Submitted:
09 August 2024
Posted:
12 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
-
Agriculture and automation:
- -
- Agricultural robotics AND agriculture AND emerging technologies
- -
- Robotic systems AND crops AND environmental sustainability in agriculture
- -
- Automation technologies AND agricultural practices
- -
- Trends in modular robotics AND agriculture
-
Multi-robot systems and control forms:
- -
- Autonomous robotic systems AND precision agriculture
- -
- Synthetic biology AND modular robots AND agricultural optimization
- -
- Bio-inspired robotics AND motion control
-
Modular robots, Multicellular robots, and Bacterial Quorum Sensing:
- -
- Modular robots AND multicellular robots
- -
- Bacterial quorum sensing AND robots
- -
- Synthetic biology AND modular robots AND agricultural optimization
3. Robots and Agriculture
3.1. Individual Robotic System
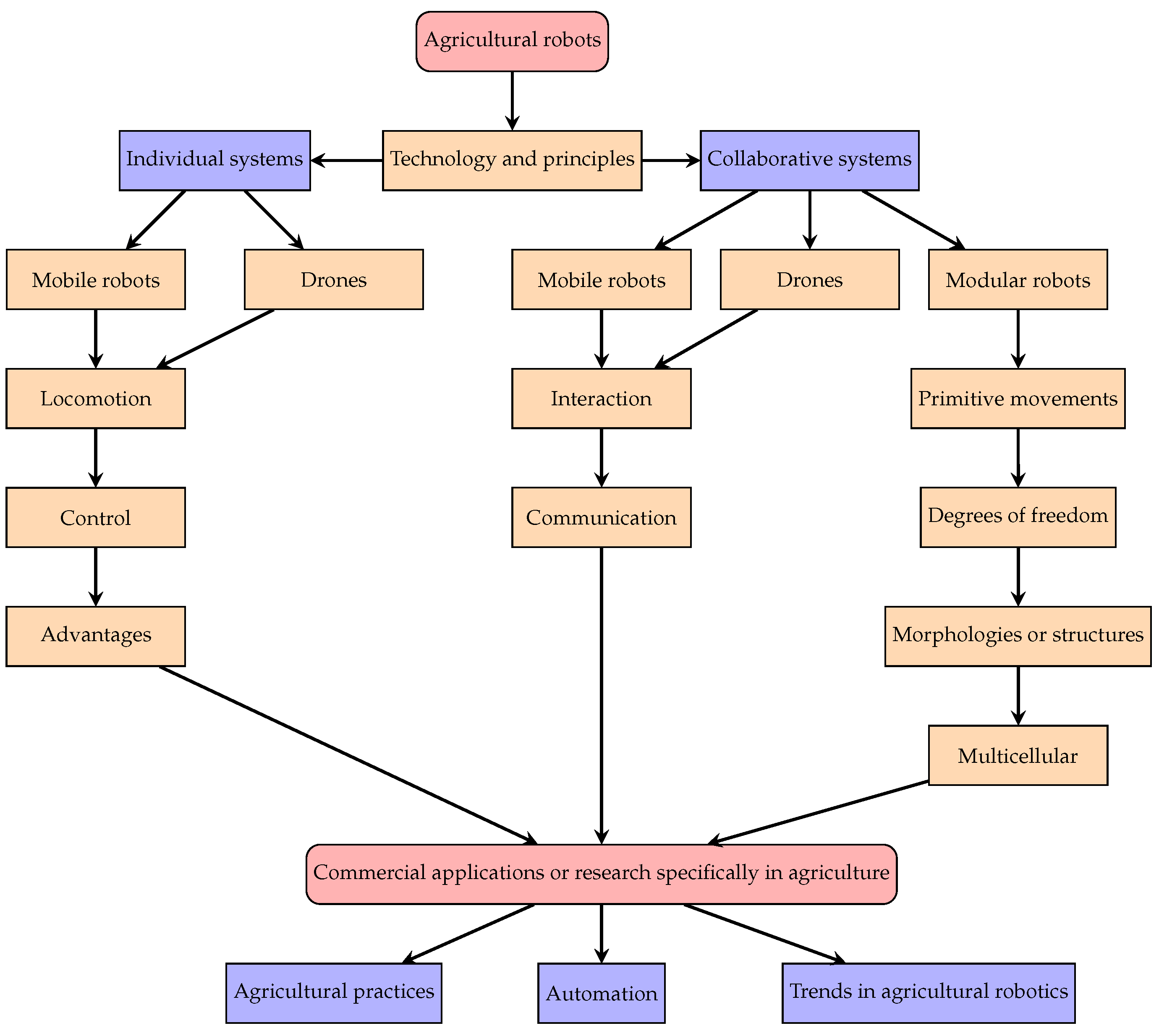
- CropScout (Figure 2) is a robot designed for crop inspection and analysis, equipped with multispectral cameras and temperature and humidity sensors to monitor crop health and growth. Moreover, this robot implements Wi-Fi technology to transmit data in real-time to a database, where it is analyzed to provide insights about the crop condition. CropScout is capable of autonomously navigating through fields, using wheels designed to adapt to various types of agricultural terrain [20].
