Submitted:
09 August 2024
Posted:
12 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design and Crop Management
2.3. Plant Sampling and Nutrient Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Grain Yields, Yield Components and Other Agronomic Traits
3.2. Grain Nutrient Concentrations and Acquisition
3.3. Concentrations of Phytic Acid and Phytate-P, Phytate-P/P Ratios, and Molar Ratios of PA/Zn, PA × Ca/Zn, PA/Fe and PA × Ca/Fe in Wheat Grains
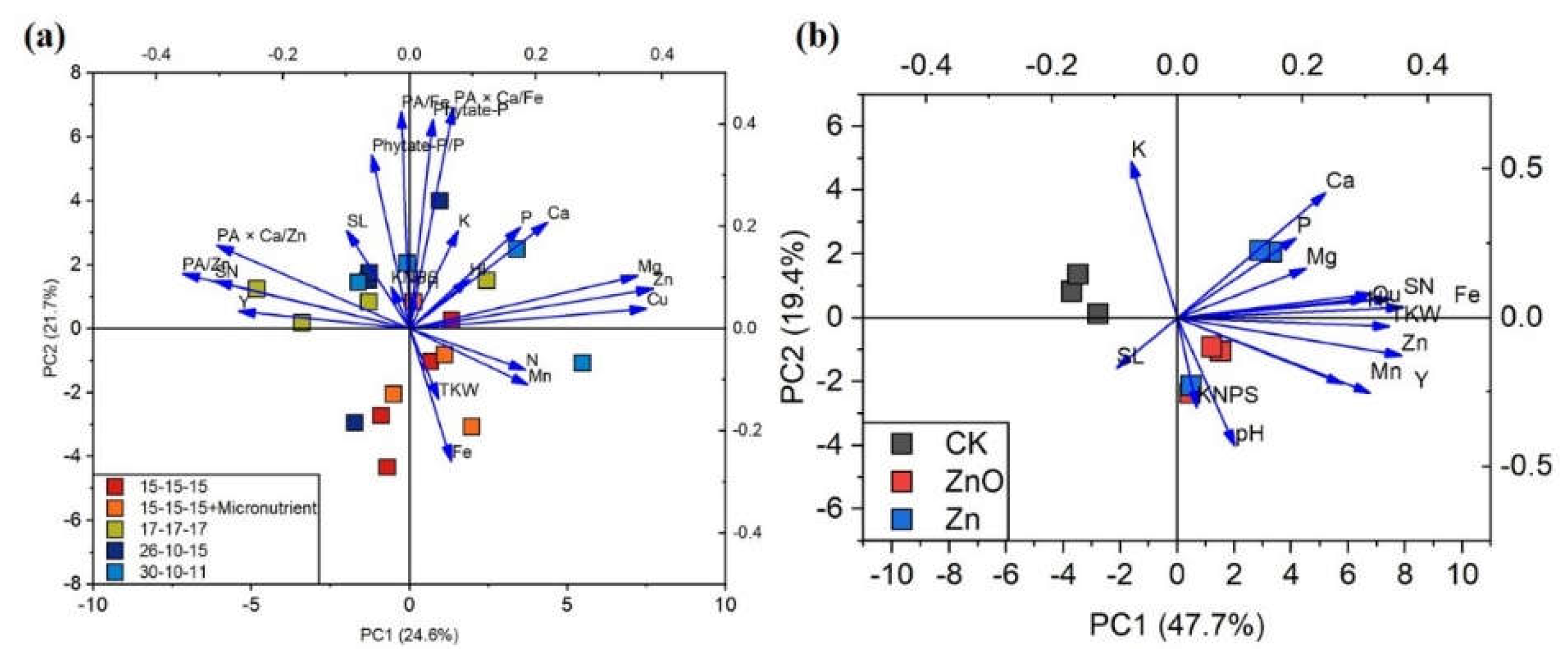
3.4. Principle Component Analysis (PCA) of Various Parameters of Wheat as Affected by Soil Fertilization and Foliar Spraying
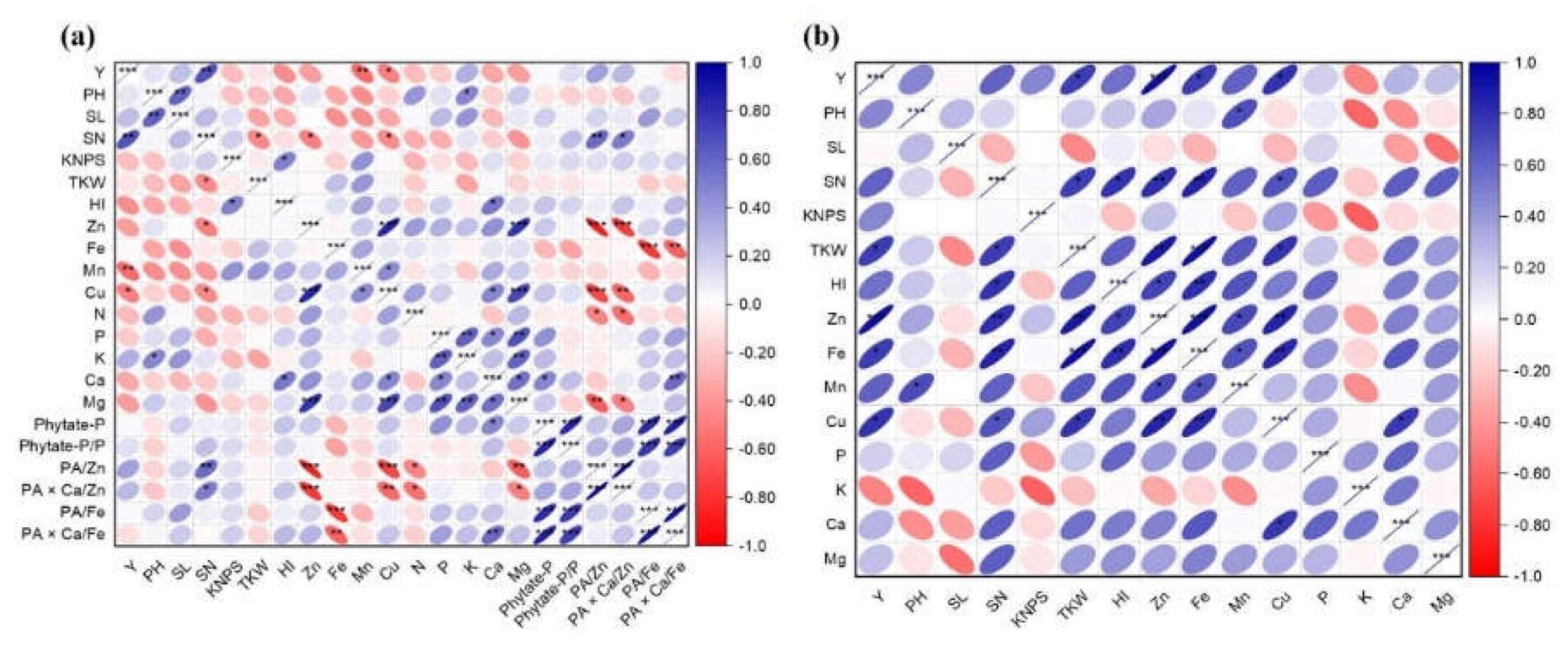
3.5. Relationships among Grain Yield Traits and Nutritional Quality-Related Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Appropriate Soil