Submitted:
07 August 2024
Posted:
08 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genome Analyses
2.2. Classification of the Horse TR Genes
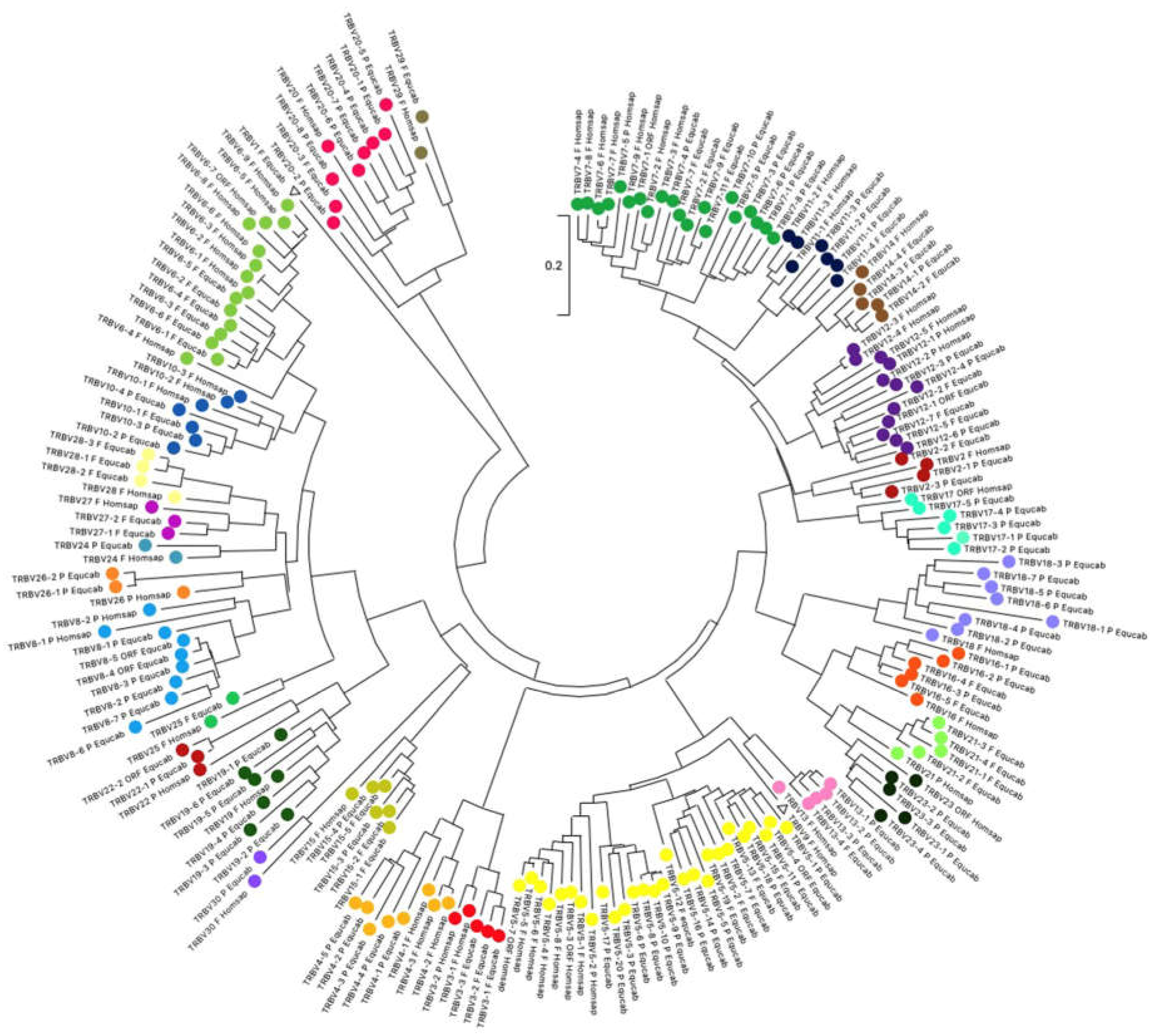
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Horse Transcriptome Analysis
3. Results
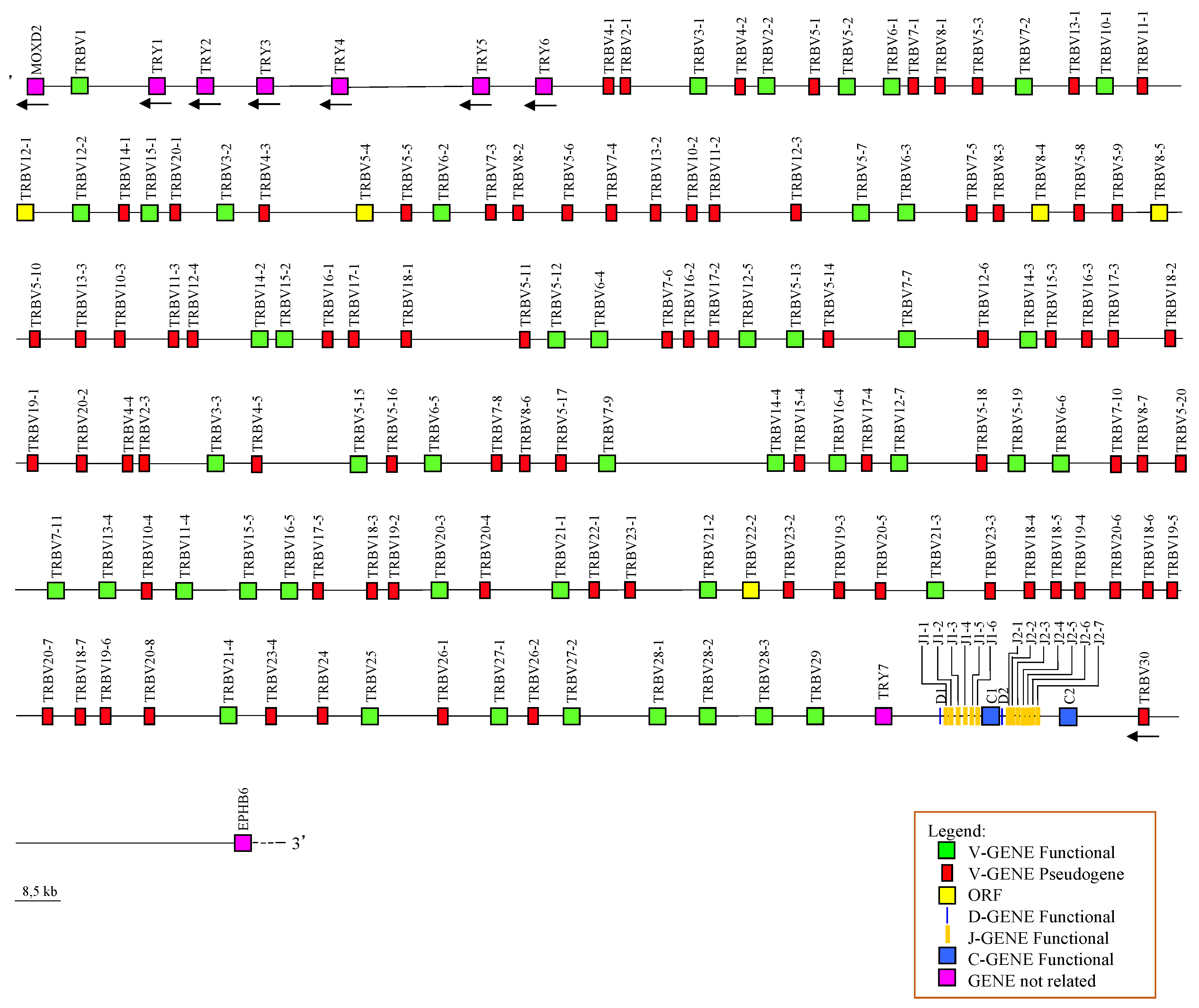
3.1. General Organization of the Horse TRB Locus
3.2. Sequence Analysis of the TRBV Genes and Classification
3.3. Classification and Structure of the TRBD, TRBJ and TRBC Genes
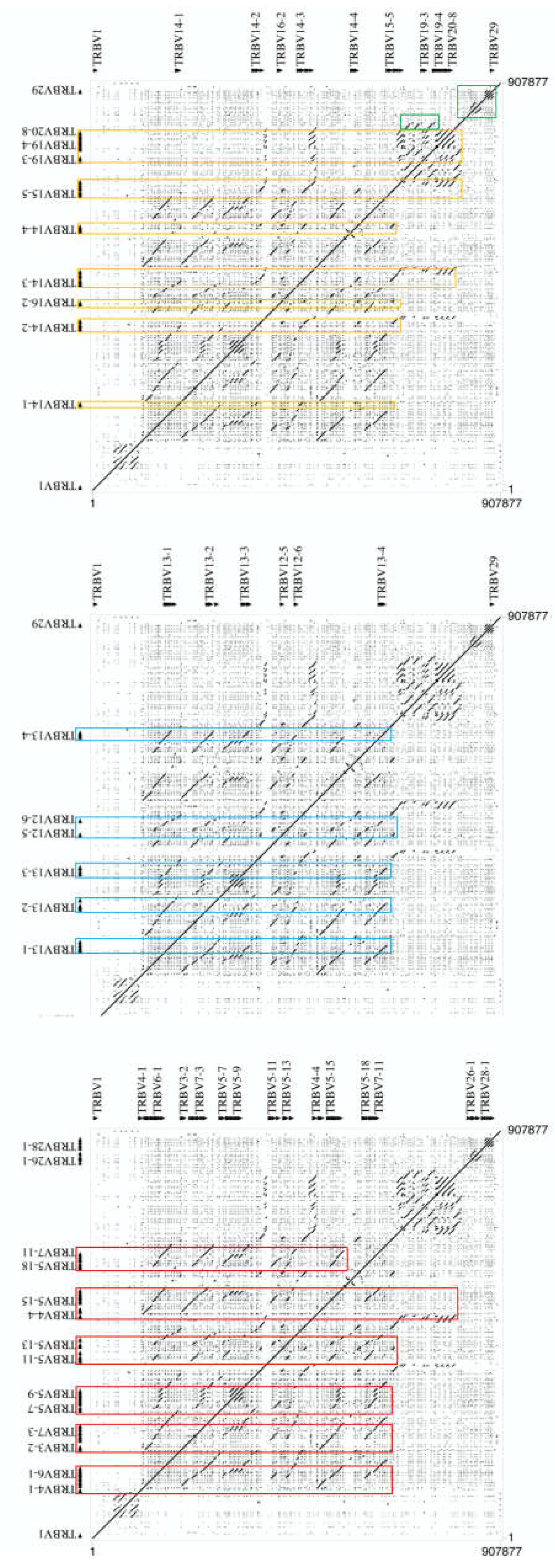
3.4. Genomic Architecture of the TRBV-Cluster
3.5. Clonotype Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casal, M.; Haskins, M. Large animal models and gene therapy. Eur J Hum Genet 2006, 14, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, S.; Rusitzka, T.V.; Diesterbeck, U.S.; Czerny, C.P. Equine immunoglobulins and organization of immunoglobulin genes. Developmental and comparative immunology 2015, 53, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, E.K.; Brandon Wiese, R.; Graham, M.R.; Tyler, A.J.; Settlage, J.M.; Werre, S.R.; Petersson-Wolfe, C.S.; Kanevsky-Mullarky, I.; Dahlgren, L.A. Serum and synovial fluid serum amyloid A response in equine models of synovitis and septic arthritis. Veterinary Surgery 2016, 45, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkowski, L.; Cywinska, A.; Paschalis-Trela, K.; Crisman, M.; Kita, J. Multiple etiologies of equine recurrent uveitis—a natural model for human autoimmune uveitis: a brief review. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 2016, 44, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, M.; Gu, X.; Sitnikova, T. Evolution by the birth-and-death process in multigene families of the vertebrate immune system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 7799–7806. [Google Scholar]
- Antonacci, R.; Massari, S.; Linguiti, G.; Caputi Jambrenghi, A.; Giannico, F.; Lefranc, M.P.; Ciccarese, S. Evolution of the T-Cell Receptor (TR) Loci in the Adaptive Immune Response: The Tale of the TRG Locus in Mammals. Genes 2020, 11, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, M.-P.; Lefranc, G. The T Cell Receptor FactsBook; Academic Press Harcourt Science and Technology Company: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Flajnik, M.F.; Kasahara, M. Origin and evolution of the adaptive immune system: genetic events and selective pressures. Nature reviews. Genetics 2010, 11, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pégorier, P.; Bertignac, M.; Chentli, I.; Nguefack Ngoune, V.; Folch, G.; Jabado-Michaloud, J.; Hadi Saljoqi, S.; Giudicelli, V.; Duroux, P.; Lefranc, M.P.; Kossida, S. IMGT® Biocuration and Comparative Study of the T Cell Receptor Beta Locus of Veterinary Species Based on Homo sapiens TRB. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonacci, R.; Di Tommaso, S.; Lanave, C.; Cribiu, E.P.; Ciccarese, S.; Massari, S. Organization, structure and evolution of 41kb of genomic DNA spanning the D-J-C region of the sheep TRB locus. Mol Immunol 2008, 45, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonacci, R.; Bellini, M.; Pala, A.; Mineccia, M.; Hassanane, M.S.; Ciccarese, S.; et al. The occurrence of three D-J-C clusters within the dromedary TRB locus highlights a shared evolution in Tylopoda, Ruminantia and Suina. Dev Compar Immunol 2017, 76, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, S.; Bellini, M.; Ciccarese, S.; Antonacci, R. Overview of the Germline and Expressed Repertoires of the TRB Genes in Sus scrofa. Frontiers in Immunology 2018, 9, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonacci, R.; Bellini, M.; Linguiti, G.; Ciccarese, S.; Massari, S. Comparative Analysis of the TRB Locus in the Camelus Genus. Frontiers in Genetics 2019, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannico, F.; Massari, S.; Jambrenghi, A.C.; Soriano, A.; Pala, A.; Linguiti, G.; Ciccarese, S.; Antonacci, R. The expansion of the TRB and TRG genes in domestic goats (Capra hircus) is characteristic of the ruminant species. