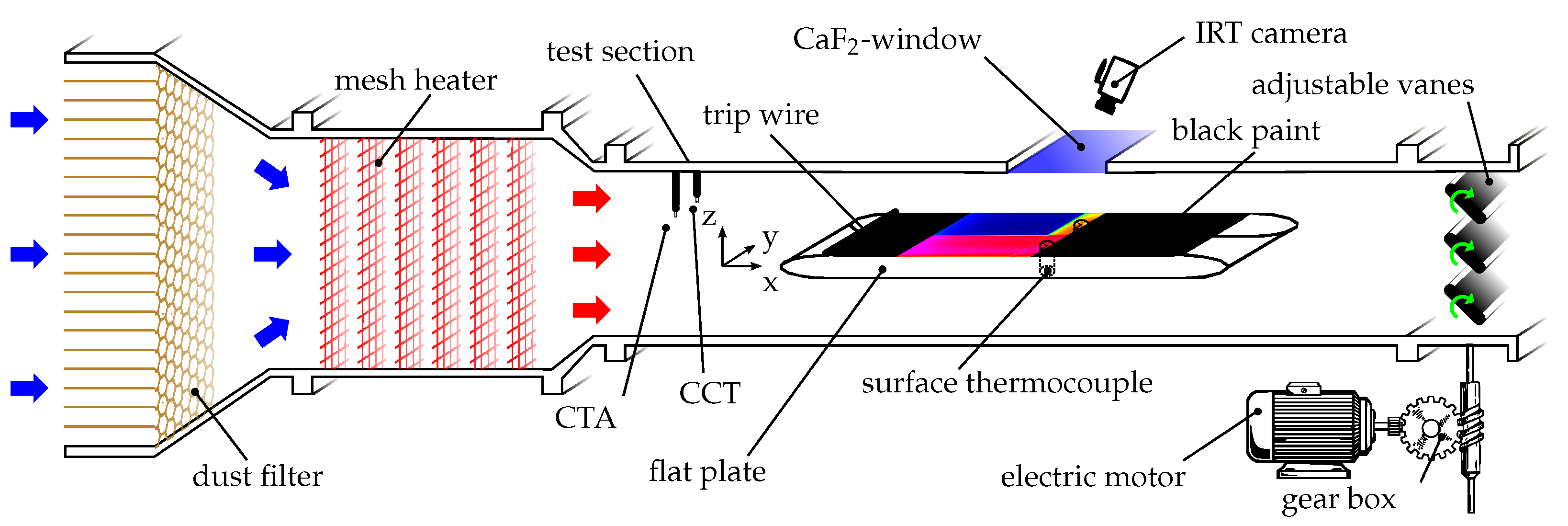
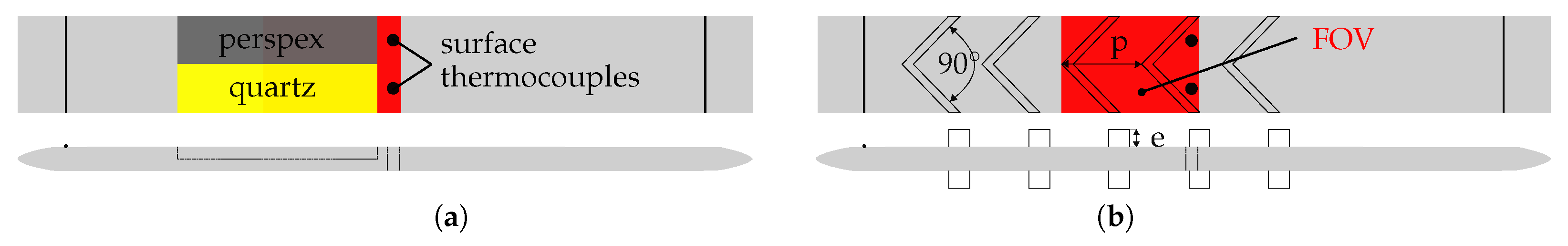
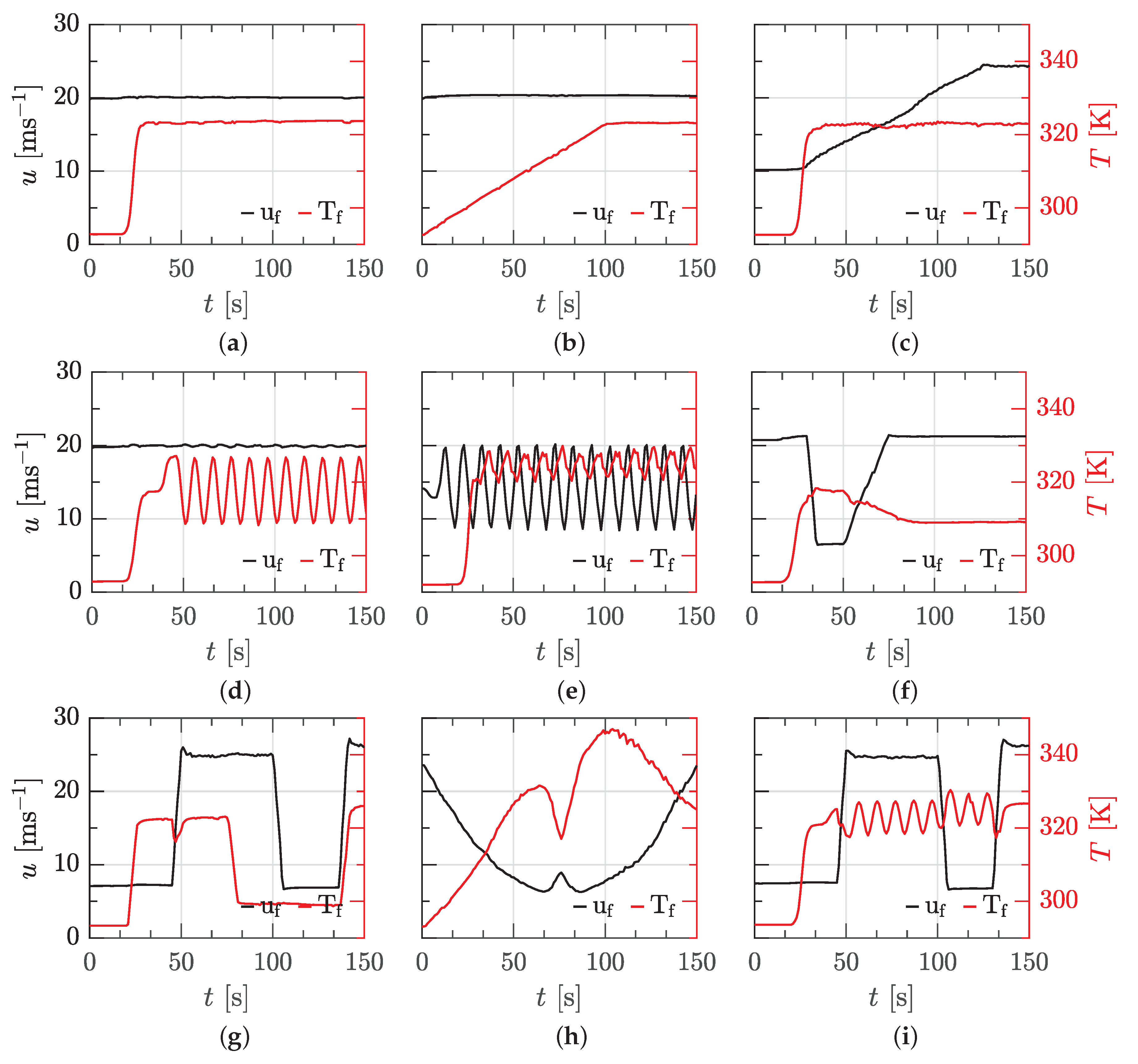
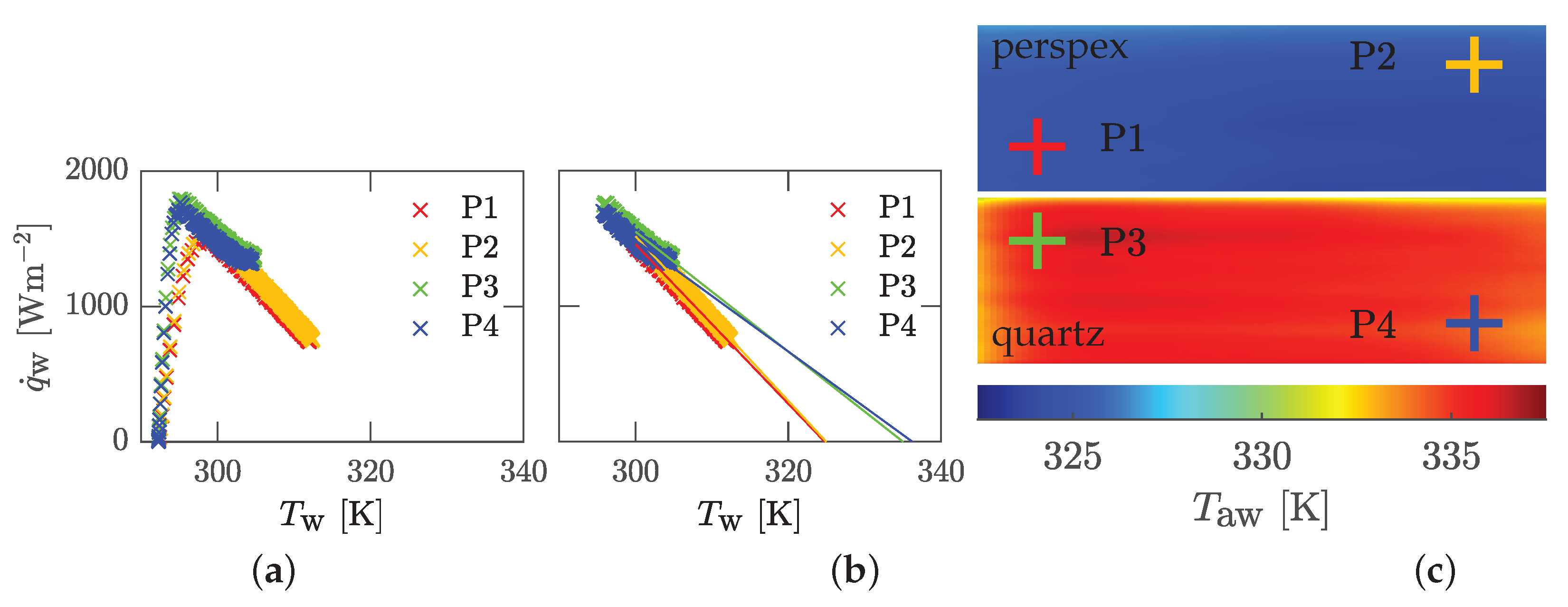
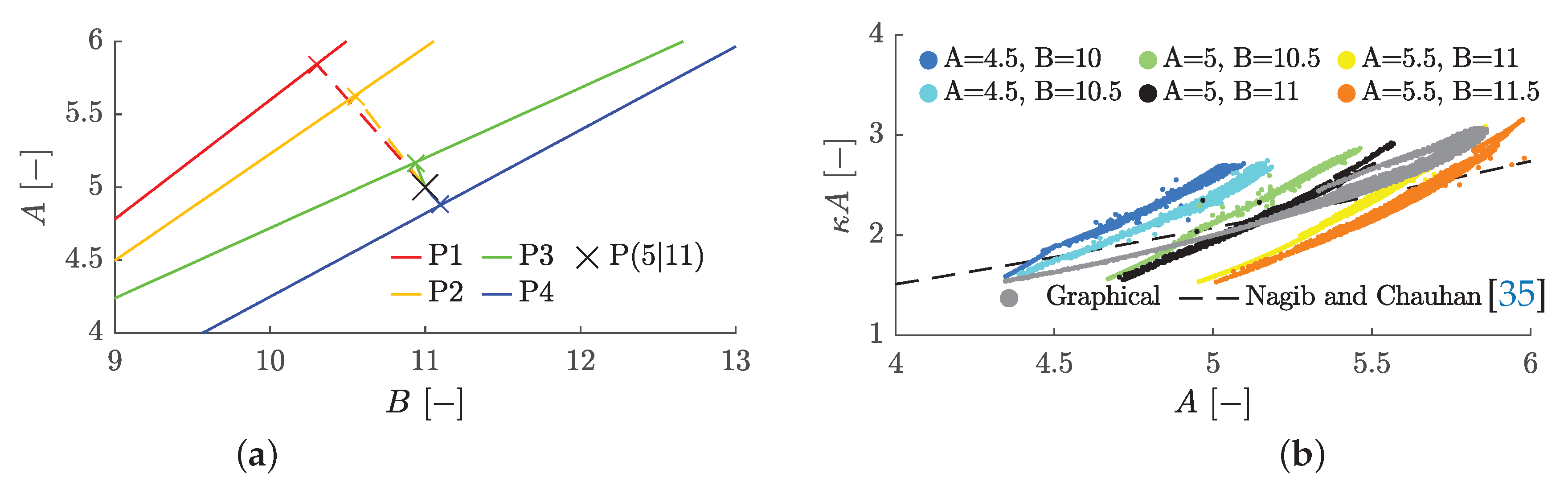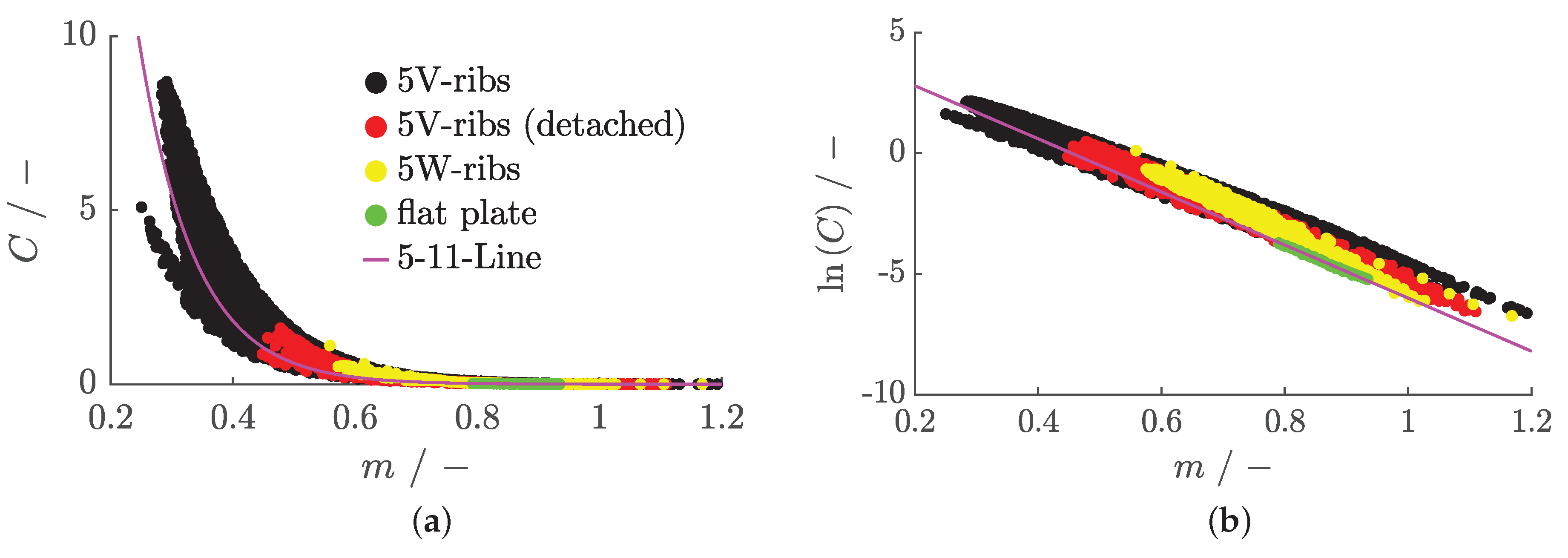First, a method for determining adiabatic wall temperatures under arbitrary flow and temperature boundary conditions is derived. The parameters found are then interpreted for the case of the flat plate and a relationship to calculate friction factors is introduced. Finally, the method is applied to more complex flow situations.
