Submitted:
10 August 2024
Posted:
12 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
- Those who could not continuously consume research foods because of business trips during the intake period (those who knew in advance that their eating rate would be <80%);
- Those who were judged to be inappropriate based on the answers to the lifestyle-related questionnaire and measurements of visceral fat area and abdominal circumference;
- Those who had abnormal laboratory test values or cardiopulmonary function and were judged to have problems participating in the study;
- Those with food allergies;
- Those who would face difficulty in treatment (including dietary guidance) by participating in the trial;
- Those who used implantable medical electrical equipment such as pacemakers;
- Those who used implantable metal medical equipment;
- Those undergoing dialysis;
- Those whose physical measurements, physical tests, and clinical test values before the start of ingestion showed significant deviations from the standard range;
- Those in other clinical studies at the start of the trial;
- Those who regularly consumed foods for specified health use, foods with functional claims, health foods, and supplements that may affect test results;
- Those who regularly consumed large amounts of alcohol;
- Those who smoked extremely often (≥21 cigarettes per day);
- Those with extremely irregular diets;
- Those with irregular life rhythms, such as shift and late-night workers;
- Those who underwent health examinations two weeks before the pre-intake examination;
- Those who planned to donate blood during the research period; and
- Those judged to be inappropriate by the principal investigator.
2.3. Randomization
2.4. Interventions
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Procedures
2.7. Statistical Analysis
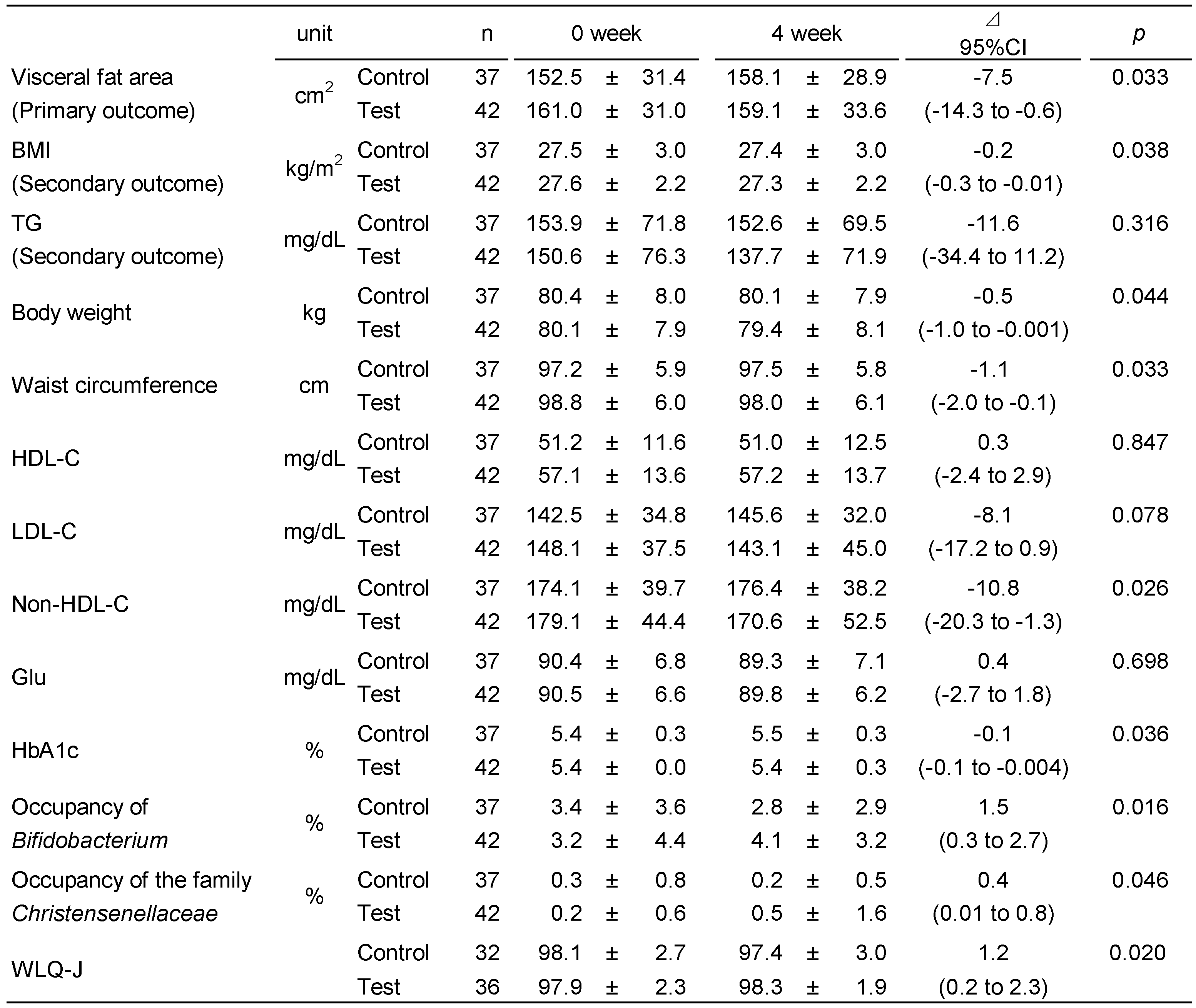
3. Results
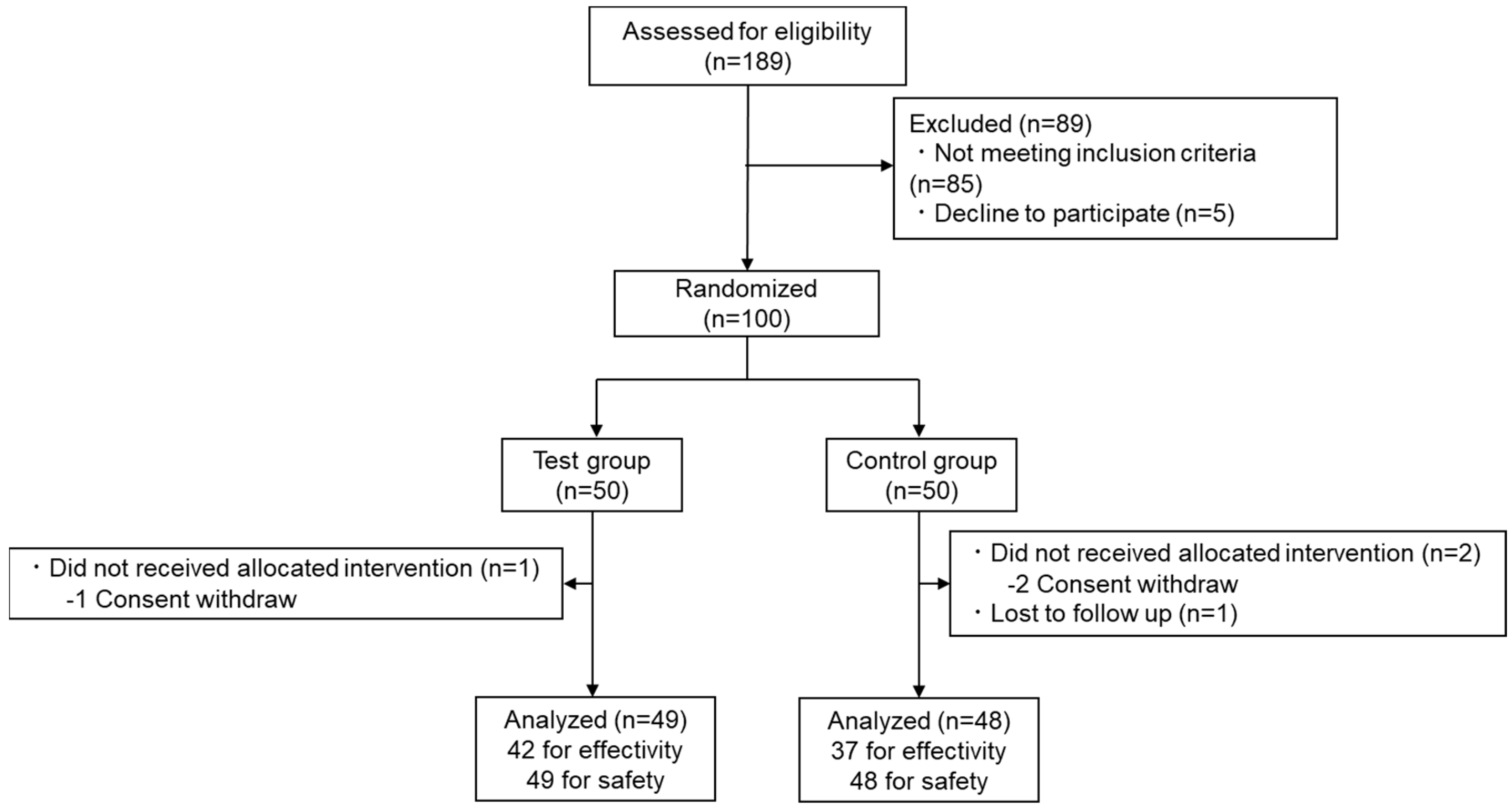
3.1. Participants
3.2. Efficiency
3.3. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neeland, I.J.; Ross, R.; Després, J.P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Shai, I.; Seidell, J.; Magni, P.; Santos, R.D.; Arsenault, B.; et al. Visceral and Ectopic Fat, Atherosclerosis, and Cardiometabolic Disease: A Position Statement. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2019, 7, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Horimai, C.; Katsukawa, F. Ethnic Differences in Abdominal Visceral Fat Accumulation between Japanese, African-Americans, and Caucasians: A Meta-Analysis. In Proceedings of the Acta Diabetologica; October 2003; Vol. 40. [Google Scholar]
- Drewnowski, A. Impact of Nutrition Interventions and Dietary Nutrient Density on Productivity in the Workplace. Nutr Rev 2020, 78, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geaney, F.; Kelly, C.; Greiner, B.A.; Harrington, J.M.; Perry, I.J.; Beirne, P. The Effectiveness of Workplace Dietary Modification Interventions: A Systematic Review. Prev Med (Baltim) 2013, 57, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, K.A.; Chamoli, M.; Hilsabeck, T.A.; Pandey, M.; Bansal, S.; Chawla, G.; Kapahi, P. Evaluating the Beneficial Effects of Dietary Restrictions: A Framework for Precision Nutrigeroscience. Cell Metab 2021, 33, 