Fertilization can Simultaneously Increase the Wheat Grain Yield while Improving Grain Zn Nutritional Quality, but the Overall Effect is Limited
4.2. Foliar Zn Spraying using Agricultural Drones is a High-efficient Approach to Biofortify Wheat Grains with Zn while Enhancing Grain Yields, thus Showing a Great Potential to be Adopted in Large Areas by Farmers
4.3. A Double-win in Wheat Grain Yield and Micronutrient Nutrition rather than a “Dilution Effect” on Zn due to Yield Increase could be Effectively Achieved through Appropriate Soil Fertilization and Foliar Zn Spraying
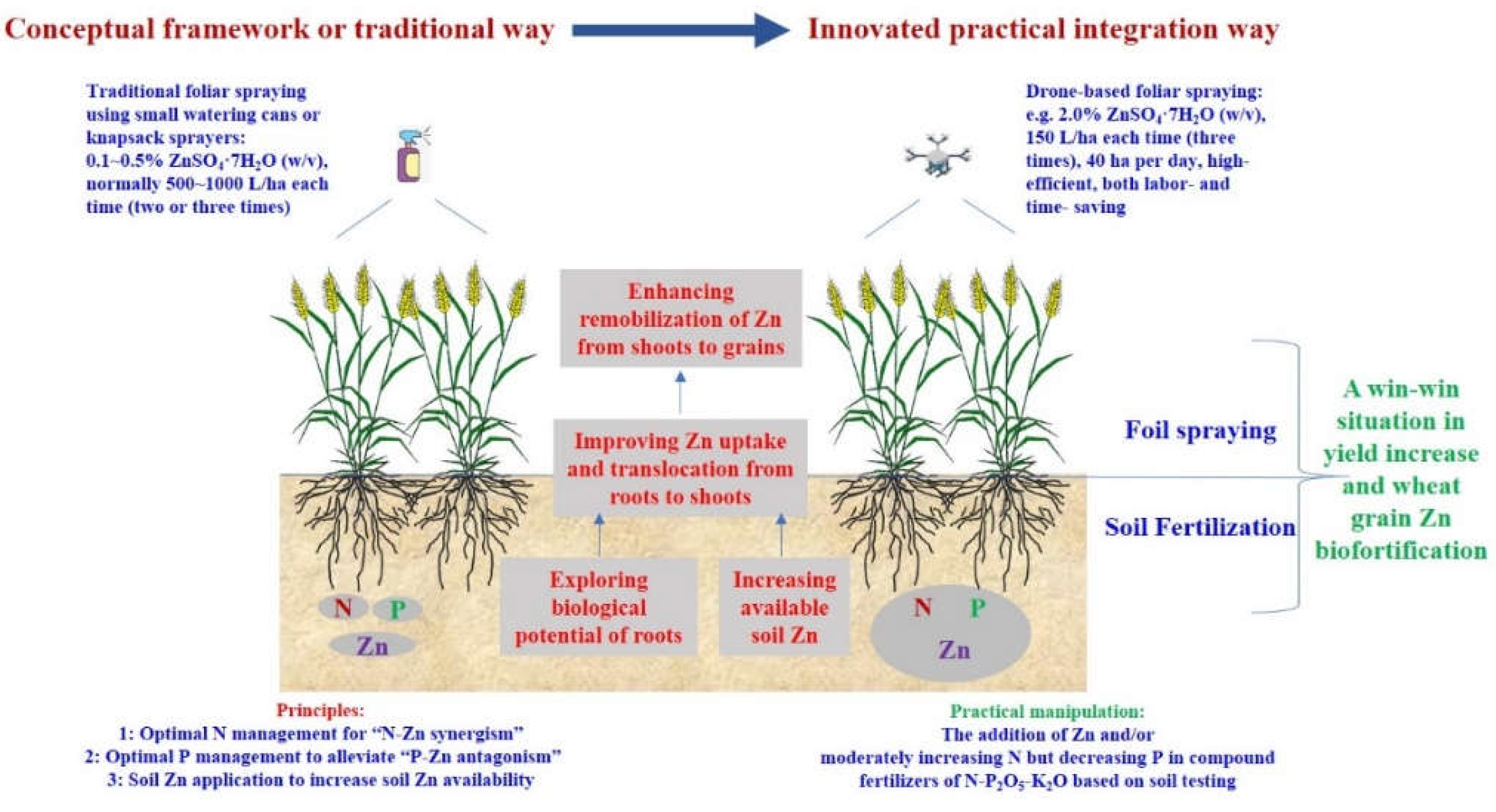
4.4. Integrated Practical Strategies for Simultaneously Improving Yield and Micronutrient (Particularly for Zn) Nutritional Quality of Wheat Grains
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cakmak, I. Enrichment of cereal grains with zinc: Agronomic or genetic biofortification? Plant Soil 2008, 302, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursarebani, N.; Nussbaumer, T.; Šimková, H.; Šafář, J.; Witsenboer, H.; van Oeveren, J.; Doležel, J.; Mayer, K.F.X.; Stein, N.; Schnurbusch, T. Whole-genome profiling and shotgun sequencing delivers an anchored, gene-decorated, physical map assembly of bread wheat chromosome 6A. Plant J. 2014, 79, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenstein, O.; Jaleta, M.; Abdul Mottaleb, K.; Sonder, K. , Donovan, J.; Braun, H.-J. Global trends in wheat production, consumption and trade. In Wheat Improvement: Food Security in a Changing Climate; Reynolds, M.P., Braun, H.-J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing, 2022; pp. 47–66.
