1. Introduction
Precision agriculture (PA) or precision farming is an agricultural management concept that utilizes spatial and temporal data representing the variability of the agricultural landscape with the aim of a) reducing the cost of managing crops, b) increasing the quality and quantity of production, and c) protecting the environment by reducing the use of agrochemicals and water [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. PA relies mainly on data obtained from ground sensors and remote sensing (RS) and utilizes Global Positioning System (GPS) and Geographic Information System (GIS) technologies to improve the accuracy and efficiency of agricultural practices [
3,
5]. PA addresses, among other things, soil variability, which can be caused by a variety of factors. Soil variability is related to the topography of the field, e.g. elevation and slope and to factors such as nutrient content (e.g. P, K, N, Ca), soil moisture and other physical or chemical properties. Crop variability refers to the quantity and quality of production as well as plant health and characteristics such as height. Yield variability refers to temporary or permanent differences in crop yields [
18]. For example, one plot may consistently produce better yields than a neighboring area. Variability in crop management is primarily related to human intervention, such as fertilization strategies or weed control methods. Ploughing, for example, can significantly change the behavior of the soil. The way an area is managed can lead to variations within the plot. Different areas require different approaches. PA is based on the identification and management of variations. Therefore, the plot is subdivided based on its characteristics, and areas with common characteristics are referred to as soil management zones (MZs) [
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29] or agricultural management zones (AMZs) in this work. AMZs are areas that show significant uniformity in certain characteristics. The main objective is to manage each zone according to its specific constraints. Two main techniques can be used to delineate these zones. In the first method, the data is grouped based on a specific characteristic, e.g. soil conductivity. In the second method, the boundaries are derived using an algorithm [
25]. In the past, AMZs were often determined based on farmers' experience, especially when fields were relatively of small spatial extent. Today, AMZs can be determined remotely and without physical presence on the plot using techniques known as RS. RS is the acquisition of data and information about an object or phenomenon from a distance using sensors that usually detect the electromagnetic radiation that the object absorbs or re-emits [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38]. The returned signals are correlated or converted into variables that are useful in agriculture, such as vegetation index, water availability, and plant growth [
30]. Numerous studies have been conducted to determine the physical and chemical properties of soil using satellite data [
38]. RS has many applications in agriculture, including monitoring soil moisture, vegetation indices and nutrient content. RS is also used for applications related to plant diseases and pests [
17]. Several parameters can influence the accuracy and cost of RS data. These include spatial resolution and spectral range, which can vary significantly depending on the type of sensor used. In many cases, RS techniques alone are not sufficient and need to be verified. Therefore, they are often used in conjunction with ground methods such as soil sampling, chemical analyses and geophysical mapping [
29].
In this work, we combine spatio-temporal data from RS, such as Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) flights, and ground techniques (apparent electrical conductivity mapping, soil analyses and the IRRIGOPTIMAL® system) along with machine learning to establish an optimum protocol for the delineation of AMZs at field scale for olive trees and an annual alfalfa in the prefecture of Heraklion (Crete, Greece). The trees in the olive grove, planted in 2013, are about 2 meters high and root systems estimated to extend to a depth of about 1.5 meters.
With this protocol, the site-specific conditions (such as irrigation and fertilization need) of olive and alfalfa fields can be easily estimated with a resolution of less than one meter.
2. The Study Area
The environment
Crete is in the southernmost part of Greece and separates the Aegean Sea from the Libyan Sea (
Figure 1a). It is characterised by a distinct geographical relief, with 56% of the area being semi-mountainous (200 m - 800 m) and about 26% lowland (<200 m) [
39,
40]. This pronounced morphological relief, combined with the geographical location, has a significant influence on Crete's Mediterranean climate, which is characterised by mild winters and relatively hot summers. The average annual rainfall on Crete is around 750 mm, but there are significant differences in both the spatial distribution and the amount of rainfall on the island. The western part of Crete receives significantly more precipitation, about 2188 mm, which is up to five times more than the eastern part, which receives only about 440 mm [
41,
42]. Groundwater covers 92% of Crete's water needs, with the majority, 81%, being used for irrigation [
39]. Most of the island is covered by olive groves and vineyards. Besides the important agricultural sector, Crete is also a well-known tourist destination.