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linguiti, G.; Kossida, S.; Pierri, C.L.; Jabado-Michaloud, J.; Folch, G.; Massari, S.; Lefranc, M.P.; Ciccarese, S.; Antonacci, R. The T Cell Receptor (TRB) Locus in Tursiops truncatus: From Sequence to Structure of the Alpha/Beta Heterodimer in the Human/Dolphin Comparison. Genes 2021, 12, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, S.; Zhang, Z.; Frazer, K.A.; Smit, A.; Riemer, C.; Bouck, J.; Gibbs, R.; Hardison, R.; Miller, W. PipMaker – a web server for aligning two genomic DNA sequences. Genome Res 2020, 10, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, MP. Immunoglobulin and T cell receptor genes: IMGT ® and the birth and rise of immunoinformatics. Front Immunol 2014, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, F.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Lee, J.; Eusebi, A.; Niewielska, A.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Lopez, R.; Butcher, S. The EMBL-EBI Job Dispatcher sequence analysis tools framework in 2024. Nucleic Acids Res 2024, 52, W521–W525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, M.-P.; Forster, A.; Baer, R.; Stinson, M.A.; Rabbitts, TH. Diversity and rearrangement of the human T cell rearranging gamma genes: nine germline variable genes belonging to two subgroups. Cell 1986, 45, 237–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefranc, M.-P. Correspondence between Homo sapiens and Mus musculus TRBV 107 subgroups nomenclature (IMGT-NC) Report. 2023. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net.
