1. Introduction
COVID-19 is an infectious respiratory illness caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), which has caused a global pandemic resulting in over 6.8 million deaths worldwide (World Health Organisation, 2020), (Ferrara et al., 2023). The mechanism of the virus works by binding to a target cell surface using specific receptors composed of S1 and S2 units where the S1 unit will binds to ACE2, which is expressed in many tissues, hence allowing SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication. Recent study (Xiaoqing et al., 2020) which suggests that SARS-CoV- 2 can infect multiple organs beyond the respiratory tract.
In some studies, and institution, the term Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV- 2 (PASC) is also used as the term long COVID refers to persistency of COVID-19 symptoms that may last for weeks or months after initial infection with COVID-19 with varies symptoms between affected individuals (Raveendran et al., 2021). WHO also reported that different individuals might experience different type of symptoms or many symptoms at once which ranging from shortness of breath, fever, headache, fatigue, cardiac arrest, to neurological dysfunction, with symptoms lasting on average of over 2 months (World Health Organisation, 2020).
There is not yet a clear definition regarding long COVID and its underlying mechanism which had causes the proper diagnostic for long COVID may be not accurate from time to time which oftens mistakenly for other symptoms of different disease (Munblit et al., 2022). Hence it is importance for researcher across multidisciplinary in developing an effective treatment against Long Covid. In this study various ways have explored, including the utilization of computational tools to analyse long COVID pathways and its potential drug target (Gao et al., 2020). This approach involves repurposing drugs that have already undergone clinical trials and regulatory approval, which allows for a faster, safe, and cost-effective in identifying possible treatments for Long COVID (Saha et al., 2022).
2. Methodology
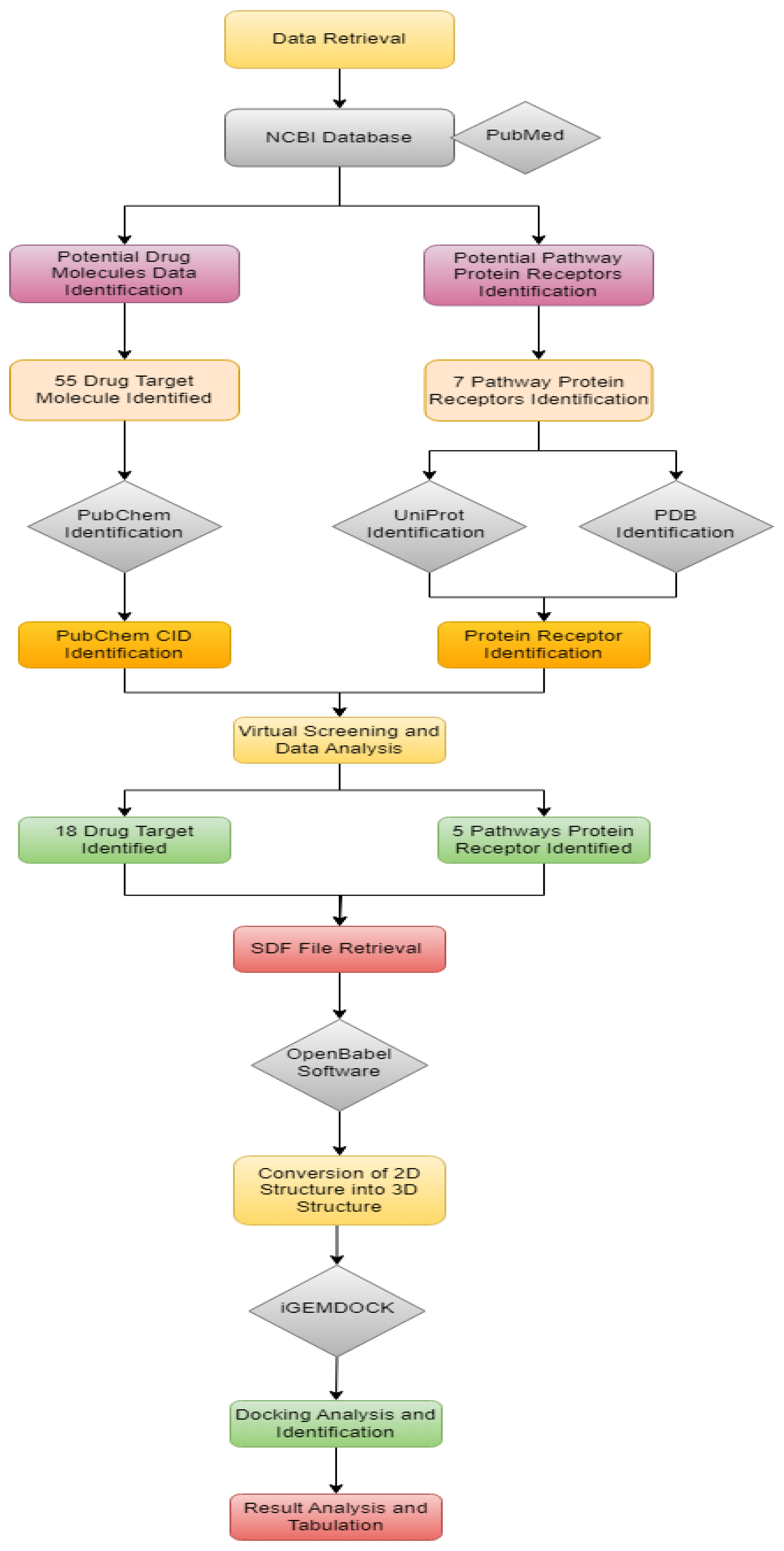
The overall workflow is shown in
Figure 1
2.1. Identification of Long COVID Pathways Receptors
A comprehensive literature review was conducted to gather information on Long COVID and its associated pathways. Relevant studies were sourced from databases such as PubMed and Google Scholar. Data on the inflammatory, cytokine, immune, coagulation, mitochondrial, oxidative stress, and autonomic dysfunction pathways were collected to understand the key molecular targets involved in Long COVID.