Method for Determining Adiabatic Wall Temperatures
A widely used method for determining adiabatic wall temperatures at constant inlet temperatures and velocities is the adiabatic method according to Goldstein et al. [
11] as a special case of the isotherm method according to Eckert [
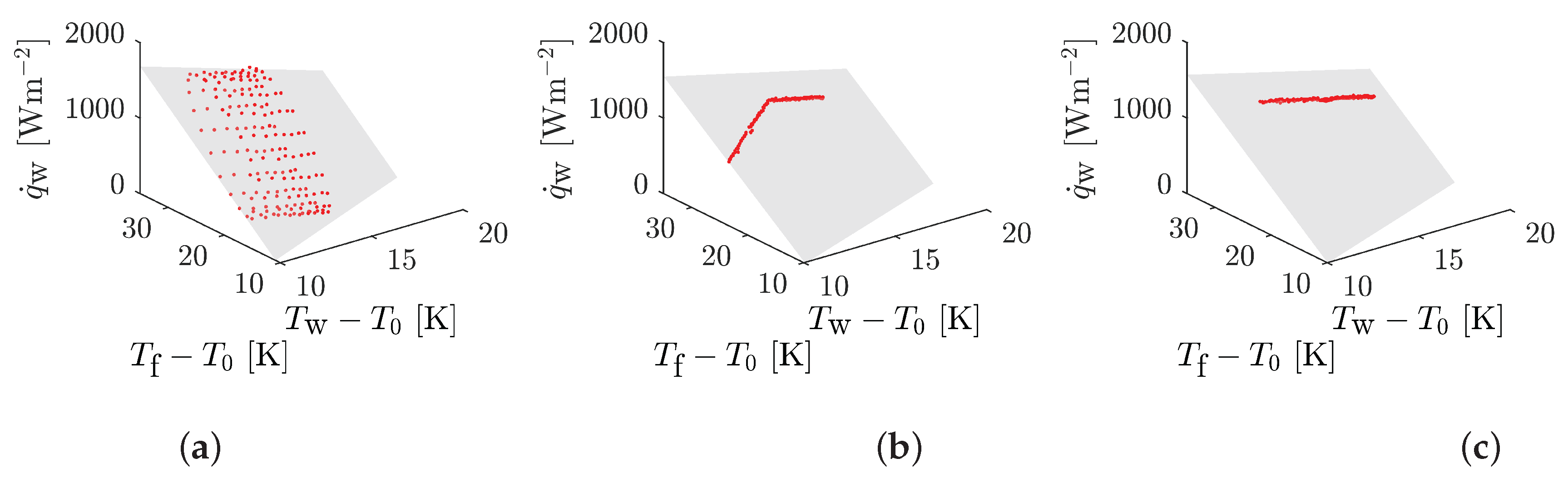
12]. Since both, the wall temperature as a measured variable and the wall heat flux, are known in the present study with spatial and temporal resolution, they can be plotted against each other for the Jump test case with a constant inlet temperature of
(cf.
Figure 3a) for selected pixels (see
Figure 4) for perspex or quartz, respectively.
Here, the resulting curve first rises at the moment of the temperature jump (see
Figure 3a), reaches its maximum there and then falls linearly. To determine the adiabatic wall temperature, a regression line of degree unity is drawn through the linear part - all time points greater than
in
Figure 4b. By extrapolating the straight line to the point of intersection with the abscissa at
, the adiabatic wall temperature is obtained. The negative slope of the extrapolation line corresponds to the constant, adiabatic heat transfer coefficient. If the method is applied to all pixels in the field, a variation of the adiabatic wall temperature between
can be seen in
Figure 4c for perspex or between
for quartz, respectively. The higher resulting adiabatic wall temperatures for quartz result from the effect, that quartz heats up much faster compared to perspex. According to Esfahani and Jafarian [
4], the lower temperature differences at constant fluid temperature and fluid velocity lead to a comparatively increased entropy generation.
To take dissipation effects into account, a coefficient
is introduced. Based on Bacci et al. [
13], this is defined as the ratio of the difference between the adiabatic wall temperature
and the start/ambient temperature of the experiment
to the fluid temperature
and
:
For a value of
, the fluid temperature and adiabatic wall temperature coincide. At this point,
formally is a time-depending variable. However, for simplicity,
is assumed as a time-invariant variable similar to Bacci et al. [
13]. Inserting
into Newton’s law of cooling (Equation
2) results in:
This corresponds to the mathematical form of a slope-intercept form of a plane with the abscissa
, the ordinate
and the applicate
. Thus, analogous to the regression line at constant inlet velocity, a regression plane can be calculated for a time-varying fluid temperature at constant inlet velocity. This is exemplified in
Figure 5 by the test cases Pulsation A, Ramp A and Jump, for point P1 (cf.
Figure 4c) and for perspex.
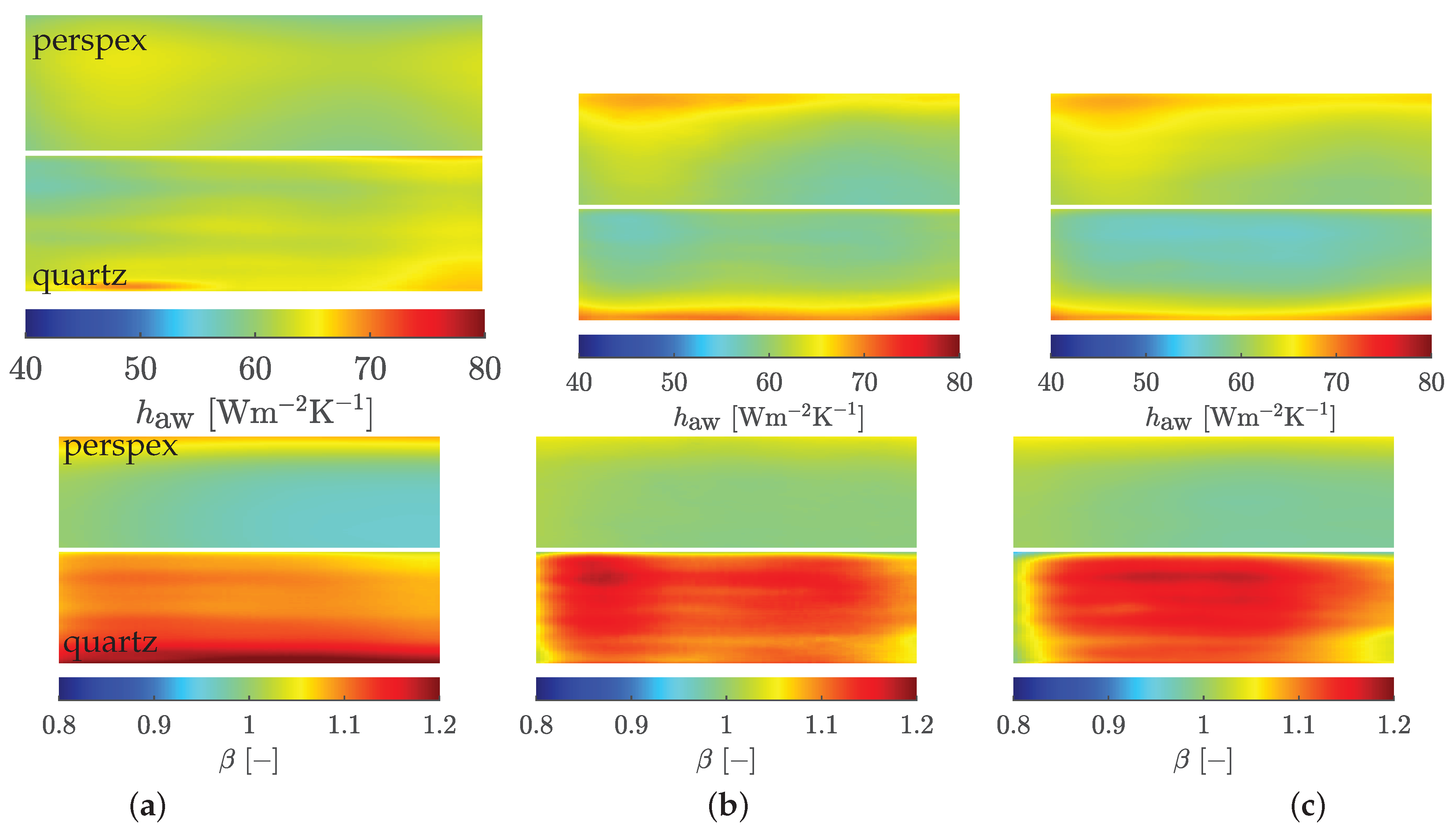
For a time-varying inlet temperature at constant velocity, the adiabatic heat transfer coefficient should be constant. This can be seen comparing the resulting adiabatic heat transfer coefficient from the three test cases with approximately equal fluid velocity
in
Figure 6. For both materials, perspex and quartz, the adiabatic heat transfer coefficient is fairly constant at
(cf. Hartmann et al. [
2]). Due to the temperature pulsation and the complex control of the inlet velocity, which varied slightly for Pulsation A (see
Figure 3d), the heat transfer coefficient
also varies barely (cf.
Figure 6a). For more constant velocity courses at Ramp A (
Figure 6b) and Jump (
Figure 6c), there are hardly any differences. Furthermore, the somewhat increased values towards the channel side walls, related to corner vortices of a channel flow (see Vinuesa et al. [
14]) are visible. The bottom line in
Figure 6 shows the resulting dissipation coefficients
. Due to the rapid heating and to assure
being approximately constant,
is higher for quartz than for perspex. However, it hardly varies for the same material on different test cases.
To take time-depending fluid velocities into account, a quasi-steady model of the form
is introduced based on typical heat transfer correlations (cf. Kays et al. [
15]). Hereby, the Nusselt number as dimensionless temperature gradient on the wall is defined as
is half the channel height of the sub-channel under consideration. The thermal conductivity
k is modeled temperature-dependent using the formula presented by Sutherland [
16] with the coefficients according to White [
17] at the corrseponding wall temperature
. The same is true for the dynamic viscosity
. This results in the Reynolds number defined as
where
is calculated from the ideal gas equation. The coupling of the temperature with the velocity field is represented by the Prandtl number, which yields with constant specific heat capacity
:
The Prandtl number is often also regarded as the ratio of velocity to temperature boundary layer. The Prandtl exponent
n depends on the thermal boundary condition. Acording to Hetsroni et al. [
18],
corresponds to a constant wall heat flux and
to a constant wall temperature boundary condition, what was selected for the presented study. With the definitions of the dimensionless variables
,
,
from Equations
6-
8, it yields
Hartmann et al. [
2] showed that the slow transient experiments studied here can be regarded as quasi-stationary, i. e. each point in time might be regarded as a stationary experiment of its own. Assuming Reynolds similarity for the flow in the investigated velocity range from
, this results in a total of
data tuples
for the eight considered experiments (cf.
