1. Introduction
Cancer vaccines and immunotherapies have emerged as revolutionary approaches to cancer treatment, offering new hope and improved patient outcomes [
1,
2,
3,
4]. However, patient response rates vary across different types of cancer and depend on patients’ individual characteristics [
5]. Notably, numerous types of cancers are poorly immunogenic, and the tumor microenvironment (TME) is often immunosuppressive and/or refractile to the infiltration of immune cells [
6]. To overcome such obstacles, efforts are underway to improve tumor immunogenicity and change the nature of the TME to an immune-active state [
6,
7].
An innovative and efficient method for developing a novel vaccine formulation is to use live bacteria as a vector to deliver heterologous (tumor-associated) antigens. This offers a unique approach to enhancing immunogenicity in the context of cancer immunotherapy [
8]. Currently, 16 active or recruiting clinical trials employ bacteria to treat cancer [
9], with countless others completed in the last two decades. Several use
Listeria monocytogenes (LM) as a therapeutic platform because of their unique characteristics and ability to strongly induce both cellular and humoral immune responses [
10,
11,
12,
13] against infectious diseases and cancer due to the properties of intracellular transmission [
14].
These engineered vectors not only deliver tumor antigens to dendritic cells but can also offer intrinsic adjuvant capacity since they activate multiple pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) present in immune cells [
10,
15]. These PRRs activate signaling pathways responsible for upregulating proinflammatory genes like type I IFNs, TNFα, IL-8, and pro-IL-1β directly. In addition, PRRs control the fate of infected or surrounded cells by their interplay with the host cell death molecular machinery [
16]. For instance, cytosolic PRRs may assemble multimolecular structures called
Inflammasomes, which initiate caspase-1-dependent inflammatory cell death (pyroptosis) [
17,
18,
19]. Inflammasomes are important in innate immunity to pathogens, but their role in modulating adaptive immunity is still not fully understood [
19]. Interestingly enough, inflammasome activation was shown to limit the generation of antigen-specific T-cell response to
L. monocytogenes [
20,
21].
Necroptosis is another inflammatory cell death process that can be triggered by PRRs, such as Toll-like receptor (TLR) 3 and 4, DNA-dependent activator of IFN-regulatory factors (DAI), Retinoic acid Inducible Gene I (RIG-I) and Melanoma Differentiation-Associated protein 5 (MDA-5) [
16,
22]. Necroptosis is essentially controlled by RIPK3 phosphorylation of MLKL, which in turn migrates to the cell membrane, forming lytic pores. Remarkably, although the RIPK3-MLKL axis was shown to be activated by
L. monocytogenes and to contribute to an efficient host defense mechanism, it seems that the phosphorylation of MLKL-induced by
L. monocytogenes infection did not lead to the death of the host cell [
23].
Overall, it is not clear how pyroptosis- or necroptosis-related genes participate at the immune response triggered by L. monocytogenes, particularly in the context of vector-delivering tumor-associated genes. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the ability of the live recombinant L. monocytogenes to stimulate CD8+ T cell-mediated anti-tumor immunity in animal models lacking the essential regulatory and effector molecules of necroptosis (RIPK3 and MLKL) and pyroptosis (Caspase 1/11 and Gasdermin D).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
C57BL/6 ripk3-/-, casp-1/11-/- and gsdmd-/- mice were generously provided by Vishva Dixit (Genentech, Inc., USA), Richard Flavell (Yale University, USA), and Petr Broz (University of Lausanne), respectively. mlkl-/- mice were obtained from Douglas Green (St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, USA) and used under the terms of the material transfer agreement obtained from James Murphy (The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research - WEHI, Melbourne, Australia). Six to eight weeks-old WT, casp-1/11-/-, gsdmd-/-, ripk3-/-, and mlkl-/- mice were used as control and experimental groups. All mice experiments were performed in the animal facilities of the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, University of São Paulo, under the guidelines of the Ethics Committee on Animal Use, University of São Paulo.
2.2. Recombinant Listeria Monocytogenes Culture and Infection
Recombinant
LM strain (10403S) expressing OVA has been described previously by Dudani and collaborators [
24]. For infections/vaccinations, frozen stocks of
LM-OVA were thawed, serially diluted in PBS, and used to intravenously infect/vaccinate mice via the retro-orbital plexus at 1 × 10
3 CFU in 100 µl of PBS or otherwise indicated.
2.3. Bacterial Burden Per Spleen
Spleens of all infected mice were harvested on days 3 and 7 post-infection, and single-cell suspensions were prepared in an RPMI-1640 medium (Life Technologies, Burlington, Ontario, Canada). CFU/spleen was determined by plating 10-fold serial dilutions of single-cell suspension on BHI-Streptomycin agar plates.
2.4. In Vivo Evaluation of CD8 T Cell Effector Activity
Evaluation of in vivo antigen-specific CTL killing was accomplished as previously described by Clemente and collaborators [
25]. Briefly, spleens from WT donor mice were harvested and processed for single-cell suspension by tweezing the organs in a cell strainer with a syringe plunger. Cells were counted, divided equally into two populations, and marked separately with low (1 µM) or high (10 µM) concentrations of carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE). CFSE
High cells were pulsed with 10 nM of OVA
257--264 (SIINFEKL) peptide, while the control CFSE
Low remained unpulsed. The two populations of cells were washed and mixed in a 1:1 ratio. A total of 2 × 10
7 cells in 100 µl of non-supplemented RPMI-1640 were injected into the LM-OVA-vaccinated and control mice via the retro-orbital sinus, at 7- or 27 days post-infection. After 16–20 hours, spleens from recipient mice were excised, processed, and submitted to flow cytometry (BD CANTO, BD, Mountain View, CA). Data were analyzed using the FlowJo v10 workspace.
2.5. In Vivo Tumor Growth
To address the anti-tumor potential of LM-OVA, mice were vaccinated or not and 7 or 27 days later, they were inoculated with 1 × 106 B16F0 and 1 × 106 B16F0.OVA melanoma cells in each right and left flank, respectively. Tumor diameters were measured using a caliper at 2-day intervals using the formula below.
Mice were euthanized, and tumors were excised when the tumor diameter reached about 1 cm3.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was done using GraphPad Prism version 8 (GraphPad Software Company, Inc.). Ordinary one-way ANOVA or two-way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance, followed by Bonferroni post-tests. Statistical differences are considered significant when the P value is less than 0.05.
