Submitted:
09 August 2024
Posted:
12 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. UN Sustainable Development Goals and Sustainable Value Creation at Micro- and Macro-Levels within the Earth System Boundaries
3. Enzyme Catalysis for Sustainable Value Creation Using Renewable Biobased Resources
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Future Directions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aouizerat, T.; Gutman, I.; Paz, Y.; Maeir, A.M.; Gadot, Y.; Gelman, D.; Szitenberg, A.; Drori, E.; Pinkus, A.; Schoemann, M.; Kaplan, R.; Ben-Gedalya, T.; Coppenhagen- Glazer, S.; Reich, E.; Saragovi, A.S.; Lipschits, O.; Klutstein, M.; Hazan, R. Isolation and characterization of live yeast cells from ancient vessels as a tool in bio-archaeology. mBio 2019, 10, e00388-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salque, M.; Bogucki, P.I.; Pyzel, J.; Sobkowiak-Tabaka, I.; Grygiel, R.; Szmyt, M.; Evershed, R.P. Earliest evidence for cheese making in the sixth millennium BC in northern Europe. Nature 2013, 493, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGovern, P.; Jalabadze, M.; Batiuk, S.; Michael P Callahan, M.P.; Smith, K.E.; Hall, G.R.; Kvavadze, E.; Maghradze, D.; Rusishvili, N.; Bouby, L.; Failla, O.; Cola, G.; Mariani, L.; Boaretto, E.; Bacilieri, R.; This, P.; Wales, N.; Lordkipanidze; D. Early Neolithic wine of Georgia in the South Caucasus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114(48), E10309–E10318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühne, W. Über das Verhalten verschiedener organisirter und sog. ungeformter Fermente. Verhandlungen des Naturhistorisch-medicinischen Vereins zu Heidelberg. Neue Folge 1877, 1, 190–193. [Google Scholar]
- Teich, M. Ferment or Enzyme: What's in a name? History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences, 1981, 3, 193–215. [Google Scholar]
- Buchner, E. Alkoholische Gährung ohne Hefezellen. Ber. Dt. Chem: Ges. 1897, 30, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenicke, L. Centenary of the Award of a Nobel Prize to Eduard Buchner, the Father of Biochemistry in a Test Tube and Thus of Experimental Molecular Bioscience. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 6776–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumner, J.B. The isolation and crystallization of the enzyme urease: preliminary paper. J. Biol. Chem. 1926, 69, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrop, J.H. Crystalline pepsin: I. Isolation and tests of purity. J. Gen. Physiol. 1930, 13, 739–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, A.G.; Tipton, K.F. Enzyme nomenclature and classification: the state of the art. FEBS J 2023, 290, 2214–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmeyer, H.U. (Ed.) , Methods of enzymatic analysis. 2012, Elsevier.
- Saiki, R.K.; Gelfand, D.H.; Stoffel, S.; Scharf, S.J.; Higuchi, R.; Horn, G.T.; Mullis, K.B.; Erlich, H.A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 1988, 239, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, K.; Fessner, W.D.; Turner, N.J. (Eds.) , Science of Synthesis: Biocatalysis in Organic Synthesis. 2015, Vol. 1–3; Thieme, Stuttgart, Germany.
- Wohlgemuth, R. Asymmetric biocatalysis with microbial enzymes and cells. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2010, 13, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Snajdrova, R.; Moore, J.C.; Baldenius, K.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Biocatalysis: enzymatic synthesis for industrial applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 88–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara, A.R.; Domínguez de María, P.; Littlechild, J.A.; Schürmann, M.; Sheldon, R.A.; Wohlgemuth, R. Biocatalysis as Key to Sustainable Industrial Chemistry. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202102709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liese, A.; Seelbach, K.; Wandrey, C. (Eds.) , Industrial biotransformations. Second, completely revised and extended edition, 2009, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany.
- Ghisalba, O. , Meyer, H.P. and Wohlgemuth, R. Industrial biotransformation. In: Encyclopedia of industrial biotechnology: bioprocess, bioseparation, and cell technology, 2009, 1-34. [CrossRef]
- Arbige, M.V.; Shetty, J.K.; Chotani, G.K. Industrial enzymology: the next chapter. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.P.; Eichhorn, E.; Hanlon, S.; Lütz, S.; Schürmann, M.; Wohlgemuth, R.; Coppolecchia, R. The use of enzymes in organic synthesis and the life sciences: perspectives from the Swiss Industrial Biocatalysis Consortium (SIBC). Cat. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, F.H. Innovation by evolution: bringing new chemistry to life (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14420–14426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reetz, M.T. Witnessing the birth of directed evolution of stereoselective enzymes as catalysts in organic chemistry. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 3326–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornscheuer, U.T. The fourth wave of biocatalysis is approaching. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2017, 376, 20170063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeymer, C.; Hilvert, D. Directed evolution of protein catalysts. Ann. Rev: Biochem: 2018, 87, 131–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; May, O. Industrial Enzyme Applications. 2019, ISBN:9783527343850, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany.