Seven potential pathways for long COVID were identified by searching peer-reviewed publications. The pathways analyzed include the inflammatory pathway, cytokine, immune system, coagulation, mitochondria, oxidative stress, and autonomic dysfunction, which are considered possible underlying mechanisms of long COVID as recorded in
Table 1. Key pathways implicated in Long COVID were mapped using bioinformatics tools. Pathways related to inflammation, cytokine signaling, immune response, coagulation, mitochondrial function, oxidative stress, and autonomic dysfunction were identified. Pathway analysis involved reviewing existing literature and pathway databases such as KEGG and Reactome. Receptor proteins associated with each pathway were identified through UniProt and related pathway databases. The role of each receptor in Long COVID was reviewed based on its function and interaction within the pathway.
For the inflammatory pathway, identified receptors include Nuclear Factor-kappa B (NF-κB), cytokine receptors, Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4) inhibitors, and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) inhibitors (Yarmohammadi et al., 2021). In the cytokine pathway, inhibitors include Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α), Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and Interleukin-1 (IL-1). For the immune system pathway, potential docking receptors identified include programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), and T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-containing protein 3 (TIM-3). The coagulation pathway identified receptors for potential inhibitors such as Factor Xa, thrombin inhibitors, antiplatelet inhibitors, antiplatelet agents, and anticoagulants. For the mitochondrial pathway, identified receptors include mitochondrial uncoupling proteins (UCPs), mitochondrial complex I inhibitors, mitochondrial complex III inhibitors, and mitochondrial antioxidant agents. The autonomic dysfunction pathway identified potential receptors for drug target docking, including beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, alpha-2 agonists, and antidepressants. Lastly, the oxidative stress pathway identified potential inhibitor sites, including antioxidant enzymes, redox-active compounds, Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2 (Nrf2) activators, and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) agonists.
However, some pathways could not be analyzed for potential mechanism receptors in identifying drug targets due to insufficient information available in the queried databases. These pathways include cytokine, autoimmune dysfunction, and immune system pathways.
