscle Electrolyte and Water Contents. Clin. Sci. 1997, 92, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hille, Bertil. "Ion channels of excitable membranes (Sinauer, Sunderland, MA)." (2001).
- Ashcroft, Frances M., and Patrik Rorsman. "Electrophysiology of the pancreatic β-cell." Progress in biophysics and molecular biology 54, no. 2 (1989): 87-143.
- DiFrancesco, J.C.; DiFrancesco, D. Dysfunctional HCN ion channels in neurological diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 174–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepeta, K.; Lourenco, M.; Schweitzer, B.C.; Adami, P.V.; Banerjee, P.; Catuara-Solarz, S.; Revenga, M.D.L.F.; Guillem, A.M.; Haidar, M.; Ijomone, O.; et al. Synaptopathies: synaptic dysfunction in neurological disorders - A review from students to students. J. Neurochem. 2016, 138, 785–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A McCormick, D.; Contreras, D. On The Cellular and Network Bases of Epileptic Seizures. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2001, 63, 815–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubetzki, Catherine, and Bruno Stankoff. "Demyelination in multiple sclerosis." Handbook of clinical neurology 122 (2014): 89-99.
- Friese, M.A.; Schattling, B.; Fugger, L. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and axonal dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varró, A.; Tomek, J.; Nagy, N.; Virág, L.; Passini, E.; Rodriguez, B.; Baczkó, I. Cardiac transmembrane ion channels and action potentials: cellular physiology and arrhythmogenic behavior. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 1083–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudicessi, J.R.; Ackerman, M.J. Potassium-channel mutations and cardiac arrhythmias—diagnosis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2012, 9, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, S.; Machado, A.G.; Nagel, S.J. Basic Anatomy and Physiology of Pain Pathways. Neurosurg. Clin. North Am. 2014, 25, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubin, A.E.; Patapoutian, A. Nociceptors: the sensors of the pain pathway. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3760–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayak, Manjula, and Ajeet Kumar Singh. "Signaling of Nociceptors and Pain Perception: Impact of Age." Models, Molecules and Mechanisms in Biogerontology: Physiological Abnormalities, Diseases and Interventions (2019): 91-107.
- Berridge, M.J. Smooth muscle cell calcium activation mechanisms. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 5047–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, M. Calcium-Induced Calcium Release in Skeletal Muscle. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 1153–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Ivana Y., and Barbara E. Ehrlich. "Signaling in muscle contraction." Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 7, no. 2 (2015): a006023.
- Amior, N. "Developing models to study the mechanisms of weakness and myotonia in Periodic Paralysis." PhD diss., UCL (University College London), 2018.
- Lehmann-Horn, Frank, Reinhardt Rüdel, and Karin Jurkat-Rott. "Nondystrophic myotonias and periodic paralyses." Myology 3 (2004): 1257-1300.
- Cannon, S.C. PATHOMECHANISMS IN CHANNELOPATHIES OF SKELETAL MUSCLE AND BRAIN. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 29, 387–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodstad, Heidi. "Genetic and Functional Studies of Severe Ventricular Arrhythmias." PhD diss., Helsingin yliopisto, 2005.
- Celesia, G.G. Disorders of membrane channels or channelopathies. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2000, 112, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, Michael R. "Neurological channelopathies: Dysfunctional ion channels may cause many neurological diseases." BMJ 316, no. 7138 (1998): 1104-1105.
- Motschall, E.; Falck-Ytter, Y. Searching the MEDLINE Literature Database through PubMed: A Short Guide. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2005, 28, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmucker, C.M.; Blümle, A.; Schell, L.K.; Schwarzer, G.; Oeller, P.; Cabrera, L.; von Elm, E.; Briel, M.; Meerpohl, J.J. ; on behalf of the OPEN consortium Systematic review finds that study data not published in full text articles have unclear impact on meta-analyses results in medical research. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0176210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, Stephen PH, Jörg Striessnig, Eamonn Kelly, Neil V. Marrion, John A. Peters, Elena Faccenda, Simon D. Harding et al. "The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2017/18: Voltage-gated ion channels." British journal of pharmacology 174 (2017): S160-S194.
