Study Objective: The aim of this study is to scientifically examine the biological characteristics and medicinal potential of the endemic plant species Scorzonera uzbekistanica, native to Uzbekistan. By detailing the morphological and chemical composition of the plant, the study seeks to evaluate the health effects of its bio-active compounds (such as inulin, flavonoid, oxyacetylene, etc.). Additionally, by investigating the plant’s ecological distribution and habitat characteristics, the study aims to highlight its importance as a species that needs to be conserved. Furthermore, by exploring the traditional medicinal uses of Scorzonera uzbekistanica, the study aims to provide new perspectives on its possible applications in modern medicine. This research aims to contribute to the scientific literature on this plant and raise awareness about the conservation of Uzbekistan’s biological diversity.
Conclusion: This study provides a detailed examination of the biological and chemical properties of the endemic plant species Scorzonera uzbekistanica, revealing its medicinal potential. Analyses show that the plant’s roots contain high amounts of inulin, while its leaves and flowers contain important bio-active compounds like flavonoid and oxyacetylene. These compounds are known for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and prediction properties, indicating that Scorzonera uzbekistanica is a notable plant for digestive health, immune support, and potential anticancer effects.
However, additional laboratory and clinical research is required to better understand the pharmacological effects and medicinal uses of this plant. The findings of this study support the potential use of Scorzonera uzbekistanica in modern medicine and highlight the need to protect this endemic plant. Additionally, this study contributes to the conservation of Uzbekistan’s biological diversity and sustainable use, providing a foundational resource for future research.
1. Introduction:
Scorzonera uzbekistanica is an endemic plant of the Asteraceae family, found only in Uzbekistan. Endemic plants are species that grow exclusively in a specific geographical region and are unique to that ecosystem. Uzbekistan, a region rich in biological diversity in Central Asia, hosts many endemic plants. However, many of these plants are under threat, making the investigation of their biological and medicinal properties of great importance both scientifically and for conservation efforts.
Limited information is available on the traditional medicinal uses of Scorzonera uzbekistanica, but the bioactive compounds it contains provide a strong basis for investigating its medicinal potential. This study aims to contribute to the scientific literature by thoroughly examining the morphological, ecological, chemical, and medicinal properties of the plant.
