Submitted:
10 August 2024
Posted:
13 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
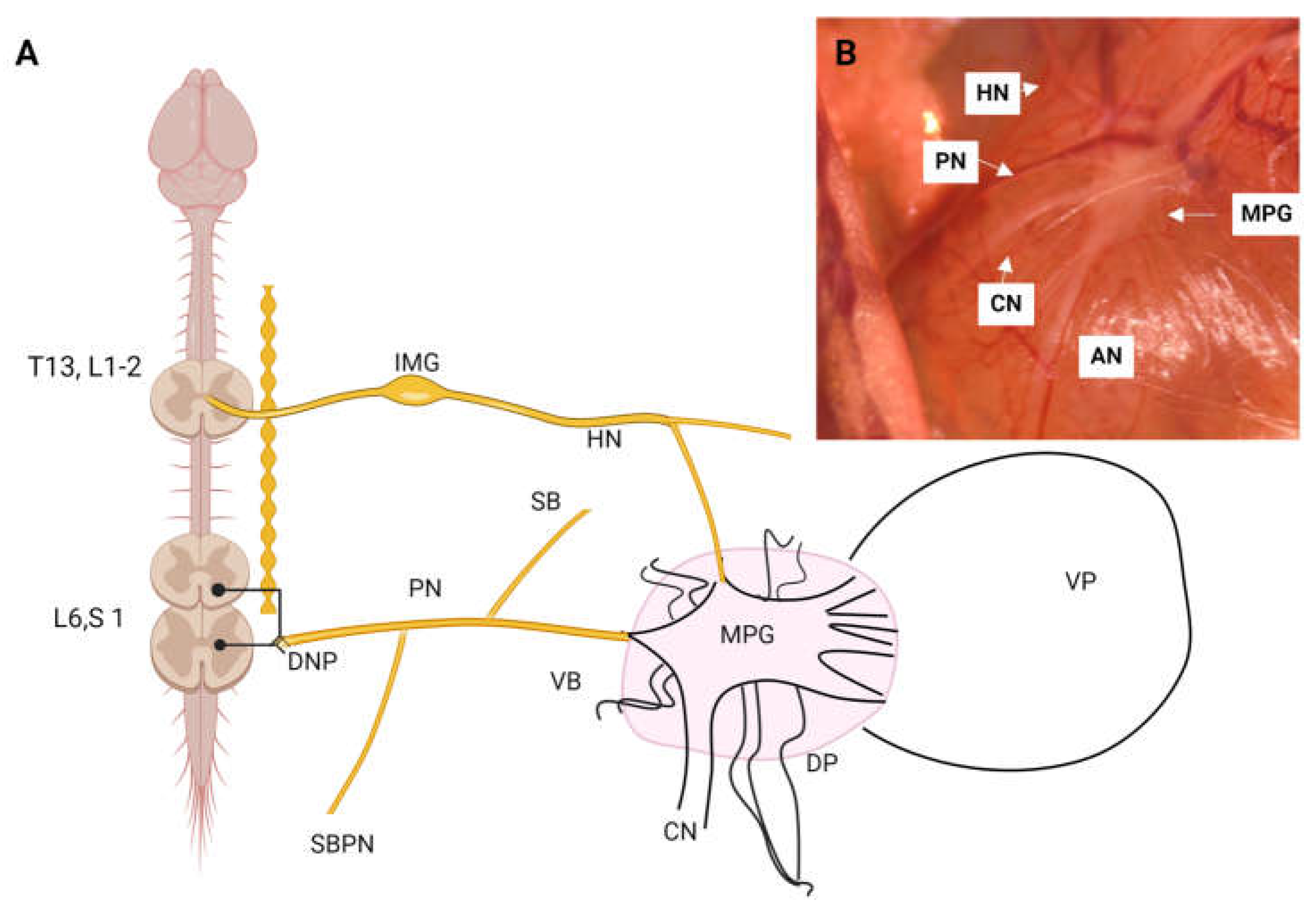
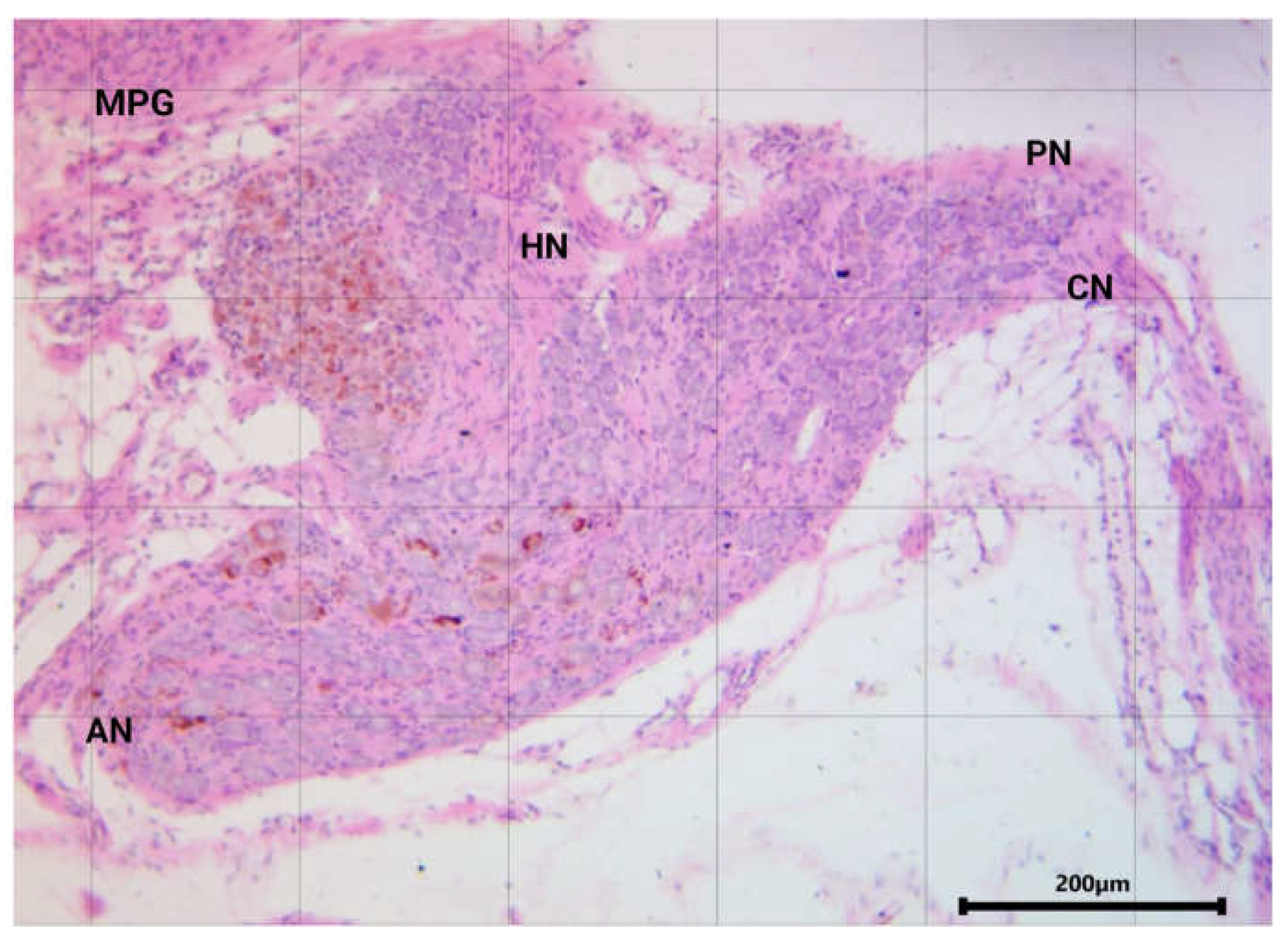
General Overview and Anatomical Organization
Preganglionic and Postganglionic Connections
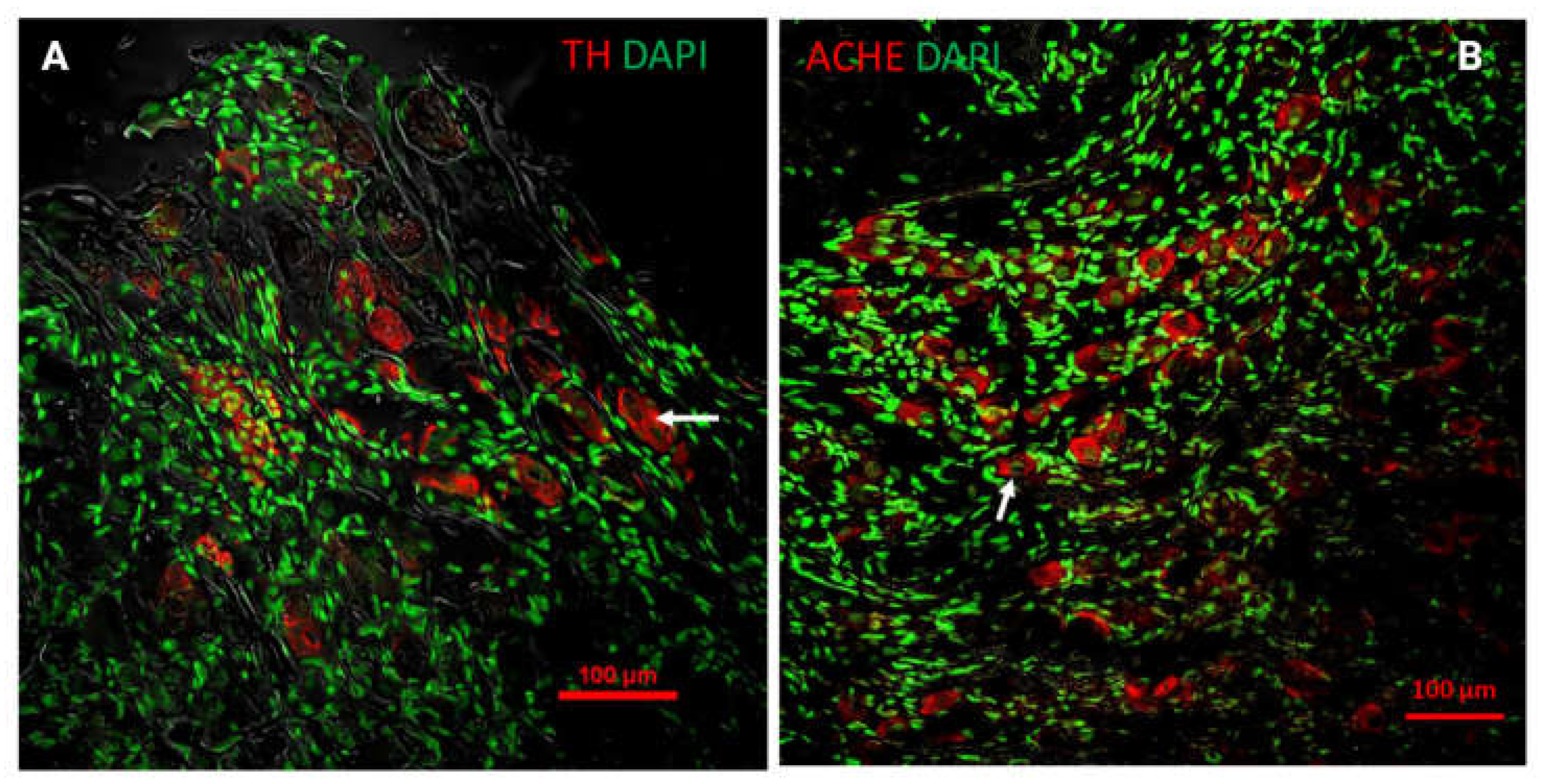
Neurotransmitters and Receptors in the Pelvic Plexus
Hormonal Regulation in the Pelvic Ganglia
2. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bradley WE, Teague CT. The Pelvic Ganglia. J Urol. 1968;100(5):649-652. [CrossRef]
- Keast JR. Plasticity of Pelvic Autonomic Ganglia and Urogenital Innervation. Int Rev Cytol. 2006;248:141-208. [CrossRef]
- Keast JR. Visualization and immunohistochemical characterization of sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons in the male rat major pelvic ganglion. Neuroscience. 1995;66(3):655-662. [CrossRef]
- Crowcroft PJ, Szurszewski JH. A study of the inferior mesenteric and pelvic ganglia of guinea-pigs with intracellular electrodes. J Physiol. 1971;219(2):421-441. [CrossRef]
