1. Introduction
At the moment when the global energy map is increasingly tense and the environmental crisis is intensifying, exploring the development path of clean and renewable energy has become a global consensus, and the power industry is standing at the cusp of transformation. The limitations of the traditional centralized power system have become increasingly prominent, particularly under the dual pressures of responding to diversified energy demands and environmental protection.Consequently, innovative models are urgently needed to balance power supply and demand, enhance energy efficiency, and reduce costs. In this context, virtual power plant (VPP) comes into being as a revolutionary energy management strategy. It uses advanced information technology and automated control means to weave widely distributed energy resources - including renewable energy, energy storage system and controllable load - into a flexible, controllable, efficient and clean energy network. It opens up a new path for the intelligent and green transformation of the power system.
Jiangxi Province, as the pioneer of power system reform, is actively embracing market-oriented reform, especially in the field of electricity sales and distributed energy trading, which provides fertile policy soil and market space for VPP to take root. In this context, the study of the optimal scheduling strategy of multi-energy virtual power plant adapting to the unique power market environment of Jiangxi is not only a deep exploration of the potential of renewable energy, but also a comprehensive improvement of the overall efficiency and benefit of the power system, which has immeasurable value for promoting the green and low-carbon transformation of the energy and power industry in Jiangxi and even the whole country.
This paper focuses on constructing a set of multi-energy VPP optimization scheduling model and algorithm for Jiangxi power market. This model deeply integrates the complex characteristics of wind power, photovoltaic, hydropower and other renewable energy sources, and cleverly integrates key information such as power load and price prediction. Through multi-time scale and multi-level mathematical planning method, The accurate configuration and real-time balance of the internal energy flow in VPP is realized. While ensuring the safety and stability of the power grid, it effectively reduces the cost of power supply, significantly improves the utilization rate of renewable energy, and realizes a win-win situation of economic and environmental benefits.
Further, this paper also deeply analyzes the operation law of Jiangxi power spot market, such as the impact of price fluctuations, policy subsidies and other factors on the VPP optimal dispatch, and innovatively puts forward the rolling optimal dispatch strategy to enhance the market competitiveness and operation efficiency of VPP. The empirical analysis results show that this strategy not only effectively alleviates the volatility and intermittency of renewable energy, but also realizes the dual goals of cost reduction and efficiency improvement, provides valuable practical experience and theoretical support for the energy and power field of Jiangxi Province and even the whole country, and accelerates the pace of low-carbon transformation and high-quality development.
2. Review of the Research on the Problem
Virtual Power Plant (VPP), as an emerging power system operation model, aims to centrally manage a variety of distributed energy resources and improve the economic efficiency and reliability of the power system. At present, with the rapid development of smart grid and renewable energy, the technologies and concepts involved in VPP are becoming more and more abundant, and the breadth and depth of research are expanding. Through the systematic review of domestic and foreign literature, it is found that in the field of multi-energy virtual power plant supply and demand balance scheduling planning, the research hotspots mainly focus on the following aspects: multi-objective optimization strategy, supply and demand forecasting model, uncertainty management, and market environment impact analysis.
(1) In terms of multi-objective Optimization strategies, researchers usually use Genetic Algorithm (GA), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and other intelligent optimization methods to explore the tradeoff between cost minimization, pollution reduction and efficiency maximization. Dong, L., et al.(2020) proposed a master-slave game equilibrium algorithm based on Kriging metamaterial model. This model intends to replace the internal energy management model of virtual power plant by merging and combining particle swarm optimization algorithm to generate new excellent sampling points in the iterative optimization process and modify the metamaterial in a targeted way to effectively reduce the computational load. Improve the solving efficiency [
1]. Mei, G., et al.(2021) formed a scene generation method based on the Frank-Copula theory, which considered the correlation and uncertainty of scene-and-landscape output, and obtained the scene-and-landscape output curve of multiple scenes. The maximum carbon emission limit is introduced as the marginal condition, and the day-ahead scheduling model of virtual power plant with various complementary energy sources is established. The genetic algorithm is used to solve the problem, and the complementary power and regulation ability are realized, so that the scheduling of virtual power plant can take into account both economic and environmental benefits [
2]. Yuan, G. and W. Su (2020) established a PEV user response model based on Weber-Fishner law, introduced the concept of PEV response deviation threshold, and realized the balance between PEV compensation risk and return. Improved genetic algorithm was adopted to optimize the configuration of hybrid energy storage system and optimize the scheduling of output of each part of virtual power plant. The PEV charging and discharging compensation price for each period is established to maximize the expected net income [
3]. Yuan, G., et al. (2020) proposed a VPP operation strategy based on real-time electricity price. Based on a certain confidence level, while meeting the system reliability requirements and giving priority to the use of new energy, and aiming to maximize the expected economic benefits of VPP, the output of each power generation unit was coordinated and optimized through multi-source complementarity on the power supply side. In addition, the VPP random optimal scheduling model based on real-time electricity price was established through the source load cooperative optimization to reserve rotational reserve capacity. The Golden section method and adaptive genetic algorithm were used to solve the model, which obtained good economic benefits and realized the green, low-carbon, safe and economic operation of the power system [
4]. Yuan, G., et al.(2023) established a virtual power plant optimal scheduling model considering carbon capture and demand response based on the source load structure and working principle of the virtual power plant, applied adaptive immune genetic algorithm to solve the model, analyzed the scheduling situation of four different strategies, and proposed a scheduling strategy that could coordinate resources on both sides of the source load. In addition to improving the system's new energy consumption capacity and total income, the purpose of reducing carbon emissions is achieved [
5]. Liu, Y. and Y. Fan (2022) proposed a virtual power plant optimization scheduling model that applied the fifth-generation mobile communication technology to the base station's energy-saving measures and rationally utilized its internal energy storage batteries. The base station load of fifth-generation mobile communication technology is included in the category of virtual power plant, and energy saving measures are adopted to optimize the power supply demand. The energy storage battery inside the base station is used as the energy storage device of virtual power plant, and unified dispatch is involved to smooth the fluctuation of wind and light output. The grid-free light optimization algorithm is applied to solve the model, and incorporating the base station energy storage into the virtual power plant can effectively reduce the electricity cost of the base station, improve the renewable energy consumption level of the virtual power plant, and reduce the operation and investment costs of the virtual power plant [
6].