2.2. Identification of Drugs
Potential drug molecules were identified from PubChem, focusing on compounds known to interact with the receptors involved in Long COVID pathways. The selection of drug molecules was based on their known or predicted interaction with pathway receptors. The identification and selection of potential drugs for long COVID were conducted using repurposed drugs that have been approved by the FDA. A total of 55 different potential inhibitors and drug targets were identified for the inflammatory, cytokine, immune system, coagulation, mitochondria, oxidative stress, and autonomic dysfunction pathways. These receptors were individually searched and analyzed in the PubChem database, a public resource containing millions of chemical substances, including their structures, properties, and biological functions, as recorded in
Table 1.
2.2. Data Collection for Drug Targets (2D Structure)
All identified drug targets were searched in PubChem using the drug's chemical name and molecular formula, after which the Compound Identification (CID) numbers were recorded in
Table 1. These CIDs were then analyzed to obtain the 2D structures of the drugs in the form of Structure Data Files (SDF) for individual docking with correlated pathway receptors.
2.3. Data Collection for Long COVID Pathway Receptors
The 3D structures of all pathway receptors were obtained and analyzed from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) (
https://www.rcsb.org/). Each pathway receptor was individually searched in the database and downloaded.
2.4. Conversion of 2D Structures into 3D Structures
The 2D structures of both drug targets and pathway receptors were converted from the 2D SDF file format into 3D PDB, Mol, or Mol2 formats, which are necessary for docking analyses using iGEMDOCK. This software requires the 3D structures of both the ligand (drug target) and the receptor (target protein). The conversion was performed using OpenBabel at
http://www.cheminfo.org/Chemistry/Cheminformatics/FormatConverter/index.html.
2.5. Molecular Docking
The process of analyzing and calculating the binding affinity and docking between the drugs and their respective pathway receptors was performed using iGEMDOCK. The natural compounds, serving as the drugs, were uploaded in batches according to their pathways as ligands, with their respective pathway receptors as the target proteins. iGEMDOCK allows users to dock a single receptor against multiple compounds simultaneously, making the process more efficient. All results, including binding energy, Van der Waals forces (VDW), hydrogen bonds (H-bonds), and electrostatic interactions (Elec), were saved in text file format (TXT) and later compiled into Excel files. The recorded data are presented in
Table 2.
3. Discussion
3.1. Inflammatory Pathway
Inflammation is an innate defense mechanism of the body's immune system in response to injury, infection, or tissue damage. It has been suggested that both acute COVID-19 and long COVID are associated with hyperinflammatory syndrome, cytokine storms, and organ and tissue damage due to a dysregulated immune system (Rizvi et al., 2022). Inflammatory signaling in long COVID is activated by the Janus Kinase signaling pathway, Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Nuclear Factor-kappa B (TNFα-NF-κB) pathway, Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) pathway, Lipoxygenase (LOX) pathway, and Cytokine receptor pathway, all of which can be targeted for drug treatment to reduce and relieve various symptoms. To mitigate these symptoms, potential drug targets were identified by searching keywords related to these signaling pathways in PubMed. The list of drugs identified in the PubChem database includes Tocilizumab, Sarilumab, Bortezomib, Tofacitinib, Ruxolitinib, Baricitinib, Apremilast, Roflumilast, and Zileuton, each serving a different function and targeting a specific signaling pathway.
3.1.1. Janus Kinase Pathway Receptors and Drugs
The Janus Kinase pathway is a major signaling pathway associated with inducing cytokine storms, leading to inflammation in affected individuals due to dysregulation. This pathway converts extracellular signals into transcriptional responses (Choudhary et al., 2021). Inhibition or reduction of Janus Kinase signaling could decrease inflammation by reducing cytokine production in hospitalized individuals, using drugs such as Ruxolitinib and Baricitinib. The Janus Kinase pathway receptor has been docked against both drugs, with the results shown in
Table 2: Ruxolitinib (-81.4519) and Baricitinib (-77.2579). Ruxolitinib may potentially suppress CD4-positive cells, thereby reducing inflammation (Yajnanarayana et al., 2015). Baricitinib is a reversible inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2, with a high affinity for AAK1 and reduced affinity for GAK. By inhibiting these enzymes, Baricitinib interferes with cytokine and growth factor receptor signaling pathways, reducing immune dysregulation.