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D. , Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martre, P.; Dueri, S.; Guarin, J.R.; Ewert, F.; Webber, H.; Calderini, D.; Molero, G.; Reynolds, M.; Miralles, D.; Garcia, G.; Brown, H.; George, M.; Craigie, R.; Cohan, J.-P.; Deswarte, J.-C.; Slafer, G.; Giunta, F.; Cammarano, D.; Ferrise, R. , Gaiser, T.; Gao, Y.; Hochman, Z.; Hoogenboom, G.; Hunt, L.A.; Kersebaum, K.C.; Nendel, C.; Padovan, G.; Ruane, A.C.; Srivastava, A.K.; Stella, T.; Supit, I.; Thorburn, P.; Wang, E.; Wolf, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Z.; Asseng, S. Global needs for nitrogen fertilizer to improve wheat yield under climate change. Nat. Plants 2024, 10, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Guinness World Records. Available online: https://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/highest-wheat-yield/ (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- van Ittersum, M.K.; Cassman, K.G.; Grassini, P.; Wolf, J.; Tittonell, P.; Hochman, Z. Yield gap analysis with local to global relevance-a review. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 143, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202307/t20230715_1941239.html (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- Natasha, N.; Shahid, M.; Bibi, I.; Iqbal, J.; Khalid, S.; Murtaza, B.; Bakhat, H.F.; Farooq, A.B.U.; Amjad, M.; Hammad, H.M.; Niazi, N.K.; Arshad, M. Zinc in soil-plant-human system: a data-analysis review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 808, 152024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I.; Kutman, U.B. Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: a review. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69(1), 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Tong, Y.P.; Xue, Y.F.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhang, W.; Deng, Y.; Meng, Q.F.; Yue, S.C.; Yan, P.; Cui, Z.L.; Shi, X.J.; Guo, S.W.; Sun, Y.X.; Ye, Y.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Jia, L.L.; Ma, W.Q.; He, M.R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Kou, C.L.; Li, Y.T.; Tan, D.S.; Cakmak, I.; Zhang, F.S.; Zou, C.Q. Harvesting more grain zinc of wheat for human health. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Wang, L.; Qiao, Y.; Kong, W.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kong, L.; Xue, Y.; Sizmur, T. Elucidating the source-sink relationships of zinc biofortification in wheat grains: a review. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9(4), e243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Xue, Yanf.; Liu, D.; Kong, W.; Xue, Yanh.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Mei, P. Rational application of fertilizer nitrogen to soil in combination with foliar Zn spraying improved Zn nutritional quality of wheat grains. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 677.
- Guttieri, M.J.; Peterson, K.M.; Souza, E.J. Agronomic performance of low phytic acid wheat. Crop Sci. 2006, 46(6), 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; Pellny, T.K.; Lovegrove, A. Is modern wheat bad for health? Nat. Plants. 2016, 2(7), 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R.; Hassall, K.L.; Grausgruber, H.; Andersson, A.A.M.; Lampi, A.-M.; Piironen, V.; Rakszegi, M.; Ward, J.L.; Lovegrove, A. Do modern types of wheat have lower quality for human health? Nutr. Bull. 2020, 45, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvin, D.F.; Welch, R.M.; Finley, J.W. Historical shifts in the seed mineral micronutrient concentration of US hard red winter wheat germplasm. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86(13), 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Su, Y.H.; Dunham, S.J.; Rakszegi, M.; Bedo, Z.; McGrath, S.P. Variation in mineral micronutrient concentrations in grain of wheat lines of diverse origin. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 49(2), 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velu, G.; Ortiz-Monasterio, I.; Cakmak, I.; Hao, Y.; Singh, R.P. Biofortification strategies to increase grain zinc and iron concentrations in wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 59(3), 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.E.; Sands, D.C. The breeder’s dilemma—yield or nutrition? Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1078–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashu, D.; Nalivata, P.C.; Amede, T.; Ander, E.L.; Bailey, E.H.; Botoman, L.; Chagumaira, C.; Gameda, S.; Haefele, S.M.; Hailu, K.; Joy, E.J.M.; Kalimbira, A.A.; Kumssa, D.B.; Lark, R.M.; Ligowe, I.S.; McGrath, S.P.; Milne, A.E.; Mossa, A.W.; Munthali, M.; Towett, E.K.; Walsh, M.G.; Wilson, L.; Young, S.D.; Broadley, M.R. The nutritional quality of cereals varies geospatially in Ethiopia and Malawi. Nature 2021, 594, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.Y.; Li, X.J.; Qiao, Y.T.; Xue, Y.H.; Yan, W.; Ma, L.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Kong, L.A.; Xue, Y.F.; Cui, Z.L.; van der Werf, W. Dissecting the relationship between yield and mineral nutriome of wheat grains in double cropping as affected by preceding crops and nitrogen application. Field Crop. Res. 2023, 293, 108845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xue, Y.-F.; Chen, X.-P.; Zhang, F.-S.; Zou, C.-Q. Zinc nutrition for high productivity and human health in intensive production of wheat. Adv. Agron. 