Introduction.
Our current therapeutic approaches fall short in adequately restoring knee joint function, preventing subsequent injuries, and staving off post-traumatic osteoarthritis. This shortcoming highlights a significant gap in our rehabilitation methods, which often rely on largely pre-planned techniques and standardized test batteries. These methods, while systematic, fail to account for the unpredictable and dynamic nature of sports, as emphasized by dynamic systems theory. The chaotic environment of sports requires a more adaptive and responsive approach to rehabilitation, one that can quickly adjust to the varying demands placed on athletes.
As coaches, physiotherapists, and healthcare professionals, it is imperative that we acknowledge and accept these limitations in our current practices. Recognizing the complexity and multifaceted nature of this problem is the first step towards finding effective solutions. The interplay between various factors such as biomechanics, physiology, psychology, and even external environmental influences means that a one-size-fits-all approach is inadequate. Each athlete’s recovery process is unique, influenced by their specific injury, personal health history, mental state, and the particular demands of their sport.
To bridge this gap, we must adopt a holistic perspective, integrating insights and methods from multiple disciplines within health and sports sciences. This includes not only traditional rehabilitation techniques but also innovations in sports science, neurology, nutrition, and mental health. By fostering a more interdisciplinary approach, we can develop more robust and resilient rehabilitation protocols that better prepare athletes for the rigors and unpredictability of their sports. In doing so, we can enhance recovery outcomes, reduce the risk of re-injury, and promote long-term joint health, ultimately leading to better overall performance and well-being for athletes.
Additionally, advancements in technology and data analytics offer promising avenues for improving rehabilitation strategies. Wearable technology, for instance, can provide real-time feedback on an athlete’s movements, enabling more precise adjustments to their rehabilitation exercises. Data analytics can help identify patterns and risk factors for injuries, allowing for more personalized and preventative care. Virtual reality and augmented reality can create immersive training environments that simulate the chaotic conditions of actual sports, helping athletes better prepare for the demands of their activities.
Moreover, the psychological aspect of recovery cannot be overlooked. Mental resilience and confidence are crucial for an athlete’s return to sport. Psychological support, including mental health counseling and cognitive-behavioral techniques, should be integrated into rehabilitation programs to address anxiety, fear of re-injury, and other mental barriers that athletes may face. By addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of recovery, we can provide more comprehensive care that supports the whole athlete.
In conclusion, our current therapeutic approaches must evolve to meet the complex needs of athletes recovering from knee injuries. By embracing a multifaceted, interdisciplinary approach and leveraging technological advancements, we can develop more effective rehabilitation protocols. This will not only improve recovery outcomes but also enhance the overall health and performance of athletes, ensuring they are better equipped to handle the challenges of their sports [
1].
More Than Biomechanics
ACL injuries arise due to biomechanical flaws (e.g., excessive knee valgus, etc.), right? Well, sort of. As previously discussed by Dr. Chaput and Harjiv Singh in the field of science, these injuries result from complex failures of nonlinear systems. Biomechanical errors are necessary but insufficient on their own to cause injuries [
2].
Sports are a complex system. The ultimate outcome of any game is determined by a multitude of factors beyond just the individual skills and performance of players. Each player’s interaction with teammates and the coach, the strategies employed, and the constantly evolving dynamics of the game all play critical roles. For instance, substitutions can alter the pace and energy levels of a team, crowd noise can influence player focus and decision-making, and refereeing decisions can impact the flow and momentum of the game. Moreover, managing the game clock effectively is crucial for maximizing scoring opportunities and defensive plays.
Two competing teams rarely play “perfectly.” Instead, each team continuously adjusts to mistakes and unexpected events to score points, maximize possession, and ultimately win the game. This adaptive characteristic is a hallmark of all complex systems: despite apparent flaws, complexity allows for variability in how systems operate. This means that even with biomechanical imperfections, athletes can still perform effectively without necessarily sustaining injuries.
In this context, biomechanical flaws can be seen as “minor imperfections” in human movement. These flaws do not always lead to injuries because the body’s natural variability and adaptability often compensate for them. For example, an athlete with a slight knee valgus might adjust their movement patterns to reduce stress on the knee joint during play. Additionally, strength and conditioning programs, proprioceptive training, and sport-specific drills can enhance an athlete’s ability to cope with these imperfections [
3].
The broader implication is that natural biomechanical variability should not be scapegoated for system failures. Instead, it should be understood as part of the complex interplay of factors that influence injury risk. Addressing ACL injuries and similar issues requires a comprehensive approach that considers the athlete’s overall biomechanics, training environment, psychological state, and external influences. By embracing the complexity of sports and human movement, we can develop more effective injury prevention and rehabilitation strategies that go beyond merely correcting biomechanical flaws.
In the realm of injury prevention, a multifaceted approach that includes education, technique refinement, and conditioning is crucial. Educating athletes about the risks and proper techniques for movements can significantly reduce the incidence of injuries. For example, teaching proper landing techniques can help mitigate the forces on the knee during high-impact activities, reducing the likelihood of ACL injuries.
Moreover, refining athletic techniques through personalized coaching can address individual biomechanical issues. Coaches can work closely with athletes to modify their movements, ensuring they perform in ways that minimize undue stress on vulnerable joints. This personalized attention can identify and correct subtle biomechanical flaws before they contribute to injury [
4].
Conditioning programs that focus on strength, flexibility, and neuromuscular control are also essential components of injury prevention. Strengthening the muscles around the knee can provide better support and stability, reducing the strain on the ACL. Flexibility exercises ensure that the muscles and ligaments can handle a wide range of motion without becoming overstretched or damaged. Neuromuscular control exercises improve the body’s ability to coordinate movements and maintain balance, which is crucial for preventing falls and awkward landings that could lead to injury.
Psychological factors also play a significant role in injury prevention and recovery. Athletes’ mental resilience, confidence, and stress levels can influence their risk of injury and their ability to recover. Psychological support, including mental health counseling and techniques such as visualization and mindfulness, can help athletes manage anxiety, maintain focus, and stay motivated during rehabilitation.
Finally, the role of external factors, such as playing surfaces, equipment, and environmental conditions, should not be underestimated. Ensuring that athletes train and compete on well-maintained surfaces, using appropriate footwear and protective gear, can reduce the risk of injury. Awareness of environmental conditions, such as weather and lighting, can help prevent accidents that might lead to injury.
In conclusion, ACL injuries and other sports-related injuries cannot be attributed solely to biomechanical flaws. They result from a complex interplay of factors within a dynamic system. By adopting a holistic approach that considers biomechanics, training, psychological factors, and external influences, we can develop more effective strategies for preventing and rehabilitating injuries. This comprehensive perspective allows us to better support athletes in achieving optimal performance while minimizing the risk of injury [
5].
Sports Navigation
In sports, the interactions between two adaptive systems, such as teams, play a crucial role in disrupting each other’s effectiveness in scoring points. These interactions are not static; they contribute to the ongoing evolution of the larger system, which is the game itself, over time. This dynamic nature of sports means that individual athletes must constantly adapt to changing conditions. The motor options available to each athlete are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including the dynamics of the environment, the specific tasks they need to perform, and their own physical and psychological states. This concept, rooted in ecological psychology, emphasizes that the way a task is performed and initiated is contingent upon these interacting elements [
6].
Suggesting that an athlete’s injury risk can be determined solely by the presence of a biomechanical defect is overly simplistic. It fails to consider the broader context of interpersonal dynamics during a game. For instance, an athlete’s movements and decisions are influenced by the actions of their teammates and opponents, as well as the immediate situational demands. These factors can either mitigate or exacerbate the impact of any biomechanical issues [
7].
To take these considerations into account, we must adopt a holistic approach to understanding and managing athletes’ performance and injury risks. This approach should integrate biomechanical assessments with an analysis of the athlete’s interactions within their sporting environment. By doing so, we can develop more effective training and rehabilitation programs that address not only the physical aspects of performance but also the strategic and adaptive elements inherent in sports. This comprehensive perspective can help in devising strategies that enhance performance while minimizing injury risks, acknowledging that an athlete’s success and safety depend on a multifaceted array of factors beyond mere biomechanics [
8].
Furthermore, this approach should involve continuous monitoring and assessment of athletes during training and competition. Advanced technologies, such as motion capture systems, wearable sensors, and real-time analytics, can provide valuable data on how athletes move and interact within the game context. By analyzing this data, coaches and medical professionals can identify patterns that may indicate potential injury risks or areas for performance improvement.
Additionally, psychological factors play a significant role in how athletes navigate the complexities of their sport. Mental resilience, decision-making under pressure, and the ability to anticipate opponents’ actions are all crucial components of athletic performance. Training programs should, therefore, incorporate psychological skills training to help athletes develop these mental attributes.
Injury prevention strategies should also be dynamic and adaptable, just like the sports environment itself. This includes developing personalized training regimens that account for an athlete’s unique physical and psychological profile, as well as their role within the team and the specific demands of their sport. Regular feedback and adjustment of these programs are essential to ensure they remain effective as the athlete and the game evolve [
9].
In conclusion, the interplay between athletes, teams, and the sporting environment is a complex and dynamic process that requires a holistic and adaptive approach to performance and injury management. By considering the ecological context of sports, incorporating advanced technologies, and addressing both physical and psychological factors, we can better support athletes in achieving their full potential while minimizing the risk of injury. This comprehensive perspective is crucial for the ongoing development and success of athletes in the ever-evolving landscape of sports [
10].
Interpersonal Dynamics: Nonlinear Pedagogy
More than two-thirds of ACL injuries result from non-contact mechanisms, many of which involve avoiding collisions such as changing direction to evade a defender. Anecdotally, many of us believe that the interpersonal dynamics of sports contribute to ACL injuries, which tend to occur more frequently in games than in training. This raises the question: do individuals at risk for (or following) ACL injuries perform worse in reactive interpersonal coordination tasks? Can this be optimized through training? If so, how?
The awareness that an opponent’s actions disrupt movement patterns challenges the validity of traditional rehabilitation approaches, which often focus on isolated skill development rather than the complex, dynamic interactions encountered in actual sports scenarios. Traditional rehabilitation might emphasize strength, stability, and controlled movements in a clinical setting, but it may not adequately prepare athletes for the real-world demands where quick, unpredictable decisions are crucial. This discrepancy raises important questions about whether we are effectively preparing athletes for the real demands of their sports [
11].
In sports, the ability to respond to the actions of others—teammates, opponents, or even the movement of the ball—requires a high level of coordination and agility. These reactive skills are crucial in preventing injuries like ACL tears, as they enable athletes to make quick, safe movements in high-stakes environments. To better prepare athletes for these challenges, a deeper understanding of our patients’ ability to adapt to environmental disruptions is essential. This involves exploring how the sensorimotor system—the integration of sensory input and motor responses—can be trained to improve an athlete’s readiness for sports.