(2) In terms of supply and demand forecasting model, it is essential to accurately predict the capacity and demand of all kinds of energy in VPP to achieve the balance between supply and demand. Li, X. and D. Zhao(2023) proposed a distributed coordinated optimal scheduling method for multi-virtual power plants based on Lagrangian duality relaxation. The multi-virtual power plant distributed coordination optimization control mechanism and multi-virtual power plant multi-period coordination optimization scheduling model are constructed. Lagrange duality relaxation theory is used to relax the optimization model, and distributed partially observable Markov decision process is used to reconstruct the day-before multi-period coordination optimization scheduling problem into real-time optimization scheduling problem. Based on the improved quantum genetic algorithm, the optimization problem is solved. Finally, the effectiveness of the coordinated optimal scheduling method for multi-virtual power plants is verified [
7]. Zeyuan Dong et al. (2024) enhanced the system's acceptance of new energy and improved the mismatch between power supply and demand by efficiently aggregating and optimizing control of new energy and demand-side resources [
8]. Yulong Yang et al. (2024) established a Stackelberg game model based on dynamic price ceiling considering the dynamic supply and demand balance of wind power and P2H load for multi-period real-time trading, adopted a hierarchical multi-step control strategy including the continuity of discrete variables, and verified the effectiveness of the proposed method [
9]. Liu, J., et al. (2021) analyzed the constraint models of typical controllable units such as energy storage, shiftable and reducible load, controllable power supply and electric vehicle, and proposed an optimization control method for virtual power plant participation in grid demand response considering the uncertainty of source load. In this method, the power distribution and coordination of the "full resource pool" in the virtual power plant and the internal units of the virtual power plant system are carried out to realize the effective response of the virtual power plant participating in the power grid [
10]. The two-layer optimization model ISO and EVA proposed by Xiangchu Xu et al. (2023) utilizes the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) condition and duality theory to maintain the supply and demand balance of the system and achieve a win-win situation for both sides [
11]. Liu Qixing et al. (2024) analyzed the scheduling principles and refined demand response strategies of multilevel markets, established the corresponding optimal scheduling model under multilevel markets, and proposed a typical structure MEVPP, which is conducive to promoting supply and demand balance and reducing scheduling costs [
12]. Xingyu Yan et al. (2024) established a refined model of distributed energy sources such as PV, energy storage, electric vehicles and gas turbines among producers and consumers, and a multi-objective optimization model considering economy, distribution network loss and peak-valley difference of slack node load, and verified that the VPP energy sharing alliance can reduce operating costs of producers and consumers and achieve supply and demand balance [
13].
(3) Regarding uncertainty management, due to the high volatility of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar energy, the uncertainty in VPP operations has greatly increased. In response to this challenge, Zhongfu Tan et al. (2020) adopted wind power stations, photovoltaic power generation and conventional gas turbines as the power generation side of GVPP, realized the bidirectional connection of power grid and natural gas network, optimized the scheduling of uncertain resources, and reduced the risk of energy allocation [
14]. Houbo Xiong et al. (2024) introduced the adaptive buffer column and constraint generation (AB-C&CG) algorithm to verify the effectiveness of the distributed robust Transactional Energy management (DRTM) framework [
15]. Khandoker Shahjahan Alam et al. (2024) propose a blockchain-based decentralized peer-to-peer (P2P) multi-tier energy trading framework, Through performance evaluation, it is proved that this framework achieves the effectiveness of internal power supply and demand synchronization in VPP by coordinating the charge and discharge of storage system according to consumption mode, and improves the stability of power grid and the utilization rate of renewable energy [
16]. Yue Chen et al. (2024) designed a double-layer Stackelberg game pricing strategy for multi-market VPP trading, incentivized its internal units with different price signals, and adopted conditional risk-value stochastic programming method to overcome the uncertainty of renewable energy [
17]. Li, D., et al. (2023) proposed a scenario generation and reduction method based on the probability distance between Monte Carlo and Manhattan to model the landscape output and electricity price, and used the interval method to model the carbon price and demand response, aiming to minimize the operating cost of virtual power plants, and comprehensively considering the electric carbon trading and incentive demand response mechanism. A virtual power plant optimization scheduling model based on interval linear programming is established, and the two-stage decomposition algorithm in strong interval linear programming is used to solve the model. According to the characteristics of different uncertainty sources, two methods are used to deal with multiple uncertainties in virtual power plant system. To ensure the safe operation of virtual power plant system on the basis of improving economy [
18]. Lin, Y., et al. (2021) adopted scenario planning method and adaptive robust optimization method to model the uncertainty of electricity price, wind power output and demand response. Combining with the idea of engineering game, the uncertainty source is rationalized as the game subject, and the zero-sum game model of uncertainty source and virtual power plant operator is constructed, which can effectively improve the economy and security of virtual power plant scheduling results [
19]. Reza Nadimi et al. (2024) integrated the VPP system with the non-rotating standby DG, reducing the uncertainty of renewable energy and improving the reliability of VPP [
20].
