Submitted:
10 August 2024
Posted:
13 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
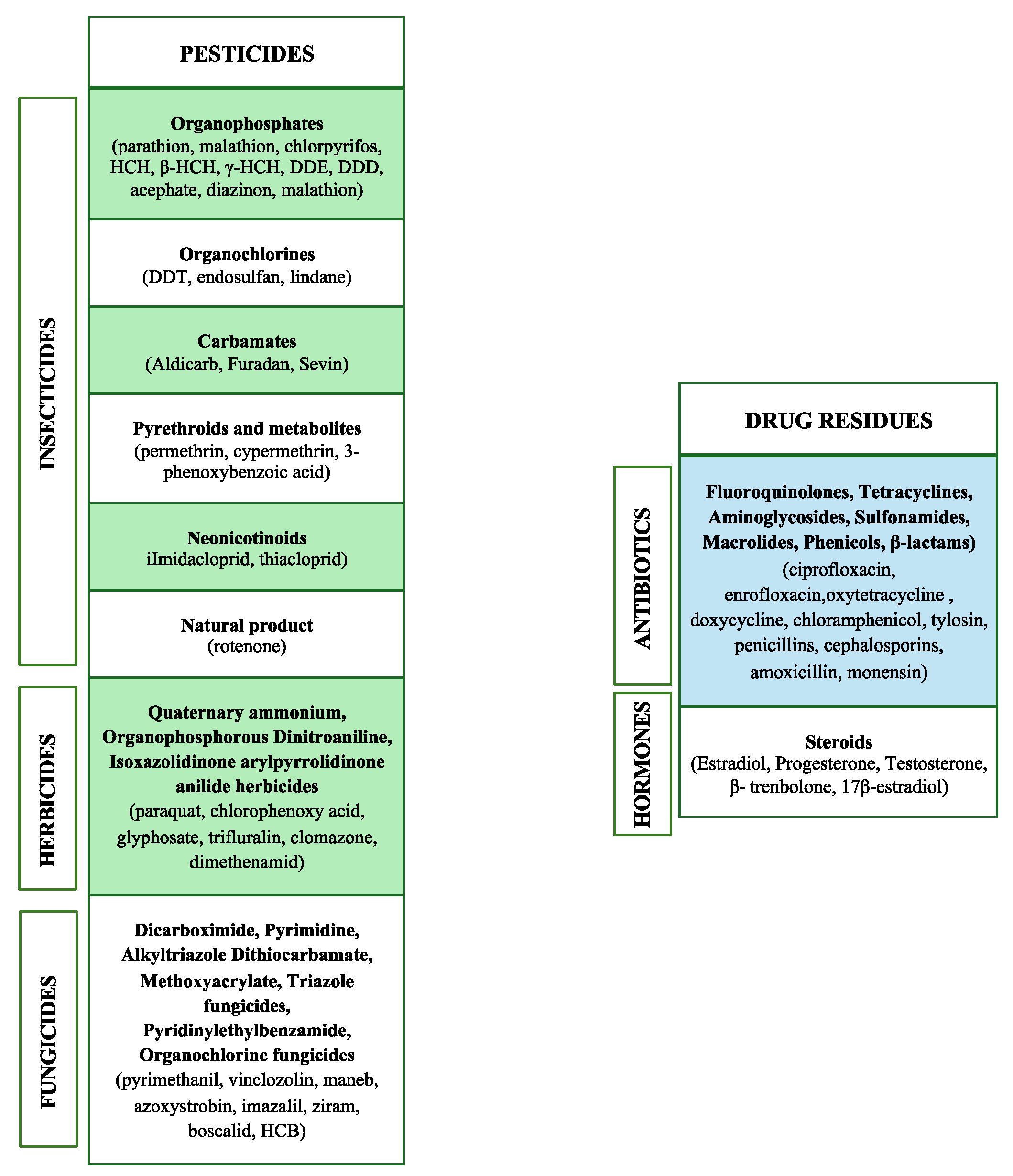
2. Food Contaminants of Agricultural and Veterinary Origin
2.1. Pesticides
2.2. Drug Residues
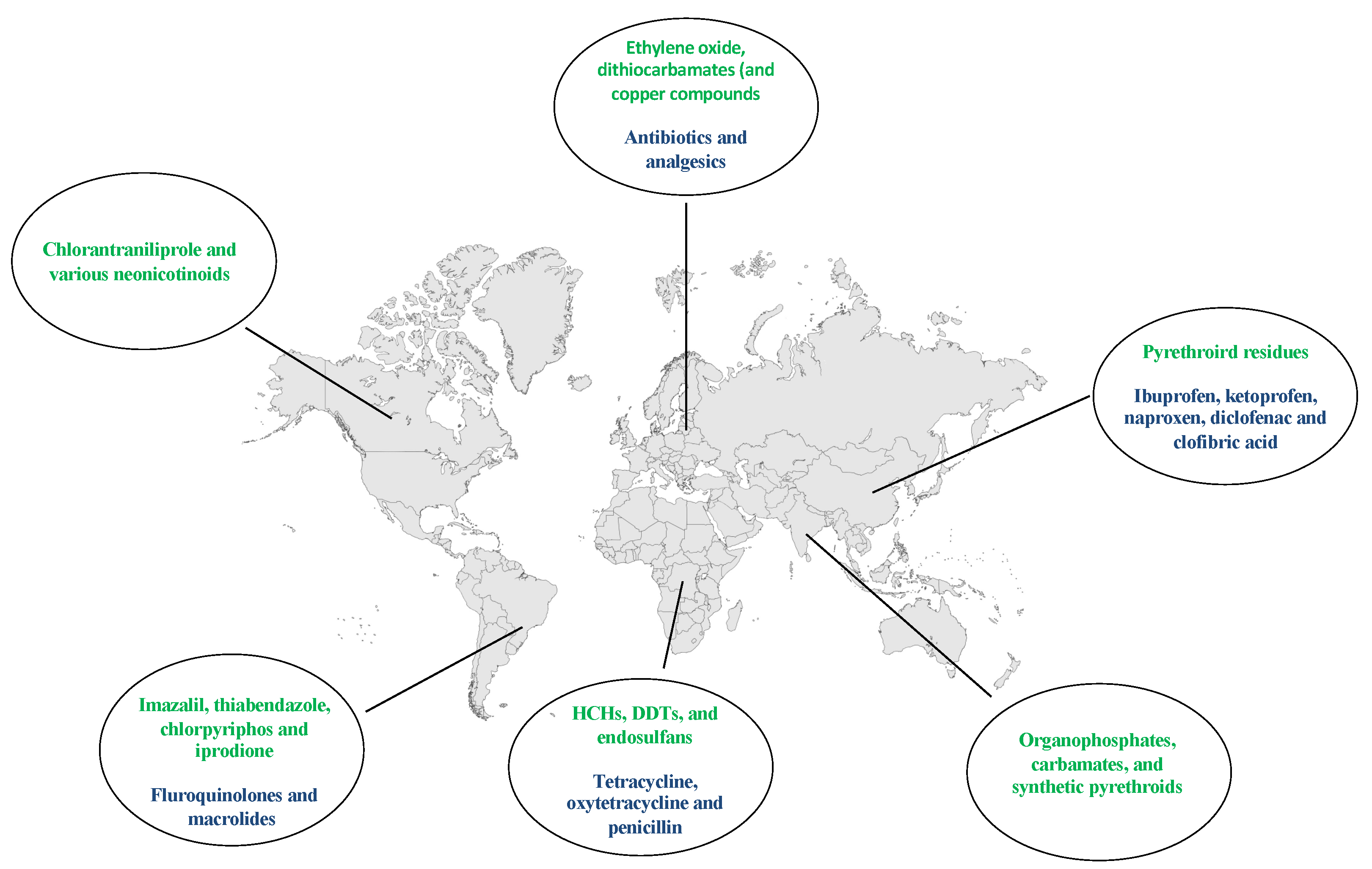
3. Worldwide Distribution of Pesticides and Drugs Contaminants
3.1. Pesticides
3.2. Drug Residues
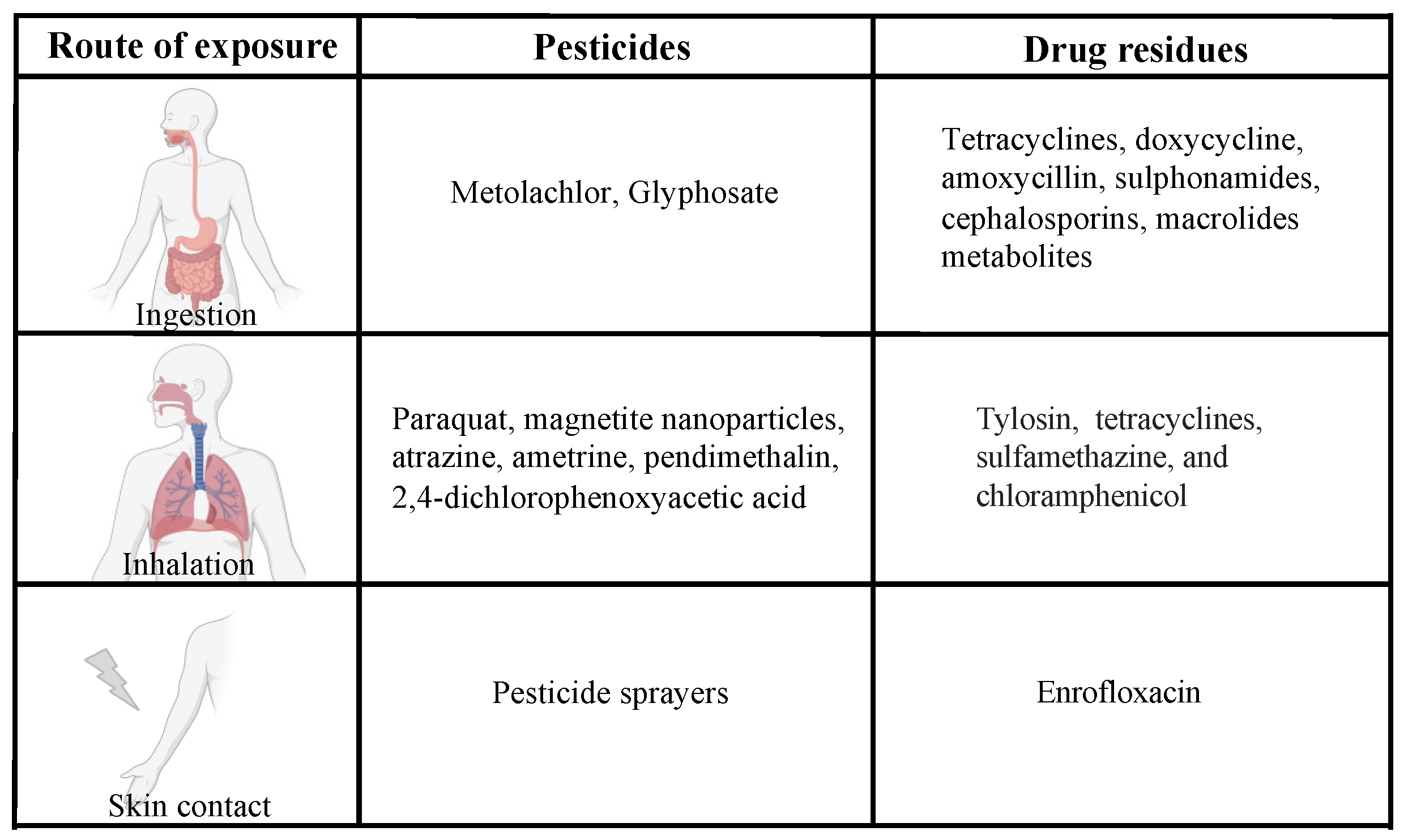
4. Routes of Exposure
4.1. Oral Exposure
4.2. Other Routes of Exposure
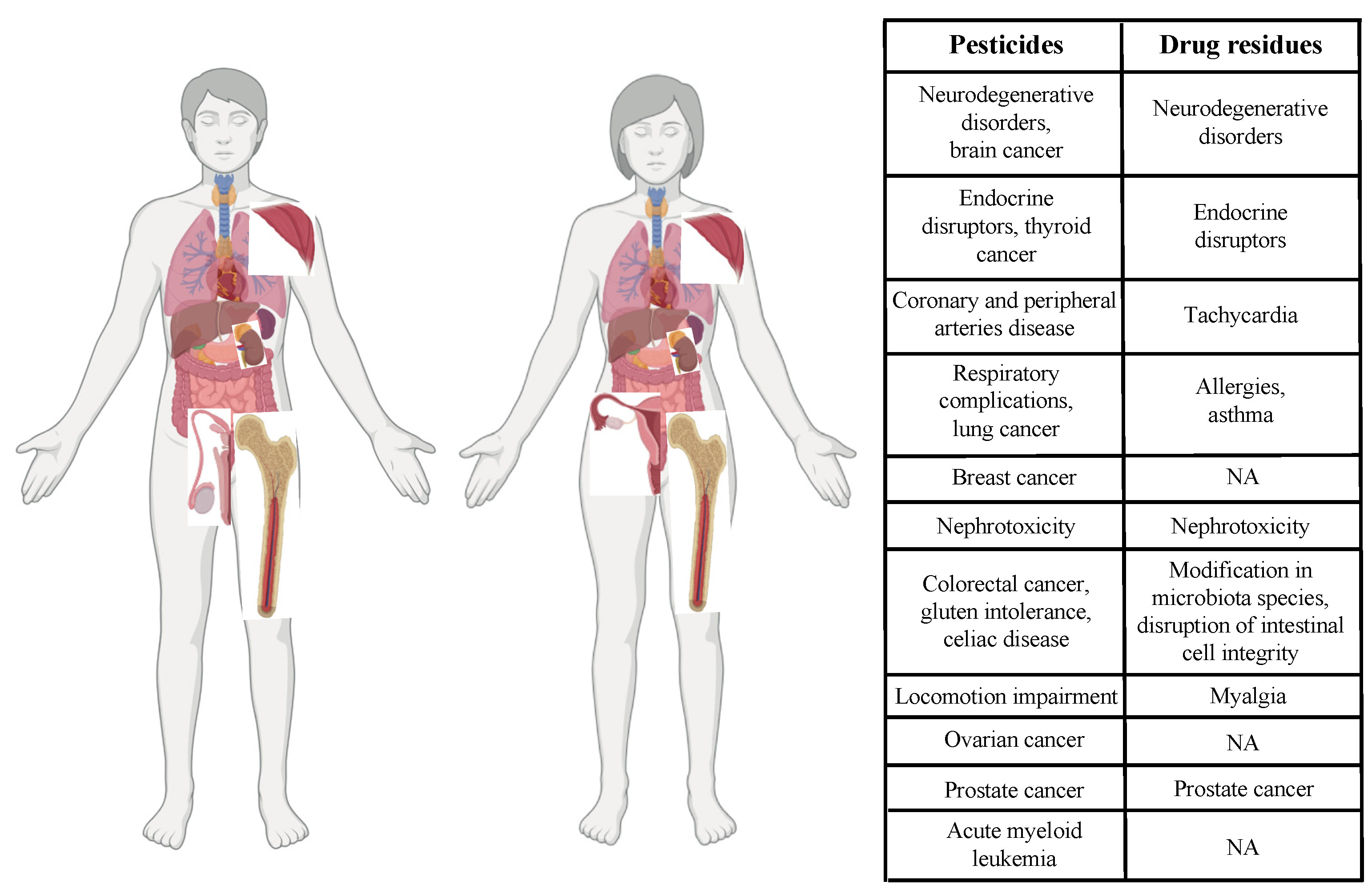
5. Impact of Pesticides and Drug Residues on Human Health at the Cellular Level
5.1. Pesticides
5.2. Drug Residues
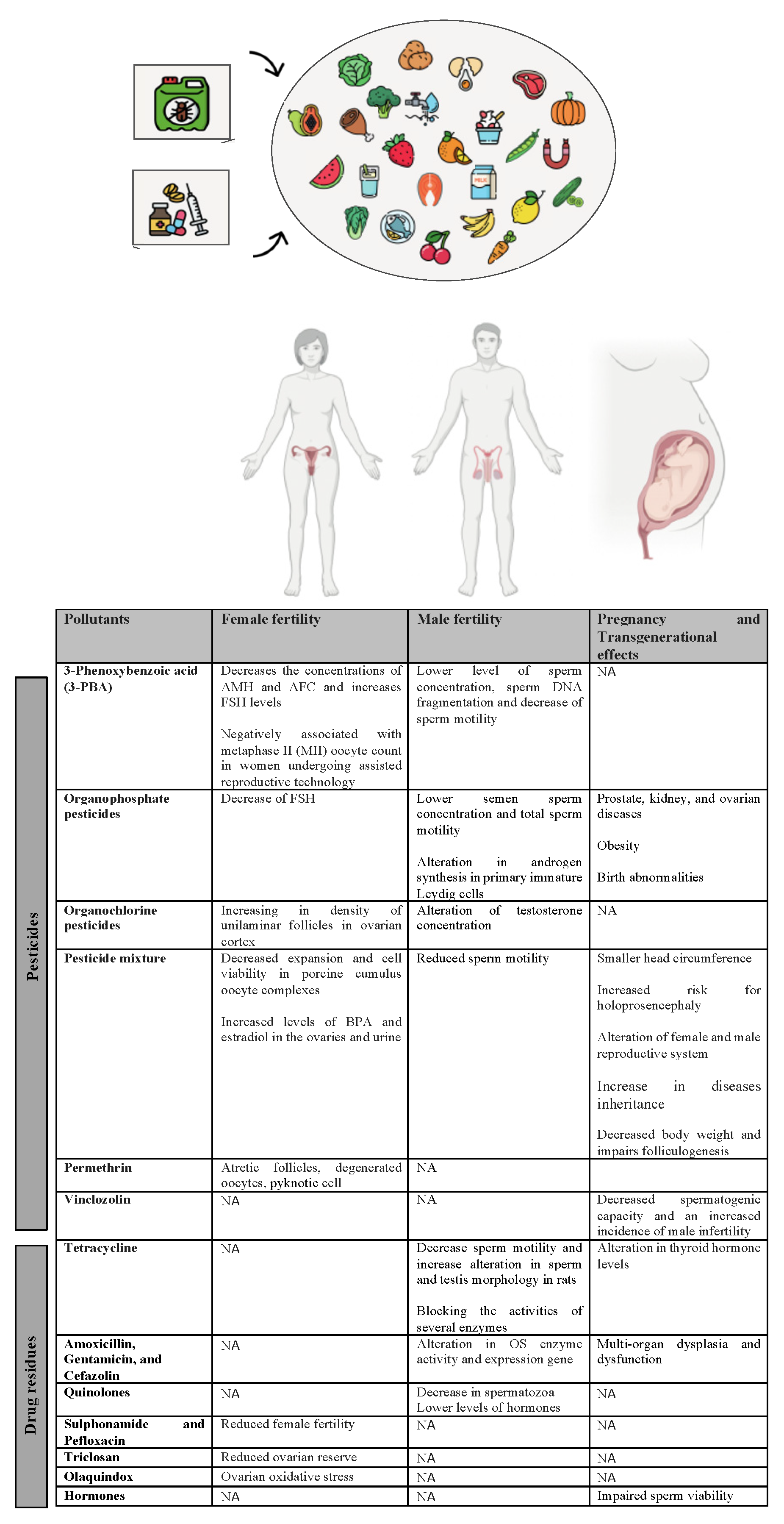
6. Effects of Pesticide and Drug Residues on Human Fertility, Embryo Development and Transgenerational Inheritance
6.1. Adverse Effects on Female Fertility and Pregnancy
6.1.1. Pesticides
6.1.2. Antibiotics
6.2. Adverse Effects on Male Fertility
6.2.1. Pesticides
6.2.2. Antibiotics
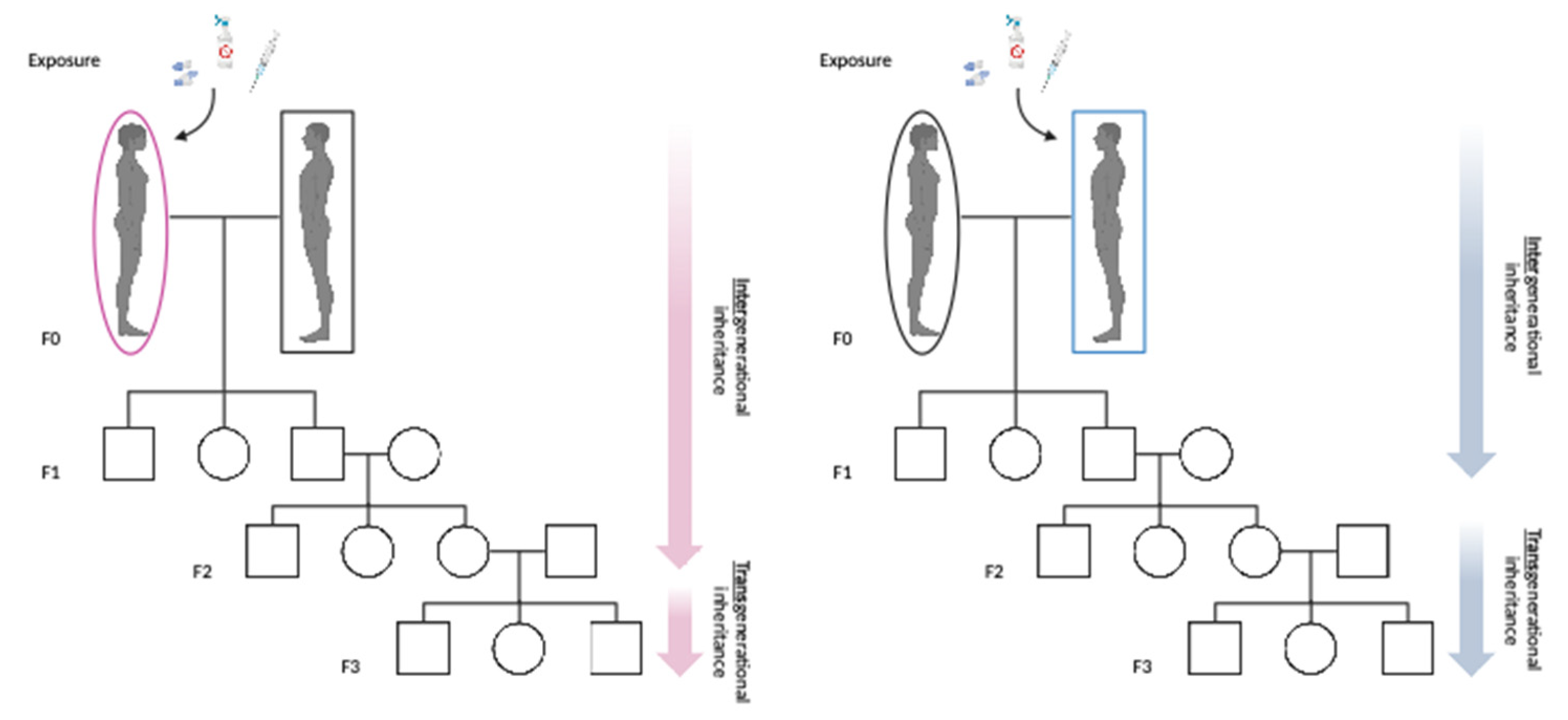
7. Intergenerational and Transgenerational Effects
8. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pathak, V. M.; Verma, V. K.; Rawat, B. S.; Kaur, B.; Babu, N.; Sharma, A.; Dewali, S.; Yadav, M.; Kumari, R.; Singh, S.; Mohapatra, A.; Pandey, V.; Rana, N.; Cunill, J. M. , Current status of pesticide effects on environment, human health and it’s eco-friendly management as bioremediation: A comprehensive review. Front Microbiol 2022, 13, 962619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takele Beyene, B. T. , Rational veterinary drug use: Its significance in public health. J.Vet.Med. Anim. Health 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Okeke, E. S.; Enochoghene, A.; Ezeudoka, B. C.; Kaka, S. D.; Chen, Y.; Mao, G.; ThankGod