Submitted:
09 August 2024
Posted:
12 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Study Areas
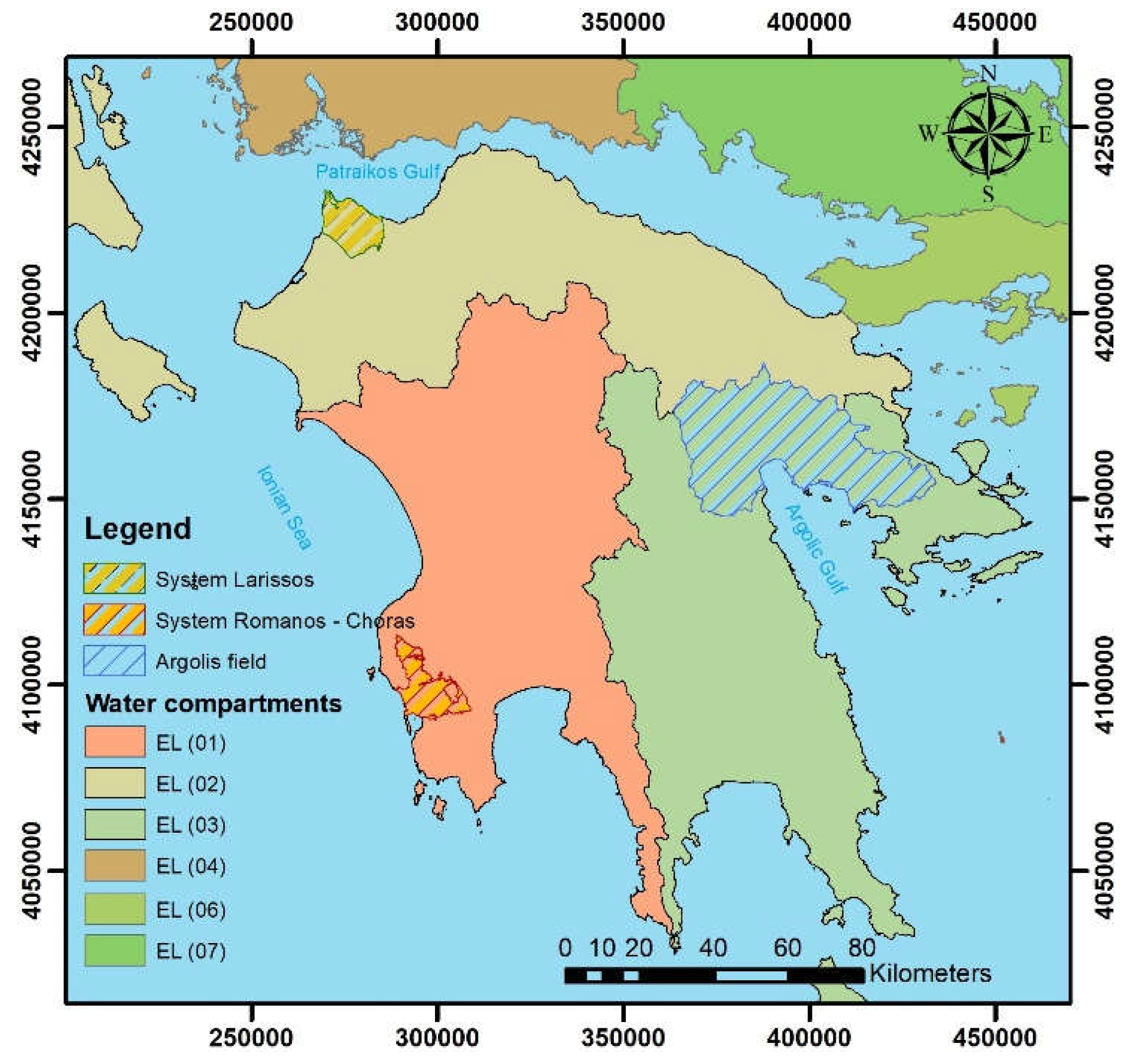
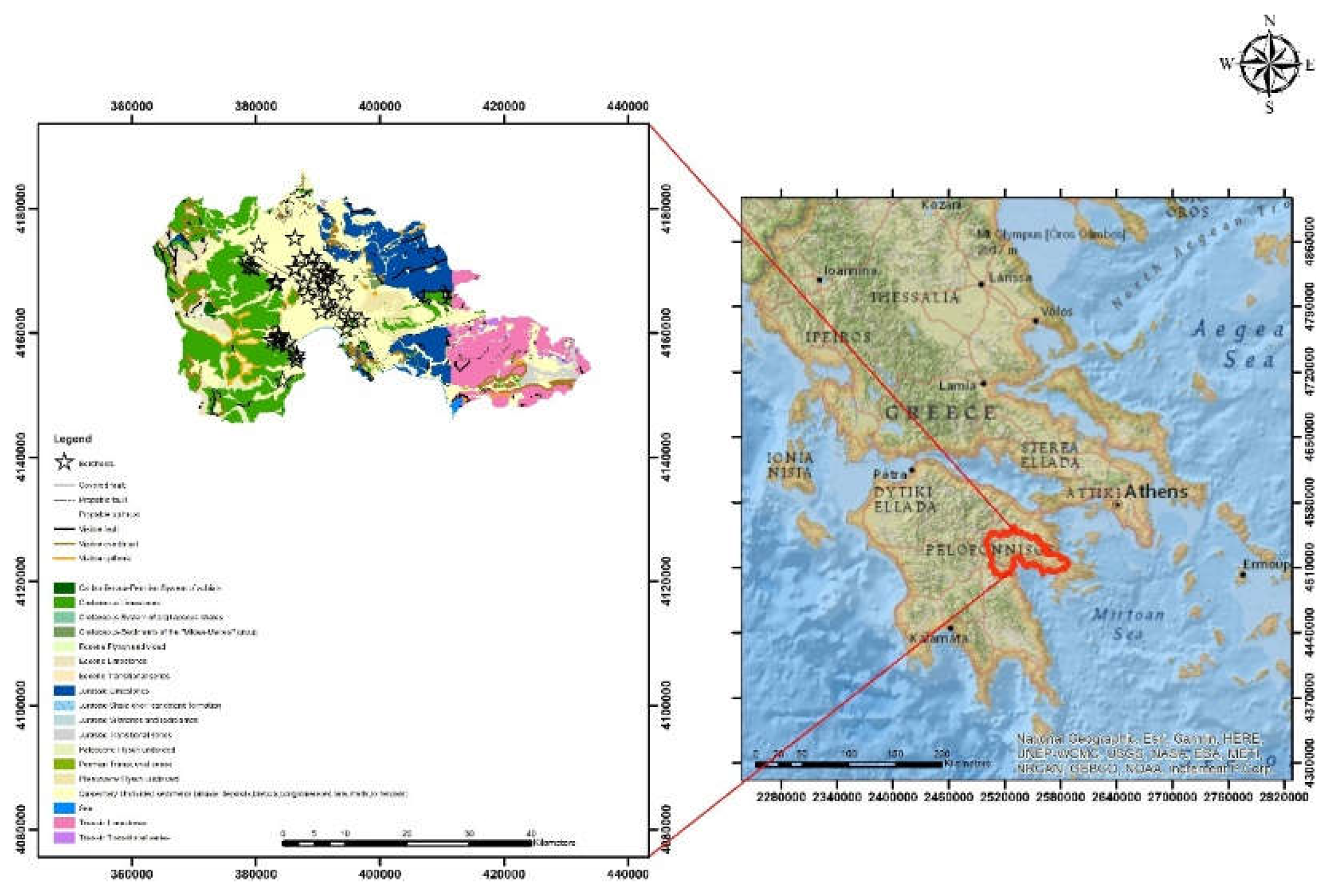
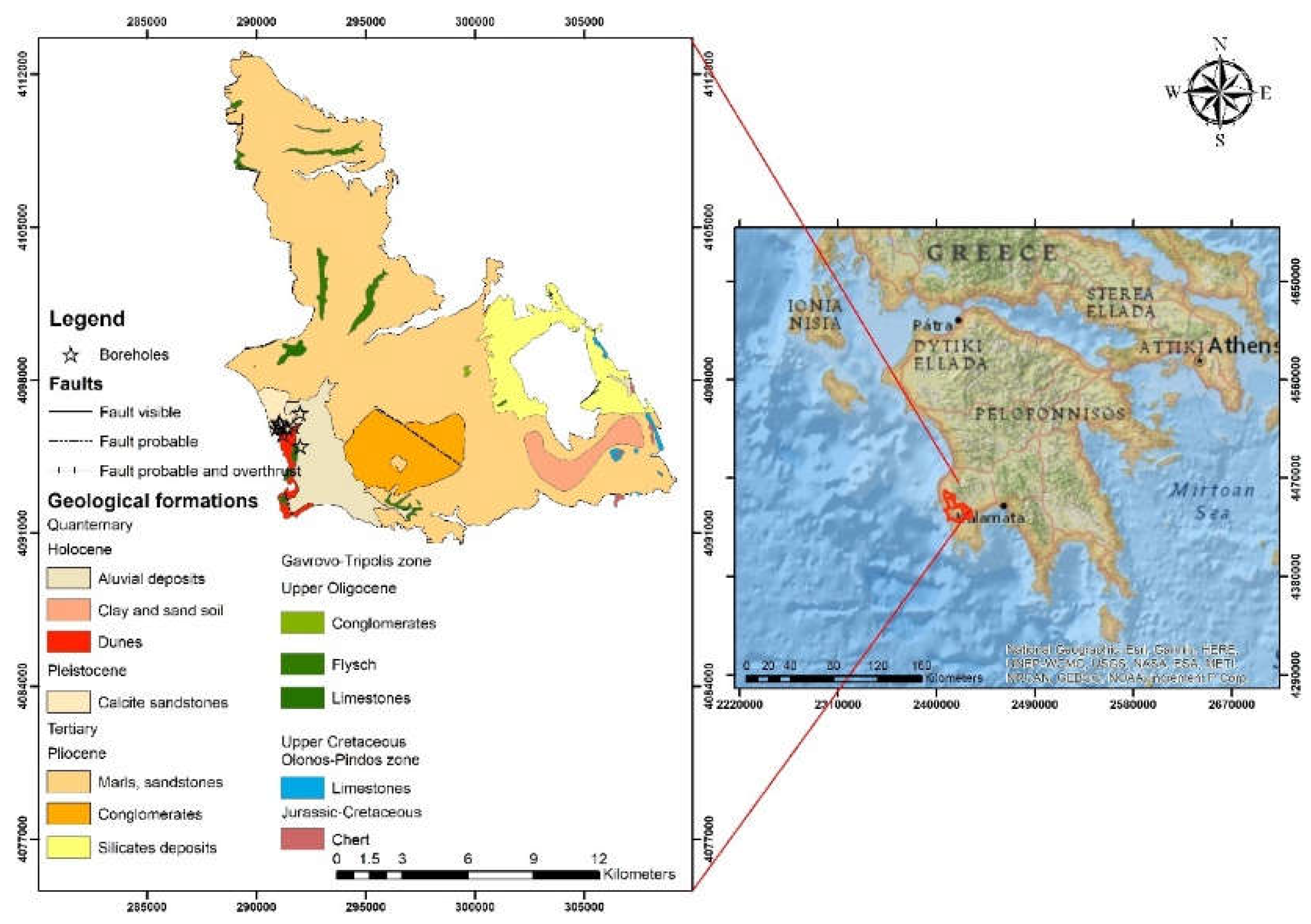
2.1. Study Areas
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Preparation, Sampling and Analytical Procedure
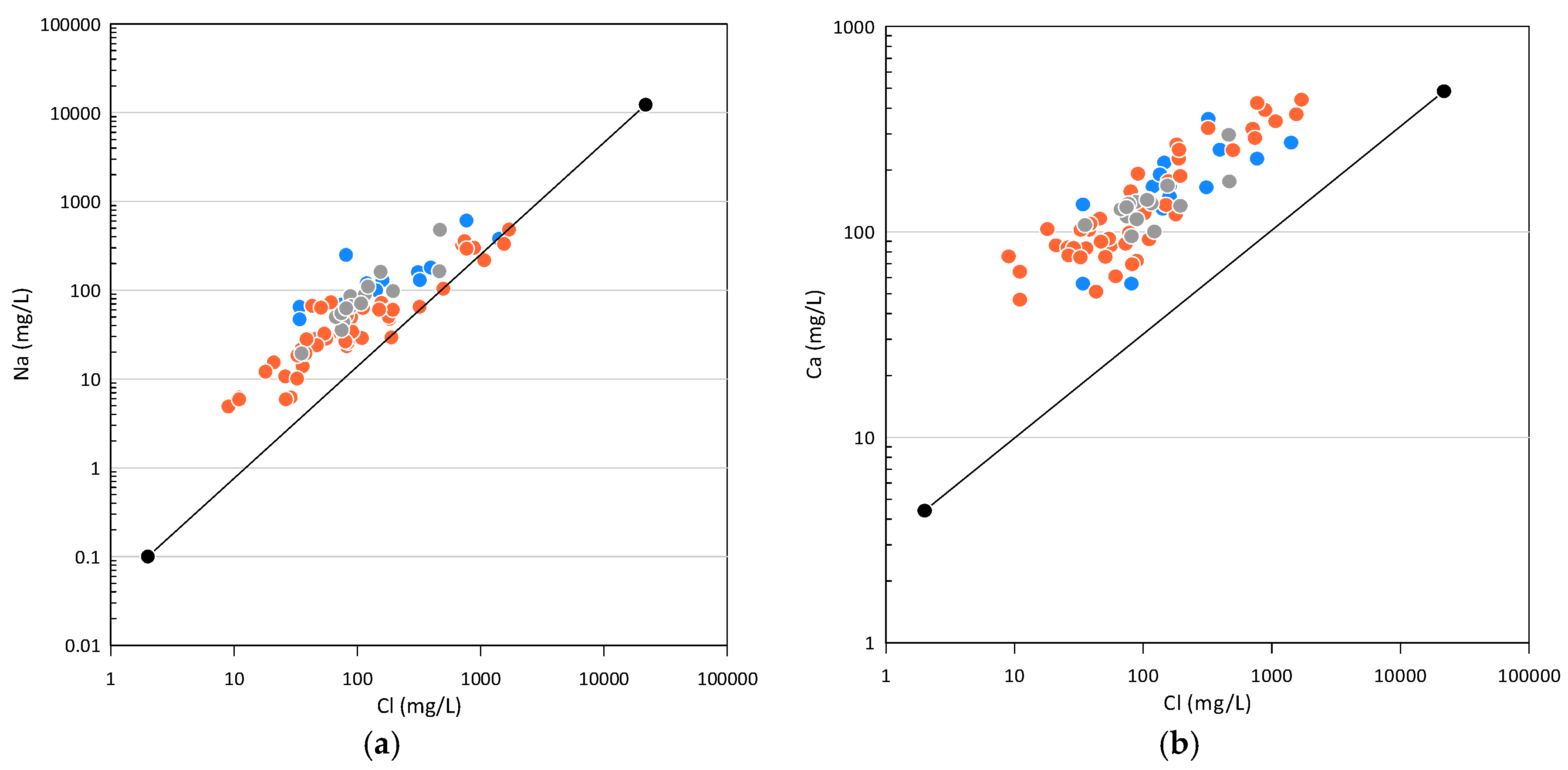
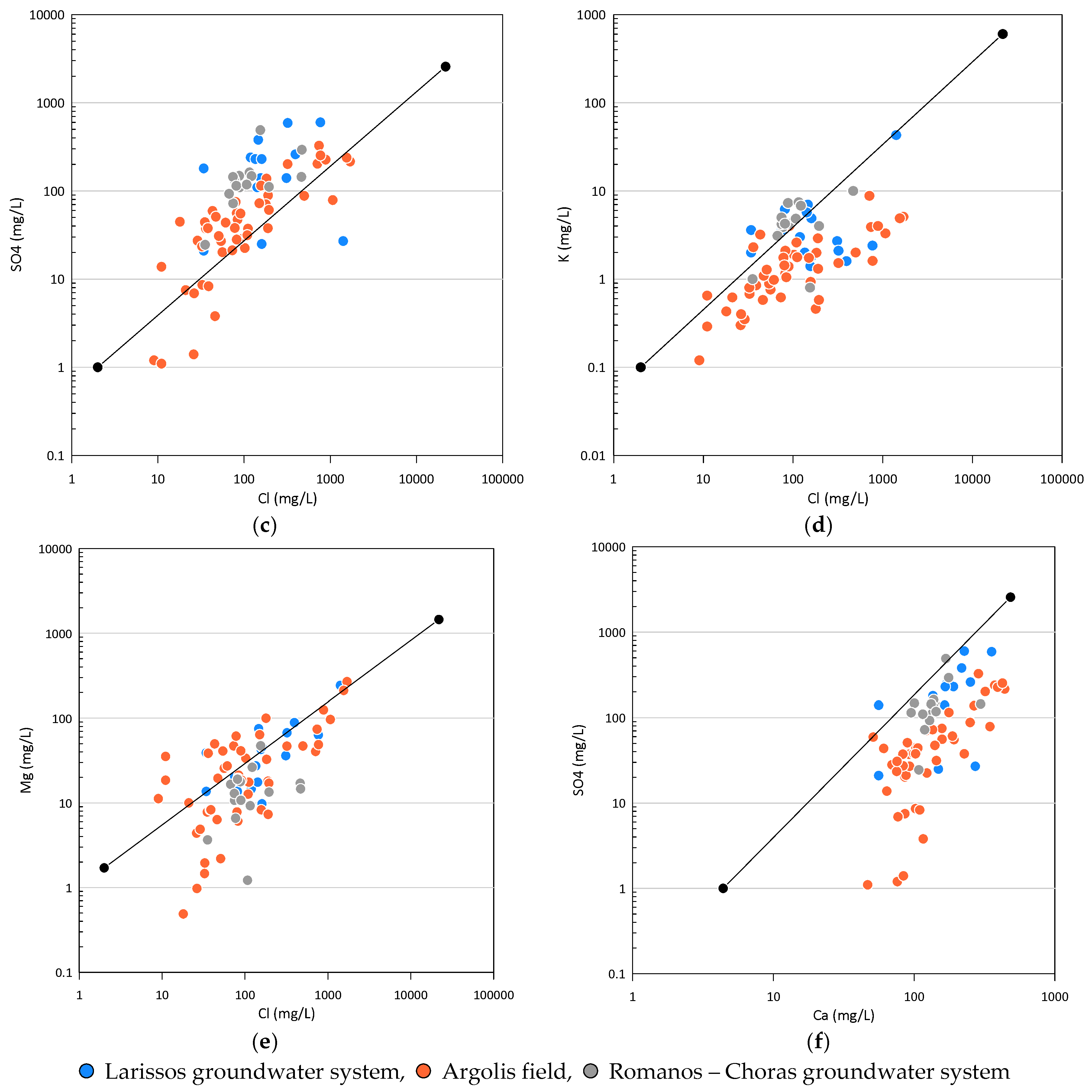
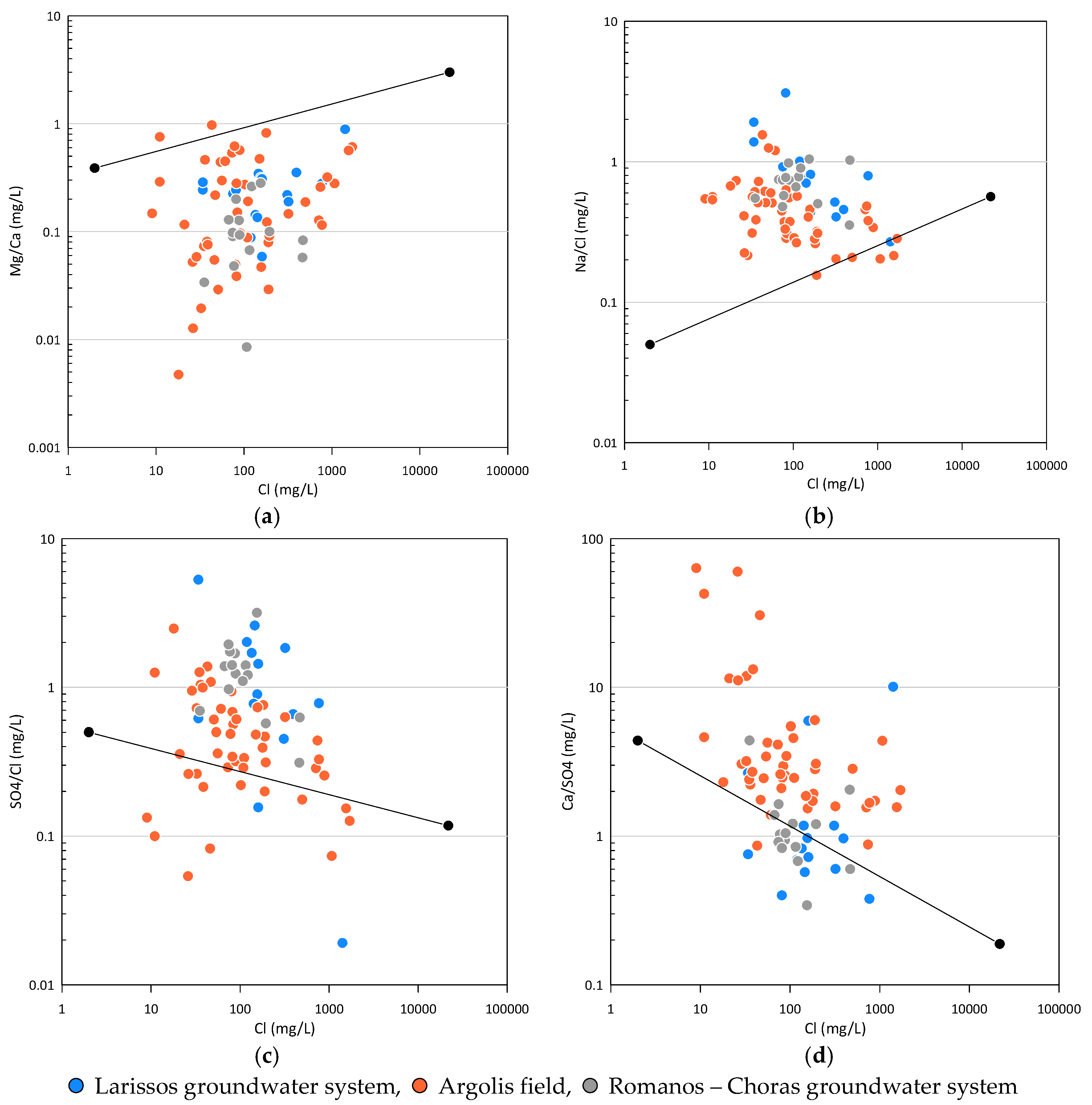
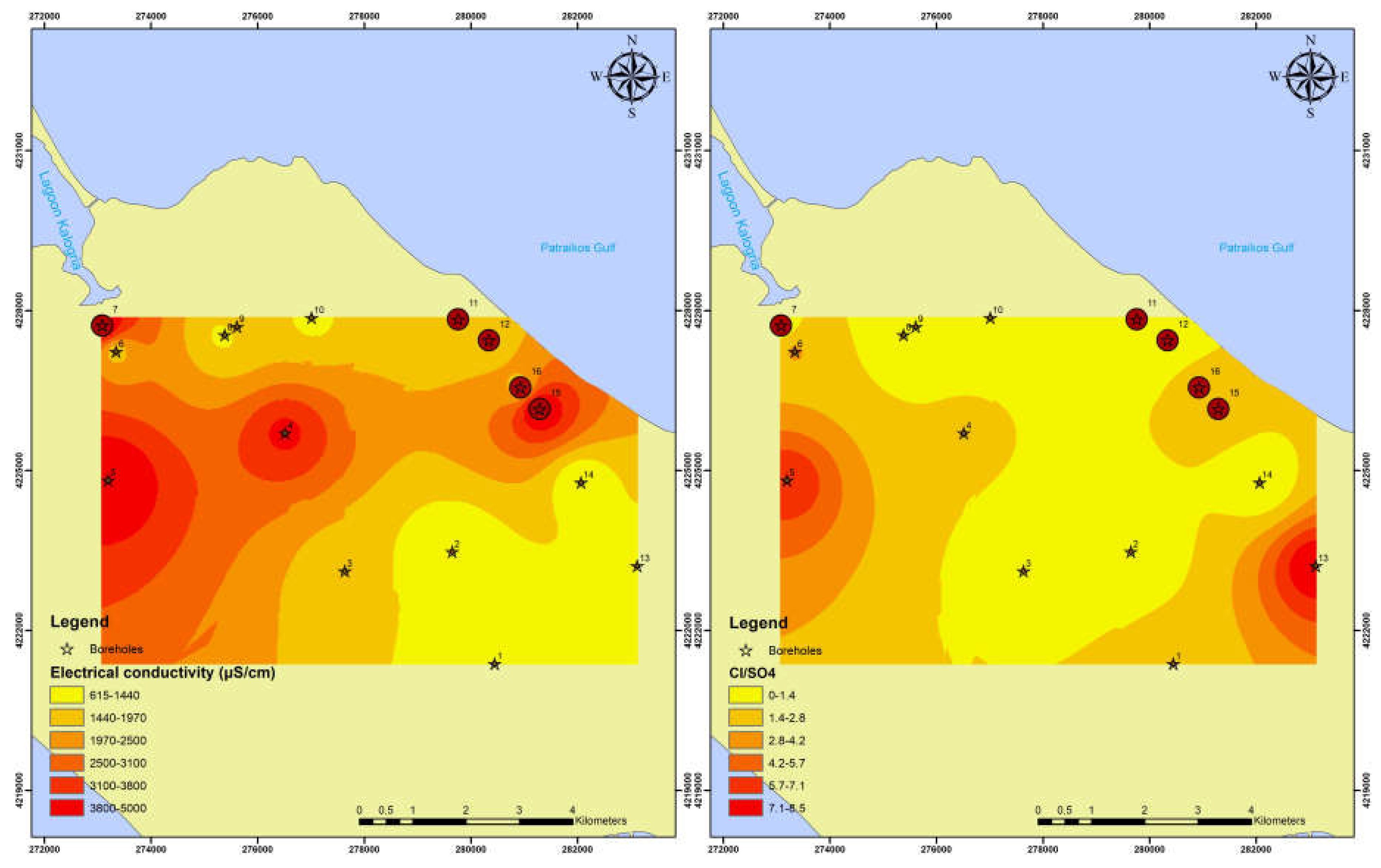
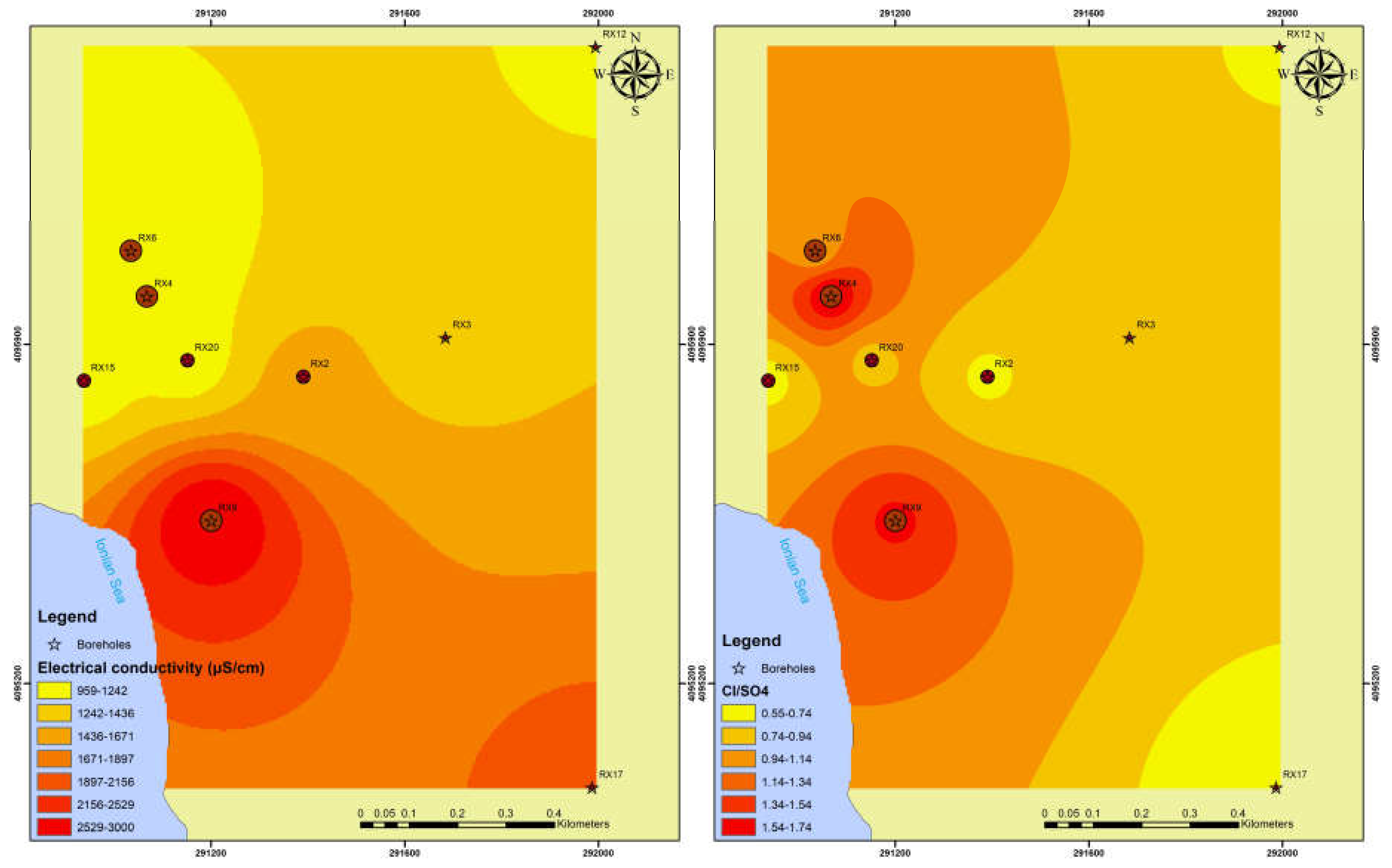
3.2. Ionic Ratio
3.3. Hydrochemical Analysis
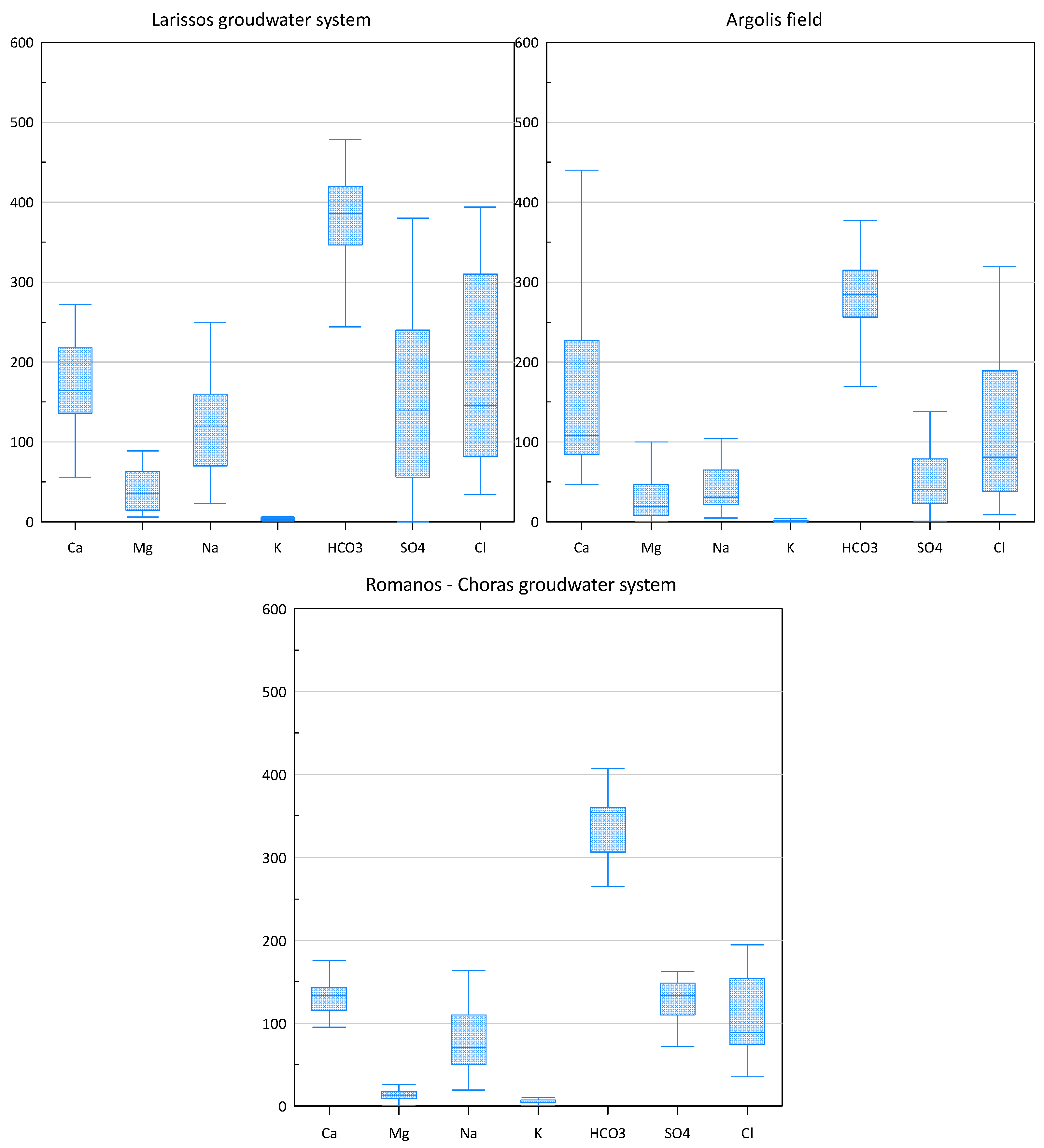
3.4. Major Ion Indicators
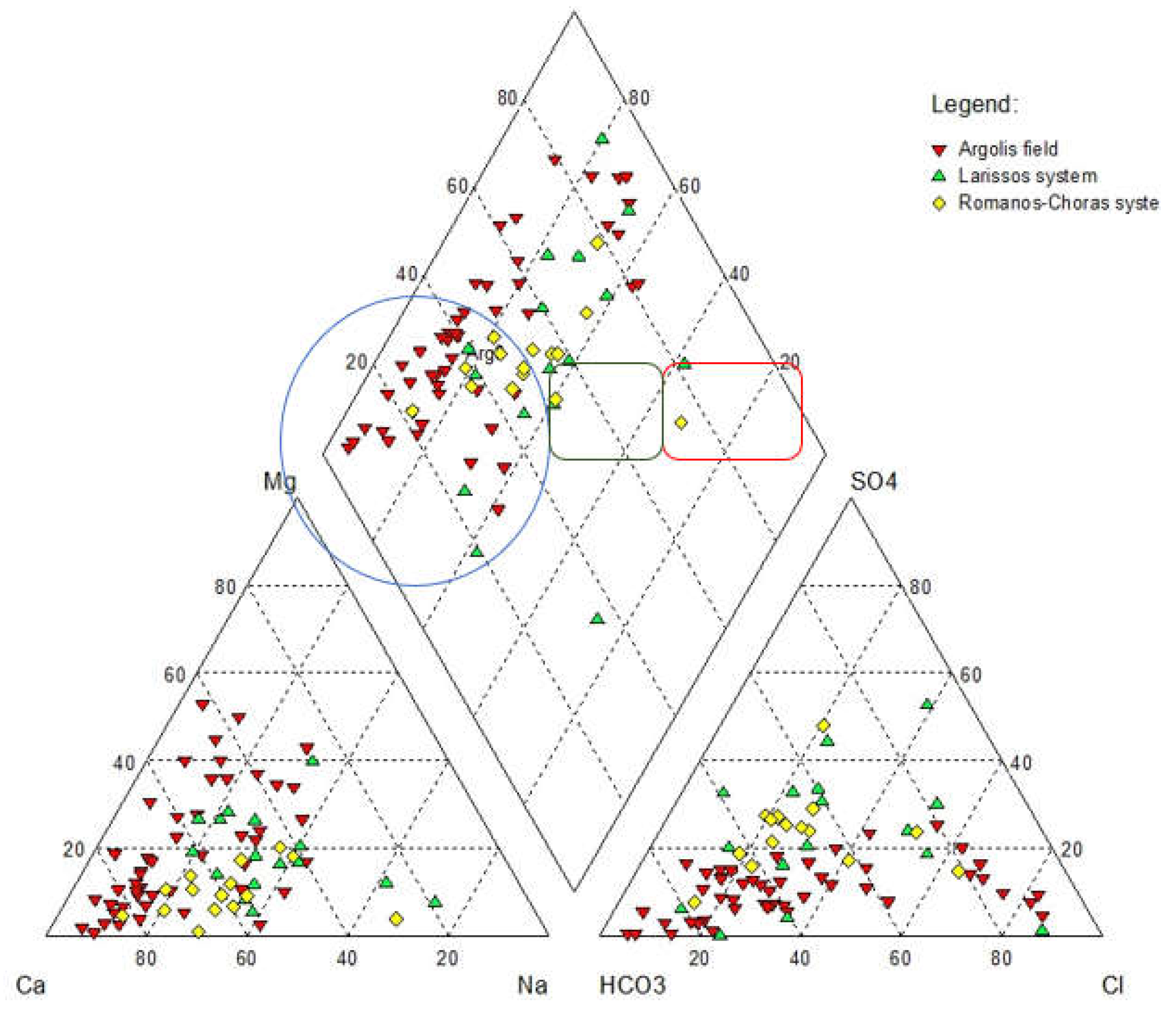
3.5. Piper Diagram
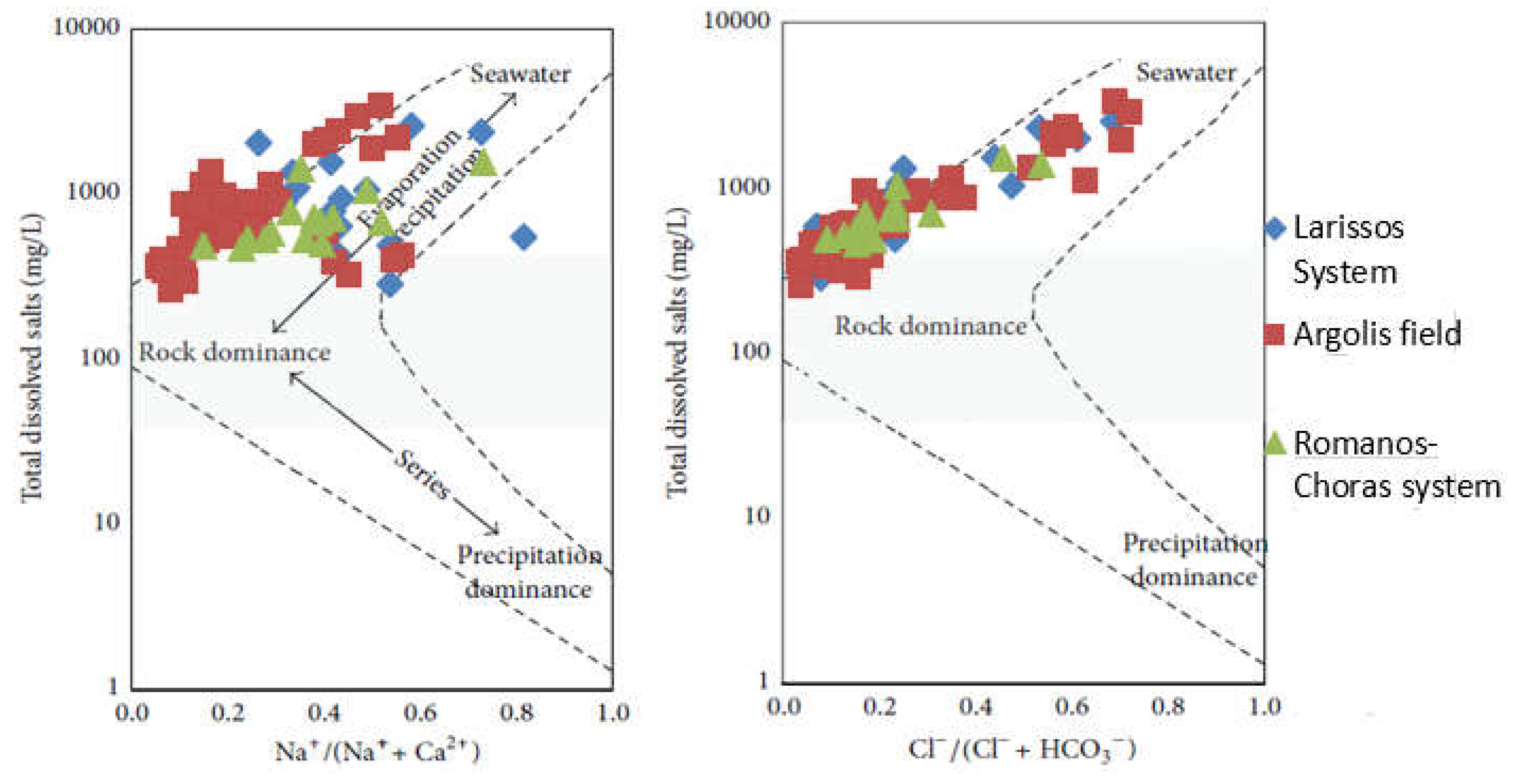
3.6. Gibbs Diagram
3.7. Statistical Analysis
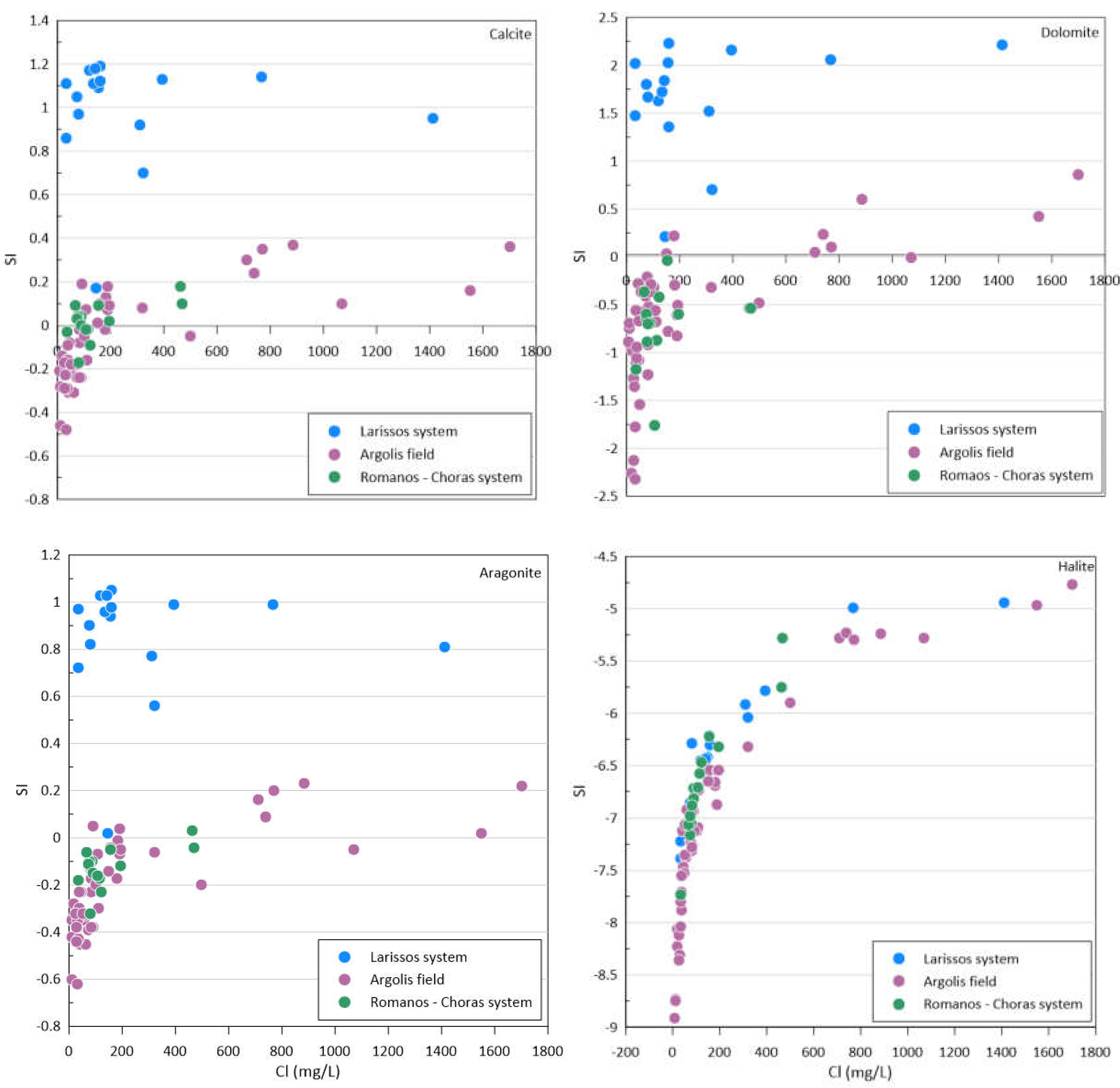
3.8. Mineral Saturation Indices
3.9. Correlation Analysis
| pH | EC | TDS | HCO3 | Cl | SO4 | NO3 | Na | K | Ca | Mg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||||
| EC | -0.209 | 1 | |||||||||
| TDS | -0.219 | 0.897 | 1 | ||||||||
| HCO3 | 0.313 | -0.451 | -0.446 | 1 | |||||||
| Cl | 0.138 | 0.745 | 0.851 | -0.234 | 1 | ||||||
| SO4 | -0.637 | 0.540 | 0.577 | -0.351 | 0.129 | 1 | |||||
| NO3 | -0.447 | 0.494 | 0.412 | -0.721 | 0.008 | 0.686 | 1 | ||||
| Na | 0.002 | 0.606 | 0.708 | 0.120 | 0.745 | 0.433 | -0.046 | 1 | |||
| K | 0.449 | 0.407 | 0.529 | -0.093 | 0.818 | -0.285 | -0.190 | 0.369 | 1 | ||
| Ca | -0.460 | 0.840 | 0.865 | -0.680 | 0.572 | 0.665 | 0.694 | 0.332 | 0.285 | 1 | |
| Mg | 0.161 | 0.702 | 0.768 | -0.311 | 0.904 | 0.013 | 0.035 | 0.473 | 0.884 | 0.603 | 1 |
| pH | EC | TDS | HCO3 | Cl | SO4 | NO3 | Na | K | Ca | Mg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||||
| EC | -0.619 | 1 | |||||||||
| TDS | -0.657 | 0.955 | 1 | ||||||||
| HCO3 | -0.391 | 0.289 | 0.315 | 1 | |||||||
| Cl | -0.567 | 0.927 | 0.967 | 0.210 | 1 | ||||||