- WeedBot (Figure 2) is a robot that uses cameras and computer vision sensors to identify weeds among the crops and mechanically remove them without using herbicides. Additionally, this robot communicates via Wi-Fi to receive updates and send information to operators, and its compact design allows it to maneuver easily between the crops [21].
- GrapeBot (Figure 2) is a robot designed for viticulture, equipped with specialized sensors to measure the maturity and environmental conditions of grapes, and then harvest them. This robot communicates with the operator via Wi-Fi, is capable of making autonomous decisions based on the collected data, and its modular design allows it to adapt to different grape varieties and cultivation techniques [22].
| Name | Application | Loco-motion | Functional advantages | User interface | Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Preparation | John deere autonomous tractor   [23] [23] |
Commercial | 4WD | - High traction on rough terrains. - Reduces operator fatigue. | Cabin control panel, mobile app | 2022 |
Kubota X Tractor   [24] [24] |
Commercial | 4WS | - High-efficiency electric vehicle. - Reduces environmental impact and saves energy. | Mobile app, touch control panel | 2020 | |
Agrobot SW6010  [25] [25] |
Commercial | 2WS | - Stability on uneven terrains. - Minimizes soil compaction. | Remote control, mobile app | 2019 | |
SoilAnalyzer  [26] [26] |
Research | 4WD | - Adaptable to various soil types. - Analyzes soil composition. | Mobile app, web interface | 2021 | |
| Land Preparation | John Deere Autonomous Tractor   [23] [23] |
Commercial | 4WD | High traction on difficult terrains. Reduces operator fatigue. | Cabin control panel, mobile app | 2022 |
Kubota X Tractor   [24] [24] |
Commercial | 4WS | High-efficiency electric vehicle. Reduces environmental impact and saves energy. | Mobile app, touch control panel | 2020 | |
Agrobot SW6010  [25] [25] |
Commercial | 2WS 1WD | Stability on uneven terrain. Minimizes soil compaction. | Remote control, mobile app | 2019 | |
SoilAnalyzer  [26] [26] |
Research | 4WD | Adapts to various soil types. Analyzes soil composition. | Mobile app, web interface | 2021 | |
| Plant Treatment | Ecorobotix ARA   [27] [27] |
Commercial | 4WD | Uses solar energy for mobility. Reduces the use of chemicals or fertilizers. | Mobile app, touch control panel | 2021 |
Dino   [28] [28] |
Commercial | 4WS | Maneuverability in tight spaces. Controlled weeding in vegetable crops. | Cabin control panel, mobile app | 2019 | |
DJI Agras T20   [29] [29] |
Commercial | UAV | Aerial access for precise spraying. Improves spraying efficiency. | Remote control, mobile app | 2024 | |
PlantHealth   [30] [30] |
Research | 4WS | Precision in soil treatment application. Diagnosis and treatment of plant diseases. | Mobile app, web interface | 2022 |
| Name | Application | Loco-motion | Functional advantages | User interface | Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sowing | Rowbot   [31] [31] |
Commercial | 4WD | Quickly fertilizes row crops. Reduces excessive seed expenditure. | Mobile app, web interface | 2022 |
AgriBots   [32] [32] |
Research | 4WD | Precision and reduction in seeding waste. | Control panel, mobile app | 2022 | |
FarmBot Genesis   [33] [33] |
Commercial | Robotic arm | Customization for home gardening. Automation in small gardens. | Web app, remote control | 2020 | |
SeedMaster  [34] [34] |
Research | 4WD | Precision seeding efficiency. Reduces variability in seeding. | Mobile app, web interface | 2021 | |