- Petkov, Georgi V. "Ion channels." In Pharmacology, pp. 387-427. Academic Press, 2009.
- Hucho, Ferdinand, and Christoph Weise. "Ligand-gated ion channels." Angewandte Chemie International Edition 40, no. 17 (2001): 3100-3116.
- Delmas, P.; Coste, B. Mechano-Gated Ion Channels in Sensory Systems. Cell 2013, 155, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijman, Jordi, and Dobromir Dobrev. "Ion channels as part of macromolecular multiprotein complexes: Clinical significance." Herzschrittmachertherapie & Elektrophysiologie 29, no. 1 (2018): 30.
- Davis, Michael J., Xin Wu, Timothy R. Nurkiewicz, Junya Kawasaki, Peichun Gui, Michael A. Hill, and Emily Wilson. "Regulation of ion channels by protein tyrosine phosphorylation." American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology 281, no. 5 (2001): H1835-H1862.
- Bootman, Martin D., Katja Rietdorf, Holly Hardy, Yana Dautova, Elaine Corps, Cristina Pierro, Eloise Stapleton, Esther Kang, and Diane Proudfoot. "Calcium signalling and regulation of cell function." eLS (2006).
- Huston, Elaine. Involvement of voltage activated calcium channels in neurotransmitter release and its modulation in cultured rat cerebellar granule neurones. University of London, University College London (United Kingdom), 1995.
- Aggarwal, N.T.; Makielski, J.C. Redox Control of Cardiac Excitability. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 432–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan, P.; Ingley, E.; Hool, L. Identifying the Site/S of Modification on Human L-type Calcium Channel Protein Isoforms During Oxidative Stress. Hear. Lung Circ. 2013, 22, S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic, S.M.; Meyenburg, A.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. Redox modulation of peripheral T-type Ca2+ channels in vivo: alteration of nerve injury-induced thermal hyperalgesia. Pain 2004, 109, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziato, L.; Pannaccione, A.; Cataldi, M.; Secondo, A.; Castaldo, P.; Direnzo, G.; Taglialatela, M. Modulation of ion channels by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: a pathophysiological role in brain aging? Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Bielefeldt, K. Regulation of sodium currents through oxidation and reduction of thiol residues. Neuroscience 2000, 101, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chapleau, M.W.; Bates, J.N.; Bielefeldt, K.; Lee, H.-C.; Abboud, F.M. Nitric Oxide as an Autocrine Regulator of Sodium Currents in Baroreceptor Neurons. Neuron 1998, 20, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Hishikari, K.; Ogawa, M.; Watanabe, R.; Suzuki, J.-I.; Nagashima, A.; Masumura, M.; Takayama, K.; Hirata, Y.; Nagai, R.; et al. Clarithromycin attenuates myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Bondarenko, V.E.; Morales, M.J.; Strauss, H.C. Closed-state inactivation in Kv4.3 isoforms is differentially modulated by protein kinase C. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2009, 297, C1236–C1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Yaping, Jun Weng, Yu Cao, Rahul C. Bhosle, and Ming Zhou. "Functional Coupling between the Kv1. 1 Channel and Aldoketoreductase Kvβ1*♦." Journal of Biological Chemistry 283, no. 13 (2008): 8634-8642.
- DiChiara, Timothy J., and Peter H. Reinhart. "Redox modulation of hslo Ca2+-activated K+ channels." Journal of Neuroscience 17, no. 13 (1997): 4942-4955.
- Tang, X.D.; Daggett, H.; Hanner, M.; Garcia, M.L.; McManus, O.B.; Brot, N.; Weissbach, H.; Heinemann, S.H.; Hoshi, T. Oxidative Regulation of Large Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2001, 117, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mistry, D. K. , and C. J. Garland. "Nitric oxide (NO)-induced activation of large conductance Ca2+-dependent K+ channels (BKCa) in smooth muscle cells isolated from the rat mesenteric artery." British journal of pharmacology 124, no. 6 (1998): 1131-1140.