Morphological Characteristics of Scorzonera uzbekistanica:
Scorzonera uzbekistanica belongs to the Asteraceae family and is a perennial herbaceous plant. The morphological characteristics of this plant can be detailed as follows:
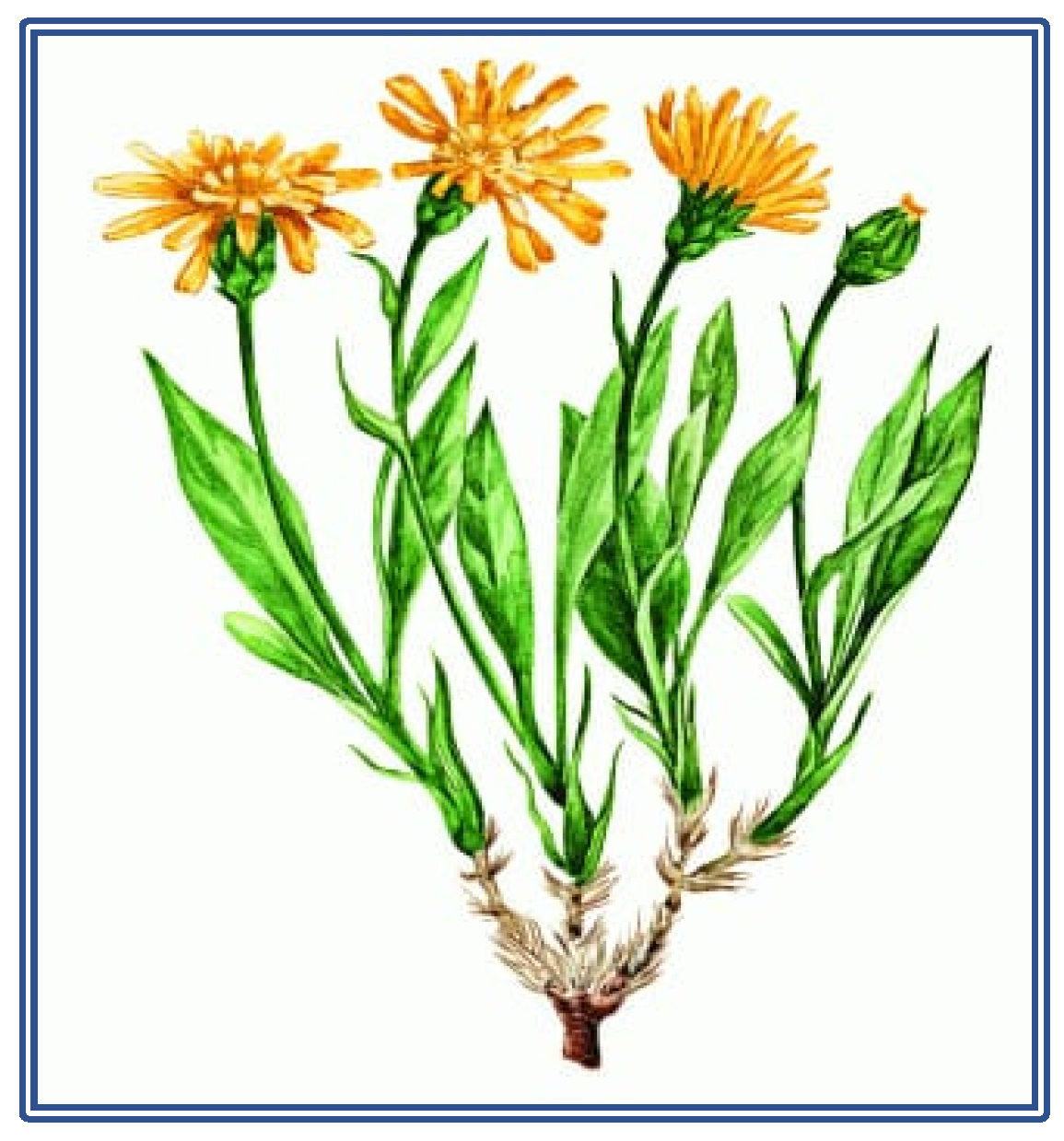
Height and General Structure: Scorzonera uzbekistanica typically grows to a height of 30-50 cm, with an erect and slender stem. The stem is usually glabrous and grows vertically.
Leaves:The leaves are concentrated at the base of the plant and are arranged in a rosette formation. They are long, narrow, and have a linear or lanceolate shape, typically gray-green in color. The edges of the leaves are generally smooth or slightly wavy, with prominent veins extending from the central part of the leaf. The leaves are alternately arranged on the stem.
Flowers: The flowers of Scorzonera uzbekistanica are the most striking part of the plant, yellow in color, and resemble daisies. The flowers are typically solitary or grouped in small clusters at the ends of the stems. The flower heads are approximately 2-3 cm in diameter and usually arranged in a composite form (spike-like). The flower head has tubular (disc) flowers in the center, surrounded by ungulate flowers, giving the plant its typical daisy family appearance.
Root System: The root system is well-developed and plays a significant role in the plant’s survival. Scorzonera uzbekistanica has swollen, fleshy roots that allow it to store water and nutrients, increasing its drought resistance. The deep root structure enables the plant to survive in harsh environmental conditions.
Fruit and Seeds: The plant’s fruit is a small, hard, and dry structure that carries the seeds. The fruit is usually an achene, meaning it is single-seeded and encased in a woody shell. When mature, the fruits are dispersed by the wind, which is part of the plant’s reproduction and dispersal strategy.
Visual 1:Morphological characteristics of Scorzonera uzbekistanica.
Visual 1:Morphological characteristics of Scorzonera uzbekistanica.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Morphological and Ecological Studies:
Samples of Scorzonera uzbekistanica were collected from various regions of Uzbekistan, particularly from high-altitude, arid, and semi-arid areas. The structural features of the plant, including leaf shape, flower structure, and root systems, were examined in detail. The habitat conditions, soil types, climatic characteristics, and geographical locations of the sites where the plant was found were recorded.The ecological distribution of the plant is limited due to its concentration in specific regions and its narrow range of habitat, indicating that it plays a special role within its ecosystem and needs to be conserved.
