Submitted:
09 August 2024
Posted:
09 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- This paper demonstrates the need to fine-tune LLMs for domain adaptation and thus propose the use of a fine-tuned RoBERTa algorithm for EV sentiment prediction.
- Our paper demonstrate a SA approach that took advantage of language understanding of the transformer models to complement the lexicon-based approach when labelled datasets are unavailable.
- We conduct an experimental comparison of LLMs in the EV context and thus present state-of-the-art results.
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
- Duplicate Data: Ensuring that duplicate data is removed using unique comment IDs.
- Removing Unnecessary Items: Eliminating irrelevant elements from the text, including blank spaces, stop words (e.g., "a," "the," "is," "are"), hashtags, emojis, URLs, numbers, and special characters.
- Lowercasing: Converting all text to lowercase for smoother processing.
- Whitespace Removal: Eliminating unnecessary or excessive white spaces in the text.
3.1. Data Labelling
3.2. Transformer Based ML Models
3.2.1. Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT)
- Input embedding—In this stage, the process of tokenization occurs. This is the breaking down of text into smaller tokens for numerical encoding. Afterwards, the tokens are transformed into continuous vector representations (token embedding).
- Positional encoding—The position encoding of the tokens are calculated using sine or cosine functions (as an example) and thus added to the token embeddings.
- Self- Attention—The aim is to detect how similar each token is to others. The process involves generating the query and key matrices. Afterwards, calculates value (vectors) using the dot product.
