1. Introduction
The trajectory of human progress and scientific advancement is profoundly intertwined with the exploration of space and the extraction of extraterrestrial resources. As Earth’s resources become increasingly scarce due to rapid population growth and escalating demands for energy and materials, the imperative to extend our resource acquisition efforts beyond terrestrial confines grows ever more urgent. The prospect of discovering and harnessing extraterrestrial resources offers substantial promise in addressing some of humanity’s most pressing challenges, such as ensuring long-term energy sustainability and enabling the colonization of distant celestial bodies[
1,
2].
Advancements in space exploration technologies have dramatically enhanced our understanding of the cosmos and expanded the range of accessible space resources. For instance, asteroids rich in precious metals and rare earth elements present untapped opportunities for material acquisition that could revolutionize terrestrial industries. Furthermore, the utilization of lunar regolith for in-situ construction and resource extraction exemplifies the potential for self-sustaining operations on other celestial bodies. These developments underscore the transformative potential of extraterrestrial resource exploitation in fostering sustainable development on Earth and laying the groundwork for human expansion into the broader solar system[
3]. As we continue to advance in space exploration, the strategic integration of extraterrestrial resources into our economic and technological frameworks will be pivotal in shaping the future trajectory of human civilization [
4,
5,
6,
7].
In space exploration, integrating autonomous structural design and construction is essential due to the vast distances and resulting communication delays. These time lags make Earth-based directives impractical for timely decision-making during missions. Autonomous processes allow spacecraft and habitats to adapt in real-time to changing environments and unforeseen challenges without relying on continuous Earth-based input. By using artificial intelligence and advanced robotics, these systems can autonomously generate and implement optimized designs, improving the efficiency and resilience of space missions while mitigating the impact of delayed communications [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17].
In this research, we focus on advancing topology optimization as a key methodology within the realm of non-parametric structural design. Our objective is to develop an autonomous design tool grounded in rigorous mathematical optimization, specifically tailored for the simulation of structures using the finite element method (FEM). This approach seeks to enhance the structural design process by providing a robust framework that operates independently of predefined geometric parameters, thereby enabling the creation of optimized structural configurations driven purely by mathematical principles [
18,
19,
20]. The advent of topology optimization, originated by Michell [
21] based on solving Maxwell’s lemma [
22], has propelled computer-aided design to unprecedented heights, facilitating the comprehensive development of designs rooted in mathematical optimization principles. Although the realization of fully computer-based evaluation and design remains an aspirational objective, it stands as a pivotal imperative for propelling the frontiers of future transportation endeavors, particularly within the domain of deep space missions [
23,
24,
25].
Amidst such missions, characterized by extensive distances from the central control center and potential communication disruptions stemming from orbital dynamics (excluding quantum communication and informatics), spacecraft may encounter hazardous events necessitating on-site repairs, such as damage induced by asteroid impacts or mechanical fatigue. In scenarios involving manned missions, where crew members are theoretically in a state of deep hibernation, the execution of repairs by human personnel becomes unviable. Moreover, future deep space missions, encompassing endeavors such as mining, may prioritize unmanned operations for economic reasons, mandating the incorporation of artificial intelligence to orchestrate the design process and execute repairs autonomously.
Topology optimization, a discipline that encompasses both layout optimization and generalized shape optimization, involves the discretization of a design domain into finite components with defined spatial relationships—such as finite differences, boxes, elements, and volumes. Originating as a layout problem, topology optimization is primarily concerned with the strategic design of specific regions within a given space, where the locations of traction and support points are predetermined. This method enables the systematic exploration of optimal structural configurations by adjusting material distribution within the design domain to achieve desired performance criteria [
26,
27,
28,
29]. Topology optimization has advanced significantly, driven by various methodologies. A key development was the use of numerical discretization by Dorn et al. [
30], enabling precise structural representation and enhancing optimization accuracy. Bartel [
31] minimized structure weight using sequential unconstrained minimization and Constrained Steepest Descent techniques. Charrett and Rozvany [
32] applied the Prager–Shield method for optimal design in rigid-perfectly plastic systems under varied loads, while Rozvany and Prager [
33] optimized grillage-like continua. Rossow and Taylor [
34] employed FEM to optimize variable thickness sheets, introducing shape optimization with holes in plates. Cheng and Olhoff [
35] refined FEM for optimizing annular plates, incorporating homogenization. Bendsoe’s discretized continuous optimality criterion (DCOC) led to the Solid Isotropic Material with Penalization (SIMP) method, crucial for reducing stress concentrations and utilizing image processing in design transformations [
36,
37,
38]. Other notable methods include Evolutionary Structural Optimization (ESO) and the Metaheuristic Structure Binary-Distribution (MSB) method[
39,
40]. Additionally, shape optimization methods, particularly the level-set [
41,
42]
and H1 gradient methods[
43], are showing promising results by focusing on structural boundaries. These approaches collectively represent significant progress in topology optimization, enhancing both structural efficiency and design precision.