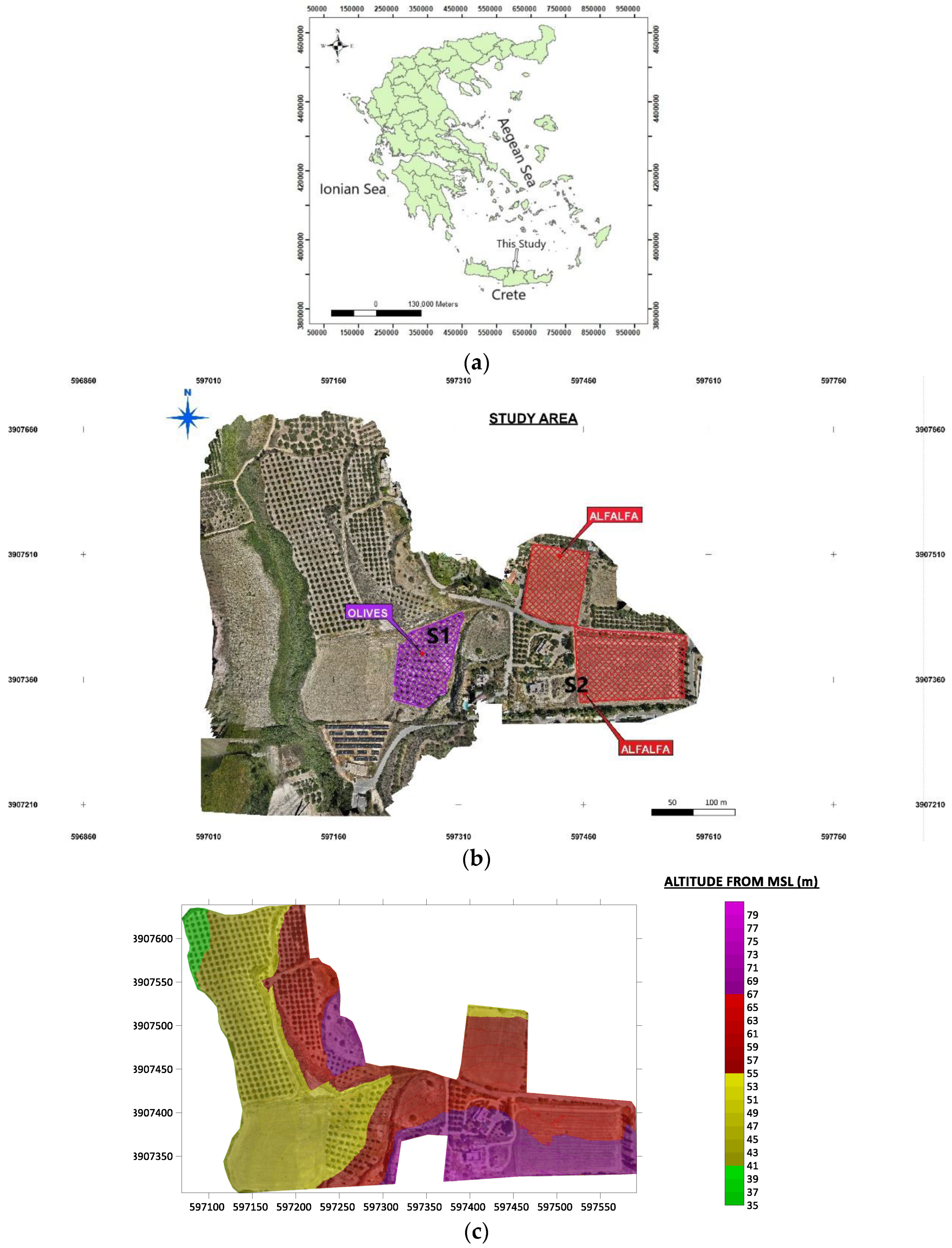
The study area (85350.603 m
2) of this work is in the central part of Crete, west of Heraklion (
Figure 1a, b), which is considered representative of Cretan cultivated land. It is covered by Holocene sediments corresponding to river and closed basin deposits [
29]. The altitude ranges from 35 m to about 80 m above mean sea level (
Figure 1c) and the relief is predominantly flat with slopes between 0 and 73% (rare). There are extensive agricultural plots in the wide area of this study, mainly cultivated with vineyards, olive trees and alfalfa (
Figure 1b).
The soil analyses [
43] for the study area to calibrate the IRRIGOPTIMAL® sensors characterise the soil as clay soil (clay - 41.93%, silt - 25.81%, sand - 32.86% and water holding capacity - 125 mm/m) for the olive grove and sandy clay loam soil (clay - 27.27%, silt - 27.27%, sand - 45.45% and water holding capacity - 110 mm/m) for the alfalfa plots. Previous soil analyses of an alfalfa plot in the same area showed that the soil was slightly alkaline, with a pH of about 7.5 and organic matter between 2.34% and 2.8%. The potassium content varied considerably between 162 mg/kg, which is considered sufficient for the crop, and 283 mg/kg, which is considered high. The phosphorus content varied between 6.3 mg/kg and 14.9 mg/kg at the maximum. Potassium levels ranged from 142 mg/kg to 231 mg/kg. The boron content showed no significant differences and was between 0.223 and 0.262 mg/kg. These results show that soil composition can vary considerably even within a single plot, making the delineation of AMZs particularly useful.