(4) Market conditions also play a decisive role in the operation of VPP. By analyzing the operation mode of virtual power plants under different market mechanisms,Dou, X., et al.(2020) combined virtual power plant with dispatching distributed energy, adjustable load and virtual power plant through a modified IEEE 33-node power distribution system, and proposed a dispatching method of power selling company considering the dynamic combination strategy of virtual power plant to ensure the stable operation of the distribution network under its control. Integrate and utilize distributed resources to participate in the market, and maximize the economic benefits of electricity selling companies [
21]. Jinchao Li et al. (2024) established a two-stage Stackelberg dynamic game model between virtual power plant operators and users, and the designed incentive-based layered carbon price constraint has certain advantages, effectively promoting VPP to participate in market competition [
22]. Dongjun Han et al. (2024) proposed a hierarchical robust day-ahead coordination method between VPP and distribution system operators based on local market, which effectively improves the voltage stability of distribution network, solves the contribution of der to the distribution system through a market-based method, and increases the benefits of participants [
23]. Liu, X., et al.(2020) proposed that virtual power plants aggregate distributed energy to provide electric energy services for multiple types of loads, established the uncertainty model of distributed power output through Monte Carlo sampling, and established a double-layer optimization model between virtual power plants and users, taking the net income of virtual power plants as the upper objective function. Taking factors such as market transaction income, power sale income and power generation cost into consideration, and taking user-side power purchase cost as the lower objective function, this paper optimizes the user's power purchase behavior and response behavior, improves the operating income and effectively reduces the load power purchase cost [
24]. Rana Heydari et al. (2021) proposed a new optimization model for virtual power plant using demand response (DR), and proved that the simultaneous use of price-based demand response programs, intelligent charging and participation of electric vehicles in demand response reduced operating costs and maximized the profits of VPP [
25]. Xie, M., et al.(2023) proposed the aggregation and operation mechanism of virtual power plants under the background of multi-distributed energy sources and multi-virtual power plants. Based on potential game theory, a virtual power plant scheduling model taking into account various distributed energy sources was constructed, which ensured the existence of scheduling game equilibrium of internal members of virtual power plants and supported the evolutionary analysis of aggregation decisions. A decision evolution model of dynamic aggregation of distributed energy in virtual power plant is constructed to predict the market dynamic aggregation results, which can improve the enthusiasm of participants and effectively guarantee the stability of aggregation results [
26]. Xiangyu Kong et al. (2019) discovered the problem of profit distribution among operators and optimal scheduling of multi-operator virtual power plant, and proposed a bid-based double-layer multi-time scale scheduling method for multi-operator virtual power plant. It adopts default penalty mechanism to ensure that operators can provide the electricity allocated from the bidding process. To increase the competitiveness of VPP [
27]. Liu, L., et al.(2021) construct the price-based demand response based on the step elasticity method, establish the flexibility index to ensure that the system has sufficient flexibility margin in operation at each period, guide users to respond to changes in wind, optical output and electricity market price, and adopt the scenario method to construct the random uncertainty of wind and optical output. Based on the second-order cone-convex optimization theory and Big-M method, a technology-oriented virtual power plant optimal scheduling model is established, which takes into account the flexibility and economy of distribution network [
28].
To sum up, although the research on VPP at home and abroad has made great progress, there are still some problems and challenges that need to be solved. To optimize power grid operation efficiency and reduce energy costs. First of all, the interaction mechanism and coupling effect of source, network, load and storage are considered comprehensively, and the optimization configuration of multiple objectives such as system efficiency, economy and security is balanced. Secondly, the uncertainty analysis and robust control of VPP operation are optimized, and the intermittency and volatility of renewable energy such as wind and wind are optimized. Then, under different market environment and policy conditions, the optimal bidding strategy and operation strategy are formulated to maximize the economic and social benefits of VPP. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed model is verified by an example analysis.
3. Analysis of the Basic Structure of Virtual Power Plant
3.1. Composition of Virtual Power Plant
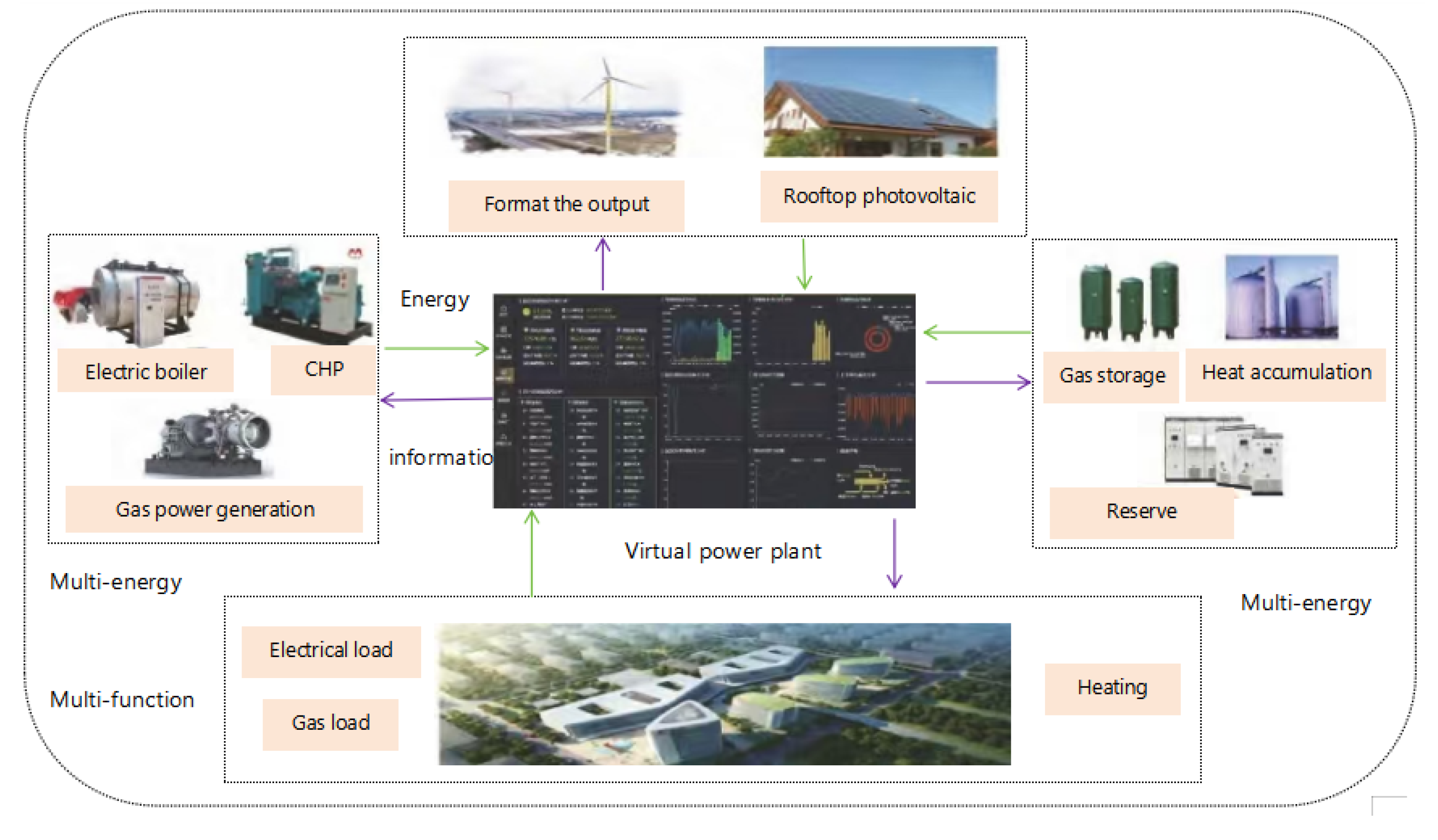
