1. Introduction
The pathophysiological association between pollution induced oxidative stress and lung injury features a complex interplay with significant health implications. Environmental pollutants, such as PM2.5 particulate matter, can induce oxidative stress in the respiratory system [
1]. This oxidative stress disrupts the balance between antioxidant defenses and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, leading to cellular damage and inflammation in the respiratory system, especially lung. Oxidative stress is a key driver of inflammatory responses in lung tissues. It activates signaling pathways that promote the release of proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) like HMGB1 where collectively exacerbate inflammation and contribute to lung tissue injury [
2].
HMGB1, in particular, is highlighted as a critical mediator in this process. It accumulates extracellularly in response to oxidative stress induced by pollutants, further amplifying inflammatory reactions and impairing immune cell functions. The accumulation of HMGB1 in the airways and lungs is associated with increased severity of inflammatory lung injury. The pathophysiology involves a cascade of events where oxidative stress initiates inflammatory responses, leading to tissue damage and compromising lung function. This relationship underscores the need for effective strategies to mitigate pollutant exposure, enhance antioxidant defenses, and potentially target HMGB1 to protect against pollution-induced oxidative stress and mitigate lung injury [
3,
4].
Previously, Yimam et al. 2023 proposed that reducing extracellular HMGB1 levels could restore immune cell functions and protect the lungs from oxidative stress-induced injuries. They tested their hypothesis using animal models and immune cell cultures exposed to oxidative stress or bacterial challenges [
5]. UP446 was found to significantly reduce mortality rates, inhibit proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6), and chemokines (CINC-3), facilitate enhanced bacterial clearance from the lungs, and decrease airway protein levels, notably through the reduction of extracellular HMGB1 levels. Based on these facts, the authors concluded that the botanical composition as a potential intervention to protect the lung against oxidative stress-induced injuries.
Oxidative stress, arising from an imbalance between antioxidants and reactive oxygen species (ROS), intensifies with age due to cumulative exposure to environmental factors, lifestyle choices, and declining cellular repair mechanisms. As such, the relationship between oxidative stress, old age, and compromised immunity has damaging consequence impacting overall respiratory health and susceptibility to diseases. In particular, the consequence is detrimental for the respiratory system as it is an easy target for constant exogenous harmful attacks during respiration [
6].
In aging population, physiological changes such as decreased antioxidant defenses and mitochondrial dysfunction contribute to heightened oxidative stress. This oxidative burden can impair immune function by disrupting signaling pathways crucial for immune cell activation, proliferation, and response to pathogens. Compromised immunity in aging is characterized by reduced efficiency of innate and adaptive immune responses. This includes impaired phagocytosis by macrophages, decreased production of cytokines and antibodies by lymphocytes, dysregulation of inflammatory processes, and compromised immune responses [
7,
8]. These alterations make senior adults more vulnerable to infections due to chronic inflammatory conditions, less responsive to vaccination, and slower recovery from illnesses. Moreover, oxidative stress-induced damage to immune cells and thymus tissues exacerbates age-related immune dysfunction. This can lead to a vicious cycle where impaired immunity further enhances susceptibility to oxidative stress and associated health challenges [
9,
10]. Therefore, addressing oxidative stress in aging populations through lifestyle interventions, supplementation of dietary antioxidants, and potentially targeted interventions represents a promising approach to mitigate immune decline and improve overall health outcomes in senior adults.
Dietary supplements containing natural polyphenols offer a distinct advantage in oxidative stress management compared to basic antioxidant vitamins. These polyphenols, characterized by their diverse structures, potentially provide additional benefits beyond simple antioxidation [
11]. Extracts of Scutellaria baicalensis roots and Acacia catechu heartwoods, along with their active bioflavonoid constituents present in the UP446 composition, are recognized for their notably varied antioxidant properties. For instance, baicalin, a flavonoid from the root of S. baicalensis, effectively scavenges DPPH free radicals (IC50 = 27.21 µM), inhibits CuSO4-induced lipid peroxidation (IC50 = 95.09 µM), demonstrates significant metal-chelating activity (IC50 = 352.04 µM) [
12]; mitigated ROS production and MDA levels, while restoring SOD activity [
13]. Similarly, catechins from green teas and the heartwoods of Acacia catechu demonstrate potent abilities to neutralize reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, effectively protecting against oxidative stress-induced lipid peroxidation and associated damage. They act as scavengers of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and chelators of metal ions. Additionally, catechins exert indirect antioxidant effects by inducing antioxidant enzymes, inhibiting pro-oxidant enzymes, and stimulating the production of phase II detoxification and antioxidant enzymes [
14].
Hence, in the current study, we evaluated the effect of a standardized bioflavonoid composition, UP446, in oxidative stress accelerated immune senescence and chemical induced immune suppression models for its impact on mitigating aging associated declines of immune response, anti-inflammatory and antioxidation capacity. It’s antioxidation potential was also tested in vitro.
2. Material and Method
2.1. Composition
UP446 is a formulation containing extracts from heartwoods of Acacia catechu (Senegalia catechu) and roots of Scutellaria baicalensis, with preparation details disclosed in a US patent [
15]. The process for preparing the extracts and quantification of their full composition using High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) have been described by Yimam et al. [
16,
17]. UP446 is a greenish-yellow to brown powder with standardized bioflavonoid composition that contains not less than 60% baicalin from Scutellaria as its major component and not less than 10% catechins from Acacia plus other minor bioflavonoids from both plants [
16,
17].
2.2. Antioxidant Assay by Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC)
UP446 Sample was diluted in PBS (Phosphate-buffered saline) to generate 500, 250 and 50 µg/mL solutions for testing. Two independent dilution series were prepared. A Trolox standard curve was generated to give 100, 50, 25, 12.5 and 6.125 µM in PBS. 150 µl of fluorescein dilution was added to each well of a black 96-well plate. 25 µl of Trolox dilutions or sample dilutions were added to triplicate wells. The plate was incubated at 37oC for 10 minutes. AAPH (2,2′-Azodiisobutyramidine dihydrochloride) solution was prepared fresh for the assay using the assay buffer. The assay was initiated by adding 25 µl of the AAPH solution. The plate was inserted into the plate reader and a kinetic analysis of fluorescence decay was monitored every minute for 30 minutes at 37oC. Trolox antioxidant activity was used as a standard to compare the test sample dilutions. The area under the curve of normalized decay curves was determined for each concentration of control and sample. Trolox net AUC (Area Under the Curve) was used as a standard curve to calculate the Trolox equivalence of the test samples. Assay Plates: Black 96-well clear bottom plates; Reagents: Phosphate buffered saline (Lot: PBS104, ZenBio); Assay buffer Fluorescein (Lot: 041019, ZenBio); Trolox (Lot: 010622, ZenBio) AAPH (Lot: 0554100, ZenBio); Instruments: Tecan Infinite F500 Plate Reader.
2.3. Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppression in Mice
Purpose bred CD-1 mice were purchased from Charles River laboratories (Wilmington, MA, USA) at 22 – 24 g body weight and acclimated for 1 week. Following acclimation, weighed animals for their baseline weights and randomized them into 5 groups. There were 10 animals per group. Groups include G1 = Control animals without Cyclophosphamide, G2 = Model control with Cyclophosphamide, G3 = Cyclophosphamide + Levamisole 10 mg/kg, G4 = Cyclophosphamide + UP446 100 mg/kg and G5 = Cyclophosphamide + UP446 200 mg/kg. Immunosuppression was induced by administering Cyclophosphamide (Cy) at 80 mg/kg i.p. for 3 consecutive days. Study lasted for 3 weeks. For days 1-3, administered Cyclophosphamide (Cy) in all groups except normal Control (-). Cy dissolved in saline was injected intraperitoneally at 0.2 ml volume per animal. For days 4-21, gavaged mice orally once per day for the indicated test materials. During intervention period, mice received no Cy. Weighed animals weekly to determine subsequent dosages. Solutions was prepared for treatment groups in 0.5% CMC (Carboxy Methylcellulose) for oral delivery; 0.4 ml was administered per animal orally. on day 22 (Necropsy Day), blood was collected using serum separator tube and was kept for at least 30 minutes before spinning at 11,000 rpm for 5 minutes at 4 ͦ C. Serum was aspirated into microcentrifuge tubes (with about 400 µl yield) and stored in freezer until use.