Weather data
The Hellenic National Meteorological Service (HNMS) has been collecting meteorological data for Heraklion since 1955.
Figure A1 (
Appendix A) shows the weather data for each month based on the data from 1955 to 2010. The ombrothermal diagram (
Figure A1a) shows the mean monthly temperatures for the same period in relation to the mean monthly precipitation, while
Figure A1b shows the annual wind frequencies in terms of wind intensity and direction.
Figure 2a,b and
Table A1 (
Appendix A) show the weather data (December 2023 – May 2024) for the study area using the IRRIGOPTIMAL® system with the following weather parameters: a) air temperature (
oC), b) dew point (
oC), c) solar radiation (W/m²), d) vapor pressure deficit (VPD) in kPa, e) relative humidity (%), f) precipitation (mm) and g) delta T (
oC).
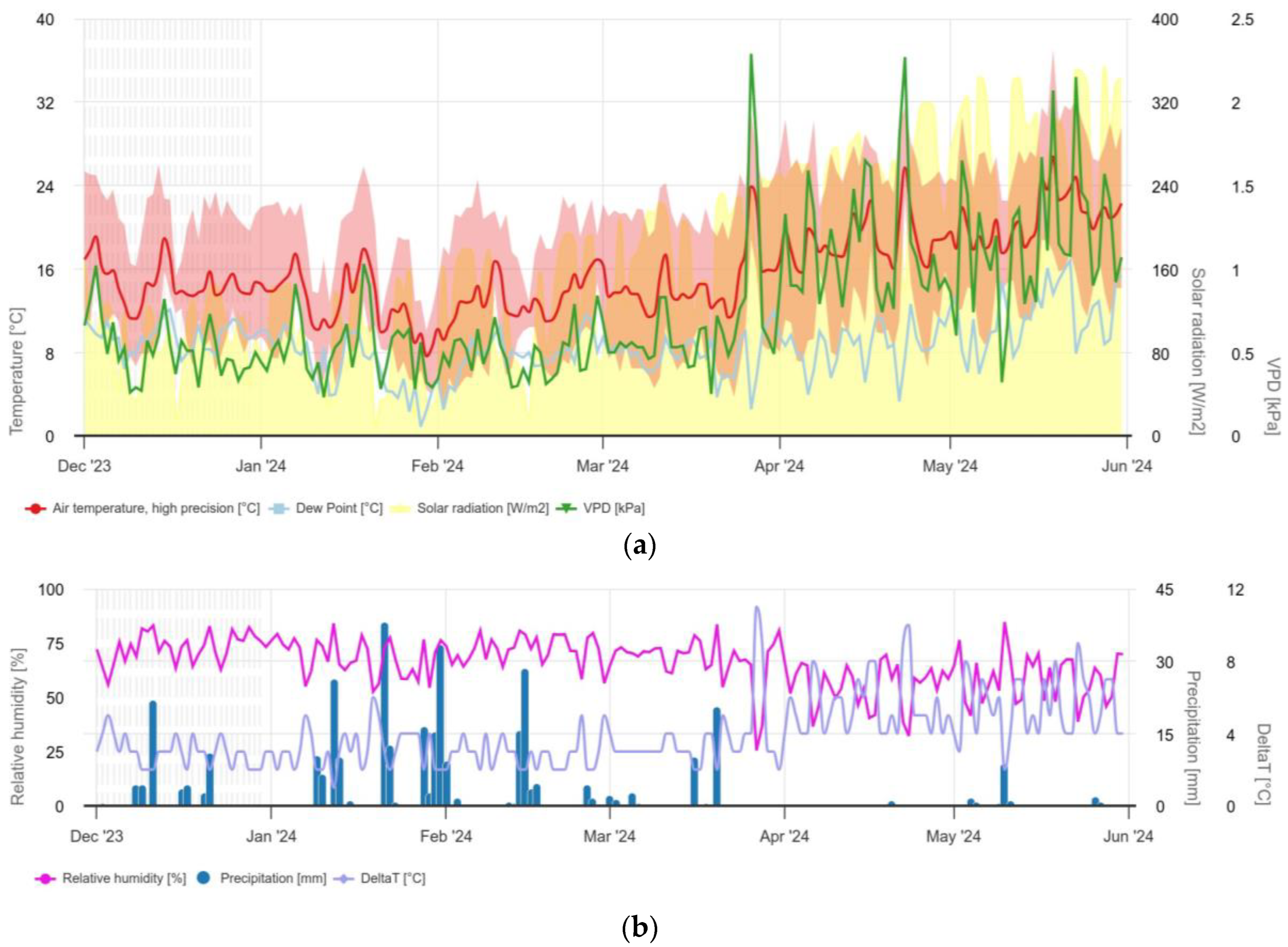
The air temperature rarely dropped below 10°C from December 2023 to May 2024, while the dew point closely follows the changes in air temperature (
Figure 3a,
Table A1,
Appendix A). At higher temperatures, the air can generally absorb more moisture, resulting in a higher dew point. Crete is an island with abundant sunshine and has one of the highest solar potentials in Europe. The average sunshine intensity was around 90 W/m² in December 2023 and January 2024, gradually increasing to 278 W/m² in May 2024 (
Figure 3a,
Table A1,
Appendix A). High temperatures fluctuating between 14.7°C (December 2023) and 20.4°C (May 2024) and prolonged solar radiation combined with water scarcity create a stressful environment for plants (
Figure 3a,
Table A1,
Appendix A). In addition, a high vapor pressure deficit (VPD), which is directly related to the movement of water from the surface to the atmosphere, in combination with water scarcity, contributes to water stress (
Figure 3a,
Table A1,
Appendix A). Specifically, the average VPD in December 2023 was 0.52, while in April and May 2024 it was 1.13 and 1.17, respectively. This increase in VPD is to be expected due to the rise in temperature and the decrease in precipitation. However, the VPD shows clear peaks of over 2 kPa in April 2024 and May 2024 (
Figure 2a), which indicates potential water stress.
Precipitation is a particularly important factor as it directly influences plant growth. During the analysed period (December 2023 – end of May 2024), there were significant fluctuations in precipitation followed by a decrease in Delta T (
Figure 2b,
Table A1,
Appendix A). In December 2023, the total amount of precipitation was 53.2 mm (
Figure 2b,
Table A1,
Appendix A), while in January 2024 there was more than three times higher precipitation at 174 mm (