Research suggests that athletes who can effectively process and respond to complex stimuli are better equipped to handle the dynamic nature of sports. Therefore, incorporating drills that mimic the dynamic, unpredictable nature of sports can help athletes develop better reactive strategies, enhancing their ability to avoid injuries. This method of training not only aims to improve physical readiness but also the cognitive aspects of sports performance, ultimately leading to a more holistic approach to injury prevention and rehabilitation [
12].
Key to this research is understanding how the sensorimotor system can be trained to improve an athlete’s performance in real-time, reactive situations. Nonlinear pedagogy, which emphasizes variability and adaptability in learning, can be particularly beneficial in this context. Unlike traditional training methods that rely on repetitive, predictable drills, nonlinear pedagogy involves exercises that are varied and mimic the chaotic environment of a real game. This approach helps athletes develop flexibility and resilience, enabling them to better cope with unexpected changes and avoid injuries.
For instance, training sessions could include drills where athletes must react to the sudden movements of others, adjust their trajectories on the fly, or make quick decisions under pressure. These scenarios help simulate the stress and unpredictability of actual gameplay, fostering better coordination and decision-making skills. By focusing on how athletes respond to the unpredictable actions of opponents, we can develop more effective training protocols that better simulate game conditions [
13].
Moreover, this approach to training emphasizes the importance of cognitive readiness. Athletes must be mentally prepared to make split-second decisions, which can significantly impact their physical movements and overall performance. Therefore, incorporating cognitive training elements, such as decision-making drills or situational awareness exercises, can further enhance an athlete’s ability to navigate the complexities of their sport [
14].
In conclusion, to effectively reduce the risk of ACL injuries and enhance overall athletic performance, it is crucial to integrate training methods that account for the dynamic, interpersonal nature of sports. By focusing on the sensorimotor system and employing nonlinear pedagogy, we can better prepare athletes for the real-world challenges they face, ultimately leading to safer and more effective sports participation.
Brains and Sprains
The brain is the director of sensorimotor control, orchestrating the intricate coordination between sensory input and motor output. This central role involves processing information from various sensory systems, such as visual, auditory, and proprioceptive inputs, and translating this data into precise and coordinated motor actions. Over the past two decades, extensive research has increasingly highlighted the critical role that sensorimotor control plays in determining behaviors and biomechanical deficiencies. These deficiencies can significantly contribute to the occurrence of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries or emerge as a consequence of the injury’s pathophysiology [
15].
Sensorimotor control encompasses a range of complex processes that involve the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and muscles working together to ensure proper movement and stability. The sensorimotor system operates within a constantly evolving environment, continually adapting to new stimuli and changes in the body’s internal and external conditions. This dynamic interaction underscores the complexity of the mechanisms involved in musculoskeletal rehabilitation. For instance, when an individual sustains an ACL injury, the damage can disrupt normal sensorimotor control, leading to altered movement patterns, reduced stability, and an increased risk of further injury.
A deeper investigation into these mechanisms is essential for understanding and addressing the full scope of issues related to sensorimotor control and its impact on injury prevention and recovery. By examining the intricate pathways and interactions within the sensorimotor system, researchers and clinicians can identify specific factors that contribute to the development and persistence of biomechanical flaws. Such insights are crucial for developing effective rehabilitation strategies that can mitigate the risk of ACL injuries and improve outcomes for individuals recovering from these injuries. These strategies may include targeted exercises to enhance proprioception, neuromuscular training to improve coordination, and interventions to correct faulty movement patterns [
16].
In conclusion, the brain’s role as the director of sensorimotor control is fundamental to maintaining proper movement and preventing injuries. As research continues to unravel the complexities of sensorimotor control and its influence on musculoskeletal health, it will pave the way for more effective prevention and rehabilitation approaches. This ongoing exploration holds the promise of reducing the incidence of ACL injuries and facilitating better recovery for those affected, ultimately contributing to improved long-term outcomes and quality of life for individuals engaged in physical activities [
17].
The Sensorimotor System is a Feedback Loop in Dynamic Systems
The sensorimotor system is a fundamental feedback loop within dynamic systems, intricately linking sensory input and motor output in a seamless and continuous cycle. Our central nervous system (CNS) plays a crucial role by continuously integrating sensory information from various modalities, such as visual, vestibular, somatosensory, and auditory inputs. This integration helps create a comprehensive and real-time representation of our environment, allowing us to navigate and interact with the world effectively. Subsequent motor actions are then influenced by this sensory information, altering the sensory stimuli, which in turn perpetuates the cycle. The continuous nature of this feedback loop is essential for successful motor behavior, enabling us to perform complex tasks with precision and adaptability [
18].
Beneath the surface of movement, the sensorimotor system must first distinguish between stimuli generated by the environment and the anticipated feedback produced by our own actions. This process, known as sensory discrimination and prediction, is crucial for maintaining accurate and coordinated movements. Impairments in sensory stimuli processing or sensory weighting, such as visual dependency, can disrupt the accuracy of distinguishing between external environmental stimuli and self-generated feedback. This distinction is critical because errors in sensory and motor predictions are believed to contribute to injuries, such as those involving the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). For instance, an athlete who relies too heavily on visual cues might not adequately process proprioceptive information from their joints and muscles, leading to poor movement patterns and increased injury risk [
19].
When we consider how individual variability and impairments, such as movement errors, can influence sensorimotor feedback loops, the complexity of intra-personal coordination (i.e., the ability to control our body in space) becomes apparent. This complexity is particularly pronounced in the dynamic context of sports, where precise control, rapid adjustments, and adaptation are paramount. Each individual’s unique combination of sensory integration and motor response capabilities can lead to significant differences in performance, coordination, and susceptibility to injury.
In sports and other high-demand activities, the sensorimotor system’s ability to adapt and accurately predict sensory outcomes is continuously tested. Athletes must constantly adjust their movements based on sensory feedback to maintain balance, coordination, and optimal performance. Variations in an individual’s sensory integration and motor response capabilities can lead to differences in performance and injury risk. For example, a basketball player must rapidly integrate visual information about the position of the ball and other players with proprioceptive feedback from their muscles and joints to execute precise movements and avoid collisions.
Understanding the intricacies of the sensorimotor feedback loop and its role in motor control not only provides insights into everyday movements but also highlights the importance of tailored training and rehabilitation programs to enhance performance and reduce injury risk. Rehabilitation programs, for instance, often focus on improving sensory integration and motor control through targeted exercises that challenge the sensorimotor system. By doing so, individuals can develop better coordination, reduce the risk of injury, and improve overall performance [
20].
In essence, the sensorimotor system’s feedback loop is a cornerstone of both our everyday functioning and our ability to excel in complex physical activities. It underscores the importance of a well-coordinated CNS, capable of integrating and responding to sensory information with precision and adaptability. This system’s efficiency directly impacts our ability to perform tasks ranging from simple daily activities to complex athletic maneuvers, highlighting the profound interconnectedness of sensory and motor processes in shaping human movement and behavior.
To further illustrate, consider the role of the vestibular system, which helps maintain balance and spatial orientation. It provides crucial information about head movements and spatial orientation, enabling us to keep our balance while walking, running, or performing complex movements. When the vestibular system’s input is integrated with visual and proprioceptive information, it allows for smooth and coordinated movements. However, if the vestibular system is impaired, it can lead to dizziness, imbalance, and an increased risk of falls, underscoring the delicate balance required in sensorimotor integration [
21].
Moreover, the auditory system also contributes to the sensorimotor feedback loop by providing information about the environment, such as the location of sounds and changes in auditory stimuli. This information can influence motor actions, such as turning the head towards a sound or adjusting movements in response to auditory cues. The integration of auditory information with other sensory inputs enhances our ability to react and adapt to the environment.
In summary, the sensorimotor system’s feedback loop is a dynamic and intricate process that integrates sensory information from multiple modalities to guide motor actions. The ability to accurately discriminate and predict sensory stimuli is essential for coordinated movement and injury prevention. Understanding the complexities of this system can inform the development of effective training and rehabilitation programs, ultimately enhancing performance and reducing injury risk. This comprehensive integration of sensory and motor processes is fundamental to human movement and behavior, highlighting the importance of the sensorimotor system in our daily lives and athletic endeavors [
22].
Intrinsic Dynamics
Consider a basketball point guard attempting to execute an effective lay-up. As the player approaches the basket, the sensorimotor system manages an infinite number of degrees of freedom while simultaneously perceiving the evolving environment. The player’s brain must quickly process visual information about the position of the basket, the location of defenders, and the trajectory of the ball. Simultaneously, proprioceptive feedback from the muscles and joints informs the brain about the body’s position and movement. Such sports activities require the precise coordination of distributed muscle groups and joints, which involves complex neuromuscular control. The player must constantly adjust their movements in response to dynamic visual and proprioceptive feedback, ensuring a smooth and effective lay-up. This intricate coordination showcases the remarkable adaptability of the human body, allowing athletes to perform under varying and often unpredictable conditions [
23].
Several studies support this concept, showing that individuals with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction (ACLR) exhibit a reduced ability to adapt joint coordination during single-limb balance tasks. This reduction in adaptability often manifests as increased joint stiffness, which can indicate a higher risk of re-injury. For instance, during a single-leg balance task, an individual with ACLR might display more rigid and less fluid movements compared to a healthy individual, reflecting a compromised ability to dynamically stabilize the joint. The same pattern of less variable joint coordination is also observed in gait, where ACLR patients might demonstrate a more uniform and less adaptable walking pattern. Unfortunately, these disturbances in joint coordination are less clinically tangible than more apparent issues like muscle weakness or a restricted range of motion, making them harder to diagnose and address effectively in a clinical setting. Clinicians often rely on subjective assessments and functional tests, which may not fully capture the subtle deficits in coordination and adaptability [
24].
What modifiable factors contribute to these impairments and movement errors? How can we ensure we address them effectively? It is believed that disruptions in sensory feedback within the knee joint, differences in perceptual and cognitive processing, and subsequent changes in muscle recruitment patterns significantly affect intrinsic coordination. These disruptions can stem from altered proprioceptive signals following ACL injury or reconstruction, leading to compromised sensory integration and motor output. For example, damage to the ACL can impair the sensory receptors in the knee, resulting in diminished proprioceptive feedback and a reduced ability to sense joint position and movement. Consequently, the brain receives less accurate information, affecting the precision and adaptability of motor responses [
25].
As we navigate through the complexities of the sensorimotor system, it is crucial to remember that sensory stimuli and sensory integration play vital roles in informing motor output and facilitating effective movement patterns. Addressing these issues requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates proprioceptive training, cognitive-motor exercises, and targeted rehabilitation strategies to enhance sensory feedback and coordination. Proprioceptive training might include exercises that challenge balance and joint position sense, such as single-leg stands on unstable surfaces. Cognitive-motor exercises could involve tasks that require simultaneous cognitive processing and motor execution, like dribbling a basketball while solving arithmetic problems. By focusing on these modifiable factors, we can develop more effective interventions to improve joint coordination, reduce the risk of re-injury, and enhance overall athletic performance. Moreover, advanced technologies like motion capture systems and wearable sensors can provide detailed insights into movement patterns, enabling more precise assessments and personalized rehabilitation protocols [
26].