- Erdos, Benedek. "Cerebrovascular dysfunction in insulin-resistance." PhD diss., Semmelweis Egyetem (Hungary), 2004.
- Miura, T.; Liu, Y.; Goto, M.; Tsuchida, A.; Miki, T.; Nakano, A.; Nishino, Y.; Ohnuma, Y.; Shimamoto, K. Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+channels play a role in cardioprotection by Na+-H+exchange inhibition against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ. 2001, 37, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokube, K.; Kiyosue, T.; Arita, M. Effects of hydroxyl radicals on K ATP channels in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. Pfl?gers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 1998, 437, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krippeit-Drews, Peter, Claudia Krämer, Susanne Welker, Florian Lang, Hermann PT Ammon, and Gisela Drews. "Interference of H2O2 with stimulus-secretion coupling in mouse pancreatic β-cells." The Journal of physiology 514, no. Pt 2 (1999): 471.
- Trapp, S.; Proks, P.; Tucker, S.J.; Ashcroft, F.M. Molecular Analysis of ATP-sensitive K Channel Gating and Implications for Channel Inhibition by ATP. J. Gen. Physiol. 1998, 112, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, W.; Chen, X.; Cui, N.; Konduru, A.S.; Shi, Y.; Trower, T.C.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, C. Molecular Basis and Structural Insight of Vascular KATP Channel Gating by S-Glutathionylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 9298–9307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.-L.; Nieves, A.; Bin Im, W.; Old, D.W.; Dinh, D.T.; Wheeler, L. The Prevention of Colitis by E Prostanoid Receptor 4 Agonist through Enhancement of Epithelium Survival and Regeneration. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 320, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, A.R.; Kang, M.; Akbarali, H.I. Hydrogen Sulfide as an Allosteric Modulator of ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels in Colonic Inflammation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguinetti, M.C.; Tristani-Firouzi, M. hERG potassium channels and cardiac arrhythmia. Nature 2006, 440, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trudeau, M.C.; Warmke, J.W.; Ganetzky, B.; Robertson, G.A. HERG, a Human Inward Rectifier in the Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel Family. Science 1995, 269, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fermini, B.; Fossa, A.A. The impact of drug-induced QT interval prolongation on drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, Jamie I. "Oxidative stress fine-tunes the dance of hERG K+ channels." The Journal of Physiology 588, no. Pt 16 (2010): 2975.
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Wang, H.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; Villeneuve, L.R.; Zhang, H.; Bai, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, Z. Restoring depressed HERG K+ channel function as a mechanism for insulin treatment of abnormal QT prolongation and associated arrhythmias in diabetic rabbits. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H1446–H1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, C.; Thakkar, R. In Silico Electrophysiological Investigation of Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin-4 Ion Channel Biophysics to Study Detrusor Overactivity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, Chitaranjan. "Simulation study of transient receptor potential current in urinary bladder over activity: student research abstract." In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing, pp. 74-75. 2018.
- Yamamoto, S.; Takahashi, N.; Mori, Y. Chemical physiology of oxidative stress-activated TRPM2 and TRPC5 channels. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2010, 103, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzer, M.; Lintschinger, B.; Groschner, K. Evidence for a role of Trp proteins in the oxidative stress-induced membrane conductances of porcine aortic endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999, 42, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groschner, Klaus, Christian Rosker, and Michael Lukas. "Role of TRP channels in oxidative stress." In Mammalian TRP Channels as Molecular Targets: Novartis Foundation Symposium 258, vol. 258, pp. 222-235. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2004.