2142–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Martin, C.K.; Ravussin, E.; Redman, L.M. Effect of 2-Year Caloric Restriction on Organ and Tissue Size in Nonobese 21- To 50-Year-Old Adults in a Randomized Clinical Trial- To CALERIE Study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2021, 114, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmingsson, E.; Johansson, K.; Eriksson, J.; Sundström, J.; Neovius, M.; Marcus, C. Weight Loss and Dropout during a Commercial Weight-Loss Program Including a Very-Low-Calorie Diet, a Low-Calorie Diet, or Restricted Normal Food: Observational Cohort Study. Am J Clin Nutr 2012, 96, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, C.K.; Barnard, R.J.; Croymans, D.M. Weight Loss with a Low-Carbohydrate, Mediterranean, or Low-Fat Diet. New England Journal of Medicine 2008, 359, 2169–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, L.; Cioccoloni, G.; Falco, S.; Abenavoli, L.; Moia, A.; Sinibaldi Salimei, P.; De Lorenzo, A. Influence of FTO Rs9939609 and Mediterranean Diet on Body Composition and Weight Loss: A Randomized Clinical Trial NCT01890070 NCT. J Transl Med 2018, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentella, M.C.; Scaldaferri, F.; Ricci, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; Miggiano, G.A.D. Cancer and Mediterranean Diet: A Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D. Mediterranean Diet and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2014, 30, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, M.; Kushida, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Tomata, Y.; Tsuji, I.; Tsuduki, T. Abdominal