Eze, C.; Feng, W.; Wu, X. , A review of heavy metal risks around e-waste sites and comparable municipal dumpsites in major African cities: Recommendations and future perspectives. Toxicology 2024, 501, 153711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, E. S.; Okagu, I. U.; Okoye, C. O.; Ezeorba, T. P. C. , The use of calcium carbide in food and fruit ripening: Potential mechanisms of toxicity to humans and future prospects. Toxicology 2022, 468, 153112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkoh, J. N.; Shang, C.; Okeke, E. S.; Ejeromedoghene, O.; Oderinde, O.; Etafo, N. O.; Mgbechidinma, C. L.; Bakare, O. C.; Meugang, E. F. , Antibiotics soil-solution chemistry: A review of environmental behavior and uptake and transformation by plants. J Environ Manage 2024, 354, 120312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eze, C. G.; Okeke, E. S.; Nwankwo, C. E.; Nyaruaba, R.; Anand, U.; Okoro, O. J.; Bontempi, E. , Emerging contaminants in food matrices: An overview of the occurrence, pathways, impacts and detection techniques of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Toxicol Rep 2024, 12, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, H. O.; Shikoray, L.; Mohamed, M. I.; Habib, I.; Matsumoto, T. , Veterinary Drug Residues in the Food Chain as an Emerging Public Health Threat: Sources, Analytical Methods, Health Impacts, and Preventive Measures. Foods, 2024; 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles Obinwanne Okoye, C. I. A. , Olayinka Oderinde,Joseph Onyekwere Okoro,Jean Yves Uwamungu, Chukwudozie Kingsley Ikechukwu,Emmanuel Sunday Okeke, Onome Ejeromedoghene, Elijah Chibueze Odii Toxic Chemicals and Persistent Organic Pollutants Associated with Micro-and Nanoplastics Pollution. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances 2022, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Chukwuebuka Gabriel Eze, C. E. N. , Satarupa Dey, Suresh Sundaramurthy & Emmanuel Sunday Okeke, Food chain microplastics contamination and impact on human health: a review. Environ Chem Lett 2024, 22, 1889–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson Nkoh Nkoh, O. O., Nelson Oshogwue Etafo,Ghebretensae Aron Kifle,Emmanuel Sunday Okeke,Onome Ejeromedoghene,Chiamaka Linda Mgbechidinma,Emmanuel A. Oke, Saheed Abiola Raheem, Omonike Christianah Bakare,Olumuyiwa O. Ogunlaja, Omotayo Sindiku, Olatunde Sunday Oladeji Recent perspective of antibiotics remediation: A review of the principles, mechanisms, and chemistry controlling remediation from aqueous media. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 881.
- United Nation.
- Woodruff, T. J.; Zota, A. R.; Schwartz, J. M. , Environmental chemicals in pregnant women in the United States: NHANES 2003-2004. Environ Health Perspect 2011, 119(6), 878–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fini, J. B.; Mughal, B. B.; Le Mevel, S.; Leemans, M.; Lettmann, M.; Spirhanzlova, P.; Affaticati, P.; Jenett, A.; Demeneix, B. A. , Human amniotic fluid contaminants alter thyroid hormone signalling and early brain development in Xenopus embryos. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 43786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Dhok, A. , Effects of Pollution on Pregnancy and Infants. Cureus 2023, 15(1), e33906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- https://www.who.int.