2.4. IgA and IgG ELISA
ELISAs for serum IgA and IgG were carried out following manufacturer’s instructions. ELISA products Abcam ab157719 and Abcam ab157717 were used for IgG and IgA respectively. While 0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 200 and 400 ng/ml concentrations were used for IgA standards; 0, 3.91, 7.81, 15.6, 31.3, 62.5, 125 and 250 ng/ml concentrations were used for IgG. Briefly, pipetted 100 μL of each standard and samples in duplicate, into predesignated wells. Incubated the micro titer plate at room temperature for sixty (60 ± 2) minutes. Washed and added 100 μL of 1X Enzyme-Antibody Conjugate to each well. Incubated at room temperature for thirty (30 ± 2) minutes. Washed and blotted the wells. Pipetted 100 μL of TMB Substrate Solution into each well. Incubated in the dark at room temperature for ten minutes. After ten minutes, added 100 μL of Stop Solution to each well and determine the absorbance (450 nm) of the contents of each well.
2.5. D-Galactose Induced Accelerated Immune Senescence Model
Twelve-week-old purpose-bred CD-1 mice were obtained from Charles River Laboratories, Inc. (Wilmington, MA) and used for the study after a week acclimation period. The mice were kept in a temperature-controlled room (71-72 ºF) with a 12-hour light-dark cycle and had free access to food and water. They were randomly divided into four groups of immunized and non-immunized groups. The groups were as follows: G1 = normal control + vehicle (0.5% CMC), G2 = D-galactose + vehicle, G3 = D-galactose + UP446 100 mg/kg, and G4 = D-galactose + UP446 200 mg/kg. Each group consisted of 10 mice.
To induce accelerated immune senescence, mice were injected subcutaneously with D-galactose at a dose of 500 mg/kg daily for 10 weeks. Four weeks after the induction period began, at the beginning of the 5th week, treatment commenced with two doses of UP446 (100 mg/kg as the low dose and 200 mg/kg as the high dose), administered orally in a 0.5% CMC suspension for both immunized and non-immunized groups. In the eighth week, each mouse, except those in the non-immunized groups, received an intramuscular injection of 3 μg Fluarix quadrivalent influenza seasonal vaccine (2020-2021) (Lot # UJ477AA, 2020-2021) from GSK. This vaccine contained 60 μg hemagglutinin per 0.5 mL single human dose, formulated with 15 μg of each of the four influenza strains: H1N1, H3N2, B-Victoria lineage, and B-Yamagata lineage.
At the time of necropsy, (i.e. 14-days after immunization), blood (1 mL) was collected and aliquoted - 110 μL for a flow cytometry immunity panel in BD Microtainer® Tubes w/ Dipotassium EDTA (Lavender), which were delivered on ice to Flow Contract Site Laboratory (Bothell, WA), serum was isolated from the remaining blood (SST, centrifuged at 1,500 rpm for 10 min at 4°C, about 400 μL serum yield) for antibody ELISAs and enzymatic assays. Weights of the thymus for each animal were taken to determine thymus indices. The spleens were kept on dry ice at the time of necropsy and transferred to -80°C for future use.
Daily oral gavaging of UP446 was performed for six weeks, from the fifth week to the tenth week. At the time of necropsy, 14 days after immunization, 1 mL of blood was collected. A 110 μL aliquot was taken for a flow cytometry immunity panel in BD Microtainer® Tubes with Dipotassium EDTA (Lavender) and delivered on ice to Flow Contract Site Laboratory (Bothell, WA). Serum was isolated from the remaining blood using SST, centrifuged at 1500 rpm for 10 minutes at 4°C, yielding approximately 400 μL, for antibody ELISAs and enzymatic assays. The thymus weights were recorded for each animal to determine thymus indices. The spleens were preserved on dry ice at necropsy and then transferred to -80°C for future use.
2.6. Flow Cytometry Method
Whole blood was collected via cardiac puncture and transferred to EDTA blood collection tubes. Non-immunized samples were refrigerated overnight, while immunized samples were kept at room temperature on a nutator for up to 6 hours. The whole blood samples were then delivered on ice to the Flow Contract Site Lab (Bothell, WA) for 10-marker flow cytometry analysis. Doublets and debris were excluded, and the total cell population was identified using forward and side scatter gating. Fluorescent antibodies were used to identify cell populations. The whole blood was incubated for 15 - 20 minutes with the following antibodies: Mouse (m)CD45 V510 clone 30-F11 (BioLegend, #103137), mCD3 APCCy7 clone 17A2 (BioLegend, #100221), mCD4 PECy7 clone GK1.5 (BioLegend, #100421), mCD8 AF700 clone 53-6.7 (BioLegend, #100729), mCD49b FITC clone DX5 (BioLegend, #108905), mLy6G APC clone 1A8 (BioLegend, #127613), mCD45R/B220 V605 clone RA3-6B2 (BioLegend, #103243), mNKp46 V421 clone 29A1.4 (BioLegend, #137611), mTCRγδ PE clone GL3 (BioLegend, #118107), and 7-AAD (BD or BioLegend, #420403). Red blood cells were lysed with PharmLyse (BD, #555899), and the samples were centrifuged and resuspended in calcium and magnesium-free DPBS (ThermoFisher Scientific, #J67802K2) before being mixed with CountBright beads (ThermoFisher Scientific, #C36950). Flow cytometric data acquisition was performed using a FACSCantoA, FACSCanto 10 Color flow cytometer, and BD FACSDivaTM software. Cell populations were determined by electronic gating based on forward versus side scatter.
2.7. Serum Glutathione Peroxidase Activity
Mouse serum samples were tested for Glutathione Peroxidase activity using a Glutathione Peroxidase Assay Kit (Colorimetric) (Abcam ab102530) following manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, a reaction mix was prepared by adding 33 µl Assay Buffer, 3 µl 40 mM NADPH solution, 2 µl GR solution and 2 µl GSH solution. While standard wells were prepared at 100 µL standard dilutions; sample, and reagent control wells were prepared at 50 µL per well. Added 40 µL Reaction Mix to sample, and reagent control wells only. Incubated plate at room temperature for 15 mins. Read absorbance at OD 340 nm. Added 10 µL cumene hydroperoxide solution to sample and reagent control wells only. Measured output (A1) on a microplate reader at T1 at OD340 nm. Incubated at 25ºC for 5 min, protected from light. Measured output (A2) on a microplate reader at T2 at OD340 nm. Each sample was assayed in duplicate and the absorbances of each sample were compared to a NADPH Standard curve.
2.8. Spleen Homogenate NFκB Measurement Method
Mouse spleen tissues were homogenized in RIPA Lysis Buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 150 mM NaCl, 1% NP-40, 0.5% Sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS) at a concentration of 100 mg tissue/mL buffer for 3 x 10 seconds on ice. The homogenates were then incubated on ice for 30 minutes to enhance tissue lysis and centrifuged at 16,000 RCF for 10 minutes at 4°C. The supernatants were transferred to new microcentrifuge tubes and frozen at -80°C. Spleen homogenates were run on SDS-PAGE and expressions of markers were detected using primary antibodies against NFκB (Abcam, ab140751) with a Goat anti-Rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor Plus 488 secondary antibody, and anti-β-actin (Life Technologies, MA5-15739-D680).