PlantingDrone   [35] [35] |
Research | UAV | Aerial seeding in inaccessible terrains. Expands the reach of seeding. | Remote control, mobile app | 2022 | |
| Harvesting | Harvest CROO Robotics   [36] [36] |
Commercial | 4WD | Increases productivity in harvesting. | Cabin control panel, mobile app | 2023 |
Abundant Robotics   [37] [37] |
Commercial | 4WD | Automated apple harvesting. | User interface with panel | 2022 | |
AppleHarvester AI   [38] [38] |
Research | 4WD | AI-based smart harvesting. Reduces damage and improves fruit selection. | Control panel, mobile app | 2022 | |
TerraSentia   [39] [39] |
Research | 4WD | Mobility in high-density crops. Detailed monitoring and crop performance improvement. | Mobile app, web interface | 2019 | |
SoilScan AI   [40] [40] |
Research | UAV | Real-time soil analysis. Soil fertility optimization and nutrient detection. | Mobile app, web interface | 2022 |
3.2. Multi-Robot Systems
3.3. Modular Robots
3.4. Control Systems
3.5. Multicellular Robots
- Modularity: Multicellular systems are characterized by their modular structure, where each module can perform specific functions.
- Self-organization: The ability of multicellular robots to form complex structures or behavior patterns without centralized direction, similar to biological processes like embryonic development or tissue formation.
- Adaptability: These robots can adapt to changes in the environment or in the task being performed, autonomously adjusting their configuration or behavior.
- Communication: Interaction among robotic cells often involves some form of communication, whether through direct physical connections or via wireless signals, allowing coordination and cooperation between modules.
Conclusions
References
- Seo, J.; Paik, J.; Yim, M. Modular Reconfigurable Robotics. The Annual Review of Control, Robotics, and Annu. Rev. Control Robot. Auton. Syst 2019, 2, 63–88. [CrossRef]
- Pavlic, T.P.; Hanson, J.; Valentini, G.; Walker, S.I.; Pratt, S.C. Quorum sensing without deliberation: biological inspiration for externalizing computation to physical spaces in multi-robot systems. Swarm Intelligence 2021, 15, 171–203. [CrossRef]
- Nations, U. World population projected to reach 9.8 billion in 2050, and 11.2 billion in 2100 | UN DESA | United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs.
- Nations, U. World Population Prospects 2022 World Population Prospects 2022 Summary of Results.
- Considine, D.M.; Considine, G.D., Robot Technology Fundamentals. In Standard Handbook of Industrial Automation; Considine, D.M.; Considine, G.D., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, 1986; pp. 262–320. [CrossRef]
- Azimi, S.; Abidin, M.S.Z.; Emmanuel, A.A.; Hasan, H.S.; Mahmud, M.S.A.; Emmanuel, A.A. Robotics and Automation in Agriculture: Present and Future Applications APPLICATIONS OF MODELLING AND SIMULATION Robotics and Automation in Agriculture: Present and Future Applications, 2020.
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Niu, Y.; Han, W. Mapping maizewater stress based on UAV multispectral remote sensing. Remote Sensing 2019, 11. [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, A.; Husain, M.A.; Singh, S.P.; Chauhan, A.; Khan, M.T.; Kumar, N.; Chauhan, A.; Soni, S.K. Implementation of drone technology for farm monitoring & pesticide spraying: A review, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Boehlje, M.; Langemeier, M. Automation and Robotics in Production Agriculture, 2022.