- Singh, A.; Dhiman, N.; Kar, A. K.; Singh, D.; Purohit, M. P.; Ghosh, D.; Patnaik, S. , Advances in controlled release pesticide formulations: Prospects to safer integrated pest management and sustainable agriculture. J Hazard Mater 2020, 385, 121525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danjou, A. M. N.; Perol, O.; Coste, A.; Faure, E.; Beranger, R.; Boyle, H.; Belladame, E.; Grassot, L.; Dubuis, M.; Spinosi, J.; Bouaoun, L.; Flechon, A.; Bujan, L.; Drouineaud, V.; Eustache, F.; Berthaut, I.; Perrin, J.; Brugnon, F.; Charbotel, B.; Schuz, J.; Fervers, B.; group, T. s. , Domestic use of pesticides during early periods of development and risk of testicular germ cell tumors in adulthood: a French nationwide case-control study. Environ Health 2021, 20(1), 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, S.; Pesaresi, P.; Mizzotti, C.; Bulone, V.; Mezzetti, B.; Baraldi, E.; Masiero, S. , Game-changing alternatives to conventional fungicides: small RNAs and short peptides. Trends Biotechnol 2022, 40(3), 320–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, A. K.; Dix, D. J. , Mode of action for reproductive and hepatic toxicity inferred from a genomic study of triazole antifungals. Toxicol Sci 2009, 110(2), 449–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaabane, M.; Koubaa, M.; Soudani, N.; Elwej, A.; Grati, M.; Jamoussi, K.; Boudawara, T.; Ellouze Chaabouni, S.; Zeghal, N. , Nitraria retusa fruit prevents penconazole-induced kidney injury in adult rats through modulation of oxidative stress and histopathological changes. Pharm Biol 2017, 55(1), 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, S. O. , The history and current status of glyphosate. Pest Manag Sci 2018, 74(5), 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiesa, L. M.; Nobile, M.; Panseri, S.; Arioli, F. , Detection of glyphosate and its metabolites in food of animal origin based on ion-chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (IC-HRMS). Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 2019, 36(4), 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacanli, M.; Basaran, N. , Importance of antibiotic residues in animal food. Food Chem Toxicol 2019, 125, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarrazin, S.; Joosten, P.; Van Gompel, L.; Luiken, R. E. C.; Mevius, D. J.; Wagenaar, J. A.; Heederik, D. J. J.; Dewulf, J.; consortium, E. , Quantitative and qualitative analysis of antimicrobial usage patterns in 180 selected farrow-to-finish pig farms from nine European countries based on single batch and purchase data. J Antimicrob Chemother 2019, 74(3), 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C. X.; Li, Z. Y.; Zheng, Z. Y.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, R. F.; Fang, J. , Detection of fluoroquinolone and sulfonamide residues in poultry eggs in Kunming city, southwest China. Poult Sci 2022, 101(6), 101892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, T.; Duan, J.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Shi, H.; Kang, W. , Determination of Sulfonamide Residues in Food by Capillary Zone Electrophoresis with On-Line Chemiluminescence Detection Based on an Ag(III) Complex. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18, (6). [CrossRef]
- Eur. Union. 2019 December 11;L 4/43:43–167, R. E. o. t. E. P. a. o. t. C. o. D. o. v. m. p. a. r. D. E. O. J.
- Moussa, F.; Doumiati, S.; Bernabo, N.; Barboni, B.; Jaber, F.; Mokh, S. , Hormones residues in bovine animals: Sampling, analysis and health risk assessment. Steroids 2022, 181, 108994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaly, H. F.; Sharkawy, A. A. , Hormonal residues in chicken and cattle meat: A risk threat the present and future consumer health. Food Chem Toxicol 2023, 182, 114172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S. H.; Kang, D.; Lim, M. W.; Kang, C. S.; Sung, H. J. , Risk assessment of growth hormones and antimicrobial residues in meat. Toxicol Res 2010, 26(4), 301–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, R. J.; Bauman, D. E. , Update on human health concerns of recombinant bovine somatotropin use in dairy cows. J Anim Sci 2014, 92(4), 1800–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshad, A. A.; Enferadi, M.; Bakand, S.; Jamshidi Orak, R.; Mirkazemi, R. , Penicillin dust exposure and penicillin resistance among pharmaceutical workers in Tehran, Iran. Int J Occup Environ Health 2016, 22(3), 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M. N.; Lewis, D. F. , Steroid hormone receptors and dietary ligands: a selected review. Proc Nutr Soc 2002, 61(1), 105–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussa, F.; Mokh, S.; Doumiati, S.; Barboni, B.; Bernabo, N.; Al Iskandarani, M. , LC-MS/MS method for the determination of hormones: Validation, application and health risk assessment in various bovine matrices. Food Chem Toxicol 2020, 138, 111204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.; Pestana, D.; Faria, G.; Vasconcelos, F.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Calhau, C.; Domingues, V. F. , Method development for the determination of Synthetic Musks and Organophosphorus Pesticides in Human Adipose Tissue. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2020, 191, 113598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhilash, P. C.; Singh, N., Pesticide use and application: an Indian scenario. J Hazard Mater 2009, 165, (1-3), 1-12. [CrossRef]
- FDA, Pesticide Residue Monitoring Program Fiscal Year 2021 Pesticide Report. 2021.
- Lalonde, B.; Garron, C. , Temporal and Spatial Analysis of Surface Water Pesticide Occurrences in the Maritime Region of Canada. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 2020, 79(1), 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K. Hjorth, K. J., B. Holen,A. Andersson, H.B. Christensen, K. Siivinen, M. Toome Pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables from South America – A Nordic project. Food Control, 2011, 22.
- Wen Jun Zhang, F. J. , JianFeng O, Global pesticide consumption and pollution: with China as a focus. International Academy of Ecology and Environmental Sciences,.
- Anket Sharma, V. K., Babar Shahzad, Mohsin Tanveer, Gagan Preet Singh Sidhu, Neha Handa, Sukhmeen Kaur Kohli, Poonam Yadav, Aditi Shreeya Bali, Ripu Daman Parihar, Owias Iqbal Dar, Kirpal Singh, Shivam Jasrotia, Palak Bakshi, M. Ramakrishnan, Sandeep Kumar, Renu Bhardwaj & Ashwani Kumar Thukral Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. SN Appl. Sci 2019.
- Tang, W.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, L.; Huang, M.; Xu, S.; Yan, D. , Pyrethroid pesticide residues in the global environment: An overview. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 990–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis Carrasco Cabrera, G. D. P. , Bruno Dujardin and Paula Medina Pastor, The 2021 European Union report on pesticide residues in food. EFSA Journa 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Liguoro, M.; Bona, M. D.; Gallina, G.; Capolongo, F.; Gallocchio, F.; Binato, G.; Di Leva, V. , A monitoring of chemical contaminants in waters used for field irrigation and livestock watering in the Veneto region (Italy), using bioassays as a screening tool. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2014, 21(5), 3546–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storelli, M. M. , Evaluation of toxic metal (Hg, Cd, Pb), polychlorinated biphenyl (PCBs), and pesticide (DDTs) levels in aromatic herbs collected in selected areas of Southern Italy. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2014, 21(2), 946–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olisah, C.; Okoh, O. O.; Okoh, A. I. , Occurrence of organochlorine pesticide residues in biological and environmental matrices in Africa: A two-decade review. Heliyon 2020, 6(3), e03518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240057586.
- Soares, V. M.; Pereira, J. G.; Barreto, F.; Jank, L.; Rau, R. B.; Dias Ribeiro, C. B.; Dos Santos Castilhos, T.; Tomaszewski, C. A.; Hillesheim, D. R.; Mondadori, R. G.; Tadielo, L. E.; Dos Santos, E. A. R.; da Cruz Encide Sampaio, A. N.; Cerqueira-Cezar, C. K.; Duval, E. H.; da Silva, W. P. , Residues of Veterinary Drugs in Animal Products Commercialized in the Border Region of Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay. J Food Prot 2022, 85(6), 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houtman, C. J.; ten Broek, R.; de Jong, K.; Pieterse, B.; Kroesbergen, J. , A multicomponent snapshot of pharmaceuticals and pesticides in the river Meuse basin. Environ Toxicol Chem 2013, 32(11), 2449–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Serna, R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Petrovic, M.; Barcelo, D. , Multi-residue enantiomeric analysis of pharmaceuticals and their active metabolites in the Guadalquivir River basin (South Spain) by chiral liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 2013, 405(18), 5859–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, D.; Hilton, M.; Thomas, K. V. , Investigating the environmental transport of human pharmaceuticals to streams in the United Kingdom. Sci Total Environ, 2004, 333, (1-3), 167-84.
- Chau, H. T. C.; Kadokami, K.; Duong, H. T.; Kong, L.; Nguyen, T. T.; Nguyen, T. Q.; Ito, Y. , Occurrence of 1153 organic micropollutants in the aquatic environment of Vietnam. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2018, 25(8), 7147–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z. H.; Chen, L.; Meng, X. Z.; Duan, Y. P.; Zhang, Z. S.; Zeng, E. Y. , Occurrence and human health risk of wastewater-derived pharmaceuticals in a drinking water source for Shanghai, East China. Sci Total Environ 2014, 490, 987–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K. P.; Rai, P.; Singh, A. K.; Verma, P.; Gupta, S. , Occurrence of pharmaceuticals in urban wastewater of north Indian cities and risk assessment. Environ Monit Assess 2014, 186(10), 6663–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ergen, A. M.; Yalcin, S. S. , Unexpected drug residuals in human milk in Ankara, capital of Turkey. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19(1), 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatoye, O.; Kayode, S. T. , Oxytetracycline residues in retail chicken eggs in Ibadan, Nigeria. Food Addit Contam Part B Surveill 2012, 5(4), 255–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizuka, W. S. D. A. E. T. E. T. E. a. a. , Antibiotic residues in food: the African scenario. Japanese Journal of Veterinary Research 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, N.; Sun, P.; Sun, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Ji, X.; Zou, H.; Ottoson, J.; Nilsson, L. E.; Berglund, B.; Dyar, O. J.; Tamhankar, A. J.; Stalsby Lundborg, C. , Presence of antibiotic residues in various environmental compartments of Shandong province in eastern China: Its potential for resistance development and ecological and human risk. Environ Int 2018, 114, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K. H.; Kabir, E.; Jahan, S. A. , Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects. Sci Total Environ 2017, 575, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Wong, M. H.; Wang, M.; Andrews, C. B.; Zheng, C. , Efficient detection and assessment of human exposure to trace antibiotic residues in drinking water. Water Res 2020, 175, 115699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, S. Y.; Ismail, N. A. H.; Haron, D. E. M.; Yusoff, F. M.; Praveena, S. M.; Aris, A. Z. , Pharmaceuticals, hormones, plasticizers, and pesticides in drinking water. J Hazard Mater 2022, 424(Pt A), 127327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngigi, A. N.; Magu, M. M.; Muendo, B. M. , Occurrence of antibiotics residues in hospital wastewater, wastewater treatment plant, and in surface water in Nairobi County, Kenya. Environ Monit Assess 2019, 192(1), 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, M. E.; Santos, L.; Rodriguez Castro, M. C.; Giorgi, A.; Barcelo, D.; Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; Ame, M. V. , Distribution of antibiotics in water, sediments and biofilm in an urban river (Cordoba, Argentina, LA). Environ Pollut 2021, 269, 116133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad Bilal 1, S. M., Tahir Rasheed 3, Hafiz M.N. Iqbal Antibiotics traces in the aquatic environment: persistence and adverse environmental impact. 2020, 68-74.