2.9. Serum Advanced Glycation End Products AGE
Mouse serum samples were tested for AGEs using the Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) Assay Kit (Colorimetric Assay, Abcam ab273298) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, samples were diluted to a protein concentration of 1 mg/mL with AGEs Assay Buffer. 10 µL of the diluted samples were added to the wells of a white 96-well plate, and the volume was adjusted to 200 µL with AGEs Assay Buffer. A 1 mg/mL AGEs Positive Control was prepared by adding 2 µL of 10 mg/mL AGEs Positive Control to 18 µL of AGEs Assay Buffer. The same volume of the 1 mg/mL AGEs Positive Control was added to the wells designated as "Positive Control," and the volume was adjusted to 200 µL with AGEs Assay Buffer. The plate was incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes, protected from light. Fluorescence was measured at room temperature in end-point mode using a Tecan fluorescence microplate reader with excitation/emission settings of 360/460 nm.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using SigmaPlot 14.5 data analysis software (Palo Alto, CA). Results are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical significance between groups was determined using single-factor analysis of variance and a paired t-test. P-values of 0.05 or less (p ≤ 0.05) were considered statistically significant. Percent changes from the vehicle were calculated using the formula: % changes = {(Mean value of Vehicle - Mean value of active test article) / Mean value of Vehicle} × 100
3. Results
3.1. Antioxidation Activity of UP446 as Measured by ORAC
UP446 has been found to possess strong anti-oxidation activity as measured in ORAC with a total ORAC value of 70,930 (µmole TE) per gram (Table 1). The ability of UP446 to neutralize Peroxyl Radicals, Hydroxyl Radicals, Peroxy Nitrite, Super Oxide Anion and Singlet Oxygen radicals was measured and found as described in Table 1.
| Material |
Specification |
Peroxyl Radicals |
Hydroxyl Radicals |
Peroxy
Nitrite
|
Super Oxide Anion |
Singlet Oxygen |
ORAC 5.0 (Total Score) |
| UP446 |
≥ 60% baicalin
≥ 10% catechins |
8,375 |
55,660 |
1,397 |
4,767 |
731 |
70,930 |
The ORAC result is expressed as micromole Trolox equivalency (µmole TE) per gram. The ORAC (Trolox equivalents, TE) value was calculated by dividing the area under the sample curve by the area under the Trolox curve, with both areas being corrected by subtracting the area under the blank curve. Trolox was used as a positive control
3.2. Immunomodulation Effect of UP446 on Cyclophosphamide-Induced Immunosuppression
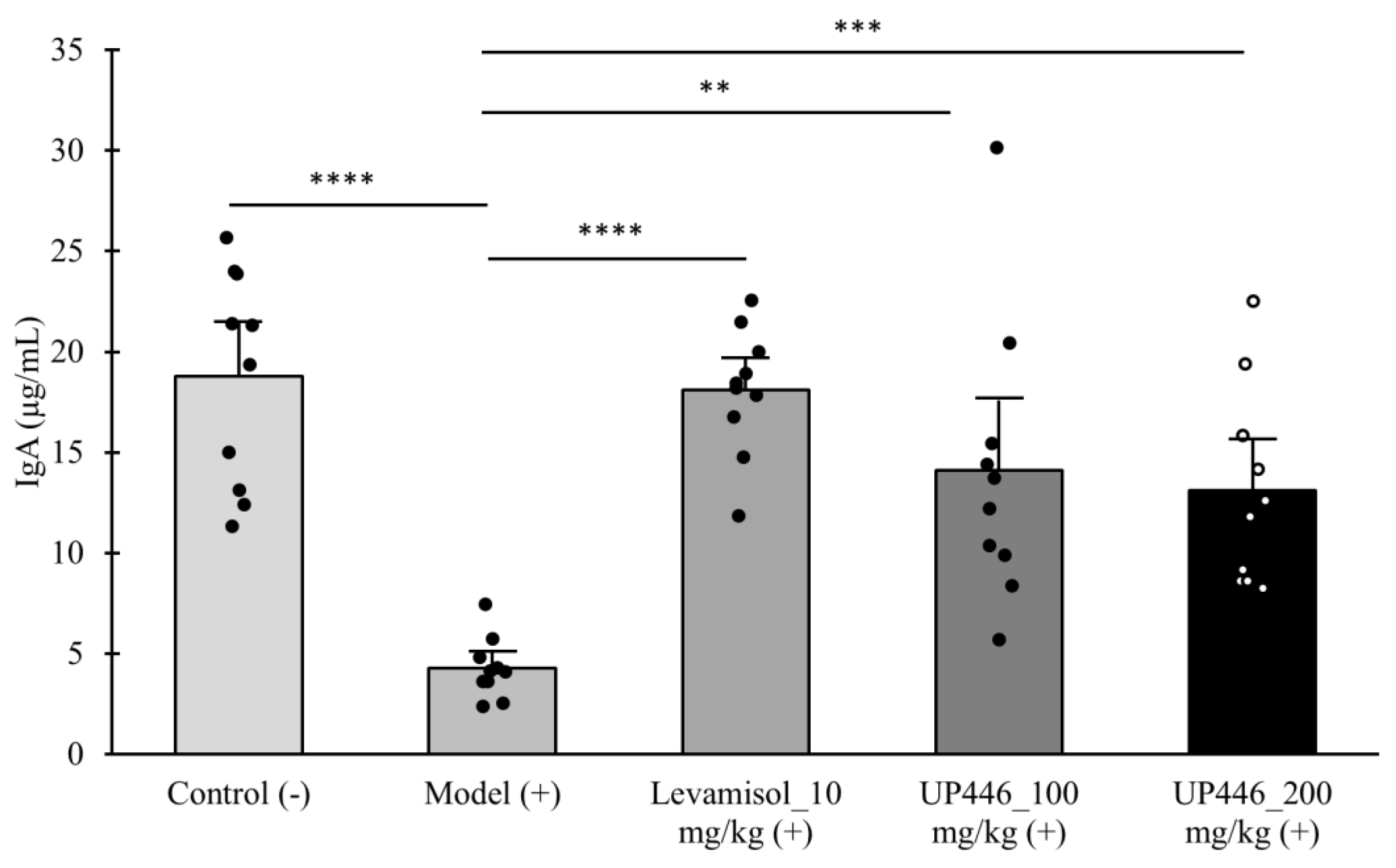
Injection of Cy to mice resulted in a 4.38- and 2.03-fold significant reduction in the serum level of IgA and IgG in CD-1 mice, respectively (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). These reductions were restored by oral supplementation of UP446. In the case of IgA, mice treated with UP446 at 100 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg showed a 3.26- and 3.06-fold increases in the serum IgA level of mice, respectively (
Figure 1). These increases in the level of serum IgA were statistically significant compared to the immune suppressed group.
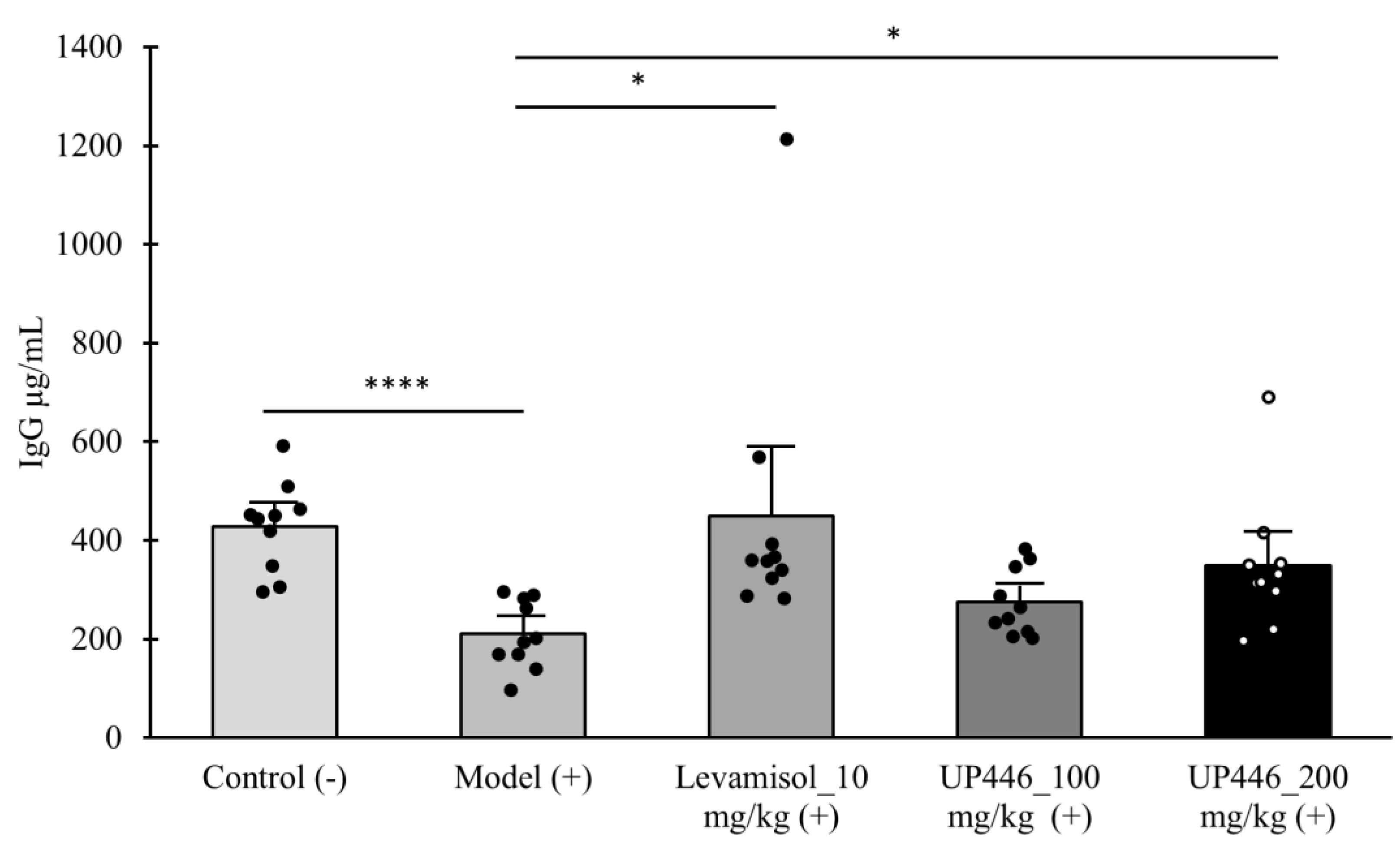
A similar immune modulation was observed for IgG. Mice treated with UP446 at 100 and 200 mg/kg showed a 1.3- and 1.66-fold increases in the level of serum IgG, respectively. The induction in IgG was statistically significant for the 200 mg/kg of UP446 (
Figure 2). The reference compound (Levamisole) produced statistically significant 4.22- and 2.13-fold increase in the level of serum IgA and IgG, respectively.