Ultimately, understanding and improving intrinsic dynamics in athletes, especially those recovering from injuries like ACLR, can lead to better outcomes not only in terms of physical rehabilitation but also in achieving peak performance levels. Integrating multidisciplinary approaches that combine insights from biomechanics, neuroscience, and sports science will be essential in advancing our ability to support athletes in their pursuit of excellence and long-term health.
Somatosensory Afferents: What Happens to ACL Mechanoreceptors After Injury?
Proprioception, the body’s ability to sense its position, movement, and effort, is generated by specialized receptors located in ligamentous tissues, joint capsules, and the muscle-tendon units throughout the body. These receptors, known as proprioceptors, are essential for maintaining balance, coordination, and overall bodily awareness. The signals from these receptors enable the brain to perceive the position and movement of different body parts, as well as the amount of effort required to perform various tasks. The integration of this diverse and distributed array of somatosensory afferents is a highly complex process, involving multiple neural pathways and centers, including the spinal cord, cerebellum, and higher-order central nervous system (supraspinal level) [
27].
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and surrounding structures of the knee joint collectively form one of the most significant sensory organs in the human body. The ACL, which is crucial for stabilizing the knee joint, is densely packed with proprioceptors that provide critical information about joint position and movement. Unfortunately, current neuroscience techniques are not yet advanced enough to fully describe the specific information encoded in the afferent signals from these structures. However, it is evident that the presence or absence of these signals can provide critical insights into knee function following an ACL injury. For instance, individuals without an intact ACL tend to increase joint stiffness and hamstring tendon activity to compensate for the lost ligament, thereby achieving a form of active stability. This compensatory mechanism helps to maintain some degree of functionality and prevent further injury, even in the absence of the ACL [
28].
Despite these compensatory mechanisms, the state of the proprioceptive pathway following ACL reconstruction (ACLR) continues to have significant functional and clinical implications. This is particularly relevant considering that all individuals who have undergone ACLR initially experienced a period of ACL deficiency. The functional state of this pathway remains largely unknown or unmeasured during the early postoperative stages. This raises important questions about the potential clinical symptoms that could provide insights into the sensorimotor status of patients during recovery. Identifying these symptoms could help in the development of better rehabilitation protocols and improve long-term outcomes for individuals undergoing ACLR [
29].
For example, clinical symptoms such as altered gait patterns, increased reliance on visual cues for balance, and decreased coordination may indicate deficits in proprioception. Additionally, subjective reports of instability or a sense of giving way in the knee joint could also signal proprioceptive impairment. By closely monitoring these symptoms, clinicians can gain valuable information about the sensorimotor status of their patients and tailor rehabilitation programs to address specific deficits. Furthermore, advanced imaging techniques and biomechanical assessments could be utilized to measure changes in proprioceptive function over time, providing a more objective evaluation of the recovery process [
30].
In conclusion, proprioception plays a crucial role in maintaining bodily awareness and coordination, and its impairment following ACL injury and reconstruction has significant functional and clinical implications. While current neuroscience techniques are not yet able to fully describe the information encoded in proprioceptive signals, the presence or absence of these signals can provide valuable insights into knee function. By closely monitoring clinical symptoms and utilizing advanced assessment techniques, clinicians can develop more effective rehabilitation protocols to improve long-term outcomes for individuals undergoing ACL reconstruction.
Disinhibition at the Spinal Level: Effective Therapies for Inhibiting the Quadriceps Muscles
Joint injury and surgical procedures cause swelling in the joint capsule, leading to a condition known as arthrogenic muscle inhibition (AMI). AMI is a spinal-level dysfunction that disrupts the normal activation of muscles surrounding the injured joint, resulting in a significant reduction in muscle strength and function. This phenomenon is particularly evident in the quadriceps muscles following an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury and subsequent reconstruction surgery. Despite the absence of direct muscle damage, patients often experience rapid and pronounced muscle atrophy due to AMI. This is a major concern because it hampers the rehabilitation process and can delay a full recovery [
31].
Arthrogenic muscle inhibition is primarily driven by altered sensory inputs from the swollen and injured joint capsule. These abnormal inputs inhibit the motor neurons that control the quadriceps, preventing them from generating sufficient force. This inhibition is a protective mechanism intended to prevent further injury, but it also leads to muscle weakness and atrophy [
32].
Recent research has identified several disinhibitory interventions that target these altered sensory signals to mitigate the effects of AMI. Techniques such as Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and focal joint cooling have shown considerable promise in addressing the underlying neuronal mechanisms that cause AMI. TENS involves the application of low-voltage electrical currents to the skin, which stimulates sensory nerves and can modulate pain signals and muscle activation patterns. Similarly, focal joint cooling, or cryotherapy, reduces local inflammation and swelling, thereby normalizing sensory inputs and reducing muscle inhibition.
By masking the inhibitory sensory stimuli with TENS or ice, these interventions create a temporary therapeutic “window of opportunity.” During this period, the excitability and strength of the quadriceps motor units are partially restored, allowing patients to engage in more effective strengthening exercises. This temporary restoration is crucial for maximizing quadriceps strengthening during the early stages of rehabilitation, often referred to as achieving a “quiet knee.” A “quiet knee” is a state where pain and inflammation are minimized, and normal muscle function begins to return, facilitating better overall recovery [
33].
It is essential for clinicians to consider incorporating these disinhibitory techniques into their treatment protocols for patients recovering from ACL injuries. By doing so, they can enhance muscle activation, improve strength gains, and potentially expedite the rehabilitation process. However, it is important to note that while these treatments have shown effectiveness in the short term, the long-term impact on brain and central nervous system adaptations remains uncertain. Further research is needed to fully understand the chronic effects of these interventions and their role in the overall rehabilitation strategy.
In conclusion, joint injury and surgical procedures can lead to significant muscle inhibition due to altered sensory inputs and swelling. Disinhibitory interventions such as TENS and focal joint cooling offer promising solutions to mitigate these effects and aid in the recovery process. Clinicians should consider these methods to enhance muscle strength and function during the critical early stages of rehabilitation, although the long-term benefits and mechanisms still require further investigation.
Joint injury and surgical procedures cause swelling in the joint capsule, leading to a condition known as arthrogenic muscle inhibition (AMI). AMI is a spinal-level dysfunction that disrupts the normal activation of muscles surrounding the injured joint, resulting in a significant reduction in muscle strength and function. This phenomenon is particularly evident in the quadriceps muscles following an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury and subsequent reconstruction surgery. Despite the absence of direct muscle damage, patients often experience rapid and pronounced muscle atrophy due to AMI. This is a major concern because it hampers the rehabilitation process and can delay a full recovery [
34].
Arthrogenic muscle inhibition is primarily driven by altered sensory inputs from the swollen and injured joint capsule. These abnormal inputs inhibit the motor neurons that control the quadriceps, preventing them from generating sufficient force. This inhibition is a protective mechanism intended to prevent further injury, but it also leads to muscle weakness and atrophy.
Recent research has identified several disinhibitory interventions that target these altered sensory signals to mitigate the effects of AMI. Techniques such as Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and focal joint cooling have shown considerable promise in addressing the underlying neuronal mechanisms that cause AMI. TENS involves the application of low-voltage electrical currents to the skin, which stimulates sensory nerves and can modulate pain signals and muscle activation patterns. Similarly, focal joint cooling, or cryotherapy, reduces local inflammation and swelling, thereby normalizing sensory inputs and reducing muscle inhibition.
By masking the inhibitory sensory stimuli with TENS or ice, these interventions create a temporary therapeutic “window of opportunity.” During this period, the excitability and strength of the quadriceps motor units are partially restored, allowing patients to engage in more effective strengthening exercises. This temporary restoration is crucial for maximizing quadriceps strengthening during the early stages of rehabilitation, often referred to as achieving a “quiet knee.” A “quiet knee” is a state where pain and inflammation are minimized, and normal muscle function begins to return, facilitating better overall recovery.
It is essential for clinicians to consider incorporating these disinhibitory techniques into their treatment protocols for patients recovering from ACL injuries. By doing so, they can enhance muscle activation, improve strength gains, and potentially expedite the rehabilitation process. However, it is important to note that while these treatments have shown effectiveness in the short term, the long-term impact on brain and central nervous system adaptations remains uncertain. Further research is needed to fully understand the chronic effects of these interventions and their role in the overall rehabilitation strategy [
35].
In conclusion, joint injury and surgical procedures can lead to significant muscle inhibition due to altered sensory inputs and swelling. Disinhibitory interventions such as TENS and focal joint cooling offer promising solutions to mitigate these effects and aid in the recovery process. Clinicians should consider these methods to enhance muscle strength and function during the critical early stages of rehabilitation, although the long-term benefits and mechanisms still require further investigation.
The Role of the Integrative Cortex and Neurocognition
“It appears that periods of deafferentation following ACL injury are sufficient to catalyze long-term neuroplastic changes in the brain, and functional differences in brain activity exist even before the injury.” - Dave Sherman. Periods of deafferentation, which refers to the loss of sensory nerve input, following an ACL injury can lead to significant and long-lasting changes in the brain’s structure and function. This process of neuroplasticity involves the brain adapting to the new conditions by reorganizing its neural pathways. Research suggests that these changes can result in functional differences in brain activity that may even predate the injury, indicating that athletes with ACL injuries might have pre-existing neurocognitive vulnerabilities [
36].
After sensory signals are initially processed and integrated in the spinal cord, they are transmitted to the brain where higher-level sensory integration occurs. This integration is crucial for accurately predicting and responding to the dynamic environment in which an athlete operates. During a game, an athlete must rapidly interpret a vast amount of sensory information to make hundreds of motor decisions. This involves a complex interplay between visual, auditory, and proprioceptive inputs that guide movements and strategic decisions.
The key to athletic success lies in the athlete’s ability to deliberately search for, interpret, and anticipate relevant information related to both the current and future dynamics of their tasks and environment. This perceptual-cognitive control is essential for high performance. Performance is therefore constrained not only by the situational context and the athlete’s physical capabilities but also by their ability to process and act on sensory information. For instance, individuals who suffer from ACL injuries often exhibit slower neurocognitive processing speeds and delayed visuomotor reaction times even before the injury occurs. These impairments likely persist and may worsen after the injury, further complicating the recovery and return-to-play processes [
37].
Given these challenges, the question arises: can we train these perceptual-cognitive skills to enhance recovery and improve performance? The answer is yes, and there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this: Neurocognitive training programs aim to enhance brain functions such as attention, memory, and decision-making. By using computerized cognitive training, neurofeedback, and virtual reality simulations, athletes can improve their ability to process information quickly and make effective decisions under pressure. Visual training exercises improve visual skills such as tracking, depth perception, and peripheral vision, helping athletes better interpret fast-moving environments. Drills that focus on these areas can enhance eye-hand coordination and overall visual processing speed.