- Gianduzzo TRJ, Colombo JR, El-Gabry E, Haber GP, Gill IS. Anatomical and Electrophysiological Assessment of the Canine Periprostatic Neurovascular Anatomy: Perspectives as a Nerve Sparing Radical Prostatectomy Model. J Urol. 2008;179(5):2025-2029. [CrossRef]
- Paxinos G. The Rat Nervous System. The Rat Nervous System. Published online May 4, 2004:1-1309. [CrossRef]
- Dowling P, Ranson RN, Santer RM. Age-associated changes in distribution of the P2X2 receptor in the major pelvic ganglion of the male rat. Neurosci Lett. 2006;404(3):320-323. [CrossRef]
- Keast JR, de Groat WC. Immunohistochemical characterization of pelvic neurons which project to the bladder, colon, or penis in rats. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1989;288(3):387-400. [CrossRef]
- Keast JR, Booth AM, de Groat WC. Distribution of neurons in the major pelvic ganglion of the rat which supply the bladder, colon or penis. Cell Tissue Res. 1989;256(1):105-112. [CrossRef]
- Wanigasekara Y, Kepper ME, Keast JR. Immunohistochemical characterisation of pelvic autonomic ganglia in male mice. Cell Tissue Res. 2003;311(2):175-185. [CrossRef]