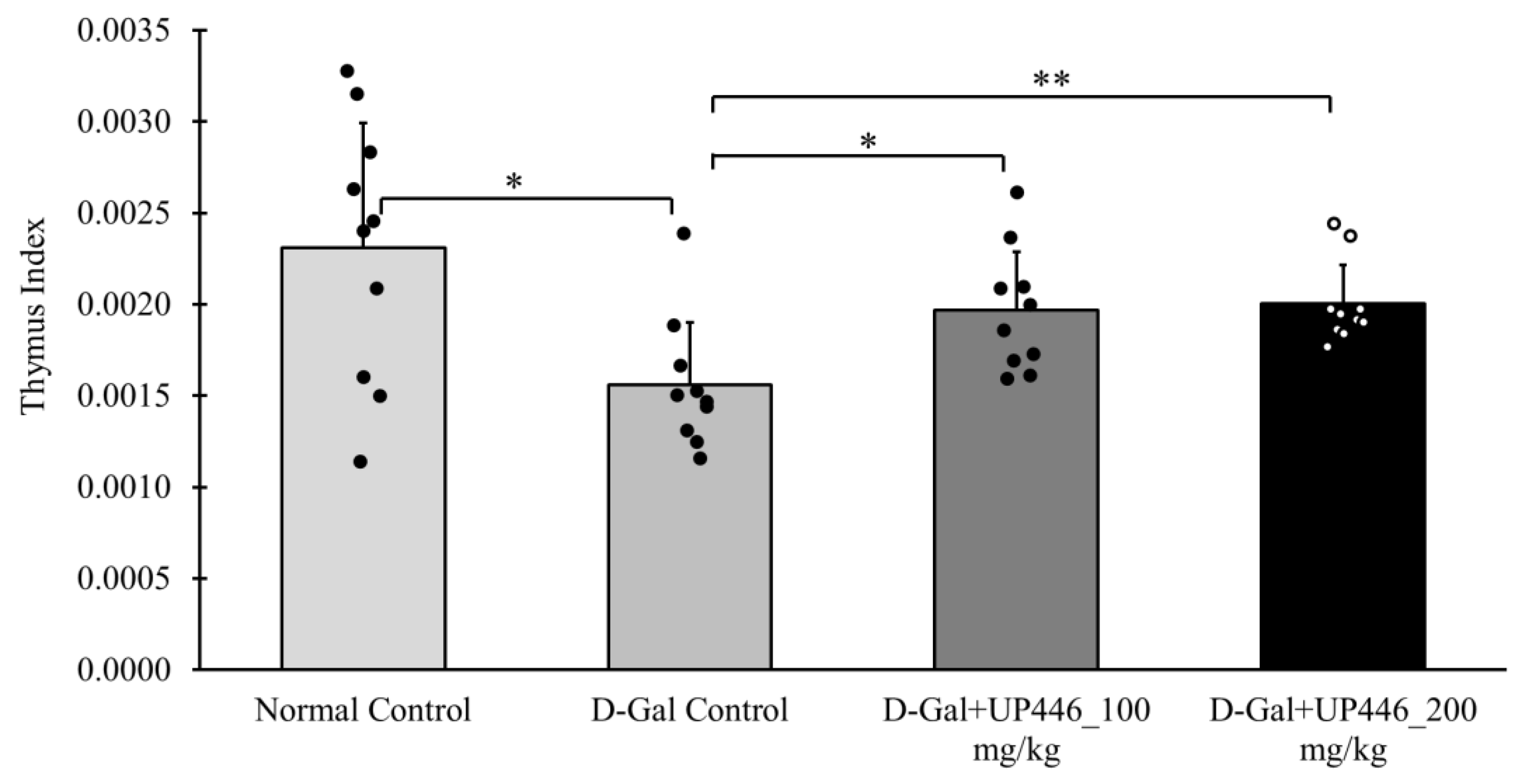
3.3. Effect of UP446 on the Immune Organ: The Thymus
In the immunized mice, D-Gal-induced immune senescence mice given the vehicle displayed a significant 30.3% reduction in the thymus index compared to the normal control mice (
Figure 3). This reduction was reversed by UP446 at both dosages. Mice treated orally with UP446 at 100 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg showed a 47.4% and 49.4% increase in thymus index, respectively, compared to the vehicle-treated immune compromised group (
Figure 3). This reversal was statistically significant for both doses of UP446.
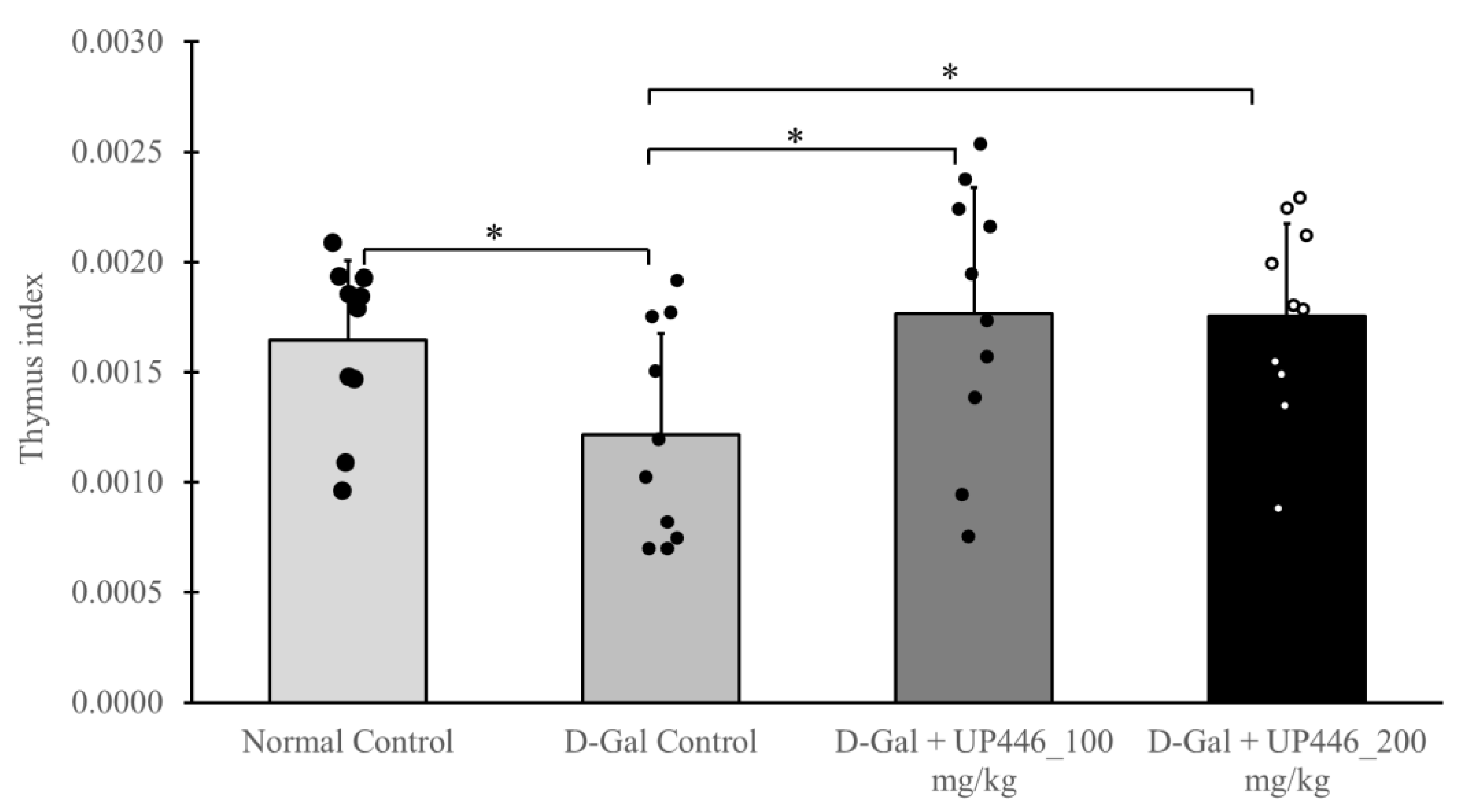
Similarly, in non-immunized mice, UP446 at 200 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg also led to statistically significant increases in the thymus index, with increases of 27.4% and 31.6%, respectively, compared to the vehicle-treated immune compromised mice (
Figure 4).