Figure 3a-h), neglecting the first
of each experiment, because of the initial isothermal situation. To calculate the unknowns, the overdetermined system of equations is solved at each pixel. This is done using a nonlinear least-squares algorithm, the trust-region-reflective algorithm, as a subspace trust-region method based on the interior-reflective Newton method described in [
19,
20,
21]. The optimized values for
C,
m and
are shown in
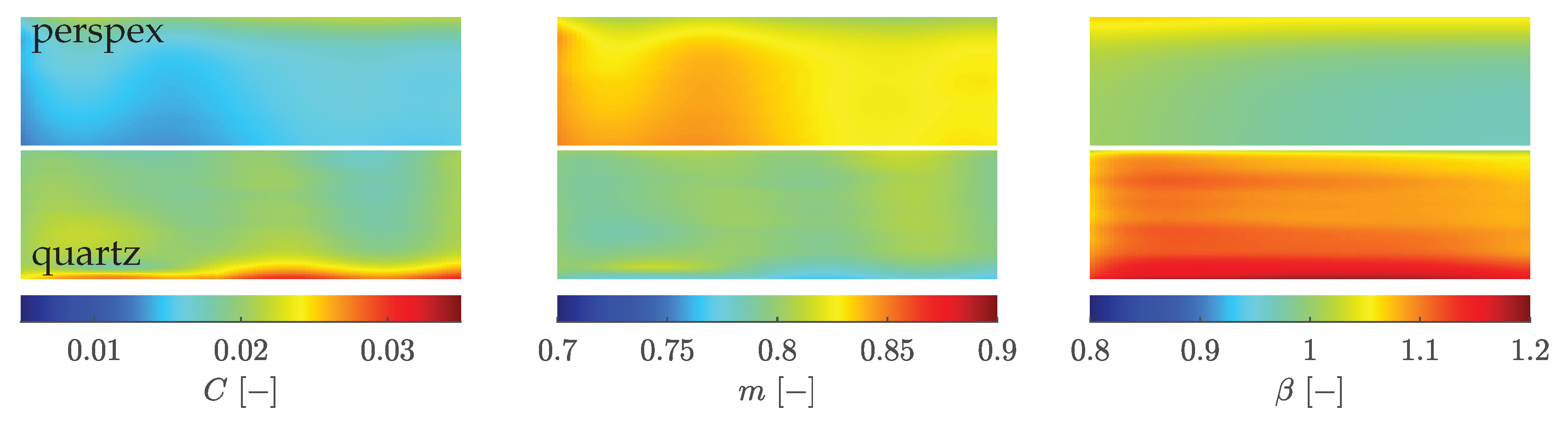
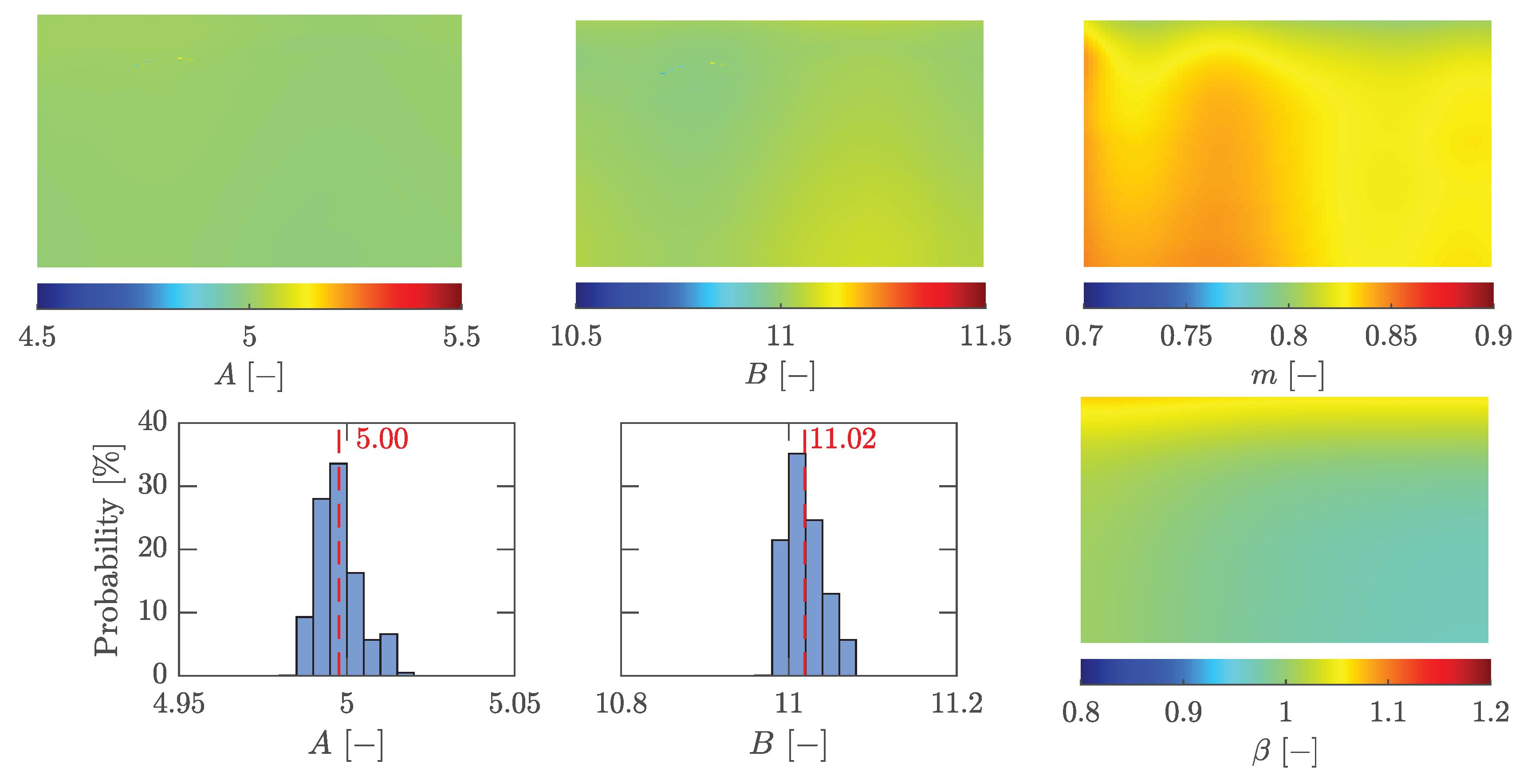
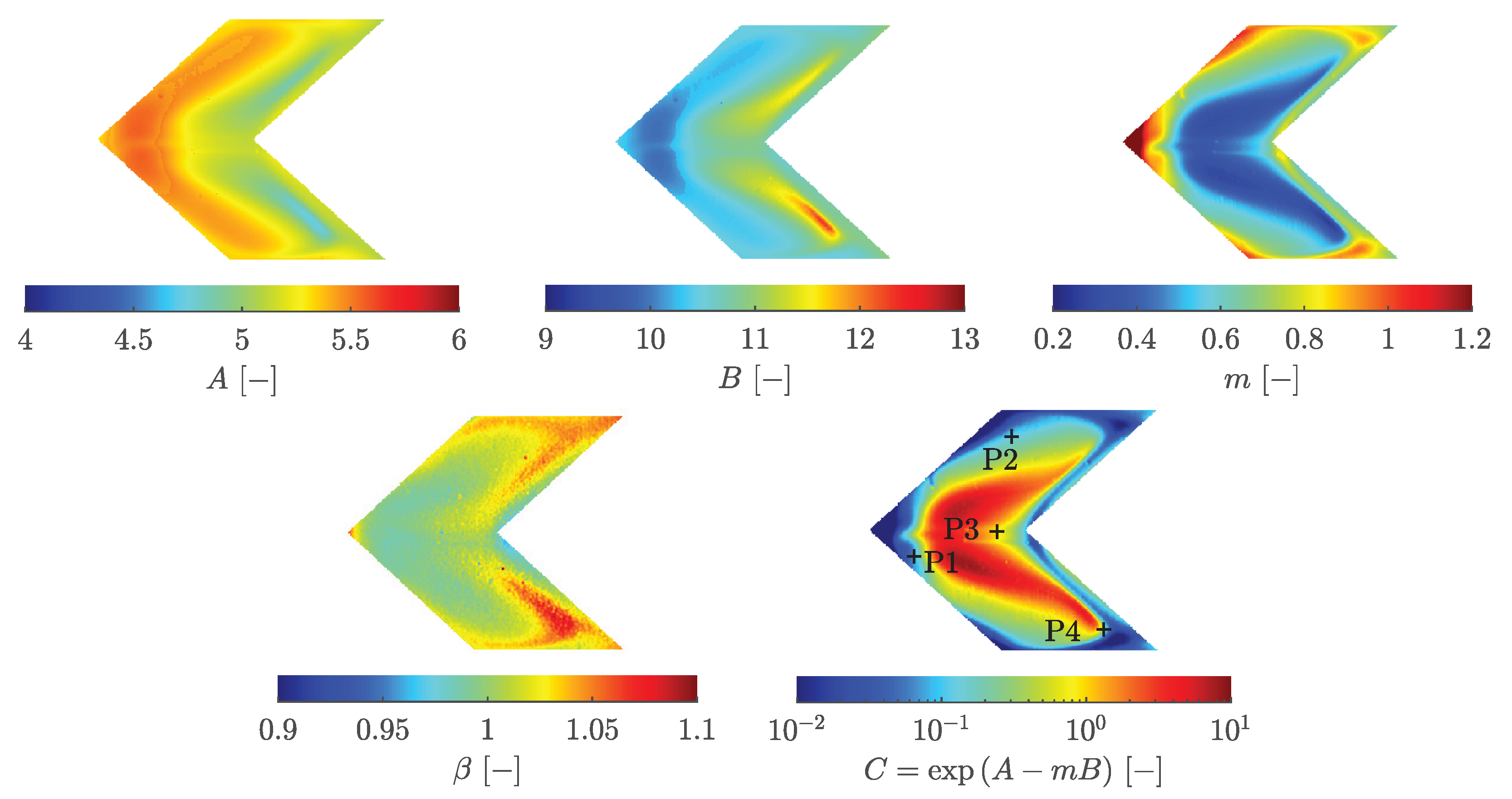
Figure 7 for perspex or quartz, respectively.
C and
m are relatively constant over the entire surface and
shows a similar distribution as in
Figure 6 using Equation
4. Slight differences are visible between the two materials, resulting from the approximated choice of
. However, it is noticeable that
C and
m interact with each other. For example,
C is slightly larger for quartz than for perspex, while
m is slightly smaller.
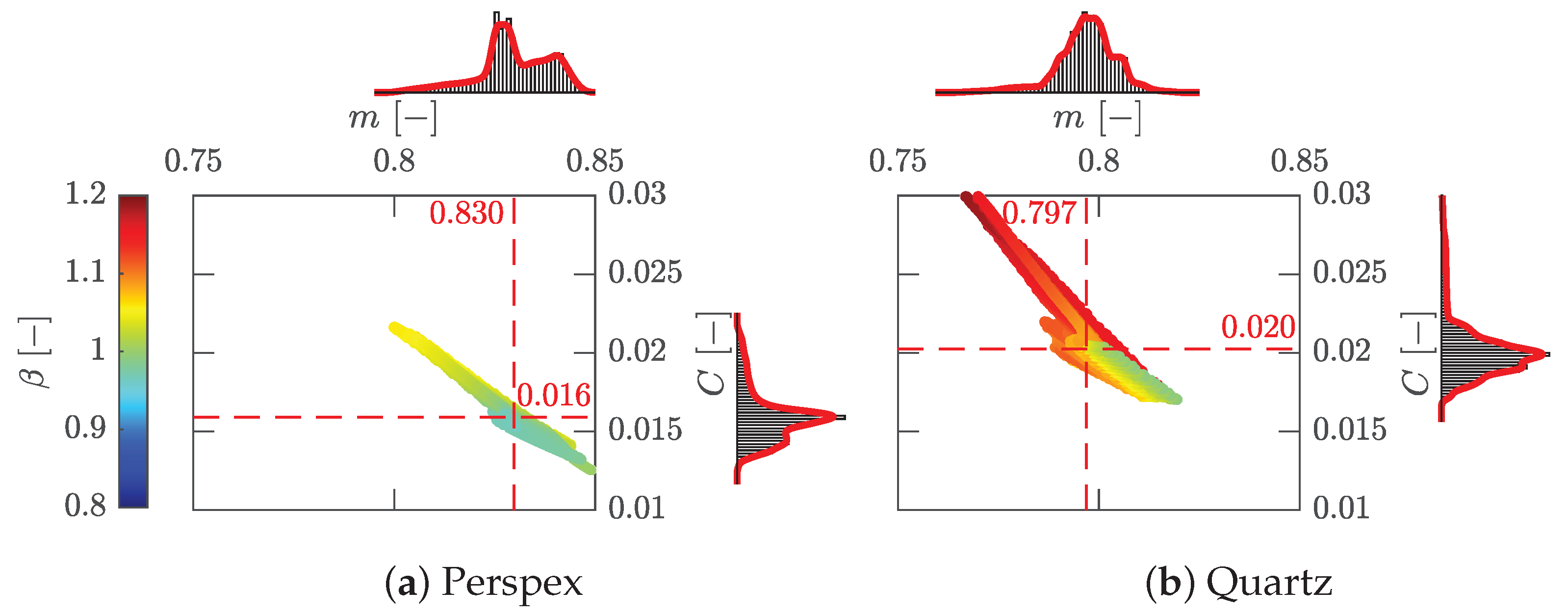
This becomes visible plotting
C over
m locally and adding
as color information as shown in
Figure 8, where also the histograms of the optimized variables
C and
m as well as their statistical mean value are shown. The range of
and
correspond to typical values for turbulent channel or pipe flow correlations.