- Adams, J.P.; Brown, M.J.; Diaz-Rodriguez, A.; Lloyd, R.C.; Roiban, G.D. Biocatalysis: A pharma perspective. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 2421–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.S. , Ruscoe, R.E. and Turner, N.J., 2022. The beauty of biocatalysis: sustainable synthesis of ingredients in cosmetics. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 335–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, K.; Meyer, H.P.; Wohlgemuth, R.; Buller, R. Biocatalysis in the Swiss manufacturing environment. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, P.N.; Howard, R.M.; Kumar, R.; Thompson, M.P.; Truppo, M.D.; Turner, N.J. Extending the application of biocatalysis to meet the challenges of drug development. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioni, P.; Gabellieri, E.; Campanini, B.; Bettati, S.; Raboni, S. Use of Exogenous Enzymes in Human Therapy: Approved Drugs and Potential Applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 411–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. The E factor at 30: a passion for pollution prevention. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 1704–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhacham, E.; Ben-Uri, L.; Grozovski, J.; Bar-On, Y.M.; Milo, R. Global human-made mass exceeds all living biomass. Nature 2020, 588, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutzen, P.J. Geology of Mankind. Nature 2002, 415(6867), 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, W.; Grinevald, J.; Crutzen, P.; McNeill, J. The Anthropocene: conceptual and historical perspectives. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A. 2011, 369, 842–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.L.; Maslin, M.A. Defining the Anthropocene. Nature 2015, 519, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, C.W.; Zalasiewicz, J.; Summerhayes, C.; Barnosky, A.D.; Poirier, C.; Gałuszka, A.; Cearreta, A.; Edgeworth, M.; Ellis, E.C.; Ellis, M.; Jeandel, C.; Leinfelder, R.; McNeill, J.R.; deB Richter, D.; Steffen, W.; Syvitski, J.; Vidas, D.; Wagreich, M.; Williams, M.; Zhisheng, A.; Grinevald, J.; Odada, E.; Oreskes, N.; Wolfe, A.P. The Anthropocene is functionally and stratigraphically distinct from the Holocene. Science 2016, 351, aad2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, C.N.; Turner, S.D.; Zalasiewicz, J.; Head, M.J. Candidate sites and other reference sections for the Global boundary Stratotype Section and Point of the Anthropocene series. The Anthropocene Review 2023, 10, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; Richardson, K.; Rockström, J.; Cornell, S.E.; Fetzer, I.; Bennett, E.M.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.R.; De Vries, W.; De Wit, C.A.; Folke, C. Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 2015, 347, 1259855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, K. , Steffen, W., Lucht, W., Bendtsen, J., Cornell, S.E., Donges, J.F., Drüke, M., Fetzer, I., Bala, G., von Bloh, W. and Feulner, G., Fiedler, S.; Gerten, D.; Gleeson, T.; Hofmann, M.; Huiskanmp, W.; Kummu, M.; Mohan, C.; Nogués-Bravo, D.; Petri, S.; Porkka, M.; Rahmstorf, S.; Schaphoff, S.; Thonicke, K.; Tobian, A.; Virkki, V.; Wang-Erlandsson, L.; Weber, L.; Rockström, J. Earth beyond six of nine planetary boundaries. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh2458. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayor, M. Nobel Lecture: Plurality of worlds in the cosmos: A dream of antiquity, a modern reality of astrophysics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2020, 92, 030502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Pathways to Discovery in Astronomy and Astrophysics for the 2020s. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. 2023. [CrossRef]