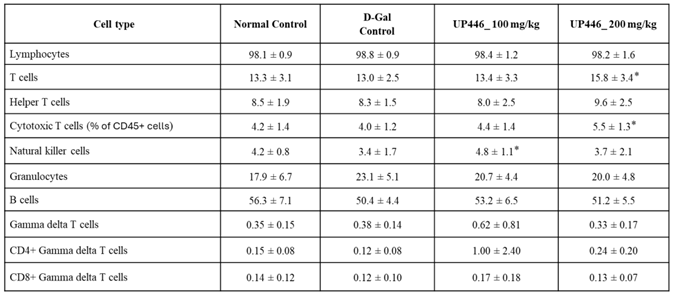
3.4. Effect of UP446 on Circulating Immune Cell Populations in Immunized Mice
The levels of circulating immune cells in the immunized groups of mice were evaluated at the study’s conclusion. Expressed as a percentage of all white blood cells (CD45+ cells), dose -correlated 22.5% and 42.5% increases in the natural killer cells (NK-cells) were observed for mice treated with UP446 at 100 and 200 mg/kg, respectively. These elevations of circulating NK-cells were statistically significant when compared to the D-gal + vehicle group. Changes for other immune cells were minimal (Table 2).
Table 2.
Effect of UP446 on circulating immune cell populations in immunized mice.
Table 2.
Effect of UP446 on circulating immune cell populations in immunized mice.
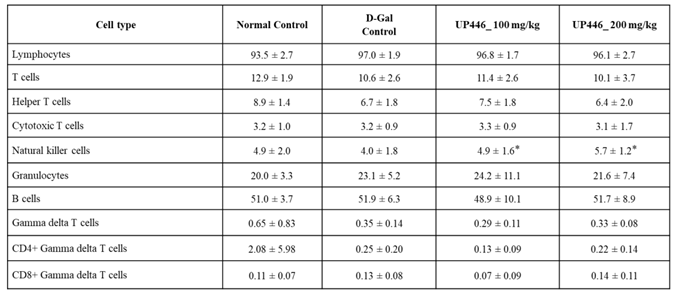
3.5. Effect of UP446 on Circulating Immune Cell Populations in Non-Immunized Mice
In comparison to the D-gal non-immunized group, the non-immunized 200 mg/kg UP446 + D-gal group had a statistically significant 21.5% higher level of T-cells (CD3+ cells), expressed as a percentage of all white blood cells (CD45+ cells) (Table 3). A similar increase of 37.5% was also observed for CD3+CD8+ cytotoxic T-cells in non-immunized D-gal mice treated with 200 mg/kg of UP446 (Table 3). At the lower dosage of 100 mg/kg, non-immunized D-gal mice treated with UP446 showed a statistically significant 41.2% increase in natural killer cells (Table 3). Statistically non-significant moderate to minimal changes were observed for other immune cells at both dosages.
Table 3.
Effect of UP446 on circulating immune cell populations in non-immunized mice.
Table 3.
Effect of UP446 on circulating immune cell populations in non-immunized mice.
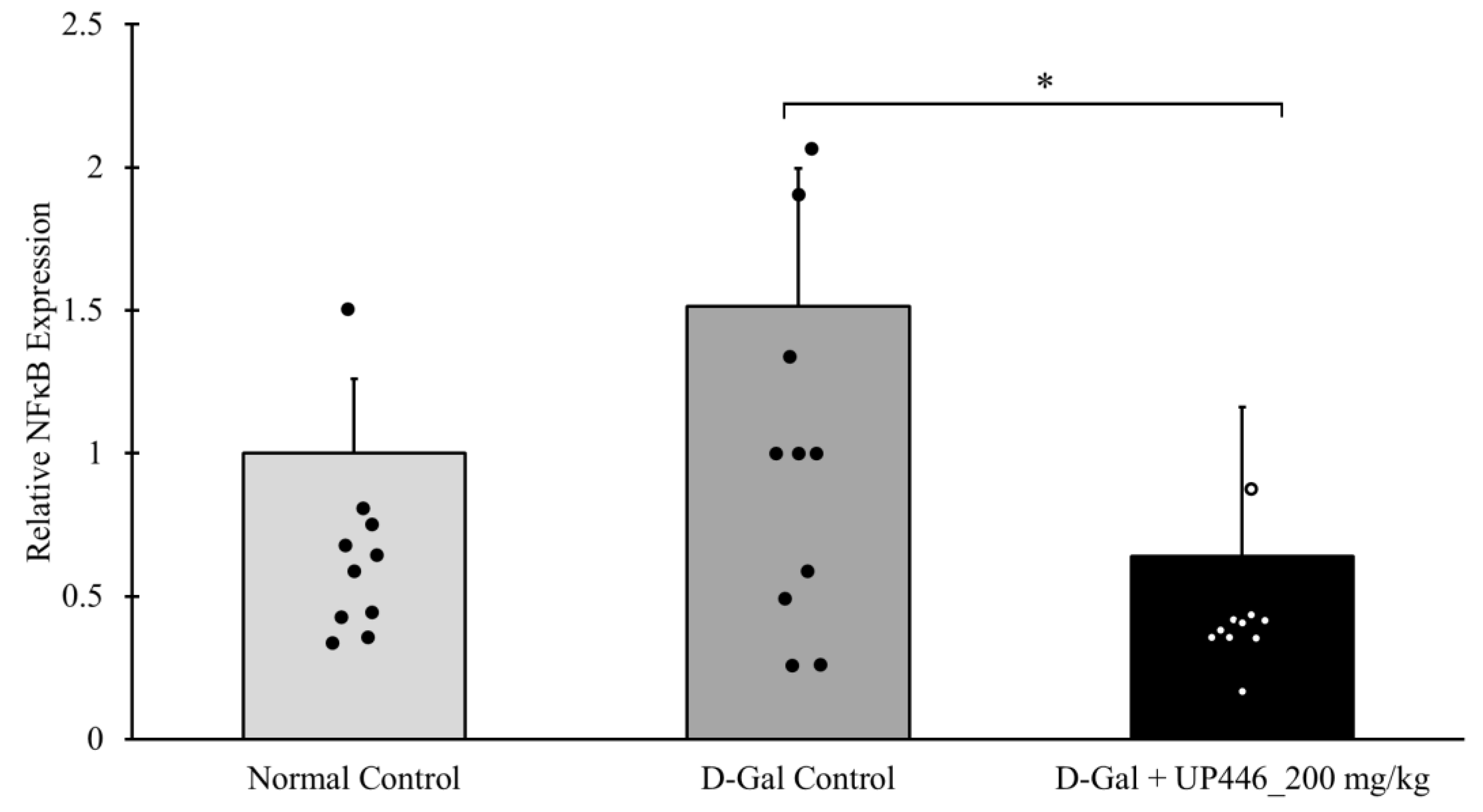
3.6. Effect of UP446 on a Transcription Factor NFκB
The SDS-PAGE assay showed that non-immunized D-gal mice treated with the vehicle had a 51.6% increase in the expression of NFκB. This elevation in the expression of the inflammatory transcription factor was mitigated by the use of UP446. A statistically significant 57.9% suppression in the expression of NFκB was observed in mice treated with 200 mg/kg of UP446 in the non-immunized group (
Figure 5).