- Purinton PT, Oliver JE. Spinal cord origin of innervation to the bladder and urethra of the dog. Exp Neurol. 1979;65(2):422-434. [CrossRef]
- Langworthy OR. Commissures of autonomic fibers in the pelvic organs of rats. Anat Rec. 1965;151(4):583-587. [CrossRef]
- Arellano J, Xelhuantzi N, Mirto N, Hernández ME, Cruz Y. Neural interrelationships of autonomic ganglia from the pelvic region of male rats. Auton Neurosci. 2019;217:26-34. [CrossRef]
- Dail WG, Harji F, Gonzales J, Galindo R. Multiple vasodilator pathways from the pelvic plexus to the penis of the rat. International Journal of Impotence Research 1999 11:5. 1999;11(5):277-285. [CrossRef]
- Costa M, Furness JB. The origins of the adrenergic fibres which innervate the internal anal sphincter, the rectum, and other tissues of the pelvic region in the guinea-pig. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1973;140(2):129-142. [CrossRef]
- Pidsudko Z. Immunohistochemical characteristics and distribution of neurons in the paravertebral, prevertebral and pelvic ganglia supplying the urinary bladder in the male pig. J Mol Neurosci. 2014;52(1):56-70. [CrossRef]
- Kaleczyc J, Kasica-Jarosz N, Pidsudko Z, Dudek A, Klimczuk M, Sienkiewicz W. Effect of castration on pelvic neurons in the male pig. Histochem Cell Biol. 2020;153(3):135-151. [CrossRef]
- Elfvin LG, Holmberg K, Emson P, Schemann M, Hökfelt T. Nitric oxide synthase, choline acetyltransferase, catecholamine enzymes and neuropeptides and their colocalization in the anterior pelvic ganglion, the inferior mesenteric ganglion and the hypogastric nerve of the male guinea pig. J Chem Neuroanat. 1997;14(1):33-49. [CrossRef]
- Luckensmeyer GB, Keast JR. Projections from the prevertebral and major pelvic ganglia to the ileum and large intestine of the male rat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1994;49(3):247-259. [CrossRef]
- G DW. The Pelvic Plexus: Innervation of Pelvic and Extrapelvic Visceral Tissues. Microsc Res Tech. 1996;35(2):95-106. Accessed June 29, 2024. https://jglobal.jst.go.jp/en/detail?JGLOBAL_ID=200902195749010476.