| SO4 | -0.584 | 0.857 | 0.872 | 0.336 | 0.779 | 1 | |||||
| NO3 | -0.392 | 0.132 | 0.244 | 0.093 | 0.057 | 0.263 | 1 | ||||
| Na | -0.579 | 0.944 | 0.944 | 0.405 | 0.936 | 0.865 | 0.005 | 1 | |||
| K | -0.533 | 0.755 | 0.715 | 0.416 | 0.689 | 0.646 | 0.092 | 0.754 | 1 | ||
| Ca | -0.651 | 0.933 | 0.930 | 0.168 | 0.867 | 0.862 | 0.351 | 0.835 | 0.649 | 1 | |
| Mg | -0.468 | 0.755 | 0.849 | 0.328 | 0.881 | 0.616 | 0.088 | 0.794 | 0.557 | 0.650 | 1 |
| pH | EC | TDS | HCO3 | Cl | SO4 | NO3 | Na | K | Ca | Mg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||||
| EC | -0.476 | 1 | |||||||||
| TDS | -0.318 | 0.928 | 1 | ||||||||
| HCO3 | -0.314 | -0.028 | 0.054 | 1 | |||||||
| Cl | -0.403 | 0.948 | 0.945 | -0.049 | 1 | ||||||
| SO4 | -0.007 | 0.396 | 0.584 | 0.509 | 0.371 | 1 | |||||
| NO3 | -0.179 | 0.593 | 0.556 | -0.469 | 0.533 | -0.018 | 1 | ||||
| Na | -0.369 | 0.853 | 0.857 | 0.335 | 0.828 | 0.571 | 0.250 | 1 | |||
| K | -0.402 | 0.785 | 0.621 | -0.232 | 0.716 | 0.015 | 0.748 | 0.582 | 1 | ||
| Ca | -0.273 | 0.737 | 0.805 | -0.249 | 0.804 | 0.310 | 0.654 | 0.430 | 0.547 | 1 | |
| Mg | 0.150 | 0.145 | 0.304 | 0.498 | 0.153 | 0.789 | -0.074 | 0.244 | -0.131 | 0.155 | 1 |
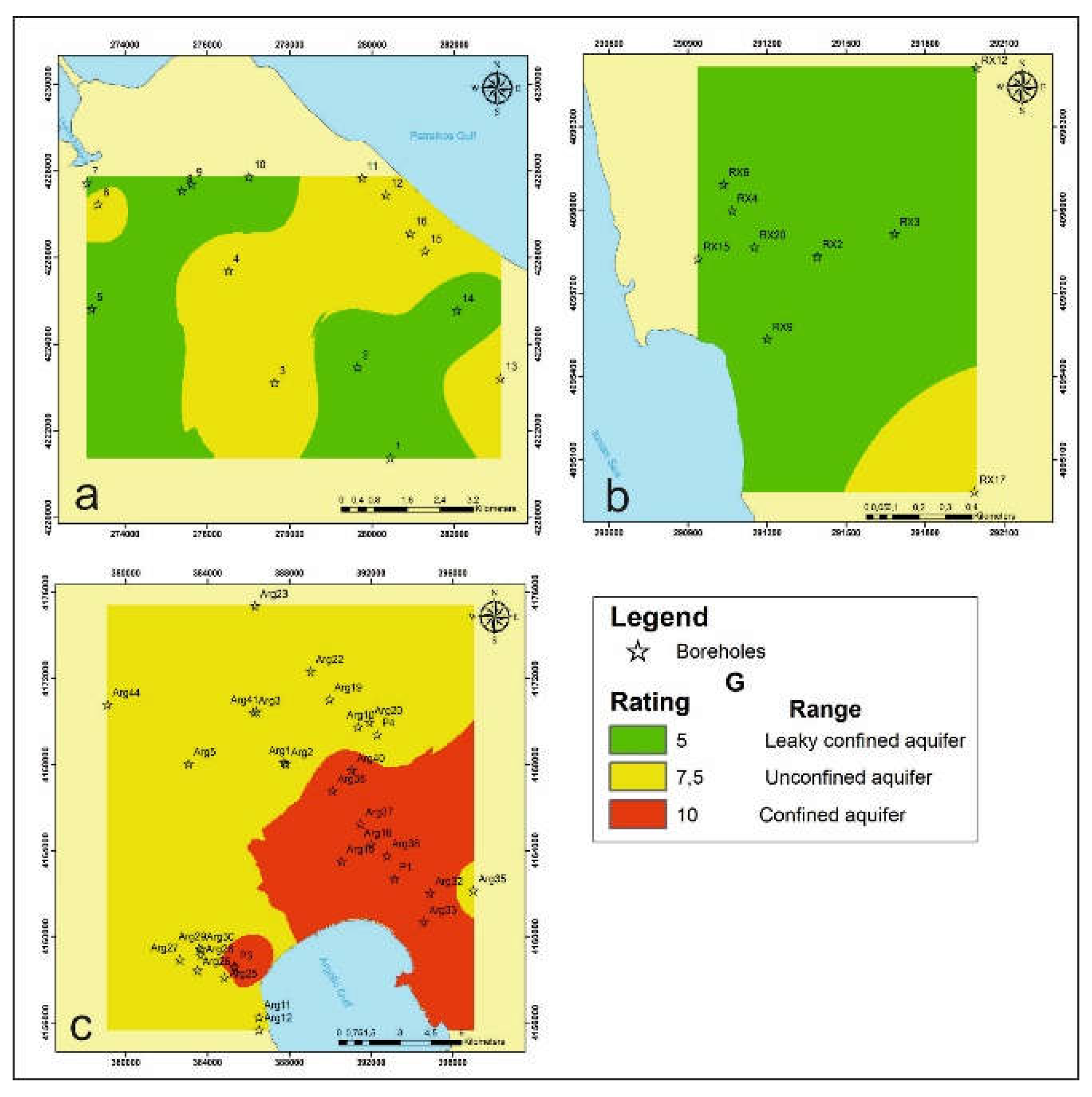
3.10. GALDIT Framework
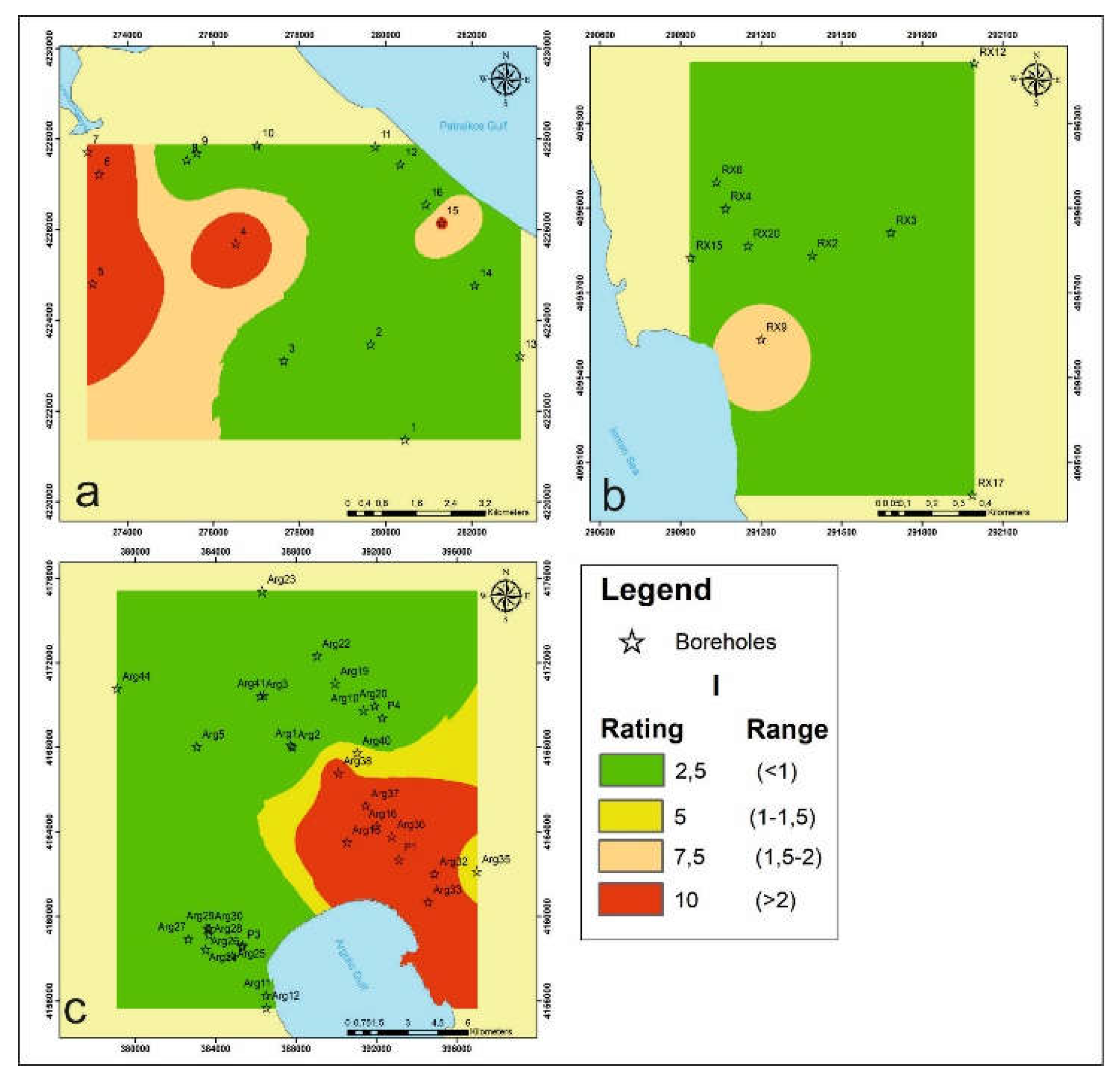
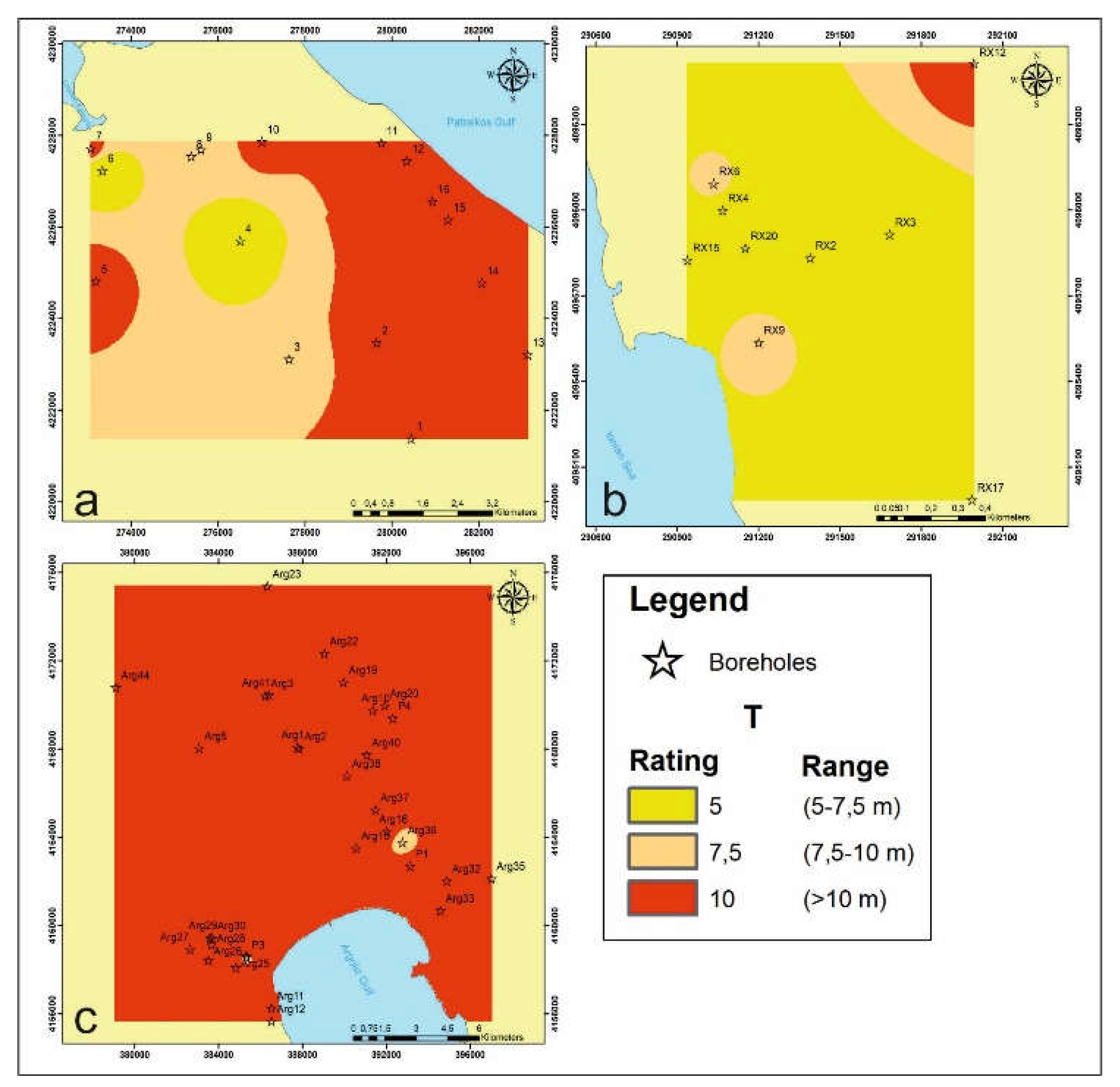
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. GALDIT Layers
4.1.1. Groundwater Occurrence G
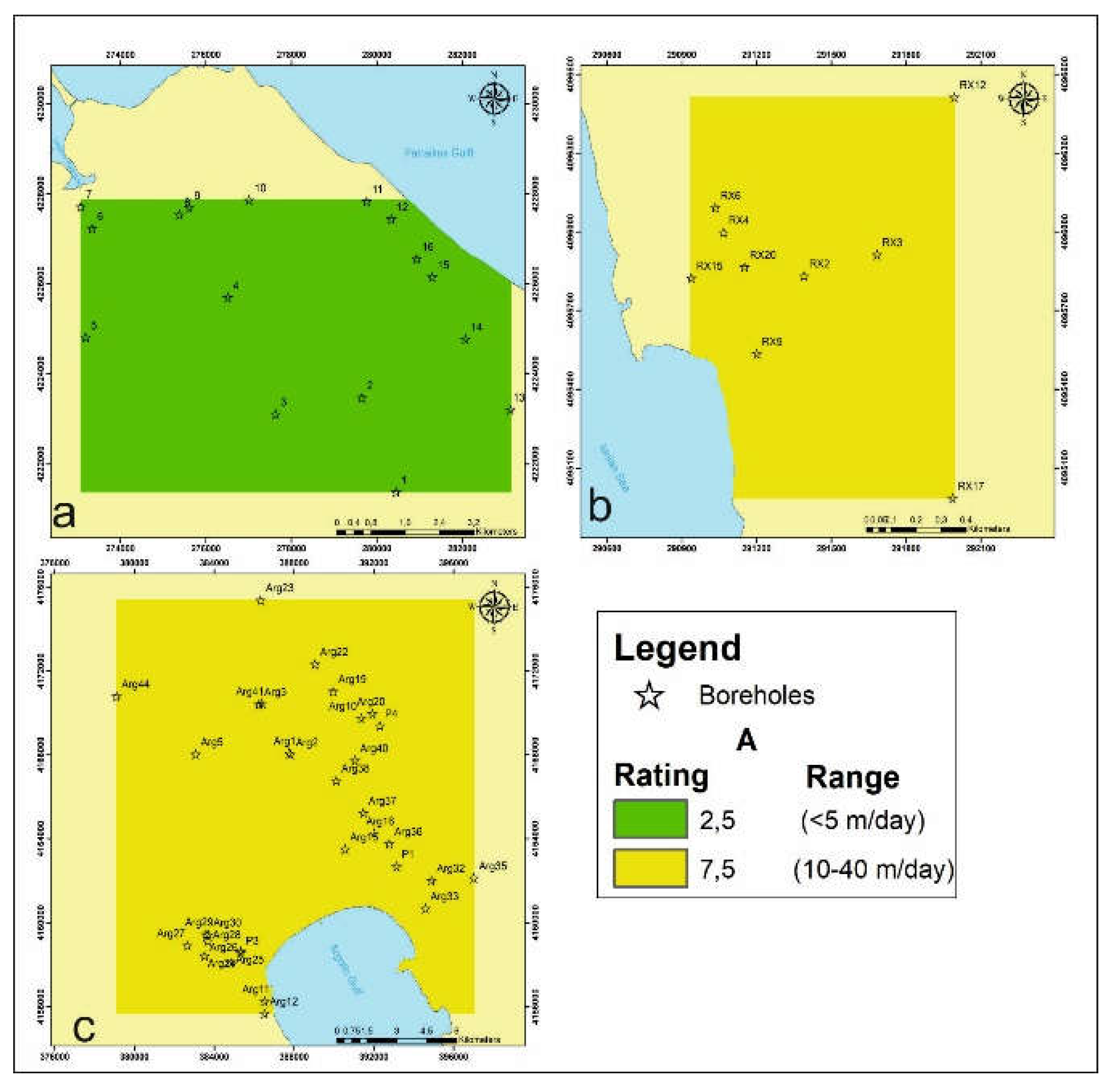
4.1.2. Aquifer Hydraulic Conductivity A
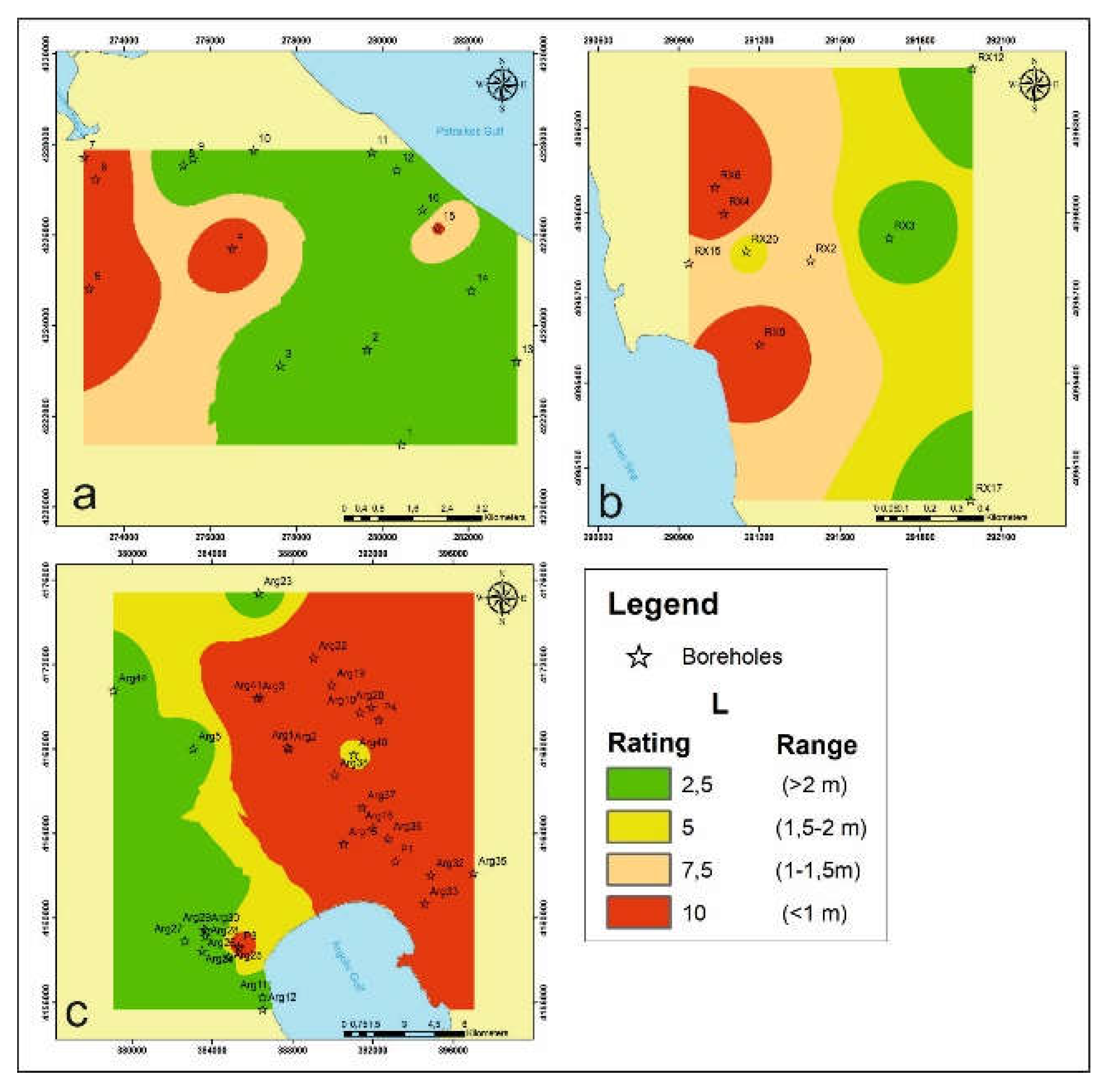
4.1.3. Level of Groundwater above the Sea Level L
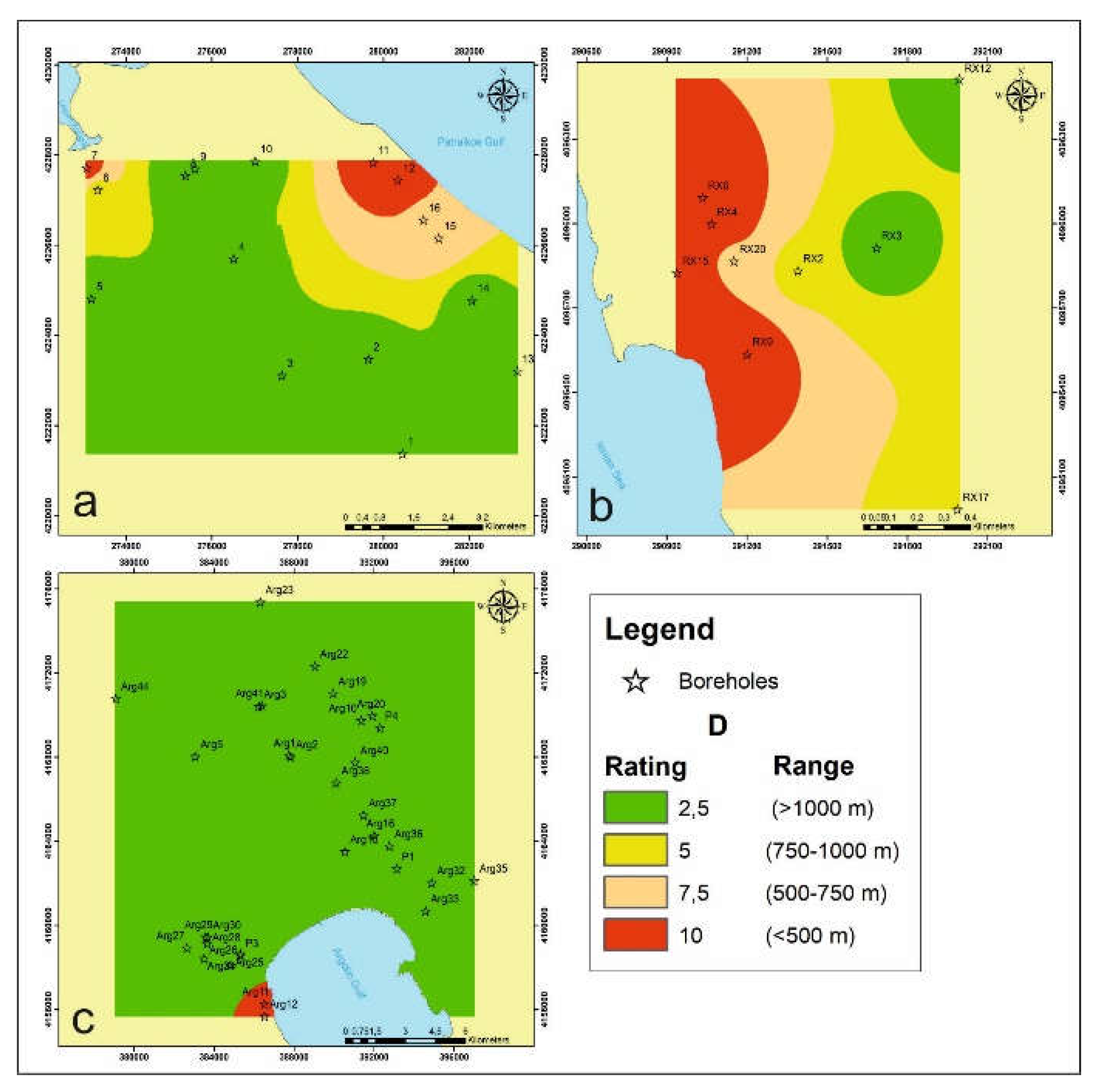
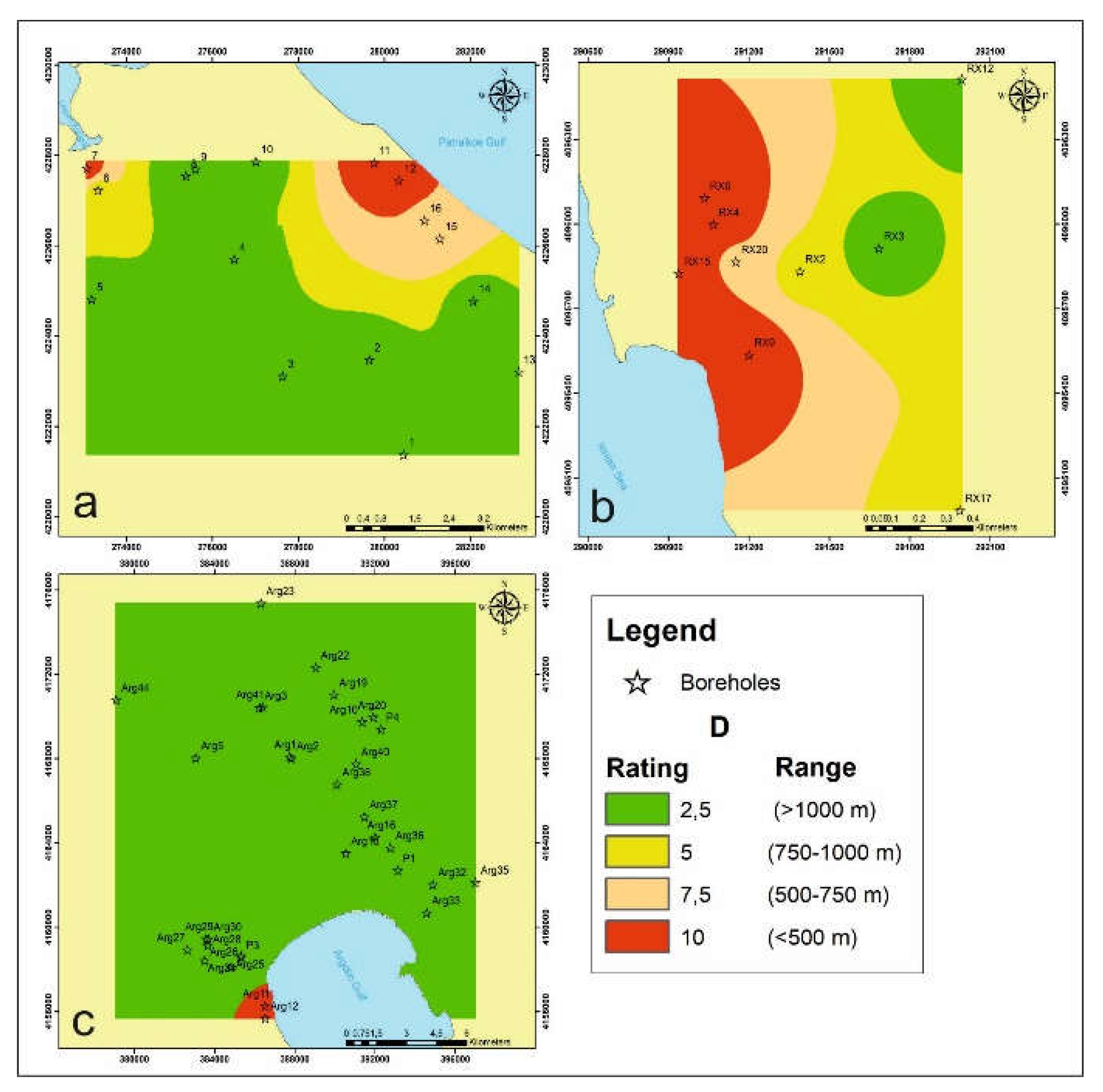
4.1.4. Distance from the Shoreline D
4.1.5. Impact of Existing Status of Seawater Intrusion I
4.1.6. Thickness of the Aquifer T
4.2. GALDIT Framework
4.3. Validation Method
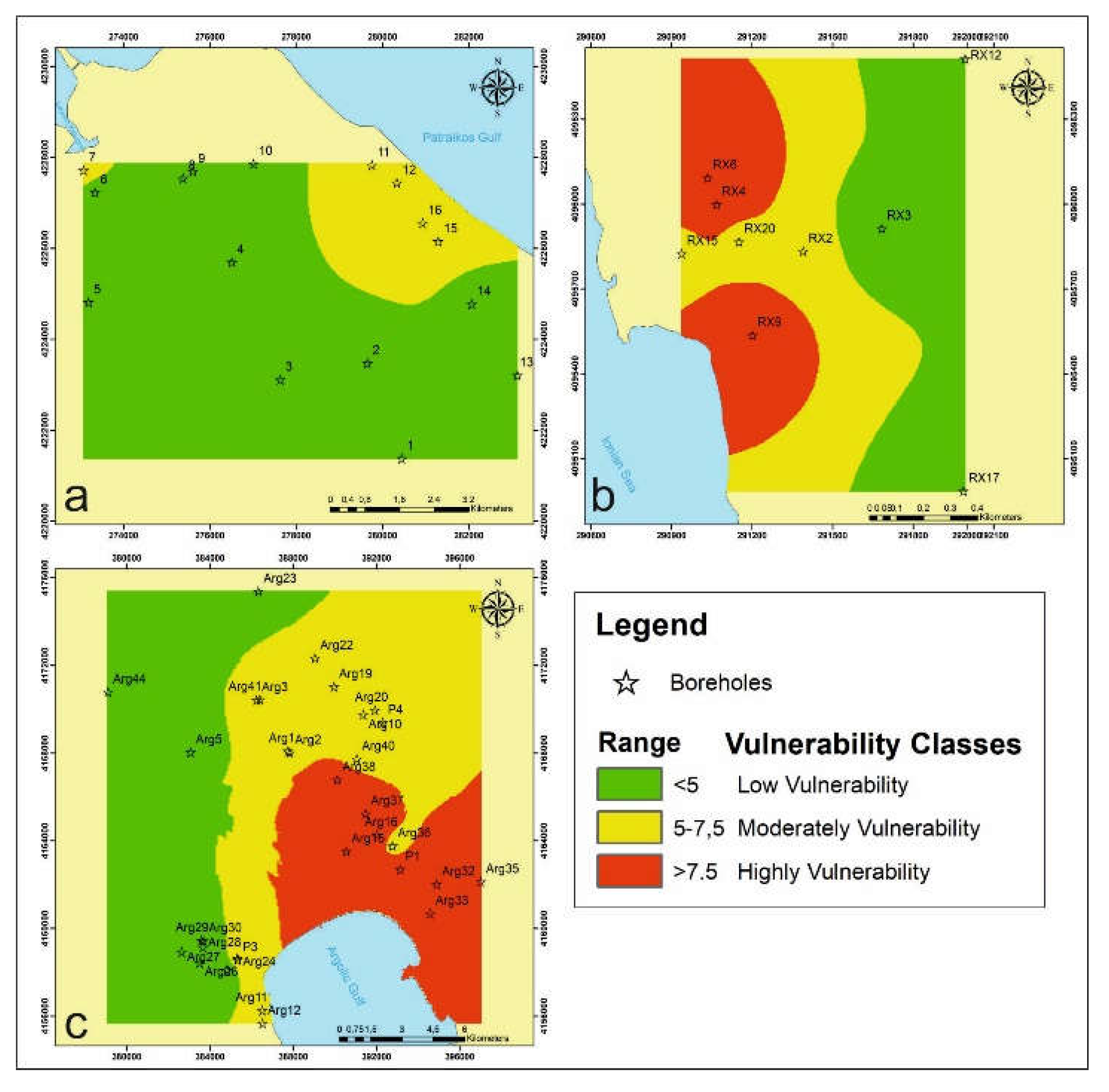
5. Conclusions