3.1.2. Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NF-κB) Pathway Receptors and Drugs
The role of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is associated with regulating innate immune cells and manipulating the gene expression profile of numerous cytokines in response to foreign stimuli. Many proinflammatory factors are documented to activate the NF-κB signaling cascade. NF-κB signaling involves the phosphorylation of IκB kinase beta and has been shown to increase the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which is speculated to cause inflammation in various organs and tissue systems (Kandasamy, 2021). To counteract inflammation, drugs such as Bortezomib and Tofacitinib have been identified to alleviate the clinical manifestations caused by this pathway, with binding affinities shown in
Table 2.
Bortezomib is a proteasome inhibitor that can manipulate many signaling pathways, including suppressing NF-κB activation, a causative agent of inflammation. It is commonly used to treat inflammation related to tumors with a high risk of relapse that involves the NF-κB pathway, ultimately leading to apoptosis. Tofacitinib, an orally administered medication, has been identified as a suitable candidate for inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. Tofacitinib can dysregulate and inhibit intracellular transduction pathways after a cytokine binds to its receptor, resulting in the suppression of cytokine production. This is particularly useful in treating long COVID manifestations that induce cytokine storms, which can damage body systems.
3.1.3. Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) Pathway Receptors and Drugs
Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) is an enzyme responsible for regulating inflammation and maintaining epithelial integrity. It has been suggested that targeting PDE4 could be a potential strategy for immune system regulation by suppressing cytokine production, thereby reducing the risk of cytokine storms that could lead to inflammation in affected organs or tissue systems. In the body, PDE4 regulates both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory multicomplex proteins, including the repression of cytokine signaling pathways (Dalamaga et al., 2020). The identified potential drugs for this pathway are Apremilast and Roflumilast, which have been docked against PDE4 as the receptor using iGEMDOCK, with energy scores of -66.2507 and -67.8479, respectively, as shown in
Table 2.
Roflumilast is a PDE4 inhibitor that affects neutrophils, CD4+, and CD8+ cells, and suppresses TNF-alpha synthesis, all of which contribute to inflammation. It has been recognized and approved for safe use by many institutions and authorities worldwide for treating pulmonary disease, which is a manifestation of long COVID, making it a suitable candidate for targeting the PDE4 pathway (Shah, 2020). Additionally, Apremilast has demonstrated the potential to inhibit TNF-alpha production by 46%, as shown by McCann et al. (2010). By inhibiting the production of TNF-alpha and PDE4, Apremilast could potentially reduce the inflammatory risk associated with skin diseases and gastrointestinal issues, which are clinical manifestations of long COVID, making it another suitable candidate for targeting the PDE4 pathway.
3.1.4. Lipoxygenase (LOX) Pathway Receptors and Drug Targets
Lipoxygenases are a class of oxidative enzymes containing a non-heme iron atom that regulate the immune system by producing pro-inflammatory mediators called leukotrienes, as well as lipoxins, which are anti-inflammatory proteins. To combat inflammation, a suitable drugs identified for inhibiting this pathway is Zileuton, which has a docking energy of -88.1074 in iGEMDOCK. Zileuton is one of the few drugs approved to inhibit lipoxygenase production and thereby reduce inflammation (Wu et al., 2020). While Zileuton has been shown to influence Ca2+-activated K+ currents for lipoxygenase, its overall ionic impact on neurons remains unidentified.
3.2. Coagulation Pathway
Coagulation is a common clinical manifestation of both COVID-19 and long COVID and is often correlated with the severity of the disease. Individuals affected by COVID-19 and long COVID are at risk of developing thrombosis, which can lead to microvascular thrombosis and hemorrhage due to chronic alveolar inflammation (McGonagle et al., 2020).