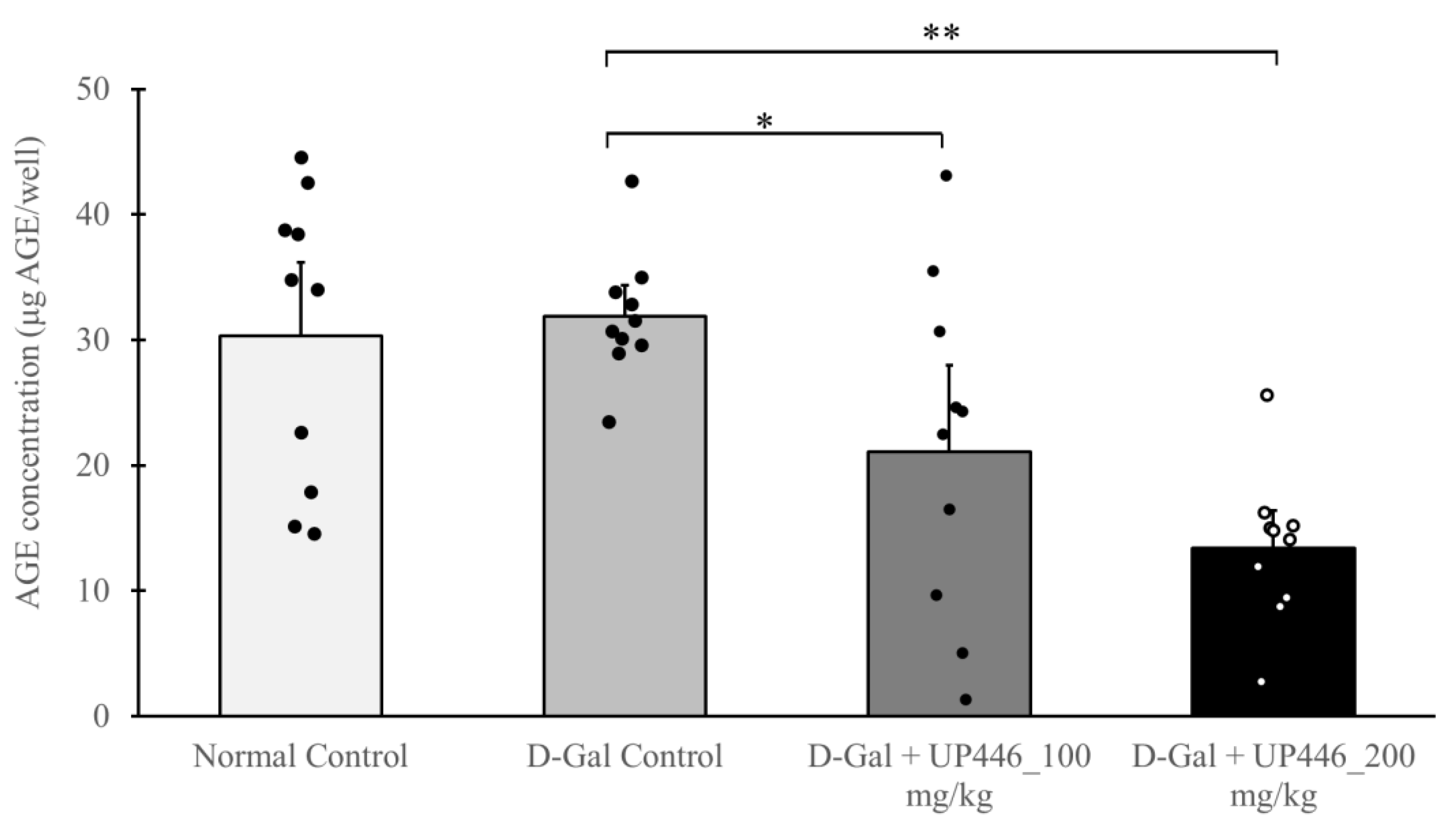
3.7. Effect of UP446 on Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)
Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) were measured in non-immunized and immunized serum samples. The data showed that the non-immunized D-Gal + UP446 groups had significantly lower serum AGEs than the non-immunized D-Gal mice treated with the vehicle. These reductions were dose-correlated, with 33.9% and 58.0% reductions in serum AGE levels for the 100 and 200 mg/kg UP446, respectively (
Figure 6).
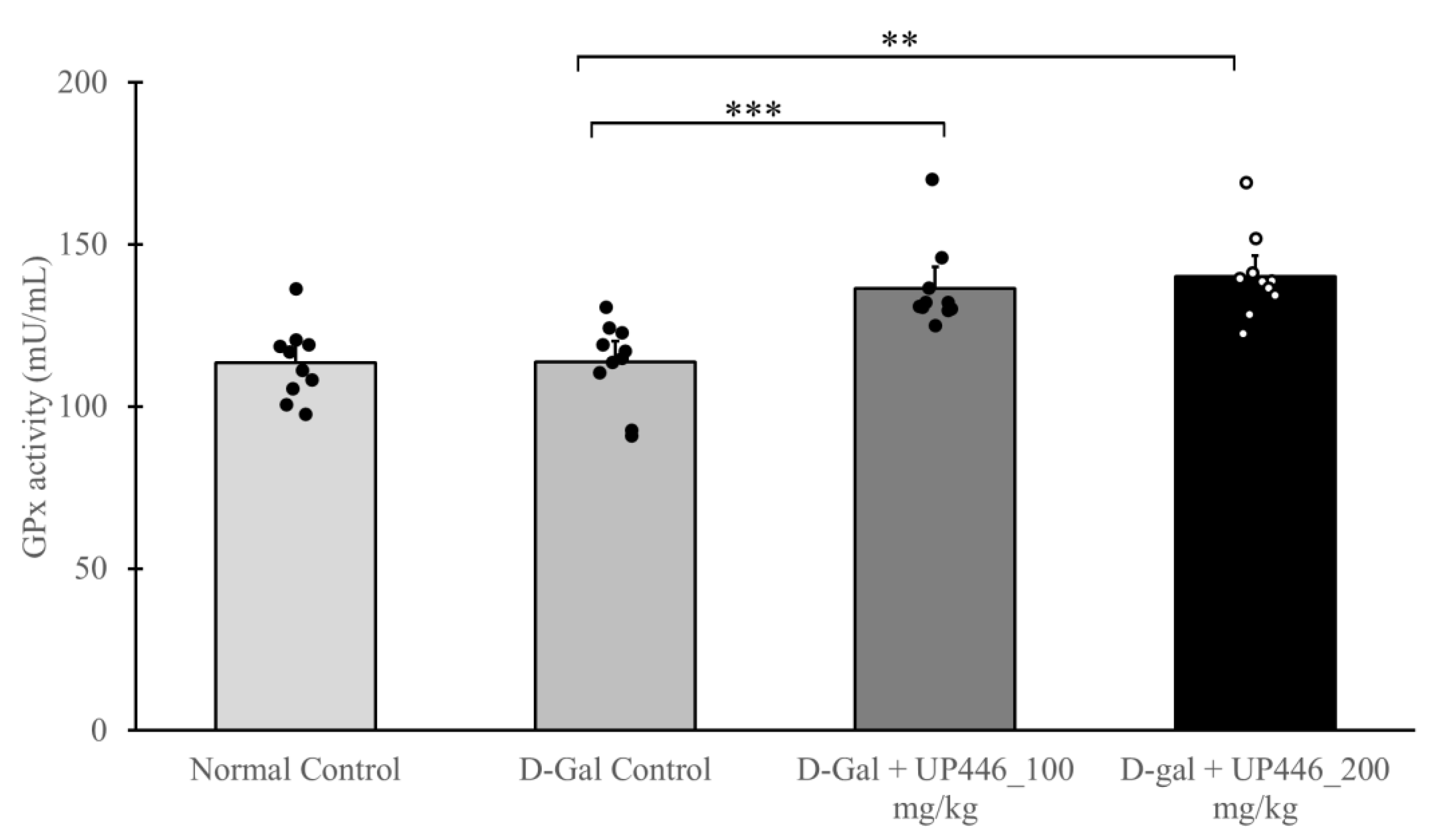
3.8. Effect of UP446 on Antioxidant Enzyme Glutathione Peroxidase In Vivo
Increased antioxidation enzymes indicates the capability of an intervention to enhance the host’s capacity to neutralize excess reactive oxygen species. The activity of glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) was determined in serum samples from immunized mice. A dose-correlated, statistically significant increase of 20.1% and 23.3% in glutathione peroxidase activity was observed in immunized D-Gal mice treated with 100 and 200 mg/kg UP446, respectively (
Figure 7).