The present study delves into the innovative integration of camera technology within spacefaring vehicles to facilitate the comprehensive design and construction of habitable structures through advanced 3D printing methodologies [
44,
45,
46,
47]. Leveraging the concept of camera vision, the computational system discerns the parameters of the design domain, subsequently employing topology optimization techniques for streamlined design execution. The impetus driving this investigation stems from four primary considerations. Firstly, the inherent payload sensitivity of space missions necessitates stringent weight management, thereby advocating for the minimization of additional measurement devices, such as laser scanners, to mitigate associated costs. Secondly, mindful of energy consumption, the adoption of computationally intensive methodologies like machine learning, while efficacious in expert system emulation, imposes significant computational burdens, contrasting with more resource-efficient optimization approaches such as the Method of Moving Asymptotes or the optimality criteria [
48]. Thirdly, the logistical challenges posed by vast astronomical distances mandate expeditious communication between Earth and extraterrestrial habitats, underscoring the need for locally executable design processes. Finally, topology optimization emerges as a matured technique for 3D printing applications, further affirming its suitability for the envisaged spaceborne construction endeavors. The paper unfolds in a structured manner: elucidating computer vision in
Section 2, expounding on topology optimization in
Section 3, detailing the numerical investigation in
Section 4, and concluding with
Section 5.
2. Computer Vision 3D Simulation Using Computer Vision
This study introduces the integration of photogrammetry into design engineering, utilizing camera-based techniques to enable 3D modeling of the design domain [
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55]. The laying foundational concepts of photogrammetry can be traced to the 1480s with the works of Leonardo da Vinci and his early research on perspective [
56]. The first one to recognizes the potential of using camera for mapping was Aimé Laussedat who is often credited as the “father of photogrammetry” [
56]. Photogrammetry as a numerical technique began to be developed in the 1990s, through the works of the computer community vision [
57]. The development of algorithms to realize the automatics matching between feature also represent the beginning of actual photogrammetry. The different elements of the process involved in photogrammetry can be divided into two key steps: image processing and mathematical calculations. The beginning of the process of image processing consists of image alignment (also known as image registration). This step involves creating a coherent dataset by matching corresponding points in overlapping images. This is achieved using algorithms to detect common features, such as edges and corners, and align the images accordingly. An image rectification corrector is applied to reduce the distortion caused by the camera lens, ensuring that the images accurately represent the geometry of the captured scene. Rectified images are essential for precise measurements and modeling. Image stitching involves combining multiple overlapping images into a single mosaic. This is a particularly important procedure for large-scale projects where multiple images are required to cover the entire area of interest. The resulting mosaic facilitates detailed analysis and measurements. The other key step in photogrammetry involves using mathematical calculations to derive accurate measurements and create detailed models from the processed images. The fundamental principle behind photogrammetry is triangulation. This involves determining the position of a point in 3D space by measuring the distances and angles from two or more known positions. By using images of the same object or detail from different perspectives, photogrammetry software can precisely calculate the coordinates of each point,. The basic formula for triangulation can be expressed as follows:
Where:
- -
, , are the coordinates of the point in 3D space.
- -
is the baseline distance between the two camera positions.
- -
, , , are the coordinates of the point in the images.
- -
, are the principal points of the images.
- -
is the focal length of the camera.
A mathematical optimization technique used to refine the accuracy of the derived measurements is the bundle adjustment. This involves adjusting the positions and orientations of the cameras, as well as the coordinates of the measured points, to minimize errors and ensure the consistency of the dataset. Bundle adjustment is crucial for achieving high precision results in photogrammetry.
The objective function for bundle adjustment can be expressed as:
Where:
- -
are the 3D coordinates of the points.
- -
are the parameters of the camera poses.
- -
are the observed image coordinates.
- -
is the projection function mapping 3D points to 2D image coordinates.
Finally, using the dataset and algorithms, high-resolution 3D models can be generated for visualization, analysis, and further processing.
3. Topology and Shape Optimization
Topology optimization began as a deterministic discipline focused on physical models, evolving with advancements in mathematical methodologies. Initially, parametric optimization used heuristic methods to adjust parameters within structural designs, like cross-sectional dimensions or material properties, to meet specific objectives such as minimizing stress. However, optimizing material distribution within a structural domain proved complex, as it couldn’t be easily defined by conventional quantities like mass or load. This led to the development of non-parametric methods, particularly topology optimization, which optimizes structural layout and shape based on mathematical logic and objective criteria. Topology optimization represents a new design frontier, delivering the most efficient solutions within predefined constraints, driven purely by the requirements of the optimization process.