Dual-task training involves engaging in tasks that require simultaneous physical and cognitive effort, mimicking the demands of athletic competition. For example, performing a physical exercise while responding to cognitive challenges can train the brain to handle complex situations more efficiently. Mindfulness and focus training techniques like mindfulness meditation, focus exercises, and concentration drills can improve mental clarity and reduce the cognitive load during high-pressure situations, helping athletes maintain optimal performance levels.
Sport-specific cognitive drills integrate cognitive challenges into sport-specific drills to ensure relevance and applicability to real-game scenarios. These might include drills that require quick thinking, strategic decision-making, and rapid adaptation to changing conditions. Consistent monitoring and adaptation involve regular assessment of cognitive function using tools like reaction time tests, neurocognitive evaluations, and brain imaging to track progress and adjust training programs to meet the evolving needs of the athlete.
Implementing these training methods effectively involves a structured approach: Start with a comprehensive evaluation of the athlete’s current neurocognitive abilities to identify specific areas of weakness. Develop a tailored plan that targets the identified weaknesses while enhancing overall cognitive function. Combine cognitive and physical training regimens to create a holistic development program. Monitor progress regularly through both subjective reports and objective measurements, making necessary adjustments to the training plan. Recognize that cognitive training, like physical training, requires a long-term commitment to achieve and maintain significant improvements [
38].
By addressing the neurocognitive aspects of performance, athletes can improve their ability to process information quickly, make better decisions, and react more effectively during competition. This not only enhances performance but also reduces the risk of re-injury, promoting a safer and more effective return to play. Training these perceptual-cognitive skills can also help athletes to better anticipate the movements of their opponents, enhance their strategic thinking, and adapt to the rapid changes in the game environment. Additionally, it can help in developing mental resilience, enabling athletes to stay focused and composed under pressure, which is crucial for peak performance.
Incorporating these neurocognitive training techniques into regular practice sessions can make them a natural part of an athlete’s routine, ensuring continuous improvement. It is also beneficial to use technology and data analytics to track progress and adjust training protocols as needed, providing a more personalized and effective training experience. By integrating these methods, coaches and trainers can help athletes reach their full potential, both physically and mentally, leading to improved overall performance and a reduced likelihood of injury.
Neuronal Efficiency in Athletes
Neuronal efficiency refers to the ability of an individual to integrate a greater amount of perceptual-cognitive information compared to another, assuming a similar capacity for neural abilities. This involves not only processing more information but also executing motor actions more efficiently and exhibiting higher activity levels in the brain’s sensorimotor areas. Essentially, neuronal efficiency allows individuals to perform complex tasks with greater precision and less cognitive effort, making it a critical factor in high-level performance across various domains [
40].
Neuronal efficiency is demonstrated in various domains such as higher intelligence, musical abilities, and specialized motor skills. For instance, individuals with higher intelligence or advanced musical abilities often display enhanced neural processing capabilities, enabling them to perform tasks with minimal neural effort. In these domains, experts require less neural activity to complete standardized tasks compared to novices. This indicates a more efficient use of their brain’s resources, allowing them to perform at higher levels with less cognitive load. Musicians, for example, can play complex pieces with minimal conscious effort due to their finely tuned neural pathways developed through extensive practice and experience.
However, in complex and dynamic environments such as sports, the scenario is different. Instead of showing reduced neural activity, experts in sports utilize more neural activity. This increased activity is particularly evident in the mirror motor neuron system, which is crucial for predicting and analyzing the movements of opponents. Highly skilled athletes show greater activation of this system compared to their less skilled counterparts, enabling them to anticipate and respond to opponents’ actions more effectively. This heightened neural activity helps them navigate the fast-paced and unpredictable nature of sports, making quick decisions and executing precise movements [
41].
These findings suggest that for athletes, neuronal efficiency involves a complex interplay of increased neural activity and efficient information processing. By gradually reducing the cortical demand for simpler tasks, athletes can free up cognitive resources to handle the more demanding aspects of their sport. This allows them to process more information simultaneously and respond to the complexities and chaos inherent in sports environments more effectively. In essence, their brains become more adept at managing and integrating the barrage of sensory inputs and motor outputs required for peak performance.
Currently, research has shown that individuals who have undergone ACL reconstruction (ACLR) often exhibit increased fMRI activity in visual and attentional networks during simple rhythmic tasks. This increase in neural activity indicates a state of neuronal inefficiency, as their brains are working harder to perform tasks that would typically require less effort. This inefficiency likely stems from disruptions in neural pathways and sensory-motor integration caused by the injury and subsequent surgery. The increased demand on visual and attentional networks suggests that these individuals may be compensating for deficits in proprioceptive feedback and motor control, leading to a greater cognitive load for tasks that should be more automatic [
42].
These findings highlight the potential for neuromodulatory intervention practices aimed at enhancing neurocognitive and integrative networks. Interventions such as neurofeedback, cognitive training, and targeted physical therapy could help restore neuronal efficiency by retraining the brain to process information more effectively and reduce unnecessary neural activity. Neurofeedback, for example, can provide real-time feedback on brain activity, allowing individuals to learn how to regulate their neural processes more efficiently. Cognitive training exercises can improve attention, memory, and executive function, which are crucial for processing complex information and making quick decisions. Targeted physical therapy can focus on restoring proper motor patterns and proprioceptive feedback, reducing the cognitive load required for movement control.
In addition to these interventions, incorporating sports-specific cognitive drills into training can be beneficial. These drills can simulate the high-pressure, fast-paced environment of competitive sports, helping athletes to improve their decision-making and motor skills in a context that closely resembles actual gameplay. Techniques such as dual-task training, where athletes perform cognitive tasks while engaging in physical activities, can further enhance the integration of cognitive and motor functions [
43].
In summary, neuronal efficiency is crucial for optimal performance in both cognitive and physical domains. While it involves reduced neural activity for simpler tasks, in complex environments like sports, it requires increased neural activity to handle the additional demands. Understanding and improving neuronal efficiency through targeted interventions can lead to better performance, quicker recovery from injuries, and overall enhanced brain function. By focusing on enhancing perceptual-cognitive skills and integrating them with physical training, athletes can achieve higher levels of performance and resilience, ultimately improving their ability to compete at elite levels.
Mindfulness and Cognition
In general, selective attention prepares the cognitive system to distinguish between relevant and irrelevant features of the environment. This ability is crucial for effective interaction with the world, enabling individuals to focus on important stimuli while ignoring distractions. An increasing body of research suggests that goal-directed attention, known as external focus, results in better performance compared to self-directed attention, known as internal focus. This distinction has significant implications for ACL rehabilitation, where the focus of attention can impact recovery outcomes. Findings suggest that an external focus of attention facilitates the ability to plan, select, and execute actions with better environmental perception. This means that athletes and patients who concentrate on external cues related to their movements, such as the trajectory of a ball or the position of an opponent, perform more effectively. In contrast, an internal focus of attention, where individuals concentrate on their own movements or body parts, can divert perception away from the surrounding environment, potentially leading to suboptimal performance and slower recovery [
44].
Following ACL reconstruction (ACLR), fMRI results suggest greater cognitive demands during rhythmic motor tasks such as the infinity walk. This indicates that patients recovering from ACLR may need to exert more cognitive effort to perform tasks that would typically be more automatic. Additionally, healthy individuals at high risk of ACLR injury exhibit less variable cortical activity and cortical signs indicating less adaptive motor coordination. This lack of variability and adaptability in cortical activity suggests that these individuals might struggle with adjusting their movements to changing environments, increasing their risk of injury [
45].
Although the relationship remains theoretical, neuromuscular training strategies based on attention are targeted at these suboptimal cognitive-motor strategies. These strategies aim to enhance the adaptability and efficiency of motor coordination by training individuals to focus their attention externally. This could involve exercises that require participants to respond to external stimuli or navigate dynamic environments, thereby improving their ability to process and integrate sensory information effectively.
But does this address all aspects of neurocognitive training? What implications does the premovement period of silence have? The premovement period of silence, or the brief moment of cognitive preparation before initiating a movement, is critical for effective motor execution. During this period, the brain organizes and plans the forthcoming action, integrating sensory inputs and motor commands. Understanding and optimizing this premovement phase can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of movements, particularly in athletes recovering from injuries [
46].
The neural processes of the limbic system, which encompass emotions and memory, are intricately intertwined with motor behavior. Neuroplasticity in this system is theoretically linked to negative behavioral changes in models of lower back pain and chronic pain and has been extended to the ACLR population. This connection suggests that emotional and psychological factors can significantly impact motor control and recovery. For instance, athletes experiencing fear, anxiety, or pain may exhibit altered motor patterns and reduced coordination, hindering their rehabilitation progress. This means we need to consider the impact of motivation, fear, anxiety, pain, memory, and other factors on the motor control of our athletes. Addressing these elements through comprehensive rehabilitation programs that include psychological support and stress management techniques can improve outcomes.
Several recent articles highlight a wide range of psychological, social, and contextual factors that affect our patients’ recovery from knee injuries. Critically important for mental and social health and well-being, psychological factors have also been directly linked to quadriceps function and re-injury rates after ACLR. For example, athletes with higher levels of motivation and lower levels of fear are more likely to engage fully in rehabilitation exercises and achieve better functional outcomes. Conversely, those experiencing high levels of anxiety or depression may struggle with adherence to rehabilitation protocols and exhibit poorer recovery [
47].
Psychological, social, and contextual factors evolve with the stages of recovery and should be prioritized in the management of individuals post-ACLR. Early in the recovery process, patients may need more support to manage pain and anxiety, while later stages might focus on rebuilding confidence and returning to sport-specific activities. By integrating these factors into rehabilitation programs, clinicians can provide a more holistic approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of recovery, ultimately leading to better long-term outcomes for patients recovering from ACL injuries.
The Notorious 3 Sets of 10 Repetitions is a Myth
The basal ganglia and the connected motor cortex are crucial for action selection, initiation, and task switching of motor activities. These brain regions work together to coordinate and execute movements by integrating sensory information and motor commands. In the context of rehabilitation and training, we often focus on largely pre-planned and intentional motor activities. This approach involves repetitive exercises, such as the well-known “3 sets of 10 repetitions,” which heavily rely on the supplementary motor area (SMA). While this method can help in building strength and muscle memory, it also leads to an overreliance on a specific motor system. This traditional method of training has been the cornerstone of many rehabilitation programs due to its simplicity and effectiveness in structured environments [
48].
However, differences in neural activation between control groups and individuals with ACL reconstruction (ACLR) suggest a decreased propensity for reactive motor control in the latter group. Reactive motor control, which involves adjusting movements in response to unexpected changes or stimuli in the environment, is less utilized in traditional rehabilitation exercises. This type of movement is crucial in sports and other dynamic activities where athletes must constantly adapt to rapidly changing conditions. The premotor areas of the brain, rather than the SMA, play a significant role in these reactive movements. The premotor cortex is involved in the planning of movements, understanding the intentions of others, and integrating sensory information to guide actions [
49].