4. Discussion
Immunosenescence, the gradual decline of the immune system associated with aging, is closely linked with oxidative stress. In the context of the respiratory system, oxidative stress exacerbates the decline in immune function by compromising phagocytosis of immune cells and initiating chronic inflammation. The lungs are especially susceptible to oxidative stress due to constant exposure to environmental pollutants, pathogens, and other harmful agents inhaled during respiration. Immunosenescence further reduces the lungs’ ability to respond to infections and repair damage, increasing vulnerability to respiratory diseases and chronic conditions. Together, oxidative stress and immunosenescence create a vicious cycle, where impaired immune function enhances susceptibility to oxidative damage, and oxidative stress further weakens the immune response. This highlights the importance of interventions to manage oxidative stress and support immune function in aging populations to protect lung health. Herbal medicines are seen as safer alternatives to conventional therapies for respiratory system support; however, most are not scientifically validated for their safety and effectiveness as alternatives to natural supplements.
Data compiled in this report suggest that UP446 as a natural standardized bioflavonoid composition extracted from roots of Scutellaria baicalensis and heartwoods of Acacia catechu could potentially disrupt the oxidative stress and immunosenescence perpetual occurrence by mitigating age associated immune decline and possessing strong antioxidation properties.
UP446 showed strong anti-oxidation properties in vitro. The Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) measures a substance’s ability to neutralize free radicals. Higher ORAC values suggest a greater capacity to neutralize free radicals. UP446 showed to possess high ORAC value at 70,930 (µmole TE) per gram. While the body typically maintains a balance between free radicals and antioxidants, excessive free radical production may require intervention. As such, UP446 could serve as a metabolism “sink” for the excess ROS to minimize their unwanted signaling and tissue damage.
Antioxidants such as UP446 play a crucial role in mitigating the formation and effects of advanced glycation end products (AGEs). By neutralizing reactive oxygen species and inhibiting glycation processes, UP446 helps reduce oxidative stress and AGE accumulation. In this study, an age-associated increase in advanced glycation end products (AGEs) was observed in Galactose induced aging mice treated with a vehicle. UP446 significantly decreased the level of AGEs up to 58.0% after oral administration 200 mg/kg.
The accumulation of AGEs accelerates the decline in multiple system functions seen with aging, thus contributing to the aging process [
18]. AGEs are known to cause extensive tissue damage by increasing inflammation and oxidative stress. Consistent with our findings, some antioxidants, like resveratrol, have shown potential in preventing AGE formation and breaking existing AGE cross-links, which can alleviate tissue damage and improve vascular health [
19]. Therefore, incorporating UP446 into a daily supplement could promote wellness and combat age-related complications linked to AGE accumulation.
Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) is a key endogenous antioxidant enzyme that plays a critical role in protecting cells from oxidative stress [
20]. It safeguards the body against oxidative stress-induced cellular dysfunction and contributes to overall health. Its regulation is significant in defending against age-related diseases. D-Gal induced aged mice supplemented with UP446 showed a dose-dependent increase in the level of GPx. Previously, individual components of UP446 have shown a significant increase in the level of GPx. For example, the antioxidative actions of flavonoids quercetin and catechin were reported through the activation of hepatocyte glutathione peroxidase [
21]. Similarly, multiple studies have shown the impact of baicalin in reversing oxidative stress-induced reduction of glutathione peroxidase [
22,
23]. The results observed in our study could be the combined and synergistic effect of those 2 bioactive flavonoids in stimulating the production of GPx.
As maintaining adequate GPx function is crucial for supporting optimal antioxidant defense mechanisms and mitigating oxidative stress-related health risks, the inclusion of UP446 as a dietary supplement could provide significant benefits for overall health.
The NF-kB as a transcription factor complex is one of the cellular sensors that responds to oxidative stress and regulates gene expression [
24]. Oxidative stress and the NF-κB signaling pathway are closely interconnected and significantly influence the aging process [
25]. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) from oxidative stress activate NF-κB, a transcription factor that drives the gene expressions of many pro-inflammatory cytokines. This leads to chronic sterile inflammation, a key feature of aging and related chronic diseases. The feedback loop between ROS and NF-κB exacerbates oxidative damage and inflammation, contributing to immune cellular senescence and tissue function decline.
In the current study, aged D-gal mice treated with a vehicle showed a significant increase in the expression of NF-kB. In contrast, when these aged mice were orally administered UP446, the expression of NF-kB was significantly reduced. In agreement with our findings, it was previously reported that the inflammatory gene transcriptional factor controller, NF-κB, was down-regulated by UP446 in LPS-induced cellular models, highlighting the anti-inflammatory activities of UP446 [
26]. Therefore, targeting oxidative stress and NF-κB activity through supplementation with UP446, which possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, could promote healthy aging and mitigate age-related chronic diseases.
Repetitive subcutaneous administration of D-galactose into mice induces significantly oxidative stress that causes the damage of immune organ such as thymus, resembling changes that occur in the normal aging process. A higher thymus index corresponds to a stronger immune response [
27]. The thymus indices for the normal control group and both UP446 + D-gal treatment groups were found to be significantly higher than the vehicle + D-gal group, demonstrating the protection of this immune organ from oxidative stress induced senescence, which could lead to increased immune cell production and maturation. Substantiating our findings using this model, Wei et al. have demonstrated Resveratrol enhanced proliferation of immune cells as a result of amelioration of thymus senescence and prevention of involution [
28].
Supplementation with the bioflavonoid composition UP446 induced mucosal immunity, in particular by increasing the production of IgA while also increasing IgG levels. This suggests the potential application of UP446 in the protection of the lung and maintenance of mucosal immunity. A declined immune response, as reflected by reduced antibody production (IgA and IgG) and suppressed innate (NK cells) and adaptive immune cells (T cells and cytotoxic T cells), has been documented in the Endoxan-induced immune suppression and accelerated aging models. Reduced efficiency of both innate and adaptive immune responses, characterized by weakened macrophage activity, lower cytokine and antibody production, and impaired inflammatory regulation, are among the key features of immunosenescence. Supplementation with UP446 has reversed these age-associated and chemically induced immune senescence.
In particular, the increase in IgA plays a significant role in mucosal protection of the respiratory system, where this immunoglobulin is known to shield the mucosal surfaces from microorganisms and foreign antigens. It also neutralizes bacterial products and eliminates pathogens or antigens that have breached the mucosal surface [
29]. These preclinical findings were later corroborated in a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, where total IgA and IgG levels were found to be increased in senior participants who were orally supplemented with UP446 250 mg b.i.d compared to those on placebo. In the same clinical study, Lewis et al. reported that serum glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) was increased as a result of 500 mg/day UP446 supplementation, supporting the current preclinical antioxidation findings [
30].
