1. Introduction
In dementia, language difficulties primarily manifest in terms of word access, word meaning, and the pragmatic aspects of communication. For instance, individuals affected by AD frequently tend to use semantically “empty" words like “thing" or “stuff," which lack specificity and nuance [
1]. They also tend to employ relatively lower portions of nouns and, notably, fewer verbs that carry significant informational content [
2]. This can result in their communication appearing less precise and more challenging to follow. Furthermore, their overall discourse may seem disorganized, making it harder for others to engage in meaningful conversations with them.
On the other hand, it is generally believed that other language components such as syntax (the structure of sentences), phonology (the sound system of language), and articulation (the physical production of speech sounds) remain relatively well-preserved until the later stages of the disease [
3]. However, this particular conclusion remains a subject of controversy within the research community, with some experts challenging the notion that these aspects of language remain unaffected throughout the course of Alzheimer’s Disease, but not in the late stages of the disease [
4,
5].
The advent of large language models (LLMs) has led to significant achievements across various domains, including sentiment analysis, question answering, summarization, and more [
6,
7]. These models have demonstrated their ability to tackle intricate tasks effectively. Notably, models like BERT [
8] and similar variants [
9,
10,
11] have shown their capacity for comprehending the context within textual data, encompassing diverse aspects of language, such as semantics and syntax [
12].
In recent years, researchers have integrated LLMs into their studies on various forms of dementia. They have approached this by either analyzing textual data or speech independently or by combining both modalities simultaneously, as referenced in a series of studies [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. In most cases, obtaining transcriptions of speech involves the use of automatic speech recognition (ASR) models. Our primary focus here is on the text-based aspects of their methodologies. For example, one study [
14] introduced a novel approach by incorporating pauses (special characters) in the textual data, aiming to leverage these pause-related cues within the textual context. This inclusion led to performance enhancements compared to utilizing plain text alone. Another prevalent strategy in dementia detection is the utilization of transfer learning, as demonstrated in multiple studies [
14,
16,
18], highlighting its effectiveness in enhancing performance.
It’s worth noting that training LLMs can be challenging due to limited datasets for dementia detection. To address this challenge, several authors proposed various data augmentation techniques in studies [
19,
20,
21], which have proven to be effective in augmenting the available data for training models. Additionally, some researchers have explored the robustness and sensitivity of LLMs in predicting Alzheimer’s disease. In a particular study [
22], the investigation focused on evaluating the robustness and sensitivity of BERT-like models in Alzheimer’s disease prediction. This research is crucial not only for the development of more reliable classification models, but also for gaining a better understanding of the capabilities and limitations of these models.
In this paper, we aim to detect dementia through textual input with in-text pause encoding. In our methodology, three different pauses (short, medium, and long) are extracted from the audio and encoded with the corresponding text by different encoding techniques. We perform a combinatorial search to find the best combination of in-text pause encoding scheme that results in superior performance. To the best of our knowledge this type of approach is novel and the in-text pause encoding techniques have not been tested on the
Pitt Corpus Cookie Theft dataset [
23]. Our main results indicate that this approach is effective in improving performance compared to the baseline. These results show the advantage of incorporating pause information within the text.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: In
Section 2, the data preparation, pause encoding, and modeling are discussed. In
Section 3, the results are presented. Lastly, we present our conclusions in
Section 4.
2. Methodology
In our experiments, the
Pitt Corpus Cookie Theft dataset [
23] is used. This dataset contains audio and transcripts from different individuals for different tasks. In the first step of our methodology, we clean the dataset from the special characters that would not be used in our experiments. Next, we encode different types of pauses within the textual input to the model, as explained in
Section 2.2. In
Section 2.3, different model architectures are proposed. These models are carefully selected to study the effect of model complexity on performance.
2.1. Data Preparation
In here we outline the procedure for data cleaning in our study, which utilizes transcripts from the
Pitt Corpus Cookie Theft dataset [
23]. These transcripts are rich in detail, including the patients’ demographic information like gender and age, as well as clinical data such as dementia severity. Additionally, they contain syntactic details to ensure language consistency, timestamps, and dialogues between researchers and participants. This dataset contains 243 and 305 recordings and CHAT style transcriptions for
control and
dementia groups, respectively. throughout our experiments, we use the transcriptions for our training and evaluation. For our analysis, we specifically exclude certain special characters found in the conversations, such as “xxx", “(.)", “&-uh", “. exc", among others.
Table 1 illustrates the process. Each of these symbols has its meaning, which can be found in the DementiaBank documentation [
23].
2.2. In-Text Pause Encoding
In this research, the relationship between speech pauses and the likelihood of dementia is a key focus, a topic extensively explored in various studies [
14,
24]. These studies often classify different types of dementia based on the frequency and duration of pauses in speech.