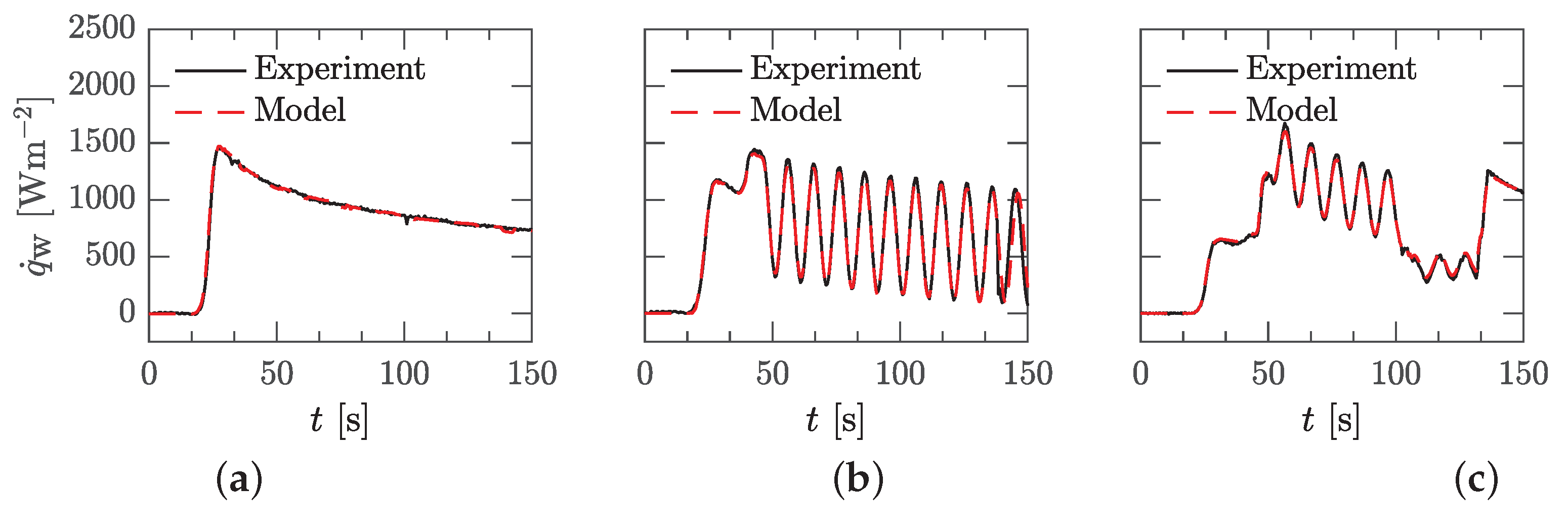
To evaluate the quality of the model, in
Figure 9 the recalculated heat flux over time for three cases at evaluation point P1 (
,
,
) is shown. Firstly, for the known cases of the Jump (cf.
Figure 3a) and Pulsation A (cf.
Figure 3d), which were part of the input data set. Secondly, for Cycle D (cf.
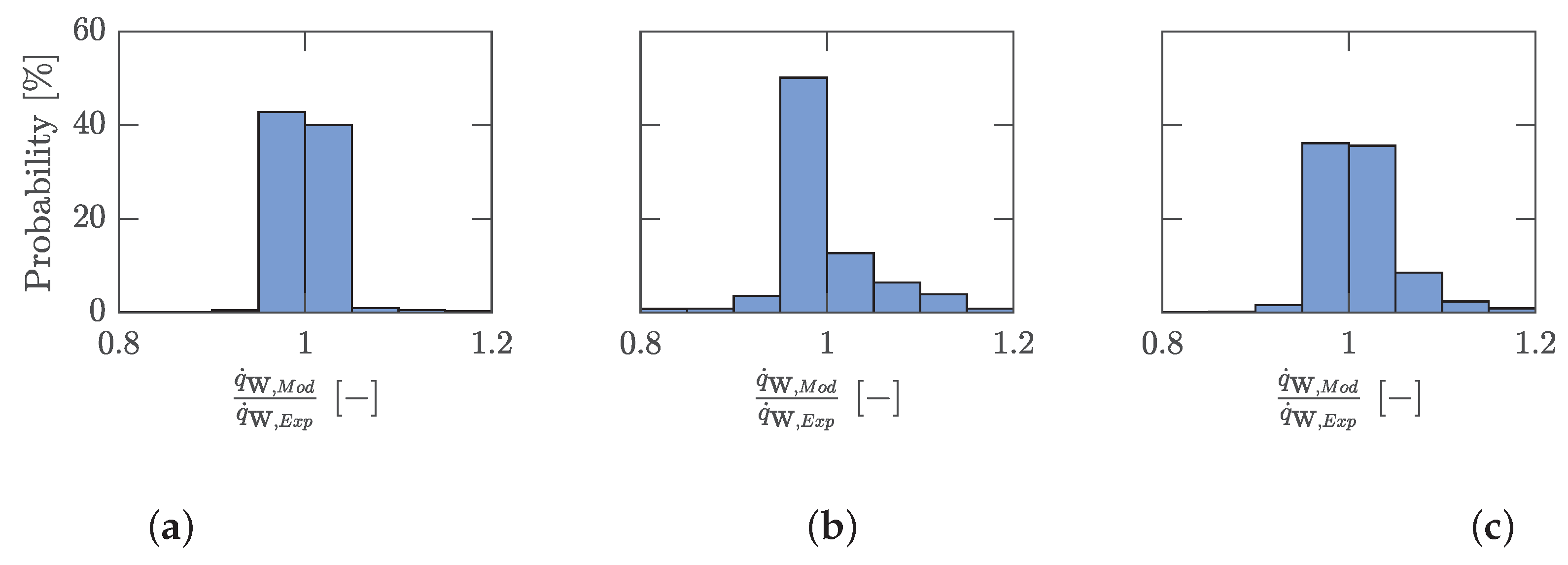
Figure 3i), which was not part of the input data set, but was examined using the same experimental data evaluation and with highly non linear flow and temperature boundary conditions. The heat flux course over time is reproduced very well for all three test cases. In areas with strong gradients in the boundary conditions, the back-calculated curve is somewhat smoother, resulting from the optimization, which acts as a kind of filtering of all data. However, even the initial period without a temperature jump is reproduced very well. The deviations between the experimentally determined heat flux and the calculated one from the model are in agreement by
as can be seen in
Figure 10, where all points in time are added in the histograms. Thus, a model could be derived which is able to reproduce the heat flux very well even for an unknown test case.
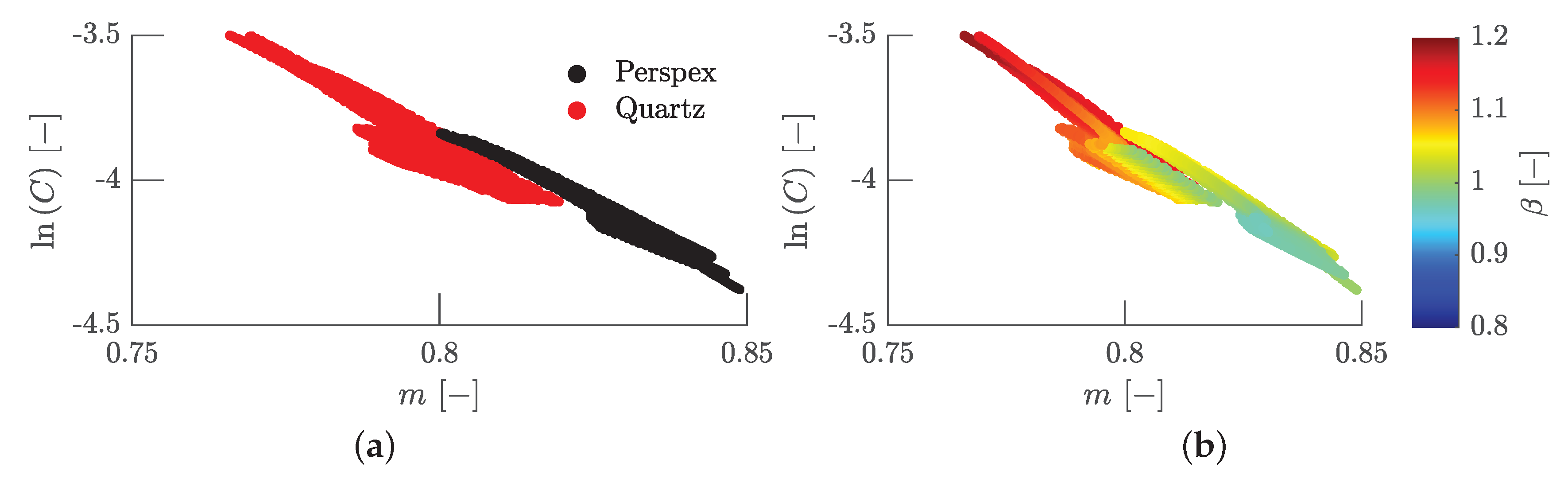
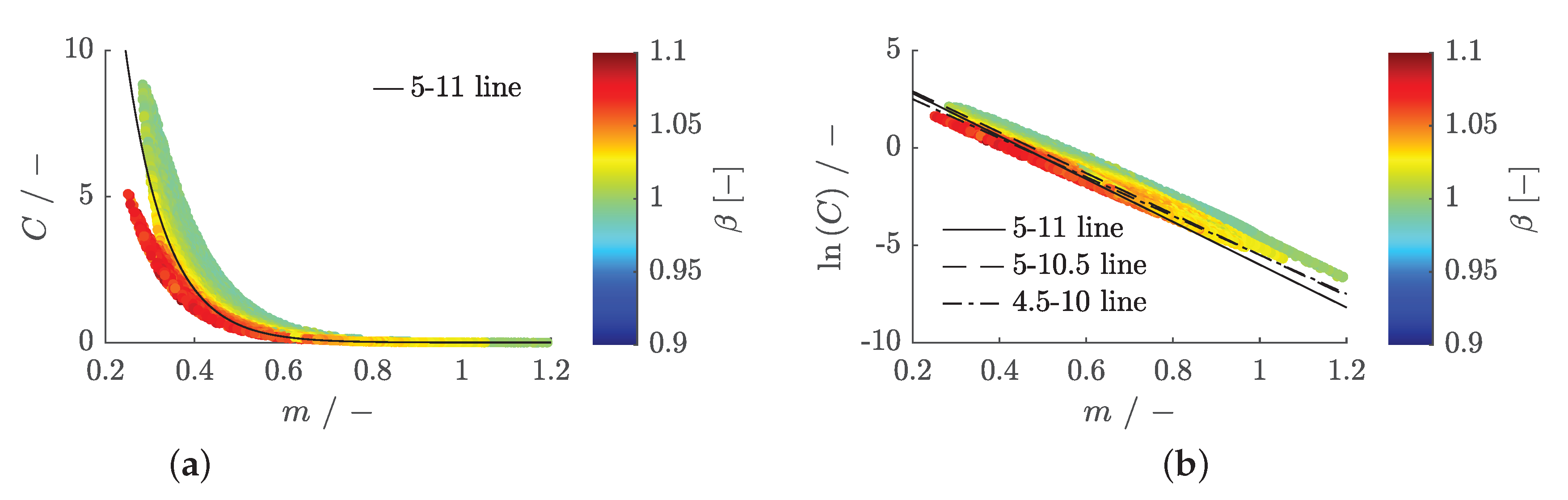
Flat Plate Flow
Figure 11 presents a composite diagram of the data from
Figure 8a and
Figure 8b. The logarithmic plot of
C reveals a linear relationship between
and
m, allowing the integration of perspex and quartz data into a single dataset. By incorporating the dissipation coefficient’s color information for both independently optimized parameters, a gradation according to
is observed. The slope of a resulting fitting line varies between
and
, with the offset ranging from
to
, depending on the data considered.
From
Figure 11 with the new, also time-invariant, parameters
A and
B, it might be approximated:
In order to analyze the parameters
A and
B further, only perspex is considered. First, the basic approach from Equation
5 is evaluated. It is assumed that all heat fluxes are approximately dissipation corrected due to the introduction of
. Furthermore, the Prandtl number in the experiments is only weakly temperature dependent and will be regarded as a constant in the following. Logarithmizing and rearranging Equation
5 then yields:
A simple comparison of Equations
11 and
10 gives:
Interestingly, the same result is obtained if the approach from Equation
10 is used in Equation
5 and a functional equation is derived:
Setting this equation to zero, forms an envelope to the family of
-
-curves (c.f. Afzal [
22]) and substitute
again by
yields:
Since the Nusselt number can never be zero, . Formally, this representation is independent of the Prandtl number and its exponent n.