- United Nations General Assembly Seventieth session, Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015, A/RES/70/1, 1-35. https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda.
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Global Sustainable Development Report 2023, Advance, Unedited Version. https://sdgs.un.org/gsdr/gsdr2023.
- United Nations Environment Programme, Global Chemicals Outlook II - From Legacies to Innovative Solutions: Implementing the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2019. ISBN No: 978-92-807-3745-5.
- Roubini, N. Megathreats - Ten Dangerous Trends That Imperil Our Future, And How to Survive Them. Little, Brown and Company, New York, USA, 2022. ISBN 9780316284059.
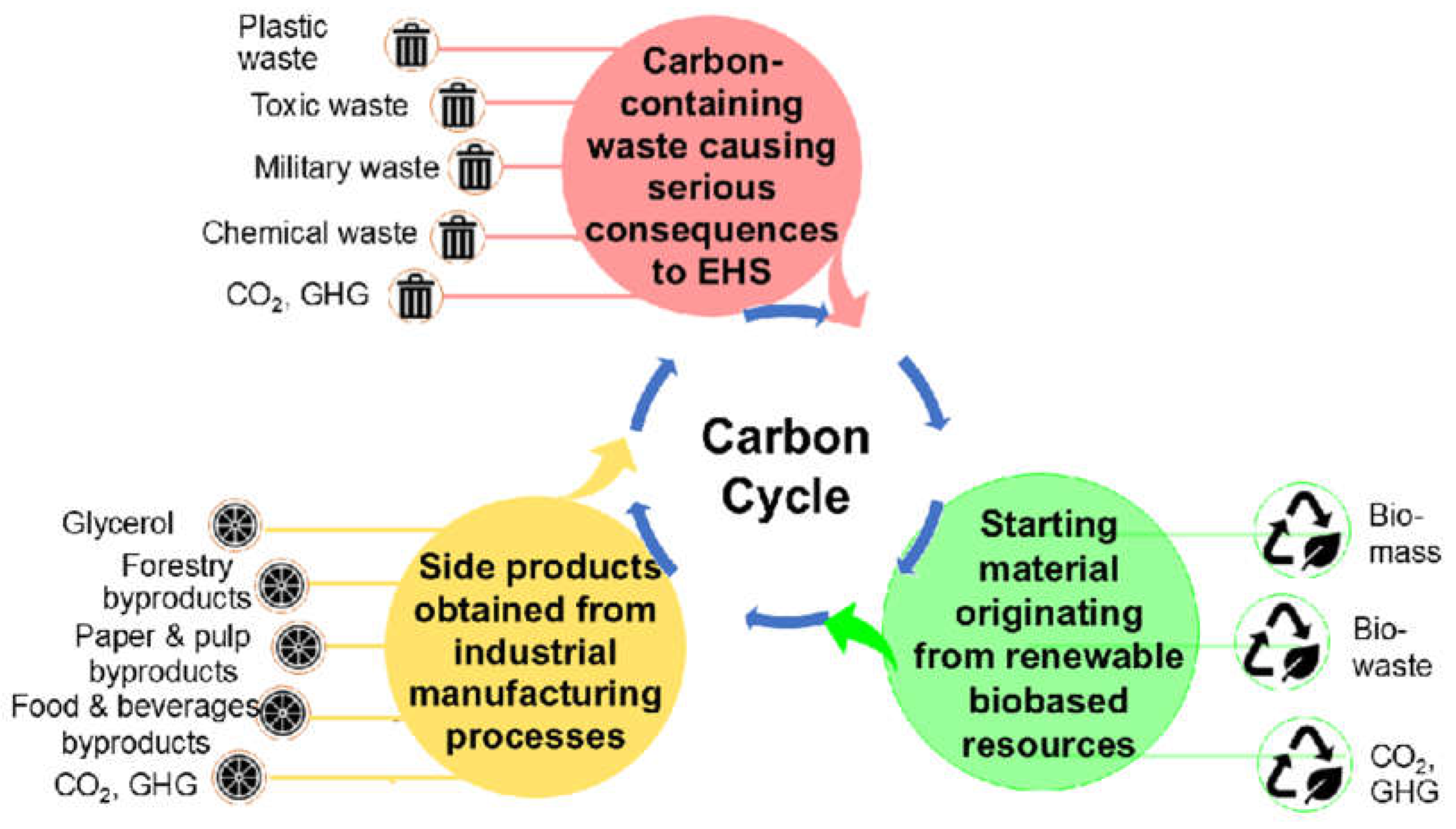
- Shaw, W.J.; Kidder, M.K.; Bare, S.R.; Delferro, M.; Morris, J.R.; Toma, F.M.; Senanayake, S.D.; Autrey, T.; Biddinger, E.J.; Boettcher, S.; Bowden, M.E.; Britt, P.B.; Brown, R.C.; Bullock, R.M.; Chen, J.G.; Daniel, C.; Dorhout, P.K.; Efroymson, R.A.; Kelly, J. Gaffney, K.J.; Gagliardi, L.; Harper, A.S.; Heldebrant, D.J.; Luca, O.R.; Lyubovsky, M.; Male, J.L.; Miller, D.J.; Prozorov, T.; Rallo, R.; Rana, R.; Rioux, R.M.; Sadow, A.D.; Schaidle, J.A.; Schulte, L.A.; Tarpeh, W.A.; Vlachos, D.G.; Vogt, B.D:, Weber, R.S.; Yang, J.Y.; Arenholz, E.; Helms, B.A.; Huang, W.; Jordahl, J.L.; Karakaya, C.; Kian, K.; Kothandaraman, K.; Lercher, J.; Liu, P.; Malhotra, D.; Mueller, K.T.; O’Brien, C.P.; Palomino, R.M.; Qi, L.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Rousseau, R.; Russell, J.C.; Sarazen, M.L.; Sholl, D.S.; Smith, E.A.; Stevens, M.B.; Surendranath, Y.; Tassone, C.T.; Tran, B.; Tumas; W.; Walton; K.S., A US perspective on closing the carbon cycle to defossilize difficult-to-electrify segments of our economy. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2024, 8, 376–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanza, R.; dArge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; Oneill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; Raskin, R.G.; Sutton, P.; van den Belt, M. , The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387(6630), 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; de Groot, R.; Braat, L.; Kubiszewski, I.; Fioramonti, L.; Sutton, P.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M. Twenty years of ecosystem services: How far have we come and how far do we still need to go? Ecosystem Services 2017, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Fenchel, T.; Delong, E.F. The microbial engines that drive Earth's biogeochemical cycles. Science 2008, 320, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnier, P.; Resplandy, L.; Najjar, R.G.; Ciais, P. The land-to-ocean loops of the global carbon cycle. Nature 2022, 603, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, X.; He, Y.; Shen, S.; Hou, Z.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Yao, L.; Huang, J. The oxygen cycle and a habitable Earth. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, C.T.; Planavsky, N.J.; Gill, B.C.; Ozaki, K.; Robbins, L.J.; Lyons, T.W.; Fischer, W.W.; Wang, C.; Cole, D.B.; Konhauser, K.O. Evolution of the global phosphorus cycle. Nature 2017, 541, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ward, B.B.; Sigman, D.M. Global nitrogen cycle: critical enzymes, organisms, and processes for nitrogen budgets and dynamics. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 5308–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievert, S.M.; Kiene, R.P.; Schulz-Vogt, H.N. The sulfur cycle. Oceanography 2007, 20, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.J.P.; Rickaby, R.E.M. Evolution's Destiny: Co-evolving Chemistry of the Environment and Life. 2012, Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, UK.