- Hara, Y.; Wakamori, M.; Ishii, M.; Maeno, E.; Nishida, M.; Yoshida, T.; Yamada, H.; Shimizu, S.; Mori, E.; Kudoh, J.; et al. LTRPC2 Ca2+-Permeable Channel Activated by Changes in Redox Status Confers Susceptibility to Cell Death. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehage, Edith, Jörg Eisfeld, Inka Heiner, Eberhard Jüngling, Christof Zitt, and Andreas Lückhoff. "Activation of the cation channel long transient receptor potential channel 2 (LTRPC2) by hydrogen peroxide: a splice variant reveals a mode of activation independent of ADP-ribose." Journal of Biological Chemistry 277, no. 26 (2002): 23150-23156.
- Kolisek, M.; Beck, A.; Fleig, A.; Penner, R. Cyclic ADP-Ribose and Hydrogen Peroxide Synergize with ADP-Ribose in the Activation of TRPM2 Channels. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perraud, A.-L.; Takanishi, C.L.; Shen, B.; Kang, S.; Smith, M.K.; Schmitz, C.; Knowles, H.M.; Ferraris, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Accumulation of Free ADP-ribose from Mitochondria Mediates Oxidative Stress-induced Gating of TRPM2 Cation Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 6138–6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Takahashi, N.; Mori, Y. Chemical physiology of oxidative stress-activated TRPM2 and TRPC5 channels. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2010, 103, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Thébault, S.; van der Wijst, J.; van der Kemp, A.; Lasonder, E.; Bindels, R.J.; Hoenderop, J.G. RACK1 Inhibits TRPM6 Activity via Phosphorylation of the Fused α-Kinase Domain. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadtman, E.R.; Levine, R.L. Free radical-mediated oxidation of free amino acids and amino acid residues in proteins. Amino Acids 2003, 25, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, T.; Eder, C. Importance of the non-selective cation channel TRPV1 for microglial reactive oxygen species generation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 216, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Grice, D.M.; Faddy, H.M.; Nguyen, N.; Leitch, S.; Wang, Y.; Muend, S.; Kenny, P.A.; Sukumar, S.; Roberts-Thomson, S.J.; et al. Store-Independent Activation of Orai1 by SPCA2 in Mammary Tumors. Cell 2010, 143, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogeski, I.; Kummerow, C.; Al-Ansary, D.; Schwarz, E.C.; Koehler, R.; Kozai, D.; Takahashi, N.; Peinelt, C.; Griesemer, D.; Bozem, M.; et al. Differential Redox Regulation of ORAI Ion Channels: A Mechanism to Tune Cellular Calcium Signaling. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coddou, Claudio, Juan F. Codocedo, Shuo Li, Juan G. Lillo, Claudio Acuña-Castillo, Paulina Bull, Stanko S. Stojilkovic, and J. Pablo Huidobro-Toro. "Reactive oxygen species potentiate the P2X2 receptor activity through intracellular Cys430." Journal of Neuroscience 29, no. 39 (2009): 12284-12291.