Insertion into the original model Equation
9 then results in an equivalent representation
This gives a total of four parameters to optimize on the experimental data (
A,
B,
m,
). Since
C and
m are considered as time-invariant variables, according to Equation
10,
A and
B are also considered time-invariant. Similar to
, both might be regarded as an effective Reynolds number
with a corresponding effective Nusselt number
. The ratio is
In view of the the quasi-steady assumption,
and
are treated as time-invariant parameters in the following. The results of the new optimization of Equation
15 can be seen in
Figure 12. Due to the linear dependence of
on
m,
m itself and
remain unchanged, as expected. However, the optimization algorithm requires the specification of initial values. Since
C now depends on
A and
B via Equation
10, there are an infinite number of equivalent combinations for
A and
B. Nevertheless, the initial values
and
as mean values of the observed range in
Figure 11 are motivated by the fit of Equation
10 to the data for perspex and quartz. Thus,
A and
B show significantly less variation than
C and are statistically distributed around the values
and
(cf.
Figure 12).
With the values for
and
,
can also be written as
whereby
C in Equation
5 becomes a function of
m. With
it yields
, what is similar to the known pre-factor and exponent of the Dittus-Boelter correlation, as introduced by McAdams [
23,
24]. By introducing the Stanton number,
, in Equation
5 with Equation
10 it yields:
which reminds of the Colburn analogy
(cf. [
25]) for the chosen Prandtl number dependency. Thus, the friction factor
f can be written as
With the values for
and
from the optimization as well as with
m between
, a comparison to known friction correlations can be made. With
, this results in a pre-factor of
close to the correlation given by Blasius [
26] with
or for
,
and
close to the one given by Nikuradse [
27]. The correlation of Blasius is only valid up to a Reynolds number of
and thereafter that of Nikuradse. It can therefore be concluded that both
C and
m are functions of the Reynolds number similar to the velocity profiles given by power law models (see Schlichting [
6]). However, in the investigated Reynolds number range,
C and
m might be assumed to be constant as implied in Equation
9. Interestingly, going back to Equation
19 and using
it yields
which does not depend on
m any further. Friction factor relationships without a dependency on
m were introduced, e.g. by Prandtl [
28] in an implicit form for all Reynolds numbers derived from the log law. Classically, according to von Kármán [
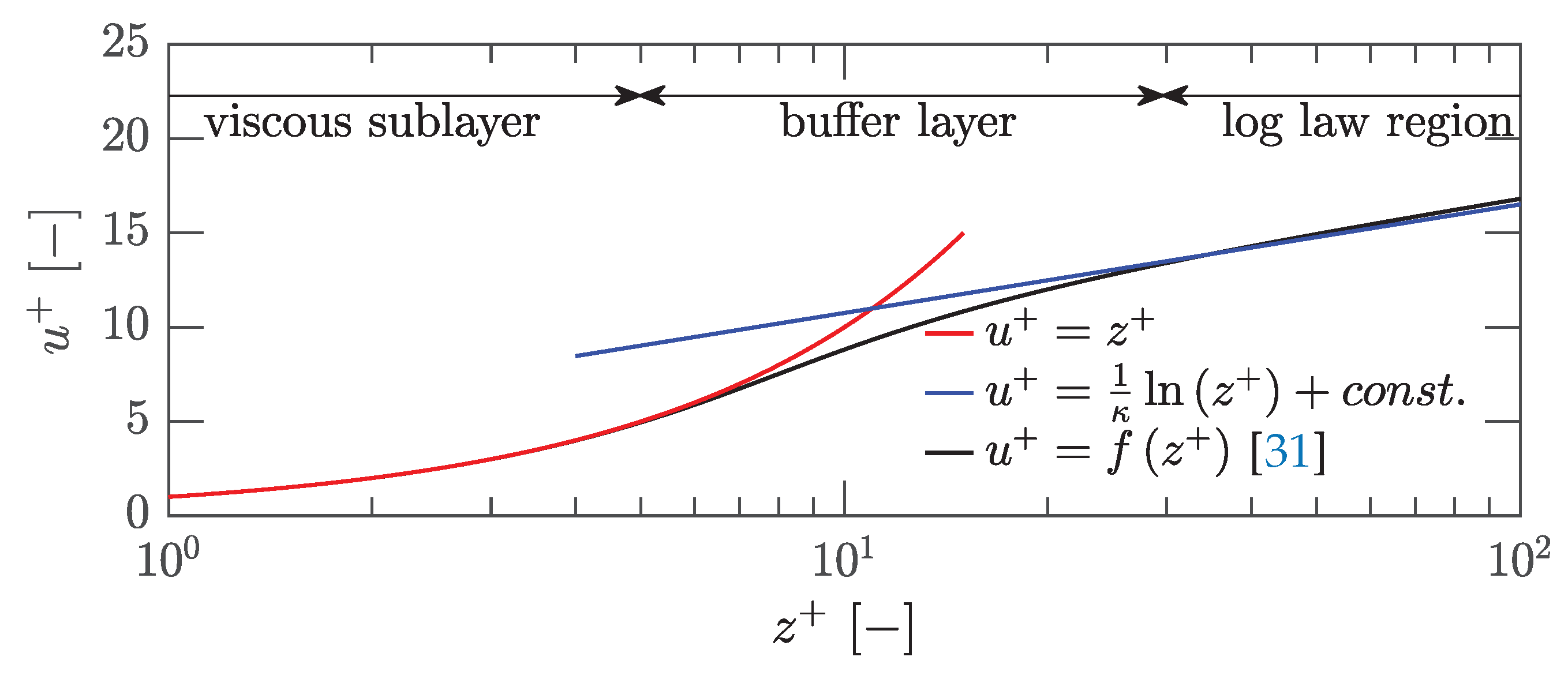
29], the viscous sublayer extends to
, followed by a buffer zone and the logarithmic region. The mean velocity distribution within the viscous sublayer is obtained by
, whereas in the logarithmic region
according to von Kármán [
29] and Prandtl [
28] is accepted. For turbulent flows with smooth walls the von Kármán constant of momentum transfer
and the integration constant are specified in Coles [
30] as
and
. Generalized functions for the velocity profile are given, e.g. by Reichardt [
31] or Spalding [
32]. In the equations to compare kinematic boundary layers, dimensionless velocities
are introduced, where the friction velocity
is correlated with the wall shear stress
, which can be expressed in dimensionless form by:
Introducing the dimensionless wall coordinate
a characteristic velocity profile within the kinematic boundary layer is shown in
Figure 13 assuming
and
.
The extrapolation of the inner law in the viscous sublayer
with the law of the wall at
, within the so-called buffer layer, gives
Thus,
A can be seen as the log law intercept and
B would mark the match point between the extrapolated linear viscous sublayer and the logarithmic laws. At this point it holds [
33]:
Hence,
B might be regarded as a measure of the sublayer thickness and will interact with the log law intercept
A, and the von Kármán coefficient
. All of them might vary with pressure gradient as described for example by Nickels [
34], Nagib and Chauhan [
35], Dixit and Ramesh [
36] or Baxerres et al. [
37]. From Equation
27,
is given by
If
B continues to represent a varying Reynolds number, according to Equation
27 for each
B, there is an
A representing the corresponding dimensionsless gradient at the wall. If
and
are set,
. Furthermore, inserting Equation
27 into Equation
20 yields
which are explicit relationships describing friction factors and Nusselt numbers related to turbulent fully developed pipe or channel flow. Comparing Equations
29 and
30 in
Figure 14 with correlations between Nusselt and Reynolds numbers or friction factors and Reynolds number in literature gives good agreement. Here, the derived relationships are compared with the friction correlations of Blasius
1[
26], Nikuradse
2[
27], Prandtl
3 [
28] and Petukhov
4[
38] or the Nusselt correlations of Dittus-Boelter
5[
23,
24] and Kays et al.
6[
15], respectively.
and Equation
20, it yields
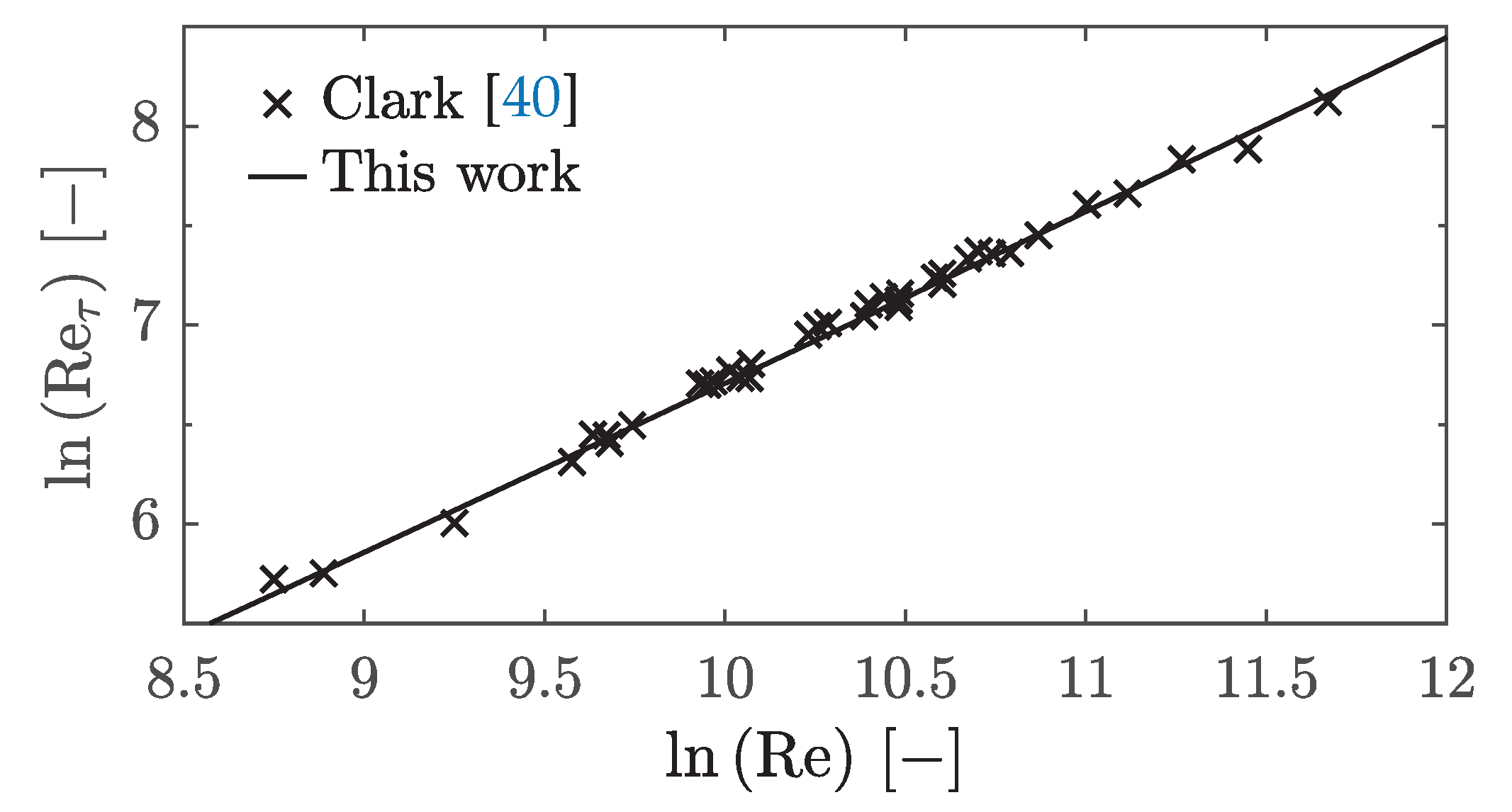
For turbulent channel flows Hussain and Reynolds [
39] determined a range of
and Clark [
40] for
, respectively. In
Figure 15 is plotted over
. Interpreting
B again as Reynolds number according to Equation
12, varying
A with
B according to Equation
27 and assuming
as used by Clark [
40], it is possible to reproduce Clark’s data fairly well.
The relationship
from Equation
10 is obtained from Blasius’ friction law [
26]. Therefrom the velocity power law is derived as first shown by Prandtl [
28] and taken up by Schlichting [
6]. In general,
Thus, for the wall shear stress it yields:
with Equations
32 and
33 it yields
showing the relationship between
and
m with
and
. An alternative description of the velocity distribution in pipe or channel flows is the so-called power law
Schlichting [
6] showed that the
is a good approximation to the log law Equation
21 for
, where the pre-factor
D and the exponent
varying with the Reynolds number. Several relationships for the power law are given for example by Afzal et al. [
41]. Barenblatt [
42] specifies
D and
as a function of the Reynolds number for pipe flows:
Barenblatt et al. [
43] stated this scaling law holds also for turbulent boundary layers if the Reynolds number is chosen appropriate. Using Barenblatt’s [
42] relationship in Equation
39 between
and
and again interpreting
as Reynolds number, it is possible by Equation
20 to reproduce his friction factors given by
Furthermore, Barenblatt [
42] gives a formulation for
depending on
:
Using this and additionally Equation
32 gives
A, and with Equation
28 also
depending on the Reynolds number only. For any Reynolds number, with the resulting parameters
A and
B,
is obtained. Barenblatt [
42] showed that the resulting envelope of power-law curves matches a logarithmic law with
, see also e.g. Afzal et al. [
44].