- Normalization Layer—the SoftMax function helps normalize the vectors.
- Classification Head—Converting sequential output into classification results and the SoftMax function helps normalize class scores into probability values.
- Training loss—Measuring the difference between predicted probabilities and true labels, often using loss functions like cross-entropy.
- Optimization—updating model parameters to minimize loss using the Adam algorithm (backpropagation).
3.2.2. Robustly Optimized BERT Approach (RoBERTa)
3.2.3. XLNet
3.3. Evaluation Metrics
3.3. Criteria to Choose BERT, XLNet, and RoBERTa
- Innovative Architecture and Techniques:
- BERT: BERT was chosen for its bidirectional training mechanism, which allows it to understand the context within text from both directions. This innovation significantly improves its performance in various NLP tasks by developing knowledge of the relationship between words in a sentence.
- XLNet: XLNet was selected because it addresses the limitations of BERT by using a permutation-based training objective. This method captures bidirectional context without the need for masked tokens, enhancing the model's ability to utilize information in the text comprehensively. XLNet integrates autoregressive (AR) and autoencoding (AE) methods, solving the disadvantages of BERT's masked language model [36].
- RoBERTa: RoBERTa was included due to its improvements over BERT, such as dynamic masking, increased training data, and longer training durations. These enhancements lead to superior performance in downstream tasks, making RoBERTa a robust model for comparison.
- 2.
- Performance and Pretraining Enhancements:
- BERT: The model's ability to understand the context and meaning of text through self-attention mechanisms makes it a strong baseline for NLP tasks.