Fat in Individuals with Overweight Reduced by Consumption of a 1975 Japanese Diet: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Obesity 2019, 27, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakane, N.; Osaki, N.; Takase, H.; Suzuki, J.; Suzukamo, C.; Nirengi, S.; Suganuma, A.; Shimotoyodome, A. The Study of Metabolic Improvement by Nutritional Intervention Controlling Endogenous GIP (Mini Egg Study): A Randomized, Cross-over Study. Nutr J 2019, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shobako, N.; Itoh, H.; Honda, K. Typical Guidelines for Well-Balanced Diet and Science Communication in Japan and Worldwide. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shobako, N.; Goto, C.; Nakagawa, T.; Yamato, T.; Kondo, S.; Nakamura, F.; Nakazeko, T.; Hirano, Y.; Honda, K. Hypotensive and HbA1c Reducing Effect of Novel Dietary Intervention Program “COMB Meal Program”: Two Randomized Clinical Trials. J Funct Foods 2022, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazeko, T.; Shobako, N.; Hirano, Y.; Nakamura, F.; Honda, K. Novel Dietary Intervention Program “COMB Meal Program” Approaching Health and Presenteeism: Two Pilot Studies. J Funct Foods 2022, 92, 105050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryo, M.; Maeda, K.; Onda, T.; Katashima, M.; Okumiya, A.; Nishida, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Nakamura, T.; et al. 2005.