Non-parametric optimization methodologies, such as topology optimization, employ a series of cascade approximations that originate from the design variables. These methodologies, exemplified by techniques like the SIMP method, progress through successive stages of refinement, encompassing discretization methods, objective criteria formulation, and concluding with iterative updates to the design variables [
18,
41,
58].
Topology optimization, guided by predefined objective criteria, typically revolves around compliance-based optimization objectives as presented in Equation 1. These criteria serve as fundamental pillars guiding the optimization process, ensuring that the resultant designs meet specified performance standards while adhering to structural integrity requirements.
In the context of the present study, MATLAB with COMSOL was employed to develop customized algorithms tailored to facilitate the topology optimization process.
Where is objective function, of the design variables . Here represents the elemental penalized elastic tensor in terms of penalized design variable to power q. When the design variable is near zero, the elastic tensor of the discretization unit become , while the design variable when it reaches one, the elastic tensor become . Moreover, is the volume reduction condition, withing the design domain .
The significant strides made in advancing topology optimization also bring to light critical challenges that require careful consideration. Foremost among these challenges is the derivation of sensitivities in gradient-based optimization, particularly when dealing with complex, multi-layered functions. While numerical sensitivity analysis presents a viable approach, it is often accompanied by substantial costs in terms of time and computational resources. Achieving the desired outcomes typically necessitates high-resolution models, which, in turn, escalate the computational burden.
Moreover, the trade-offs inherent in discretization and simplification—although necessary and widely accepted—inevitably obscure certain physical phenomena, potentially compromising the accuracy of the solutions. The mathematical complexities present in intricate models further exacerbate these challenges, introducing a significant risk of computational instability and failure.
These challenges underscore the mathematical intricacies intrinsic to topology optimization. The design of the objective function stands out as a particularly critical aspect within the realm of mathematical optimization, necessitating meticulous attention and innovative strategies to effectively navigate these complexities.
A well-crafted objective function can sometimes yield optimal solutions that diverge from the expectations set by the original mathematical model. A notable example is the topology optimization of heat conduction, which often results in tree-like structures. Contrary to the intuitive expectation of uniform heat distribution through a solid medium, the optimized tree structure exhibits an uneven mass distribution, challenging conventional assumptions. Yan et al. further substantiates these findings with alternative models that question the validity of traditional approaches. Additionally, the discretization process itself presents significant challenges, occasionally leading to non-feasible design regions, especially when higher-order degrees of freedom are involved. To address these issues, designers often employ additional filtering techniques, relying on their expertise and judgment to refine and enhance the optimization process.
4. Topology and Shape Optimization
This section presents a numerical study that investigates the integration of computer vision with topology optimization for designing structures tailored for additive manufacturing. We developed custom software for photogrammetry, employing camera systems to capture high-resolution, dynamic images within the designated design domain. These images enable the creation of detailed 3D models through comprehensive scanning protocols, ensuring the meticulous capture of intricate domain features. Upon completing the 3D modeling, the model is converted into a Stereolithography (STL) file, the standard format for additive manufacturing. This conversion, performed using an automated, precision-driven approach, ensures the accurate preservation of details captured during the scanning phase. The STL file then undergoes remeshing using an adaptive meshing algorithm within the COMSOL Multiphysics environment, controlled by a MATLAB application. This integrated framework leverages MATLAB’s computational strengths and COMSOL’s versatile simulation capabilities, optimizing the mesh structure for subsequent computational analyses. The adaptive meshing dynamically responds to geometric complexity, enhancing the fidelity and accuracy of simulations. Given the resource constraints in extraterrestrial environments like the Moon or Mars, the study focuses on optimizing printing time and minimizing material use. By implementing a volumetric reduction strategy, we aim to reduce the original solid block configuration by 50% while preserving structural integrity and functionality. The design domain is imported into MATLAB for topology optimization, with COMSOL providing high-quality finite element meshes and simulations to explore material-efficient design configurations for advanced additive manufacturing.
The integration of MATLAB’s optimization capabilities with COMSOL’s simulation tools creates a synergistic framework that enhances the fidelity and efficiency of the optimization process. This combined approach allows for a thorough exploration of design alternatives, leading to the identification of optimal structural configurations that balance material efficiency with structural performance.