- XLNet: By overcoming BERT's limitations with permutation language modeling, XLNet improves performance in understanding contextual information.
- RoBERTa: With dynamic masking and extensive training datasets, RoBERTa optimizes BERT's approach, resulting in higher performance in NLP applications.
- 3.
- State-of-the-Art Achievements:
4. Result
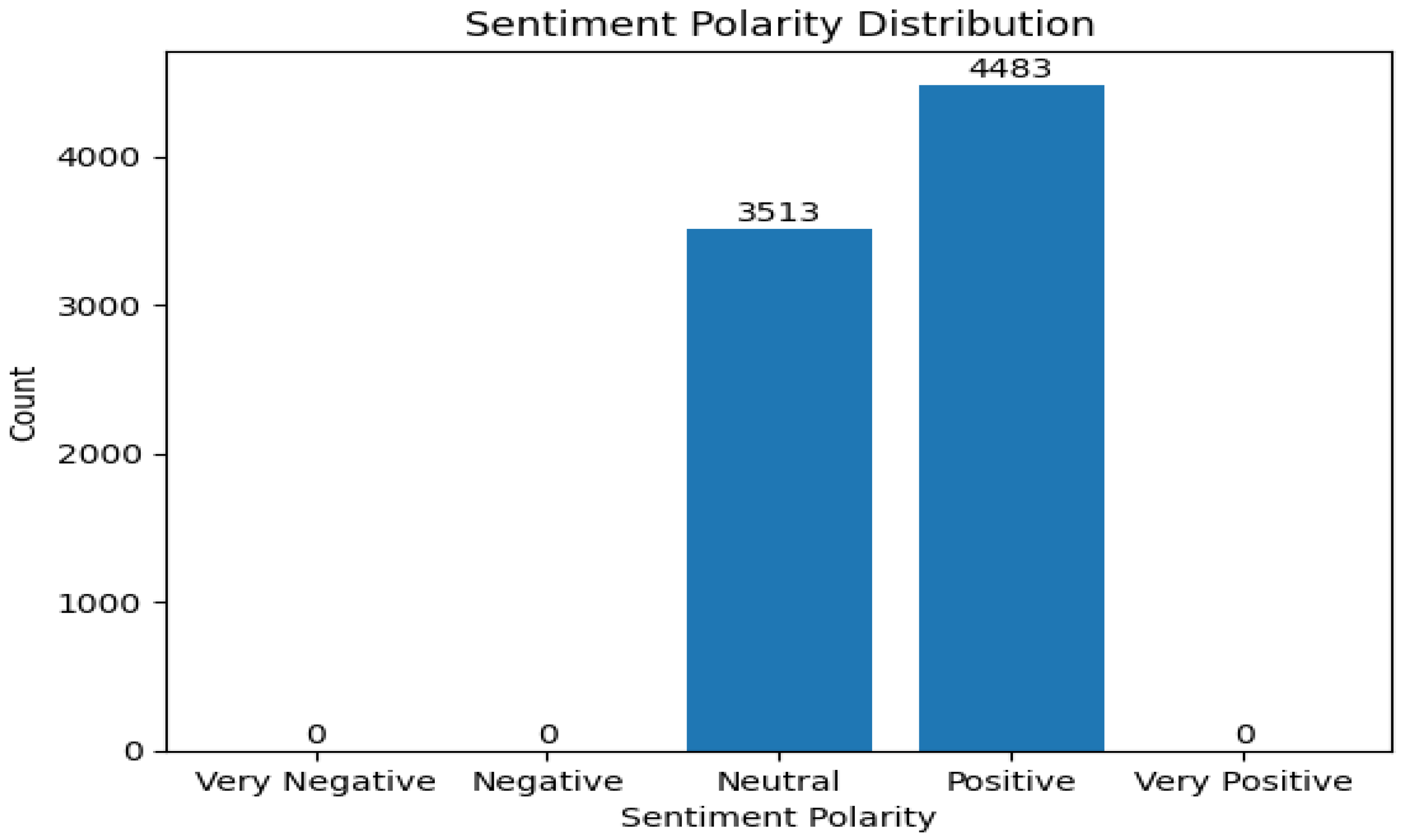
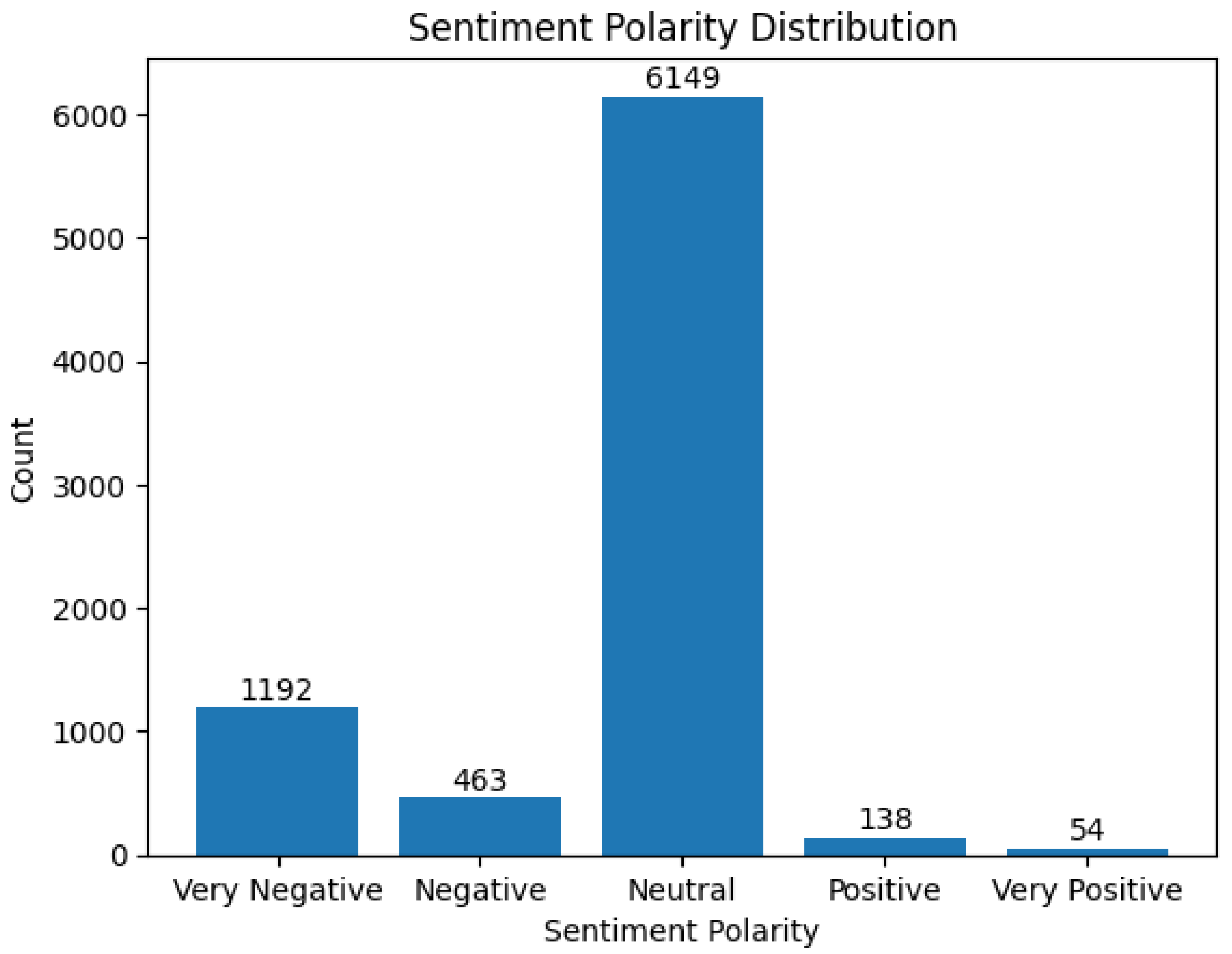
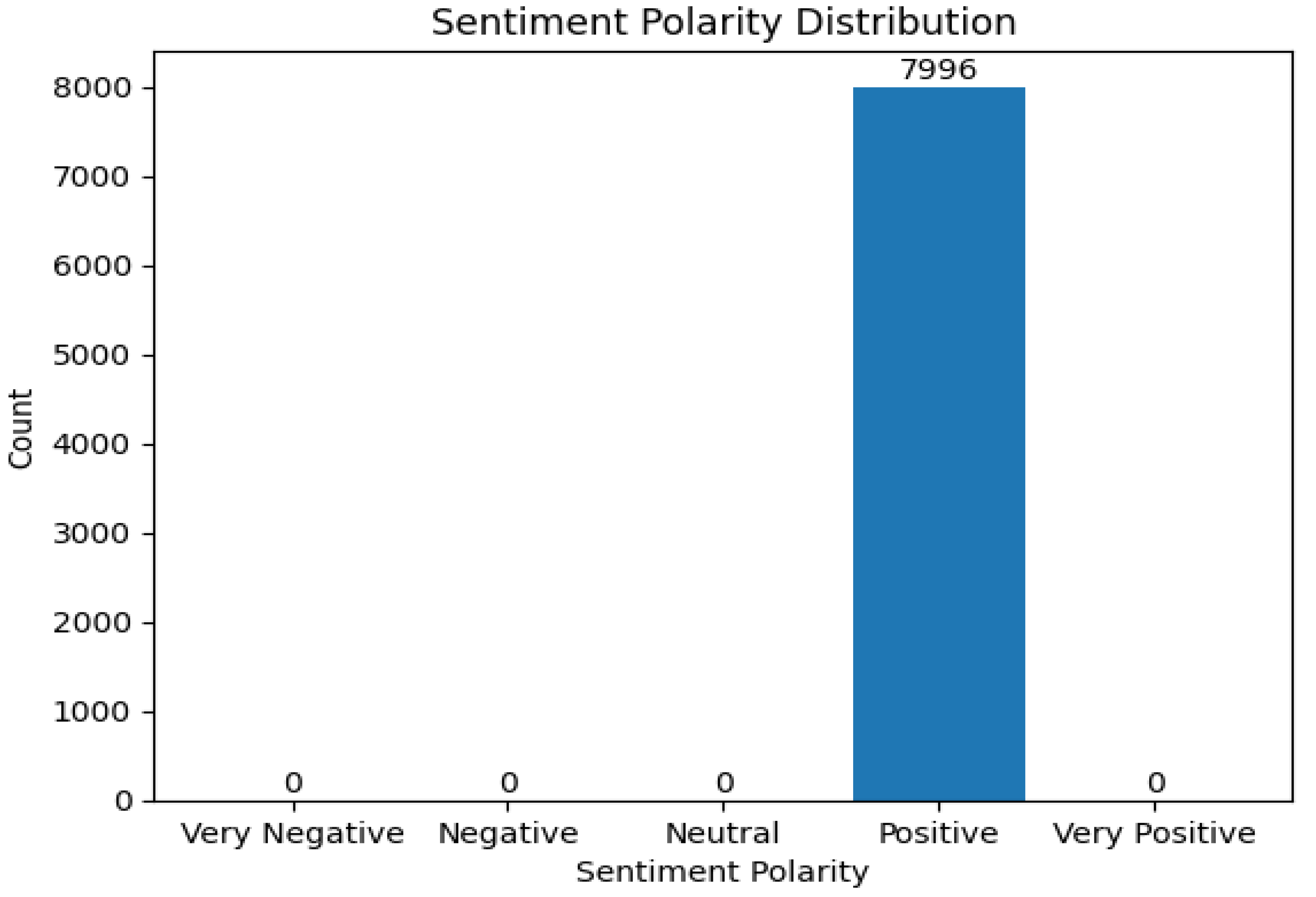
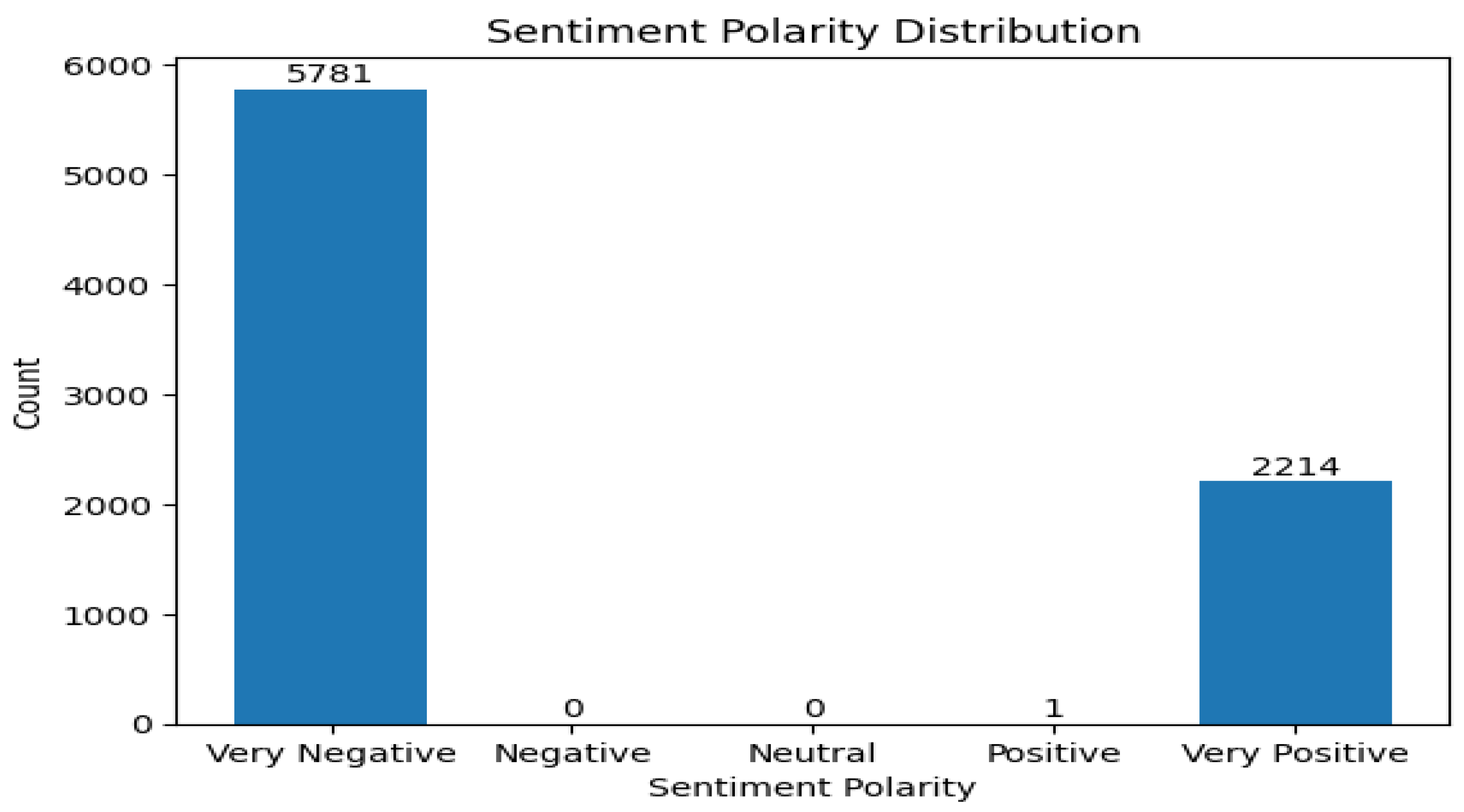
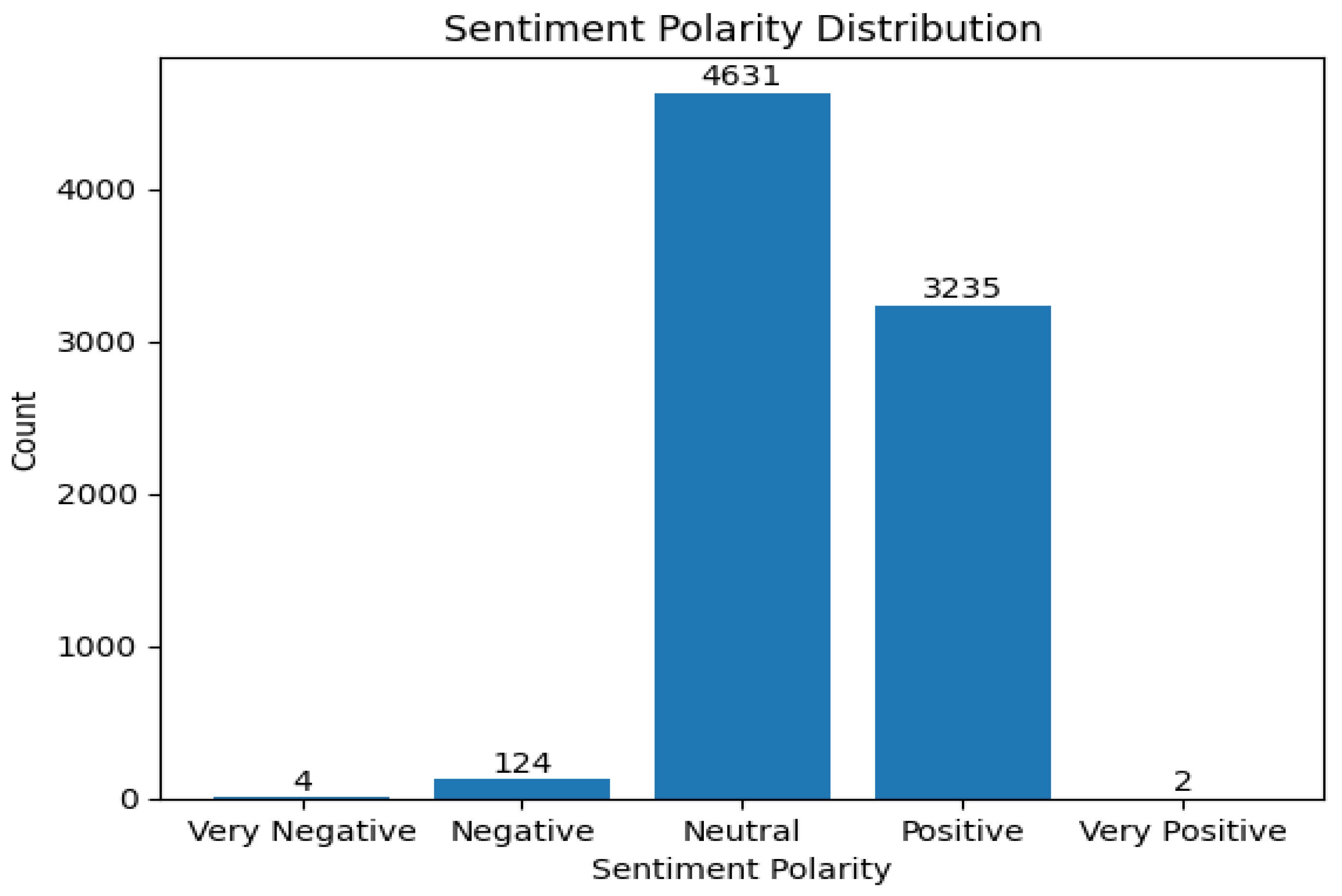
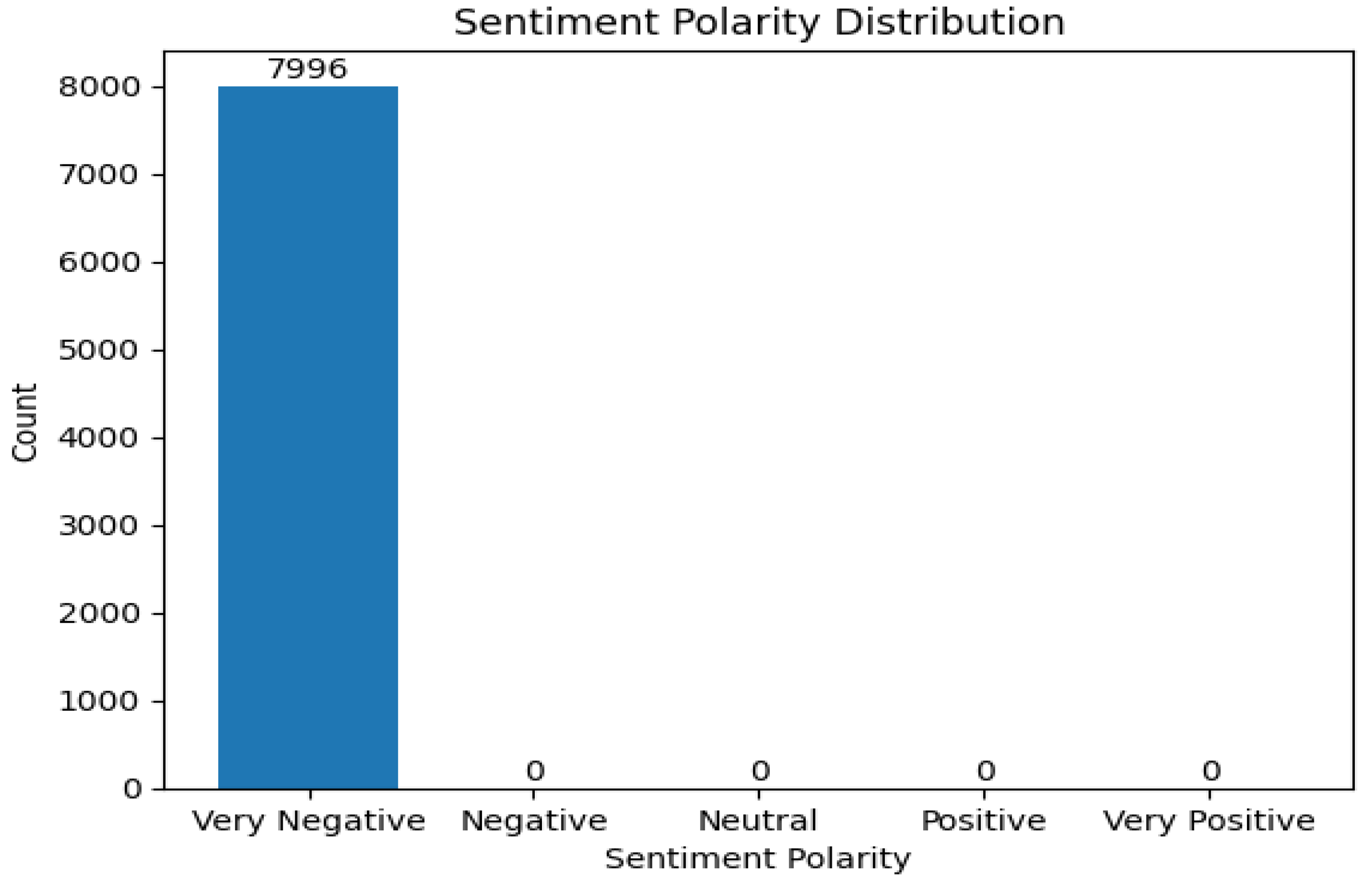
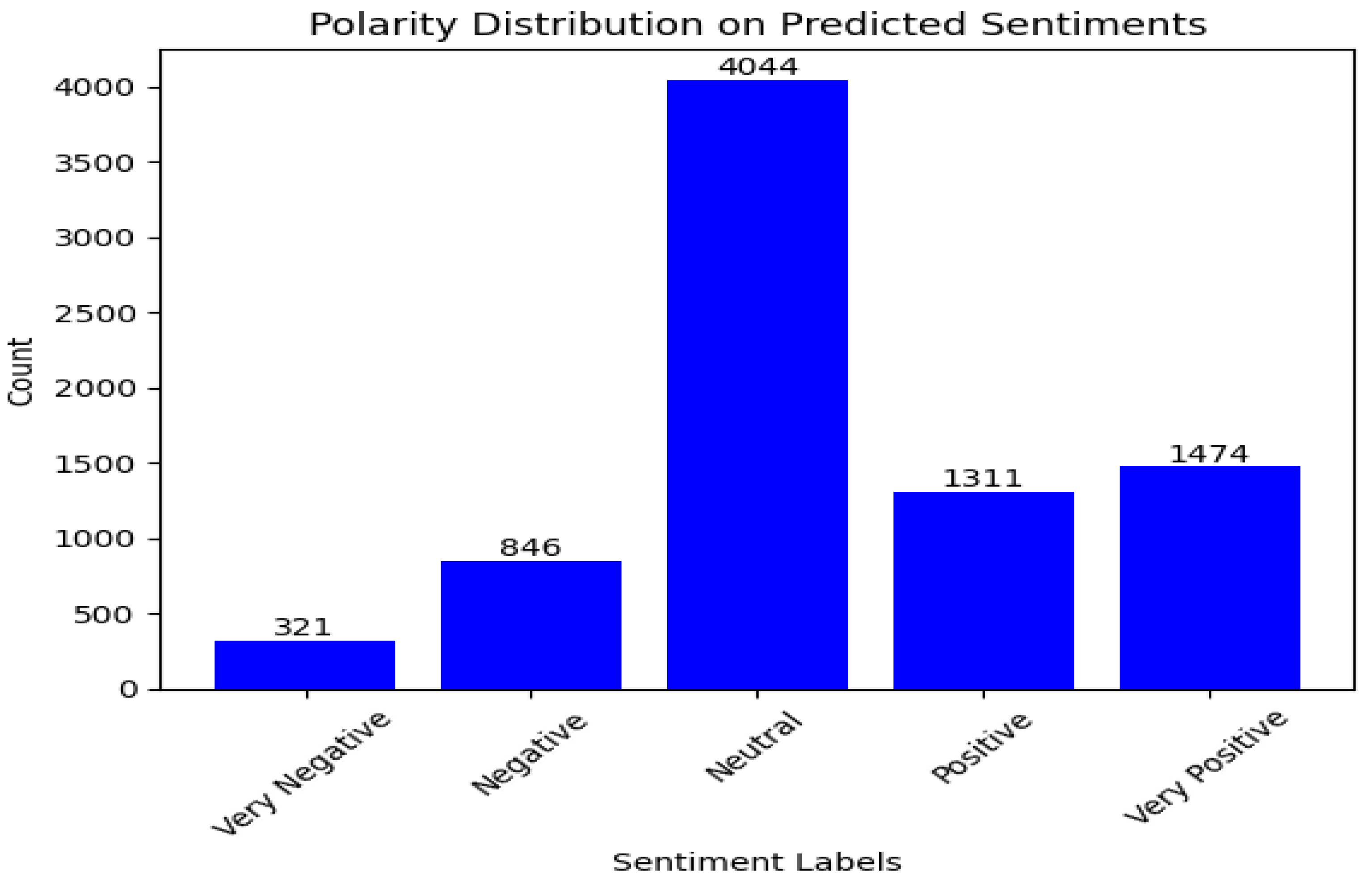
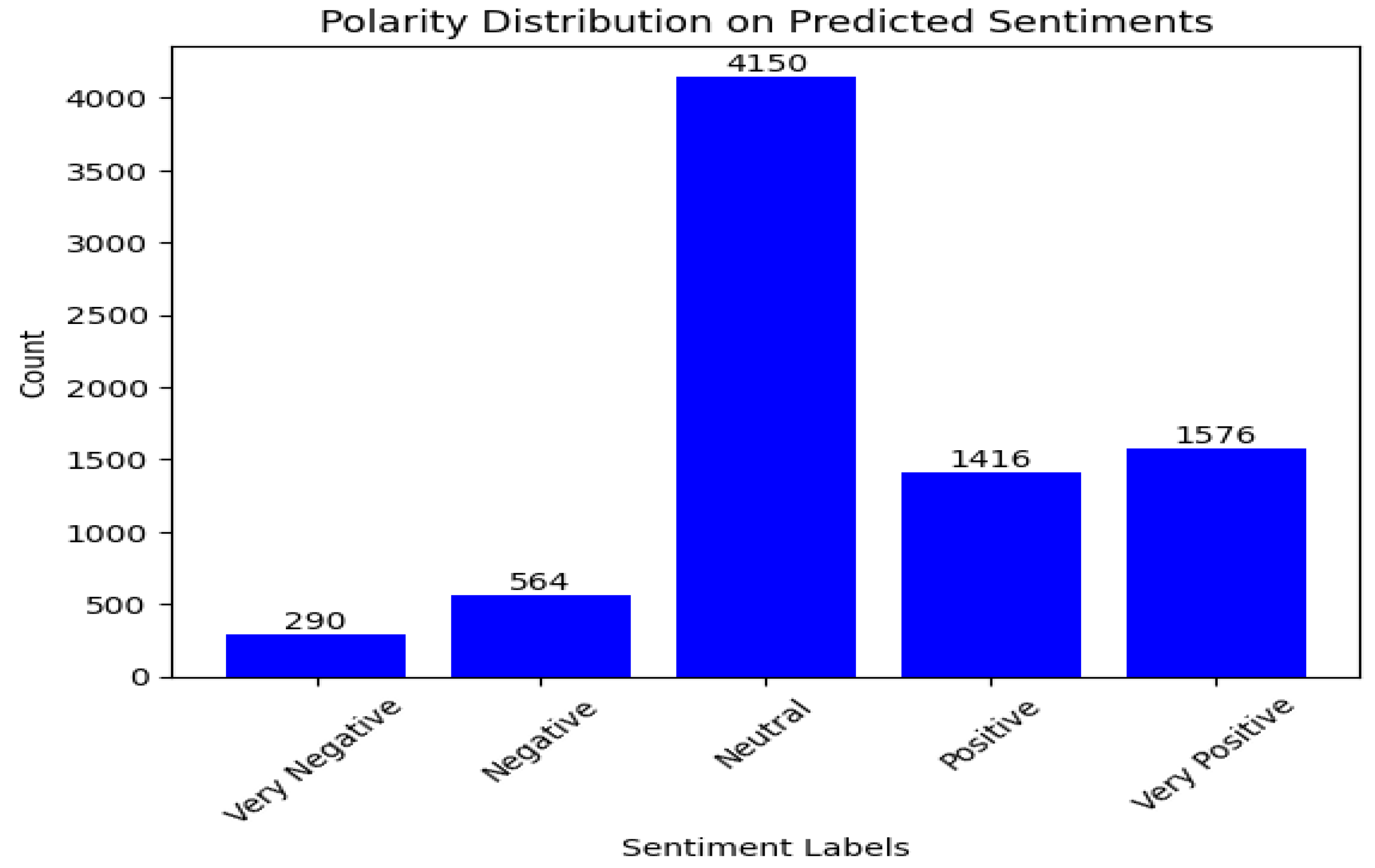
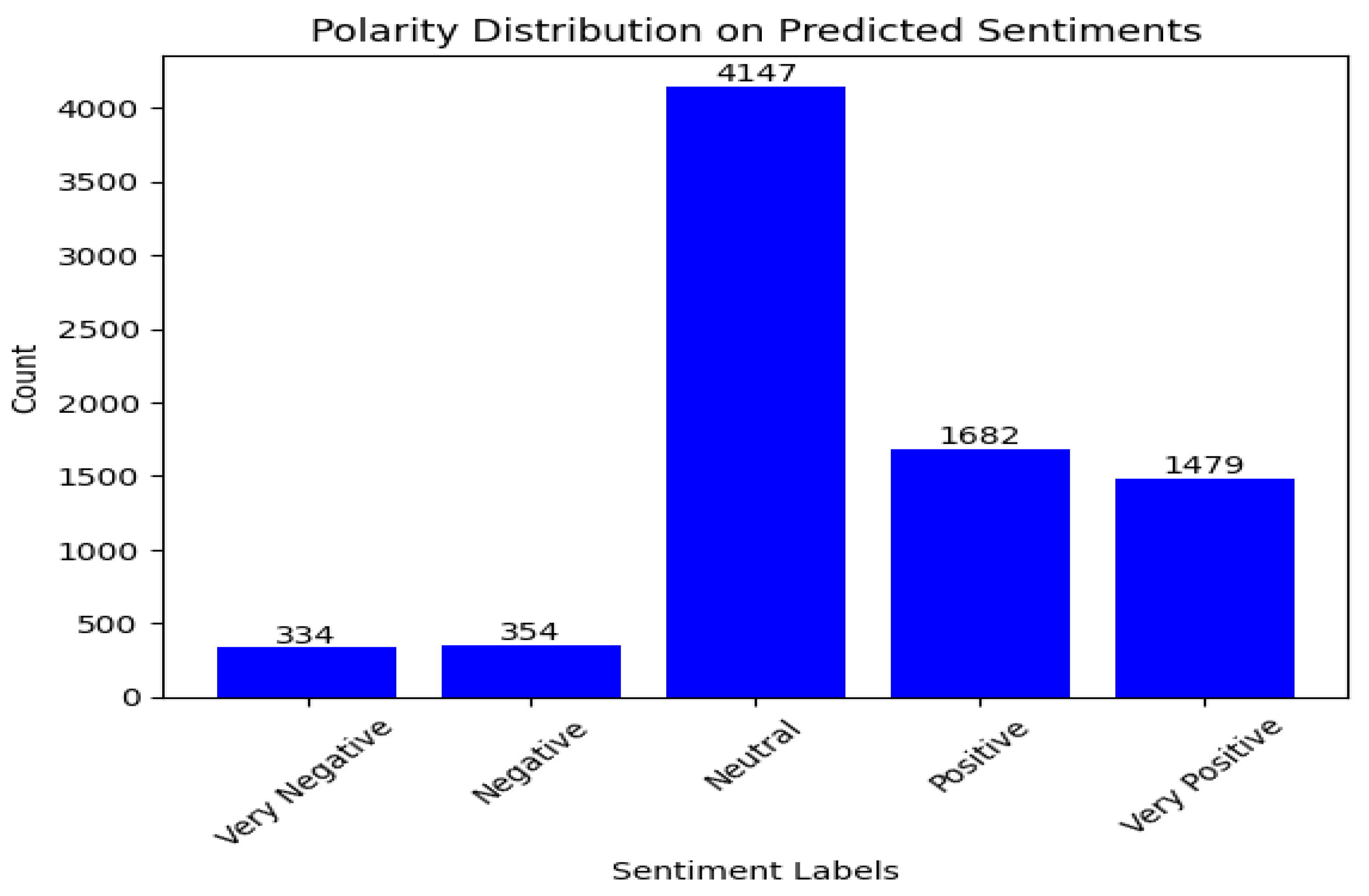
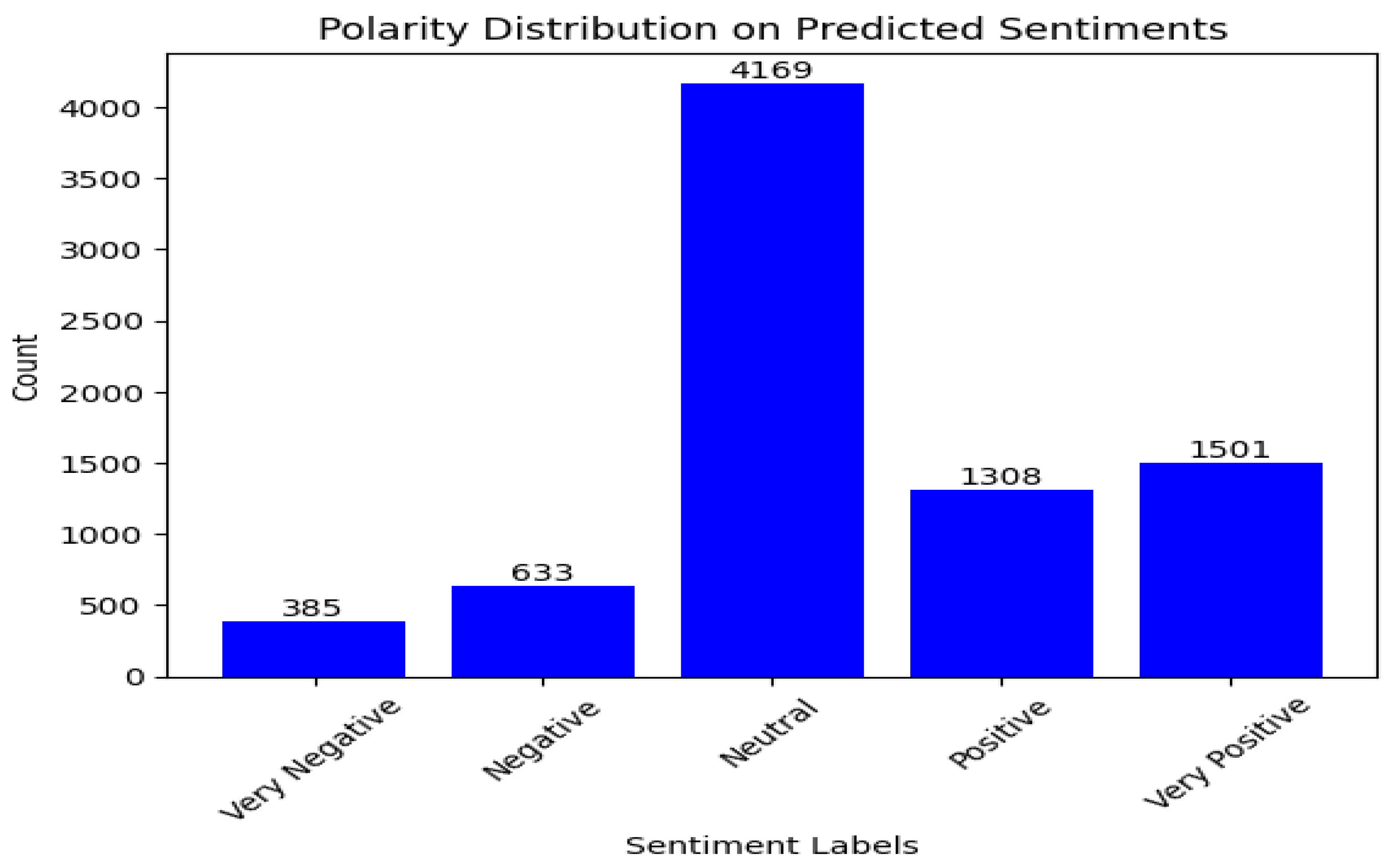
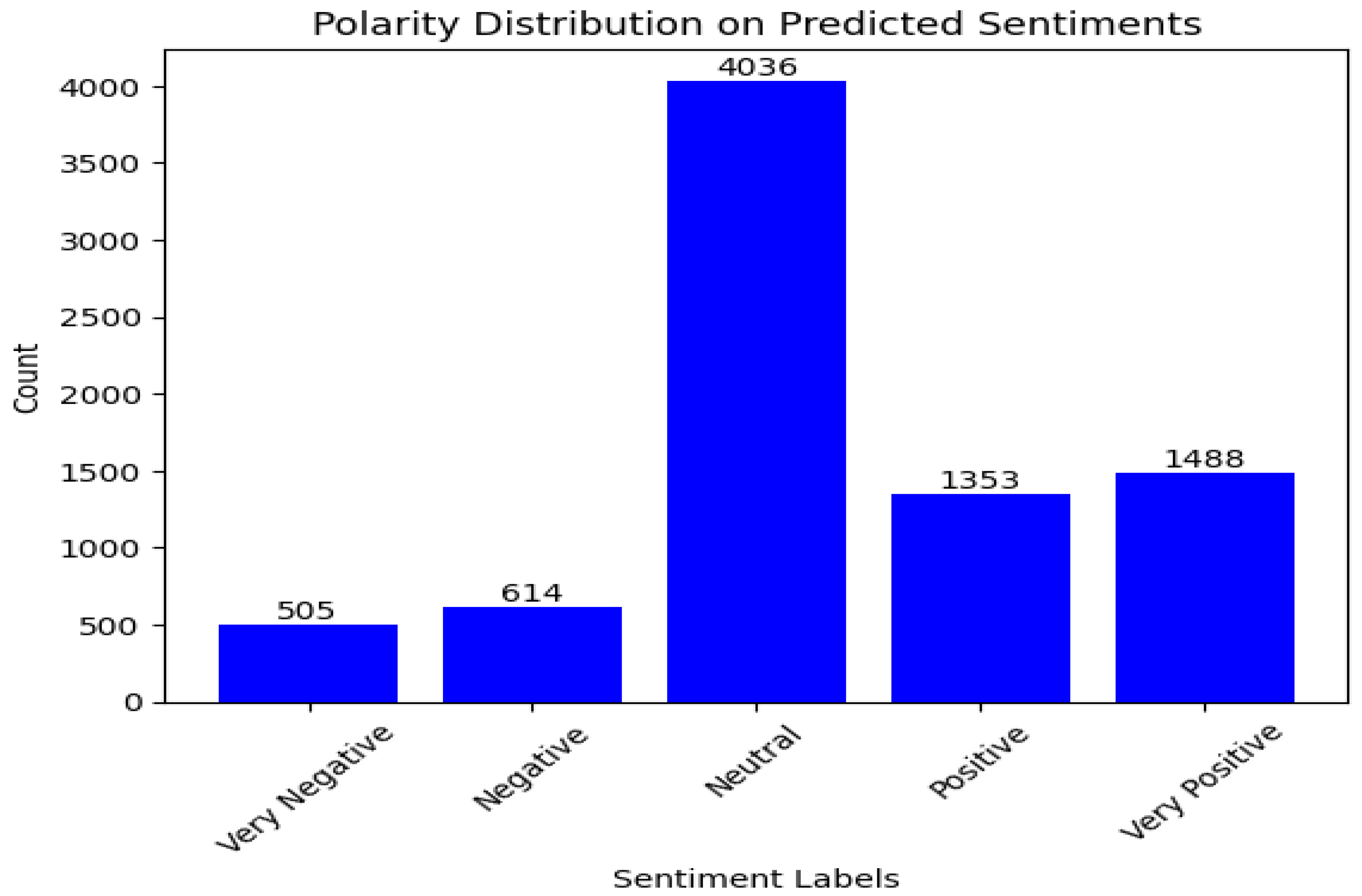
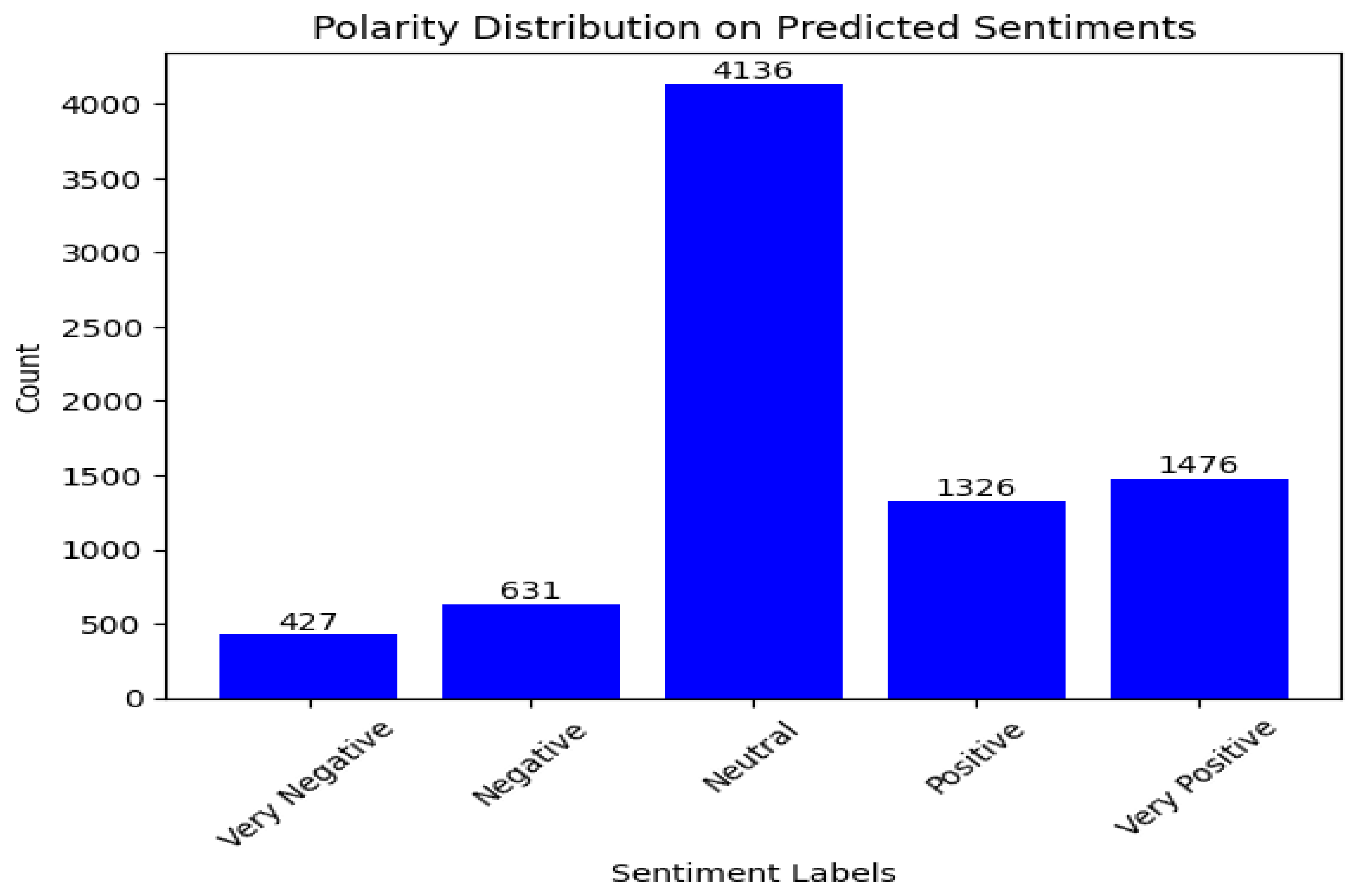
| Lucid Motors | BERT | RoBERTa | XLNet | ||||
| Without Fine-tuning | Fine-tuning | Without Fine-tuning | Fine-tuning | Without Fine-tuning | Fine-tuning | ||
| A | 37.06% | 90.33% | 17.30% | 92.33% | 43.88% | 90.90% | |
| P | 33.46% | 91.85% | 2.99% | 92.90% | 37.78% | 91.01% | |
| R | 37.06% | 90.33% | 17.30% | 92.31% | 43.88% | 90.90% | |
| F | 33.00% | 90.76% | 5.10% | 92.22% | 35.53% | 90.92% | |
5. Conclusions
Supporting Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolinetz, M.; Axsen, J. How policy can build the plug-in electric vehicle market: Insights from the REspondent-based Preference And Constraints (REPAC) model. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2017, 117, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateen, S.; Amir, M.; Haque, A.; Bakhsh, F.I. Ultra-fast charging of electric vehicles: A review of power electronics converter, grid stability and optimal battery