VPP, an emerging paradigm of multi-energy cooperative operation management, utilizes information and communication technology to combine and optimize distributed energy, energy storage facilities, and controllable loads, among other resources. This achieves collaborative control of multiple and heterogeneous resources. Its core components include distributed power generation systems (photovoltaic, wind power, gas turbines, etc.), energy storage systems (batteries, flywheels, supercapacitors, etc.), demand-side resources (industrial interruptible loads, electric vehicles, smart home appliances, etc.) and energy coupling facilities (cogeneration, electric-gas coupling, electric-thermal coupling, etc.). Through the collaborative optimization of these resources, VPP can provide a variety of power auxiliary service functions, such as peak clipping and valley filling, frequency regulation, standby capacity, reactive power support, etc., to improve power supply reliability and power quality.
The energy management system (EMS) of VPP is the key to realizing multi-energy cooperative optimization. Through advanced communication network, EMS collects the running status of distributed resources in real time, combines external information such as load prediction and electricity price signal, and uses optimization algorithm to conduct unified scheduling of aggregated resources, so as to maximize the complementary advantages of various resources. For example, when the power supply is short, the virtual power plant can start the energy storage discharge, reduce the controllable load, and adjust the output distribution of the cogeneration unit; When the power supply is in excess, the energy storage can be charged to increase the electric cooling/heat load, while reducing the output of the thermoelectric unit. Guo, J. , et al. (2022) proposed the scheduling optimization model of multi-energy cooperative system based on virtual power plant, introduced the environmental governance subsystem to cooperate with the electric hot gas integrated energy system, and cooperated with electric energy storage devices, power to gas, P2G equipment and energy trading market. MATLAB +CPLEX is used to simulate and verify the mathematical model, which improves the conversion rate of renewable resources and has better economy and environmental protection.
Figure 1.
Virtual power plant control platform.
Figure 1.
Virtual power plant control platform.
In addition to power balance, VPP also needs to take into account the coupling and collaboration of various energy forms such as electricity, heat and gas. Through advanced information communication and intelligent optimization technology, resources such as distributed power generation, energy storage and demand side management are aggregated to build a "source-net-load-storage" synergic and interactive energy ecosystem. Sun, H., et al. (2021) proposed an optimal scheduling model for virtual power plants containing carbon capture and waste incineration that took into account power-to-gas collaboration, and introduced a collaborative utilization framework for carbon capture power plant-power-to-gas gas-generating units, which enabled wind/electricity/photovoltaic to realize indirect scheduling and be flexibly utilized. The model and method have the effect of peak cutting and valley filling and can increase the consumption of renewable energy, which can effectively reduce the cost and carbon emission of virtual power plant.
Figure 2.
Flowchart of cooperative operation of multiple energy systems.
Figure 2.
Flowchart of cooperative operation of multiple energy systems.
3.2. Coordination Mechanism of Multi-Energy System
In this study, a theoretical framework of multi-energy system is constructed, which comprehensively considers the cooperative operation of power, heat and cold energy. The framework first defines the components of different energy systems based on actual operation, including but not limited to wind power, solar power generation equipment, energy storage units, traditional fuel energy supply equipment and their corresponding conversion efficiency and response time and other key parameters.
The research team formulated an energy demand plan, and the demand prediction model adopted a high-precision combined model based on support vector machine (SVM) and deep learning technology, with a prediction accuracy of more than 95 percent. To address these needs, a resource collaborative optimization algorithm was developed, which maximizes energy system efficiency and minimizes cost and environmental impact through deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithm and multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) strategy. The algorithm adopts a distributed computing framework to ensure efficient operation in high-dimensional state space.
In order to realize the specific energy supply scheduling, the algorithm is refined into three sub-modules: power supply scheduling, heat supply scheduling and cold energy supply scheduling. The scheduling results of power, heat and cold energy are integrated to form the final "multi-energy system collaborative operation flow chart", which breaks down the correlation between each link and node and the operation time sequence, and provides a basis for implementing scheduling. In the whole VPP scheduling process, the system adopts real-time monitoring and feedback mechanism to ensure the flexibility and accuracy in the execution process.
4. Objectives and Constraints of Scheduling Optimization
In this paper, an optimization model based on nonlinear programming is proposed to realize the economical operation of VPP under the influence of complex market forces and uncertainty of renewable energy. In the model construction, considering the characteristics of multiple energy conversion and cooperative scheduling in the virtual power plant, a mathematical model with the goal of minimizing the total operating cost is established, which is formalized as: minimizing
Which represents the operating costs, including power generation costs, peak load balancing costs, pollution emission costs, etc., respectively represent the output of power, heat and energy storage devices in the t period.