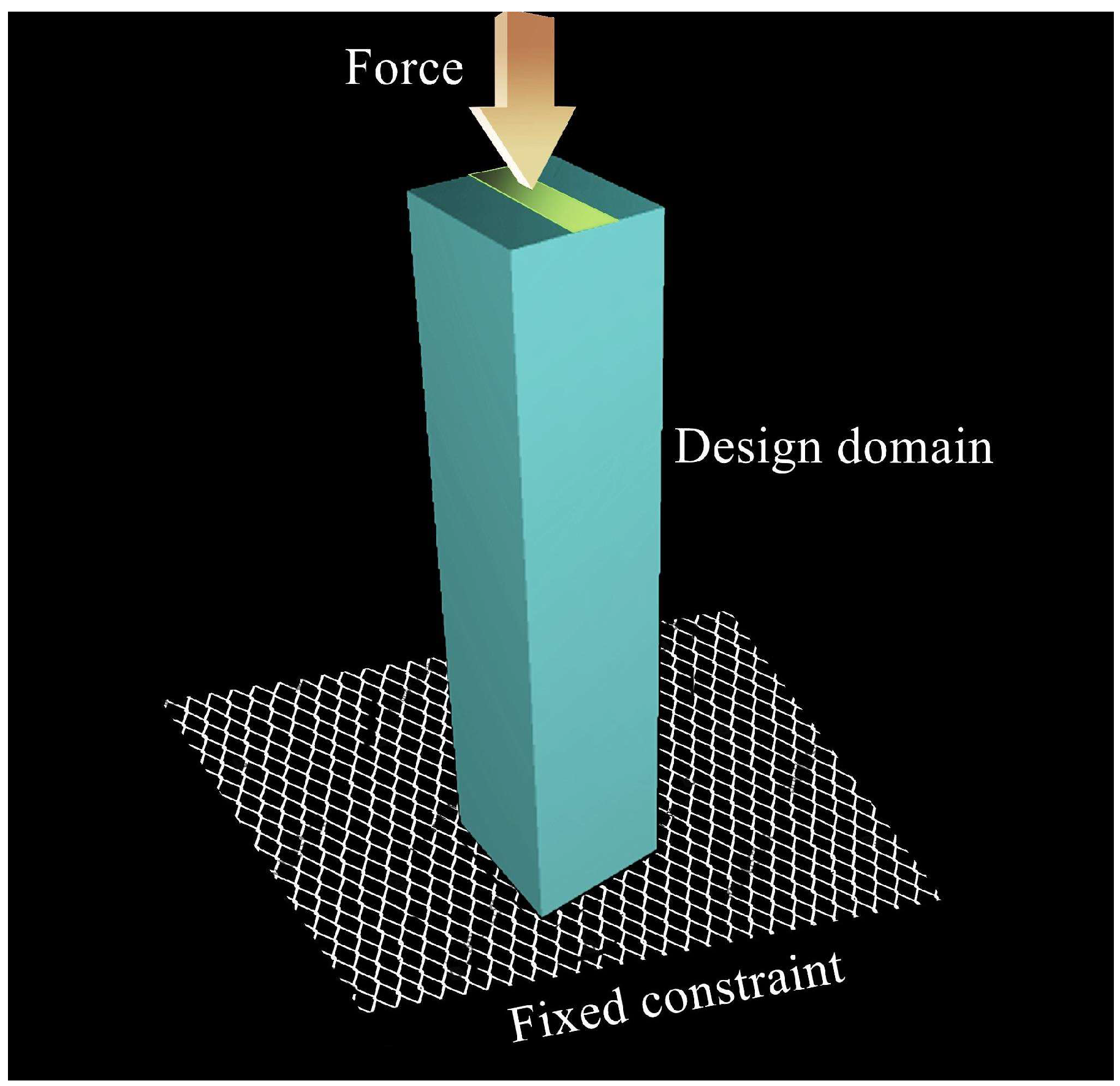
Figure 2 illustrates the computer modeling for topology optimization, featuring a pillar subjected to vertical loading and securely anchored to the ground, thereby establishing fixed boundary conditions. The objective of the topology optimization is to minimize the design volume while simultaneously enhancing stiffness through the reduction of mechanical compliance. This method aligns with Tikhonov’s reciprocity principle, which addresses the non-convex nature of both stiffness and compliance optimization problems. In this study, the Young’s modulus of elasticity is normalized to unity, and the Poisson ratio is set at 0.3 to ensure consistency across all analyses. The results of this optimization process are presented in
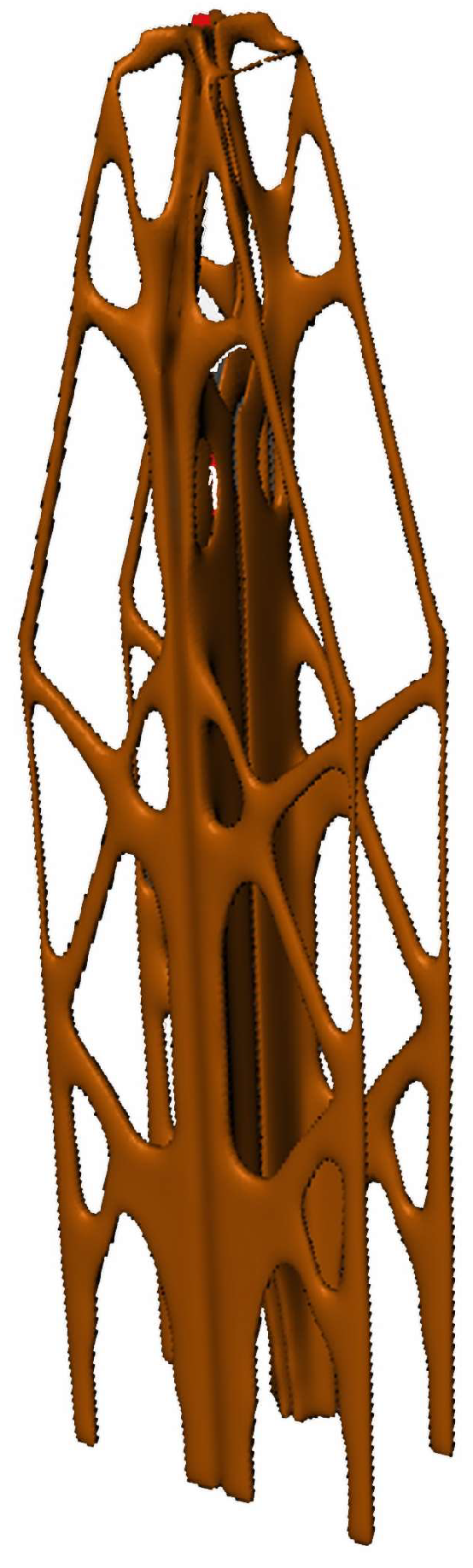
Figure 3.
Our study demonstrates a substantial reduction in the design domain’s volume, a primary goal of the optimization framework. This volume reduction follows a distinct spatial pattern, with the most significant reductions occurring centrally and tapering towards the peripheral areas near structural constraints. This strategic material distribution enhances structural stability while optimizing material usage, analogous to civil engineering techniques where weight reduction is achieved by incorporating hollow structures within solid frameworks. Such design strategies aim to maximize structural efficiency and performance while minimizing material consumption.