We choose to use transcripts for our analysis rather than audio recordings. While audio data offers a richer source of information, its high dimensionality presents significant computational challenges. To circumvent these challenges and efficiently process the data, we rely on transcripts. There are various transcription tools available that can accurately convert speech to text, facilitating our analysis. These tools allow us to effectively analyze the data without the computational burden associated with processing high-dimensional audio files.
In the Cookie Theft dataset used in our study, specific special characters indicate different lengths of pauses: short, medium, and long. The symbols “(.)", “(..)", and “(...)" represent these pauses, respectively. To simplify processing, we substitute these symbols with more model-friendly terms: “ShPause", “MePause", and “LoPause". In [
24], authors are using a similar concept to encode pauses within the text. Their approach is different from ours in how they incorporate encoded pauses in the text. Their methodology is applied to the ADReSS dataset [
23], and they utilize temporal word alignment, which is not the case in our approach. Additionally, we analyze the impact of incorporating frequency of each pause type within the text.
We refer to the baseline model with the text input with all symbols removed as
. The models performed better when they were provided with a secondary numerical vector input corresponding to the frequencies of the pauses in the form
where
#Sh,
#Me and
#Lo represent the number of short, medium and long pauses, respectively. All variants of the models discussed below include this vector as a secondary input and employ the architecture described in the next section.
We consider the combinations of 4 different ways of encoding pauses within the text: In-place (
I), End-Sequence (
S), Frequency (
F), and Vector (
V). As an example, consider the original text with pauses (after replacing the pause symbols with our previously defined terms) in the form:
where
seg1 indicates a segment of text, and
ShPause represents a short pause, and so on. We refer to this as a text with in-place encoding. A text without in-place encoding takes the form:
The end-sequence encoding creates a sequence of the pauses in the order in which they are present and takes the form:
This sequence is concatenated at the end of the original text. The frequency encoding creates a text with the count of each pause type attached to each pause type. It takes the form:
and it also concatenated at the end of the original text. Finally, the vector encoding is similar to the frequency encoding except that it does not contain the pause type. It takes the form:
Our simplest model does not contain any of these encodings and is denoted as
. The model inputs that include in-place and frequency encoding will be denoted as
. Other inputs are denoted similarly. We will explore all 16 combinations of the pause encoding in
Section 3. Note that the frequency and vector encodings contain the same information. They are used to verify that the LLM does process that information in the same way.
2.3. Modeling
As mentioned in
Section 1, there are many models using LLMs to process textual data. In our experiments, we will be using BERT-base-uncased model [
8] as the base for feature extraction. We conducted extensive experiments to find the best setup to optimize performance. As shown in
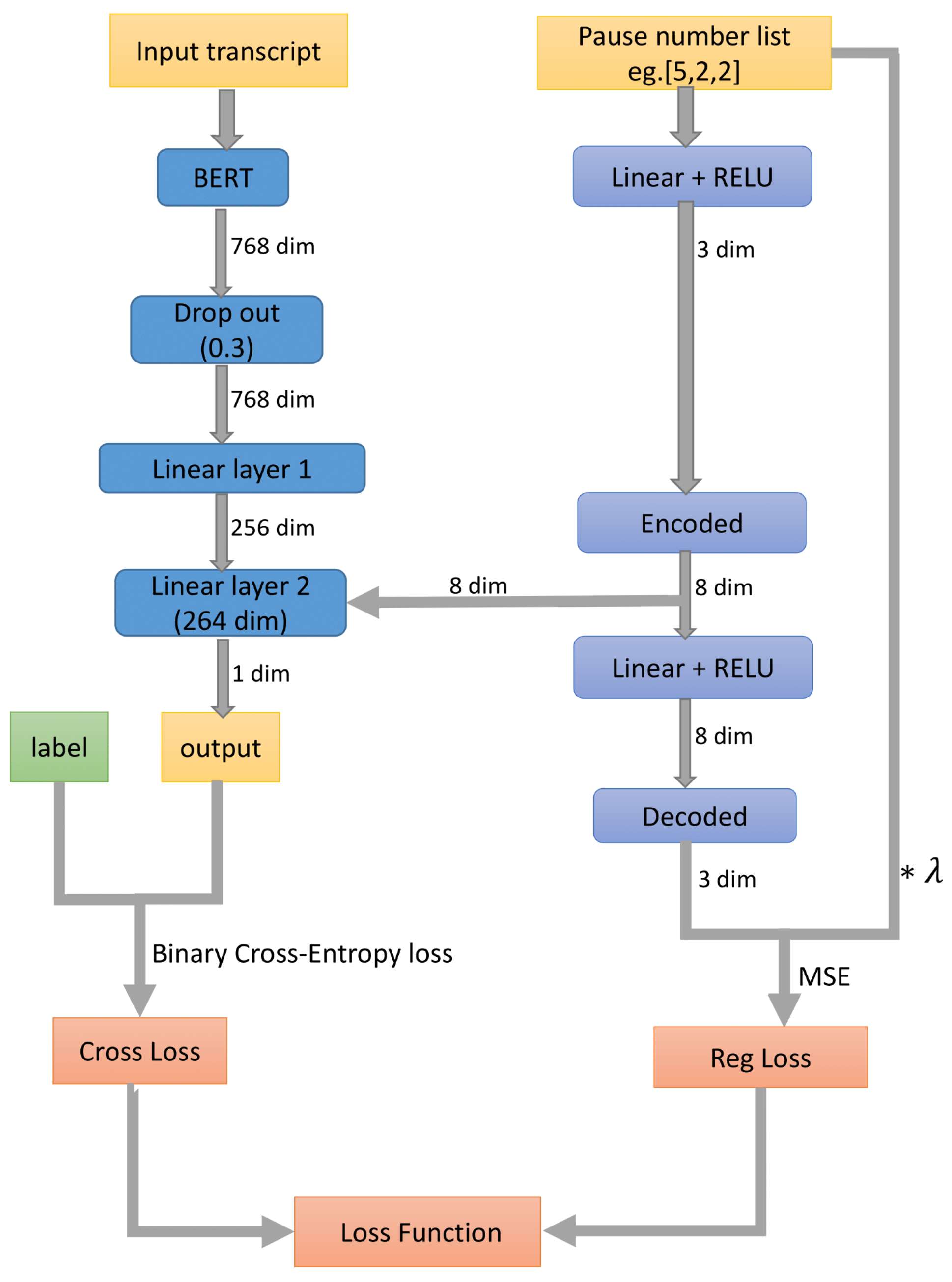
Figure 1, our architecture has BERT as its base, followed by one dropout layer and two linear layers to perform classification. Also, to process the frequency vector, an encoder-decoder model is introduced. This model consisted of linear layers.
For our setup, we use cross-entropy as one of our optimization terms as follows