Funding
References
- Zhang, Z.; Yi, L. Research Methods for Seawater Intrusion in China and Recommendations for Novel Radium-Radon Technologies. Marine Environmental Research 2024, 198, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarni, N.; Fernane, L.; Naili, M.; Lounas, R.; Belkessa, R. Mapping of the Vulnerability to Marine Intrusion “in Coastal Cherchell Aquifer, Central Algeria” Using the GALDIT Method. Groundwater for Sustainable Development 2020, 11, 100481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.N.V.S.; Satyanarayana, A.N.V.; Bhaskaran, P.K.; Rice, L.; Kantamaneni, K. Assessment of Groundwater Vulnerability Using Integrated Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques for the West Bengal Coast, India. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 2021, 238, 103760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayed, B.; Jmal, I.; Sahal, S.; Bouri, S. The Seawater Intrusion Assessment in Coastal Aquifers Using GALDIT Method and Groundwater Quality Index: The Djeffara of Medenine Coastal Aquifer (Southeastern Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 2018, 11, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telahigue, F.; Mejri, H.; Mansouri, B.; Souid, F.; Agoubi, B.; Chahlaoui, A.; Kharroubi, A. Assessing Seawater Intrusion in Arid and Semi-Arid Mediterranean Coastal Aquifers Using Geochemical Approaches. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C 2020, 115, 102811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Rai, A.K. Identifying Intrusion of Seawater in Coastal Aquifers by Modified GALDIT (M-GALDIT) Index. Groundwater for Sustainable Development 2024, 25, 101173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Montety, V.; Radakovitch, O.