- Haraguchi, H. Metallomics as integrated biometal science. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2004, 19, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maret, W. The quintessence of metallomics: a harbinger of a different life science based on the periodic table of the bioelements. Metallomics 2022, 14, mfac051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlgemuth, R. Bio-based resources, bioprocesses and bioproducts in value creation architectures for bioeconomy markets and beyond – What really matters, Bioeconomy Journal, 2021, 1, 100009. 1. [CrossRef]
- Winkler, C.K.; Schrittwieser, J.H.; Kroutil, W. Power of biocatalysis for organic synthesis. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wender, P.A.; Miller, B.L. Synthesis at the molecular frontier. Nature 2009, 460, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrittwieser, J.H.; Velikogne, S.; Hall, M.; Kroutil, W. Artificial biocatalytic linear cascades for preparation of organic molecules. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 270–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
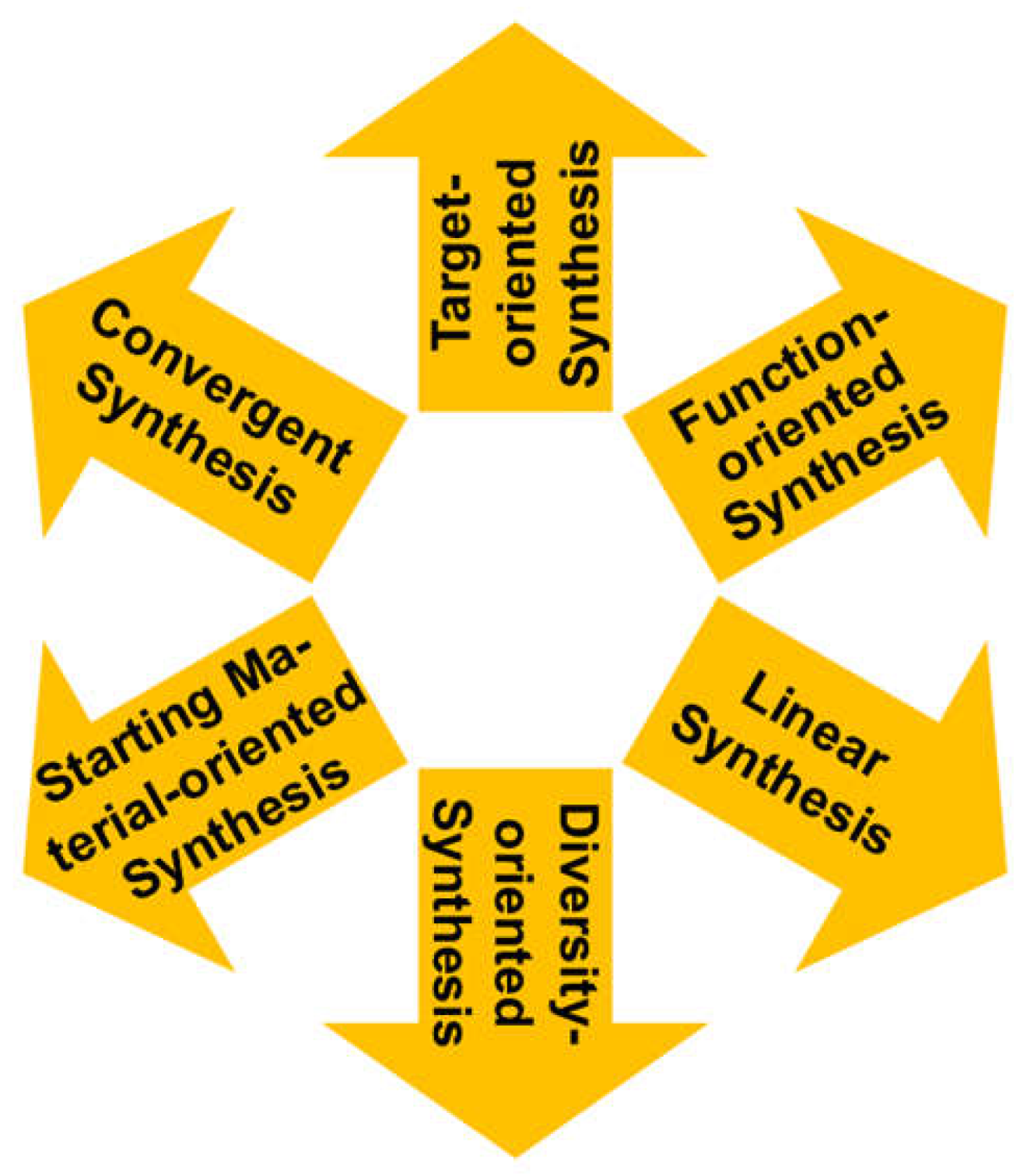
- Zetzsche, L.E.; Chakrabarty, S.; Narayan, A.R. The transformative power of biocatalysis in convergent synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 5214–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerry, C.J.; Schreiber, S.L. Recent achievements and current trajectories of diversity-oriented synthesis. Curr. Opin. Chem: Biol. 2020, 56, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlgemuth, R. Selective biocatalytic defunctionalization of raw materials. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202200402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reetz, M.T.; Qu, G.; Sun, Z. Engineered enzymes for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and other high-value products. Nat. Synth 2024, 3, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hönig, M.; Sondermann, P.; Turner, N.J.; Carreira, E.M. Enantioselective Chemo- and Biocatalysis: Partners in Retrosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 8942–8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, R.O.M.A.; Miranda, L.S.M.; Bornscheuer, U.T. A Retrosynthesis Approach for Biocatalysis in Organic Synthesis. Chem. - Eur. J. 2017, 23, 12040–12063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlgemuth, R. Route selection and reaction engineering for sustainable metabolite synthesis. React. Chem. Eng. 2023, 8, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, S.; Zukić, E.; Schmermund, L.; Faber, K.; Winkler, C.K.; Kroutil, W. Shortening synthetic routes to small molecule active pharmaceutical ingredients employing biocatalytic methods. Chem. Rev. 2021, 122, 1052–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlgemuth, R. Biocatalysis–Key enabling tools from biocatalytic one-step and multi-step reactions to biocatalytic total syn- thesis. New Biotechnol. 2021, 60, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissman, E.N.; Sosa, M.B.; Millar, D.C.; Koleski, E.J.; Thevasundaram, K.; Chang, M.C.Y. Expanding chemistry through in vitro and in vivo biocatalysis. Nature 2024, 631, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibodeaux, C.J.; Melançon, C.E.; Liu, H.-w. Unusual sugar biosynthesis and natural product glycodiversification. Nature 2007, 446, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlodek, A.; Steve, G. Kendrew, S.G.; Coates, N.J.; Hold, A.; Pogwizd, J.; Rudder, S.; Sheehan, L.S.; Higginbotham, S.J.; Stanley-Smith, A.E.; Warneck, T.; Nur-E-Alam, M.; Radzom, M.; Martin, C.J.; Overvoorde, L.; Samborskyy, M.; Alt, S.; Heine, D.; Carter, G.T.; Graziani, E.I.; Koehn, F.E.; McDonald, L.; Alanine, A.; Rodríguez Sarmiento, R.M.; Keen Chao, S.; Ratni, H.; Steward, L.; Norville, I.H.; Sarkar-Tyson, M.; Moss, S.J.; Leadlay, P.F.; Wilkinson, B.; Gregory, M.A. Diversity oriented biosynthesis via accelerated evolution of modular gene clusters. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, B.J.; Knight, A.M.; Hofstra, J.L.; Reisman, S.E.; Kan, S.B.J.; Arnold, F.H. Diversity-Oriented Enzymatic Synthesis of Cyclopropane Building Blocks. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 7112–7116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, T.J.; Zarzycki, J. A short history of RubisCO: the rise and fall (?) of Nature's predominant CO2 fixing enzyme. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Diehl, C.; He, H.; Bae, Y.; Klose, M.; Claus, P.; Socorro Cortina, N.; Alvarez Fernandez, C.; Schulz-Mirbach, H.; McLean, R.; Ramírez Rojas, A.A.; Schindler, D.; Paczia, N.; Erb, T.J. Construction and modular implementation of the THETA cycle for synthetic CO2 fixation. Nat Catal 2023, 6, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-R.; Xia, P.