3. Results
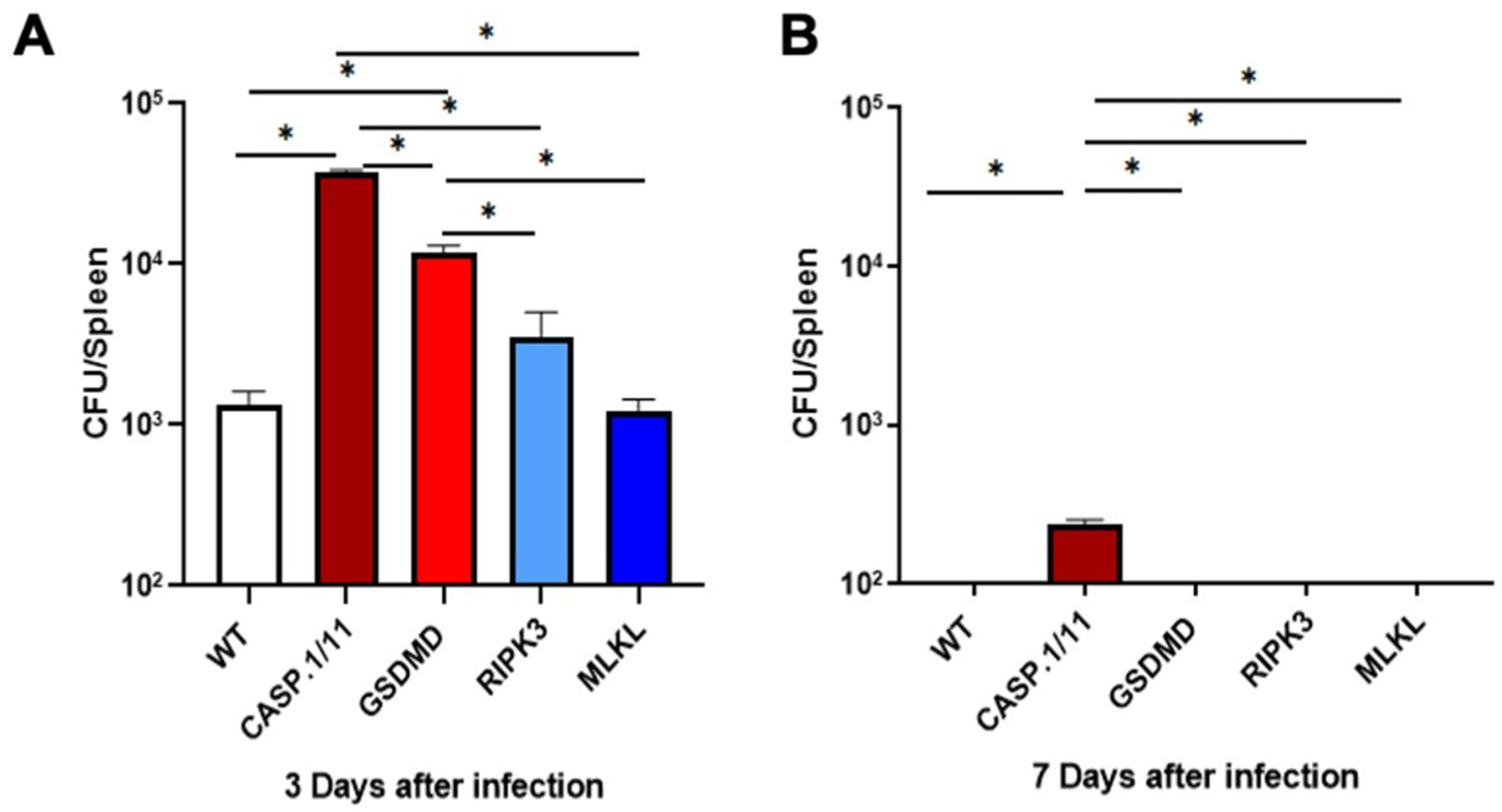
3.1. Pyroptosis- but Not Necroptosis-Related Proteins Affect LM-OVA Bacterial Burden
We first evaluated the ability of our genetically modified mice to control the LM-OVA bacterial burden as a measure of the efficiency of the immune response triggered by our recombinant vaccine vector. At the same time, we examined the safety of our vaccine strategy in each genetic background. On day 3, the number of colony-forming units (CFU) found in the spleens of casp.1/11
-/- and gsdmd
-/- mice was higher compared to WT, ripk3
-/- and mlkl
-/- mice. This suggests that pyroptosis- but not necroptosis-related proteins are important for controlling the early stages of LM-OVA infection in our experimental conditions (
Figure 1A). It is worth noting that on day 7 post-infection, mice from all deficient backgrounds resolved the infection, except for casp.1/11
-/- mice that still showed a low but significant level of bacterial burden in their spleens (
Figure 1B). Our findings indicate that the LM-OVA vaccine is safe in all deficient genetic backgrounds and that the Caspase 1/11-GSDMD axis participates in the clearance of LM-OVA infection. These results suggest that the deficiency of these pyroptosis-related proteins may impact the immune responses to the recombinant vaccine antigen (OVA), thereby weakening the LM-OVA vaccine potential in individuals displaying such defects.