- Laura, I. Mas, V. C. A., Eduardo De Gerónimo & José L. Costa Pesticides in water sources used for human consumption in the semiarid region of Argentina. SN Appl. Sci 2020, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Colombo, R.; Papetti, A. , Advances in the Analysis of Veterinary Drug Residues in Food Matrices by Capillary Electrophoresis Techniques. Molecules, 2019, 24, (24). [CrossRef]
- Chantziaras, I.; Boyen, F.; Callens, B.; Dewulf, J. , Correlation between veterinary antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in food-producing animals: a report on seven countries. J Antimicrob Chemother 2014, 69(3), 827–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez, C. G.; Macklin, K. S.; Kumar, S.; Bailey, M.; Ebner, P. E.; Oliver, H. F.; Martin-Gonzalez, F. S.; Singh, M. , Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Salmonella isolated from poultry farms in southeastern United States. Poult Sci 2018, 97(6), 2144–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiana Goia R. de Oliveira a, M. C. b., Francieli F. Lucchette b, José Luis Salgon b, Almir Sales, A technical note on the relationship between ultrasonic velocity and moisture content of Brazilian hardwood (Goupia glabra). Building and Environment 2005, 40, (Building and Environment2), 297-300.
- Sangeeta Singh a, A. S. Y. a. , Satyendra Mohan Singh b, Priyanka Bharti, Prevalence of Salmonella in chicken eggs collected from poultry farms and marketing channels and their antimicrobial resistance. Food Research International 2010, 43(8), 2027–2030. [Google Scholar]
- https://www.oecd.org/publications/oecd-fao-agricultural-outlook-19991142.htm.
- Lin, Z.; Vahl, C. I.; Riviere, J. E. , Human Food Safety Implications of Variation in Food Animal Drug Metabolism. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 27907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callens, B.; Persoons, D.; Maes, D.; Laanen, M.; Postma, M.; Boyen, F.; Haesebrouck, F.; Butaye, P.; Catry, B.; Dewulf, J. , Prophylactic and metaphylactic antimicrobial use in Belgian fattening pig herds. Prev Vet Med 2012, 106(1), 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cuong, N.; Nhung, N. T.; Nghia, N. H.; Mai Hoa, N. T.; Trung, N. V.; Thwaites, G.; Carrique-Mas, J. , Antimicrobial Consumption in Medicated Feeds in Vietnamese Pig and Poultry Production. Ecohealth 2016, 13(3), 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, L. E.; Daeseleire, E.; Devreese, M.; Rasschaert, G.; Smet, A.; Dewulf, J.; Heyndrickx, M.; Imberechts, H.; Haesebrouck, F.; Butaye, P.; Croubels, S. , Residues of chlortetracycline, doxycycline and sulfadiazine-trimethoprim in intestinal content and feces of pigs due to cross-contamination of feed. BMC Vet Res 2016, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baazize-Ammi, D.; Dechicha, A. S.; Tassist, A.; Gharbi, I.; Hezil, N.; Kebbal, S.; Morsli, W.; Beldjoudi, S.; Saadaoui, M. R.; Guetarni, D. , Screening and quantification of antibiotic residues in broiler chicken meat and milk in the central region of Algeria. Rev Sci Tech 2019, 38(3), 863–877. [Google Scholar]
- Penagos-Tabares, F.; Sulyok, M.; Faas, J.; Krska, R.; Khiaosa-Ard, R.; Zebeli, Q. , Residues of pesticides and veterinary drugs in diets of dairy cattle from conventional and organic farms in Austria. Environ Pollut 2023, 316(Pt 2) Pt 2, 120626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, A. K.; Schnabel, K.; Billenkamp, F.; Buhler, S.; Frahm, J.; Kersten, S.; Huther, L.; Meyer, U.; von Soosten, D.; Trakooljul, N.; Teifke, J. P.; Danicke, S. , Effects of glyphosate residues and different concentrate feed proportions in dairy cow rations on hepatic gene expression, liver histology and biochemical blood parameters. PLoS One 2021, 16(2), e0246679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger1, M.; , P. S.; , W. S.; , H.-W. H.; , W. L.; Shehata, a. A. A., Detection of Glyphosate Residues in Animals and Humans. J Environ Anal Toxicol 2014.
- von Soosten, D.; Meyer, U.; Huther, L.; Danicke, S.; Lahrssen-Wiederholt, M.; Schafft, H.; Spolders, M.; Breves, G. , Excretion pathways and ruminal disappearance of glyphosate and its degradation product aminomethylphosphonic acid in dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 2016, 99(7), 5318–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foldager, L.; Winters, J. F. M.; Norskov, N. P.; Sorensen, M. T. , Impact of feed glyphosate residues on broiler breeder egg production and egg hatchability. Sci Rep 2021, 11(1), 19290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connolly, A.; Basinas, I.; Jones, K.; Galea, K. S.; Kenny, L.; McGowan, P.; Coggins, M. A. , Characterising glyphosate exposures among amenity horticulturists using multiple spot urine samples. Int J Hyg Environ Health 2018, 221(7), 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, N. S.; Banerjee, K.; Utture, S.; Kamble, N.; Rao, B. M.; Panda, S. K.; Mathew, S. , Assessment of polyaromatic hydrocarbons and pesticide residues in domestic and imported pangasius (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus) fish in India. J Sci Food Agric 2016, 96(7), 2373–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu Rico a, T. M. P. b. c., Kriengkrai Satapornvanit d, Jiang Min e, A.M. Shahabuddin f g, Patrik J.G. Henriksson h, Francis J. Murray i, David C. Little i, Anders Dalsgaard c, Paul J. Van den Brink, Use of veterinary medicines, feed additives and probiotics in four major internationally traded aquaculture species farmed in Asia. 2013, Volumes 412–413, 231-243.
- Song, S.; Zhu, K.; Han, L.; Sapozhnikova, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, W. , Residue Analysis of 60 Pesticides in Red Swamp Crayfish Using QuEChERS with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 2018, 66(20), 5031–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnipseed, S. B.; Storey, J. M.; Lohne, J. J.; Andersen, W. C.; Burger, R.; Johnson, A. S.; Madson, M. R. , Wide-Scope Screening Method for Multiclass Veterinary Drug Residues in Fish, Shrimp, and Eel Using Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 2017, 65(34), 7252–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oerlemans, A.; Figueiredo, D. M.; Mol, J. G. J.; Nijssen, R.; Anzion, R. B. M.; van Dael, M. F. P.; Duyzer, J.; Roeleveld, N.; Russel, F. G. M.; Vermeulen, R. C. H.; Scheepers, P. T. J. , Personal exposure assessment of pesticides in residents: The association between hand wipes and urinary biomarkers. Environ Res 2021, 199, 111282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwman, H.; Sereda, B.; Meinhardt, H. M. , Simultaneous presence of DDT and pyrethroid residues in human breast milk from a malaria endemic area in South Africa. Environ Pollut 2006, 144(3), 902–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkiene, E.; Ruzauskas, M.; Bartkevics, V.; Pugajeva, I.; Zavistanaviciute, P.; Starkute, V.; Zokaityte, E.; Lele, V.; Dauksiene, A.; Grashorn, M.; Hoelzle, L. E.; Mendybayeva, A.; Ryshyanova, R.; Gruzauskas, R. , Study of the antibiotic residues in poultry meat in some of the EU countries and selection of the best compositions of lactic acid bacteria and essential oils against Salmonella enterica. Poult Sci 2020, 99(8), 4065–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- www.efsa.europa.eu/en/news/efsa-reassesses-safety-feed-additive-ethoxyquin.