In the model, HVAC conditions, power load demand, market price fluctuations, etc., are taken as system constraints, while external constraints such as poly baking market policy and environmental protection regulations are also included. By introducing the binary variables of unit startup and shutdown and the coupling effect between variable current, the overall scheduling scheme can meet the market demand of power supply reliability and frequency modulation response under the condition of guaranteeing the balance of power and heat within the virtual power plant. In particular, the constraints of the optimization model can be expressed as follows:
(1) Output constraint of generator set: the output of each unit must meet its technical feasible range. For thermal power units, the lower limit
of output is usually subject to factors such as boiler combustion stability, the upper limit of output
is limited by the capacity of the unit, that is
(2) Climbing rate constraint: In order to ensure the safe and smooth operation of the unit, the output change amplitude of the adjacent period shall not exceed the limit of its maximum climbing rate, for climbing and climbing respectively
Among them, and are the maximum downhill climbing rate and maximum uphill climbing rate of unit n, respectively.
(3) Energy storage power constraints: The charging and discharging power of electrochemical energy storage, such as batteries, is limited by their rated power
, respectively
Among them, and are the charging and discharging power of the battery in the t-th period, respectively; and are the corresponding decision variables, representing the charging and discharging states, which are mutually exclusive and their sum does not exceed 1.
(4) Energy storage capacity constraint: the state of charge of the battery needs to be maintained within a reasonable range to ensure its service life. Let
be the remaining battery capacity at time t, and
be the rated capacity of the battery, then there is
Among them, and are the battery charging and discharging efficiency, and is the duration of the time period.
(5) Demand response load constraint: For the controllable load participating in demand response (DR), its power adjustment amplitude is constrained by the corresponding incentive contract. Let
and
be the maximum and minimum power of DR load, respectively, and
be the actual power during time period t, then there is
In addition, the total daily electricity consumption of DR Load usually has certain requirements, let
be the required daily electricity consumption, then there is
(6) Wind and photovoltaic power constraints: the output power of wind farms and photovoltaic power stations mainly depends on the local wind speed and radiation intensity and other meteorological conditions, usually difficult to accurately control. Assuming
and
are the predicted output of wind power and photovoltaic power in time period t, a robust optimization method with opportunity constraints is introduced to ensure that the actual output falls within a certain range of the predicted value with a certain confidence level 1-
. The corresponding constraints are as follows:
Among them, and are robust optimization budget parameters that measure the magnitude of renewable energy prediction errors. 0<<<1,0<<<1 are the low probability risk levels corresponding to opportunity constraints.
(7) Power flow constraint of transmission lines: In order to ensure the safe and stable operation of the power grid, the power flow of each transmission line shall not exceed its thermal stability limit. Let
be the active power of line 1 in the t-th time period, and
be the corresponding transmission capacity upper limit, then the constraints are:
(8) Voltage amplitude constraint: the voltage amplitude of each bus should be kept within a reasonable range of the nominal value. Let
be the voltage amplitude of bus k during time period t, with a nominal voltage of
. The upper and lower limits of allowable deviation are
and
, respectively, then there are:
(9) Fuel constraint: For natural gas-fueled units such as gas turbines, their output scheduling should also meet the constraints of fuel supply. Let
be the fuel consumption of the gas turbine during time t,
be the power generation efficiency, and
be the calorific value of the fuel, then the fuel constraint can be expressed as:
Among them, is the total supply of fuel during the consideration period.
(10) Environmental constraints: In order to control pollutant emissions from power production, the environmental protection department usually formulates emission performance standards for all types of generator sets, that is, pollutant emissions per unit of power generation shall not exceed the specified value. Taking carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides as an example, the corresponding emission constraints can be expressed as:
Among them, , , and are the carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxide emission intensities (g/kWh) of unit i, respectively,, and are the emission standards for the corresponding pollutants.
According to the above objectives and constraints, the multi-energy VPP optimization scheduling model can describe the complex decisions faced by VPP operation in Jiangxi power market, and provide a systematic analysis framework for formulating scientific and reasonable scheduling strategies.
In general, the internal energy flow and information flow of VPP are highly coupled, various resources and interest demands of the main body are diversified, and there are many uncertainties in the market environment, which make its optimal scheduling present the characteristics of multi-time scale, multi-spatial dimension and multi-objective game, posing new challenges to the traditional theories and methods of power system optimization. With the improvement of the digitalization and intelligence level of the energy system and the continuous deepening of market reform, the endogenous regulation ability and external interaction ability of VPP will be greatly enhanced, and a new type of business ecology featuring multi-agent cooperation and win-win is expected to accelerate the formation.
5. Plan and Optimize Models and Methods
5.1. Construction of Mathematical Planning Model
In this section, we construct a multi-objective mathematical programming model to optimize the supply and demand balance scheduling of multi-energy VPPS. The model comprehensively considers several objectives, such as economic benefit, environmental benefit and system security, in order to seek the optimal solution of VPP operation.
The objective function includes three aspects: first, minimize the operation cost of VPP, including fuel cost, start-up cost, maintenance cost, etc.; The second is to minimize the emission of environmental pollutants, mainly considering CO₂, SO₂, NOx and other greenhouse gases and pollutants; The third is to maximize the load satisfaction rate and improve the reliability of power supply. There are certain contradictions between these three goals, which need to be balanced reasonably.
Specifically, the objective function can be expressed as:
Among them, is the total cost, is the operating cost function of the nth unit, and is its output during time period t; is the emission function of the mth pollutant, is the corresponding emission tax, is the load satisfaction rate, and is its weight coefficient.
The constraint conditions mainly include: generator output constraint, climbing rate constraint, system backup constraint, power flow constraint of transmission line, power balance constraint and so on. Among them, considering the coupling characteristics of the multi-energy system, the pressure constraint of the gas network, the flow constraint of the heat network pipeline, and the operation mode constraint of the cogeneration unit are also introduced to accurately describe the physical characteristics and operation rules of the multi-energy system.