2020, 163, 179–217. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Cao, W.; Chen, X.; Stomph, T.J.; Zou, C. Global analysis of nitrogen fertilization effects on grain zinc and iron of major cereal crops. Glob. Food Secur. 2022, 33, 100631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Rashid, A.; Ram, H.; Savasli, E.; Arisoy, R.Z.; Ortiz-Monasterio, I.; Simunji, S.; Wang, Z.H.; Sohu, V.; Hassan, M.; Kaya, Y.; Onder, O.; Lungu, O.; Yaqub Mujahid, M.; Joshi, A.K.; Zelenskiy, Y.; Zhang, F.S.; Cakmak, I. Biofortification of wheat with zinc through zinc fertilization in seven countries. Plant Soil, 2012; 361, 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.; Bucher, M.; Schaaf, G.; Sawers, R.J.H.; Chen, X.; Hochholdinger, F.; Zou, C.; Yu, P. Maize zinc uptake is influenced by arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis under various soil phosphorus availabilities. New Phytol. 2024, 243(5), 1936–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wu, P.; Ling, H.; Xu, G.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Q. Plant nutriomics in China: an overview. Ann. Bot. 2006, 98, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P. Marschner's Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Academic Press, Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Posma, J.M.; Garcia-Perez, I.; Frost, G.; Aljuraiban, G.S.; Chan, Q.; Van Horn, L.; Daviglus, M.; Stamler, J.; Holmes, E.; Elliott, P.; Nicholson, J.K. Nutriome–metabolome relationships provide insights into dietary intake and metabolism. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xia, H.; Li, X.; Qiao, Y.; Xue, Yanh. ; Jiang, X.; Yan, W.; Liu, Y.; Xue, Yanf.; Kong, L. Source-sink manipulation affects accumulation of zinc and other nutrient elements in wheat grains. Plants 2021, 10, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, W.; Lantzsch, H.J. Sensitive method for the rapid determination of phytate in cereals and cereal products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1983, 34(12), 1423–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.-F.; Yue, S.-C.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Cui, Z.-L.; Chen, X.-P.; Yang, F.-C.; Cakmak, I.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhang, F.S.; Zou, C.-Q. Grain and shoot zinc accumulation in winter wheat affected by nitrogen management. Plant Soil, 2012; 361, 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, D.Y.; Li, C.; Cui, Z.L.; Chen, X.P.; Russell, Y.; Zou, C.Q. Zinc accumulation and remobilization in winter wheat as affected by phosphorus application. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 184, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, D.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Cui, Z.L.; Chen, X.P.; Zou, C.Q. Zinc uptake and accumulation in winter wheat relative to changes in root morphology and mycorrhizal colonization following varying phosphorus application on calcareous soil. Field Crop. Res. 2016, 197, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, D.Y.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, X.P.; Zou, C.Q. Overuse of phosphorus fertilizer reduces the grain and flour protein contents and zinc bioavailability of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M. Integrated effect of phosphorous and zinc on wheat quality and soil properties. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2016, 10, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bingham, F.T.; Garber, M.J. Solubility and availability of micronutrients in relation to phosphorus fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1960, 24, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Zou, C.; Chen, X. Quantitative evaluation of the grain zinc in cereal crops caused by phosphorus fertilization. A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, D.; Degryse, F.; da Silva, R.C.; Baird, R.; McLaughlin, M.J. Agronomic effectiveness of zinc sources as micronutrient fertilizer. Adv. Agron. 2016, 139, 215–267. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.Y.; Zhang, W.; Pang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, X.Z.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S.; Zou, C.Q. Effects of zinc application rate and zinc distribution relative to root distribution on grain yield and grain Zn concentration in wheat. Plant Soil 2017, 411, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Sun, Y.X.; Ye, Y.L.; Karim, M.R.; Xue, Y.F.; Yan, P.; Meang, Q.F.; Cui, Z.L.; Cakmak, I.; Zhang, F.S. Zinc biofortification of wheat through fertilizer applications in different locations of China. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 125, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhao, R.R.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S.; Zou, C.Q. Alleviation of drought stress in winter wheat by late foliar application of zinc, boron, and manganese. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I. Role of zinc in protecting plant cells from reactive oxygen species. New Phytol. 2000, 146, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I.; Kalayci, M.; Kaya, Y.; Torun, A.A.; Aydin, N.; Wang, Y.; Arisoy, Z.; Erdem, H.; Yazici, A.; Gokmen, O.; Ozturk, L.; Horst, W.J. Biofortification and localization of zinc in wheat grain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9092–9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. Investigations of the Effects of Zn biofortification in Different Wheat Genotypes. PhD Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, H.; Lv, Z.; Cui, L.; Mao, H.; Kopittke, P.M. Using synchrotron-based approaches to examine the foliar application of ZnSO4 and ZnO nanoparticles for field-grown winter wheat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66(11), 2572–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutman, U.; Kutman, B.; Ceylan, Y.; Ova, E.; Cakmak, I. Contributions of root uptake and remobilization to grain zinc accumulation in wheat depending on post-anthesis zinc availability and nitrogen nutrition. Plant Soil, 2012; 361, 177–187. [Google Scholar]