- Janig W, McLachlan EM. Organization of lumbar spinal outflow to distal colon and pelvic organs. 1987;67(4):1332-1404.
- TSAKNAKIS A. Morphological Studies of the Pelvic Plexus of the Pig. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A. 1971;18(4):310-324. [CrossRef]
- Keast JR. Visualization and immunohistochemical characterization of sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons in the male rat major pelvic ganglion. Neuroscience. 1995;66(3):655-662. [CrossRef]
- CARLSTEDT A, NORDGREN S, FASTH S, HULTEN L. The influence of the pelvic nerves on. anorectal motility in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989;135(1):57-64. [CrossRef]
- Dail WG, Evan AP, Eason HR. The major ganglion in the pelvic plexus of the male rat - A histochemical and ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res. 1975;159(1):49-62. [CrossRef]
- Evan AP, Dail WG, Dammrose D, Palmer C. Scanning electron microscopy of cell surfaces following removal of extracellular material. Anat Rec. 1976;185(4):433-445. [CrossRef]
- Pannese E. Cuantitativo, cambios estructurales y moleculares en la neuroglia de mamíferos en envejecimiento: Una revisión. Revista europea de histoquímica. 2021;65(s1). [CrossRef]
- Pannese E, Ledda M, Arcidiacono G, Rigamonti L. Clusters of nerve cell bodies enclosed within a common connective tissue envelope in the spinal ganglia of the lizard and rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1991;264(2):209-214. [CrossRef]
- Ledda M, De Palo S, Pannese E. Ratios between number of neuroglial cells and number and volume of nerve cells in the spinal ganglia of two species of reptiles and three species of mammals. Tissue Cell. 2004;36(1):55-62. [CrossRef]
- van Velzen M, Laman JD, KleinJan A, Poot A, Osterhaus ADME, Verjans GMGM. Neuron-Interacting Satellite Glial Cells in Human Trigeminal Ganglia Have an APC Phenotype. The Journal of Immunology. 2009;183(4):2456-2461. [CrossRef]
- Hanani M, Verkhratsky A. Satellite Glial Cells and Astrocytes, a Comparative Review. Neurochemical Research 2021 46:10. 2021;46(10):2525-2537. [CrossRef]
- Andreeva D, Murashova L, Burzak N, Dyachuk V. Satellite Glial Cells: Morphology, functional heterogeneity, and role in pain. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:1019449. [CrossRef]
- Auld DS, Robitaille R. Glial cells and neurotransmission: An inclusive view of synaptic function. Neuron. 2003;40(2):389-400. [CrossRef]
- Darabid H, Arbour D, Robitaille R. Glial Cells Decipher Synaptic Competition at the Mammalian Neuromuscular Junction. Journal of Neuroscience. 2013;33(4):1297-1313. [CrossRef]
- Negro S, Pirazzini M, Rigoni M. Models and methods to study Schwann cells. J Anat. 2022;241(5):1235. [CrossRef]
- Salzer J, Feltri ML, Jacob C. Schwann Cell Development and Myelination. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. Published online March 19, 2024:a041360. [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Medina I, Saha O, Boismoreau F, Brunet JF. The “sacral parasympathetic”: ontogeny and anatomy of a myth. Clinical Autonomic Research. 2018;28(1):13-21. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Zavaleta V. Efecto de la conducta sexual y la denervación preganglionar sobre las características histológicas de la próstata y del ganglio pélvico mayor en la rata. Published online 2021. Accessed June 29, 2024. https://repositorioslatinoamericanos.uchile.cl/handle/2250/4146189.