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, P.; Lin, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Zou, J. Modular Soft Robotics: Modular Units, Connection Mechanisms, and Applications. Advanced Intelligent Systems 2020, 2. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.F.; Moreira, A.P.; Silva, M.F. Advances in agriculture robotics: A state-of-the-art review and challenges ahead, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Theraulaz, G.; Trianni, V. Swarm Robotics: Past, Present, and Future [Point of View]. Proceedings of the IEEE 2021, 109, 1152–1165. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, H.R.; Polania, E.C.M.; Garcia, A.P.; Mendonza, O.B.; Albiero, D. Agricultural unmanned ground vehicles: A review from the stability point of view. Revista Ciência Agronômica 2020, 51, e20207761. [CrossRef]
- Chitre, N.; Dogra, A.; Singla, E. Optimal synthesis of reconfigurable manipulators for robotic assistance in vertical farming. Robotica 2023, 41, 2283 â 2297. Cited by: 1, . [CrossRef]
- Cristóvão, M.P.; Portugal, D.; Carvalho , A.E.; Ferreira , J.F. A LiDAR-Camera-Inertial-GNSS Apparatus for 3D Multimodal Dataset Collection in Woodland Scenarios. Sensors 2023, 23. Cited by: 1; All Open Access, Gold Open Access, Green Open Access, . [CrossRef]
- Dyshekov, A.; Mirzaev, M.; Pavlov, D.; Smirnov, I. Design of an autonomous self-propelled platform for performing agricultural tasks. 2023, Vol. 2697. Cited by: 0; All Open Access, Bronze Open Access, . [CrossRef]
- Pincheira, M.; Shamsfakhr, F.; Hueller, J.; Vecchio, M. Overcoming Limitations of IoT Installations: Active Sensing UGV for Agricultural Digital Twins. 2023, p. 319 â 324. [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D.M.; Santhosh, S.; Yesudas, K.; Sojan, A.; Mahanta, G.B. A preliminary study on design of a modular agricultural mobile robot. 2022, Vol. 2670. Cited by: 0; All Open Access, Bronze Open Access, . [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Shang, H. Design and Implementation of a Novel Agricultural Robot with Multi-Modal Kinematics. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 2023, 14272 LNAI, 395 â 406. Cited by: 0, . [CrossRef]
- Design, Y. AI-POWERED CROP SCOUTING ROBOT PROMISES BETTER YIELDS WITH SENSIBLE FARMING, 2023.
- Tran, D.; Schouteten, J.J.; Degieter, M.; Krupanek, J.; Jarosz, W.; Areta, A.; Emmi, L.; Steur, H.D.; Gellynck, X. European stakeholdersâ perspectives on implementation potential of precision weed control: the case of autonomous vehicles with laser treatment. Precision Agriculture 2023, 24, 2200–2222. [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Vougioukas, S.; Slaughter, D.; Fei, Z.; Arikapudi, R. A strawberry harvest-aiding system with crop-transport collaborative robots: Design, development, and field evaluation. Journal of Field Robotics 2022, 39, 1231–1257, [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/rob.22106]. [CrossRef]
- US, J.D. Autonomous Tractor | John Deere US, 2024.
- KUBOTA. Kubota Concept Tractor | Innovation | Kubota Global Site, 2024.
- AGROBOT. The first pre-commercial robotic harvesters for gently harvest strawberries., 2024.
- Rao, V.R.; Krishna, G.B. Soil sampler robot with localization for agro purposes.
- ARA, E. ARA is a high-precision sprayer developed by Ecorobotix, 2024.
- Technologies, N. Dino has completed its transformation into Orio, 2024.
- DJI. DJI AGRASMG-1, 2024.