consideration in multi-energy systems. Sustainable Energy, Grids and Networks 2023, 101112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Global EV Outlook 2023. https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2023 (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Qin, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Fan, B. Sentiment and attention of the Chinese public toward electric vehicles: A big data analytics approach. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2024, 127, 107216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.W.; Yuan, X.; Tao, R.; Umar, M. Can new energy vehicles help to achieve carbon neutrality targets? Journal of Environmental Management 2021, 297, 113348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Shao, S.; Ma, T. What determines consumers' acceptance of electric vehicles: A survey in Shanghai, China. Energy Economics 2022, 108, 105805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, S.; La Croix, S.; Coffman, M. Understanding changes in electric vehicle policies in the US states, 2010–2018. Transport Policy 2021, 103, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, C.; Anable, J.; Nelson, J.D. Exploring consumer preferences towards electric vehicles: The influence of consumer innovativeness. Research in Transportation Business & Management 2016, 18, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Carley, S.; Krause, R.M.; Lane, B.W.; Graham, J.D. Intent to purchase a plug-in electric vehicle: A survey of early impressions in large US cites. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment 2013, 18, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunleye, B.O. Statistical learning approaches to sentiment analysis in the Nigerian banking context. PhD Thesis, Sheffield Hallam University, United Kingdom, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunleye, B.; Brunsdon, T.; Maswera, T.; Hirsch, L.; Gaudoin, J. Using Opinionated-Objective Terms to Improve Lexicon-Based Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Soft Computing for Problem-Solving (SocProS 2023); Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems. Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2023; Volume 995, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Chang, Y.C. What drives purchase intention on Airbnb? Perspectives of consumer reviews, information quality, and media richness. Telematics and Informatics 2018, 35, 1512–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Kumawat, S.; Yadav, I.; Pahal, N.; Goel, D. Sentiment analysis using language models: A study. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence); IEEE, 2021; pp. 984–988. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, H.; Zhou, T.; Ali Babar, M.; Liu, X.Y. Enhancing financial sentiment analysis via retrieval augmented large language models. In Proceedings of the Fourth ACM International Conference on AI in Finance; 2023; pp. 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Ashari, N.; Al Firdaus, M.Z.M.; Budi, I.; Santoso, A.B.; Putra, P.K. Analyzing Public Opinion on Electrical Vehicles in Indonesia Using Sentiment Analysis and Topic Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Computer Science, Information Technology and Engineering (ICCoSITE); IEEE, 2023; pp. 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Wei, Y.; Xu, F.; Wang, T.