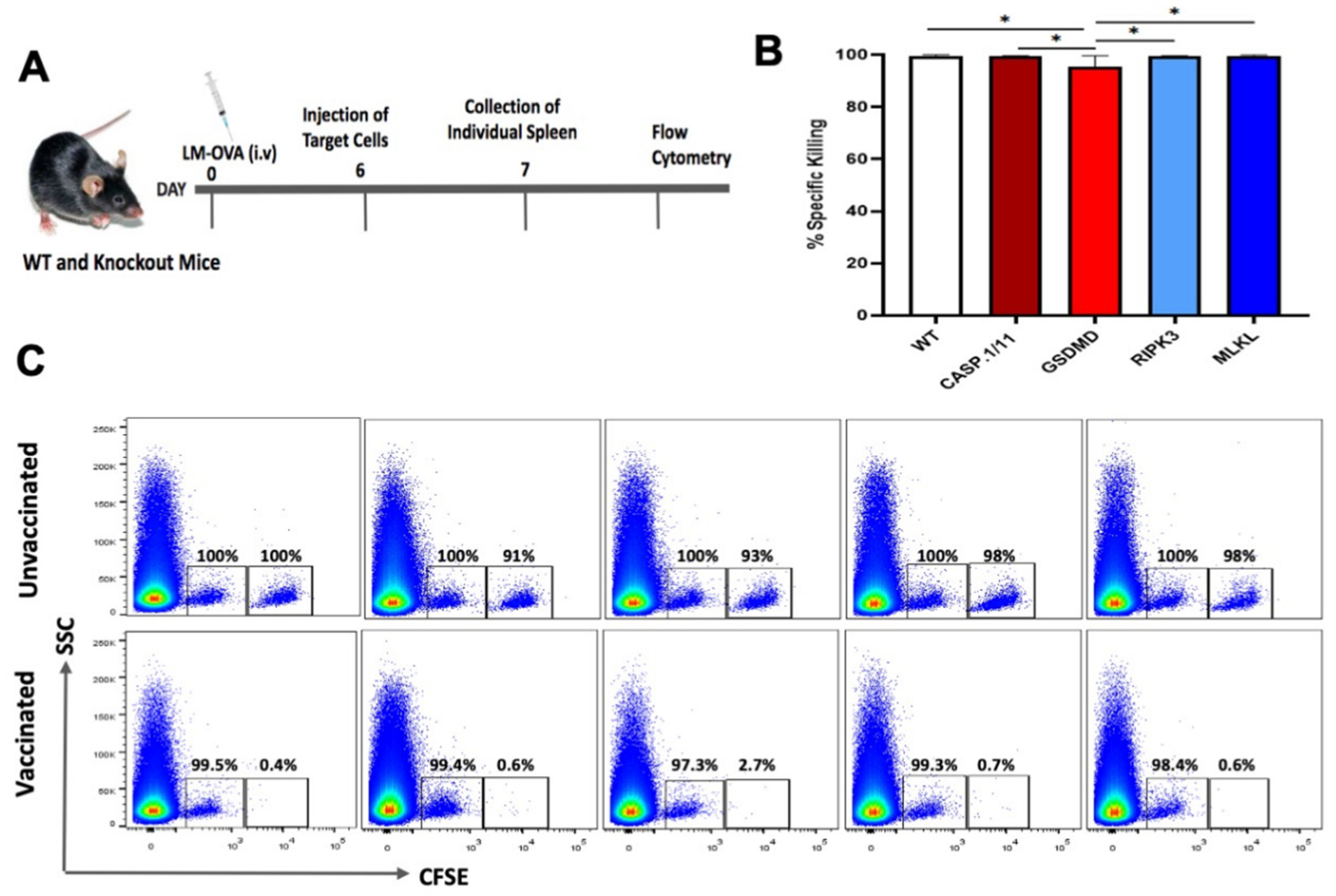
3.2. Deficiency of Pyroptosis- or Necroptosis-Related Proteins Did Not Impair the Early Antigen-Specific CTL Response Triggered by LM-OVA Vaccination
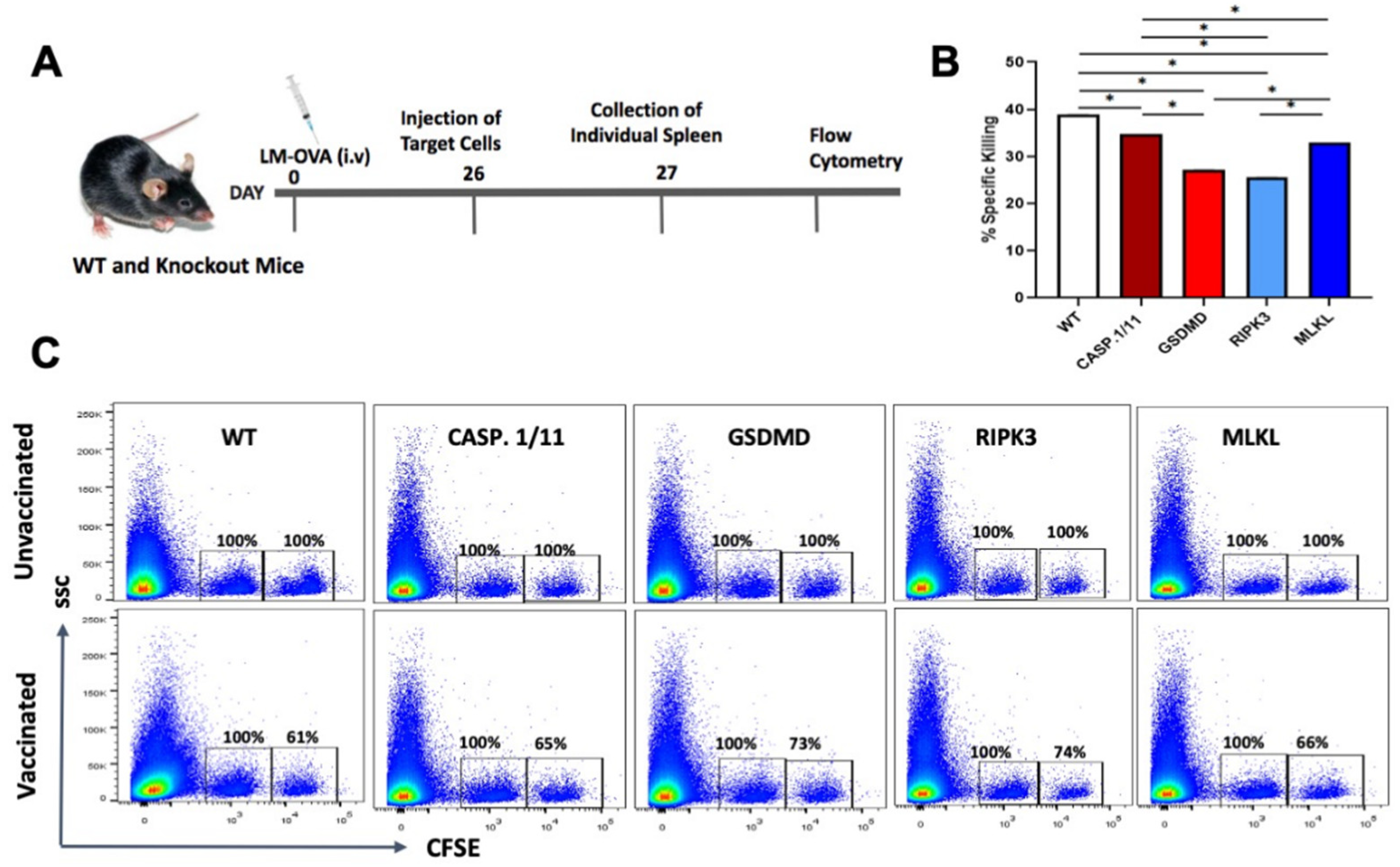
To test the possibility that LM-OVA would induce an inferior OVA-specific CD8+ T cell-mediated immune responses when presented in the pyroptosis- or necroptosis-deficient backgrounds, we measured the in vivo elimination of OVA
257-264 peptide-pulsed target cells in WT and knockout mice vaccinated or not with LM-OVA using the in vivo cytotoxicity assay as previously described [
25].