Furthermore, Barenblatt et al. [
45] consider the intermediate region between the viscous sublayer and the external flow consisting of two self-similar structures described by power laws and separated by a sharp boundary. The inner region scaling law is assumed to be universal, whereas the outer scaling law depends on the pressure gradients. In fact, the match point determines a characteristic length for an effective Reynolds number, which lies within the range
for different experimental data (cf. [
45]) and is according to Barenblatt et al. [
46] related to the wall-region thickness for turbulent boundary layer flows. The parameters
and
found for the flat plate, were linked to the extrapolated interaction between the linear part,
, of the viscous sublayer and the log law in the buffer layer (cf. Wosnik et al. [
47]). However, the presented observations might also be interpreted as the interaction of the two scaling laws proposed by Barenblatt et al. [
45] in the intermediate or overlap region.
A similar interpretation of a parameter
m - probably by incidence - as a measure for the thickness of the inner layer, which is still influenced by the wall was made by Szablewski [
48] in his mixing length model, which he suggested as an outer region analogon to the model of van Driest in the buffer layer [
49]. Therefore,
m should be pressure gradient dependent similar as the van Driest damping length parameter (see e.g. Cebeci and Bradshaw [
50]) and might be interpreted as an connecting parameter for so called quasi-equilibrium pressure-gradient boundary layers, see e.g. Baxerres et al. [
37].
Complex Flow Situations
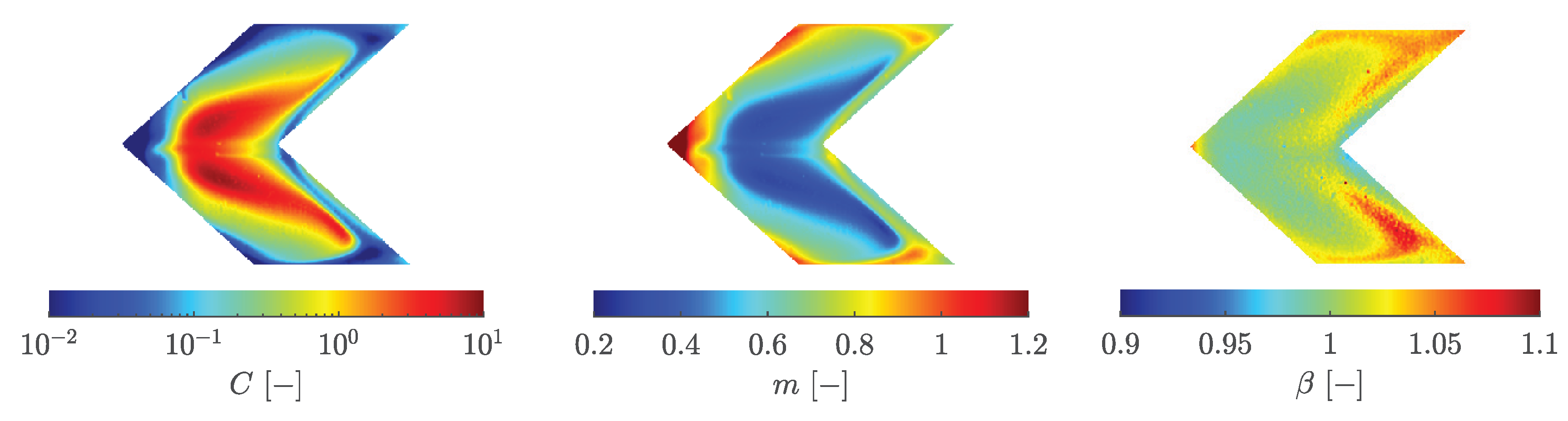
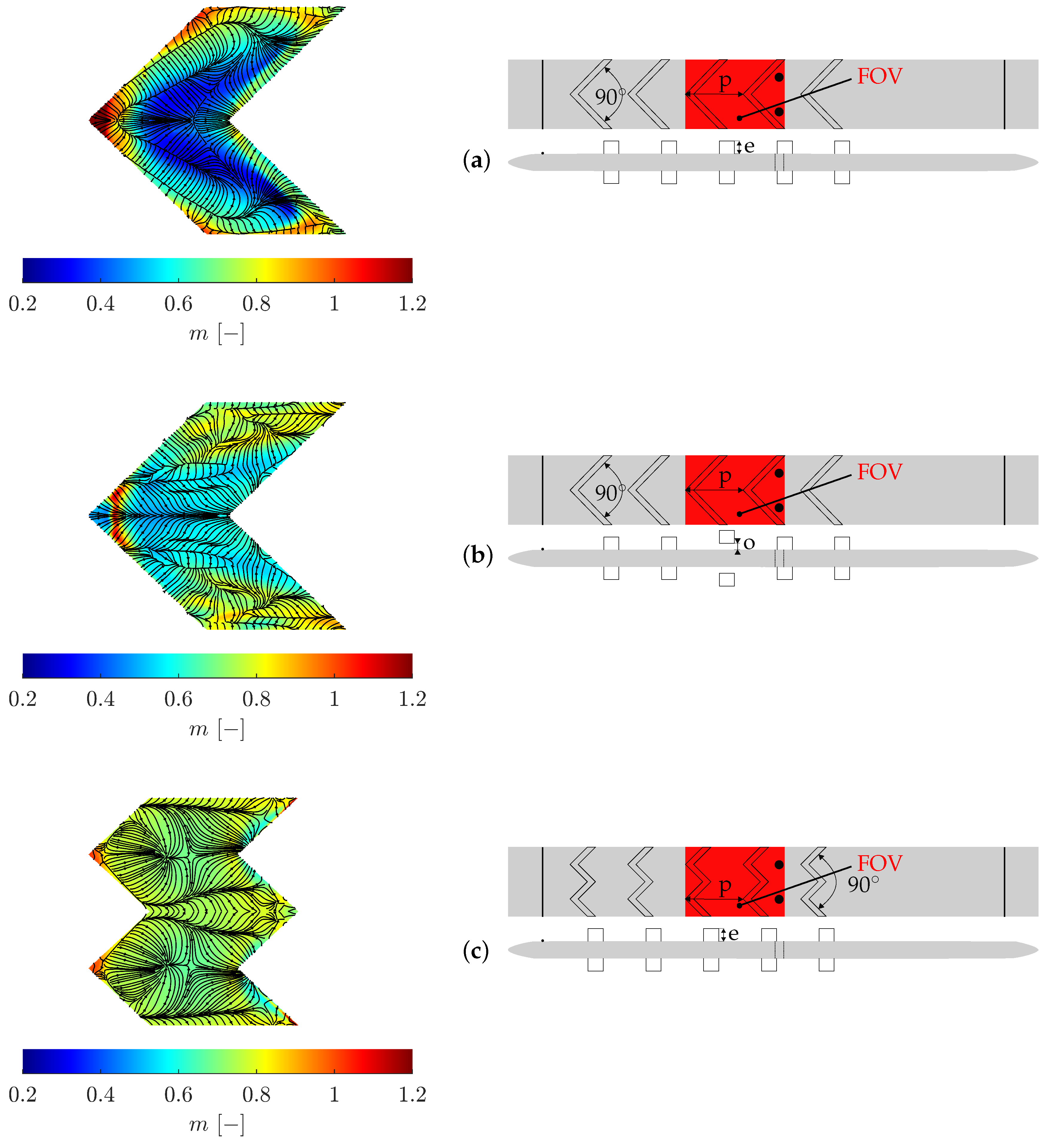
So far, only the experimental data for a flow over a flat plate have been considered. The pressure forces occurring here are moderate and the question arises how the model behaves with a more complex flow. For this purpose, a further geometry with five V-shaped ribs arranged one behind the other was investigated (cf.
Figure 2b). First,
Figure 16 shows the optimized values of Equation
9 with the initial values
,
and
analogous to the optimization of the experimental data of the flat plate.
In contrast to the flat plate, there is a significantly larger variation in
C and
m.
remains in a similar range as for the flat plate geometry. This consistency is expected, as the temperature and velocity boundary conditions are unchanged, and the resulting wall temperatures for the individual test cases have not increased drastically (see Hartmann et al. [
2]). However, the rib geometry induces additional vortices, evident in the distribution of
C and
m. In the core zone, the flow is strongly accelerated by the preceding rib, causing the
m value to decrease significantly, reaching a lower limit of about
. Behind and along the front rib, significantly increased values of
m are observed. The flow vortices impact the wall in these areas, follow the rib contour towards the outer walls, and then separate again in front of the rear rib, where the
m values decrease again towards
. Conversely,
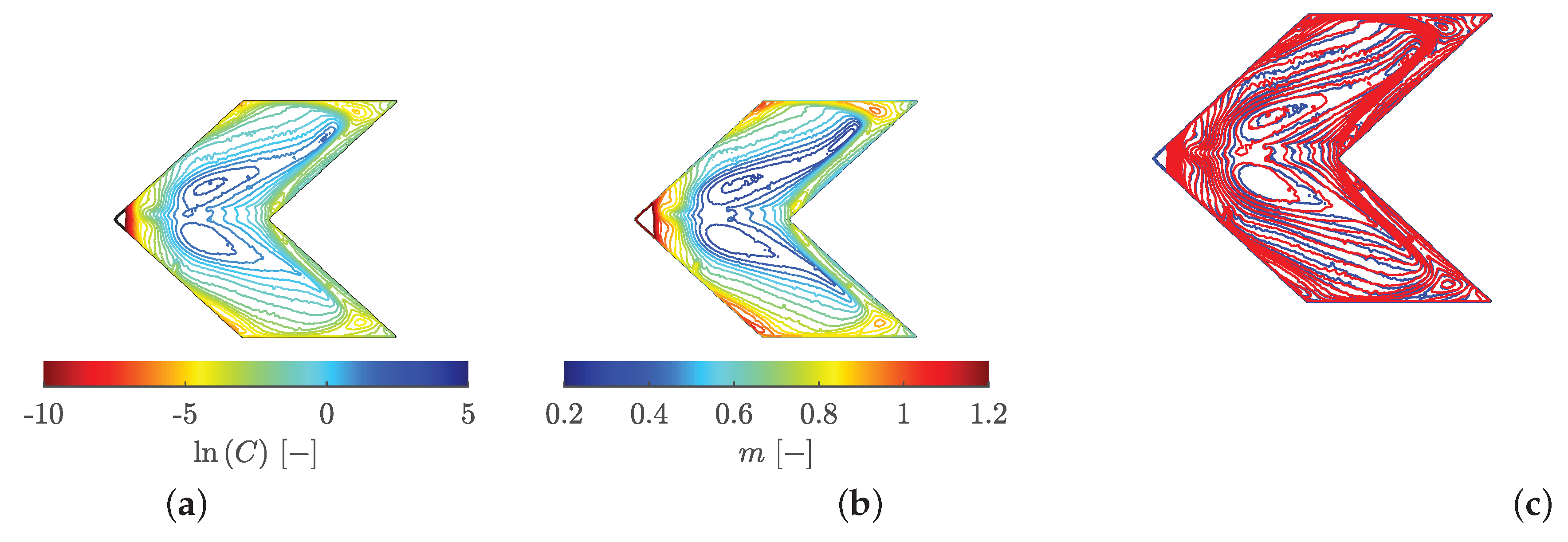
C shows an opposite trend, what is more clearly visible by the isoline representation of
and
m in
Figure 17a and b.
If the isolines of both distributions,
in red and
m in blue, are superimposed (
Figure 17c), the corresponding structure of both distributions is visible. The parallels to flow physics, as illustrated by oil visualization and the distribution
m, were also noted by Terzis et al. [
51] for a flow around obstacles or in multiple jet impingement situations [
52].
This complex flow situation significantly expands the
C-
m space, shown in
Figure 18a. Here, the two-dimensional values from
Figure 16 are presented with
C over
m and
as color information. Two branches are visible for
and
.
adjusts the dissipation component due to heat transfer or heat conduction but not the component due to kinematic heating. According to Rotta [
53], the self-heating part cannot be guaranteed by
formulated in temperatures alone. For a comprehensive dissipation description, local velocities would also need to be included. However, since these velocities are indirectly present in the heat transfer data, their contribution might be hidden in
C by the optimizer. Interestingly, the earlier found
and
from the data of the flat plate, are a good fit to the data of the ribbed geometry, holding
(cf.
Figure 18a).
However, one can argue from
Figure 18b that a negative slope
or an offset
would be an equivalently reasonable fit. To investigate this further, similar to the flat plate, Equation
15 should therefore be optimized according to the parameters
A,
B,
m and
. The parameters of the optimization for the initial values
,
,
and
are shown in
Figure 19 as well as
C calculated back from Equation
10. Analogous to the flat plate case,
m and
remain unchanged optimizing Equation
9 or
15. The optimizer can “play” with the two new parameters
A and
B in such a way that the final result is the same
C as with a direct optimization of
C,
m and
. The parameters
A and
B from the optimization with Equations
29,
28 and
32 result in
f,
and
distributions, which are shown in
Figure 20. All three distributions vary locally due to the dependence of
A and
B on the flow conditions and the pressure gradient. Because
is split into
A and
B using Equation
10, different combinations of
A and
B with the same
m can result in the same
C.