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Blavoux, B.; Hermitte, D.; Valles, V. Origin of Groundwater Salinity and Hydrogeochemical Processes in a Confined Coastal Aquifer: Case of the Rhône Delta (Southern France). Applied Geochemistry 2008, 23, 2337–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, I.; Weaver, T.R.; Cendón, D.I.; Fifield, L.K.; Tweed, S.O.; Petrides, B.; Swane, I. Constraining Groundwater Flow, Residence Times, Inter-Aquifer Mixing, and Aquifer Properties Using Environmental Isotopes in the Southeast Murray Basin, Australia. Applied Geochemistry 2012, 27, 1698–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motevalli, A.; Moradi, H.R.; Javadi, S. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Groundwater Vulnerability to Saltwater Up-Coning and Sea Water Intrusion in a Coastal Aquifer (Case Study: Ghaemshahr-Juybar Aquifer). Journal of Hydrology 2018, 557, 753–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moujabber, M.E.; Samra, B.B.; Darwish, T.; Atallah, T. Comparison of Different Indicators for Groundwater Contamination by Seawater Intrusion on the Lebanese Coast. Water Resour Manage 2006, 20, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Mahlknecht, J.; Ledesma-Ruiz, R.; Sanford, W.E.; Lesser, L.E. Dynamics of Major and Trace Elements during Seawater Intrusion in a Coastal Sedimentary Aquifer Impacted by Anthropogenic Activities. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 2020, 232, 103653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, K.; Bordbar, M.; Paryani, S.; Saco, P.M.; Kazakis, N. New Hybrid-Based Approach for Improving the Accuracy of Coastal Aquifer Vulnerability Assessment Maps. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 767, 145416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordbar, M.; Neshat, A.; Javadi, S.; Pradhan, B.; Aghamohammadi, H. Meta-Heuristic Algorithms in Optimizing GALDIT Framework: A Comparative Study for Coastal Aquifer Vulnerability Assessment. Journal of Hydrology 2020, 585, 