Reactive movement is likely more important in sports and utilizes a different motor system, specifically the premotor areas. This type of movement requires the brain to integrate sensory input and motor output quickly and efficiently, allowing for rapid adjustments to new or unexpected situations. In sports, athletes need to respond to opponents’ actions, changes in play, and other environmental factors, all of which demand high levels of reactive motor control. The ability to perform well under such conditions is what often separates elite athletes from their peers. Their brain’s ability to swiftly process information and execute precise movements gives them a competitive edge [
50].
This suggests the need for therapeutic exercises and research paradigms that focus on reactive motor planning in complex and changing environments. Traditional “3 sets of 10 repetitions” may not sufficiently prepare athletes for the unpredictable nature of sports. Instead, incorporating drills that simulate real-game scenarios can enhance an athlete’s ability to make quick decisions and adapt their movements accordingly. This includes exercises that require continuous adaptation of new movement assumptions and learning from predictive errors. For instance, agility drills that involve reacting to a coach’s commands, or unexpected changes in direction can help improve reactive motor skills. Such drills can include sudden stops, starts, changes in direction, and responding to visual or auditory cues, all of which mimic the unpredictable nature of sports competition.
Furthermore, incorporating technology such as virtual reality (VR) can create immersive environments where athletes can practice reactive movements in a controlled yet dynamic setting. VR can simulate various sports scenarios, providing real-time feedback and allowing athletes to refine their reactive motor skills. Additionally, neuromuscular training that emphasizes balance, coordination, and proprioception can support the development of reactive motor control by enhancing the brain’s ability to process and respond to sensory information. Tools like motion capture systems and force plates can also provide detailed insights into an athlete’s movement patterns, helping to identify areas for improvement [
51].
Cognitive training programs that include decision-making under pressure, multi-tasking exercises, and memory tasks can also play a role in enhancing reactive motor control. These programs can be designed to improve cognitive functions that are critical for sports performance, such as attention, processing speed, and working memory. For example, drills that require athletes to remember a sequence of movements or make rapid decisions based on changing scenarios can enhance both their cognitive and motor skills.
In summary, while pre-planned and repetitive exercises like “3 sets of 10 repetitions” are valuable for building foundational strength and muscle memory, they should be complemented with training that enhances reactive motor control. By incorporating exercises that simulate real-life sports scenarios and emphasize the importance of adaptability and quick decision-making, we can better prepare athletes for the dynamic and unpredictable nature of their sports. This holistic approach to training not only improves performance but also reduces the risk of injury by promoting a more responsive and adaptable motor system. It acknowledges the complexity of human movement and the need for a comprehensive strategy that addresses both the physical and cognitive aspects of athletic performance [
52].
Integrating these advanced training methods into rehabilitation and athletic training programs can significantly enhance the effectiveness of these programs. It ensures that athletes are not only physically prepared but also mentally equipped to handle the demands of their sports. This comprehensive approach can lead to better performance, quicker recovery from injuries, and a lower risk of re-injury, ultimately contributing to the long-term success and well-being of athletes.
“All or Nothing” is a Bit Harder to Achieve
The descending corticospinal pathway is crucial for initiating voluntary muscle contractions and regulating descending motor control. This neural pathway acts as a bridge between the brain and the spinal cord, transmitting signals that allow for precise and controlled movements. Within this system, the balance between excitatory and inhibitory potentials determines the transmission and activation of motor neurons, following the “all or nothing” principle. When a sufficient level of excitatory input is reached, motor neurons fire and initiate muscle contractions. However, reduced excitability of the corticospinal tracts following ACL reconstruction means that a higher level of activation is required before movement can begin. This increased threshold for activation can lead to delayed responses and decreased muscle efficiency, affecting the overall coordination and timing of muscle contractions [
53].
Despite ongoing treatment efforts, this impairment tends to worsen over time. The decreased excitability is not just a temporary setback; it reflects an underlying degeneration of the pathway itself. This degeneration can result in a progressive decline in motor function, making it increasingly difficult for patients to perform voluntary movements with the same ease and precision they once had. The weakening of this critical pathway underscores the importance of early and effective intervention to prevent long-term deficits. Over time, the continued degradation of the corticospinal tract can lead to chronic motor impairments, further complicating the rehabilitation process and limiting the potential for full recovery [
54].
Furthermore, corticospinal excitability is strongly linked to key characteristics of quadriceps muscle function, such as the rate of torque development. The rate of torque development is essential for activities that require quick and powerful muscle contractions, such as jumping, sprinting, and sudden directional changes. A reduction in corticospinal excitability can therefore lead to a decrease in these functional capabilities, hindering the overall recovery of motor functions. This relationship highlights the importance of maintaining and enhancing corticospinal excitability as a central goal of rehabilitation programs. Reduced rate of torque development not only impacts athletic performance but also daily activities, increasing the risk of falls and other injuries due to compromised muscle function [
55].
To address this challenge, it is crucial to develop and adopt treatment strategies that enhance the excitability of the corticospinal system. EMG biofeedback is one promising option. This technique involves providing patients with real-time feedback on their muscle activity, helping them to consciously improve their motor control and activation patterns. By visualizing their muscle activity, patients can make adjustments to their movements, fostering greater awareness and control. Motor imagery, another effective strategy, involves patients mentally rehearsing movements without actually performing them, which has been shown to enhance motor pathway activation and improve physical performance. Imagery practice can stimulate similar neural pathways as actual movement, promoting motor learning and recovery.
Ballistic exercises, which involve rapid and forceful muscle contractions, can also stimulate the corticospinal pathway and enhance neuromuscular function. These exercises challenge the neuromuscular system to generate quick bursts of power, which can improve the speed and efficiency of neural transmission. Eccentric exercises, which focus on the controlled lengthening of muscles under tension, are known to be particularly effective in strengthening muscles and improving motor control. Eccentric training helps in muscle hypertrophy and neuromuscular adaptation, providing a strong stimulus for recovery and rehabilitation [
56].
In addition to these specific interventions, a multi-faceted approach that combines various therapies may yield the best outcomes. For example, integrating strength training, balance exercises, and proprioceptive training with neuromuscular reeducation techniques can create a comprehensive rehabilitation program. Using technology, such as virtual reality (VR) and robotic-assisted therapy, can also enhance rehabilitation by providing immersive and interactive environments for patients to practice and refine their motor skills [
57].
Furthermore, understanding the psychological aspects of recovery is crucial. Motivation, fear, and anxiety can significantly impact the rehabilitation process. Psychological support, including motivational interviewing and cognitive-behavioral therapy, can help patients overcome mental barriers and stay engaged in their recovery. Addressing these factors can improve compliance with rehabilitation protocols and enhance overall outcomes [
58].
Integrating these techniques into rehabilitation programs can create a more comprehensive approach to restoring motor function. By focusing on enhancing corticospinal excitability, we can help patients regain their ability to perform voluntary movements efficiently and effectively. This holistic approach not only addresses the physical aspects of recovery but also supports the neural mechanisms underlying motor control, leading to more sustainable and long-term improvements in function. Ultimately, a well-rounded rehabilitation program that combines physical, technological, and psychological interventions will provide the best chance for patients to achieve full recovery and return to their desired activities.
What Happens in the Muscle
A primary clinical feature in individuals with ACLR (anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction) is quadriceps muscle atrophy. This condition is characterized by a significant reduction in muscle mass and strength, which can severely impact the overall functionality and performance of the affected leg. Clinicians struggle with persistent inhibition, atrophy, and weakness of the quadriceps muscle. These challenges are often compounded by the difficulty in fully reactivating the muscle and achieving pre-injury levels of strength and control. Addressing quadriceps atrophy is crucial because the quadriceps play a vital role in knee stability, shock absorption, and overall lower limb functionality [
59].
Denervation, which is the separation of nerve tissue from muscles, severely limits the ability to voluntarily contract muscles. This condition disrupts the normal communication between the nervous system and the muscle fibers, leading to a cascade of detrimental changes within the muscle tissue. One of the most noticeable changes is an increase in intramuscular fat deposits. These fat deposits can interfere with muscle contraction and further weaken the muscle, making it less efficient and more prone to fatigue. This accumulation of fat within the muscle tissue not only affects muscle strength but also its metabolic health, potentially leading to further complications such as insulin resistance [
60].
In addition to fat accumulation, denervation catalyzes fiber type transformations within the muscle. Typically, muscle fibers can be classified into different types based on their contraction speed and endurance properties. Denervation often causes a shift from fast-twitch to slow-twitch muscle fibers, or vice versa, depending on the specific conditions and duration of denervation. These changes can alter the muscle’s performance characteristics, making it less suited for rapid, powerful movements or sustained endurance activities. The loss of fast-twitch fibers, which are essential for explosive movements, can significantly impair an athlete’s ability to perform at high levels [
61].
Furthermore, denervation enhances circulating atrophy mediators. These mediators, such as inflammatory cytokines and other biochemical signals, promote muscle breakdown and prevent muscle growth. The presence of these mediators accelerates the process of muscle atrophy, leading to a more rapid loss of muscle mass and strength. Chronic inflammation associated with these mediators can further exacerbate muscle weakness and delay the healing process. The inflammatory response also affects surrounding tissues and can contribute to pain and discomfort, complicating the rehabilitation process [
62].
Another critical effect of denervation is the decrease in the number of satellite cells. Satellite cells are essential for muscle repair and regeneration. They are a type of stem cell that resides within the muscle tissue and can differentiate into new muscle fibers in response to injury or stress. A reduction in satellite cells compromises the muscle’s ability to recover from damage, making it harder to rebuild muscle mass and regain strength after ACLR. The depletion of these regenerative cells can lead to incomplete or inadequate muscle repair, prolonging recovery times and reducing overall functional outcomes [
63].
To address these myological disturbances, treatments such as blood flow restriction (BFR) and eccentric exercises have been developed. Blood flow restriction involves applying a constrictive device to the limb to partially restrict blood flow during exercise. This technique creates a hypoxic environment within the muscle, which has been shown to stimulate muscle growth and strength gains even with low-intensity exercises. BFR can enhance muscle protein synthesis, increase the recruitment of muscle fibers, and promote greater muscle hypertrophy. The hypoxic environment also encourages the production of growth factors and other anabolic signals that facilitate muscle repair and growth [
64].
Eccentric exercises, on the other hand, focus on the lengthening phase of muscle contractions. These exercises place a high level of tension on the muscle, which can induce muscle damage and subsequently stimulate muscle repair and growth. Eccentric training is particularly effective in increasing muscle strength and size, as it engages more muscle fibers and creates a more significant adaptive response compared to concentric or isometric exercises. The mechanical stress from eccentric contractions helps to realign muscle fibers, reduce intramuscular fat, and improve overall muscle architecture [
65].
In addition to these specific interventions, a comprehensive rehabilitation approach that integrates various therapeutic modalities can yield optimal results. For example, combining BFR and eccentric exercises with neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) can further enhance muscle activation and strength. NMES uses electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contractions, helping to maintain muscle mass and prevent atrophy during periods of reduced voluntary activity.