- Giudicelli, V.; Chaume, D.; Lefranc, M.P. IMGT/GENE-DB: a comprehensive database for human and mouse immunoglobulin and T cell receptor genes. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 93, D256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, RC. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform 2004, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knynar, C.; Tamura, K. MEGAX: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol Biol Evol 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stecher, G.; Tamura, K.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) for macOS. Mol Biol Evol 2020, 37, 1237–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructingphylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004, 101, 11030–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, M.P.; Pommié, C.; Ruiz, M.; Giudicelli, V.; Foulquier, E.; Truong, L.; Thouvenin-Contet, V.; Lefranc, G. IMGT unique numbering for immunoglobulin and T cell receptor variable domains and Ig superfamily V-like domains. Dev Comp Immunol 2003, 27, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineccia, M.; Massari, S.; Linguiti, G.; Ceci, L.; Ciccarese, S.; Antonacci, R. New insight into the genomic structure of dog T cell receptor beta (TRB) locus inferred from expression analysis. Dev Compar Immunol 2012, 37, 279–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonacci, R.; Giannico, F.; Ciccarese, S.; Massari, S. Genomic characteristics of the T cell receptor (TRB) locus in the rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) revealed by comparative and phylogenetic analyses. Immunogenetics 2014, 66, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudicelli, V.; Chaume, D.; Lefranc, M.P. IMGT/GENE-DB: a comprehensive database for human and mouse immunoglobulin and T cell receptor genes. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 93, D256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, M.P.; Giudicelli, V.; Duroux, P.; Jabado-Michaloud, J.; Folch, G.; Aouinti, S.; Carillon, E.; Duvergey, H.; Houles, A.; Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Hadi-Saljoqi, S.; Sasorith, S.; Lefranc, G.; Kossida, S. IMGT®, the international ImMunoGeneTics information system® 25 years on. Nucleic acids research 2015, 43, D413–D422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tommaso, S.; Antonacci, R.; Ciccarese, S.; Massari, S. Extensive analysis of D-JC arrangements allows the identification of different mechanisms enhancing the diversity in sheep T cell receptor beta-chain repertoire. BMC Genomics 2010, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.A.; Lanchbury, J.S. Healthy human T-cell receptor beta chain repertoire. Quantitative analysis and evidence for J beta-related effects on CDR3 structure and diversity. Hum Immunol 1995, 43, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massari, S.; Giannico, F.; Paolillo, N.V.; Pala, A.; Jambrenghi, A.C.; Antonacci, R. Genomic and Comparative Analysis of the T Cell Receptor Gamma chain Locus in the Equus Genus. Front Immunol 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinni, B.; Massari, S.; Jambrenghi, A.C.; Giannico, F.; Lefranc, M.P.; Ciccarese, S.; Antonacci, R. Sheep (Ovis aries) T cell receptor alpha (TRA) and delta (TRD) genes and genomic organization of the TRA/TRD locus. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, J.D.; Warren, R.L.; Webb, J.R.; Nelson, B.H.; Holt, R.A. Profiling the T-cell receptor beta-chain repertoire by massively parallel sequencing. Genome Res 2009, 19, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curry, J.D.; Geier, J.K.; Schlissel, M.S. Single-strand recombination signal sequence nicks in vivo: evidence for a capture model of synapsis. Nat Immunol 2005, 6, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefranc, M.-P.; Pommié, C.; Kaas, Q.; Duprat, E.; Bosc, N.; Guiraudou, D.; et al. IMGT unique numbering for immunoglobulin and T cell receptor constant domains and Ig superfamily c-like domains. Dev Comp Immunol 2005, 29, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Horse TRB | Human TRB | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgroups | No. of genes | P | F | ORF | No. of genes | P | F | ORF |