124768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pérez, L.; Luquot, L.; Carrera, J.; Marazuela, M.A.; Goyetche, T.; Pool, M.; Palacios, A.; Bellmunt, F.; Ledo, J.; Ferrer, N.; et al. A Multidisciplinary Approach to Characterizing Coastal Alluvial Aquifers to Improve Understanding of Seawater Intrusion and Submarine Groundwater Discharge. Journal of Hydrology 2022, 607, 127510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D, A.T.; Nair, A.M.; Prasad, K.R.; J, A.T.; Srinivas, R. Groundwater Vulnerability Assessment of an Urban Coastal Phreatic Aquifer in India Using GIS-Based DRASTIC Model. Groundwater for Sustainable Development 2022, 19, 100810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busico, G.; Kazakis, N.; Colombani, N.; Mastrocicco, M.; Voudouris, K.; Tedesco, D. A Modified SINTACS Method for Groundwater Vulnerability and Pollution Risk Assessment in Highly Anthropized Regions Based on NO3− and SO42− Concentrations. Science of The Total Environment 2017, 609, 1512–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayed, M.A.; Kamal, A.S.M.M.; Hossain, A.; Hasan, M.; Khan, M.R.; Ahmed, K.M.U.; Knappett, P.S.K. Groundwater Vulnerability Assessment to Pollution Using GIS-Based DRASTIC and GOD Methods in Araihazar Upazila of Narayanganj District, Bangladesh. Groundwater for Sustainable Development 2023, 23, 100984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Bandara, U.G.C.; Diyabalanage, S.; Senaratne, S.; Barth, J.A.C. Application of Water Quality Index as a Vulnerability Indicator to Determine Seawater Intrusion in Unconsolidated Sedimentary Aquifers in a Tropical Coastal Region of Sri Lanka. Groundwater for Sustainable Development 2022, 19, 100831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.; Song, J.; Yin, Z.; Wu, J.; Wu, J. Integrated SEAWAT Model and GALDIT Method for Dynamic Vulnerability Assessment of Coastal Aquifer to Seawater Intrusion. Science of The Total Environment 2024, 925, 171740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakis, N.; Spiliotis, M.; Voudouris, K.; Pliakas, F.