At day 7 post-vaccination, the peak of CD8 T cell response, we observed a virtually complete elimination of OVA-peptide pulsed target cells from the spleens of both WT and knockout mice (
Figure 2), suggesting that individual deficiency of casp.1/11
-/-, gsdmd
-/-, ripk3
-/- or mlkl
-/- did not blight the early antigen-specific CTL effector response triggered by LM-OVA vaccination.
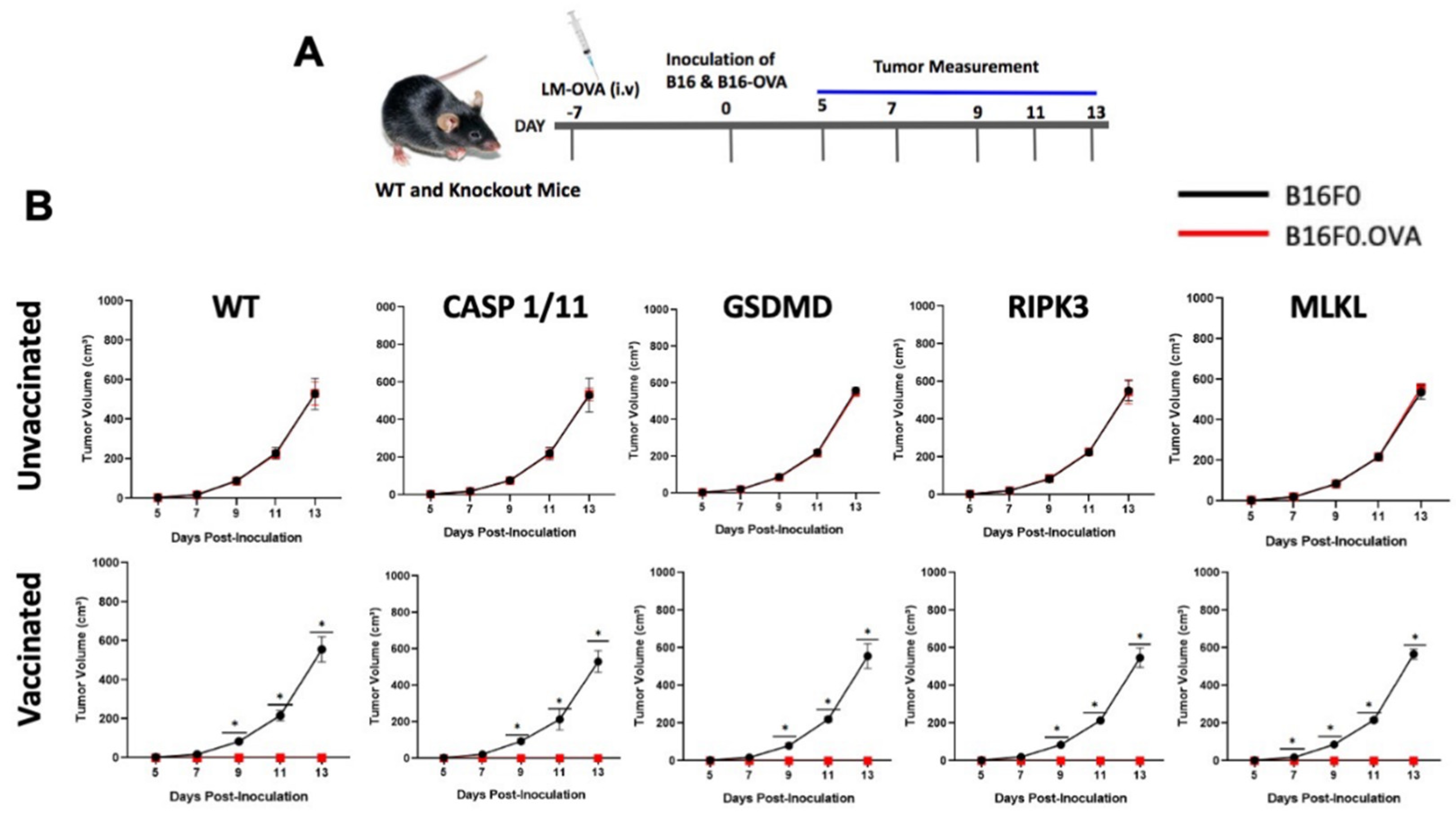
To further support these observations, we asked whether the absence of either of these proteins would hamper anti-tumor immune responses triggered by LM-OVA. B16F0 and B16F0.OVA melanoma cell lines were inoculated subcutaneously in the right or left flanks of WT and knockout mice on day 7 post-LM-OVA vaccination, and tumor growth was monitored every other day (
Figure 3A). Remarkably, while B16F0 cells formed tumors in all LM-OVA-vaccinated animals, no B16F0.OVA tumors were observed in either WT or knockout mice, suggesting the LM-OVA vaccine conferred protective anti-tumor activity regardless of the genetic deficiency of pyroptosis- or necroptosis-related proteins (
Figure 3B). Our results also confirmed that the anti-tumor effect of the LM-OVA vaccination is antigen (OVA)-specific. It is important to mention that in vivo elimination of target cells completely depends on CD8 T lymphocytes, as shown by the lack of anti-tumor effect of LM-OVA vaccinated cd8
-/- mice (
Supplementary Figure S1). Also, importantly, least, B16F0 and B16F0.OVA tumors displayed similar growth in all unvaccinated groups, as expected (
Figure 3B).