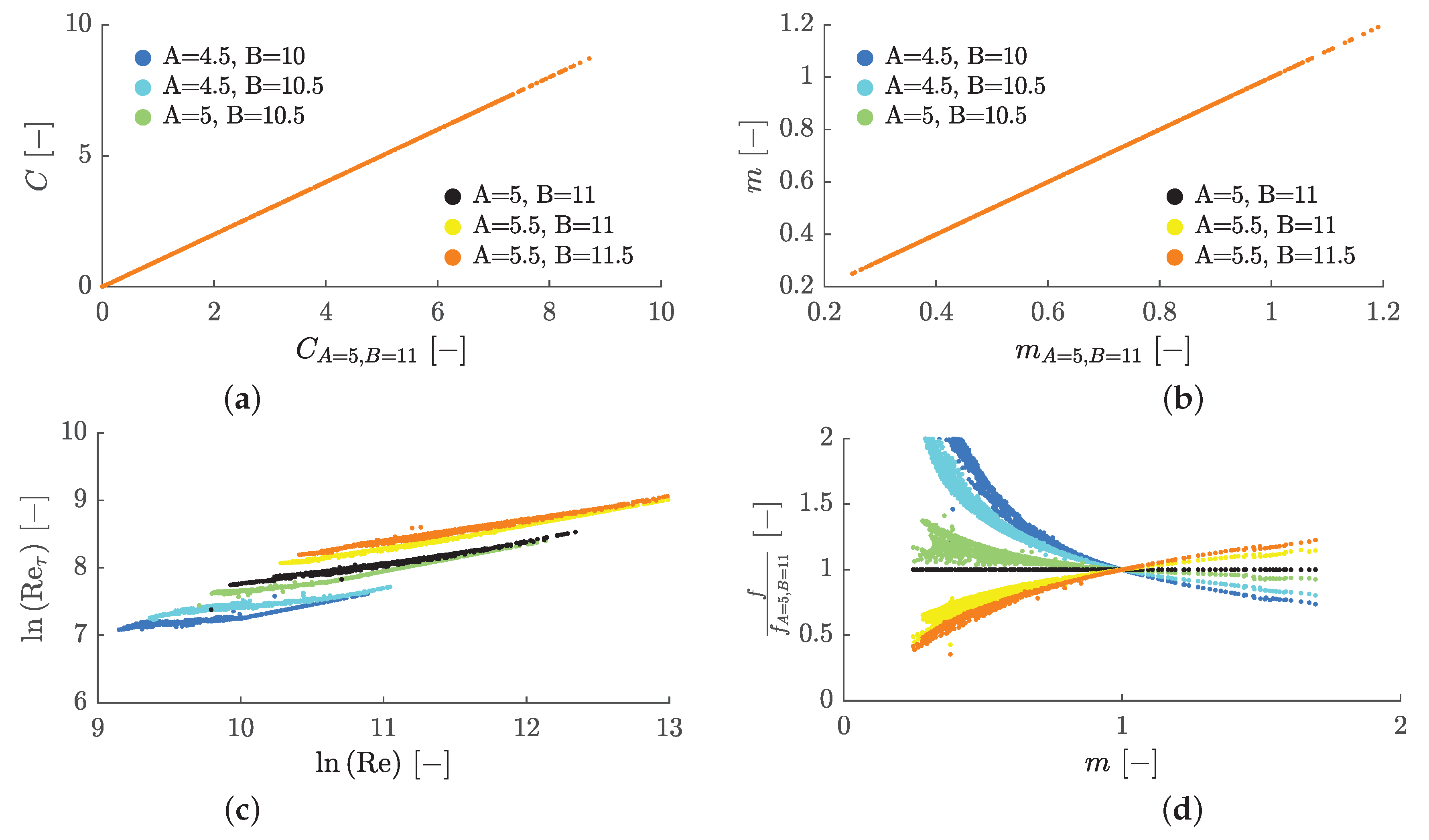
To analyze the dependency on initial values, different initial value combinations between
and
were chosen. The results are shown in
Figure 21.
First of all, it is noticeable that the back-calculated
C-distribution (a) and that for the parameter
m (b) obtained directly from the optimization are independent of the initial value combination. Next, the physical quantities derived from
A and
B are investigated. In
Figure 21c,
is plotted against
. The distribution varies depending on the initial value. The parameter range for
increases with a larger initial value
B. In contrast, the value of
A determines the level of
and the range of
, as curves with the same initial value
A merge. Hereby, the initial value of parameter
B exerts minimal influence on
. Notably, when the friction factors from Equation
20 are normalized to the case with initial values
and
in
Figure 21d, all
f-values for
coincide. For these, it is possible to combine all experimental Reynolds numbers from the different boundary condition courses to a unique solution, since for
in Equation
34,
is independent of the Reynolds number. In consequence,
must apply for
. Since different Reynolds numbers occur in the different tests, there is no unique solution for
and the optimizer searches for the nearest minimum depending on the initial values. However, for those
m values, significant variations in
f can be observed, with differences exceeding
for smaller
m values.
Another approach to determine
A and
B without the dependency on initial values is shown in
Figure 22a. For this, the more reliable parameters
C and
m from optimization of Equation
9 are used. In the
A-
B diagram,
B is varied as a running variable and
A is calculated for each
B and each
C-
m-combination according to Equation
10. Different lines result for different evaluation points (see
Figure 19). To determine
A and
B, the point on the straight line with the smallest distance from a target point is sought
7 using the values of the flat plate (
,
), where Reynolds or Colburn analogy should hold. The advantage of the graphical solution is that there is a unique solution for
A and
B. To evaluate the different initial value combinations, the parameters from the optimization are compared with a correlation of Nagib and Chauhan
8 [
35], who investigated the dependence of
and
A with various pressure gradients. As can be seen in
Figure 22b, the graphical solution lies best on the correlation of Nagib and Chauhan. The data from the optimization with the initial values
and
also lie mostly on the correlation curve and are the best approximation of the cases investigated. The other two data sets, which also fulfill the formal condition
for
,
,
and
,
, deviate significantly more from the correlation curve.
An interpretation for the parameter
m might be given following White and Christoph [
54]. They investigated the influence of pressure gradient, heat transfer and compressibility for turbulent boundary layers on inner variables only, neglecting the “wake” flow effects. If all three vanish the logarithmic law, Equation
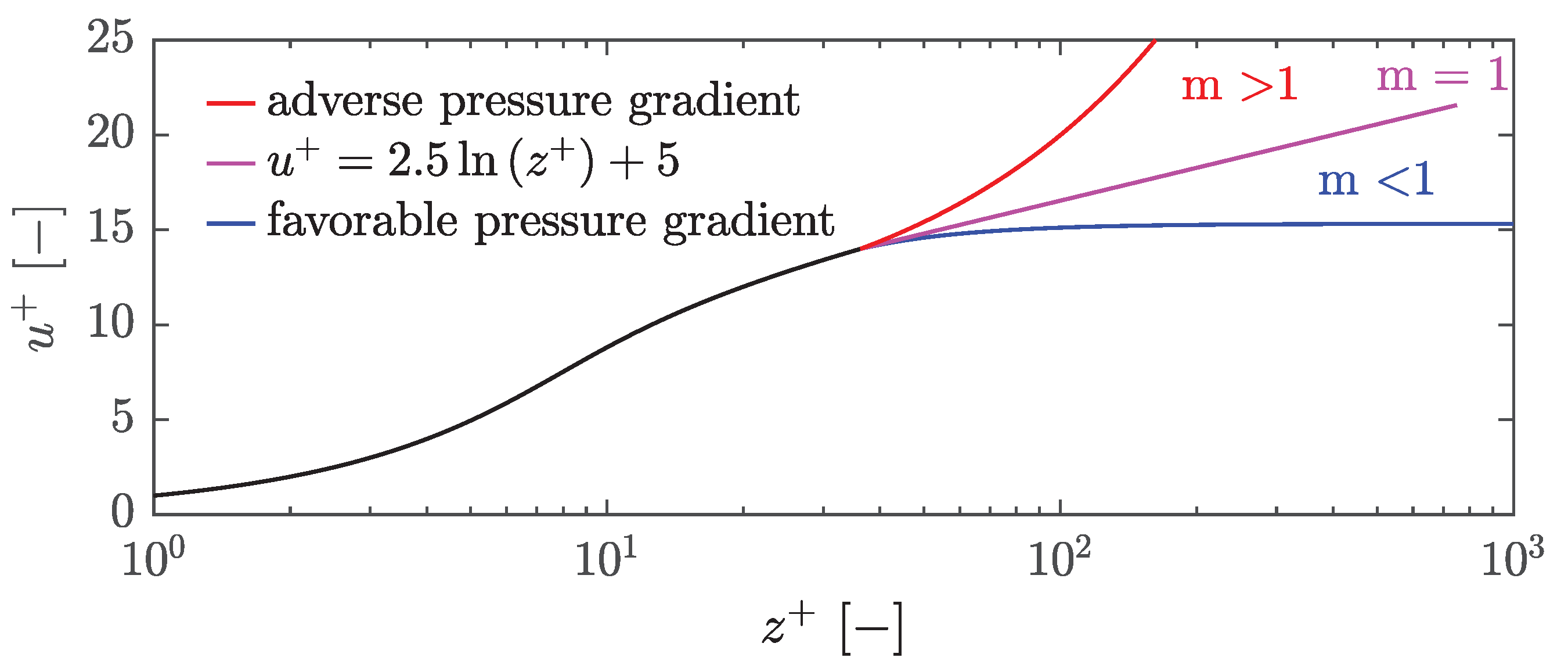
21, holds. Heating or favorable pressure gradients usually tend to depress the velocity profile, whereas cooling or adverse pressure gradients tend to raise the profile above the log law. The different effects can also compensate for each other, resulting in the log law again.
Figure 23 illustrates our interpretation of
m, which occur locally depending on the flow situation and pressure gradient condition. For a flow without a pressure gradient, the velocity profile follows the log law, resulting in
. For flows with a favorable pressure gradient, the profile flattens out; for flows with an adverse pressure gradient, it detaches, resulting in
for favorable pressure gradients and
for adverse pressure gradients.
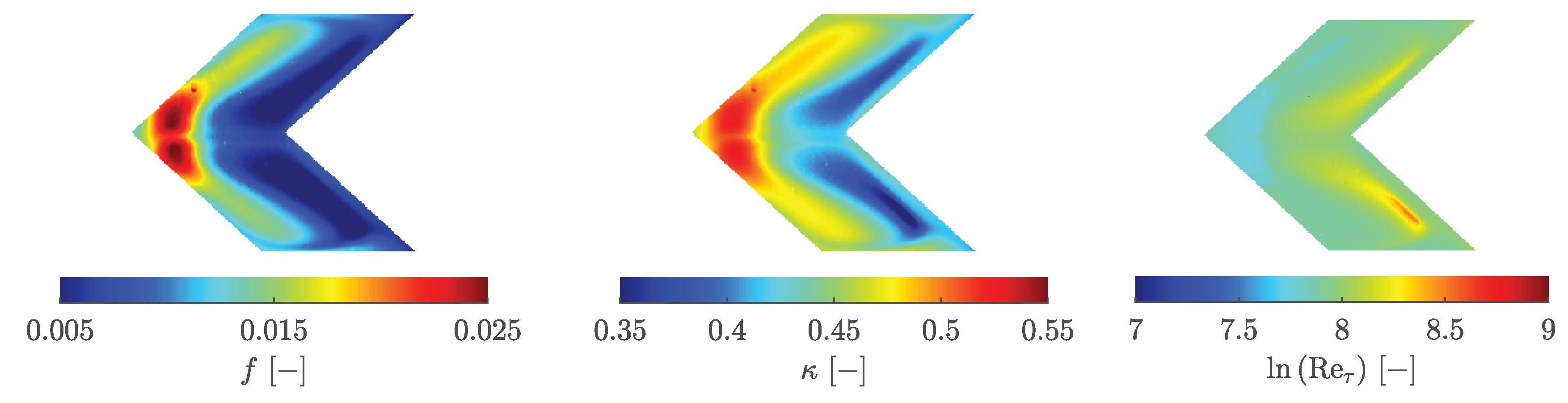
Finally, to determine a more reliable friction factor
f for a complex flow, the data from the
C,
m,
optimization are used in the following, because of their independence of initial values. As the data of parameter
C might still be influenced of dissipation effects and in order to account for deviations from an analogy situation, the optimized
C values are normalized to the 5-11 line. This results in
,
as a Reynolds analogy factor. Hence,
is given by
Figure 24a illustrates the surface distribution of
, while
Figure 24b presents a histogram of
. In regions where
, the Reynolds or Colburn analogy
formally holds. The range of
extends to values around 5 in the area directly behind the ribs, aligning with the range reported by So [
55] in his study on the effects of pressure gradients on the Reynolds analogy in equilibrium boundary layers. The minimum value of
would correspond to the lower boundary for Reynolds analogy factors found by So [
55], which equates to a Clauser pressure parameter of approximately
. According to Mellor and Gibson [
56], this is the smallest value at which equilibrium accelerated boundary layers still exist. In accelerated turbulent boundary layers,
decreases, whereas it increases in regions with adverse pressure gradients.