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, J.Z. Semi-supervised Aspect-level Sentiment Classification Model based on Variational Autoencoder. Knowledge Based Systems 2019, 171, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.M.; Shobayo, O.; Ogunleye, B. An Exploration of Clustering Algorithms for Customer Segmentation in the UK Retail Market. Analytics 2023, 2, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iparraguirre-Villanueva, O.; Guevara-Ponce, V.; Sierra-Liñan, F.; Beltozar-Clemente, S.; Cabanillas-Carbonel, M. Sentiment analysis of tweets using unsupervised learning techniques and the k-means algorithm. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, R. An empirical case study on Indian consumers' sentiment towards electric vehicles: A big data analytics approach. Industrial Marketing Management 2020, 90, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Marchetto, D.J.; Dharur, S.; Asensio, O.I. Topic classification of elec-tric vehicle consumer experiences with Transformer-based deep learning. Patterns 2021, 2, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Young, K.; Griffith, J. Automatic Sentiment Labelling of Multimodal Data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Management Technologies and Applications; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, 2021; pp. 154–175. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, K.; Bhatia, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Platos, J.; Bag, R.; Hassanien, A.E. Sentiment Analysis of COVID-19 tweets by Deep Learning Classifiers—A study to show how popularity is affecting accuracy in social media. Applied Soft Computing 2020, 97, 106754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, E.; Din, S.; Jamil, R.; Rustam, F.; Mehmood, A.; Ashraf, I.; Choi, G.S. Determining the efficiency of drugs under special conditions from users’ reviews on healthcare web forums. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 85721–85737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Moin, S.; Karim, A.; Shamshirband, S. Machine learning-based sentiment analysis for twitter accounts. Mathematical and Computational Applications 2018, 23, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.A.; Shovon, S.D.; Joy, N.H.; Islam, M.S. Automatic labeling of twitter data for developing COVID-19 sentiment dataset. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Electrical Information and Communication Technology (EICT); IEEE, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunleye, B.; Sharma, H.; Shobayo, O. Sentiment Informed Sentence BERT-Ensemble Algorithm for Depression Detection. Preprints 2024, 2024071325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, T.; Lv, Q. Public perception of electric vehicles on Reddit and Twitter: a cross-platform analysis. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives 2023, 21, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JustAnotherArchivist. Justanotherarchivist/snscrape: A social networking service scraper in Python. 2020, GitHub. https://github.com/JustAnotherArchivist/snscrape.
- Grzegorzewski, P.; Kochanski, A. “Data Preprocessing in Industrial Manufacturing” Soft Modeling in Industrial Manufacturing, Studies in Systems, Decision and Control. Springer Nature Switzerland, 2019; Volume 183, pp. 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qorib, M.; Oladunni, T.; Denis, M.; Ososanya, E.; Cotae, P. Covid-19 vaccine hesitancy: Text mining, sentiment analysis and machine learning on COVID-19 vaccina-tion Twitter dataset. Expert Systems with Applications 2023, 212, 118715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunleye, B.; Dharmaraj, B. The Use of a Large Language Model for Cyberbullying