3.2.1. Factor Xa Pathway Receptors and Drug Targets
Human factor Xa (FXa) is a key serine protease in the coagulation pathway. FXa catalyzes the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, leading to the formation of blood clots and subsequent coagulation. The catalytic process of lipoxygenases involves a single-electron oxidation by the active site iron atom, which alternates between Fe²⁺ and Fe³⁺ redox states (Wisastra & Dekker, 2014). FXa binds to factor Va, calcium, and phospholipids to form prothrombinase, which converts prothrombin (factor II) into thrombin (factor IIa). Thrombin then converts fibrinogen (factor I) monomers into fibrin (factor Ia) monomers. Factor XIII, also stimulated by thrombin, transforms soluble fibrin monomers on the surface of active platelets into insoluble cross-linked fibrin polymers, leading to blood clot formation (Al-Horani & Kar, 2020; Mohammed et al., 2018; Rk & Krishnaswamy, 1994).
Three potential drugs—apixaban, edoxaban, and rivaroxaban—have been identified and are clinically approved for anticoagulation. These drugs were docked against factor Xa receptors using iGEMDOCK, with energy scores of -128.794 for apixaban, -101.15 for rivaroxaban, and -89.3458 for edoxaban, as recorded in
Table 2.
Apixaban is a factor Xa inhibitor authorized for medical use to manage various thrombosis-related conditions, including reducing the risk of stroke and preventing thromboprophylaxis following replacement surgery. It offers a significant benefit-risk alternative to conventional anticoagulants such as VKAs, aspirin, and low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) for patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF). Rivaroxaban, another factor Xa inhibitor, has been shown to reduce inflammation, swelling, and fibrosis caused by tension overload, and improve diastolic function, even at below-therapeutic doses. It has been associated with decreased FX expression in these cell populations. Rivaroxaban also inhibits the production of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA) caused by angiotensin II and calcium chloride by reducing aortic remodeling and inflammation. It may serve as a viable therapeutic option for preventing AAA by inhibiting FXa-induced aortic wall inflammation, thereby protecting the aortic wall by reducing leukocyte infiltration, inflammatory cytokine expression—which could trigger cytokine storms—and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs).
3.1.3. Thrombin Pathway Receptors and Drug Targets
Thrombin, also known as factor IIa, is a serine protease involved in the coagulation pathway. It plays a crucial role in coagulation by promoting the formation of fibrin clots from prothrombin, a process that also involves phospholipids, calcium, and factor Va (Davie et al., 1991). Thrombin is essential for hemostasis and thrombosis, as it stimulates platelet activation and the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin.
Given the significant risk of coagulation disorders in COVID-19 and long COVID patients, the use of dabigatran as an anticoagulant is highly beneficial. Anticoagulation has been shown to enhance survival in these patients and may help reduce inflammation associated with the symptoms (Benati et al., 2021). Dabigatran's binding affinity is -79.963, as recorded in
Table 2.
3.3. Mitochondrial Pathway
3.3.1. Mitochondrial Uncoupling Proteins (UCPs) Pathway Receptors and Drug Targets
Uncoupling proteins (UCPs) are part of the mitochondrial anionic transporter family, consisting of transmembrane proteins found in the mitochondrial membrane. UCPs are characterized by tandem repeat domains, each containing two alpha-helix regions. This paper identifies six homologs of mammalian UCPs, ranging from UCP1 to UCP6. However, only UCP2 will be discussed in depth due to insufficient and irrelevant information available for the other UCPs from PubChem, which limited the ability to perform docking studies using iGEMDOCK.
UCP2 is among the most highly expressed UCP homologs in the body, with expression noted in the kidneys, placenta, lungs, and brain. It has been researched for its potential benefits in preventing several disorders linked to increased oxidative stress, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, arteriosclerosis, and diabetes mellitus. UCP2 is also thought to have regulatory functions in inflammation and insulin secretion, and it may play a role in protection against stroke and ethanol poisoning.
In individuals affected by long COVID, cytokine storms may interfere with mitochondrial function, leading to a significant rise in reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. This increase in ROS can trigger the expression of IL-1, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), IL-8 receptor-β (CXCR2), monocyte chemotactic protein-1, and cell adhesion molecule 1 (Konishi et al., 2019). UCP2 may respond to counteract this oxidative stress. The use of 2,4-Dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP) could potentially serve as a drug target to support UCP2 in combating inflammation caused by elevated ROS levels. 2,4-DNP's protonophoric abilities could aid UCP2 by enhancing mitochondrial proton transport, thereby stabilizing ROS levels and mitigating their adverse effects on the respiratory and nervous systems, which are among the clinical manifestations of long COVID.