2.2. Chemical Analyses:
Collected plant samples were subjected to various chemical analyses in a laboratory setting. Samples from the roots, leaves, and flowers of the plant were tested for the presence of bio-active compounds such as inulin, flavonoid, oxyacetylene, and lac-tones.
Inulin Analysis: Inulin is a type of polyacrylamide found in the roots of many plants. It has positive effects on digestive system health as it promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Flavonoid Analysis: Flavonoid s are polyphonic compounds commonly found in plants. Due to their antioxidant properties, they can prevent cellular damage caused by free radicals.
Poly acetylene Analysis:Oxyacetylene are carbon-chain compounds found in plants that can exhibit anticancer, antibacterial, and antifungal properties.
Lactones:Lac-tones, which give the plant its bitter taste, have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
2.3. Literature Review:
Existing scientific research on Scorzonera species was reviewed, and information on the known medicinal uses, chemical composition, and pharmacological effects of this plant was collected. Information on how this plant is used in traditional medicine in Uzbekistan was also gathered and compared with scientific data.
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Features:
Visual 3:Morphological characteristics of Scorzonera uzbekistanica.
Visual 3:Morphological characteristics of Scorzonera uzbekistanica.
Scorzonera uzbekistanica is a perennial herbaceous plant that can reach heights of 30-50 cm. Its leaves are narrow, long, and gray-green in color, while its flowers are yellow and resemble daisies. The plant’s root system is robust, contributing to its resistance to drought conditions. The swollen and fleshy structure of the roots enhances the plant’s water retention capacity, giving it a survival advantage in arid environments.
3.2. Ecological Distribution:
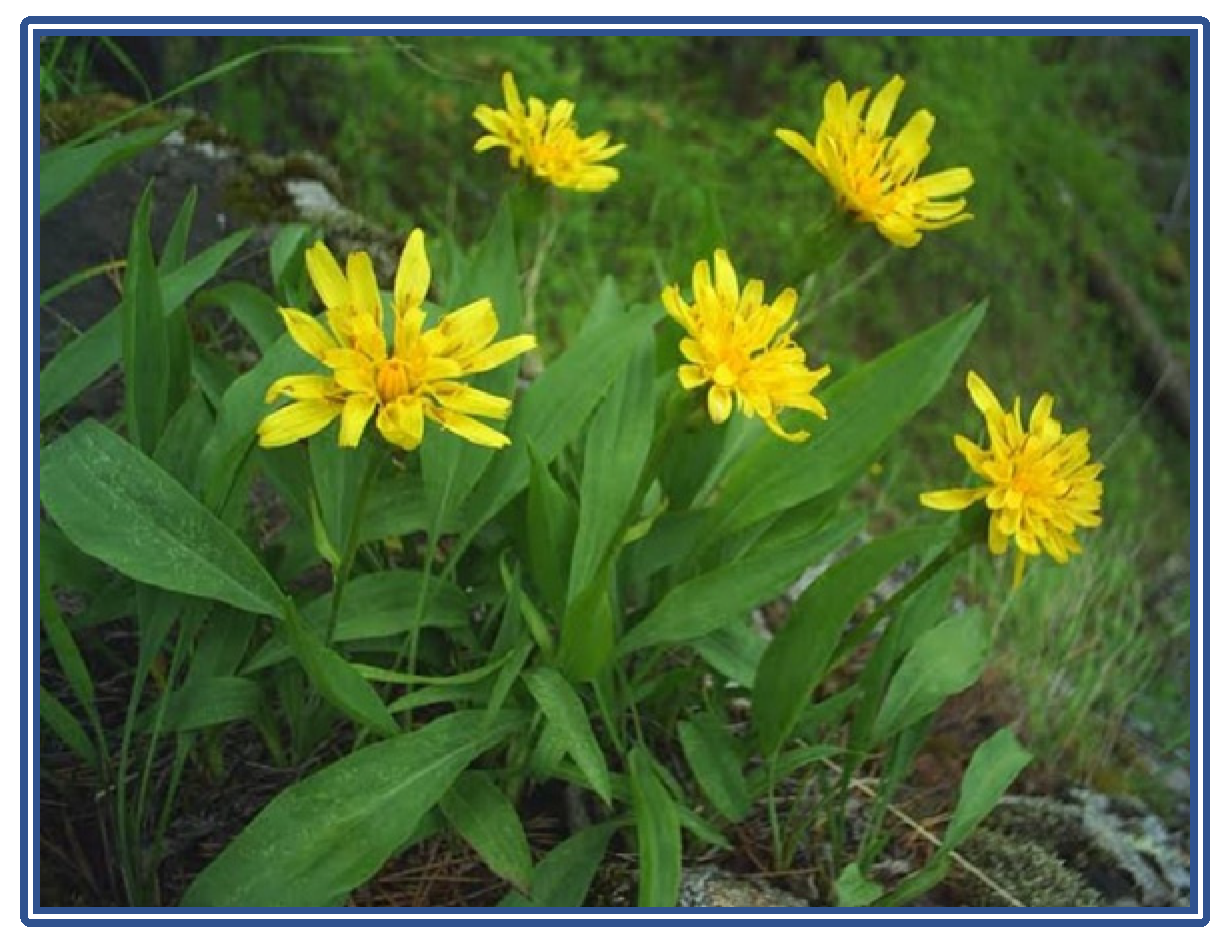
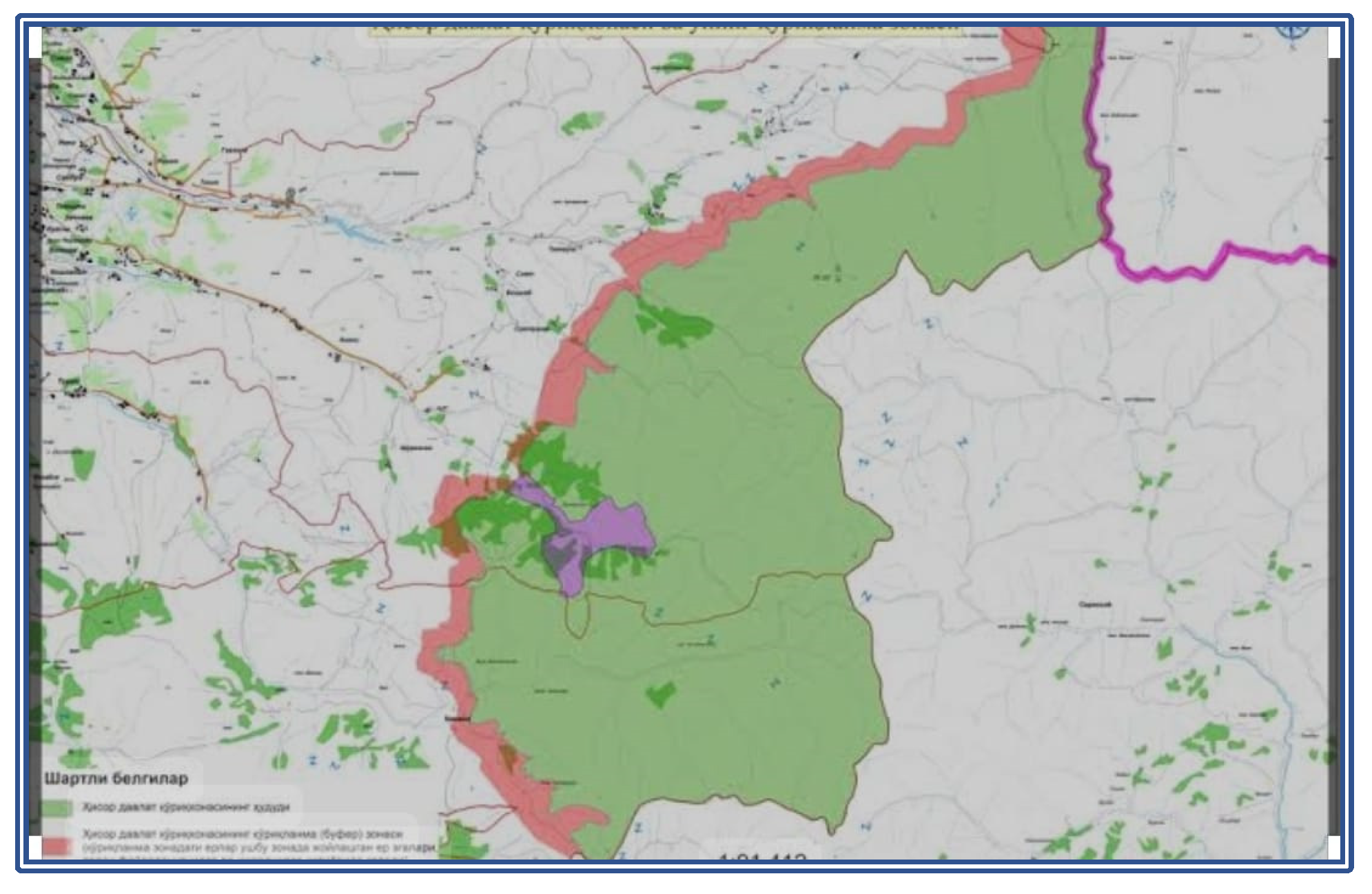
Scorzonera uzbekistanica is typically found in arid and semi-arid regions of Uzbekistan, particularly on rocky slopes and mountain foothills. The plant is common in steppe areas and is particularly concentrated in high-altitude regions, indicating that it has adapted to its ecological niche and can only survive under specific environmental conditions.