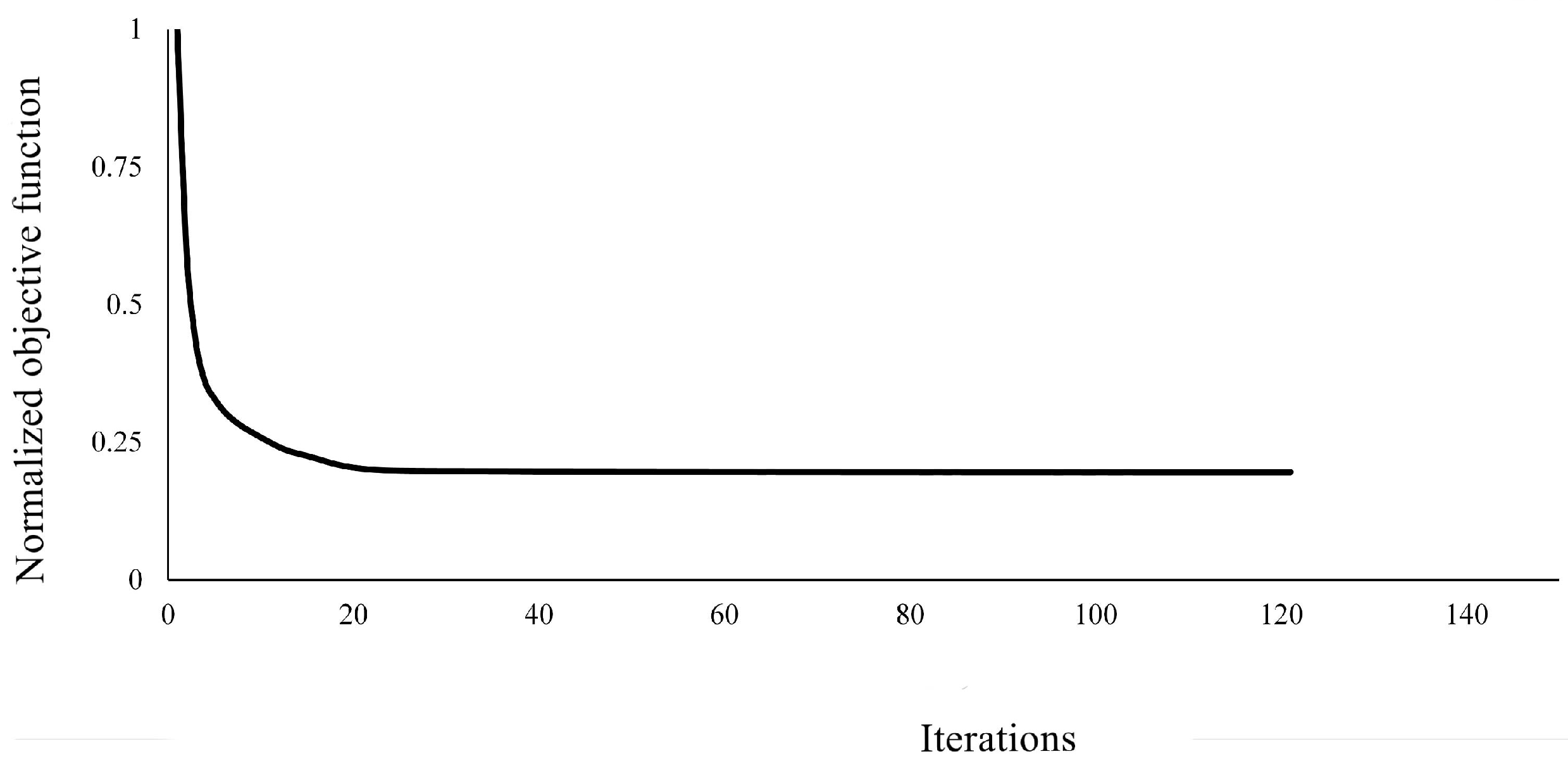
Figure 4 illustrates the convergence behavior of the optimization algorithm over successive iterations. The x-axis represents the number of iterations, while the y-axis depicts the normalized objective function value. Initially, the objective function value is near 1, indicating suboptimal conditions. However, as iterations advance, the objective function value significantly decreases, demonstrating the algorithm’s rapid convergence towards an optimal solution. By the 20th iteration, the curve begins to plateau near zero, indicating that the algorithm has effectively minimized the objective function and is approaching optimality. The initial steep decline followed by an asymptotic plateau highlights the algorithm’s efficiency and stability in the optimization process. This rapid reduction in the objective function value suggests that the method swiftly identifies a near-optimal solution, with subsequent iterations offering diminishing returns. The convergence graph underscores the algorithm’s ability to balance rapid convergence with stable minimization, ensuring the efficient achievement of an optimal or near-optimal solution.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this numerical study presents an innovative approach that combines computer vision with topology optimization to advance designs for additive manufacturing. By employing specialized photogrammetry software developed for camera systems, we capture dynamic, high-resolution images of the design domain, enabling the creation of precise 3D models through detailed scanning protocols. These models are then converted into STL file format, preserving the intricate details from the initial scans. This conversion is followed by remeshing using an adaptive meshing algorithm within the COMSOL Multiphysics environment, managed via a custom MATLAB application. This integrated framework facilitates seamless interaction between MATLAB’s computational capabilities and COMSOL’s simulation tools, ensuring optimal mesh resolution and accuracy in subsequent analyses.
The preliminary phase of our investigation involved designing a concrete pillar for 3D printing, aiming for a 75% reduction in volume to enhance material efficiency and structural stability, which is particularly critical for extraterrestrial environments with limited resources. The design was scanned using a comprehensive 360-degree camera array, capturing detailed spatial data that informed the MATLAB-based topology optimization process. Utilizing MATLAB’s optimization algorithms alongside COMSOL’s meshing and FEM solver, we explored various material-efficient design configurations.