where
, and
are the cross-entropy loss, ground-truth label, and predicted label, respectively. For the auto-encoder, we introduce the following optimization term
where
is the mean square error loss, and
and
are true frequency input and its reconstruction, respectively. So, the total optimization cost becomes
where
is a hyper-parameter to be optimized.
Note that the baseline model does not have the auto-encoder network because processing the frequency vector is not part of the raw text for analysis. For all other experiments, this network is present.
3. Results and Discussion
This section details the outcomes of various experiments
1 which utilized different in-text encoding methods, as outlined in
Section 2.2, and various models discussed in
Section 2.3. All experiments employed the BERT [
8] base uncased model in conjunction with the AdamW optimizer [
25] with default parameters, and each model was trained for 10 epochs. For all experiments, we used
. To ensure the reliability of the results, a 20-fold cross-validation was conducted for each encoding scheme. The performance of the encodings scheme is presented in
Table 2. The metrics used to evaluate performance include accuracy and f1-score, with the best result highlighted in red.
For the baseline, , where no pause encoding is included, the model achieves and in accuracy and f1-score, respectively. When adding the numeric vector of counts as secondary input using our proposed architecture, the accuracy remains at , but the f1-score increases to . That is a 7% improvement on f1-score. However, the most significant improvements occur when the encoding are incorporated.
When just in-text encoding () is used the performance reaches and in accuracy and f1-score, respectively, which shows a significant improvement. For other encodings, the gap is even larger. The model achieved the highest performance for all the metrics overall with and for accuracy and f1-score. Compared to the baseline, the f1-score increases by a factor greater than 2.
Table 2.
Performance for All Models. The best overall performance is highlighted in red.
Table 2.
Performance for All Models. The best overall performance is highlighted in red.
| Model |
Acc. |
f1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A possible reason for the success of this method might be attributed to how these encoded pause characters create recognizable patterns in the text, simplifying the task for the model to identify and classify the inputs. Additionally, the occurrence frequency and distribution of each pause type within the text might serve as a distinctive feature, helping the model differentiate between the dementia group and the control group. This distinction could significantly contribute to the model’s ability to accurately separate these groups. Also, it should be mentioned that our proposed encoding scheme resulted in more stability in performance as could be observed in
Table 2. All the models with encoding have a smaller standard deviation, which shows the robustness that these encodings introduce to the model. Perhaps illustrating the power of transfer learning from an LLM.
Table 3 shows the aggregate difference between models with and without an encoding. The best performance take place when frequency encoding
, vector encoding
and end-sequence encoding
are present. All get an average f1 score of 0.85. This is consistent with the best mode performance found in
Table 2, and validates the fact that these models contain very similar information. We observe that the averages for models that include an encoding are smaller than those that do include an encoding (e.g.,
has higher performance overall than
). This difference is due to the low performance of
which contains no encoding.