Moreover, incorporating functional training that mimics real-life movements can improve the transfer of strength gains to daily activities and sports. Exercises that challenge balance, coordination, and agility can enhance neuromuscular control and overall functional performance. Plyometric exercises, which involve explosive movements like jumping and hopping, can also be beneficial for rebuilding power and speed in the quadriceps [
66].
Nutritional support plays a crucial role in muscle recovery as well. Adequate protein intake is essential for muscle protein synthesis and repair. Nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and antioxidants can help reduce inflammation and support muscle health. Hydration and overall dietary balance are also important for optimizing recovery and performance.
Psychological factors should not be overlooked in the rehabilitation process. Motivation, adherence to the rehabilitation program, and mental well-being significantly impact recovery outcomes. Providing psychological support and setting realistic, achievable goals can help patients stay committed to their rehabilitation journey [
67].
Integrating these techniques into rehabilitation programs can create a more comprehensive approach to restoring motor function. By focusing on enhancing corticospinal excitability and addressing the multiple factors contributing to muscle atrophy and weakness, we can help patients regain their ability to perform voluntary movements efficiently and effectively. This holistic approach not only addresses the physical aspects of recovery but also supports the neural mechanisms underlying motor control, leading to more sustainable and long-term improvements in function. Ultimately, a well-rounded rehabilitation program that combines physical, technological, nutritional, and psychological interventions will provide the best chance for patients to achieve full recovery and return to their desired activities [
68].
Neuromuscular Control as a Transistor to Understanding ACL Injuries
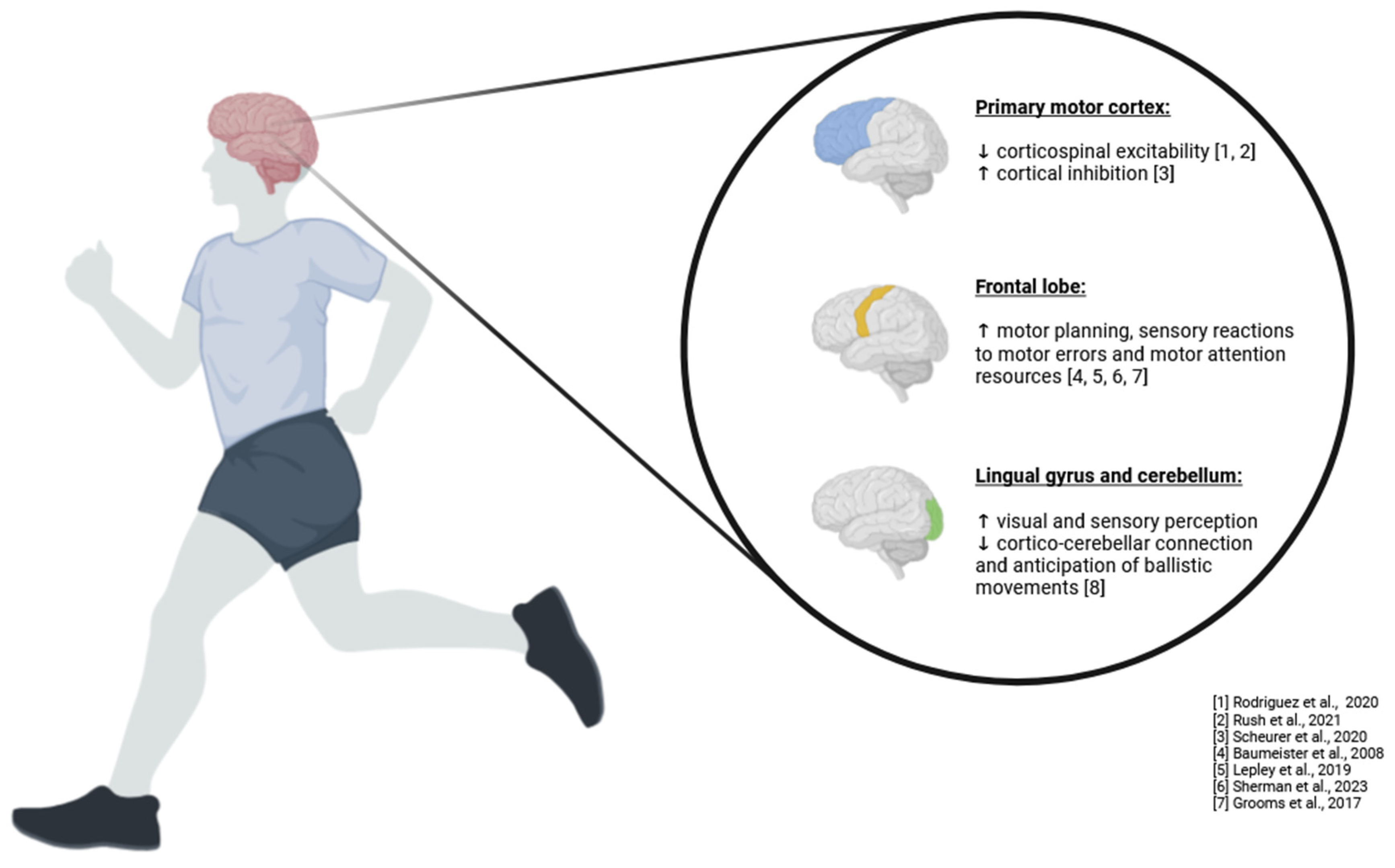
The term “neuromuscular control” encompasses a spectrum of human functions, ranging from afferent input, processing of this input, generation of efferent output, and overall system coordination. Neuromuscular control involves the ability to effectively manage and execute movement by seamlessly integrating sensory information from the body with motor commands from the brain (
Figure 1). This complex process is essential for maintaining balance, performing coordinated movements, and adapting to changing environments [
69].
Neuromuscular control also has a temporal component in continuous feedback loops between sensory and motor processing that contribute to the final measurable outcome. As muscles contract and body segments move, the afferent system continuously sends new signals to the motor system to update position, generate force, represent the environment, and account for other factors related to the output signal. These feedback loops ensure that movements are precise, adaptable, and efficient, allowing for real-time adjustments to maintain optimal performance. This constantly updated system represents the profile of neuromuscular control, which is crucial for movement control and the execution of motor tasks. Effective neuromuscular control enables individuals to perform complex tasks, such as walking on uneven surfaces or catching a ball, with accuracy and confidence [
70].
To experimentally capture the neuromuscular control system, a largely behaviorist and functionalist methodology has dominated the field, relying on a postural-structural-biomechanical approach. This dominant method primarily concerns measuring the final performance of the system in terms of joint biomechanics without quantifying the underlying mechanisms driving this mechanics. While this approach provides valuable insights into movement patterns and joint function, it often overlooks the intricate neural processes that underpin these behaviors. This behaviorist or outcome-oriented approach does not consider the extensive neural computations involved in sensory processing along vestibular, visual, and somatosensory pathways, which in turn allow for stability and control in a changing environment. Proprioception, force control, and the kinesthetic input from the sensory system are crucial for organizing motor performance and maintaining the integrity of neuromuscular control. Understanding these neural computations and their contributions to movement can lead to more effective rehabilitation strategies and improved outcomes for individuals with movement disorders or injuries [
71].
The ACL is unique compared to most ligamentous structures because it has strong afferent connections to the spinal cord and brain. This extensive neural connectivity allows the ACL to play a significant role in providing sensory feedback that influences motor control and stability. This is due to the large number of mechanoreceptors, such as free nerve endings, Ruffini’s endings, Pacinian corpuscles, and Golgi receptors in the synovial membrane of the ACL, which significantly contribute to its afferent function. These mechanoreceptors detect changes in joint position, movement, and load, sending critical information to the CNS to help coordinate protective reflexes and conscious movement adjustments. Restoring these important neurological features has not been well understood in clinical settings but may prove crucial for future functioning post-ACL injury. The interaction between proprioceptive stimuli, such as those from the ACL, and visual stimuli plays a key role in providing the overall afferent signal to the CNS for regulating the movement control feedback loop. This integration ensures that movements are well-coordinated and appropriately adjusted based on the current context and environmental demands [
72].
The brain receives somatosensory information in the thalamus and primary somatosensory cortex (through Brodmann areas 3-1-2), then integrates this afferent information in the posterior parietal cortex, in areas 5 and 7. These regions are involved in processing sensory input and transforming it into spatial representations of the body and surroundings. The temporal lobe is also involved here, playing a role in integrating sensory information with memory and other cognitive processes. Processed vestibular and visual information integrates with somatosensory input before being transmitted to the premotor cortex (area 8) and finally to the motor cortex (area 6) for motor drive. This hierarchical processing pathway allows the CNS to generate precise and coordinated motor commands that account for the body’s position, movement, and external environment [
73].
Musculoskeletal injuries can alter the flow of somatosensory, vestibular, and visual processing in the CNS to maintain motor control. These injuries can disrupt the normal feedback loops and neural computations necessary for effective movement, leading to compensatory changes in motor planning and control. To preserve neuromuscular integrity in the case of joint injury, the CNS may compensate by altering motor planning, regulating integrated sensory information reaching motor areas, increasing reliance on visual feedback or working memory, but also by changing corticospinal drive. This functional reorganization of the CNS is most likely due to the loss of mechanoreceptors in the damaged tissue, contributing to reduced afferent input. This weakened sensory function persists even years after injury and despite normalized strength in surrounding muscles [
74].
It is a likely source of neuroplasticity following musculoskeletal injury; hence, studying methods that address the sensory-visual-motor system along with the neuromuscular system in rehabilitation can improve patient function and reduce the risk of re-injury. By leveraging neuroplasticity, we can develop targeted interventions that enhance the CNS’s ability to adapt and reorganize, leading to better recovery outcomes. This approach involves using advanced techniques such as proprioceptive training, virtual reality environments, and neuromuscular electrical stimulation to stimulate the sensory-motor pathways and promote functional recovery. By integrating these methods into rehabilitation programs, we can create more effective and comprehensive treatment plans that address the complex interplay between sensory input, motor output, and neural processing. This holistic approach can help patients regain optimal neuromuscular control, improve movement quality, and reduce the likelihood of future injuries [
75].
What’s Next?
As trainers, we cannot continue doing the same thing and expect different results. Considering a single change in the sensorimotor system, such as altered sensory afferentation following ACLR, the central nervous system (CNS) must gradually adapt throughout its distributed network in a way that maintains key behavioral traits (e.g., balance, gait). This adaptation process is essential for regaining functional abilities and preventing further injury. The complexity of the CNS makes it extremely difficult to know where to intervene, but we cannot be afraid to try. The CNS is incredibly adaptable, and neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections—provides a foundation for recovery and rehabilitation. Changes in the CNS are not permanently fixed, and the potential to induce long-term neuroplastic changes has been demonstrated in populations with much greater denervation (e.g., stroke, spinal cord injury). This plasticity offers hope that, with the right interventions, we can facilitate significant recovery even in cases of severe injury [
76].