The results of the optimization, notably the significant volume reduction concentrated in the central region of the design domain, reflect a strategic approach to maximizing material efficiency while ensuring structural stability. This design strategy, which mirrors principles in civil engineering, focuses on achieving optimal performance with minimal material usage. Furthermore, the convergence behavior of the optimization algorithm demonstrates rapid and stable convergence, reaching near-optimal solutions within approximately 20 iterations. This performance underscores the method’s computational efficiency and robustness in optimizing complex designs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.; methodology, M.A., M.S.; numerical simulations, M.A. M.S., M.N.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A., M.S., and M.N.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Data Availability Statement
Data may be available from the correspondent author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dallas, J.A.; Raval, S.; Gaitan, J.P.A.; Saydam, S.; Dempster, A.G. Mining beyond Earth for Sustainable Development: Will Humanity Benefit from Resource Extraction in Outer Space? Acta Astronaut. 2020, 167, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F. The Approach to Sustainable Space Mining: Issues, Challenges, and Solutions. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; 2020; Vol. 738; p. 12014. [Google Scholar]
- Steffen, O. Explore to Exploit: A Data-Centred Approach to Space Mining Regulation. Space Policy 2022, 59, 101459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgart, A.; Vlachopoulou, E.I.; Vera, J.D.R.; Di Pippo, S. Space for the Sustainable Development Goals: Mapping the Contributions of Space-Based Projects and Technologies to the Achievement of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Sustain. Earth 2021, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiwald, V.; Schubert, D.; Quantius, D.; Zabel, P. From Space Back to Earth: Supporting Sustainable Development with Spaceflight Technologies. Sustain. Earth 2021, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, N.; Esteban, M. Sustainable Space Exploration and Its Relevance to the Privatization of Space Ventures. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 167, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santomartino, R.; Averesch, N.J.H.; Bhuiyan, M.; Cockell, C.S.; Colangelo, J.; Gumulya, Y.; Lehner, B.; Lopez-Ayala, I.; McMahon, S.; Mohanty, A.; et al. Toward Sustainable Space Exploration: A Roadmap for Harnessing the Power of Microorganisms. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernigoni, L.; Grande, A.M. Advantages and Challenges of Novel Materials for Future Space Applications. Front. Sp. Technol. 2023, 4, 1253419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.K.; Gibson, T.L.; Jolley, S.T.; Caraccio-Meier, A.J. Self-Healing Technologies for Wiring and Surfaces in Aerospace and Deep Space Exploration Applications. In Proceedings of the Smart Coatings Conference; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, M.; Bender, S.; Smith, N. Passive Self-Healing Composite Dielectric Elastomer Sensors for Structural Health Monitoring of Inflatable Space Structures. 2022.
- Chamkouri, H.; Ahmadlouydarab, M.; Chamkouri, M.; Hosseini saeidavi, F. Epoxy Resin Matrix Integrating Epoxy-Polydimethylsiloxane Based Self-Healing Microcapsules: Healing Efficiency, Mechanical and Thermal Stability. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 2302–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernigoni, L.; Lafont, U.; Grande, A.M. Self-Healing Materials for Space Applications: Overview of Present Development and Major Limitations. CEAS Sp. J. 2021, 13, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchenko, I.; Bazaka, K.; Belmonte, T.; Keidar, M.; Xu, S. Advanced Materials for Next-Generation Spacecraft. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1802201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almutairi, M.D.; Aria, A.I.; Thakur, V.K.; Khan, M.A. Self-Healing Mechanisms for 3D-Printed Polymeric Structures: From Lab to Reality. Polymers (Basel). 2020, 12, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLemore, C.A.; Kennedy, J.P.; Rose, F.A.; Evans, B.W. Exploration Challenges: Transferring Ground Repair Techniques to Space Flight Application. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; 2007; Vol. 880; pp. 719–727. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, M.; Manuel, M.; Wallace, T.; Newman, A.; Brinson, K. 2015.
- Taminger, K.; Hafley, R.A.; Dicus, D.L. Solid Freeform Fabrication: An Enabling Technology for Future Space Missions. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Conference on Metal Powder Deposition for Rapid Manufacturing; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Al Ali, M.; Shimoda, M. Hygrally Activated Displacement Inverter Using a Multiphysics Multiscale Topology Optimization with Considering Evaporation. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2023, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, P.; Maute, K. Level Set Topology Optimization of Cooling and Heating Devices Using a Simplified Convection Model. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2016, 53, 985–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Shi, T.; Wang, M.Y. A Level Set Based Shape and Topology Optimization Method for Maximizing the Simple or Repeated First Eigenvalue of Structure Vibration. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2011, 43, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michell, A.G.M. LVIII. The Limits of Economy of Material in Frame-Structures. London, Edinburgh, Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1904, 8, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, J.C. I. —on Reciprocal Figures, Frames, and Diagrams of Forces. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinburgh 1870, 26, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, J. On the Minimum Weight of Certain Redundant Structures. Acta Tech. Acad. Sci. Hungaricae 1957, 18, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Sved, G. The Minimum Weight of Certain Redundant Structures. Aust. J. Appl. Sci. 1954, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hemp, W.S. Notes on the Problem of the Optimum Design of Structures. Aust. J. Appl. Sci. 1958, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Al Ali, M.; Shimoda, M. Exploring the Influence of Initial Design Domain Dependencies in Concurrent Multiscale Topology Optimization for Heat Conductivity Maximization. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2024, 295, 108968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ali, M.; Shimoda, M.; Benaissa, B.; Kobayashi, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Al-Shawk, A.; Ranjbar, S. On Metaheuristic Aided Structural Topology Optimization Method for Heat Sink Design with Low Electromagnetic Interference. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, M.; Shimoda, M.; Al Ali, M. Concurrent Shape Optimization of a Multiscale Structure for Controlling Macrostructural Stiffness. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2022, 65, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ali, M.; Shimoda, M. Toward Multiphysics Multiscale Concurrent Topology Optimization for Lightweight Structures with High Heat Conductivity and High Stiffness Using MATLAB. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2022, 65, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, W S, Gomory, R. E., and Greenberg, H.G. Automatic Design of Optimal Structures. J. Mec. 1964, 3, 25–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.L. 1969.