Visual 2: Ecological Distribution.
Visual 2: Ecological Distribution.
3.3. Chemical Content:
Chemical analyses revealed that the roots of Scorzonera uzbekistanica contain high amounts of inulin, which is known for its prediction properties and beneficial effects on gut health. Additionally, important bio-active compounds such as flavonoid`s and oxyacetylene`s were detected in the leaves and flowers of the plant. Flavonoid are noted for their strong antioxidant properties, while oxyacetylene are known for their anticancer potential.
3.4. Medicinal Potential:
Scorzonera uzbekistanica has been traditionally used to treat digestive issues and stomach ailments. Its inulin content gives the plant prediction properties, which can have positive effects on gut health. Furthermore, the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoid suggest that the plant has potential in supporting the immune system and protecting against chronic diseases. Oxyacetylene are known to exhibit anticancer effects, indicating that the plant could have potential applications in cancer treatment.
4. Discussion:
The findings of this study highlight both the biological and chemical characteristics of Scorzonera uzbekistanica as well as its medicinal potential. The bio-active compounds contained within this plant, particularly inulin, flavonoids, and oxyacetylene, may offer various health benefits. However, additional laboratory and clinical research is needed to confirm the pharmacological effects of this plant and support its medicinal uses. Given the threats to Uzbekistan’s biodiversity and endemic plant species, the conservation and sustainable use of Scorzonera uzbekistanica are of great importance.
5. Conclusion:
This study has thoroughly documented the biological characteristics, chemical composition, and medicinal potential of Scorzonera uzbekistanica, an endemic plant native to Uzbekistan. The data obtained indicate that the bioactive compounds found in this plant, such as inulin, flavonoids, and polyacetylenes, offer significant health benefits. Promising findings have been obtained, particularly concerning digestive health, antioxidant effects, and anticancer potential.
However, advanced laboratory and clinical research is needed to better understand the pharmacological effects of Scorzonera uzbekistanica and to validate its medicinal use. This research, which provides a scientific foundation for efforts to conserve and sustainably use this plant, contributes to a broader recognition of the biological and medicinal value of Scorzonera uzbekistanica. In this context, the conservation of Uzbekistan’s biodiversity and the evaluation of the potential of such endemic plants are of great importance, both for local ecosystems and global health.
References
- Muminov, K.; Tursunov, O. Diversity and Distribution of the Genus Scorzonera in Uzbekistan. Uzbek Journal of Botany 2019, 45, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.; Brown, L. Medicinal Uses of the Scorzonera Species: A Review. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2018, 220, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Rakhimov, A.; Khodjaev, A. Ecological Adaptations of Scorzonera Species to Arid Conditions. Central Asian Journal of Ecology 2017, 12, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, L.; Petrova, V. Phytochemical Analysis of Scorzonera uzbekistanica. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research 2020, 14, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Yuldashev, M.; Karimov, R. Conservation Strategies for Endemic Plant Species in Uzbekistan: A Case Study of Scorzonera uzbekistanica. Environmental Conservation and Management Journal 2021, 29, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, Z.; Moradi, H. Comparative Study on the Inulin Content of Different Scorzonera Species. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2022, 70, 2580–2588. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).