Figure 2.
Early in vivo CTL activity triggered by LM-OVA vaccination in WT and necroptosis- or pyroptosis-deficient mice. (A) WT and knockout mice were vaccinated or not with LM-OVA and 6 days later injected with a single cell suspension containing OVA-pulsed target cells, as described in M&M. On the next day, mice were euthanized, and spleens processed for flow cytometry. (B) Bar chart showing the percentage of LM.OVA-induced in vivo elimination of target cells in all mice strains on day 7. (C) Representative flow cytometry density plots. Results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation per group (n = 5) and represent three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-tests were both used in the statistical analysis. * p < 0.05.
Figure 2.
Early in vivo CTL activity triggered by LM-OVA vaccination in WT and necroptosis- or pyroptosis-deficient mice. (A) WT and knockout mice were vaccinated or not with LM-OVA and 6 days later injected with a single cell suspension containing OVA-pulsed target cells, as described in M&M. On the next day, mice were euthanized, and spleens processed for flow cytometry. (B) Bar chart showing the percentage of LM.OVA-induced in vivo elimination of target cells in all mice strains on day 7. (C) Representative flow cytometry density plots. Results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation per group (n = 5) and represent three independent experiments. One-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-tests were both used in the statistical analysis. * p < 0.05.
Figure 3.
Early anti-tumor immune response induced by LM-OVA in WT and knockout mice. (A) Mice were vaccinated or not with LM-OVA and inoculated with B16F0 and B16F0.OVA melanoma cell lines after 7 days. (B) Tumor growth was evaluated every two days. Results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation per group (n = 5) and represent three independent experiments. A two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-tests were both used in the statistical analysis. * p < 0.05.
Figure 3.
Early anti-tumor immune response induced by LM-OVA in WT and knockout mice. (A) Mice were vaccinated or not with LM-OVA and inoculated with B16F0 and B16F0.OVA melanoma cell lines after 7 days. (B) Tumor growth was evaluated every two days. Results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation per group (n = 5) and represent three independent experiments. A two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-tests were both used in the statistical analysis. * p < 0.05.
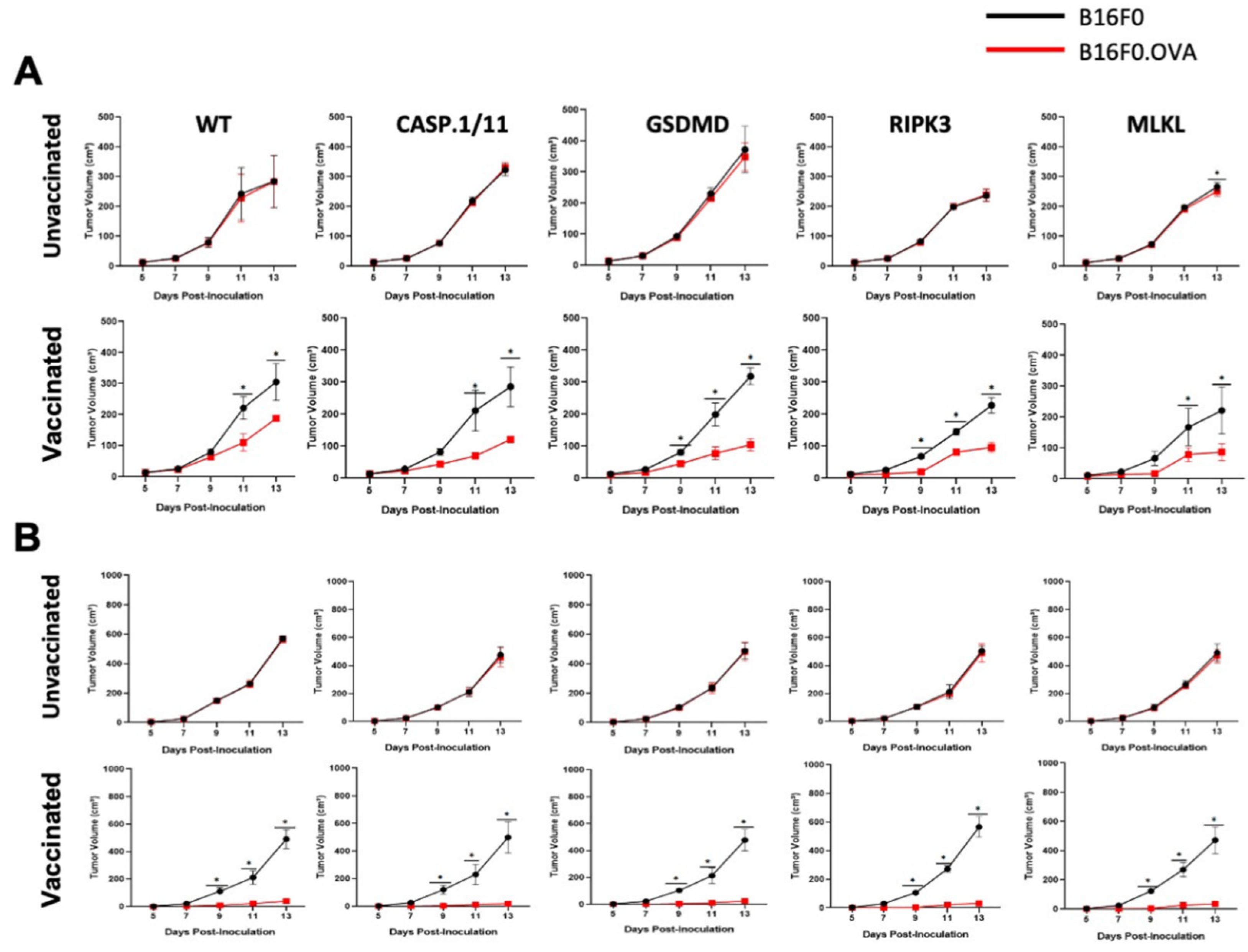
3.3. Late Antigen-Specific CTL Response Triggered by LM-OVA Vaccination Is Weakened in Pyroptosis- and Necroptosis-Deficient Mice
To verify whether the efficiency of LM-OVA vaccination was long-lasting, we repeated the in vivo cytotoxic assay at 27 days post-vaccination and found a significant decrease in the elimination of the target cells in all mouse strains, suggesting that our vaccination protocol is insufficient to induce long-lasting effector and/or memory antigen-specific CD8+ T cells (
Figure 4). Most importantly, deficiency in either pyroptosis- or necroptosis-related proteins slightly aggravated the loss of LM-OVA-induced CTL activity over time (
Figure 4).