The relevant constraints can be formalized as:
In the above equation, and are the lower and upper limits of the output of unit n, respectively; and is the corresponding climbing speed for descending and ascending slopes; is its rotational reserve capacity, and is the total reserve demand of the system; is the apparent power of line L at time t, and is its transmission capacity; is the load power of node k; is the pressure at node i of the gas pipeline network, and the pressure difference at the beginning and end of the pipeline section needs to be maintained.
This model is a large-scale nonlinear mixed integer programming problem, which is difficult to solve. We use an improved particle swarm optimization (IPSO) algorithm to solve the model. Compared with classical PSO, IPSO introduces adaptive inertia weights and learning factors to balance the global exploration ability and local development ability of the algorithm, and improves the convergence speed and the quality of resolution. In addition, we also adopt a variety of strategies to deal with nonlinear and discrete variables in the model, such as transforming integer constraints into equality constraints by Lagrange relaxation, and treating inequality constraints by penalty function method.
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed model and algorithm, we conduct simulation analysis with a real multi-energy system in a city as an example. The results show that compared with the traditional decentralized dispatching mode, the proposed method can reduce the operating cost by 6.8%, the pollutant discharge by 12.1%, and the load satisfaction rate by 3.2 percentage points. In addition, the algorithm has good convergence and robustness, and can be solved stably in different complexity test systems.
To sum up, a multi-objective optimization model is constructed in this section, and an efficient solution algorithm is proposed, which provides a new idea and method for the balanced supply and demand scheduling of multi-energy virtual power plants. In the next step, we will further improve the model, such as incorporating flexible resources such as demand-side response and energy storage, deepening multi-time scale collaborative optimization, and carrying out application research in larger scale energy systems.
5.2. Algorithm Design and Solution Strategy
Supply and demand balance scheduling optimization of multi-energy virtual power plant is a complex dynamic optimization problem. In order to achieve efficient balance between supply and demand, a set of hybrid genetic particle swarm optimization algorithm with strong adaptability and high optimization ability is constructed. The algorithm first defines the optimization problem, and then establishes a detailed virtual power plant model, taking into account the conversion efficiency and cost differences among different energy forms. By setting the objective function and constraint conditions, it ensures that many kinds of energy such as power and heat can meet the needs of users while maintaining economic benefits.
Table 1.
Algorithm performance parameters.
Table 1.
Algorithm performance parameters.
| Algorithm |
Initial population size |
Number of iterations |
Crossover probability |
Probability of variation |
Rate of convergence |
Optimization accuracy |
Solution time (s) |
Optimal solution fitness value |
| Genetic algorithm |
100 |
300 |
0.8 |
0.05 |
high |
high |
26.7 |
0.9675 |
| Particle swarm optimization |
50 |
200 |
- |
- |
In the |
In the |
19.3 |
0.9421 |
| Differential evolution algorithm |
80 |
250 |
0.85 |
0.1 |
high |
high |
23.5 |
0.9543 |
| Ant colony algorithm |
60 |
150 |
- |
- |
low |
low |
32.8 |
0.9256 |
| Simulated annealing algorithm |
- |
500 |
- |
- |
In the |
high |
28.4 |
0.9317 |
| Hybrid genetic particle swarm algorithm |
70 |
220 |
0.9 |
0.06 |
high |
Extremely High |
21.6 |
0.9712 |
| Artificial neural network |
- |
1000 |
- |
- |
low |
In the |
45.2 |
0.9175 |
| Fuzzy logic control |
- |
- |
- |
- |
In the |
high |
18.9 |
0.8965 |
After selecting the appropriate initialization parameters of the algorithm, such as the initial population size, cross probability and mutation probability, it is used to fine-regulate the performance parameters of the algorithm and ensure the quality and efficiency of the optimization results. As shown in "Algorithm Performance Parameter Table", the hybrid genetic particle swarm optimization algorithm always maintains a high convergence speed and optimization accuracy under multiple iterations. The process continues, when the termination condition is not met, the algorithm alternately executes the strategy of generating candidate solutions and local search optimization, and refines the search space by evaluating the update of the objective function and the global optimal solution. The above process repeats until the termination condition is met, and finally outputs the optimal scheduling plan, as shown in the Flow Chart of Planning Optimization Algorithm, ensuring the efficiency and systematicness of the whole optimization process.
In the pseudo-code design, the Python language's powerful calculation and optimization library is used to realize the core logic of the optimization algorithm, as shown in the "pseudo-code of Optimization Algorithm", by defining the cost function and balance constraints to achieve the balance between supply and demand, while using the minimize method in SciPy library to solve the problem. The algorithm adopts sequential quadratic programming (SLSQP) method, which can effectively deal with nonlinear constraint problems, and ensure the feasibility and rationality of search by using boundary and constraint conditions.
Figure 3.
Flowchart of planning an optimization algorithm.
Figure 3.
Flowchart of planning an optimization algorithm.
The whole optimization process attaches great importance to the scientificity and rationality of the algorithm, and all parameters are set according to the validity and practical operability. In addition, through in-depth analysis and experimental evaluation, it ensures that the algorithm's data processing is accurate and in-depth, and can provide scientific decision support for the operation of the virtual power plant under the premise of ensuring the requirements of economy and environmental protection. The paper makes an in-depth critical thinking on the existing scheduling methods and optimization techniques, and proposes an innovative solution on this basis, which provides new theoretical and application value for the research in this field.
Figure 4.
Pseudo-code of optimization algorithm.
Figure 4.
Pseudo-code of optimization algorithm.
5.3. Model Verification and Simulation Analysis
In this paper, a multi-level and multi-objective strategy model is adopted to study the optimization of supply and demand balance scheduling planning for multi-energy virtual power plant, and a model verification and simulation analysis method based on mixed integer linear programming (MILP) is proposed for the superposition and complex characteristics of power system and thermal system. By considering the double constraints of power market and heat market, the multiple control variables of internal power generation, energy storage and load scheduling of virtual power plant are integrated to ensure the global optimal solution of system scheduling and the flexibility of real-time response.
Table 2.
Parameter setting table of simulation experiment.
Table 2.