The future of ACL injury rehabilitation must incorporate interventions that guide beneficial neuroplasticity through neuromodulation. This approach involves using techniques that influence neural activity to promote healing and functional recovery. Moving forward, it will be necessary to globally appreciate the embodied sensorimotor system to systematically and scientifically test these theories. This holistic perspective acknowledges the intricate interplay between the body and the brain in movement and rehabilitation. This will require diverse neurophysiological and neurochemical assessments, such as electromyography (EMG), functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), and blood biomarkers, to understand the underlying mechanisms of recovery. With the most important aspect being the integration of clinical knowledge, consideration of patient experience, and utilization of available methods, we can develop more effective, personalized rehabilitation protocols [
77].
Areas where we need deeper understanding include interpersonal dynamics, changes in neural networks, reactive motor control, and insights into psychological, social, and contextual factors. Interpersonal dynamics, such as the interactions between patients and therapists, can significantly influence rehabilitation outcomes. Understanding changes in neural networks will help us identify which neural pathways are most affected by injury and how they can be rehabilitated. Reactive motor control is critical for responding to unexpected changes in the environment, a skill that is especially important in sports. Psychological factors, such as motivation and fear, as well as social and contextual influences, such as support systems and the rehabilitation environment, also play vital roles in recovery. For now, there are interventions that exist and should be applied to induce beneficial plasticity by targeting spinal reflex excitability, re-sensitization of the sensorimotor system, visuomotor dependency, corticospinal excitability, and local muscle growth factors. Techniques like EMG biofeedback, proprioceptive training, visual-motor integration exercises, and specific strength training protocols can be used to address these targets [
78].
In summary, embracing a multifaceted approach that integrates neuromodulation and neuroplasticity principles can significantly enhance ACL injury rehabilitation. By continually advancing our understanding of the CNS and its adaptability, we can develop innovative and effective rehabilitation strategies that not only restore function but also optimize overall performance and well-being.
References
- Griffin LY, Agel J, Albohm MJ, et al. Noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injuries: risk factors and prevention strategies. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000;8(3):141-150. [CrossRef]
- Gupta AS, Pierpoint LA, Comstock RD, Saper MG. Sex-Based Differences in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries Among United States High School Soccer Players: An Epidemiological Study. Orthopaedic journal of sports medicine. 2020;8(5):2325967120919178-2325967120919178. [CrossRef]
- Santos R, Duarte R, Davids K, Teoldo I. Interpersonal Coordination in Soccer: Interpreting Literature to Enhance the Representativeness of Task Design, From Dyads to Teams. Front Psychol. 2018;9:2550.
- Gibson JJ. The ecological approach to visual perception. 1979. [CrossRef]
- Brooks JX, Cullen KE. Predictive Sensing: The Role of Motor Signals in Sensory Processing. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2019;4(9):842-850. [CrossRef]
- Wolpert DM, Flanagan JR. Motor prediction. Curr Biol. 2001;11(18):R729-R732.
- Straka H, Simmers J, Chagnaud BP. A New Perspective on Predictive Motor Signaling. Curr Biol. 2018;28(5):R232-R243. [CrossRef]
- Diekfuss JA, Grooms DR, Yuan W, et al. Does brain functional connectivity contribute to musculoskeletal injury? A preliminary prospective analysis of a neural biomarker of ACL injury risk. J Sci Med Sport. 2019;22(2):169-174. [CrossRef]
- Kiefer AW, Ford KR, Paterno MV, et al. Inter-segmental postural coordination measures differentiate athletes with ACL reconstruction from uninjured athletes. Gait Posture. 2013;37(2):149-153. [CrossRef]
- Paterno MV, Kiefer AW, Bonnette S, et al. Prospectively identified deficits in sagittal plane hip-ankle coordination in female athletes who sustain a second anterior cruciate ligament injury after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and return to sport. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30(10):1094-1101. [CrossRef]
- Moraiti CO, Stergiou N, Ristanis S, et al. The effect of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction on stride-to-stride variability. Arthroscopy. 2009;25(7):742-749. [CrossRef]
- Riemann BL, Lephart SM. The sensorimotor system, part I: the physiologic basis of functional joint stability. J Athl Train. 2002;37(1):71-79.
- Kandel ER, Mack S. Principles of neural science. 2014.
- Johansson H, Sjolander P, Sojka P. A sensory role for the cruciate ligaments. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991(268):161-178.
- Courtney CA, Rine RM. Central somatosensory changes associated with improved dynamic balance in subjects with anterior cruciate ligament deficiency. Gait Posture. 2006;24(2):190-195. [CrossRef]
- Ochi M, Iwasa J, Uchio Y, Adachi N, Sumen Y. The regeneration of sensory neurones in the reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81(5):902-906. [CrossRef]
- Sonnery-Cottet B, Saithna A, Quelard B, et al. Arthrogenic muscle inhibition after ACL reconstruction: a scoping review of the efficacy of interventions. Br J Sports Med. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Gokeler A, McKeon PO, Hoch MC. Shaping the Functional Task Environment in Sports Injury Rehabilitation: A Framework to Integrate Perceptual-Cognitive Training in Rehabilitation. Athletic Training & Sports Health Care. 2020;12(6):283-292. [CrossRef]
- Swanik CB, Covassin T, Stearne DJ, Schatz P. The relationship between neurocognitive function and noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(6):943-948. [CrossRef]
- Guo Z, Li A, Yu L. “Neural Efficiency” of Athletes’ Brain during Visuo-Spatial Task: An fMRI Study on Table Tennis Players. Front Behav Neurosci. 2017;11:72.
- Cross ES, Schmitt PJ, Grafton ST. Neural substrates of contextual interference during motor learning support a model of active preparation. J Cogn Neurosci. 2007;19(11):1854-1871. [CrossRef]
- Dunst B, Benedek M, Jauk E, et al. Neural efficiency as a function of task demands. Intelligence. 2014;42(100):22-30. [CrossRef]
- Medina D, Barraza P. Efficiency of attentional networks in musicians and non-musicians. Heliyon. 2019;5(3):e01315. [CrossRef]
- Yang C, Luo N, Liang M, et al. Altered Brain Functional Connectivity Density in Fast-Ball Sports Athletes With Early Stage of Motor Training. Front Psychol. 2020;11:530122. [CrossRef]
- Bishop DT, Wright MJ, Jackson RC, Abernethy B. Neural bases for anticipation skill in soccer: an FMRI study. J Sport Exerc Psychol. 2013;35(1):98-109. [CrossRef]
- Orgs G, Dombrowski J-H, Heil M, Jansen-Osmann P. Expertise in dance modulates alpha/beta event-related desynchronization during action observation. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27(12):3380-3384.
- Criss CR, Onate JA, Grooms DR. Neural activity for hip-knee control in those with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A task-based functional connectivity analysis. Neurosci Lett. 2020;730:134985.
- Wulf G, Lewthwaite R. Optimizing performance through intrinsic motivation and attention for learning: The OPTIMAL theory of motor learning. Psychon Bull Rev. 2016;23(5):1382-1414. [CrossRef]
- Gokeler A, Neuhaus D, Benjaminse A, Grooms DR, Baumeister J. Principles of Motor Learning to Support Neuroplasticity After ACL Injury: Implications for Optimizing Performance and Reducing Risk of Second ACL Injury. Sports Med. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Diekfuss JA, Bonnette S, Hogg JA, et al. Practical Training Strategies to Apply Neuro-Mechanistic Motor Learning Principles to Facilitate Adaptations Towards Injury-Resistant Movement in Youth. Journal of Science in Sport and Exercise. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Bonnette S, Diekfuss JA, Grooms DR, et al. Electrocortical dynamics differentiate athletes exhibiting low- and high- ACL injury risk biomechanics. Psychophysiology. 2020:e13530. [CrossRef]
- Diekfuss JA, Grooms DR, Bonnette S, et al. Real-time biofeedback integrated into neuromuscular training reduces high-risk knee biomechanics and increases functional brain connectivity: A preliminary longitudinal investigation. Psychophysiology. 2020;57(5):e13545. [CrossRef]
- Truong LK, Mosewich AD, Holt CJ, Le CY, Miciak M, Whittaker JL. Psychological, social and contextual factors across recovery stages following a sport-related knee injury: a scoping review. Br J Sports Med. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Lisee CM, DiSanti JS, Chan M, et al. Gender Differences in Psychological Responses to Recovery After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Before Return to Sport. J Athl Train. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Burland JP, Lepley AS, Cormier M, DiStefano LJ, Lepley LK. Examining the Relationship Between Neuroplasticity and Learned Helplessness After ACLR: Early Versus Late Recovery. J Sport Rehabil. 2020:1-8. [CrossRef]
- McPherson AL, Feller JA, Hewett TE, Webster KE. Psychological Readiness to Return to Sport Is Associated With Second Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(4):857-862. [CrossRef]
- Rush JL, Glaviano NR, Norte GE. Assessment of Quadriceps Corticomotor and Spinal-Reflexive Excitability in Individuals with a History of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Lepley AS, Ly MT, Grooms DR, Kinsella-Shaw JM, Lepley LK. Corticospinal tract structure and excitability in patients with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A DTI and TMS study. Neuroimage Clin. 2020;25:102157. [CrossRef]
- Scheurer SA, Sherman DA, Glaviano NR, Ingersoll CD, Norte GE. Corticomotor function is associated with quadriceps rate of torque development in individuals with ACL surgery. Exp Brain Res. 2020;238(2):283-294. [CrossRef]
- Gabler C, Kitzman PH, Mattacola CG. Targeting quadriceps inhibition with electromyographic biofeedback: a neuroplastic approach. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2013;41(2):125-135. [CrossRef]
- Grospretre S, Lebon F, Papaxanthis C, Martin A. New evidence of corticospinal network modulation induced by motor imagery. J Neurophysiol. 2016;115(3):1279-1288. [CrossRef]