- Macfarlane, E.; Carey, R.; Keegel, T.; El-Zaemay, S.; Fritschi, L. , Dermal exposure associated with occupational end use of pesticides and the role of protective measures. Saf Health Work 2013, 4(3), 136–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slocum, A. C.; Shern, L. C. , Spray deposition patterns during simulated work activities by lawn care specialists. J Environ Sci Health B 1991, 26(3), 259–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Murison, J.; Wang, J.; Leong, G.; Wu, Z.; Li, Q. , Dermal exposure assessment to trinexapac-ethyl: a case study of workers in golf course in Hawaii, USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2021, 28(1), 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebailly, P.; Bouchart, V.; Baldi, I.; Lecluse, Y.; Heutte, N.; Gislard, A.; Malas, J. P. , Exposure to pesticides in open-field farming in France. Ann Occup Hyg 2009, 53(1), 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msibi, S. S.; Chen, C. Y.; Chang, C. P.; Chen, C. J.; Chiang, S. Y.; Wu, K. Y. , High pesticide inhalation exposure from multiple spraying sources amongst applicators in Eswatini, Southern Africa. Pest Manag Sci 2021, 77(10), 4303–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lari, S.; Jonnalagadda, P. R.; Yamagani, P.; Medithi, S.; Vanka, J.; Pandiyan, A.; Naidu, M.; Jee, B. , Assessment of dermal exposure to pesticides among farmers using dosimeter and hand washing methods. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 957774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Gai, L.; Harkes, P.; Tan, G.; Ritsema, C. J.; Alcon, F.; Contreras, J.; Abrantes, N.; Campos, I.; Baldi, I.; Bureau, M.; Christ, F.; Mandrioli, D.; Sgargi, D.; Paskovic, I.; Polic Paskovic, M.; Glavan, M.; Hofman, J.; Huerta Lwanga, E.; Norgaard, T.; Bilkova, Z.; Osman, R.; Khurshid, C.; Navarro, I.; de la Torre, A.; Sanz, P.; Angeles Martinez, M.; Dias, J.; Mol, H.; Gort, G.; Martins Figueiredo, D.; Scheepers, P. T. J.; Schlunssen, V.; Vested, A.; Alaoui, A.; Geissen, V. , Pesticide residues with hazard classifications relevant to non-target species including humans are omnipresent in the environment and farmer residences. Environ Int 2023, 181, 108280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, W.; Jones, K.; Fuhrimann, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Sams, C.; Harding, A. H.; Povey, A.; Atuhaire, A.; Basinas, I.; van Tongeren, M.; Kromhout, H.; Galea, K. S. , Factors influencing occupational exposure to pyrethroids and glyphosate: An analysis of urinary biomarkers in Malaysia, Uganda and the United Kingdom. Environ Res 2024, 242, 117651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, T.; Merrill, A. K.; Eckard, M. L.; Marvin, E.; Conrad, K.; Welle, K.; Oberdorster, G.; Sobolewski, M.; Cory-Slechta, D. A. , Paraquat Inhalation, a Translationally Relevant Route of Exposure: Disposition to the Brain and Male-Specific Olfactory Impairment in Mice. Toxicol Sci 2021, 180(1), 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, B. A.; Ahmed, I. A.; Karloukovski, V.; MacLaren, D. A.; Foulds, P. G.; Allsop, D.; Mann, D. M.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Calderon-Garciduenas, L. , Magnetite pollution nanoparticles in the human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113(39), 10797–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bus, J. S.; Cagen, S. Z.; Olgaard, M.; Gibson, J. E. , A mechanism of paraquat toxicity in mice and rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1976, 35(3), 501–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamsan, H.; Ho, Y. B.; Zaidon, S. Z.; Hashim, Z.; Saari, N.; Karami, A., Occurrence of commonly used pesticides in personal air samples and their associated health risk among paddy farmers. Sci Total Environ 2017, 603-604, 381-389. [CrossRef]
- Bluemlein, K.; Nowak, N.; Ellinghusen, B.; Gerling, S.; Badorrek, P.; Hansen, T.; Hohlfeld, J. M.; Paul, R.; Schuchardt, S. , Occupational exposure to veterinary antibiotics: Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin in humans after dermal, inhalation and oral uptake - A clinical study. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2023, 100, 104139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamscher, G.; Pawelzick, H. T.; Sczesny, S.; Nau, H.; Hartung, J. , Antibiotics in dust originating from a pig-fattening farm: a new source of health hazard for farmers? Environ Health Perspect 2003, 111(13), 1590–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed A. Ghorab, M. S. K., Toxicological Effects of Organophosphates Pesticides. International Journal of Environmental Monitoring and Analysis 2015, 3, (4).
- Garcia, J.; Ventura, M. I.; Requena, M.; Hernandez, A. F.; Parron, T.; Alarcon, R. , Association of reproductive disorders and male congenital anomalies with environmental exposure to endocrine active pesticides. Reprod Toxicol 2017, 71, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, A. E.; Gaines, S. D.; Deschenes, O. , Agricultural pesticide use and adverse birth outcomes in the San Joaquin Valley of California. Nat Commun 2017, 8(1), 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addissie, Y. A.; Kruszka, P.; Troia, A.; Wong, Z. C.; Everson, J. L.; Kozel, B. A.; Lipinski, R. J.; Malecki, K. M. C.; Muenke, M. , Prenatal exposure to pesticides and risk for holoprosencephaly: a case-control study. Environ Health 2020, 19(1), 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bast, A.; Semen, K. O.; Drent, M. , Pulmonary toxicity associated with occupational and environmental exposure to pesticides and herbicides. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2021, 27(4), 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadauriya, P.; Parihar, R.; Ganesh, S. , Pesticides DEET, fipronil and maneb induce stress granule assembly and translation arrest in neuronal cells. Biochem Biophys Rep 2021, 28, 101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witczak, A.; Pohorylo, A.; Abdel-Gawad, H., Endocrine-Disrupting Organochlorine Pesticides in Human Breast Milk: Changes during Lactation. Nutrients 2021, 13, (1). [CrossRef]
- Gea, M.; Zhang, C.; Tota, R.; Gilardi, G.; Di Nardo, G.; Schiliro, T. , Assessment of Five Pesticides as Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: Effects on Estrogen Receptors and Aromatase. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19, (4). [CrossRef]
- Iteire, K. A.; Sowole, A. T.; Ogunlade, B. , Exposure to pyrethroids induces behavioral impairments, neurofibrillary tangles and tau pathology in Alzheimer’s type neurodegeneration in adult Wistar rats. Drug Chem Toxicol 2022, 45(2), 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier, H.; Trasande, L.; Porta, M. , Exposures to pesticides and risk of cancer: Evaluation of recent epidemiological evidence in humans and paths forward. Int J Cancer 2023, 152(5), 879–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, J. R.; Quan, Y.; Sherer, T. B.; Greenamyre, J. T.; Miller, G. W. , Paraquat neurotoxicity is distinct from that of MPTP and rotenone. Toxicol Sci 2005, 88(1), 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, L.; Trombetta, L.; Hardej, D. , Ethylene bisdithiocarbamate pesticides Maneb and Mancozeb cause metal overload in human colon cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2016, 41, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stykel, M. G.; Humphries, K.; Kirby, M. P.; Czaniecki, C.; Wang, T.; Ryan, T.; Bamm, V.; Ryan, S. D. , Nitration of microtubules blocks axonal mitochondrial transport in a human pluripotent stem cell model of Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J 2018, 32(10), 5350–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherer, T. B.; Betarbet, R.; Testa, C. M.; Seo, B. B.; Richardson, J. R.; Kim, J. H.; Miller, G. W.; Yagi, T.; Matsuno-Yagi, A.; Greenamyre, J. T. , Mechanism of toxicity in rotenone models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 2003, 23(34), 10756–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Du, Z.; Yan, Z.; Yuan, X.; Dai, L.; Yu, T.; Xiong, M.; Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Meng, L.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z. , Exposure to the environmentally toxic pesticide maneb induces Parkinson’s disease-like neurotoxicity in mice: A combined proteomic and metabolomic analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 308 Pt 2, 136344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calaf, G. M. , Role of organophosphorous pesticides and acetylcholine in breast carcinogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol 2021, 76, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Lerro, C.; Lavoue, J.; Huang, H.; Siemiatycki, J.; Zhao, N.; Ma, S.; Deziel, N. C.; Friesen, M. C.; Udelsman, R.; Zhang, Y. , Occupational exposure to pesticides and other biocides and risk of thyroid cancer. Occup Environ Med 2017, 74(7), 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, N. T.; Wathieu, H.; Glasgow, E.; Peran, I.; Parasido, E.; Li, T.; Simbulan-Rosenthal, C. M.; Rosenthal, D.; Medvedev, A. V.; Makarov, S. S.; Albanese, C.; Byers, S. W.; Dakshanamurthy, S. , A novel chemo-phenotypic method identifies mixtures of salpn, vitamin D3, and pesticides involved in the development of colorectal and pancreatic cancer. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2022, 233, 113330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Park, E. Y.; Kim, J.; Park, E.; Oh, J. K.; Lim, M. K. , Occupational Exposure to Pesticides and Lung Cancer Risk: A Propensity Score Analyses. Cancer Res Treat 2022, 54(1), 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, L. A.; Beane Freeman, L. E.; Lerro, C. C.; Andreotti, G.; Hofmann, J. N.; Parks, C. G.; Sandler, D. P.; Lubin, J. H.; Blair, A.; Koutros, S. , Pesticide exposure and risk of aggressive prostate cancer among private pesticide applicators. Environ Health 2020, 19(1), 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, B. S.; Gordon, J. I. , A humanized gnotobiotic mouse model of host-archaeal-bacterial mutualism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103(26), 10011–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H. S.; Lee, J. C.; Lee, I. K.; Moon, H. B.; Chang, Y. S.; Jacobs, D. R., Jr.; Lee, D. H. , Associations among organochlorine pesticides, Methanobacteriales, and obesity in Korean women. PLoS One 2011, 6(11), e27773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, K. R.; Williams, W. M.; Mackay, D.; Purdy, J.; Giddings, J. M.; Giesy, J. P. , Properties and uses of chlorpyrifos in the United States. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 2014, 231, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Tsakiridis, E. E.; Zhang, S.; Llanos, A.; Desjardins, E. M.; Yabut, J. M.; Green, A. E.; Day, E. A.; Smith, B. K.; Lally, J. S. V.; Wu, J.; Raphenya, A. R.; Srinivasan, K. A.; McArthur, A. G.; Kajimura, S.; Patel, J. S.; Wade, M. G.; Morrison, K. M.; Holloway, A. C.; Steinberg, G. R. , The pesticide chlorpyrifos promotes obesity by inhibiting diet-induced thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue. Nat Commun 2021, 12(1), 5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallal, N.; El Khayat El Sabbouri, H.; Salami, A.; Ramadan, W.; Khachfe, H.; Moustafa, M. E.; Khalil, M.; Joumaa, W. H. , Impacts of prolonged chlorpyrifos exposure on locomotion and slow-and fast- twitch skeletal muscles contractility in rats. Toxicol Rep 2019, 6, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizah Wahab, R. H. , Noor H. Ismail,Nurnajayati Omar, The effect of pesticide exposure on cardiovascular system: a systematic review. International Journal Of Community Medicine And Public Health 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Zhou, J.; Shen, Y.; Lin, R.; Hu, H.; Zeng, K.; Bi, H.; Huang, M.; Yu, L.; Zeng, S.; Miao, J. , Studies on the interaction of five triazole fungicides with human renal transporters in cells. Toxicol In Vitro 2023, 88, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsel, A.; Seneff, S. , Glyphosate, pathways to modern diseases III: Manganese, neurological diseases, and associated pathologies. Surg Neurol Int 2015, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandro Cassini 1, L. D. H., Diamantis Plachouras 2, Annalisa Quattrocchi 2, Ana Hoxha 2, Gunnar Skov Simonsen 3, Mélanie Colomb-Cotinat 4, Mirjam E Kretzschmar 5, Brecht Devleesschauwer 6, Michele Cecchini 7, Driss Ait Ouakrim 7, Tiago Cravo Oliveira 7, Marc J Struelens 2, Carl Suetens 2, Dominique L Monnet 2; Burden of AMR Collaborative Group, Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2018.