| TRBV1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| TRBV3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||
| TRBV4 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||||
| TRBV5 | 20 | 13 | 6 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 5 | 2 |
| TRBV6 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 1 | |||
| TRBV7 | 11 | 7 | 4 | 9 | 1 | 7 | 1 | |
| TRBV8 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||
| TRBV9 | - | 1 | 1 | |||||
| TRBV10 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | |||
| TRBV11 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | |||
| TRBV12 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
| TRBV13 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| TRBV14 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||
| TRBV15 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||
| TRBV16 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||
| TRBV17 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV18 | 7 | 7 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV19 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV20 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| TRBV21 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV22 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| TRBV23 | 4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV24 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV25 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV26 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV27 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV28 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV29 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| TRBV30 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Total | 136 | 84 | 47 | 5 | 64 | 11 | 47 | 6 |
| TRBJgene | N° of Clonotype | TRBD1 gene | TRBD2 gene | TRBD gene (ND) | Mean CDR3 length(AA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRBJ1-1 | 12 | 6 | - | 6 | 12.25 (range 9-16) |
| TRBJ1-2 | 25 | 14 | 2 | 9 | 12.04 (range 9-16) |
| TRBJ1-3 | - | - | - | - | - |
| TRBJ1-4 | 4 | 2 | - | 2 | 12.75 (range 11-14) |
| TRBJ1-5 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 12.00 (range 11-13) |
| TRBJ1-6 | 19 | 9 | 1 | 9 | 12.57 (range 10-17) |
| TOTAL (Cluster1) | 64 | 32 | 4 | 28 | 12,28 (range 9-17) |
| TRBJ2-1 | 42 | 9 | 22 | 11 | 12,69 (range 9-18) |
| TRBJ2-2 | 5 | - | 1 | 4 | 12,40 (range 10-14) |
| TRBJ2-3 | 21 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 12.90 (range 10-16) |
| TRBJ2-4 | 37 | 4 | 22 | 11 | 12.76 (range 10-16) |
| TRBJ2-5 | 12 | 1 | 8 | 3 | 12.17 (range 10-16) |
| TRBJ2-6 | 9 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 13.89 (range 12-17) |
| TRBJ2-7 | 22 | - | 13 | 9 | 12.54 (range 10-15) |
| TOTAL (Cluster2) | 148 | 21 | 77 | 50 | 12,73 (range 9-18) |
| TOTAL(Cluster1 + Cluster2) | 212 | 53 | 81 | 78 | 12.60 (range 9-18) |
| Subgroups | N° of clonotype | Resolved* |
|---|---|---|
| TRBV1 | ||
| TRBV2 | 2 | V2-2 (2) |
| TRBV3 | 9 | V3-3 (5) |
| TRBV4 | ||
| TRBV5 | 26 | V5-2(1) V5-4(1) V5-7(4) V5-12(3) V5-13(4) V5-15(6) V5-19(1) |
| TRBV6 | 2 | V6-6(1) |
| TRBV7 | 7 | V7-7(4) |
| TRBV8 | 3 | V8-3(2) V8-5(1) |
| TRBV9 | ||
| TRBV10 | ||
| TRBV11 | 1 | V11-4(1) |
| TRBV12 | 11 | V12-2(10) V12-7(1) |
| TRBV13 | ||
| TRBV14 | 14 | V14-3(5) V14-4(2) |
| TRBV15 | 6 | V15-2(2) V15-5(3) |
| TRBV16 | ||
| TRBV17 | ||
| TRBV18 | ||
| TRBV19 | ||
| TRBV20 | 34 | V20-3(3) V20-8(26) |
| TRBV21 | 21 | |
| TRBV22 | ||
| TRBV23 | ||
| TRBV24 | ||
| TRBV25 | 3 | |
| TRBV26 | ||
| TRBV27 | 4 | V27-1(1) |
| TRBV28 | 17 | |
| TRBV29 | 1 | |
| TRBV30 | ||
| TOTAL | 161 | 93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