- Rizk, H.; Habib, M.K. Robotized Early Plant Health Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the IECON 2018 - 44th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, 2018, pp. 3795–3800. [CrossRef]
- Mansur, H.; Flippo, D.; Sharda, A.; Schmitz, A.; Badgujar, C.; McCornack, B. Design of a Reconfigurable Crop Scouting Vehicle for Row Crop Navigation: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Sensors 2022, 22. [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, C.O.; Hefft, D.I.; Olugbemi, O.T. Chapter 17 - Agribots: A gateway to the next revolution in agriculture. In AI, Edge and IoT-based Smart Agriculture; Abraham, A.; Dash, S.; Rodrigues, J.J.; Acharya, B.; Pani, S.K., Eds.; Intelligent Data-Centric Systems, Academic Press, 2022; pp. 301–311. [CrossRef]
- Montagnino, F.M., Beyond the âGreat Derangementâ: Will the Humanities Lead Ecological Transition?; 2020; pp. 111–142. [CrossRef]
- SeedMaster. REVOLUTIONARY ULTRA SR THE MOST ADVANCED LARGE-SCALE AIR SEEDER, 2024.
- Mohan, M.; Richardson, G.; Gopan, G.; Aghai, M.M.; Bajaj, S.; Galgamuwa, G.A.; Vastaranta, M.; Arachchige, P.S.; Amorós, L.; Corte, A.P.D.; et al. Uavâsupported forest regeneration: Current trends, challenges and implications, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Karkee, M.; Silwal, A., Robotic Fruit Harvesting. In Encyclopedia of Smart Agriculture Technologies; Zhang, Q., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yuan, X.; Wang, C. A review on structural development and recognitionâlocalization methods for end-effector of fruitâvegetable picking robots. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems 2022, 19, 17298806221104906. [CrossRef]
- advancedfarm. Robotic Apple Harveste, 2024.
- Kayacan, E.; Chowdhary, G. Tracking Error Learning Control for Precise Mobile Robot Path Tracking in Outdoor Environment. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems 2019, 95. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Chen, S.; Pi, J.; Zhao, L. A Review on Soil Nitrogen Sensing Technologies: Challenges, Progress and Perspectives. Agriculture 2023, 13, 743. [CrossRef]
- Swarfarmrobotic. Swarfarmrobotic, 2019.
- Manuel, V.; Salinas, G.; Juan, .; Santiago, G.P.; Cortes, A.; Quintanar, C.T. Artà culo: COMEII-23030 VIII CONGRESO NACIONAL Y I CONGRESO INTERNACIONAL DE RIEGO, DRENAJE Y BIOSISTEMAS.
- Harvest. MOBILE ROBOTS FOR INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTIVITY, 2016.
- Henrà quez, G.F.A.; Mauricio, C.; Torres, M.; Salvador, E.; Resumen, S. Aplicaciones de los drones en la agricultura, 2017.
- Ning, L.; Limpabandhu, C.; Tse, Z.T.H. Engineering Magnetic Soft and Reconfigurable Robots. Soft Robotics 2024, 11, 2 â 20. Cited by: 0, . [CrossRef]
- Martà nez, G.J.; Adamatzky, A.; Figueroa, R.Q.; Schweikardt, E.; Zaitsev, D.A.; Zelinka, I.; Oliva-Moreno, L.N. Computing with Modular Robots. International Journal of Unconventional Computing 2022, 17, 31 â 60. Cited by: 0.