To analyze whether the declining CTL response also impacted the anti-tumor effect of LM-OVA vaccination, we inoculated B16F0 and B16F0.OVA melanoma cells after 27 days of vaccination and measured tumor growth every two days. Similar to our previous result, we observed a decline in the efficiency of the LM-OVA vaccination to protect from B16F0.OVA melanoma growth in all mouse strains (
Figure 5A). Importantly, once again, casp.1/11
-/-, gsdmd
-/-, ripk3
-/- and mlkl
-/- mice exhibited reduced protection compared to WT mice.
Finally, we tried to circumvent this late-time inefficiency by increasing the dose of the LM-OVA vaccine 5-fold. Remarkably, all mice showed complete protection, as none of the B16F0.OVA tumors inoculated 27 days after high-dose LM-OVA vaccination have grown in this condition (
Figure 5B), much like the mice inoculated with B16F0.OVA 7 days after low-dose vaccination (
Figure 3). Taken together, our results indicate that pyroptosis- and necroptosis-related molecules fine-tuned the efficiency of LM-OVA vaccination, predominantly with respect to the generation of long-lasting effector and/or memory antigen-specific CD8+ T cells.
Figure 5.
Late anti-tumor immune response induced by LM-OVA in WT and knockout mice. (A) Mice were vaccinated or not with LM-OVA (1 × 103) and inoculated with B16F0 and B16F0.OVA melanoma cell lines after 27 days. Tumor growth was evaluated every two days. A partial protection was observed in all groups. (B) Full protection was observed in all groups of mice vaccinated with a high dose of LM-OVA (5 × 103). Results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation per group (n = 5) and represent three independent experiments. A two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-tests were both used in the statistical analysis. * p < 0.05.
Figure 5.
Late anti-tumor immune response induced by LM-OVA in WT and knockout mice. (A) Mice were vaccinated or not with LM-OVA (1 × 103) and inoculated with B16F0 and B16F0.OVA melanoma cell lines after 27 days. Tumor growth was evaluated every two days. A partial protection was observed in all groups. (B) Full protection was observed in all groups of mice vaccinated with a high dose of LM-OVA (5 × 103). Results are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation per group (n = 5) and represent three independent experiments. A two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-tests were both used in the statistical analysis. * p < 0.05.
4. Discussion
Vaccines have provided novel prospects for preventing and treating numerous diseases, including cancer [
26]. Recent research has demonstrated that immunotherapy based on live, attenuated, and/or recombinant bacteria offers advantages in increasing the immune response to immunosuppressed malignancies.
Listeria monocytogenes (
LM) has demonstrated powerful innate and adaptive immunity in numerous scenarios, making it a leading candidate for therapeutic bacteria [
26]. Indeed, there are several
LM-based vaccines used as therapeutic vaccines for cancer immunotherapy against cervical [
27], prostate [
28], pancreatic, lung, ovarian, mesothelioma [
29], and colon cancer [
30], among others, showing promising results in clinical trials.
The impact of cell death on the intricacies of adaptive immunity has been extensively investigated for decades. Regardless, the precise mechanisms by which diverse cell death pathways influence immune responses during infection remain enigmatic, particularly concerning pyroptosis and necroptosis [
21]. We set off trying to find out how well
L. monocytogenes triggers adaptive immune responses in hosts deficient in key regulatory or effector molecules of necroptosis and pyroptosis. By measuring the bacteria burden in CASP.1/11-, GSDMD-, RIPK3-, and MLKL-deficient mice, we observed that the CASP-1/GSDMD axis participates in the control of
LM-OVA infection, but the deficiency in either protein did not impose a lethal susceptibility on the mice. In comparison, the RIPK3/MLKL axis seems to be less important. This is in accordance with the studies by [
31] and [
32], which also reported that the lack of caspase-1/11 in mice makes them more vulnerable to
LM infection during the early stages of infection (days 3-7). Since caspase-1/11 processes the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1 and IL-18, leading to their release and contributing to the innate immune response and host defense, we consider that IL-1 and IL-18 might also play a role in this process, particularly because
gsdmd-/- mice did not phenocopy the sensitivity displayed by
casp.1/11-/- mice. We are currently investigating the role of IL-1/IL-18 signaling in LM-OVA-inducing CD8+ T cell responses.
Importantly, the induction of adaptive immunity requires live, replicating bacteria, as killed or inactivated vaccines generally do not induce optimal protective immunity [
33,
34]. The notion that
L. monocytogenes elicits T-cell-mediated immunity has led many researchers to consider it a promising and effective recombinant vaccine vector for the stimulation of cell-mediated immunity [
35,
36,
37]. Several pre-clinical studies have demonstrated that listeria and listeria-based vaccines can effectively induce potent anti-tumoral immunity against various tumor-specific antigens [
38,
39,
40,
41].
In our study, we evaluated the ability of
LM-OVA to induce an in vivo antigen-specific anti-tumor CD8+ T cell response in wild-type and necroptosis- or pyroptosis-deficient mice. Several studies have established that antigen-specific CD8 T cell responses peaked 7–8 days after vaccination/infection in cases of intravenous
LM infection. In our study, we also observed a strong induction of the in vivo antigen-specific CD8+ T cells at day 7, leading to almost complete clearance of the OVA-expressing target cells in all the mouse strains. In addition, our study assessed the prophylactic efficacy of
LM-OVA vaccination in WT and KO mice subcutaneously inoculated with the B16F0 and B16F0.OVA melanoma cell lines on day 7.
LM-OVA completely inhibited the growth of OVA-carrying tumors (B16F0.OVA) in WT and KO mice, showing that, at the peak of the response, the induction of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells is successfully translated to an anti-tumor therapy irrespective of the host deficiency in either pyroptosis or necroptosis machineries. This anti-tumor activity shown by
LM-OVA is completely CD8-dependent (as shown in the
Supplementary Figure S1).