By normalizing to the 5–11 line, a friction factor distribution can now be determined, what is shown in
Figure 25a. Compared to the distribution calculated from Equation
20 with
A and
B in
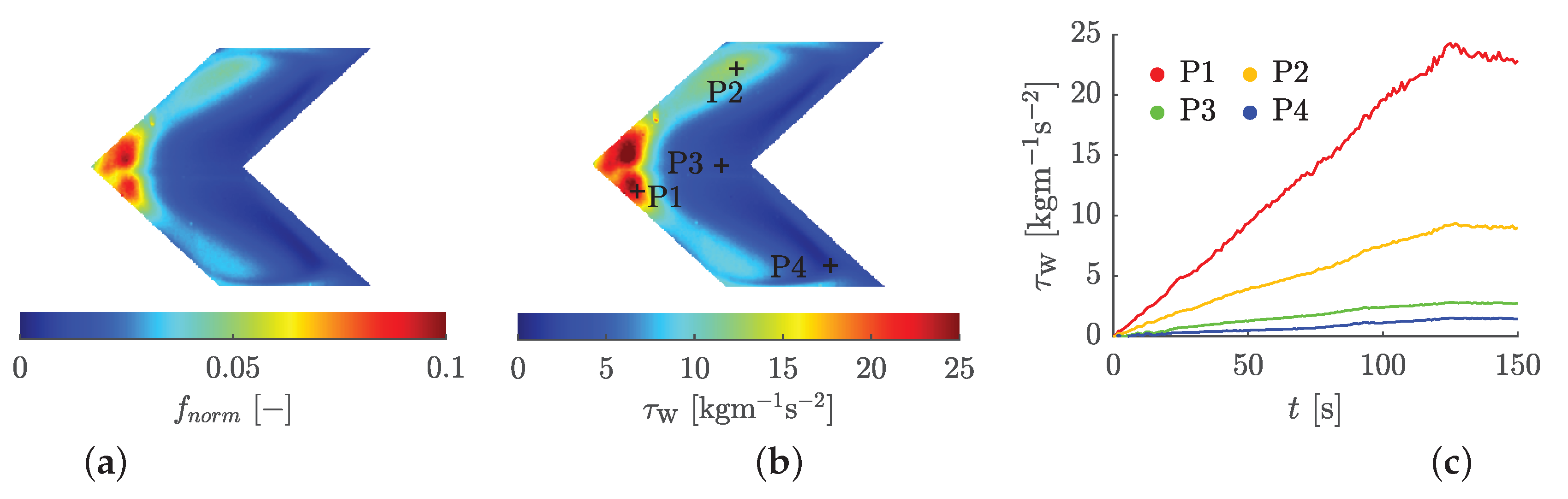
Figure 19, the range of values has been increased and the local flow effects taken into account. Furthermore, time-dependent distributions of wall shear stresses under various flow conditions can be calculated.
Figure 25b presents this distribution for the Ramp B case (cf.
Figure 3c) at
. Additionally,
Figure 25c depicts the temporal evolution of wall shear stress for four specific pixels, whose positions are indicated in
Figure 25b.
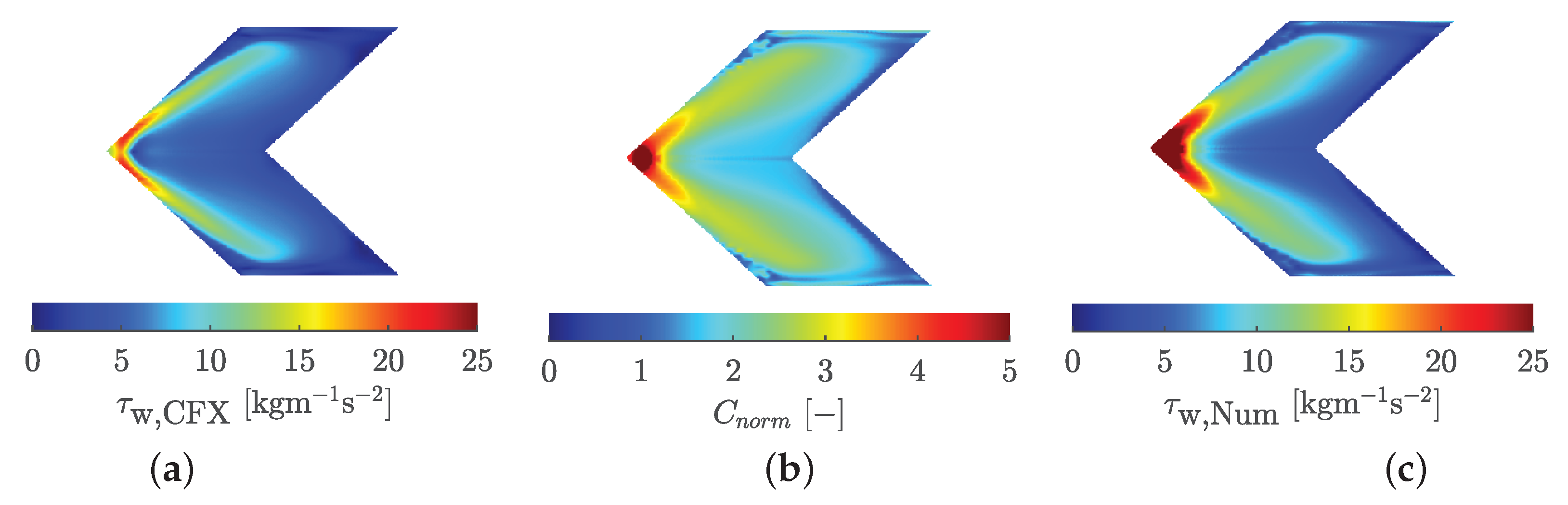
To evaluate the quality of the wall shear stresses, the methodology presented was also applied to numerical conjugate heat transfer scenarios. Detailed information on the numerical model employed can be found in Hartmann et al. [
2].
Figure 26a illustrates the wall shear stress calculated directly from the simulation, while
Figure 26b shows
obtained from the presented method using the numerically calculated heat transfer data. The resulting wall shear stress for the test case Ramp B after
is depicted in
Figure 26c.
The agreement between the wall shear stress obtained directly from the numerical simulation (
Figure 26a) and that calculated from the simulations using the presented method (
Figure 26c) is good. The largest deviations occur in the area immediately behind the rib, within the reattachment zone, and around the largest vortices. Similar deviations are observed in the distribution of wall temperatures, as reported by Hartmann et al. [
2]. These discrepancies might be attributed to the isotropic model within the underlying SST turbulence model.
To investigate a more general validity of the method, two additional geometries were examined experimentally and the data processed the same way. First, the third V-rib on the plate, specifically the front rib in the field of view, was detached by
mm. This adjustment aimed to weaken the recirculation areas due to the additional near-wall flow. Additionally, a case with five W-ribs instead of V-ribs was investigated. Both additional geometries were also measured experimentally under the presented boundary conditions (
Figure 3a-h), and
C,
m and
were determined using Equation
9. The resulting distributions are shown in
Figure 27.
It is visible that the analyzed geometry with five periodically arranged V-ribs represents a somewhat extreme case that encompasses the value range of all other geometries. Detaching a rib doubles the smallest m and homogenizes the overall flow situation. While the geometry with five V-ribs clearly shows the formation of two branches, this is only slightly recognizable in the geometry with one detached rib. For the case with five W-ribs, larger detachment areas and reattachment zones are less recognizable, and the m range shifts toward the known coefficients for turbulent plate flow. The previously discussed 5-11 line fits all geometries well for .
To visualize the relationship between pressure gradient and
m, pressure gradient streamlines from a numerical simulation are plotted over the
m distribution of the experiment in
Figure 28 for the attached (a) and detached (b) V-rib configurations as well as for the W-ribs (c). For the attached ribs, a deep valley with small
m-values might be observed in the center of the field of view, with
m values increasing towards the edges (see
Figure 16b). The streamlines follow this trend, converging at the center point of lowest
m. This close connection is even more evident with one detached rib. The additional flow below the front, detached rib creates a modified flow situation with several intermediate maxima at a more uniform
m level overall. For constant
m values in the center of the field of view, the streamlines converge. This phenomenon is also clearly observed in the W-ribs configuration, where the
m distribution exhibits only slight variations across the entire field of view. In the regions behind the two imaginary V-ribs forming the W-rib, there is a small valley with lower
m values compared to the rest of the field of view, where the pressure gradient streamlines converge. In the central area behind the W-rib, the streamlines run relatively undisturbed to the next rib at a constant
, similar to the behavior observed in flat plate flow.
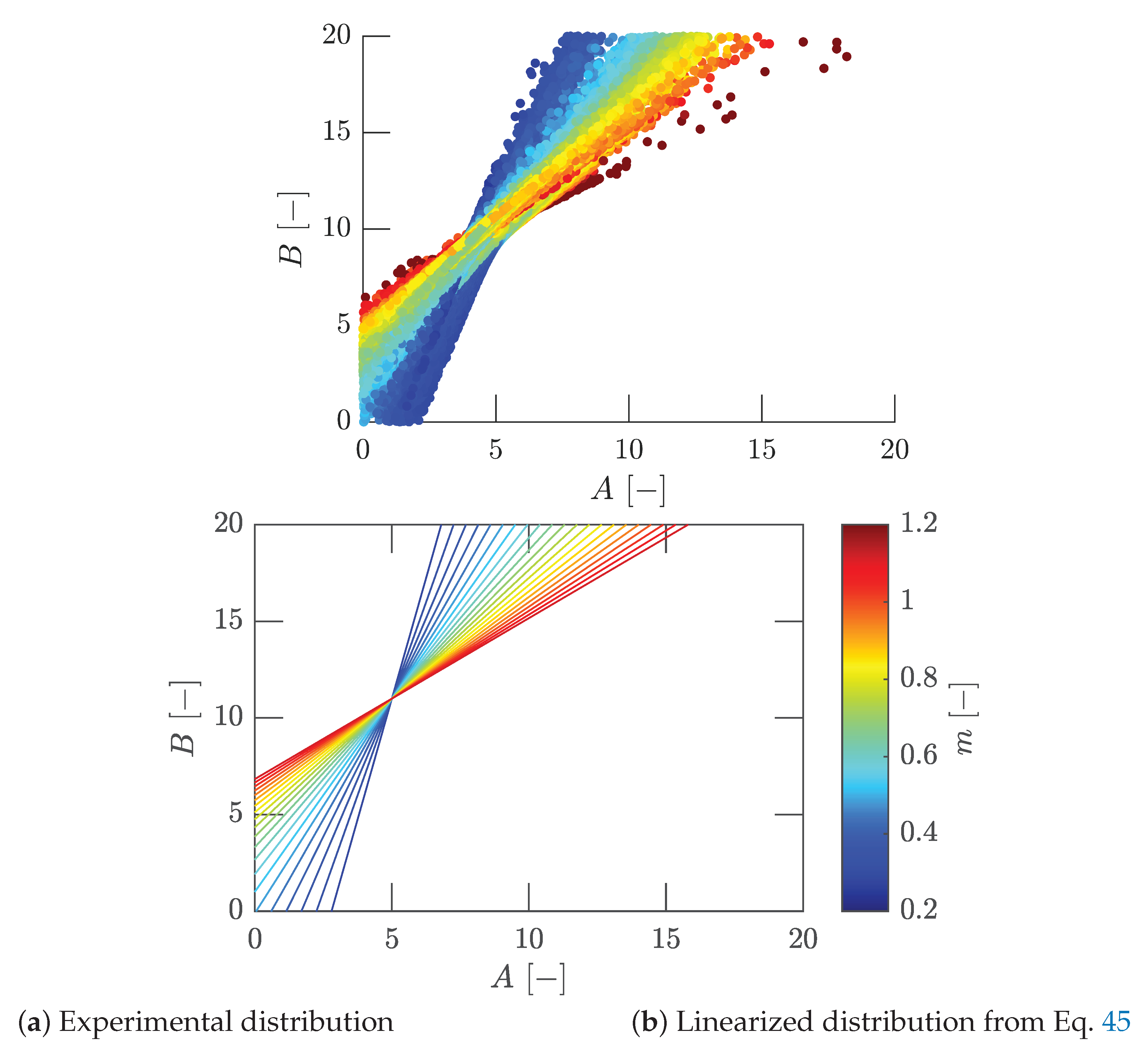
Previous analyses considered each pixel for the parameter optimization in isolation, without accounting for neighboring pixels. For an alternative method to describe the relationship between
A and
B, the information of the surrounding four pixels and therewith the spatial distribution is also be included. Therefore, the Equation
10 is differentiated with respect to
m, resulting in
This approach allows for the direct calculation of B from C and its differential with respect to m. The gradients of both parameters C and m are computed via a central difference scheme.
Figure 29 shows the resulting values of
B over
A and their histograms for the three geometries investigated. Here,
A is calculated from
C,
m and
B using Equation
10. The experimental values form a set of curves consisting of nearly straight lines as a function of
m. These all intersect approximately around the common point
and
. The slight scattering around this point is presumably due to parameter
C, which is still somewhat subject to dissipation. However, it is remarkable that all three distributions show a similar behavior independently of each other and that the majority of the points are grouped around
and
without any specifications regarding initial values.
This can also be seen in
Figure 30a, where the experimental values of the geometries were plotted together with their respective
m values. It results in a clear staggering of straight lines as a function of
m, which can be described via
where
A is used as a running variable.
Figure 30b shows Equation
45 as a set of ideal curves for different
m. By definition, these intersect
and
, which in comparison with the results in
Figure 30a directly from the differentiated experimental data, is again a very good approximation and unifies the observations of all investigated geometries. Hence, this is a further indicator for the choice of this characteristic point as a normalization condition.