- Mason, H.S.; Bourke, S.; Kemp, P.J. Selective Modulation of Ligand-Gated P2X Purinoceptor Channels by Acute Hypoxia Is Mediated by Reactive Oxygen Species. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huizinga, J.D.; Wei, R.; Chen, J.-H.; Wright, G.; Bardakjian, B. Generating bowel movements that facilitate nutrient absorption. Can. Young- Sci. J. 2014, 2014, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Liu, Z. Lipid Rafts and Oxidative Stress–Induced Cell Death. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, N.; Horiguchi, K.; Iino, S.; Nakayama, S.; Ohwada, T.; Otani, Y.; Firman; Murata, T. ; Sanders, K.M.; Ozaki, H.; et al. Nitric oxide-induced oxidative stress impairs pacemaker function of murine interstitial cells of Cajal during inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loffredo, L.; Ettorre, E.; Zicari, A.M.; Inghilleri, M.; Nocella, C.; Perri, L.; Spalice, A.; Fossati, C.; De Lucia, M.C.; Pigozzi, F.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Gut-Derived Lipopolysaccharides in Neurodegenerative Disease: Role of NOX2. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kong, P.; Chen, C.; Tang, J.; Jin, X.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y. Targeting IL-17A Improves the Dysmotility of the Small Intestine and Alleviates the Injury of the Interstitial Cells of Cajal during Sepsis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Pollock, J.; Schmidt, H.H.; Ward, S.M.; Sanders, K.M. Expression of nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity by interstitial cells of the canine proximal colon. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1994, 49, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, L.R.; Poole, D.P.; Thacker, M.; Furness, J.B. The involvement of nitric oxide synthase neurons in enteric neuropathies. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 23, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bódi, N.; Szalai, Z.; Bagyánszki, M. Nitrergic Enteric Neurons in Health and Disease—Focus on Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangula, P.R.R.; Maner, W.L.; Micci, M.-A.; Garfield, R.E.; Pasricha, P.J.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, S.; Gao, J.; Zhang, G.; Lu, Y.; et al. Diabetes induces sex-dependent changes in neuronal nitric oxide synthase dimerization and function in the rat gastric antrum. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G725–G733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Seidler, B.; Kettenberger, A.; Sibaev, A.; Rohn, M.; Feil, R.; Allescher, H.-D.; Vanderwinden, J.-M.; Hofmann, F.; Schemann, M.; et al. Interstitial cells of Cajal integrate excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission with intestinal slow-wave activity. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iino, S.; Horiguchi, K.; Nojyo, Y. Interstitial cells of Cajal are innervated by nitrergic nerves and express nitric oxide–sensitive guanylate cyclase in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract. Neuroscience 2008, 152, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhein, S.; Salameh, A. Remodeling of Cardiac Gap Junctional Cell–Cell Coupling. Cells 2021, 10, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.P.; Lau, A.F. Gap junction channel gating modulated through protein phosphorylation. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2007, 94, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Yan-Jun, Xiao-Zhou Liu, Lei Tu, and Yu Sun. "Cytomembrane trafficking pathways of Connexin 26, 30, and 43." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 12 (2023): 10349.
- Le, H.T.; Sin, W.C.; Lozinsky, S.; Bechberger, J.; Vega, J.L.; Guo, X.Q.; Sáez, J.C.; Naus, C.C. Gap Junction Intercellular Communication Mediated by Connexin43 in Astrocytes Is Essential for Their Resistance to Oxidative Stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feine, I.; Pinkas, I.; Salomon, Y.; Scherz, A. Local Oxidative Stress Expansion through Endothelial Cells – A Key Role for Gap Junction Intercellular Communication. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e41633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahapatra, C. , and R. Manchanda. "Computational assessment of calcium channel effects on subthalamic nucleus neuronal cells: Study of abnormal bursting patterns in Parkinson's disease." In MOVEMENT DISORDERS, vol. 31, pp. S620-S621. 111 RIVER ST, HOBOKEN 07030-5774, NJ USA: WILEY-BLACKWELL, 2016.
- Dave, Vijay, Chitaranjan Mahapatra, and Rohit Manchanda. "A mathematical model of the calcium transient in urinary bladder smooth muscle cells." In 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 5359-5362. IEEE, 2015.
- Mahapatra, C.; Brain, K.L.; Manchanda, R. Computational studies on urinary bladder smooth muscle: Modeling ion channels and their role in generating electrical activity. 2015 7th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, FranceDATE OF CONFERENCE; pp. 832–835.
- Mahapatra, C.; Manchanda, R. Computational Studies on Bladder Smooth Muscle: Modeling Ion Channels and their Role in Generating Electrical Activity. Biophys. J. 2015, 108, 588a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, C. , and R. Manchanda. "Effects of aging in Parkinson’s disease: Role of Ca channel in dopamine neuron computational model." In Front. Neurosci. Conference Abstract: Neuroinformatics. 2015.