-F. Carbon recycling with synthetic CO2 fixation pathways. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2024, 85, 103023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, R.; Schwander, T.; Diehl, C.; Cortina, N.S.; Paczia, N.; Zarzycki, J.; Erb, T.J. Exploring alternative pathways for the in vitro establishment of the HOPAC cycle for synthetic CO2 fixation. Science Adv. 2023, 9, eadh4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffen, M.; Marchal, D.G.; Beneyton, T.; Schuller, S.K.; Klose, M.; Diehl, C.; Lehmann, J.; Pfister, P.; Carrillo, M.; He , H.; Aslan, S.; Cortina, N.S.; Claus, P.; Bollschweiler, D.; Baret, J.C.; Schuller, J.M; Zarzycki, J.; Arren Bar-Even , A.; Erb, T.J. A new-to-nature carboxylation module to improve natural and synthetic CO2 fixation. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwander, T.; Schada von Borzyskowski, L.; Burgener, S.; Cortina, N.S.; Erb, T.J. A synthetic pathway for the fixation of carbon dioxide in vitro. Science 2016, 354, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, C.; Gerlinger, P.D.; Paczia, N.; Erb, T.J. Synthetic anaplerotic modules for the direct synthesis of complex molecules from CO2. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.; Sun, H.; Qiao, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Z.; Wei, X.; Yang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, W.; Yan, X.; Chu, H.; Wang, Q.; You, C.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Y. Cell-free chemoenzymatic starch synthesis from carbon dioxide. Science 2021, 373, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, F.; van der Marel, E.R.; Kerr, R.W.F.; McElroy, C.; Schroeder, N.; Mitchell, C.; Rosetto, G.; Chen, T.T.D.; Bailey, R.M.; Hepburn, C.; Redgwell, C.; Williams, C.K. Designing a circular carbon and plastics economy for a sustainable future. Nature 2024, 626, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tournier, V.; Duquesne, S.; Guillamot, F.; Cramail, H.; Taton, D.; Marty, A.; André, I. Enzymes’ power for plastics degradation. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 5612–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, V.; Topham, C.M.; Gilles, A.; David, B.; Folgoas, C.; Moya-Leclair, E.; Kamionka, E.; Desrousseaux, M.-L.; Texier, H.; Gavalda, S.; Cot, M.; Guémard, E.; Dalibey, M.; Nomme, J.; Cioci, G.; Barbe, S.; Chateau, M.; André, I.; Duquesne, S.; Marty, A. Enzymes’ Power for Plastics Degradation. Nature 2020, 580, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.L.; Rosetto, G.; Ingraham, M.A.; Ramirez, K.J.; Lincoln, C.; Clarke, R.W.; Gado, J.E.; Lilly, J.L.; Kucharzyk, K.H.; Erickson, E.; Beckham, G.T. Natural diversity screening, assay development, and characterization of nylon-6 enzymatic depolymerization. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, T.; Palm, G.J.; Berndt, L.; Meinert, H.; Branson, Y.; Schmidt, L.; Cziegler, C.; Somvilla, I.; Zurr, C.; Graf, L.G.; Janke, U.; Badenhorst, C.P.S.; König, S.; Delcea, M.; Garscha, U.; Wei, R.; Lammers, M.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Structural Elucidation of a Metagenomic Urethanase and Its Engineering Towards Enhanced Hydrolysis Profiles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, e202404492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, P.J.M.; da Silva, R.M.; Neto, C.A.C.G.; Gomes e Silva, N.C.; Souza, J.E.D.S.; Nunes, Y.L.; Sousa dos Santos, J.C. An overview on the conversion of glycerol to value-added industrial products via chemical and biochemical routes. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 2794–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yan, J.; Sun, J.; Xu, P.; Ma, C.; Gao, C. Production of value-added chemicals from glycerol using in vitro enzymatic cascades. Commun. Chem. 2018, 1, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moklis, M.H.; Cheng, S.; Cross, J.S. Current and future trends for crude glycerol upgrading to high value-added products. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guajardo, N.; Bernal, C.; Wilson, L.; Cabrera, Z. Selectivity of R-α-monobenzoate glycerol synthesis catalyzed by Candida antarctica lipase B immobilized on heterofunctional supports. Proc. Biochem. 2015, 50, 1870–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, N.; Neumann, M.; Liese, A.; Wohlgemuth, R.; Eggert, T.; Hummel, W. Characterisation of a Recombinant NADP-Dependent Glycerol Dehydrogenase from Gluconobacter oxydans and its Application in the Production of L-Glyceraldehyde. ChemBioChem 2009, 10, 1888–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, N.; Neumann, M.; Liese, A.; Wohlgemuth, R.; Weckbecker, A.; Eggert, T.; Hummel, W. Characterization of a whole-cell catalyst co-expressing glycerol dehydrogenase and glucose dehydrogenase and its application in the synthesis of L-glyceraldehyde. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2010, 106, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habe, H.; Shimada, Y.; Yakushi, T.; Hattori, H.; Ano, Y.; Fukuoka, T.; Kitamoto, D.; Itagaki, M.; Watanabe, K.; Yanagishita, H.; Matsushita, K.; Sakaki, K. Microbial Production of Glyceric Acid, an Organic Acid That Can Be Mass Produced from Glycerol. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7760–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, Q.; Fan, F.; Tang, J.; Zhan, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Directed evolution of alditol oxidase for the production of optically pure D-glycerate from glycerol in the engineered Escherichia coli. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. [CrossRef]
- Rios-Mercadillo, V.M.; Whitesides, G.M. Enzymic synthesis of sn-glycerol 3-phosphate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979, 101, 5828–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragauskas, A. J.; Williams, C.K.; Davison, B.H.; Britovsek, G.; Cairney, J.; Eckert, C.A.; Frederick Jr., W. J.; Hallett, J.P.; Leak, D.J.; Liotta, C.L.; Mielenz, J.R.; Murphy, R.; Templer, R.; Tschaplinski, T. The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science 2006, 311, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R. A. Biocatalysis and biomass conversion: enabling a circular economy. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A. 2020, 378, 20190274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, B.; Plassmeier, J.; Blankschien, M.; Letzel, A.C.; Kourtz, L.; Schröder, H.; Koch, W.; Zelder, O. Unlocking Nature's Biosynthetic Power—Metabolic Engineering for the Fermentative Production of Chemicals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 2258–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, T.; Grüssner, A.; Oppenauer, R. Synthesis of d-and l-ascorbic acid (vitamin C). Nature 1933, 132, 280–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, T.; Grüssner, A. Eine ergiebige Synthese der L-ascorbinsäure (C-vitamin). Helv. Chim. Acta 1934, 17, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappenberger, G.; Hohmann, H.P. Industrial production of L-ascorbic acid. In Biotechnology of Food and Feed Additives; Zorn, H., Czermak, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014; pp. 143–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Jin, Z; Zhang, D. Microbial cell factories for green production of vitamins. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 661562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.I. Discovering nature's diverse pathways to vitamin B12: a 35-year odyssey. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 2529–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Q.; Fang, H.; Xiang, M.; Xiao, K.; Jiang, P.; You, C.; Lee, S.Y.; Zhang, D. A synthetic cell-free 36-enzyme reaction system for vitamin B12 production. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, J.-H.; Barg, H.; Warren, M.J.; Jahn, D. Microbial production of vitamin B12. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 58, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jani, P.; Emmert, J.; Wohlgemuth, R. Process analysis of macrotetrolide biosynthesis during fermentation by means of direct infusion LC-MS. Biotechnol. J. 2008, 3, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smanski, M.; Zhou, H.; Claesen, J.; Shen, B.; Fischbach, M.A.; Voigt, C.A. Synthetic biology to access and expand nature's chemical diversity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, J.; Keasling, J.D. Engineering cellular metabolism. Cell 2016, 164, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.U.; Chae, T.U.; Cho, J.S.; Kim, J.W.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, D.I.; Ko, Y.-S.; Jang, W.D.; Jang, Y.-S. A comprehensive metabolic map for production of bio-based chemicals. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clomburg, J.M.; Crumbley, A.M.; Gonzalez, R. Industrial biomanufacturing: the future of chemical production. Science 2017, 355, aag0804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.; Pham, H.L.; Ranjan, B.; Saini, M.; Liang, Y.; Hossain, G.S.; Ling, H.; Foo; J. L.; Chang, M.W. Microbial engineering strategies to utilize waste feedstock for sustainable bioproduction. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, 2, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.J.; Trinh, L.T.P.; Song, Y.; Lee, Y.G.; Bae, H.-J. Bioconversion of biomass waste into high value chemicals. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlgemuth, R.; Littlechild, J. Complexity reduction and opportunities in the design, integration and intensification of biocata-lytic processes for metabolite synthesis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 958606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, H.; Ang, E.L.; Zhao, H. 2018. Biocatalysis for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and pharmaceutical intermediates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.D.; France, S.P.; Martinez, C.A. Emerging technologies for biocatalysis in the pharmaceutical industry. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 5571–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, K.; Dheeraj, S.; Jeevani, K.; Saravanan, T. Evaluating Multienzyme Cascade Routes for Pharmaceutically Relevant Mole-cules. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 27, e202301236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etit, D.; Meramo, S.; Ögmundarson, Ó.; Jensen, M.K.; Sukumara, S. Can biotechnology lead the way toward a sustainable pharmaceutical industry? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2024, 87, 103100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegman, M.A.; Janssen, M.H.A.; van Rantwijk, F.; Sheldon, R.A. Towards Biocatalytic Synthesis of β-Lactam Antibiotics. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2001, 343, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
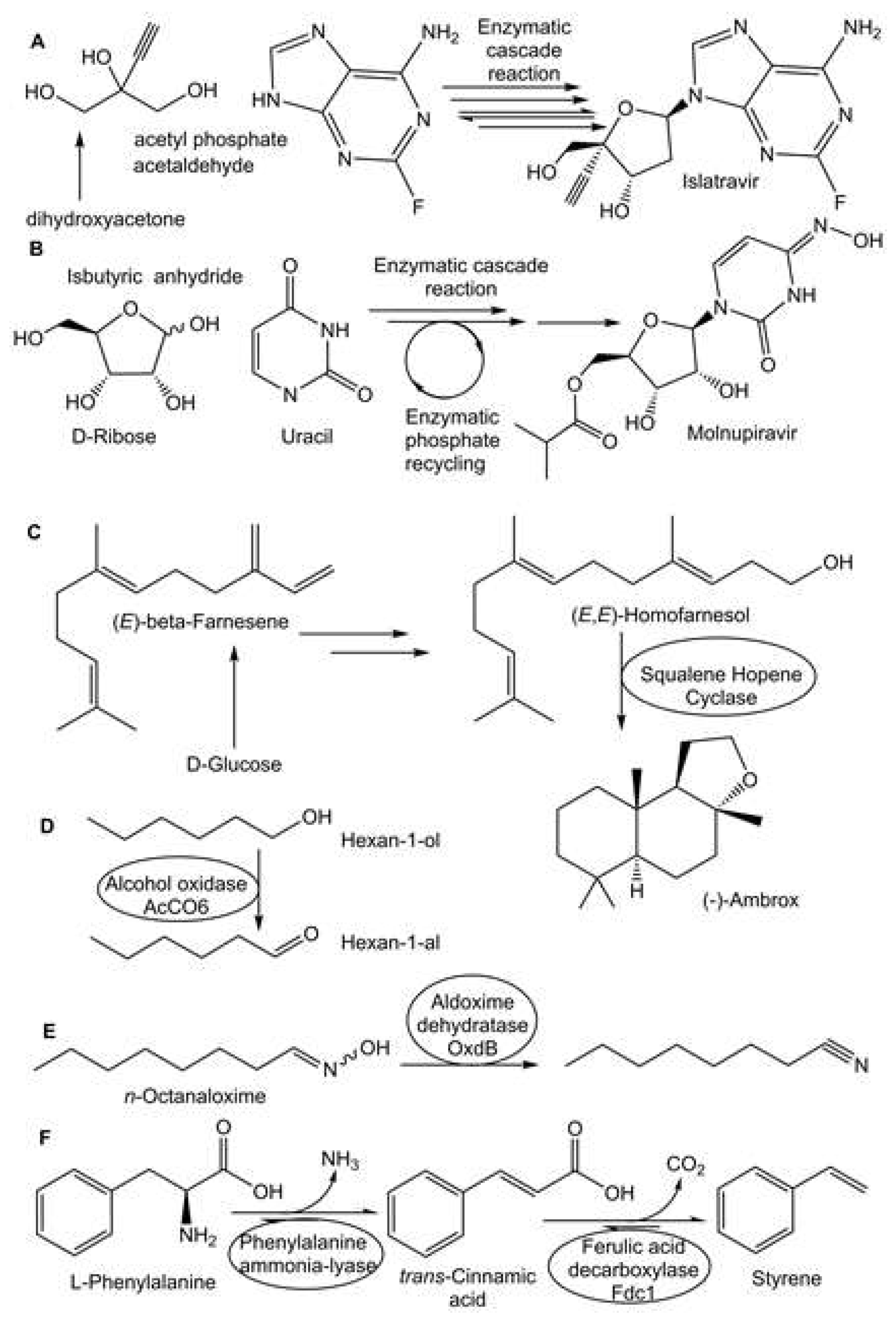
- Huffman, M.A.; Fryszkowska, A.; Alvizo, O.; Borra-Garske, M.; Campos, K.R.; Canada, K.A.; Devine, P.N.; Duan, D.; Forstater, J.H.; Grosser, S.T.; Halsey, H.M.; Hughes, G.J.; Jo, J.; Joyce, L.A.; Kolev, J.N.; Liang, J.; Maloney, K.M.; Mann, B.F.; Marshall, N.M.; McLaughlin, M.; Moore, J.C.; Murphy, G.S.; Nawrat, C.C.; Nazor, J.; Novick, S.; Patel, N.R.; Rodriguez-Granillo, A.; Robaire, S.A.; Sherer, E.C.; Truppo, M.D.; Whittaker, A. M:, Verma, D.; Li Xiao, l:, Xu, Y.; Yang, H. Design of an in vitro biocatalytic cascade for the manufacture of islatravir. Science 2019, 366, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummelt, S.M.; Qi, J.; Chen, Y.; Dropinski, J.F.; Hughes, G.; Kuethe, J.T.; Li, D.; Maloney, K.M.; Margelefsky, E.; Mathew, R.; Muzzio, D.J.; Nawrat, C.C.; Newman, J.A.; Ouyang, H.; Patel, N.R.; Qiao, Z.; Shang, G.; Sirota, E.; Song, Z.J.; Tan, L.; Varsolona, R.L.; Wan, B.; Wyvratt, B.M.; Xu, F.; Xu, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, R. 2021. Development of an Efficient Route to 2-Ethynylglycerol for the Synthesis of Islatravir. ChemRxiv. [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.H.; Fryszkowska, A.; Alvizo, O.; Attadgie, I.; Borra-Garske, M.; Devine, P.N.; Duan, D.; Grosser, S.T.; Forstater, J.H.; Hughes, G.J.; Maloney, K.M.; Margelefsky, E.; Mattern, K.A.; Miller, M.T.; Nawrat, C.C.; Nazor, J.; Orth, P.; Ouimet, C. M:, Robaire, S.A.; Ruccolo, S.; Schwalm, E.L.; Verma, D.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, V. Development of a Biocatalytic Aerobic Oxidation for the Manufacturing Route to Islatravir. ChemRxiv. 2023. [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, J.A.; Benkovics, T.; Silverman, S.M.; Huffman, M.A.; Kong, J.; Maligres, P.E.; Itoh, T.; Yang, H.; Verma, D.; Pan, W.; Ho, H.I.; Vroom, J.; Knight, A.M.; Hurtak, J.A.; Klapars, A.; Fryszkowska, A.; Morris, W.J.; Strotman, N.A.; Murphy, G.S.; Maloney, K.M.; Fier, P.S. Engineered ribosyl-1-kinase enables concise synthesis of molnupiravir, an antiviral for COVID-19. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1980–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avci, F.Y.; DeAngelis, P.L.; Liu, J.; Linhardt, R.J. Enzymatic Synthesis of Glycosaminoglycans: Improving on Nature. Frontiers in Modern Carbohydrate Chemistry, 2007, 15, 253–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Lin, X.J.; Xu, H.; Sohail, M.; Chen, L.A.; Zhang, X. Enzyme-mediated green synthesis of glycosaminoglycans and catalytic process intensification. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, J.; Elling, L. Current state on the enzymatic synthesis of glycosaminoglycans. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 61, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, J.; Aßmann, M.; Kuballa, J.; Elling, L. Repetitive Synthesis of High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid with Immobilized Enzyme Cascades. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202101071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, C.; Illanes, A.; Guerrero, C. Enzymatic production of prebiotic oligosaccharides. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 37, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castejón, N.; Señoráns, F.J. Enzymatic modification to produce health-promoting lipids from fish oil, algae and other new omega-3 sources: A review. New Biotechnol. 