- Liu, Y.; Wei, R.; Dong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J. A DESIGNATION of MODULAR MOBILE RECONFIGURABLE PLATFORM SYSTEM. Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology 2020, 20. Cited by: 2; All Open Access, Hybrid Gold Open Access, . [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhan, Q. A Hermaphrodite Electromechanical Connector for Self-Reconfigurable Robot Modules. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics 2021, 26, 3276 â 3281. Cited by: 2, . [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.A.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Cao, S.; Zan, W.P. A matrix shape formation approach and experiment for latticed swarm robots.Kongzhi yu Juece/Control and Decision 2020, 35, 2391 â 2398. Cited by: 1, . [CrossRef]
- Freeman, C.; Maynard, M.; Vikas, V. Topology and Morphology Design of Spherically Reconfigurable Homogeneous Modular Soft Robots. Soft Robotics 2023, 10, 52 â 65. Cited by: 4, . [CrossRef]
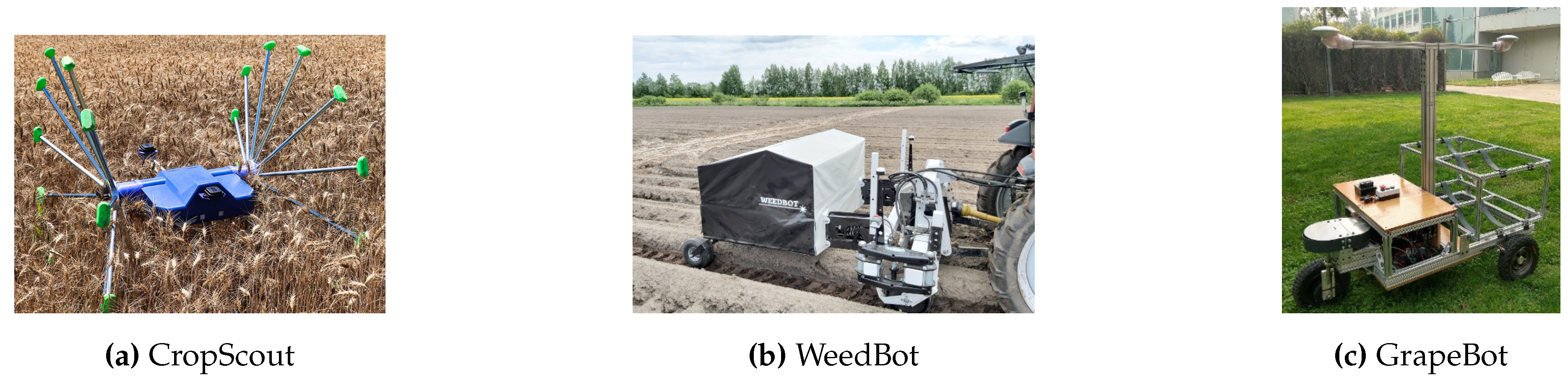
- Moreno, R.; Faiña, A. EMERGE Modular Robot: A Tool for Fast Deployment of Evolved Robots. Frontiers in Robotics and AI 2021, 8. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, R.F.M.; Lyder, A.; Christensen, D.J.; Stoy, K. Reusable electronics and adaptable communication as implemented in the odin modular robot. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2009, pp. 1152–1158. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.R.; Espinosa Oviedo, J.; Gil, A.A. Hymod: A Software For Hybrid Microgrid Optimal Design. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control (CCE), 2018, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Peck, R.H.; Timmis, J.; Tyrrell, A.M. Self-Assembly and Self-Repair during Motion with Modular Robots. Electronics (Switzerland) 2022, 11. Cited by: 3; All Open Access, Gold Open Access, Green Open Access, . [CrossRef]
- Nokhanji, N.; Santoro, N. Self-Repairing Line of Metamorphic Robots. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications (ICARA), 2021, pp. 55–59. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, S.; Cao, G.; Fei, Y. Mechatronics Design of a Modular Self-Reconfigurable and Self-Repair Robot. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation, 2007, pp. 2243–2247. [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, J. Enumerating the Nonisomorphic Configurations of a Modular Reconfigurable Robot. Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics 2022, 14. Cited by: 1, . [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Kang, M.; Baek, J. Dynamic Model Learning and Control of Robot Manipulator Based on Multi-layer Perceptron Neural Network.Transactions of the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers, A 2023, 47, 945 â 957. Cited by: 0, . [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Lam, T.L. Auto-Optimizing Connection Planning Method for Chain-Type Modular Self-Reconfiguration Robots. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2023, 39, 1353 â 1372. Cited by: 0, . [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Son, H.I. A Hybrid Systems-Based Hierarchical Control Architecture for Heterogeneous Field Robot Teams. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics 2023, 53, 1802 â 1815. Cited by: 5; All Open Access, Green Open Access, . [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Qiang, H.; Xu, G.; Liu, X.; Mo, R.; Huang, R. Extraction of navigation line based on improved grayscale factor in corn field. Ciência Rural 2020, 50, e20190699. [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, H.; Tomita, K.; Kamimura, A.; Yoshida, E.; Kokaji, S.; Murata, S. Distributed self-reconfiguration control of modular robot M-TRAN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference Mechatronics and Automation, 2005, 2005, Vol. 1, pp. 254–259 Vol. 1. [CrossRef]
- Cortez, W.S.; Verginis, C.K.; Dimarogonas, D.V. A Distributed, Event-Triggered, Adaptive Controller for Cooperative Manipulation with Rolling Contacts. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2023, 39, 3120 â 3133. Cited by: 1; All Open Access, Green Open Access, . [CrossRef]
- Stroppa, F.; Selvaggio, M.; Agharese, N.; Luo, M.; Blumenschein, L.H.; Hawkes, E.W.; Okamura, A.M. Shared-Control Teleoperation Paradigms on a Soft-Growing Robot Manipulator. Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems: Theory and Applications 2023, 109. Cited by: 1; All Open Access, Green Open Access, . [CrossRef]
- Brandt, D.; Christensen, D.J.; Lund, H.H. ATRON Robots: Versatility from Self-Reconfigurable Modules. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, 2007, pp. 26–32. [CrossRef]
- Parada, I.; Sacristán, V.; Silveira, R.I. A new meta-module design for efficient reconfiguration of modular robots. Autonomous Robots 2021, 45, 457 â 472. Cited by: 6; All Open Access, Green Open Access, Hybrid Gold Open Access, . [CrossRef]
- Kuzuya, A.; Nomura, S.I.M.; Toyota, T.; Nakakuki, T.; Murata, S. From Molecular Robotics to Molecular Cybernetics: The First Step Toward Chemical Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological and Multi-Scale Communications 2023, 9, 354–363. [CrossRef]
- Yoo, A.; Lee, K.; Kang, B.; Kim, C.s.; Han, J.; Park, J.O.; Choi, E. Actively Controllable Stem Cell Spheroid-based Microrobot for Tissue Regeneration. In Proceedings of the 2018 7th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (Biorob), 2018, pp. 1286–1290. [CrossRef]
- Tissera, P.S.S.; Choe, S.; Punmiya, R. Quorum Sensing-Based Nanonetwork Synchronization. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters 2019, 8, 893–896. [CrossRef]
- Khajepour, G.; Vakilzadeh, M.; Vatankhah, R. Controller design for discrete-time nonlinear feed-forward cascades with application to bacterial quorum sensing. Journal of the Franklin Institute 2023, 360, 3967 â 3988. Cited by: 0, . [CrossRef]
- Banzhaf, M.; Resendis-Antonio, O.; Zepeda-Mendoza, M.L. Uncovering the Dynamic Mechanisms of the Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Quorum Sensing and Virulence Networks Using Boolean Modelling. IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience 2020, 19, 394–402. [CrossRef]
- Wood, R., N.R..W.G.Y. flight of the robobees. Scientific American 2013, 308(3), 60â65.