- Haslett, B.S.; Reid, R.J.; Rengel, Z. Zinc mobility in wheat: uptake and distribution of zinc applied to leaves or roots. Ann. Bot. 2001, 87(3), 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uauy, C. , Distelfeld, A., Fahima, T., Blechl, A., Dubcovsky, J. A NAC gene regulating senescence improves grain protein, zinc, and iron content in wheat. Science, 2006; 314, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, B.M.; Uauy, C.; Dubcovsky, J.; Grusak, M.A. Wheat (Triticum aestivum) NAM proteins regulate the translocation of iron, zinc, and nitrogen compounds from vegetative tissues to grain. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60(15), 4263–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erenoglu, B.; Nikolic, M.; Römheld, V.; Cakmak, I. Uptake and transport of foliar applied zinc (65Zn) in bread and durum wheat cultivars differing in zinc efficiency. Plant Soil, 2002; 241, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Erenoglu, E.B.; Kutman, U.B.; Ceylan, Y.; Yildiz, B.; Cakmak, I. Improved nitrogen nutrition enhances root uptake, root-to-shoot translocation and remobilization of zinc (65Zn) in wheat. New Phytol. 2011, 189(2), 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, L.J.; Dias, D.A.; Boughton, B.; Roessner, U.; Graham, R.D.; Stangoulis, J.C.R. Metabolite profiling of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) phloem exudate. Plant Methods, 2014, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, S. , Tabbita, F., Cantu, D., Buffalo, V., Avni, R., Vazquez-Gross, H.; Zhao, R.; Conley, C.J.; Distelfeld, A.; Dubcovksy, J. Regulation of Zn and Fe transporters by the GPC1 gene during early wheat monocarpic senescence. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Ram, H.; Kumar, B. Mechanism of zinc absorption in plants: uptake, transport, translocation and accumulation. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, O.P.; Pandey, V.; Saini, R.; Narwal, S.; Malik, V.K.; Khandale, T.; Ram, S.; Singh, G.P. Identifying transcripts associated with efficient transport and accumulation of Fe and Zn in hexaploid wheat (T. aestivum L.). J. Biotechnol. 2020, 316, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diepenbrock, C.H.; Gore, M.A. Closing the divide between human nutrition and plant breeding. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshit, R.; Patra, A.K.; Purakayastha, T.J.; Singh, R.D.; Pathak, H.; Dhar, S. Super-optimal NPK along with foliar iron application influences bioavailability of iron and zinc of wheat. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci., India Sect. B: Biol. Sci. 2016, 86, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.Y.; Kong, W.; Wang, L.; Xue, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, S.; Li, C. Foliar Zn spraying simultaneously improved concentrations and bioavailability of Zn and Fe in maize grains irrespective of foliar sucrose supply. Agronomy 2019, 9(7), 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangoulis, J.C.R.; Knez, M. Biofortification of major crop plants with iron and zinc - achievements and future directions. Plant Soil 2022, 474, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I. , Pfeiffer, W.H., McClafferty, B. Biofortification of durum wheat with zinc and iron. Cereal Chem. 2010, 87, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Du, W.; Peng, Q.; Lv, Z.; Mao, H.; Kopittke, P.M. Development of ZnO nanoparticles as an efficient Zn fertilizer: Using synchrotron-based techniques and laser ablation to examine elemental distribution in wheat grain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68(18), 5068–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Zhong, M.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Bai, J.; Liu, J.; Mao, H. Nutrient strengthening of winter wheat by foliar ZnO and Fe3O4 NPS: Food safety, quality, elemental distribution and effects on soil bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, Z.; Akhtar, J.; Alhodaib, A.; Naz, T.; Zafar, M.I.; Iqbal, M.M.; Fatima, H.; Naz, I. Efficacy of ZnO nanoparticles in Zn fortification and partitioning of wheat and rice grains under salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Palacios, J.T.; Henry, D.; Penrose, B.; Bell, R. Formulation of zinc foliar sprays for wheat grain biofortification: a review of current applications and future perspective. Front. Plant. Sci. 2023, 14, 1247600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Monasterio, I.; Cardenas, M.E.; Cakmak, I. Zinc Biofortification in Wheat through Foliar Fertilization Combined with Pesticides. The 4th International Zinc Symposium: Improving Crop Production and Human Health, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2015.