4. Conclusions
We implemented and analyzed a novel encoding strategy within the text, incorporating special characters to enhance the performance of the model. This method, as evidenced by the results in
Table 2, outperformed the baseline model, which did not include in-text pause encoding. Additionally, this strategy demonstrated greater stability across various experiments, indicated by its lower variance. However, further research is necessary to fully understand the limitations and potential applications of this approach across diverse datasets and utilize other special language cues such as verbs, nouns, and repetition of “uh" and “um" utterances in the text.
References
- Kim, M.; Thompson, C.K. Verb deficits in Alzheimer’s disease and agrammatism: Implications for lexical organization. Brain and language 2004, 88, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentis, M.; Briggs-Whittaker, J.; Gramigna, G.D. Discourse topic management in senile dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 1995, 38, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempler, D.; Curtiss, S.; Jackson, C. Syntactic preservation in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 1987, 30, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croot, K.; Hodges, J.R.; Xuereb, J.; Patterson, K. Phonological and articulatory impairment in Alzheimer’s disease: a case series. Brain and language 2000, 75, 277–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, L.J.; Kempler, D.; Andersen, E.S. Speech Errors in Alzheimer’s Disease. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.X.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Min, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. A survey of large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.18223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, H.; Khan, A.U.; Qiu, S.; Saqib, M.; Anwar, S.; Usman, M.; Akhtar, N.; Barnes, N.; Mian, A. A Comprehensive Overview of Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.06435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Chen, M.; Goodman, S.; Gimpel, K.; Sharma, P.; Soricut, R. Albert: A lite bert for self-supervised learning of language representations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.11692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanh, V.; Debut, L.; Chaumond, J.; Wolf, T. DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.01108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Khandelwal, U.; Levy, O.; Manning, C.D. What does bert look at? an analysis of bert’s attention. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.04341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilias, L.; Askounis, D. Multimodal deep learning models for detecting dementia from speech and transcripts. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2022, 14, 830943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Bian, Y.; Cai, X.; Huang, J.; Ye, Z.; Church, K. Disfluencies and Fine-Tuning Pre-Trained Language Models for Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease. Interspeech 2020, 2020, 2162–2166. [Google Scholar]
- Searle, T.; Ibrahim, Z.; Dobson, R. Comparing Natural Language Processing Techniques for Alzheimer’s Dementia Prediction in Spontaneous Speech. Proc. Interspeech 2020, 2020, 2192–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.; Lee, J.H.; Pyo, J.; Jo, Y.; Lee, K. Exploiting Multi-Modal Features from Pre-Trained Networks for Alzheimer’s Dementia Recognition. Proc. Interspeech 2020, 2020, 2217–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohanian, M.; Hough, J.; Purver, M. Multi-Modal Fusion with Gating Using Audio, Lexical and Disfluency Features for Alzheimer’s Dementia Recognition from Spontaneous Speech. Proc. Interspeech 2020, 2020, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liang, X.; Batsis, J.A.; Roth, R.M. Exploring Deep Transfer Learning Techniques for Alzheimer’s Dementia Detection. Frontiers in Computer Science 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Wei, F.; Liu, J.; Li, H.; Liu, T.; Wang, J. CDA: A Contrastive Data Augmentation Method for Alzheimer’s Disease Detection. Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023; Rogers, A., Boyd-Graber, J., Okazaki, N., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Toronto, Canada, 2023; pp. 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlédiková, A.; Woszczyk, D.; Akman, A.; Demetriou, S.; Schuller, B. Data Augmentation for Dementia Detection in Spoken Language. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, T.; Nihei, M. Cognitive Assessment of Japanese Older Adults with Text Data Augmentation. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, J. Robustness and Sensitivity of BERT Models Predicting Alzheimer’s Disease from Text. In Proceedings of the Seventh Workshop on Noisy User-generated Text (W-NUT 2021); Xu, W., Ritter, A., Baldwin, T., Rahimi, A., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Online, 2021; pp. 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.T.; Boiler, F.; Lopez, O.L.; Saxton, J.; McGonigle, K.L. The Natural History of Alzheimer’s Disease: Description of Study Cohort and Accuracy of Diagnosis. Archives of Neurology 1994, 51, 585–594. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/articlepdf/592905/archneur_51_6_015.pdf. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Bian, Y.; Cai, X.; Huang, J.; Ye, Z.; Church, K. Disfluencies and Fine-Tuning Pre-Trained Language Models for Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease. Interspeech 2020, 2020, 2162–2166. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization. International Conference on Learning Representations; 2017. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).