3.4. Oxidative Stress Pathway
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) is crucial for regulating oxidative stress, and one of the key pathways for antioxidant and anti-inflammatory signaling is the KEAP1-NRF2-ARE pathway. Under normal homeostasis, NRF2 is anchored in the cytoplasm by binding with KEAP1. When cells are exposed to reactive oxygen species (ROS) or other harmful stimuli, NRF2 dissociates from KEAP1 and translocates to the nucleus. There, it forms a heterodimer with the transcriptional regulator and binds to the antioxidant response element (ARE). Inhibition of NRF2 expression, along with the development of the inflammasome, may contribute to the development of long COVID.
Curcumin and sulforaphane are potential agents for managing the NRF2 pathway in combating long COVID, with binding affinities of -94.0045 and -53.7559, respectively, as recorded in
Table 2. Curcumin, derived from the rhizomes of Curcuma longa, has demonstrated potential bioactivity in managing inflammation, acting as an antioxidative agent, and being used in viral drug therapies with limited side effects (Agarwal et al., 2011; Yu et al., 2018; Liao et al., 2019). Sulforaphane, a sulfur-rich phytochemical, is known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and its potential in reducing tumor development. Recent interest in sulforaphane has increased due to its broad range of effects, which could be particularly relevant for understanding long COVID, given that neurological manifestations are a common symptom of this disease (Uddin et al., 2020).
3.4.1. Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) Agonists Pathway Receptors and Drug Target
PPAR-α, PPAR-β/δ, and PPAR-γ are three subtypes of the PPAR family, each expressed by different genes and performing distinct biological roles, although they share structural similarities. Research, both in vitro and in vivo, has shown that despite their differences in biological roles, the three PPARs are responsible for regulating and controlling lipid and glucose metabolism. They also have protective functions in managing cancer cells, maintaining vascular homeostasis and atherosclerosis, supporting the immune system, and controlling inflammation (Berger & Moller, 2002; Pu et al., 2023; Sher et al., 1993).
For the purposes of this paper, pioglitazone and rosiglitazone have been identified as potential drug targets for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, with PPARγ being the most promising target compared to PPARα and PPARβ. According to
Table 2, both pioglitazone and rosiglitazone have been docked against PPARγ receptors, resulting in binding energies of -75.9458 and -68.6783, respectively. The results indicate that pioglitazone has a higher binding affinity (-75.9458) with PPARγ receptors, making it a more favorable candidate for discovering potential agonists for this pathway, while rosiglitazone scored lower at -68.6783.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, our bioinformatics analysis has successfully identified at least 18 potential drug candidates targeting five different pathway receptors. By employing advanced tools for drug molecule identification, pocket analysis, pathway mapping, and receptor protein structure analysis, we have laid the groundwork for the development of more effective drug discovery techniques. We anticipate that these findings will contribute to the advancement of rapid and efficient drug target identification, ultimately enhancing therapeutic strategies.
Acknowledgments
The researcher would like to express gratitude to the Management and Science University for providing funding for computational and resources facilities.