- Lepley LK, Davi SM, Burland JP, Lepley AS. Muscle Atrophy After ACL Injury: Implications for Clinical Practice. Sports Health. 2020:1941738120944256. [CrossRef]
- Lisee C, Lepley AS, Birchmeier T, O’Hagan K, Kuenze C. Quadriceps strength and volitional activation after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Health. 2019;11(2):163-179. [CrossRef]
- Lambert B, Hedt CA, Jack RA, et al. Blood Flow Restriction Therapy Preserves Whole Limb Bone and Muscle Following ACL Reconstruction. Orthopaedic Journal of Sports Medicine. 2019;7(3_suppl2):2325967119S2325900196. [CrossRef]
- Davies WT, Ryu JH, Graham-Smith P, Goodwin JE, Cleather DJ. Stronger Subjects Select a Movement Pattern That May Reduce Anterior Cruciate Ligament Loading During Cutting. J Strength Cond Res. 2022 Jul 1;36(7):1853-1859. Epub 2021 Mar 8. PMID: 35730770. [CrossRef]
- Della Villa F, Buckthorpe M, Grassi A, Nabiuzzi A, Tosarelli F, Zaffagnini S, Della Villa S. Systematic video analysis of ACL injuries in professional male football (soccer): injury mechanisms, situational patterns and biomechanics study on 134 consecutive cases. Br J Sports Med. 2020 Dec;54(23):1423-1432. Epub 2020 Jun 19. PMID: 32561515. [CrossRef]
- Detherage JP, Divine JG, Donaworth MA, Palmer TG, Hagen JA, Hasselfeld KA, Eifert-Mangine M, Mangine RE, Clark JF, Grawe BM. Physiological Monitoring Detected Changes During Women’s Soccer Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Cureus. 2021 May 4;13(5):e14838. PMID: 34123609; PMCID: PMC8191855. [CrossRef]
- Devana SK, Solorzano CA, Vail J, Jackson N, Pham D, Jones KJ. Outcomes of Blood Flow Restriction Training After ACL Reconstruction in NCAA Division I Athletes. Orthop J Sports Med. 2024 May 13;12(5):23259671241248589. PMID: 38745915; PMCID: PMC11092532. [CrossRef]
- Alejandra Díaz M, Smeets A, Hagen M, Sankey SP, Verschueren S, Vanrenterghem J. Postural balance strategies during landing at the moment of return-to-sports after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Biomech. 2022 Dec;145:111381. Epub 2022 Nov 8. PMID: 36403526. [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo S, Bragonzoni L, Della Villa F, Grassi A, Zaffagnini S. Do healthy athletes exhibit at-risk biomechanics for anterior cruciate ligament injury during pivoting movements? Sports Biomech. 2022 Jun 2:1-14. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35652896. [CrossRef]
- Dischiavi SL, Wright AA, Heller RA, Love CE, Salzman AJ, Harris CA, Bleakley CM. Do ACL Injury Risk Reduction Exercises Reflect Common Injury Mechanisms? A Scoping Review of Injury Prevention Programs. Sports Health. 2022 Jul-Aug;14(4):592-600. Epub 2021 Aug 25. PMID: 34433324; PMCID: PMC9214897. [CrossRef]
- Drole K, Paravlic AH. Interventions for increasing return to sport rates after an anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery: A systematic review. Front Psychol. 2022 Aug 22;13:939209. PMID: 36072023; PMCID: PMC9443932. [CrossRef]
- Dos’Santos T, McBurnie A, Donelon T, Thomas C, Comfort P, Jones PA. A qualitative screening tool to identify athletes with ‘high-risk’ movement mechanics during cutting: The cutting movement assessment score (CMAS). Phys Ther Sport. 2019 Jul;38:152-161. Epub 2019 May 23. PMID: 31153108. [CrossRef]
- Duthon VB, Barea C, Abrassart S, Fasel JH, Fritschy D, Ménétrey J. Anatomy of the anterior cruciate ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006 Mar;14(3):204-13. Epub 2005 Oct 19. PMID: 16235056. [CrossRef]
- Emami F, Negahban H, Sinaei E, Mostafaee N, Shahtahmassebi B, Ebrahimzadeh MH, Mehravar M. The Effects of Various Cognitive Tasks Including Working Memory, Visuospatial, and Executive Function on Postural Control in Patients With Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury. Motor Control. 2024 Jan 22;28(2):193-209. PMID: 38253046. [CrossRef]
- Fältström A, Hägglund M, Hedevik H, Kvist J. Poor Validity of Functional Performance Tests to Predict Knee Injury in Female Soccer Players With or Without Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2021 May;49(6):1441-1450. Epub 2021 Apr 12. PMID: 33844590. [CrossRef]
- Fausett WA, Reid DA, Larmer PJ. Current perspectives of New Zealand physiotherapists on rehabilitation and return to sport following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A survey. Phys Ther Sport. 2022 Jan;53:166-172. Epub 2021 Oct 21. PMID: 34711502. [CrossRef]
- Figueroa D, Arce G, Espregueira-Mendes J, Maestu R, Mosquera M, Williams A, Parker D, Cohen M, Karahan M, Ochoa Perea GA, Zaffagnini S, Neyret P, Karlsson J, Musahl V, Radice F, van der Merwe WM, Landreau P, Imhoff A, Menetrey J, Ayeni OR, Arliani GG, Sherman SL, Monllau JC, D’Hooghe P, Pinczewski L, Feller J, Patnaik S. Return to sport soccer after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: ISAKOS consensus. J ISAKOS. 2022 Dec;7(6):150-161. Epub 2022 Aug 23. PMID: 35998884. [CrossRef]
- Fleming BC. Fifty Years of ACL Biomechanics: What’s Next? Am J Sports Med. 2022 Dec;50(14):3745-3748. PMID: 36472484. [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez P, Pecci J, Vázquez-González S, Pareja-Galeano H. Acute and Chronic Effects of Blood Flow Restriction Training in Physically Active Patients With Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review. Sports Health. 2023 Nov 9:19417381231208636. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37946502. [CrossRef]
- Gholami F, Letafatkar A, Moghadas Tabrizi Y, Gokeler A, Rossettini G, Ghanati HA, Schöllhorn WI. Comparing the Effects of Differential and Visuo-Motor Training on Functional Performance, Biomechanical, and Psychological Factors in Athletes after ACL Reconstruction: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 13;12(8):2845. PMID: 37109182; PMCID: PMC10142379. [CrossRef]
- Giesche F, Vieluf S, Wilke J, Engeroff T, Niederer D, Banzer W. Cortical Motor Planning and Biomechanical Stability During Unplanned Jump Landings in Men With Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. J Athl Train. 2022 Jun 1;57(6):547-556. PMID: 35969662; PMCID: PMC9387379. [CrossRef]
- Gokeler A, Seil R, Kerkhoffs G, Verhagen E. A novel approach to enhance ACL injury prevention programs. J Exp Orthop. 2018 Jun 18;5(1):22. PMID: 29916182; PMCID: PMC6005994. [CrossRef]
- Gokeler A, Neuhaus D, Benjaminse A, Grooms DR, Baumeister J. Principles of Motor Learning to Support Neuroplasticity After ACL Injury: Implications for Optimizing Performance and Reducing Risk of Second
ACL Injury. Sports Med. 2019 Jun;49(6):853-865. Erratum in: Sports Med.
2019 Jun;49(6):979. doi: 10.1007/s40279-019-01078-w. PMID: 30719683; PMCID: PMC6548061. [CrossRef]
- Gokeler A, Dingenen B, Hewett TE. Rehabilitation and Return to Sport Testing After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Where Are We in 2022? Arthrosc Sports Med Rehabil. 2022 Jan 28;4(1):e77-e82. PMID: 35141539; PMCID: PMC8811523. [CrossRef]
- Gokeler A, Grassi A, Hoogeslag R, van Houten A, Lehman T, Bolling C, Buckthorpe M, Norte G, Benjaminse A, Heuvelmans P, Di Paolo S, Tak I, Villa FD. Return to sports after ACL injury 5 years from now: 10 things we must do. J Exp Orthop. 2022 Jul 30;9(1):73. Erratum in: J Exp Orthop. 2022 Nov 17;9(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s40634-022-00548-x. PMID: 35907095; PMCID: PMC9339063. [CrossRef]
- Gokeler A, Tosarelli F, Buckthorpe M, Della Villa F. Neurocognitive Errors and Noncontact Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries in Professional Male Soccer Players. J Athl Train. 2024 Mar 1;59(3):262-269. PMID: 37248515; PMCID: PMC10976343. [CrossRef]
- Golberg E, Sommerfeldt M, Pinkoski A, Dennett L, Beaupre L. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Return-to-Sport Decision-Making: A Scoping Review. Sports Health. 2024 Jan-Feb;16(1):115-123. Epub 2023 Jan 27. PMID: 36707977; PMCID: PMC10732109. [CrossRef]
- Gopinatth V, Smith MV, Matava MJ, Brophy RH, Knapik DM. Most Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries in Professional Athletes Occur Without Contact to the Injured Knee: A Systematic Review of Video Analysis Studies. Arthroscopy. 2024 Apr 23:S0749-8063(24)00275-5. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38663569. [CrossRef]
- Grooms DR, Page SJ, Nichols-Larsen DS, Chaudhari AM, White SE, Onate JA. Neuroplasticity Associated With Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2017 Mar;47(3):180-189. Epub 2016 Nov 5. PMID: 27817301. [CrossRef]
- Grooms D, Appelbaum G, Onate J. Neuroplasticity following anterior cruciate ligament injury: a framework for visual-motor training approaches in rehabilitation. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2015 May;45(5):381-93. Epub 2015 Jan 10. PMID: 25579692. [CrossRef]
- Grooms DR, Chaput M, Simon JE, Criss CR, Myer GD, Diekfuss JA. Combining Neurocognitive and Functional Tests to Improve Return-to-Sport Decisions Following ACL Reconstruction. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2023 Aug;53(8):415–419. PMID: 37186672; PMCID: PMC10847844. [CrossRef]
- Gureck AE, Crockett Z, Barsky BW, Samuels S, Frank JS, Storer SK, Fazekas ML. Do Differences Exist in Impact Test Domains between Youth Athletes with and without an Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury? Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;11(20):2764. PMID: 37893838; PMCID: PMC10606848. [CrossRef]
- Hamdan M, Haddad B, Alshrouf MA, Azzam MI, Isleem U, Hamasha R, Albtoush OM, Alhusban MT, Mubarak N, Alryalat SA. Can MRI knee joint measurements predict the population at risk of ACL injury? BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2022 Jun 2;14(1):98. PMID: 35655282; PMCID: PMC9161517. [CrossRef]
- Hamoongard M, Hadadnezhad M, Abbasi A. Effect of combining eight weeks of neuromuscular training with dual cognitive tasks on landing mechanics in futsal players with knee ligament dominance defect: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2022 Nov 22;14(1):196. PMID: 36415003; PMCID: PMC9682735. [CrossRef]
- Harput G, Demirci S, Soylu AR, Bayrakci Tunay V. Association between quadriceps muscle thickness and knee function in anterior cruciate ligament reconstructed athletes: a cross-sectional study. Physiother Theory Pract. 2023 Oct 3;39(10):2171-2179. Epub 2022 Apr 20. PMID: 35442153. [CrossRef]
- Henderson FJ, Konishi Y, Shima N, Shimokochi Y. Effects of 8-Week Exhausting Deep Knee Flexion Flywheel Training on Persistent Quadriceps Weakness in Well-Trained Athletes Following Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 14;19(20):13209. PMID: 36293790; PMCID: PMC9602677. [CrossRef]
- Hewett TE, Myer GD, Ford KR, Paterno MV, Quatman CE. Mechanisms, prediction, and prevention of ACL injuries: Cut risk with three sharpened and validated tools. J Orthop Res. 2016 Nov;34(11):1843-1855. Epub 2016 Sep 19. PMID: 27612195; PMCID: PMC5505503. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).