- Charrett, D.E.; Rozvany, G.I.N. Extensions of the Prager-Shield Theory of Optimal Plastic Design. Int. J. Non. Linear. Mech. 1972, 7, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozvany, G.I.N.; Prager, W. Optimal Design of Partially Discretized Grillages. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1976, 24, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, M.P.; Taylor, J.E. A Finite Element Method for the Optimal Design of Variable Thickness Sheets. Aiaa J. 1973, 11, 1566–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.T.; Olhoff, N. An Investigation Concerning Optimal Design of Solid Elastic Plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1981, 17, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsoe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. T: Optimization, 2003.
- Bendsoe, M.P.; Guedes, J.M.; Haber, R.B.; Pedersen, P.; Taylor, J.E. An Analytical Model to Predict Optimal Material Properties in the Context of Optimal Structural Design. 1994.
- Bendsøe, M.P. Optimal Shape Design as a Material Distribution Problem. Struct. Optim. 1989, 1, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ali, M.; Shimoda, M.; Benaissa, B.; Kobayashi, M. Non-Parametric Optimization for Lightweight and High Heat Conductive Structures under Convection Using Metaheuristic Structure Binary-Distribution Method. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 233, 121124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ali, M.; Shimoda, M.; Benaissa, B.; Kobayashi, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Al-Shawk, A.; Ranjbar, S. Metaheuristic Aided Structural Topology Optimization Method for Heat Sink Design with Low Electromagnetic Interference. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ali, M.; Shimoda, M. Investigation of Concurrent Multiscale Topology Optimization for Designing Lightweight Macrostructure with High Thermal Conductivity. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 179, 107653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wei, P.; Wang, W. Parameterized Level-Set Based Topology Optimization Method Considering Symmetry and Pattern Repetition Constraints. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 340, 1079–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, M.; Shimoda, M.; Ali, M. Al Concurrent Shape Optimization for Multiscale Structure with Desired Static Deformation. Proc. Comput. Mech. Conf. 2021, 2021.34, 3. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, B.B.; Wang, C.; Tanahashi, H.; Hirayu, H.; Niwa, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Tachibana, K.; Sasagawa, T. A Computer Vision Based Approach for 3D Building Modelling of Airborne Laser Scanner DSM Data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2006, 30, 54–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutto, M. Lo; Meli, P. Computer Vision Tools for 3D Modelling in Archaeology. Int. J. Herit. Digit. Era 2012, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aicardi, I.; Chiabrando, F.; Lingua, A.M.; Noardo, F. Recent Trends in Cultural Heritage 3D Survey: The Photogrammetric Computer Vision Approach. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 32, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, J.; Shou, W.; Ngo, T.; Sadick, A.-M.; Wang, X. Computer Vision Techniques in Construction: A Critical Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 3383–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svanberg, K. The Method of Moving Asymptotes—a New Method for Structural Optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1987, 24, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomina, I.; Molina, P. Unmanned Aerial Systems for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 92, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqersad, J.; Poozesh, P.; Niezrecki, C.; Avitabile, P. Photogrammetry and Optical Methods in Structural Dynamics--A Review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 86, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltsavias, E.P. A Comparison between Photogrammetry and Laser Scanning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.S.; Brown, D.C. Industrial Photogrammetry: New Developments and Recent Applications. Photogramm. Rec. 1986, 12, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, K.; Grussenmeyer, P. Architectural Photogrammetry: Basic Theory, Procedures, Tools. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Commission; 2002; Vol. 5; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Valença, J.; Júlio, E.; Araújo, H.J. Applications of Photogrammetry to Structural Assessment. Exp. Tech. 2012, 36, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapirstein, P. Accurate Measurement with Photogrammetry at Large Sites. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2016, 66, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Vinci, L. The Notebooks of Leonardo Da Vinci; Courier Corporation, 2012; Vol. 1;
- Boufama, B.; Mohr, R.; Veillon, F. Euclidean Constraints for Uncalibrated Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 1993 (4th) International Conference on Computer Vision; 1993; pp. 466–470. [Google Scholar]
- Al Ali, M.; Shimoda, M. On Multiphysics Concurrent Multiscale Topology Optimization for Designing Porous Heat-Activated Compliant Mechanism under Convection for Additive Manufacture. Eng. Struct. 2023, 294, 116756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).