References
- Agarwal, N. B., Jain, S., Agarwal, N., Mediratta, P. K., & Sharma, K. K. (2011). Modulation of pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling and oxidative stress by curcumin in mice. Phytomedicine, 18(8–9), 756–759. [CrossRef]
- Al-Horani, R. A. (2020). Potential Therapeutic Roles for Direct Factor Xa Inhibitors in Coronavirus Infections. American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs, 20(6), 525– 533. [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y., Li, R., Jiang, J., Cai, B., Gao, J., Le, K., Zhang, F., Chen, S., & Liu, P. (2008). Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma inhibits endothelin-1-induced cardiac hypertrophy via the calcineurin/NFAT signaling pathway. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 317(1–2), 189–196. [CrossRef]
- Benati, M., Salvagno, G. L., De Nitto, S., Gelati, M., Lavorgna, B., Fava, C., Minuz, P., & Lippi, G. (2021). Thrombin Generation in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis, 47(04), 447–450. [CrossRef]
- Berger, J., & Moller, D. E. (2002). The Mechanisms of Action of PPARs. Annual Review of Medicine, 53(1), 409–435. [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S., Sharma, K., & Silakari, O. (2021). The interplay between inflammatory pathways and COVID-19: A critical review on pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Microbial Pathogenesis, 150, 104673. [CrossRef]
- Dalamaga, M., Karampela, I., & Mantzoros, C. S. (2020). Commentary: Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors as potential adjunct treatment targeting the cytokine storm in COVID-19. Metabolism-clinical and Experimental, 109, 154282. [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, F., Zovi, A., Masi, M., Langella, R., Trama, U., Boccellino, M., & Vitiello, A. (2023). Long COVID could become a widespread post-pandemic disease? A debate on the organs most affected. Naunyn-schmiedebergs Archives of Pharmacology. [CrossRef]
- Gao, K., Nguyen, D., Wang, R., & Wei, G. (2020). Machine intelligence design of 2019- nCoV drugs. bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory). [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, P. B. V., Quirk, D., Furtado, R. H., Maia, L. N., Saraiva, J., Antunes, M. O., Filho, R. K., Madrini, V., Junior, De Matos Soeiro, A., Tognon, A. P., Veiga, V. C., Martins, P., Moia, D. D., Sampaio, B. D. S., Assis, S. R., Soares, R. V., Piano, L. P., Castilho, K., Momesso, R. G. R. a. P., Berwanger, O. (2021). Tofacitinib in Patients Hospitalized with Covid-19 Pneumonia. The New England Journal of Medicine, 385(5), 406–415. [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, A., Chauhan, P., Saha, B., Jafarzadeh, S., & Nemati, M. (2020). Contribution of monocytes and macrophages to the local tissue inflammation and cytokine storm in COVID-19: Lessons from SARS and MERS, and potential therapeutic interventions. Life Sciences, 257, 118102. [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, M. (2021). NF-κB signalling as a pharmacological target in COVID-19: potential roles for IKKβ inhibitors. Naunyn-schmiedebergs Archives of Pharmacology, 394(3), 561–567. [CrossRef]
- Liao, L., Shi, J., Jiang, C., Zhang, L., Feng, L., Lawrence, R. J., & Zhang, J. (2019). Activation of anti-oxidant of curcumin pyrazole derivatives through preservation of mitochondria function and Nrf2 signaling pathway. Neurochemistry International, 125, 82–90. [CrossRef]
- Maslennikov, R., Ivashkin, V., Vasilieva, E., Chipurik, M., Semikova, P., Semenets, V., Russkova, T., Levshina, A., Grigoriadis, D., Magomedov, S., Efremova, I. E., & Dzhakhaya, N. (2021). Tofacitinib reduces mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 Tofacitinib in COVID-19. Pulmonary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 69, 102039. [CrossRef]
- McGonagle, D., O’Donnell, J. S., McGonagle, D., Emery, P., & Bridgewood, C. (2020). Immune mechanisms of pulmonary intravascular coagulopathy in COVID-19 pneumonia. The Lancet Rheumatology, 2(7), e437–e445. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, B. M., Matafonov, A., Ivanov, I., Sun, M., Cheng, Q., Dickeson, S. K., Li, C., Sun, D. A., Verhamme, I. M., Emsley, J., & Gailani, D. (2018). An update on factor XI structure and function. Thrombosis Research, 161, 94–105. [CrossRef]