-K.; Papadopoulos, B. A Fuzzy Multicriteria Categorization of the GALDIT Method to Assess Seawater Intrusion Vulnerability of Coastal Aquifers. Science of The Total Environment 2018, 621, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen Pitchaimani, V.; Seeththa Sankar Narayanan, M.; Richard Abishek, S.; Shyamala, G. Assessment of Coastal Aquifer Vulnerability to Seawater Intrusion: Insights from Kadaladi Region Using the GALDIT MODEL. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering 2024, 10, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Xiong, H.; Ma, C. Combining the Classic Vulnerability Index and Affinity Propagation Clustering Algorithm to Assess the Intrinsic Aquifer Vulnerability of Coastal Aquifers on an Integrated Scale. Environmental Research 2023, 217, 114877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegar, R.; Razzagh, S.; Quilty, J.; Adamowski, J.; Kheyrollah Pour, H.; Booij, M.J. Improving GALDIT-Based Groundwater Vulnerability Predictive Mapping Using Coupled Resampling Algorithms and Machine Learning Models. Journal of Hydrology 2021, 598, 126370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrakis, N. Multicomponent Heterovalent Chromatography in Aquifers. Modelling Salinization and Freshening Phenomena in Field Conditions. Journal of Hydrology 2006, 323, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao Ms, G.K. Identifying Salinization Using Isotopes and Ion Chemistry in Semi-Arid Region of Punjab, India. J Geol Geosci 2013, 02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattacceca, J.C.