- Yokota, J.; Fukutani, N.; Nin, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Yasuda, M.; Tashiro, Y.; Matsushita, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Yokota, I.; Teramukai, S.; et al. Association of Low Back Pain with Presenteeism in Hospital Nursing Staff. J Occup Health 2019, 61, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, N.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Shimomura, I. Adiponectin, a Unique Adipocyte-Derived Factor beyond Hormones. Atherosclerosis 2020, 292, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalczyk, M.M.; Zajac-Gawlak, I.; Zając, A.; Pelclová, J.; Roczniok, R.; Langfort, J. Influence of Nutritional Education on the Diet and Nutritional Behaviors of Elderly Women at the University of the Third Age. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajerska, J.; Chmurzynska, A.; Muzsik, A.; Krzyżanowska, P.; Mądry, E.; Malinowska, A.M.; Walkowiak, J. Weight Loss and Metabolic Health Effects from Energy-Restricted Mediterranean and Central-European Diets in Postmenopausal Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panizza, C.E.; Lim, U.; Yonemori, K.M.; Cassel, K.D.; Wilkens, L.R.; Harvie, M.N.; Maskarinec, G.; Delp, E.J.; Lampe, J.W.; Shepherd, J.A.; et al. Effects of Intermittent Energy Restriction Combined with a Mediterranean Diet on Reducing Visceral Adiposity: A Randomized Active Comparator Pilot Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, H.L.; Itsiopoulos, C.; Tierney, A.C.; Kucianski, T.; Radcliffe, J.; Garg, M.; Willcox, J.; Thomas, C.J. Ad Libitum Mediterranean Diet Reduces Subcutaneous but Not Visceral Fat in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease: A Randomised Controlled Pilot Study. Clin Nutr ESPEN 2019, 32, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozato, N.; Saito, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Katashima, M.; Tokuda, I.; Sawada, K.; Katsuragi, Y.; Imoto, S.; Ihara, K.; Nakaji, S. Association between Nutrients and Visceral Fat in Healthy Japanese Adults: A 2-Year Longitudinal Study Brief Title: Micronutrients Associated with Visceral Fat Accumulation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosqvist, F.; Iggman, D.; Kullberg, J.; Cedernaes, J.; Johansson, H.E.; Larsson, A.; Johansson, L.; Ahlström, H.; Arner, P.; Dahlman, I.; et al. Overfeeding Polyunsaturated and Saturated Fat Causes Distinct Effects on Liver and Visceral Fat Accumulation in Humans. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2356–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Harada, S.; Tsubota, K.; Yasukawa, T.; Takebayashi, T.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Kawasaki, R. Dietary Saturated Fatty Acid Intake and Early Age-Related Macular Degeneration in a Japanese Population. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2020, 61, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteyger, C.; Larsen, T.M.; Vercruysse, F.; Pedersen, D.; Toubro, S.; Astrup, A. Visceral Fat Loss Induced by a Low-Calorie Diet: A Direct Comparison between Women and Men. Diabetes Obes Metab 2009, 11, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Million, M.; Maraninchi, M.; Henry, M.; Armougom, F.; Richet, H.; Carrieri, P.; Valero, R.; Raccah, D.; Vialettes, B.; Raoult, D. Obesity-Associated Gut Microbiota Is Enriched in Lactobacillus Reuteri and Depleted in Bifidobacterium Animalis and Methanobrevibacter Smithii. Int J Obes 2012, 36, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, A.K.; Brunius, C.; Mazidi, M.; Hellström, P.M.; Risérus, U.; Iversen, K.N.; Fristedt, R.; Sun, L.; Huang, Y.; Nørskov, N.P.; et al. Effects of Whole-Grain Wheat, Rye, and Lignan Supplementation on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Men with Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized Crossover Trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2020, 111, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor-Ibáñez, R.; Blanco-Heredia, J.; Etcheverry, F.; Sánchez-Palomino, S.; Díez-Fuertes, F.; Casas, R.; Navarrete-Muñoz, M.Á.; Castro-Barquero, S.; Lucero, C.; Fernández, I.; et al. Adherence to a Supplemented Mediterranean Diet Drives Changes in the Gut Microbiota of Hiv-1-Infected Individuals. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, K.; Hosomi, K.; Sawane, K.; Kunisawa, J. Metabolism of Dietary and Microbial Vitamin b Family in the Regulation of Host Immunity. Front Nutr 2019, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, J.K.; Waters, J.L.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Koren, O.; Blekhman, R.; Beaumont, M.; Van Treuren, W.; Knight, R.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Human Genetics Shape the Gut Microbiome. Cell 2014, 159, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Mantrana, I.; Selma-Royo, M.; Alcantara, C.; Collado, M.C. Shifts on Gut Microbiota Associated to Mediterranean Diet Adherence and Specific Dietary Intakes on General Adult Population. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Neth, B.J.; Wang, S.; Craft, S.; Yadav, H. Modified Mediterranean-Ketogenic Diet Modulates Gut Microbiome and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Association with Alzheimer’s Disease Markers in Subjects with Mild Cognitive Impairment. EBioMedicine 2019, 47, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, G. Presenteeism in the Workplace: A Review and Research Agenda. J Organ Behav 2010, 31, 519–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.D. Can Worksite Nutritional Interventions Improve Productivity and Firm Profitability? A Literature Review. Perspect Public Health 2011, 131, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, W.J.; Rico, M.; Chandler, M.; Herman, D.R.; Chang, C.; Belin, T.R.; Love, S.; Ramirez, E.; Gelberg, L. Randomized Comparative Effectiveness Trial of 2 Federally Recommended Strategies to Reduce Excess Body Fat in Overweight, Low-Income Patients: Myplate.Gov vs Calorie Counting. Ann Fam Med 2023, 21, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, N.R.; Fong, M.; Gerofi, J.; Leung, L.; Leung, C.; Denyer, G.; Caterson, I.D. A Randomized Controlled Trial to Determine the Efficacy of a High Carbohydrate and High Protein Ready-to-Eat Food Product for Weight Loss. Clin Obes 2016, 6, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurgens, T.M.; Whelan, A.M.; Killian, L.; Doucette, S.; Kirk, S.; Foy, E. Green Tea for Weight Loss and Weight Maintenance in Overweight or Obese Adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
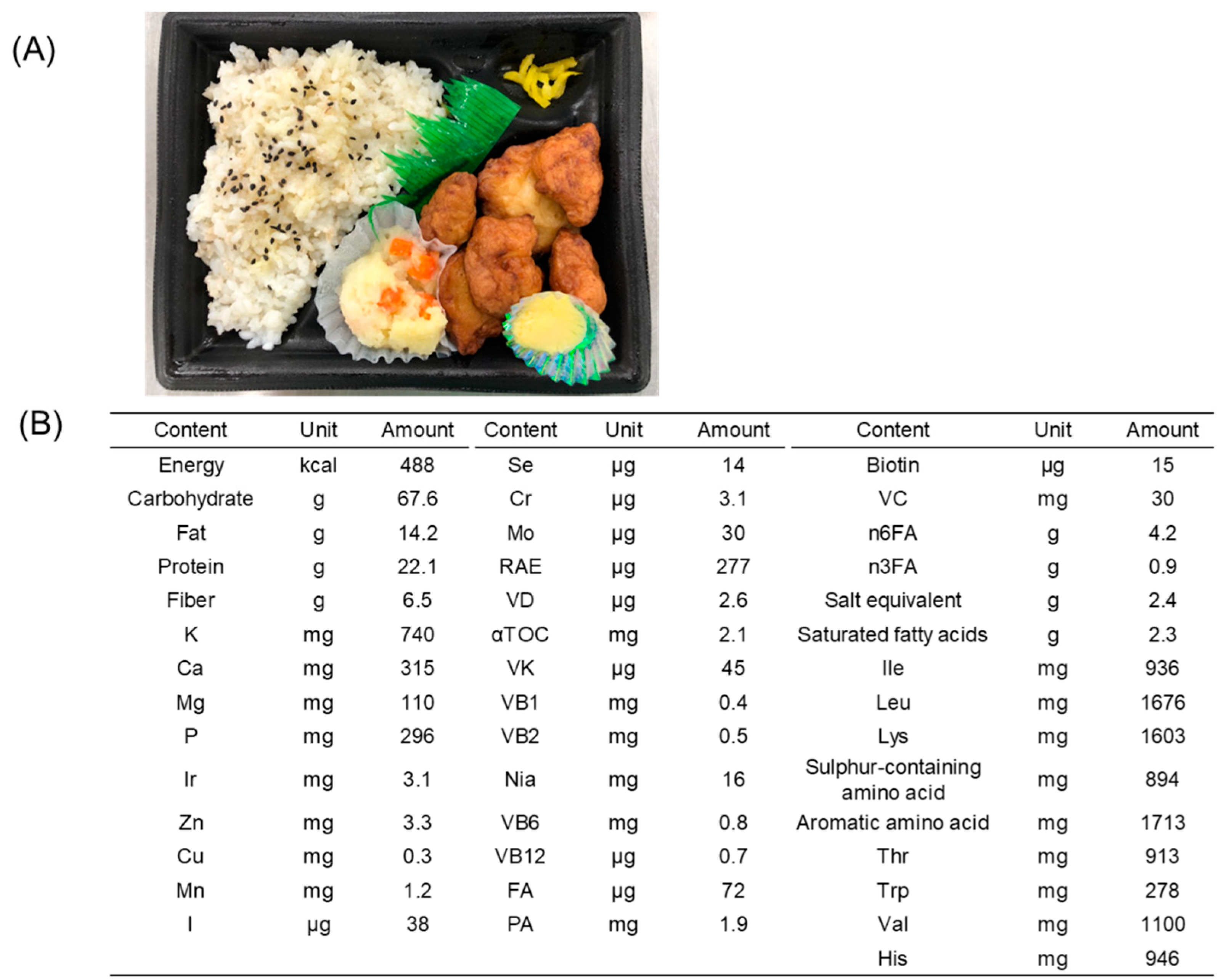
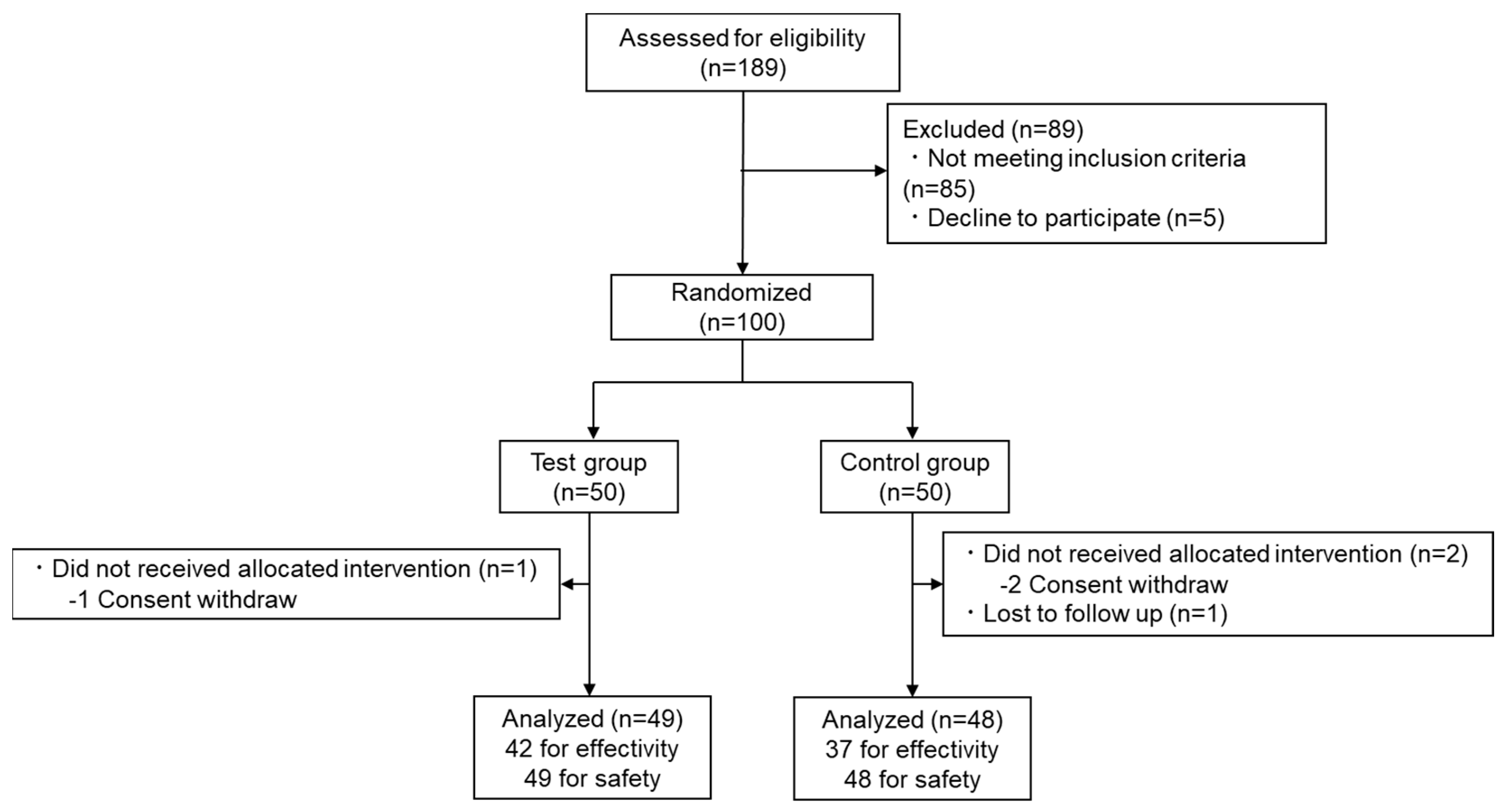
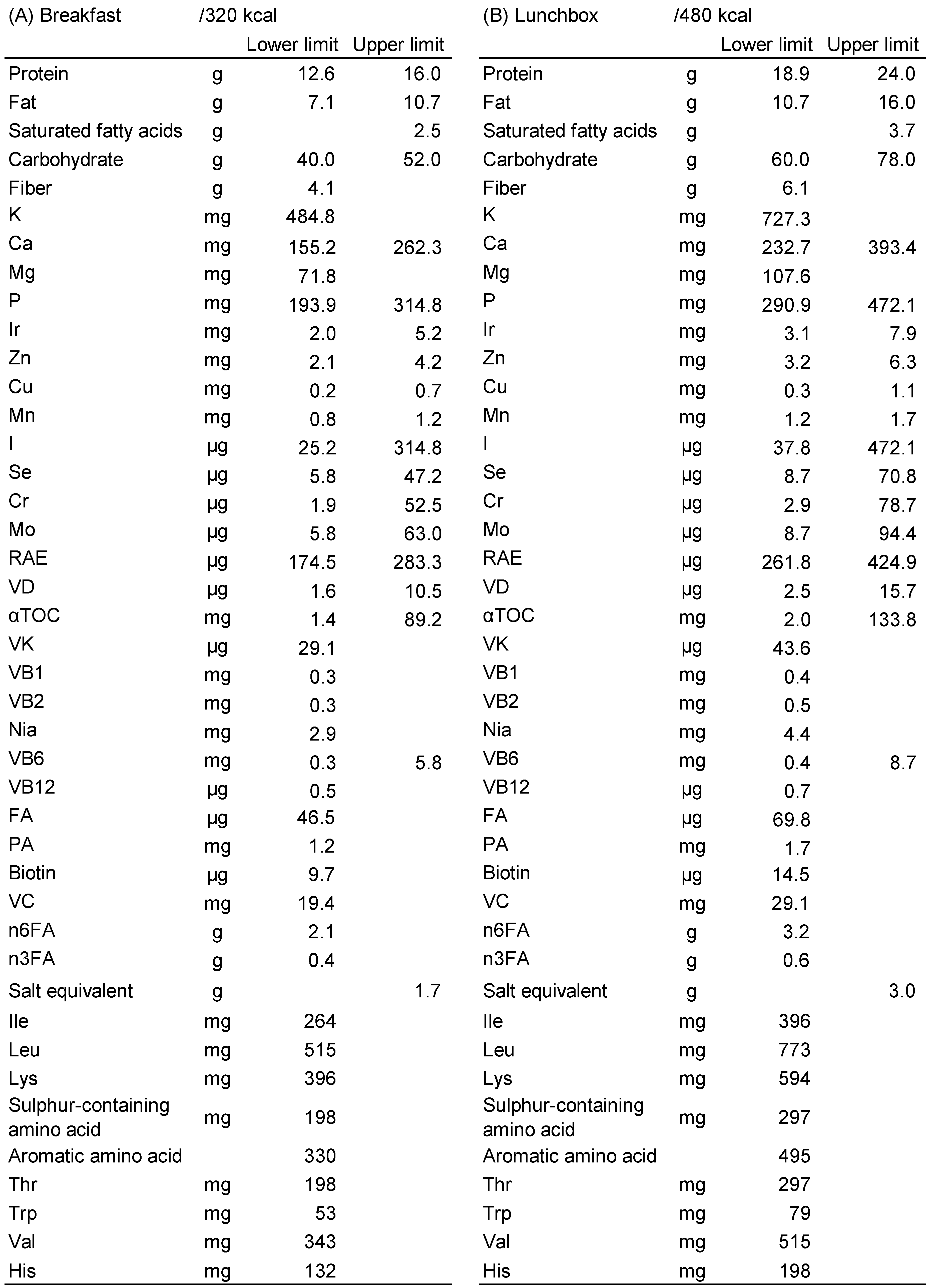 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