- Rahman, M. S.; Hassan, M. M.; Chowdhury, S. , Determination of antibiotic residues in milk and assessment of human health risk in Bangladesh. Heliyon 2021, 7(8), e07739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Wu, Z.; Fang, Z.; Cravotto, G. , Sonolytic degradation kinetics and mechanisms of antibiotics in water and cow milk. Ultrason Sonochem 2023, 99, 106518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, T. , Veterinary Drug Residues in Food-animal Products: Its Risk Factors and Potential Effects on Public Health. J Veterinar Sci Technol 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhishek Sharma, A. K. , Multi-residue detection of antibiotics in migratory goat milk and human health risk assessment in Western Himalayan region, India. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2024, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llor, C.; Bjerrum, L. , Antimicrobial resistance: risk associated with antibiotic overuse and initiatives to reduce the problem. Ther Adv Drug Saf 2014, 5(6), 229–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadighara, n.; Sadighara5, P. S. S. R. R. H. S. S. A. S. S. Y. M. M. M. S., The effect of residual antibiotics in food on intestinal microbiota: a systematic review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst 2023.
- Chen, R. A.; Wu, W. K.; Panyod, S.; Liu, P. Y.; Chuang, H. L.; Chen, Y. H.; Lyu, Q.; Hsu, H. C.; Lin, T. L.; Shen, T. D.; Yang, Y. T.; Zou, H. B.; Huang, H. S.; Lin, Y. E.; Chen, C. C.; Ho, C. T.; Lai, H. C.; Wu, M. S.; Hsu, C. C.; Sheen, L. Y. , Dietary Exposure to Antibiotic Residues Facilitates Metabolic Disorder by Altering the Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Composition. mSystems 2022, 7(3), e0017222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H. S.; Jung, D. W.; Han, S.; Kang, H. S.; Suh, J. H.; Oh, H. S.; Hwang, M. S.; Moon, G.; Park, Y.; Hong, J. H.; Koo, Y. E. , Veterinary drug, 17beta-trenbolone promotes the proliferation of human prostate cancer cell line through the Akt/AR signaling pathway. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inhorn, M. C.; Patrizio, P. , Infertility around the globe: new thinking on gender, reproductive technologies and global movements in the 21st century. Hum Reprod Update 2015, 21(4), 411–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skakkebaek, N. E.; Lindahl-Jacobsen, R.; Levine, H.; Andersson, A. M.; Jorgensen, N.; Main, K. M.; Lidegaard, O.; Priskorn, L.; Holmboe, S. A.; Brauner, E. V.; Almstrup, K.; Franca, L. R.; Znaor, A.; Kortenkamp, A.; Hart, R. J.; Juul, A. , Environmental factors in declining human fertility. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2022, 18(3), 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S. S.; D, D.; S, H.; Sonkusare, S.; Naik, P. B.; Kumari, N. S.; Madhyastha, H. , Environmental pollutants and their effects on human health. Heliyon 2023, 9(9), e19496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sifakis, S.; Androutsopoulos, V. P.; Tsatsakis, A. M.; Spandidos, D. A. , Human exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals: effects on the male and female reproductive systems. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 2017, 51, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami-Mohajeri, S.; Abdollahi, M. , Toxic influence of organophosphate, carbamate, and organochlorine pesticides on cellular metabolism of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates: a systematic review. Hum Exp Toxicol 2011, 30(9), 1119–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorson, J. L. M.; Beck, D.; Ben Maamar, M.; Nilsson, E. E.; Skinner, M. K. , Epigenome-wide association study for pesticide (Permethrin and DEET) induced DNA methylation epimutation biomarkers for specific transgenerational disease. Environ Health 2020, 19(1), 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, F.; Smitz, J. , Molecular control of oogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012, 1822(12), 1896–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimon-Dahari, N.; Yerushalmi-Heinemann, L.; Alyagor, L.; Dekel, N. , Ovarian Folliculogenesis. Results Probl Cell Differ 2016, 58, 167–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, W. L.; Auchus, R. J. , The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr Rev 2011, 32(1), 81–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretveld, R. W.; Thomas, C. M.; Scheepers, P. T.; Zielhuis, G. A.; Roeleveld, N. , Pesticide exposure: the hormonal function of the female reproductive system disrupted? Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2006, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D.E. Ray , S. A. B., Pyrethrins/Pyrethroids. Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition) 2014, 1152-1158.
- https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov.
- Kotil, T.; Yon, N. D. , The effects of permethrin on rat ovarian tissue morphology. Exp Toxicol Pathol 2015, 67(3), 279–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurewicz, J.; Radwan, P.; Wielgomas, B.; Radwan, M.; Karwacka, A.; Kaluzny, P.; Piskunowicz, M.; Dziewirska, E.; Hanke, W. , Exposure to pyrethroid pesticides and ovarian reserve. Environ Int 2020, 144, 106028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, P.; Wielgomas, B.; Radwan, M.; Krasinski, R.; Kilanowicz-Sapota, A.; Banaszczyk, R.; Jurewicz, J. , Synthetic Pyrethroids Exposure and Embryological Outcomes: A Cohort Study in Women from Fertility Clinic. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19, (9). [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, R.; Megha, P.; Sreedev, P. , Organochlorine pesticides, their toxic effects on living organisms and their fate in the environment. Interdiscip Toxicol. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, L.; Hu, Y.; Tse, L. A.; Wang, Y.; Qin, K.; Ding, G.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X.; Ouyang, F.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Tian, Y.; Shanghai Birth Cohort, S. , Exposure to Organophosphate Pesticides and Menstrual Cycle Characteristics in Chinese Preconceptional Women. Am J Epidemiol 2020, 189(5), 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medithi, S.; Kasa, Y. D.; Jee, B.; Venkaiah, K.; Jonnalagadda, P. R. , Alterations in reproductive hormone levels among farm women and their children occupationally exposed to organophosphate pesticides. Women Health 2022, (5), 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Weng, X.; Liu, S.; Tan, Y.; Liang, H.; Li, Y.; Wen, L.; Chen, Q.; Jing, C. , Associations of single and multiple organophosphate pesticide exposure with female infertility in the USA: data from the 2015-2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2023, 30(9), 23411–23421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorvang, R. D.; Hassan, J.; Stefopoulou, M.; Gemzell-Danielsson, K.; Pedrelli, M.; Kiviranta, H.; Rantakokko, P.; Ruokojarvi, P.; Lindh, C. H.; Acharya, G.; Damdimopoulou, P. , Persistent organic pollutants and the size of ovarian reserve in reproductive-aged women. Environ Int 2021, 155, 106589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagna, C.; Sirard, M. A.; Ayotte, P.; Bailey, J. L. , Impaired maturation, fertilization, and embryonic development of porcine oocytes following exposure to an environmentally relevant organochlorine mixture. Biol Reprod 2001, 65(2), 554–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, T.; Weaver, R. E.; Ghasemi, R.; deCatanzaro, D. , A mixture of five endocrine-disrupting chemicals modulates concentrations of bisphenol A and estradiol in mice. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, C.; Chevrier, C.; Durand, G.; Monfort, C.; Rouget, F.; Garlantezec, R.; Cordier, S. , Impact on fetal growth of prenatal exposure to pesticides due to agricultural activities: a prospective cohort study in Brittany, France. Environ Health 2010, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dopavogui, L.; Cadoret, F.; Loison, G.; El Fouikar, S.; Frenois, F. X.; Giton, F.; Ellero-Simatos, S.; Lasserre, F.; Polizzi, A.; Rives, C.; Loiseau, N.; Leandri, R. D.; Gatimel, N.; Gamet-Payrastre, L. , Pre- and Postnatal Dietary Exposure to a Pesticide Cocktail Disrupts Ovarian Functions in 8-Week-Old Female Mice. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23, (14). [CrossRef]