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Mayer, A.; Claude, C.; Radakovitch, O.; Conchetto, E.; Hamelin, B. Isotopic and Geochemical Characterization of Salinization in the Shallow Aquifers of a Reclaimed Subsiding Zone: The Southern Venice Lagoon Coastland. Journal of Hydrology 2009, 378, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Leboeuf, P. Seawater Intrusion and Associated Processes in a Small Coastal Complex Aquifer (Castell de Ferro, Spain). Applied Geochemistry 2004, 19, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, A.A.; Kishk, F.M.; Gaber, H.M.; Al-Omran, A.M. Long-Term Detection and Hydrochemistry of Groundwater Resources in Egypt: Case Study of Siwa Oasis. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences 2016, 15, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohan, N.; Masoud, M.H.Z.; Niyazi, B.A.M. Impact of Evaporation on Groundwater Salinity in the Arid Coastal Aquifer, Western Saudi Arabia. CATENA 2021, 196, 104864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Rao, V.V.S.G. Hydrogeochemical, Seawater Intrusion and Oxygen Isotope Studies on a Coastal Region in the Puri District of Odisha, India. CATENA 2019, 172, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakate, R.; Ratnalu, G.V.; Sankaran, S. Hydrogeochemical and Isotopic Study for Evaluation of Seawater Intrusion into Shallow Coastal Aquifers of Udupi District, Karnataka, India. Geochemistry 2020, 80, 125647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Su, Q.; Tong, H.; Xu, X.; Gao, Z.; Liu, J. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Irrigation Suitability Evaluation of Groundwater with Different Degrees of Seawater Intrusion. Water 2020, 12, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueddari, H.; Akodad, M.; Baghour, M.; Moumen, A.; Skalli, A.; Yousfi, Y.E.; Ismail, A.; Chahban, M.; Azizi, G.; Hmeid, H.A.; et al. The Salinity Origin and Hydrogeochemical Evolution of Groundwater in the Oued Kert Basin, North-eastern of Morocco. Scientific African 2022, 16, e01226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xiong, G.; Chen, G.; Fu, T.; Yu, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Su, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Characteristics