- Kepper M, Keast J. Immunohistochemical properties and spinal connections of pelvic autonomic neurons that innervate the rat prostate gland. Cell Tissue Res. 1995;281(3):533-542. [CrossRef]
- Bertrand MM, Keast JR. Dissection of pelvic autonomic ganglia and associated nerves in male and female rats. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 2020;2020(157). [CrossRef]
- McVary KT, Razzaq A, Lee C, Venegas MF, Rademaker A, McKenna KE. Growth of the Rat Prostate Gland is Facilitated by the Autonomic Nervous System. Biol Reprod. 1994;51(1):99-107. [CrossRef]
- Manzo J, Garcia LI, Hernandez ME, Carrillo P, Pacheco P. Neuroendocrine control of urine-marking behavior in male rats. Physiol Behav. 2002;75(1-2):25-32. [CrossRef]
- Forrest SL, Payne SC, Keast JR, Osborne PB. Peripheral injury of pelvic visceral sensory nerves alters GFRα (GDNF family receptor alpha) localization in sensory and autonomic pathways of the sacral spinal cord. Front Neuroanat. 2015;9(APR). [CrossRef]
- Hancock MB, Peveto CA. A preganglionic autonomic nucleus in the dorsal gray commissure of the lumbar spinal cord of the rat. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1979;183(1):65-72. [CrossRef]
- Baron R, Jänig W, McLachlan EM. The afferent and sympathetic components of the lumbar spinal outflow to the colon and pelvic organs in the cat. I. The hypogastric nerve. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1985;238(2):135-146. [CrossRef]
- Hulsebosch CE, Coggeshall RE. An analysis of the axon populations in the nerves to the pelvic viscera in the rat. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1982;211(1):1-10. [CrossRef]
- Jessica Natalia Landa García. Caracterización Anatómica y Molecular de Las Neuronas Del Ganglio Pélvico Mayor Que Inervan a La Próstata Ventral y Dorsolateral de La Rata Macho Adulta de La Cepa Wistar . Doctorado. INSTITUTO DE INVESTIGACIONES CEREBRALES, Universidad Veracruzana; 2024.
- Pacheco P, Martinez-Gomez M, Whipple B, Beyer C, Komisaruk BR. Somato-motor components of the pelvic and pudendal nerves of the female rat. Brain Res. 1989;490(1):85-94. [CrossRef]
- Nadelhaft I, Roppolo J, Morgan C, de Groat WC. Parasympathetic preganglionic neurons and visceral primary afferents in monkey sacral spinal cord revealed following application of horseradish peroxidase to pelvic nerve. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1983;216(1):36-52. [CrossRef]
- Nadelhaft I, Booth AM. The location and morphology of preganglionic neurons and the distribution of visceral afferents from the rat pelvic nerve: A horseradish peroxidase study. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1984;226(2):238-245. [CrossRef]
- Morgan CW, De Groat WC, Felkins LA, Zhang S -J. Intracellular injection of neurobiotin or horseradish peroxidase reveals separate types of preganglionic neurons in the sacral parasympathetic nucleus of the cat. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1993;331(2):161-182. [CrossRef]
- Mawe GM, Bresnahan JC, Beattie MS. A light and electron microscopic analysis of the sacral parasympathetic nucleus after labelling primary afferent and efferent elements with HRP. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1986;250(1):33-57. [CrossRef]
- Araki I, De Groat WC. Unitary excitatory synaptic currents in preganglionic neurons mediated by two distinct groups of interneurons in neonatal rat sacral parasympathetic nucleus. https://doi.org/101152/jn1996761215. 1996;76(1):215-226. [CrossRef]
- Banrezes B, Andrey P, Maschino E, et al. Spatial segregation within the sacral parasympathetic nucleus of neurons innervating the bladder or the penis of the rat as revealed by three-dimensional reconstruction. Neuroscience. 2002;115(1):97-109. [CrossRef]