Studies have demonstrated that memory CD8 T cells last for extended periods following infection or vaccination. However, sustaining memory CD8 T cells is an ongoing and ever-changing process. Memory CD8 T cells experience temporal alterations in their characteristics and abilities. Consequently, even among a group of memory CD8 T cells that target a single antigen, significant diversity exists in their physical attributes and functional capabilities. The
LM model has been extensively employed in many research studies to investigate and elucidate the mechanism(s) that regulate alterations in pathogen-specific CD8 T cells during memory development [
42]. In relation to this, we decided to explore the ability of the LM-OVA to induce antigen-specific memory CD8+ T cells in our model.
In comparison to day 7, we observed that the elimination of target cells was relatively inefficient at day 27, suggesting that our LM-OVA vaccination protocol could not provide an effective memory immune response. Similarly, modest protection against tumor growth was observed at this later time point, particularly in each deficient mouse strain, which displayed a minor yet significantly lower protection against B16.OVA tumor growth compared with WT mice. Notably, by increasing the vaccine dose (5-fold), we could expand the protective anti-tumor response in all mouse strains. Taking together, our results suggest that necroptosis or pyroptosis molecules take part in the long-lasting, fine-tuned CD8+ T cell-mediated anti-tumor activity of the recombinant Listeria monocytogenes vaccine, but the deficiency of these molecules can be circumvented by increasing vaccine concentration and perhaps adding a second or third boosting dose. This is also under investigation in our laboratory.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the ability of live vaccine vectors to trigger an efficient, protective host immune response is fine-tuned by the host genetic landscape, including genes related to necroptosis and pyroptosis. This accentuates the need for further investigation on the development of customized approaches to improve the effectiveness of vaccination protocols, particularly in immunodeficient patients [
13].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: LM-OVA vaccine anti-tumor response in CD8 mice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.O., A.V.D.S. and G.P.A.-M.; experimental procedures, A.S.O. and A.V.D.S.; formal analysis, A.S.O., A.V.D.S. and G.P.A.-M.; resources, G.P.A.-M.; data curation, A.S.O. and G.P.A.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.O.; writing—review and editing, A.S.O., A.V.D.S. and G.P.A.-M.; supervision, G.P.A.-M.; project administration, G.P.A.-M.; funding acquisition, G.P.A.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
A.S.O. and A.V.D.S. were recipients of Ph.D. (Proc. No. 2021/12143-7) and M.Sc. (Proc. No. 2021/07624-6) fellowship from the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP – Brazil). This work was supported by grants from FAPESP (Proc. No. 2018/25395-1; 2021/13486-5) and from CNPq (Proc. No. 308927/2019-2; 311122/2023-0; INCTiii 46543412014-2).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This project was approved by the Ethics and Research Committee of the Institute of Biomedical Science, University of Sao Paulo (CEUA/ICB-USP) (CEUA No. 5470081021). All mice were manipulated at the animal facilities of the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, University of São Paulo (ICB-USP), under the guidelines of the Ethics Committee on Animal Use, University of São Paulo. Mice were euthanized using the proper dose of anesthesia followed by cervical dislocation, as regulated by Normative Resolution Nº 37, February 15, 2018.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Raw data will be provided upon request
Acknowledgments
We are in debt to Drs. Vishva Dixit (Genentech, Inc., USA), Richard Flavell (Yale University, USA), Petr Broz (University of Lausanne), Douglas Green (St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, USA) and James Murphy (The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research - WEHI, Melbourne, Australia) for providing the genetically modified mouse strains.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Gupta, S.L.; Basu, S.; Soni, V.; Jaiswal, R.K. Immunotherapy: An Alternative Promising Therapeutic Approach against Cancers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 9903–9913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, M.; Ustoyev, Y. Cancer and the Immune System: The History and Background of Immunotherapy. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2019, 35, 150923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milling, L.; Zhang, Y.; Irvine, D.J. Delivering Safer Immunotherapies for Cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 114, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zheng, L.; Chen, W.; Weng, W.; Song, J.; Ji, J. Delivery Strategies of Cancer Immunotherapy: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurez, V.; Padrón, Á.; Svatek, R.S.; Curiel, T.J. Considerations for Successful Cancer Immunotherapy in Aged Hosts. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 107, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnestein, R.; Galland, L.; Kalfeist, L.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Ladoire, S.; Limagne, E. Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment Modulation by Chemotherapies and Targeted Therapies to Enhance Immunotherapy Effectiveness. OncoImmunology 2022, 11, 2120676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.M.; Marabelle, A.; Eggermont, A.; Soria, J.-C.; Kroemer, G.; Zitvogel, L. Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment: Removing Obstruction to Anticancer Immune Responses and Immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; She, Y.; Sun, Q.; Shi, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, D.-C.; Shao, F. Pore-Forming Activity and Structural Autoinhibition of the Gasdermin Family. Nature 2016, 535, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
-
https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?cond=Cancer&intr=bacteria&aggFilters=status:com.