- Munblit, D., O’Hara, M. E., Akrami, A., Perego, E., Olliaro, P., & Needham, D. M. (2022). Long COVID: aiming for a consensus. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, 10(7), 632–634. [CrossRef]
- Park, J., Dean, L. S., Jiyarom, B., Gangcuangco, L. M., Shah, P., Awamura, T., Ching, L. L., Nerurkar, V. R., Chow, D. C., Igno, F., Shikuma, C. M., & Devendra, G. (2023). Elevated circulating monocytes and monocyte activation in COVID-19 convalescent individuals. Frontiers in Immunology, 14. [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y., Cheng, C. K., Zhang, H., Luo, J., Wang, L., Tomlinson, B., & Huang, Y. (2023). Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α agonists in cardiovascular health and disease. Medicinal Research Reviews. [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, A. A., Kathuria, A., Mahmeed, W. A., Al-Rasadi, K., Al-Alawi, K., Banach, M., Banerjee, Y., Ceriello, A., Cesur, M., Cosentino, F., Galia, M., Goh, S., Janez, A., Kalra, S., Kempler, P., Lessan, N., Lotufo, P., Wu, A. W., Santos, R. D., . . .Rizzo, M. (2022). Post-COVID syndrome, inflammation, and diabetes. Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications, 36(11), 108336. [CrossRef]
- Rk, W., & Krishnaswamy, S. (1994). The activation of prothrombin by the prothrombinase complex. The contribution of the substrate-membrane interaction to catalysis. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269(44), 27441–27450. [CrossRef]
- Saha, S., Chatterjee, P., Halder, A. K., Nasipuri, M., Basu, S., & Plewczynski, D. (2022). ML-DTD: Machine Learning-Based Drug Target Discovery for the Potential Treatment of COVID-19. Vaccines, 10(10), 1643. [CrossRef]
- Schafer, P. H., Parton, A., Gandhi, A., Capone, L., Adams, M. R., Wu, L., Bartlett, J.F., Ma, L., Gilhar, A., Yf, C., Baillie, G. S., Houslay, Hw, M., Muller, G. W., & Stirling, D. I. (2010). Apremilast, a cAMP phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, demonstrates anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and in a model of psoriasis. British Journal of Pharmacology, 159(4), 842–855. [CrossRef]
- Shah, C. (2020). Can roflumilast become steroid-sparing alternative in the treatment of COVID-19? Medical Hypotheses, 144, 110246. [CrossRef]
- Shahcheraghi, S. H., Salemi, F., Peirovi, N., Ayatollahi, J., Alam, W., Khan, H., & Saso, L. (2021). Nrf2 Regulation by Curcumin: Molecular Aspects for Therapeutic Prospects. Molecules, 27(1), 167. [CrossRef]
- Sher, T., Yi, H. X., McBride, O., & Gonzalez, F. J. (1993). cDNA cloning, chromosomal mapping, and functional characterization of the human peroxisome proliferator activated receptor. Biochemistry, 32(21), 5598–5604. [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M. S., Mamun, A. A., Jakaria, M., Thangapandiyan, S., Baik, S. W., Rahman, A., Mathew, B., Abdel-Daim, M. M., & Aleya, L. (2020). Emerging promise of sulforaphane-mediated Nrf2 signaling cascade against neurological disorders. Science of the Total Environment, 707, 135624. [CrossRef]
- WI sastra, R., & Dekker, F. J. (2014). Inflammation, Cancer and Oxidative Lipoxygenase Activity are Intimately Linked. Cancers, 6(3), 1500–1521. [CrossRef]
- Wu, C., Liu, Y., Yang, Y., Zhang, P., Zhong, W., Wang, Y., Wang, Q., Xu, Y., Li, M., Li, X., Zheng, M., Chen, L. X., & Li, H. (2020). Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 10(5), 766–788. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z., Zhang, H., Zhang, W., Lai, B., & Yao, G. (2019b). Removal of nitrophenols and their derivatives by chemical redox: A review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 359, 13–31. [CrossRef]
- Yajnanarayana, S. P., Stübig, T., Cornez, I., Alchalby, H., Schönberg, K., Rudolph, J., Triviai, I., Wolschke, C., Heine, A., Brossart, P., Kröger, N., & Wolf, D. (2015a). JAK1/2 inhibition impairs T cell functionin vitroand in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms. British Journal of Haematology, 169(6), 824– 833. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y., Shen, Q., Lai, Y., Park, S., Ou, X., Lin, D., Jin, M., & Zhang, W. (2018). Anti- inflammatory Effects of Curcumin in Microglial Cells. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).