- TORBEY K, LEADBETTER WF. Innervation of the Bladder and Lower Ureter: Studies on Pelvic Nerve Section and Stimulation in the Dog. J Urol. 1963;90(4):395-404. [CrossRef]
- CREED KE, TULLOCH AGS. The Effect of Pelvic Nerve Stimulation and Some Drugs on the Urethra and Bladder of the Dog. Br J Urol. 1978;50(6):398-405. [CrossRef]
- CREED KE. THE ROLE OF THE HYPOGASTRIC NERVE IN BLADDER AND URETHRAL ACTIVITY OF THE DOG. Br J Pharmacol. 1979;65(3):367-375. [CrossRef]
- Kaleczyc J, Kasica-Jarosz N, Pidsudko Z, Przyborowska A, Sienkiewicz W. The expression of androgen receptor in neurons of the anterior pelvic ganglion and celiac-superior mesenteric ganglion in the male pig. Pol J Vet Sci. 2019;22(1):151-155. [CrossRef]
- Pidsudko Z. Immunohistochemical characteristics and distribution of sensory dorsal root ganglia neurons supplying the urinary bladder in the male pig. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience. 2014;52(1):71-81. [CrossRef]
- Janikiewicz P, Wasilewska B, Mazur U, Franke-Radowiecka A, Majewski M, Bossowska A. The Influence of an Adrenergic Antagonist Guanethidine (GUA) on the Distribution Pattern and Chemical Coding of Dorsal Root Ganglia (DRG) Neurons Supplying the Porcine Urinary Bladder. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, Vol 22, Page 13399. 2021;22(24):13399. [CrossRef]
- Kaleczyc J, Scheuermann DW, Pidsudko Z, Majewski M, Lakomy M, Timmermans JP. Distribution, immunohistochemical characteristics and nerve pathways of primary sensory neurons supplying the porcine vas deferens. Cell Tissue Res. 2002;310(1):9-17. [CrossRef]
- Andersson PO, Sjogren C, Uvnas B, Uvnas-Moberg K. Urinary bladder and urethral responses to pelvic and hypogastric nerve stimulation and their relation to vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the anaesthetized dog. Acta Physiol Scand. 1990;138(3):409-416. [CrossRef]
- Kihara K, Sato K, Ando M, Sato T, Oshima H. Lumbosacral Sympathetic Trunk as a Compensatory Pathway for Seminal Emission After Bilateral Hypogastric Nerve Transections in the Dog. J Urol. 1991;145(3):640-643. [CrossRef]
- Kihara K, Sato K, Oshima H. Sympathetic Efferent Pathways Projecting to the Vas Deferens. Microsc Res Tech. 1998;42:398-408.
- Aoki H, Matsuzaka J, Banya Y, et al. Effects of Hypogastric Nerve and Sympathetic Chain Stimulation on the Pelvic Nerve Induced Penile Erection in the Dog. Urol Int. 1991;47(1):25-34. [CrossRef]
- Elfvin LG, Holmberg K, Emson P, Schemann M, Hökfelt T. Nitric oxide synthase, choline acetyltransferase, catecholamine enzymes and neuropeptides and their colocalization in the anterior pelvic ganglion, the inferior mesenteric ganglion and the hypogastric nerve of the male guinea pig. J Chem Neuroanat. 1997;14(1):33-49. [CrossRef]
- Dail WG, Moll MA, Weber K. Localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in penile erectile tissue and in the major pelvic ganglion of the rat. Neuroscience. 1983;10(4):1379-1386. [CrossRef]
- Black IB, Geen SC. Trans-synaptic regulation of adrenergic neuron development: Inhibition by ganglionic blockade. Brain Res. 1973;63(C):291-302. [CrossRef]
- Zukowska Z, Pons J, Lee EW, Li L. Neuropeptide Y: a new mediator linking sympathetic nerves, blood vessels and immune system? 2011;81(2):89-94. [CrossRef]
- Dail WG, Evan AP, Eason HR. The major ganglion in the pelvic plexus of the male rat - A histochemical and ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res. 1975;159(1):49-62. [CrossRef]