- La Sala, G.; Farini, D.; De Felici, M. , Proapoptotic effects of lindane on mouse primordial germ cells. Toxicol Sci 2009, 108(2), 445–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, C. F.; Prates, K. V.; Siervo, G.; Mathias, P. C. F.; Fernandes, G. S. A. , Impairment of testicular development in rats exposed to acephate during maternal gestation and lactation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2020, 27(5), 5482–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Pan, W.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Gan, H.; Li, M.; Liao, T.; Yang, X.; Yang, Q.; Huang, C.; Geng, M.; Pan, G.; Liu, K.; Zhu, P.; Tao, F. , Association between antibiotic exposure and the risk of infertility in women of childbearing age: A case-control study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2023, 249, 114414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minguez-Alarcon, L.; Christou, G.; Messerlian, C.; Williams, P. L.; Carignan, C. C.; Souter, I.; Ford, J. B.; Calafat, A. M.; Hauser, R.; Team, E. S. , Urinary triclosan concentrations and diminished ovarian reserve among women undergoing treatment in a fertility clinic. Fertil Steril 2017, 108(2), 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y. Q.; Ge, L.; Han, Z.; Hao, X.; Zhang, M. L.; Zhang, X. J.; Zhou, C. J.; Zhang, D. J.; Liang, C. G. , Oral administration of olaquindox negatively affects oocytes quality and reproductive ability in female mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2020, 201, 110826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.; Gao, H.; Wang, B.; Huang, K.; Wu, X.; Liang, C.; Yan, S.; Han, Y.; Ding, P.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhu, P.; Liu, K.; Cao, Y.; Tao, F. , Urinary tetracycline antibiotics exposure during pregnancy and maternal thyroid hormone parameters: A repeated measures study. Sci Total Environ 2022, 838 Pt 2, 156146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Peng, Y.; Hu, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. , Prenatal amoxicillin exposure induces developmental toxicity in fetal mice and its characteristics. J Environ Sci (China) 2024, 137, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K. J.; Mitchell, A. A.; Yau, W. P.; Louik, C.; Hernandez-Diaz, S. , Maternal exposure to amoxicillin and the risk of oral clefts. Epidemiology 2012, 23(5), 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Fan, L.; Hu, H.; Yin, S. , Ciprofloxacin and enrofloxacin can cause reproductive toxicity via endocrine signaling pathways. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2022, 244, 114049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, G.; Xia, Y.; Gu, A.; Shi, X.; Long, Y.; Song, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. , Effects of non-occupational environmental exposure to pyrethroids on semen quality and sperm DNA integrity in Chinese men. Reprod Toxicol 2011, 31(2), 171–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurewicz, J.; Radwan, M.; Wielgomas, B.; Sobala, W.; Piskunowicz, M.; Radwan, P.; Bochenek, M.; Hanke, W. , The effect of environmental exposure to pyrethroids and DNA damage in human sperm. Syst Biol Reprod Med 2015, 61(1), 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshima, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Imai, K.; Yoshinaga, J.; Shiraishi, H.; Mizumoto, Y.; Hatakeyama, S.; Onohara, C.; Tokuoka, S. , Endocrine disrupting chemicals in urine of Japanese male partners of subfertile couples: a pilot study on exposure and semen quality. Int J Hyg Environ Health 2012, 215(5), 502–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Yoshinaga, J.; Yoshikane, M.; Shiraishi, H.; Mieno, M. N.; Yoshiike, M.; Nozawa, S.; Iwamoto, T. , Pyrethroid insecticide exposure and semen quality of young Japanese men. Reprod Toxicol 2014, 43, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, M. A.; Akhigbe, T. M.; Adeogun, A. E.; Adesoye, O. B.; Akhigbe, R. E. , Impact of organophosphate pesticides exposure on human semen parameters and testosterone: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023, 14, 1227836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Huang, T.; Li, H.; Ge, R. S. , Acephate interferes with androgen synthesis in rat immature Leydig cells. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J. Y.; Miao, Y.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y. L.; Chen, P. P.; Zhang, M.; Cui, F. P.; Shi, T.; Lu, T. T.; Liu, C. J.; Zeng, Q. , Serum multiple organochlorine pesticides in relation to testosterone concentrations among Chinese men from an infertility clinic. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yucra, S.; Gasco, M.; Rubio, J.; Gonzales, G. F. , Semen quality in Peruvian pesticide applicators: association between urinary organophosphate metabolites and semen parameters. Environ Health 2008, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, N.; Pant, A. B.; Chaturvedi, P. K.; Shukla, M.; Mathur, N.; Gupta, Y. K.; Saxena, D. K. , Semen quality of environmentally exposed human population: the toxicological consequence. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2013, 20(11), 8274–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, R.; Raghavan, S. C. , Exposure to Endosulfan can result in male infertility due to testicular atrophy and reduced sperm count. Cell Death Discov 2015, 1, 15020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Fang, C.; Liu, L.; Xia, G.; Qiao, H. , Disrupting effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on gonadal development and reproductive functions in chickens. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 2002, 37(4), 509–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faja, F.; Esteves, S.; Pallotti, F.; Cicolani, G.; Di Chiano, S.; Delli Paoli, E.; Lenzi, A.; Lombardo, F.; Paoli, D. , Environmental disruptors and testicular cancer. Endocrine 2022, 78(3), 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiola, S. Tijani a b, T. M. D. b., Ime A. Ubong c, Onaadepo Olufunke c, Elemi J. Ani c, Ebenezer O. Farombi, Rutin attenuated hexachlorobenzene-induced testicular injury via regulation of oxidative stress, steroidogenic enzymes and apoptotic process in male rats. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry Reports, 2024, 10.
- Chang, C.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Zhou, Z. , Associations between exposure to pesticides mixture and semen quality among the non-occupationally exposed males: Four statistical models. Environ Res 2024, 257, 119400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versporten, A.; Bruyndonckx, R.; Adriaenssens, N.; Hens, N.; Monnet, D. L.; Molenberghs, G.; Goossens, H.; Weist, K.; Coenen, S.; group, E. S.-N. s. , Consumption of tetracyclines, sulphonamides and trimethoprim, and other antibacterials in the community, European Union/European Economic Area, 1997-2017. J Antimicrob Chemother 2021, 76(12 Suppl 2), ii45–ii59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, I.; Roberts, M. , Tetracycline antibiotics: mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev, 2001, 65, (2), 232-60 ; second page, table of contents. [CrossRef]
- Chatzispyrou, I. A.; Held, N. M.; Mouchiroud, L.; Auwerx, J.; Houtkooper, R. H. , Tetracycline antibiotics impair mitochondrial function and its experimental use confounds research. Cancer Res 2015, 75(21), 4446–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farombi, E. O.; Ugwuezunmba, M. C.; Ezenwadu, T. T.; Oyeyemi, M. O.; Ekor, M. , Tetracycline-induced reproductive toxicity in male rats: effects of vitamin C and N-acetylcysteine. Exp Toxicol Pathol 2008, 60(1), 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, M.; Budak, H.; Ciftci, M. , Amoxicillin and gentamicin antibiotics treatment adversely influence the fertility and morphology through decreasing the Dazl gene expression level and increasing the oxidative stress. Arch Physiol Biochem 2019, (5), 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, R.; Adams, I. R.; Anderson, R. A. , Is there a role for DAZL in human female fertility? Mol Hum Reprod 2016, 22(6), 377–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, J. Y.; Rosen, M. P.; Nelson, L. M.; Turek, P. J.; Witte, J. S.; Cramer, D. W.; Cedars, M. I.; Reijo-Pera, R. A. , Novel missense mutations of the Deleted-in-AZoospermia-Like (DAZL) gene in infertile women and men. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2006, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eric A Miska, A. C. F.-S. , Transgenerational inheritance: Models and mechanisms of non-DNA sequence-based inheritance. Science 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mango, S. E. , Generations of longevity. Nature 2011, 302–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitelaw, L. D. E. , Understanding transgenerational epigenetic inheritance via the gametes in mammals. Nature Reviews Genetics 2012, 13, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Kelce, W. R.; Monosson, E.; Gamcsik, M. P.; Laws, S. C.; Gray, L. E., Jr. , Environmental hormone disruptors: evidence that vinclozolin developmental toxicity is mediated by antiandrogenic metabolites. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1994, 126(2), 276–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anway, M. D.; Cupp, A. S.; Uzumcu, M.; Skinner, M. K. , Epigenetic transgenerational actions of endocrine disruptors and male fertility. Science 2005, 308(5727), 1466–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, E. E.; Ben Maamar, M.; Skinner, M. K. , Role of epigenetic transgenerational inheritance in generational toxicology. Environ Epigenet 2022, 8(1), dvac001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubsad, D.; Nilsson, E. E.; King, S. E.; Sadler-Riggleman, I.; Beck, D.; Skinner, M. K. , Assessment of Glyphosate Induced Epigenetic Transgenerational Inheritance of Pathologies and Sperm Epimutations: Generational Toxicology. Sci Rep 2019, 9(1), 6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikkam, M.; Tracey, R.; Guerrero-Bosagna, C.; Skinner, M. K. , Pesticide and insect repellent mixture (permethrin and DEET) induces epigenetic transgenerational inheritance of disease and sperm epimutations. Reprod Toxicol 2012, 34(4), 708–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeh, J. A.; Bonilla, M. M.; Adrian, A. J.; Mesfin, S.; Zeh, D. W. , From father to son: transgenerational effect of tetracycline on sperm viability. Sci Rep 2012, 2, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duhig, K. E.; Myers, J.; Seed, P. T.; Sparkes, J.; Lowe, J.; Hunter, R. M.; Shennan, A. H.; Chappell, L. C.; group, P. t. , Placental growth factor testing to assess women with suspected pre-eclampsia: a multicentre, pragmatic, stepped-wedge cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 393(10183), 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argaw-Denboba, A.; Schmidt, T. S. B.; Di Giacomo, M.; Ranjan, B.; Devendran, S.; Mastrorilli, E.; Lloyd, C. T.; Pugliese, D.; Paribeni, V.; Dabin, J.; Pisaniello, A.; Espinola, S.; Crevenna, A.; Ghosh, S.; Humphreys, N.; Boruc, O.; Sarkies, P.; Zimmermann, M.; Bork, P.; Hackett, J. A. , Paternal microbiome perturbations impact offspring fitness. Nature 2024, 629(8012), 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