Collectively, supplementation with the standardized bioflavonoid composition of not less than 60% baicalin from roots of Scutellaria baicalensis and not less than 10% catechins from heartwoods of Acacia catechu, resulted in protection of immune senescence from oxidative stress. In addition to the previously reported traditional usage, extracellular HMGB1 suppression activity and the increase in IgA from the human clinical trial, data depicted in this report suggest that supplementation with UP446 could be beneficial for respiratory system support during immune-stressing conditions caused by aging, oxidative stress and/or pathogen challenges.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Y., T.H. and Q.J.; Data curation, M.Y., T.H. and Q.J.; Formal analysis, M.Y., T.H., and Q.J.; Funding acquisition, Q.J.; Investigation, M.Y., T.H., A.O., P.C., P.J. and M.H.; Methodology, M.Y., T.H., P.J. and M.H.; Project administration, M.Y., and Q.J.; Resources, Q.J.; Supervision, M.Y. and Q.J.; Validation, M.Y., T.H., P.J., M.H. and Q.J.; Visualization, M.Y. and Q.J.; Writing—original draft M.Y.; Writing—review and editing, M.Y., and Q.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
No outside fund was acquired for this work. All expense were covered by Unigen.
Institutional Review Board Statement
No animal or human experiments were conducted in this report.
Data Availability Statement
Conclusions were made based on data depicted on this manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their utmost gratitude to Bill Lee, the owner of Econet/Unigen, Inc., who supported the fulfillment of project.
Conflicts of Interest
M.Y., P.J., M.H., and Q.J. are current Unigen employees; therefore, they have competing financial interests.
References
- Hou T, Zhu L, Wang Y, Peng L. Oxidative stress is the pivot for PM2.5-induced lung injury. Food Chem Toxicol. 2024 Feb;184:114362. [CrossRef]
- Entezari M, Javdan M, Antoine DJ, Morrow DM, Sitapara RA, Patel V, Wang M, Sharma L, Gorasiya S, Zur M, Wu W, Li J, Yang H, Ashby CR, Thomas D, Wang H, Mantell LL. Inhibition of extracellular HMGB1 attenuates hyperoxia-induced inflammatory acute lung injury. Redox Biol. 2014 Jan 20;2:314-22. [CrossRef]
- Patel V, Dial K, Wu J, Gauthier AG, Wu W, Lin M, Espey MG, Thomas DD, Ashby CR Jr, Mantell LL. Dietary Antioxidants Significantly Attenuate Hyperoxia-Induced Acute Inflammatory Lung Injury by Enhancing Macrophage Function via Reducing the Accumulation of Airway HMGB1. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 1;21(3):977. [CrossRef]
- Wang M, Gauthier A, Daley L, Dial K, Wu J, Woo J, Lin M, Ashby C, Mantell LL. The Role of HMGB1, a Nuclear Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern Molecule, in the Pathogenesis of Lung Diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019 Nov 1;31(13):954-993. [CrossRef]
- Ymam M, Horm T, O’Neal A, Jiao P, Hong M, Brownell L, Jia Q, Lin M, Gauthier A, Wu J, Venkat Mateti K, Yang X, Dial K, Zefi S, Mantell LL. A Standardized Botanical Composition Mitigated Acute Inflammatory Lung Injury and Reduced Mortality through Extracellular HMGB1 Reduction. Molecules. 2023 Sep 11;28(18):6560. [CrossRef]
- Hajam YA, Rani R, Ganie SY, Sheikh TA, Javaid D, Qadri SS, Pramodh S, Alsulimani A, Alkhanani MF, Harakeh S, Hussain A, Haque S, Reshi MS. Oxidative Stress in Human Pathology and Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Perspectives. Cells. 2022 Feb 5;11(3):552. [CrossRef]
- Guo J, Huang X, Dou L, Yan M, Shen T, Tang W, Li J. Aging and aging-related diseases: from molecular mechanisms to interventions and treatments. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Dec 16;7(1):391. [CrossRef]
- Teissier T, Boulanger E, Cox LS. Interconnections between Inflammageing and Immunosenescence during Ageing. Cells. 2022 Jan 21;11(3):359. [CrossRef]
- Luo J, Mills K, le Cessie S, Noordam R, van Heemst D. Ageing, age-related diseases and oxidative stress: What to do next? Ageing Res Rev. 2020 Jan;57:100982. [CrossRef]
- Espino J, Pariente JA, Rodríguez AB. Oxidative stress and immunosenescence: therapeutic effects of melatonin. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:670294. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Huang, K.; Yang, X.; Xu, H. Free radical scavenging and antioxidant activities of flavonoids extracted from the radix of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 1999, 1472, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel KR, Kim DW. Microparticles-Mediated Vascular Inflammation and its Amelioration by Antioxidant Activity of Baicalin. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Sep 20;9(9):890. [CrossRef]
- Bai X, Yao M, Zhu X, Lian Y, Zhang M. Baicalin suppresses interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis, inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and extracellular matrix degradation in human nucleus pulposus cells. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2023 Dec;45(4):433-442. [CrossRef]
- Bernatoniene J, Kopustinskiene DM. The Role of Catechins in Cellular Responses to Oxidative Stress. Molecules. 2018 Apr 20;23(4):965.
- Jia, Q. Formulation of a mixture of free-B-ring flavonoids and flavans as a therapeutic agent. Patent number US751 4469B2. USA, 2009.
- Yimam M, Zhao Y, Ma W, Jia Q, Do S-G, Shin J-H. 90-day oral toxicity study of UP446, a combination of defined extracts of Scutellaria baicalensis and Acacia catechu, in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2010;48(5):1202–9. [CrossRef]
- Yimam M, Lee YC, Jia Q. 26-week repeated oral dose toxicity study of UP446, a combination of defined extracts of Scutellaria baicalensis and Acacia catechu, in beagle dogs. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016;78:66–77. [CrossRef]
- Semba RD, Nicklett EJ, Ferrucci L. Does accumulation of advanced glycation end products contribute to the aging phenotype? J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2010 Sep;65(9):963-75. [CrossRef]
- Maleki V, Foroumandi E, Hajizadeh-Sharafabad F, Kheirouri S, Alizadeh M. The effect of resveratrol on advanced glycation end products in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2022 Feb;128(1):253-260. [CrossRef]
- Averill-Bates DA. The antioxidant glutathione. Vitam Horm. 2023;121:109-141.
- Nagata H, Takekoshi S, Takagi T, Honma T, Watanabe K. Antioxidative action of flavonoids, quercetin and catechin, mediated by the activation of glutathione peroxidase. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 1999 Apr;24(1):1-11.
- Ma L, Wu F, Shao Q, Chen G, Xu L, Lu F. Baicalin Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Diabetic Nephropathy via Nrf2 and MAPK Signaling Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Jul 21;15:3207-3221. [CrossRef]
- Fang J, Wang H, Zhou J, Dai W, Zhu Y, Zhou Y, Wang X, Zhou M. Baicalin provides neuroprotection in traumatic brain injury mice model through Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Aug 10;12:2497-2508.
- Helenius M, Hänninen M, Lehtinen SK, Salminen A. Aging-induced up-regulation of nuclear binding activities of oxidative stress responsive NF-kB transcription factor in mouse cardiac muscle. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1996 Mar;28(3):487-98. [CrossRef]
- Galli F, Marcantonini G, Giustarini D, Albertini MC, Migni A, Zatini L, Gioiello A, Rossi R, Bartolini D. How Aging and Oxidative Stress Influence the Cytopathic and Inflammatory Effects of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The Role of Cellular Glutathione and Cysteine Metabolism. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jul 14;11(7):1366. [CrossRef]
- Tseng-Crank J, Sung S, Jia Q, Zhao Y, Burnett B, Park DR, Woo SS. A medicinal plant extract of Scutellaria Baicalensis and Acacia catechu reduced LPS-stimulated gene expression in immune cells: a comprehensive genomic study using QPCR, ELISA, and microarray. J Diet Suppl. 2010 Sep;7(3):253-72. [CrossRef]
- Thapa P, Farber DL. The Role of the Thymus in the Immune Response. Thorac Surg Clin. 2019 May;29(2):123-131.
- Wei TT, Li MJ, Guo L, Xie YD, Chen WH, Sun Y, Liu GH, Ding Y, Chai YR. Resveratrol ameliorates thymus senescence changes in D-galactose induced mice. Microbiol Immunol. 2020 Sep;64(9):620-629.
- Pilette C, Ouadrhiri Y, Godding V, Vaerman JP, Sibille Y. Lung mucosal immunity: immunoglobulin-A revisited. Eur Respir J. 2001 Sep;18(3):571-88.
- Lewis ED, Crowley DC, Guthrie N, Evans M. Role of Acacia catechu and Scutellaria baicalensis in Enhancing Immune Function Following Influenza Vaccination of Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Triple-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023 Sep-Oct;42(7):678-690.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).