of Coastal Aquifer Contamination by Seawater Intrusion and Anthropogenic Activities in the Coastal Areas of the Bohai Sea, Eastern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 2021, 217, 104830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution; Appelo, C.A.J., Postma, D., Eds.; 0 ed.; CRC Press, 2004; ISBN 978-0-429-15232-0.
- Vallejos, A.; Daniele, L.; Sola, F.; Molina, L.; Pulido-Bosch, A. Anthropic-Induced Salinization in a Dolomite Coastal Aquifer. Hydrogeochemical Processes. Journal of Geochemical Exploration 2020, 209, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, S.; Chandrasekar, N.; Srinivas, Y.; Selvam, S.; Kaliraj, S.; Magesh, N.S.; Venkatramanan, S. Hydrogeochemical Processes Controlling the Groundwater Salinity in the Coastal Aquifers of Southern Tamil Nadu, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2022, 174, 113264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telahigue, F.; Agoubi, B.; Souid, F.; Kharroubi, A. Assessment of Seawater Intrusion in an Arid Coastal Aquifer, South-Eastern Tunisia, Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis and Chloride Mass Balance. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C 2018, 106, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakea, A-M. Investigation of the hydro-geological conditions and salinization of the coastal part of the aquatic system of Romanos-Choras, SW Peloponnese, University of Patras: Patra, 2019.
- Stavropoulos, J. Hydrogeological conditions in a wide area below Achaias – Manolados (NW Peloponnese), National Technical University of Athens: Athens, 1992.
- Mylonas, A. Investigation of the hydrogeological conditions and salinization of the Argolis Field, University of Patras, Patra: Patra, 2019.


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