- Ureshino, R.P.; Erustes, A.G.; Bassani, T.B.; Wachilewski, P.; Guarache, G.C.; Nascimento, A.C.; Costa, A.J.; Smaili, S.S.; Pereira, G.J.d.S. The Interplay between Ca2+ Signaling Pathways and Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patergnani, Simone, Alberto Danese, Esmaa Bouhamida, Gianluca Aguiari, Maurizio Previati, Paolo Pinton, and Carlotta Giorgi. "Various aspects of calcium signaling in the regulation of apoptosis, autophagy, cell proliferation, and cancer." International journal of molecular sciences 21, no. 21 (2020): 8323.
- Ermak, G.; Davies, K.J. Calcium and oxidative stress: from cell signaling to cell death. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 38, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S.M.; Duchen, M.R. Calcium microdomains and oxidative stress. Cell Calcium 2006, 40, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, Martin, Vladimir Gogvadze, Sten Orrenius, and Boris Zhivotovsky. "Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death." Apoptosis 12 (2007): 913-922.
- Tabet, F.; Savoia, C.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Touyz, R.M. Differential Calcium Regulation by Hydrogen Peroxide and Superoxide in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells from Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2004, 44, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttemann, M.; Lee, I.; Samavati, L.; Yu, H.; Doan, J.W. Regulation of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation through cell signaling. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 1701–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahalan, Michael, and Erwin Neher. "[1] Patch clamp techniques: an overview." Methods in enzymology 207 (1992): 3-14.
- Liu, P.; Miller, E.W. Electrophysiology, Unplugged: Imaging Membrane Potential with Fluorescent Indicators. Accounts Chem. Res. 2019, 53, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, Mark B., and S. James Remington. "Redox-sensitive green fluorescent protein: probes for dynamic intracellular redox responses. A review." Redox-Mediated Signal Transduction: Methods and Protocols (2009): 50-64.
- Moutal, A.; White, K.A.; Chefdeville, A.; Laufmann, R.N.; Vitiello, P.F.; Feinstein, D.; Weimer, J.M.; Khanna, R. Dysregulation of CRMP2 Post-Translational Modifications Drive Its Pathological Functions. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 6736–6755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badar, Mohammad Sufian, Shazmeen Shamsi, Jawed Ahmed, and Md Afshar Alam. "Molecular dynamics simulations: concept, methods, and applications." In Transdisciplinarity, pp. 131-151. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022.
- Kutzner, C.; Köpfer, D.A.; Machtens, J.-P.; de Groot, B.L.; Song, C.; Zachariae, U. Insights into the function of ion channels by computational electrophysiology simulations. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, D.A. The role of quantitative structure - activity relationships (QSAR) in biomolecular discovery. Briefings Bioinform. 2002, 3, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poswar, F.d.O.; Farias, L.C.; Fraga, C.A.d.C.; Bambirra, W.; Brito-Júnior, M.; Sousa-Neto, M.D.; Santos, S.H.S.; de Paula, A.M.B.; D'Angelo, M.F.S.V.; Guimarães, A.L.S. Bioinformatics, Interaction Network Analysis, and Neural Networks to Characterize Gene Expression of Radicular Cyst and Periapical Granuloma. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cell type | RMP (mV) | AP/SW | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smooth Muscle | -45 to -65 | AP/SW | [43] | |
| Cardiac Muscle | -80 to -90 | AP | [44] | |
| Skeletal Muscle | -65 to - 91 | AP | [45] | |
| Neuronal Cell | -60 to -70 | AP | [46] | |
| Pancreatic beta cells | -60 to -70 | SW | [47] |
| Ion channel type | Role in AP/SW | |
|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ channels | RMP, AP/SW firing, Depolarization, | |
| Na+ channels | AP/SW firing, Depolarization, | |
| K+ channels | RMP, Repolarization, Hyperpolarization | |
| Cl- channels | RMP, Repolarization | |
| TRP channels | RMP, AP/SW firing, Depolarization, | |
| Leak channels | RMP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