- Wang, X.-Z.; Liu, D.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.-J.; Cakmak, I.; Zou, C.-Q. An effective strategy to improve grain zinc concentration of winter wheat, aphids prevention and farmers' income. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 184, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Zou, C.-Q.; Mirza, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Li, D.-P.; Xu, C.-L.; Zhou, X.-B.; Shi, X.-J.; Xie, D.-T.; He, X.-H.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Cost of agronomic biofortification of wheat with zinc in China. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36(3), 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.P.; Xiao, Y.H.; Xu, F.; Gao, X.K.; Cao, S.Y.; Zhang, F.X.; Wang, G.D.; Sanders, D.; Chu, C.C. Cytokinin-dependent regulatory module underlies the maintenance of zinc nutrition in rice. New Phytol. 2019, 224, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; Song, J.; Jameson, P.E. Cytokinin dehydrogenase: a genetic target for yield improvement in wheat. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18(3), 614–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Du, Q.; Yan, P.; Yu, B.; Li, W.-X.; Zou, C.-Q. The auxin signaling pathway contributes to phosphorus-mediated zinc homeostasis in maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23(1), 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Shi, R.L.; Karim, R.M.; Zhang, F.S.; Zou, C.Q. Iron and zinc concentrations in grain and flour of winter wheat as affected by foliar application. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12268–12274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.Q.; Du, Y.F.; Rashid, A.; Ram, H.; Savasli, E.; Pieterse, P.J.; Ortiz-Monasterio, I.; Yazici, A.; Kaur, C.; Mahmood, K.; Singh, S.; Le Roux, M.R.; Kuang, W.; Onder, O.; Kalayci, M.; Cakmak, I. Simultaneous biofortification of wheat with zinc, iodine, selenium, and iron through foliar treatment of a micronutrient cocktail in six countries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8096–8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Experimental year | Site | Geographic coordinates | Soil type |
pH (2.5:1 Water: soil ratio) |
Organic matter (g/kg) |
Total nitrogen (g/kg) |
Olsen-P (mg/kg) | Exchangeable K (mg/kg) |
DTPA-extractable Zn (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020-2021 | Jiyang | 116°58'E, 36°58'N | Calcareous alluvial soil | 8.1 | 12.7 | 0.94 | 23.1 | 103.5 | 1.7 |
| 2022-2023 | Liuyuan | 115°07'E, 35°02'N | Calcareous alluvial soil | 8.3 | 13.5 | 0.82 | 15.3 | 98.7 | 1.2 |
| Treatment | Number of sprays/ spraying date |
Deionized water (L/ha) |
ZnSO4·7H2O (kg/ha) |
ZnO (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK 1 | First/2023-05-08 | 150 L/ha | 0 | 0 |
| ZnO | 150 L/ha | 0 | 3 kg/ha | |
| Zn | 150 L/ha | 3 kg/ha | 0 | |
| CK | Second/2023-05-17 | 150 L/ha | 0 | 0 |
| ZnO | 150 L/ha | 0 | 3 kg/ha | |
| Zn | 150 L/ha | 3 kg/ha | 0 | |
| CK | Third/2023-05-23 | 150 L/ha | 0 | 0 |
| ZnO | 150 L/ha | 0 | 3 kg/ha | |
| Zn | 150 L/ha | 3 kg/ha | 0 |
| Experiment |
Treatment |