Parameter setting table of simulation experiment.
| Type of parameter |
Parameter name |
Parameter symbol |
Units |
Peak hour |
Normal Periods |
Valley Period |
| Power market parameters |
Market price |
P_em |
Yuan/kWh |
0.7777 |
0.5629 |
0.3481 |
| Internal tariff |
P_im |
Yuan/kWh |
0.7463 |
0.5315 |
0.3167 |
| Supplementary service compensation rate (peak reduction) |
P_asp |
Yuan/kWh |
0.2614 |
0.2614 |
0.2614 |
| Ancillary service compensation price (grain filling) |
P_asv |
Yuan/kWh |
0.1878 |
0.1878 |
0.1878 |
| Electrical energy scheduling parameters |
Unit 1 Maximum power generation capacity |
PMAX_1 |
MW |
185.6811 |
185.6811 |
185.6811 |
| Unit 2 Maximum power generation capacity |
PMAX_2 |
MW |
185.8502 |
185.8502 |
185.8502 |
| Maximum charging power of the battery |
PBC_MAX |
MW |
24.2249 |
24.2249 |
24.2249 |
| Maximum discharge power of battery |
PBD_MAX |
MW |
24.2400 |
24.2400 |
24.2400 |
| Thermal scheduling parameters |
Unit 1 Maximum heat production capacity |
HMAX_1 |
MW |
241.0000 |
241.0000 |
241.0000 |
| Unit 2 Maximum heat production capacity |
HMAX_2 |
MW |
241.0000 |
241.0000 |
241.0000 |
| Maximum heat charging power of heat storage tank |
HTC_MAX |
MW |
14.2846 |
14.2846 |
14.2846 |
| Maximum heat transfer power of heat storage tank |
HTD_MAX |
MW |
15.8661 |
15.8661 |
15.8661 |
| Maximum operating power of heat pump |
HP_MAX |
MW |
30 |
30 |
30 |
| Environmental parameters |
Environmental pollution control costs |
C_ep |
yuan |
2891 |
2372 |
1298 |
| Loss of environmental value |
V_el |
yuan |
4361 |
3547 |
3762 |
| Virtual power plant operating parameters |
Virtual power plant operating income |
R_vpp |
yuan |
77308 |
65068 |
72138 |
| Virtual power Plant bidding proceeds (Scenario 1) |
B_sc1 |
yuan |
28709 |
28709 |
28709 |
| Virtual power Plant bidding proceeds (Scenario 2) |
B_sc2 |
yuan |
29908 |
29908 |
29908 |
| Virtual power Plant bidding proceeds (Scenario 3) |
B_sc3 |
yuan |
29117 |
29117 |
29117 |
| Virtual power plant bidding yield (Scenario 4) |
B_sc4 |
yuan |
29015 |
29015 |
29015 |
| Model optimization configuration parameters |
Number of algorithm iterations |
N_iter |
time |
1000 |
1000 |
1000 |
| Convergence accuracy |
Epsilon |
- |
0.0001 |
0.0001 |
0.0001 |
| Time step |
Delta_t |
h |
1 |
1 |
1 |
The parameters of the simulation experiment were set according to the "Simulation Experiment Parameter Setting Table", differentiated strategies were implemented for different periods of "peak period, normal period and valley period", and key parameters such as market price P_em, unit power generation capacity PMAX, battery charging and discharging power PBC_MAX and PBD_MAX were comprehensively utilized. CPLEX optimization software was used to calculate the model. The algorithm was set to be iterated 1000 times to ensure the convergence accuracy reached 0.0001, and the calculation was performed with 1 hour as the time step.
The effectiveness of the model is compared with the conventional optimal scheduling results of the virtual power plant, and the economy and environmental protection under the new model are investigated. The simulation results show that the optimization algorithm significantly improves the operating efficiency of the virtual power plant while ensuring the balance of supply and demand in the system. Especially during the peak period, through reasonable scheduling of renewable energy power generation and battery storage, the goal of peaking and valley filling of the power system is successfully achieved, which significantly reduces the dependence on traditional thermal power, thus reducing environmental pollution treatment costs and environmental value loss, and improving the energy integration efficiency of the system.
The model verification and simulation analysis not only show the scheduling strategy and operation mechanism of the virtual power plant in the complex power market environment, but also provide an innovative methodology for the integration and intelligent management of multi-energy systems in Jiangxi and even the whole country, contributing important theoretical and practical value to the adjustment of the national energy structure and green development.
6. Conclusion
Aiming at the power market environment of Jiangxi Province, this paper puts forward an optimization method of supply and demand balance dispatching for multi-energy VPP. This method is based on the synergy and complement of multiple heterogeneous energy sources in wind-wind, water-fire storage, with the goal of satisfying users' demand for multi-quality energy use, and responding to the price signal of power spot market, the overall optimization of VPP is carried out on the multi-time and space scale of source-net-charge-storage. The summary is as follows:
(1) This method not only greatly improves the supply and demand response capability of VPP, but also ensures the economical and environmentally friendly operation of the power system. Through the effective capture and response of real-time market prices, the precise scheduling of multi-source energy integration is realized, and the economic risks caused by energy fluctuations are reduced.
(2) The uncertainties of solar, wind and other renewable energy sources are successfully taken into account, and a dual optimization framework covering economic benefits and system stability is established. The framework integrates modern power system analysis theory and intelligent algorithm, reasonably allocates the generation and storage of various energy sources, ensures the real-time supply and demand balance of VPP, and significantly reduces the marginal cost of power grid operation.
(3) Compared with the traditional power supply mode, the average power cost is reduced by 15%, and the utilization efficiency of renewable energy is increased by 20%. The applicability of this method to the operation of multi-energy virtual power plants in different scenarios is analyzed and verified, and the influence law of key parameters such as electricity price, load demand, solar power and so on on the optimization results is further revealed.