Detection. Analytics 2023, 2, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozanta, A.; Angco, S.; Cevik, M.; Basar, A. Sentiment analysis of stocktwits using transformer models. In Proceedings of the 2021 20th IEEE international conference on machine learning and applications (ICMLA); IEEE, 2021; pp. 1253–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Carbonell, J.; Salakhutdinov, R.R.; Le, Q.V. XLNet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2019, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, L.; Chakraborty, S.; Biswas, A.; Bose, B.; Tiwari, S. Sentiment analysis of review datasets using naïve Bayes‘ and k-nn classifier. International Journal of Infor-mation Engineering and Electronic Business 2016, 8, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhou, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, R.; Zhou, J.; Gui, T.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X. Sentiment-aware multimodal pre-training for multimodal sentiment analysis. Knowledge-Based Systems 2022, 258, 110021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennafi, M.E.; Bedlaoui, H.; Dahou, A.; Al-qaness, M.A. Arabic aspect-based sentiment classification using Seq2Seq dialect normalization and transformers. Knowledge 2022, 2, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tesla Motors | BERT | RoBERTa | XLNet | ||||
| Without Fine-tuning | Fine-tuning | Without Fine-tuning | Fine-tuning | Without Fine-tuning | Fine-tuning | ||
| A | 9.75% | 93.63% | 5.34% | 92.12% | 42.26% | 90.10% | |
| P | 3.89% | 93.77% | 0.29% | 92.26% | 43.19% | 90.47% | |
| R | 9.75% | 93.63% | 5.34% | 92.10% | 42.26% | 90.10% | |
| F | 4.94% | 93.63% | 0.54% | 92.15% | 37.10% | 90.21% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