2020, 57, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Z.; Wu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Tchuere, J.G.; Zhao, D.; Fang, Y. Essential roles of ellagic acid-to-urolithin converting bacteria in human health and health food industry: An updated review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 151, 104622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, E.; Locher, E.; Guillemer, S.; Wahler, D.; Fourage, L.; Schilling, B. Biocatalytic process for (−)-ambrox production using squalene hopene cyclase. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2018, 360, 2339–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorn, E.; Schroeder, F. From Ambergris to (−)-Ambrox: Chemistry meets biocatalysis for sustainable (−)-Ambrox production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 5042–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.S.; Birmingham, W.R.; Thompson, M.P.; Taglieber, A.; Daviet, L.; Turner, N.J. An engineered alcohol oxidase for the oxidation of primary alcohols. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M. Enzymatic strategies for asymmetric synthesis. RSC Chemical Biology, 2021, 2, 958–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlgemuth, R. Industrial asymmetric biocatalysis. In Biocatalysis in Asymmetric Synthesis, Editors: De Gonzalo, G.; Alcántara, A.R., Academic Press/Elsevier, 2024, 13, 431–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowbotham, J.S.; Ramirez, M.A.; Lenz, O.; Reeve, H.A.; Vincent, K.A. Bringing biocatalytic deuteration into the toolbox of asymmetric isotopic labelling techniques. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugford, P.F.; Wagner, U.G.; Jiang, Y.; Faber, K.; Kazlauskas, R.J. Enantiocomplementary enzymes: Classification, molecular basis for their enantiopreference, and prospects for mirror-image biotransformations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8782–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messiha, H.L.; Scrutton, N.S.; Leys, D. High-Titer Bio-Styrene Production Afforded by Whole-Cell Cascade Biotransformation. ChemCatChem 2023, 15, e202201102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinzmann, A.; Stricker, M.; Gröger, H. Chemoenzymatic Cascades toward Aliphatic Nitriles Starting from Biorenewable Feedstocks. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 46, 17088–17096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinzmann, A. , Glinski, S., Worm, M. and Gröger, H. Enzymatic synthesis of aliphatic nitriles at a substrate loading of up to 1.4 kg/L: a biocatalytic record achieved with a heme protein. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 4867–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straathof, A.J.J. Transformation of Biomass into Commodity Chemicals Using Enzymes or Cells. Chem.Rev. 2014, 114, 1871–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, J.D.; Schmidt-Traub, G.; Mazzucato, M.; Messner, D.; Nakicenovic, N.; Rockström. J. Six Transformations to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Shi, S.; Ji, Y.; Wang, K.; Tan, T.; Nielsen, J. Opportunities of CO2-based biorefineries for production of fuels and chemicals. Green Carbon 2023, 1, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, F.E. , Nogle, R., Abdalla, T.; Rasor, B.J.; Canter, C.; Jensen, R.O.; Wang, L.; Strutz, J.; Chirania, P.; De Tissera, S.; Mueller, A.P.; Ruan, Z.; Gao, A.; Tran, L.; Engle, N.L.; Bromley, J.C.; Daniell, J.; Conrado, R.; Tschaplinski, T.J.; Giannone, R.J.; Hettich, R.L.; Karim, A.S.; Simpson, S.D.; Brown, S.D.; Leang, C.; Jewett, M.C.; Köpke, M. Carbon-negative production of acetone and isopropanol by gas fermentation at industrial pilot scale. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardossi, L.; Poulsen, P.B.; Ballesteros, A.; Hult, K.; Švedas, V.K.; Vasić-Rački, Đ.; Carrea, G.; Magnusson, A.; Schmid, A.; Wohlgemuth, R.; Halling, P.J. Guidelines for reporting of biocatalytic reactions. Trends Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swainston, N.; Baici, A.; Bakker, B.M.; Cornish-Bowden, A.; Fitzpatrick, P.F.; Halling, P.; Leyh, T.S.; O’Donovan, C.; Raushel, F.M.; Reschel, U.; Rohwer, J.M. STRENDA DB: enabling the validation and sharing of enzyme kinetics data. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 2193–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, A.; Twardowski, T.; Wohlgemuth, R. Bioeconomy for sustainable development. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 14, 1800638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlgemuth, R.; Twardowski, T.; Aguilar, A. Bioeconomy moving forward step by step–A global journey. New Biotechnol. 2021, 61, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