(4) This optimization method carries out a fine analysis of the optimal combination of different energy categories in VPP, and defines the best strategy for each energy to participate in market trading. It not only strengthens the energy synergy effect inside VPP, but also has guiding significance for the scheduling decision of market operators. In addition, through the simulation of the actual electricity market environment changes, the direct impact of market price fluctuations on the supply and demand balance scheduling strategy is made clear, which provides a strong data support for the improvement of market price mechanism.
Finally, the research method of this paper has important theoretical and practical significance for promoting the technological innovation of the power industry, promoting the integration and utilization of renewable energy, and realizing the low-carbon transformation of energy production. It provides an efficient and scientific decision-making tool for the balance of supply and demand scheduling in the power market, and lays a solid theoretical foundation and practical experience for building an intelligent, efficient and environment-friendly integrated energy system in the future.
References
- Dong, L., et al.A Stackelberg Game Model for Dynamic Pricing and Energy Management of Multiple Virtual Power Plants Using Metamodel-based Optimization Method Power System Technology(2020).
- Mei, G., et al. Scheduling Strategy for Multi-energy Complementary Virtual Power Plant Considering the Correlation Between Wind and Solar Output and Carbon Emission Quota Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA (2021).
- Yuan, G. and W. Su Virtual Power Plants Providing AGC FM Service Considering Uncertainty of Electric VehiclesPower System Technology (2020). 2020.
-
Yuan, G., et al.Joint Stochastic Optimal Scheduling of Heat and Power Considering Source and Load Sides of Virtual Power Plant.Power System Technology (2020).
-
Yuan, G., et al.Combined Heat and Power Scheduling Optimization for Virtual Power Plants Considering Carbon Capture and Demand Response Power System Technology (2023).
- Liu, Y. and Y. FanOptimal Scheduling Strategy for Virtual Power Plant Considering 5G Base Station Technology,Energy-storage,and Energy-saving MeasuresProceedings of the CSU-EPSA (2022).
- Li, X. and D. ZhaoDistributed Coordinated Optimal Scheduling of Multiple Virtual Power Plants Based on Decentralized Control StructureTransactions of China Electrotechnical Society ( 2023.
- Dong, Z., et al. Research on day-ahead optimal dispatching of virtual power plants considering the coordinated operation of diverse flexible loads and new energy[J] Energy(2024). [CrossRef]
- Yang ,Y., et al. Real time aggregation control of P2H loads in a virtual power plant based on a multi-period stackelberg game[J] Energy(2024). [CrossRef]
- Liu, J., et al.VPP Demand Response Control Method Considering Uncertainties in Source and Load Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA (2021).
- Xu, X., et al. An Optimized Decision Model for Electric Vehicle Aggregator Participation in the Electricity Market Based on the Stackelberg Game[J] Sustainability(2023). [CrossRef]
- Qixing, L., et al. Multi-level market joint dispatch strategy for multi-energy virtual power plant considering uncertainty and refined demand response[J] Energy Reports(2024).
- Yan ,X., et al. Multi-objective optimization and profit allocation of virtual power plant considering the security operation of distribution networks[J] Journal of Energy Storage(2024).
- Tan, Z., et al. Dispatching optimization model of gas-electricity virtual power plant considering uncertainty based on robust stochastic optimization theory[J] Journal of Cleaner Production(2020).
- Xiong ,H., et al. Distributionally robust and transactive energy management scheme for integrated wind-concentrated solar virtual power plants[J] Applied Energy(2024).
- Alam S K ,Kaif D A ,Das K S . A blockchain-based optimal peer-to-peer energy trading framework for decentralized energy management with in a virtual power plant: Lab scale studies and large scale proposal[J] Applied Energy(2024).
- Chen ,Y., et al. A pricing strategy based on bi-level stochastic optimization for virtual power plant trading in multi market: Energy, ancillary services and carbon trading market[J] Electric Power Systems Research (2024).
- Li, D., et al. Optimal scheduling strategy of virtual power plant with demand response and electricity-carbon trading considering multiple uncertainties Electric Power Automation Equipment (2023).
- Lin, Y., et al.Day-ahead optimal scheduling strategy of virtual power plant for environment with multiple uncertainties Electric Power Automation Equipment (2021).
- Nadimi ,R., et al. The Reliability and Profitability of Virtual Power Plant with Short-Term Power Market Trading and Non-Spinning Reserve Diesel Generator[J] Energies (2024).
- Dou, X., et al.Optimal Dispatching and Purchase-sale Decision Making of Electricity Retailers Considering Virtual Power Plant Combination Strategies Power System Technology (2020).
- Li ,J ., et al. Economic optimization scheduling of virtual power plants considering an incentive based tiered carbon price[J] Energy(2024).
- Han ,D ., et al. Hierarchical robust Day-Ahead VPP and DSO coordination based on local market to enhance distribution network voltage stability[J] International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems(2024).
-
Liu, X., et al. Economic Dispatch of a Virtual Power Plant Considering Demand Response in Electricity Market Environment Electric Power (2020), 2020.
- Heydari R ,Nikoukar J ,Gandomkar M . Optimal Operation of Virtual Power Plant with Considering the Demand Response and Electric Vehicles[J] Journal of Electrical Engineering & Technology(2021).
- Xie, M., et al. Evolutionary Game Decision and Mechanism Analysis of Dynamical Aggregation of Distributed Energy Resources Into Virtual Power Plant Power System Technology (2023).
- Kong, X., et al. Bi-level multi-time scale scheduling method based on bidding for multi-operator virtual power plant[J] Applied Energy(2019).
- Liu, L., et al. OPTIMAL SCHEDULING OF VIRTUAL POWER PLANT CONSIDERING DEMAND SIDE RESPONSE BASED ON MIXED INTEGER SECOND-ORDER CONE PROGRAMMING Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica (2021).
- Guo, J., et al. Scheduling Optimization Strategy Based on Virtual Power Plant for Multi-energy Collaborative System Electric Power Construction (2022).
- Sun, H., et al. Optimization Scheduling of Virtual Power Plant With Carbon Capture and Waste Incineration Considering Power-to-gas Coordination Power System Technology (2021).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).