- Witte, C.E.; Archer, K.A.; Rae, C.S.; Sauer, J.-D.; Woodward, J.J.; Portnoy, D.A. Innate Immune Pathways Triggered by Listeria Monocytogenes and Their Role in the Induction of Cell-Mediated Immunity. In Advances in Immunology; Elsevier, 2012; Volume 113, pp. 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, S.E.F. Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses during Listeria Monocytogenes Infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, Z.T.; Powers, Z.M.; Sauer, J.-D. Listeria Monocytogenes Cancer Vaccines: Bridging Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2019, 6, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olagunju, A.S.; Rana, A.; Amarante-Mendes, G.P. Listeria Monocytogenes-Based Cancer Vaccines: Importance of Pathogen Interplay with Host’s Cell Death Machinery. Am J Biomed Sci & Res 2024, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Ma, J.; Dong, Q.; Liu, Q. Live Bacterial Vaccine Vector and Delivery Strategies of Heterologous Antigen: A Review. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 197, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regan, T.; MacSharry, J.; Brint, E. Tracing Innate Immune Defences along the Path of Listeria Monocytogenes Infection. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarante-Mendes, G.P.; Adjemian, S.; Branco, L.M.; Zanetti, L.C.; Weinlich, R.; Bortoluci, K.R. Pattern Recognition Receptors and the Host Cell Death Molecular Machinery. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The Inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoluci, K.R.; Medzhitov, R. Control of Infection by Pyroptosis and Autophagy: Role of TLR and NLR. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deets, K.A.; Vance, R.E. Inflammasomes and Adaptive Immune Responses. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.R.; Dustin, M.L.; Sauer, J.-D. Inflammasome-Mediated Inhibition of Listeria Monocytogenes-Stimulated Immunity Is Independent of Myelomonocytic Function. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theisen, E.; Sauer, J.-D. Listeria Monocytogenes-Induced Cell Death Inhibits the Generation of Cell-Mediated Immunity. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00733-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.; Roelandt, R.; Bruggeman, I.; Estornes, Y.; Vandenabeele, P. Nuclear RIPK3 and MLKL Contribute to Cytosolic Necrosome Formation and Necroptosis. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, K.; Parsons, C.; House, J.S.; Kathariou, S.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J. Necroptosis Mediators RIPK3 and MLKL Suppress Intracellular Listeria Replication Independently of Host Cell Killing. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 1994–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudani, R.; Chapdelaine, Y.; Faassen, H.V.; Smith, D.K.; Shen, H.; Krishnan, L.; Sad, S. Multiple Mechanisms Compensate to Enhance Tumor-Protective CD8(+) T Cell Response in the Long-Term despite Poor CD8(+) T Cell Priming Initially: Comparison between an Acute versus a Chronic Intracellular Bacterium Expressing a Model Antigen. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2002, 168, 5737–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, T.; Dominguez, M.R.; Vieira, N.J.; Rodrigues, M.M.; Amarante-Mendes, G.P. In Vivo Assessment of Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Killing. Methods San Diego Calif 2013, 61, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Fu, M.; Wang, M.; Wan, D.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Cancer Vaccines as Promising Immuno-Therapeutics: Platforms and Current Progress. J. Hematol. Oncol.J Hematol Oncol 2022, 15, 28–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciag, P.C.; Radulovic, S.; Rothman, J. The First Clinical Use of a Live-Attenuated Listeria Monocytogenes Vaccine: A Phase I Safety Study of Lm-LLO-E7 in Patients with Advanced Carcinoma of the Cervix. Vaccine 2009, 27, 3975–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, M.N.; Fong, L.; Tutrone, R.; Mega, A.; Lam, E.T.; Parsi, M.; Vangala, S.; Gutierrez, A.A.; Haas, N.B. ADXS31142 Immunotherapy ± Pembrolizumab Treatment for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Open-Label Phase I/II KEYNOTE-046 Study. The Oncologist 2022, 27, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Brockstedt, D.G.; Nir-Paz, R.; Hampl, J.; Mathur, S.; Nemunaitis, J.; Sterman, D.H.; Hassan, R.; Lutz, E.; Moyer, B.; Giedlin, M.; Louis, J.-L.; Sugar, E.A.; Pons, A.; Cox, A.L.; Levine, J.; Murphy, A.L.; Illei, P.; Dubensky, T.W.; Eiden, J.E.; Jaffee, E.M.; Laheru, D.A. A Live-Attenuated Listeria Vaccine (ANZ-100) and a Live-Attenuated Listeria Vaccine Expressing Mesothelin (CRS-207) for Advanced Cancers: Phase I Studies of Safety and Immune Induction. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 858–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.S.; McCormick, A.L.; Daugherity, E.A.; Oladejo, M.; Okpalanwaka, I.F.; Smith, S.L.; Appiah, D.; Wood, L.M.; Lowe, D.B. Listeria-Based Vaccination against the Pericyte Antigen RGS5 Elicits Anti-Vascular Effects and Colon Cancer Protection. Oncoimmunology 2023, 12, 2260620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, N.M.; Tsutsui, H.; Seki, E.; Kuida, K.; Okamura, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Flavell, R.A. Roles of Caspase-1 in Listeria Infection in Mice. Int. Immunol. 2004, 16, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, A.; de Almeida, F.C.; Paico Montero, H.A.; Gonzales Carazas, M.M.; Bortoluci, K.R.; Sad, S.; Amarante-Mendes, G.P. RIPK3 and Caspase-1/11 Are Necessary for Optimal Antigen-Specific CD8 T Cell Response Elicited by Genetically Modified Listeria Monocytogenes. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 536–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berche, P.; Gaillard, J.L.; Sansonetti, P.J. Intracellular Growth of Listeria Monocytogenes as a Prerequisite for in Vivo Induction of T Cell-Mediated Immunity. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 1987, 138, 2266–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Arroyo, A.; Portnoy, D.A. Why Is Listeria Monocytogenes Such a Potent Inducer of CD8+ T-Cells? Cell. Microbiol. 2020, 22, e13175–e13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, P.L.; Milon, G.; Cossart, P.; Saron, M.-F. Attenuated Listeria Monocytogenes as a Live Vector for Induction of CD8 + T Cells in vivo: A Study with the Nucleoprotein of the Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus. Int. Immunol. 1995, 7, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonomidis, G.; Paterson, Y.; Kos, F.J.; Portnoy, D.A. Delivery of a Viral Antigen to the Class I Processing and Presentation Pathway by Listeria Monocytogenes. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 2209–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Slifka, M.K.; Matloubian, M.; Jensen, E.R.; Ahmed, R.; Miller, J.F. Recombinant Listeria Monocytogenes as a Live Vaccine Vehicle for the Induction of Protective Anti-Viral Cell-Mediated Immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1995, 92, 3987–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Khairallah, C.; Sheridan, B.S. Listeria Monocytogenes: A Model Pathogen Continues to Refine Our Knowledge of the CD8 T Cell Response. Pathog. Basel Switz. 2018, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhood, B.; Najafi, M.; Mortezaee, K. CD8 + Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes in Cancer Immunotherapy: A Review. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8509–8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-M.; Oladejo, M.; Paulishak, W.; Wood, L.M. A Listeria-Based Vaccine Targeting ISG15 Exerts Anti-Tumor Efficacy in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 2023, 72, 2889–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladejo, M.; Nguyen, H.-M.; Silwal, A.; Reese, B.; Paulishak, W.; Markiewski, M.M.; Wood, L.M. Listeria-Based Immunotherapy Directed against CD105 Exerts Anti-Angiogenic and Anti-Tumor Efficacy in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1038807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.H.; Badovinac, V.P. Listeria Monocytogenes: A Model Pathogen to Study Antigen-Specific Memory CD8 T Cell Responses. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).