| Category | Basic characteristics | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual robot [13] | Capable of performing tasks autonomously or through remote operation. | Used in automated planting and harvesting, monitoring, and fertilization of crops. | Adaptability to different types of crops. | Limited in the variety of tasks they perform, high implementation and maintenance costs. |
| Multiple robots [14] | A group of robots working coordinately through a system of communication and collaboration among them. | Ideal for supervision and management of large crop areas and integrated weed control. | Increases the farmer’s reach and coverage in large expanses of land. | Coordination of individual robots is non-trivial and requires robust control methods to achieve effective interaction among them. |
| Name | Locomotion | Functional advantages | Communication mechanism | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SwarmFarm robots [41] | 4WS | Modularity and adaptability for various agricultural tasks | Centralized control panel | 2019 |
| DJI agricultural drones [29] | UAV | Quickly fumigates large crop areas | Radio signals | 2024 |
| Parrot drones for agricultural supervision [42] | UAV | Advanced imaging and sensor technology for crop monitoring and analysis | Remote control and mobile app | 2019 |
| Harvest automation HV-100 robots [43] | 4WS | Space optimization and efficiency in nurseries and garden centers | Radio signals and Wi-Fi | 2016 |
| Agrobotix harvest robots [44] | UAV | Autonomous harvesting for various types of crops | Radio signals | 2017 |
| Robot name | Degrees of Freedom per module (DOF) | Actuator type | Self-reconfigurable | Communication interface | Control type | Scalability | Year of publication and authors | Potential applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PolyBot | 1 | Motor and pneumatic cylinder | Yes | Wi-Fi - Unguided | Centralized and/or decentralized | High | Zhang, Roufas, & Yim, 2021, Brunete, Torres, Hernando, & Hernando, 2007 | Rough terrain exploration |
| M-Tran | 2 | Electric motor | Yes | Wi-Fi | Distributed | High | Kurokawa, et al., 2005; Murata & Kurokawa, 2007 | Agriculture, exploration, and rescue |
| S-BOT | 6 to 30 | Rotational servomotors, linear actuators, and stepper motors | Yes | Wi-Fi or Bluetooth | Decentralized | High | Reddy, Patlolla, Agrawal, & Anupama, 2016 | Agriculture, exploration, and rescue |
| Snake type | 6 | Electric motor | Yes | Wi-Fi | Centralized | High | Liu & Tong, 2021 | Inspection and maintenance, exploration and rescue |
| Macabot | 3 | Electric motor | Yes | Wi-Fi | Decentralized | High | Larizza, Murciano, Pappagallo, & Triggiani, 2006 | Exploration and rescue |
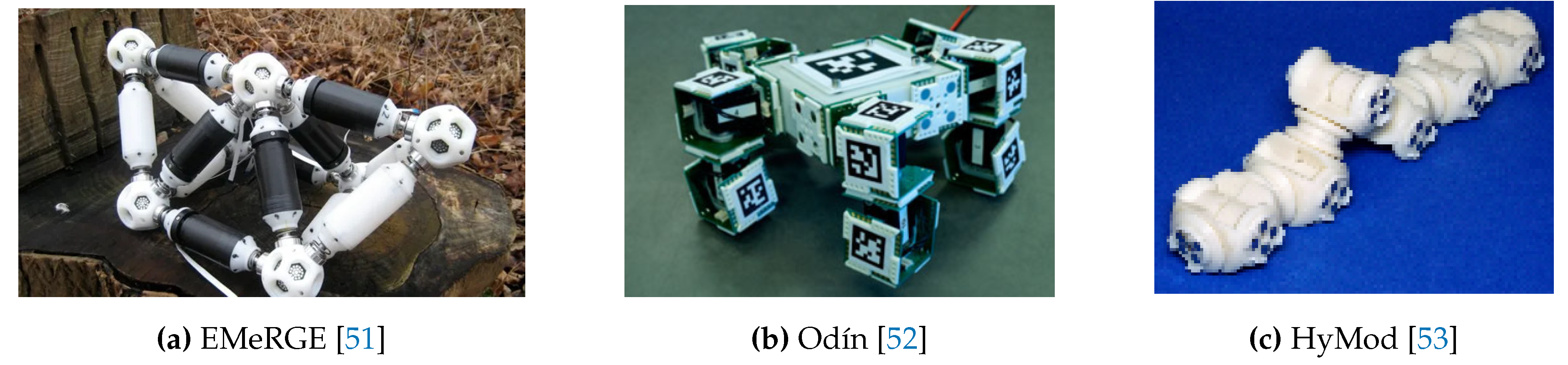
| Odin | 24 | Electric motors | Yes | Wi-Fi | Distributed | High | Lyder, Mendoza, & Stoy, 2008 | Exploration and rescue |
| HyMod | 27 | Electric motors | Yes | Wi-Fi | Distributed | High | Parrott, Dodd, & GroÃ, 2018 | Exploration and rescue, agriculture, and livestock management |
| HexaMob | 36 | Electric motors | Yes | Wi-Fi | Distributed | High | Gao, Huo, Seehra, Ramani, & Cipra, 2014 | Exploration and rescue, agriculture, and livestock management |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