- Su X, Gebhart GF. Effects of tricyclic antidepressants on mechanosensitive pelvic nerve afferent fibers innervating the rat colon. Pain. 1998;76(1-2):105-114. [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz W. Sources of the porcine testis innervation. Andrologia. 2010;42(6):395-403. [CrossRef]
- Klimczuk M, Kaleczyc J, Franke-Radowiecka A, Czaja K, Podlasz P, Lakomy M. Immunohistochemical characterisation of cholinergic nerve fibres supplying accessory genital glands in the pig. https://vetmed.agriculturejournals.cz/doi/1017221/5604-VETMED.html. 2005;50(3):119-130. [CrossRef]
- Carati CJ, Creed KE, Keogh EJ. Autonomic control of penile erection in the dog. J Physiol. 1987;384(1):525-538. [CrossRef]
- Andersson PO, Bloom SR, Mellander S. Haemodynamics of pelvic nerve induced penile erection in the dog: possible mediation by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. J Physiol. 1984;350(1):209-224. [CrossRef]
- Partanen M, Hervonen A. The effect of long-term castration on the histochemically demonstrable catecholamines in the hypogastric ganglion of the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1979;1(2):139-147. [CrossRef]
- Partanen M, Hervonen A. The formaldehyde-induced fluorescence of the developing hypogastric (main belvic) ganglion of the rat - Short adrenergic neurons and the effect of testosterone. Histochemistry. 1979;62(3):249-258. [CrossRef]
- Melvin JE, Hamill RW. Androgen-specific critical periods for the organization of the major pelvic ganglion. Journal of Neuroscience. 1989;9(2):736-742. [CrossRef]
- Melvin JE, Hamill RW. The major pelvic ganglion: androgen control of postnatal development. J Neurosci. 1987;7(6):1607-1612. [CrossRef]
- Keast JR, Saunders RJ. Testosterone has potent, selective effects on the morphology of pelvic autonomic neurons which control the bladder, lower bowel and internal reproductive organs of the male rat. Neuroscience. 1998;85(2):543-556. [CrossRef]
- Schirar A, Chang C, Rousseau JP. Localization of Androgen Receptor in Nitric Oxide Synthase- and Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide-Containing Neurons of the Major Pelvic Ganglion Innervating the Rat Penis. J Neuroendocrinol. 1997;9(2):141-150. [CrossRef]
- Purves-Tyson TD, Arshi MS, Handelsman DJ, Cheng Y, Keast JR. Androgen and estrogen receptor-mediated mechanisms of testosterone action in male rat pelvic autonomic ganglia. Neuroscience. 2007;148(1):92-104. [CrossRef]
- Félix B, Catalin D, Miolan JP, Niel JP. Effects of Testosterone on the Electrical Properties and Nicotinic Transmission of the Major Pelvic and Coeliac Ganglion Neurones. J Neuroendocrinol. 2001;13(2):193-198. [CrossRef]
- Kanjhan R, Osborne PB, Ouyang M, Keast JR. Postnatal maturational changes in rat pelvic autonomic ganglion cells: A mixture of steroid-dependent and -independent effects. J Neurophysiol. 2003;89(1):315-323. [CrossRef]
- Hervonen A, Kanerva L. Adrenergic and Nonadrenergic Axons of the Rabbit Uterus and Oviduct. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972;85(1):139-141. [CrossRef]
- Víctor Hugo Cruz Rivas. Repercusión de La Denervación Prostática y La Conducta Sexual Sobre Los Niveles Séricos de Prolactina y Testosterona y La Expresión de Sus Receptores En Ratas Sexualmente Expertas. Doctorado. Instituto de Investigaciones Cerebrales, Universidad Veracruzana; 2024.
- Mateos Moreno. Efecto de la conducta sexual y la denervación pélvica y/o hipogástrica sobre la expresión de receptores adrenérgicos, colinérgicos, andrógenos y prolactina en el ganglio pélvico mayor de la rata macho. Tesis. Published 2021. Accessed June 29, 2024. https://cdigital.uv.mx/.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