Plant height (cm) |
Spike length (cm) |
Spike number (10000/666.7 m2) |
KNPS |
TKW (g) |
Grain yield (t/ha) |
HI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Soil Fertilization |
N-P2O5-K2O (15-15-15) | 72.4a 1 | 6.5c | 34.4a | 34.5ab | 48.2a | 7.1b | 63.2a |
| 15-15-15+Micronutrient | 74.5a | 6.7bc | 36.5a | 32.3b | 48.2a | 7.5a | 61.1ab | |
| 17-17-17 | 72.3a | 6.9abc | 39.2a | 36.5a | 47.3a | 7.6a | 62.0ab | |
| 26-10-15 | 75.5a | 7.1ab | 35.7a | 33.4ab | 48.2a | 7.5a | 59.8b | |
| 30-10-11 | 75.6a | 7.3a | 36.8a | 36.2ab | 46.7a | 7.4a | 61.5ab | |
|
Foliar Spraying |
CK | 77.7a | 8.3a | 39.8a | 36.8a | 43.9b | 7.5b | 59.4a |
| ZnO | 84.5a | 8.4a | 41.4a | 37.5a | 45.7a | 8.6a | 61.5a | |
| Zn | 78.7a | 8.1a | 41.8a | 39.9a | 46.2a | 8.8a | 61.8a |
| Parameter | Treatment | Zn | Fe | Mn | Cu | N | P | K | Ca | Mg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | mg/kg | g/kg | |||||||||
| N-P2O5-K2O (15-15-15) |
19.9b 1 | 26.4a | 26.5a | 2.4ab | 19.2a | 3.1a | 4.5a | 0.33a | 1.39ab | ||
| 15-15-15+ Micronutrient |
23.5ab | 26.0ab | 25.2ab | 2.6ab | 18.6a | 3.0a | 4.7a | 0.34a | 1.41ab | ||
| 17-17-17 | 19.4b | 25.0ab | 26.1ab | 2.3b | 17.0a | 3.0a | 4.6a | 0.34a | 1.37b | ||
| 26-10-15 | 22.5ab | 22.2c | 23.9b | 2.4ab | 18.6a | 3.0a | 4.6a | 0.32a | 1.38b | ||
| 30-10-11 | 27.0a | 24.2b | 25.7ab | 2.8a | 19.9a | 3.2a | 4.8a | 0.33a | 1.45a | ||
| Acquisition | g/ha | kg/ha | |||||||||
| N-P2O5-K2O (15-15-15) |
141.2b | 187.7ab | 188.1a | 17.4b | 136.9a | 12.6b | 32.2a | 2.3a | 9.9a | ||
| 15-15-15+ Micronutrient |
176.2ab | 195.0a | 189.0a | 19.3ab | 139.7a | 14.6ab | 35.0a | 2.5a | 10.6a | ||
| 17-17-17 | 144.5b | 189.1ab | 196.6a | 17.4b | 128.1a | 14.1ab | 34.5a | 2.6a | 10.3a | ||
| 26-10-15 | 168.9ab | 167.6b | 180.1a | 17.8ab | 140.4a | 15.2a | 34.3a | 2.4a | 10.4a | ||
| 30-10-11 | 197.6a | 178.3ab | 188.5a | 20.8a | 145.9a | 14.7ab | 35.2a | 2.5a | 10.7a | ||
| Parameter | Treatment | Zn | Fe | Mn | Cu | P | K | Ca | Mg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | mg/kg | g/kg | ||||||||
| CK | 33.5c 1 | 25.9b | 13.3c | 4.5c | 3.5a | 4.3a | 0.392ab | 1.5a | ||
| ZnO | 41.9b | 28.3a | 15.9a | 4.8b | 3.6a | 4.0a | 0.389b | 1.5a | ||
| Zn | 43.6a | 29.0a | 14.4b | 5.4a | 3.7a | 4.2a | 0.430a | 1.5a | ||
| Acquisition | g/ha | kg/ha | ||||||||
| CK | 252.5b | 195.0c | 100.0c | 33.7c | 26.5b | 32.1c | 3.0c | 11.0b | ||
| ZnO | 360.8a | 243.2b | 136.7a | 41.3b | 31.0ab | 34.7ab | 3.3b | 12.8a | ||
| Zn | 383.5a | 254.9a | 126.8b | 47.3a | 32.5a | 36.9a | 3.8a | 13.0a | ||
| Treatment |
PA (g/kg) |
Phytate-P (g/kg) |
Phytate-P/P |
PA/Zn |
PA × Ca/Zn |
PA/Fe |
PA × Ca/Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-P2O5-K2O (15-15-15) | 8.1a 1 | 2.3a | 0.74a | 40.2ab | 327.1ab | 26.0c | 212.5b |
| 15-15-15+Micronutrient | 8.1a | 2.3a | 0.75a | 34.3b | 290.3b | 26.6bc | 225.9ab |
| 17-17-17 | 8.9a | 2.5a | 0.82a | 46.5a | 394.7a | 30.1abc | 257.5ab |
| 26-10-15 | 8.8a | 2.5a | 0.82a | 38.4ab | 307.6b | 33.4a | 268.6a |
| 30-10-11 | 8.8a | 2.5a | 0.79a | 33.5b | 278.5b | 31.0ab | 259.2ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