Figure 2b,
Table A1,
Appendix A). March 2024 did not match the expected precipitation amounts as only 38.4 mm was recorded compared to the usual 53.4 mm (
Figure 2b and
Figure A1a,
Appendix A). It is noteworthy that 20 mm of this total precipitation was measured on a single day (20 March 2024). April 2024 was remarkably dry with only 1.6 mm of precipitation compared to the expected 28.2 mm (
Figure A1a,
Appendix A). In other words, the total precipitation in April was in line with what is normally expected in a single day. Of the four days with precipitation in April 2024, 0.6 mm was measured on three days and only one day was close to 1 mm. These values were also confirmed by the local weather station, which reported 1.2 mm of precipitation for April 2024. Finally, 15.2 mm of precipitation was measured in May 2024 (
Figure 2b,
Table A1,
Appendix A). Of the total 353 mm of precipitation in the six months in which the IRRIGOPTIMAL® system was installed, 228 mm was recorded on 10 days, which accounts for more than 60 % of the total precipitation (
Table A1,
Appendix A).
Humidity expresses the moisture content of the atmosphere and is linked to vapor pressure and dew point (
Figure 2b). Low humidity leads to partial or complete closure of stomata in plants, resulting in reduced transpiration, photosynthesis and overall plant productivity. In the study area, humidity in the period from December 2023 to March 2024 was between 60 % and 80 % with a sudden drop from the end of March 2024 to the end of May 2024 (
Figure 2b).
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Remote Sensing/G.I.S
Satellite data (Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2) and UAV data were collected to support the delineation of the AMZs in this work [
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49]. Sentinel-1 data were used to calculate the median soil moisture (%) for the period from January 2024 to June 2024 using QGIS [
50]. Grids were created for the olive (a total of 18511 points every 0.562 m) and alfalfa (a total of 19630 points every 0.728 m) plots. Then the .tif raster file values from the Google Earth Engine were assigned to the points of the plots. The interpolation was then performed using the Kriging method. Sentinel-2 data, L2A with cloud cover <= 5% were recovered using QGIS and the SCP plugin, Semi Classification Plugin [
51] from 1 January 2024 to 30 June 2024. The Sentinel-2 data were used to calculate the Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI) [
52] and the Green Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (GNDVI) [
53] for the plots of this work (
Figure 1b).
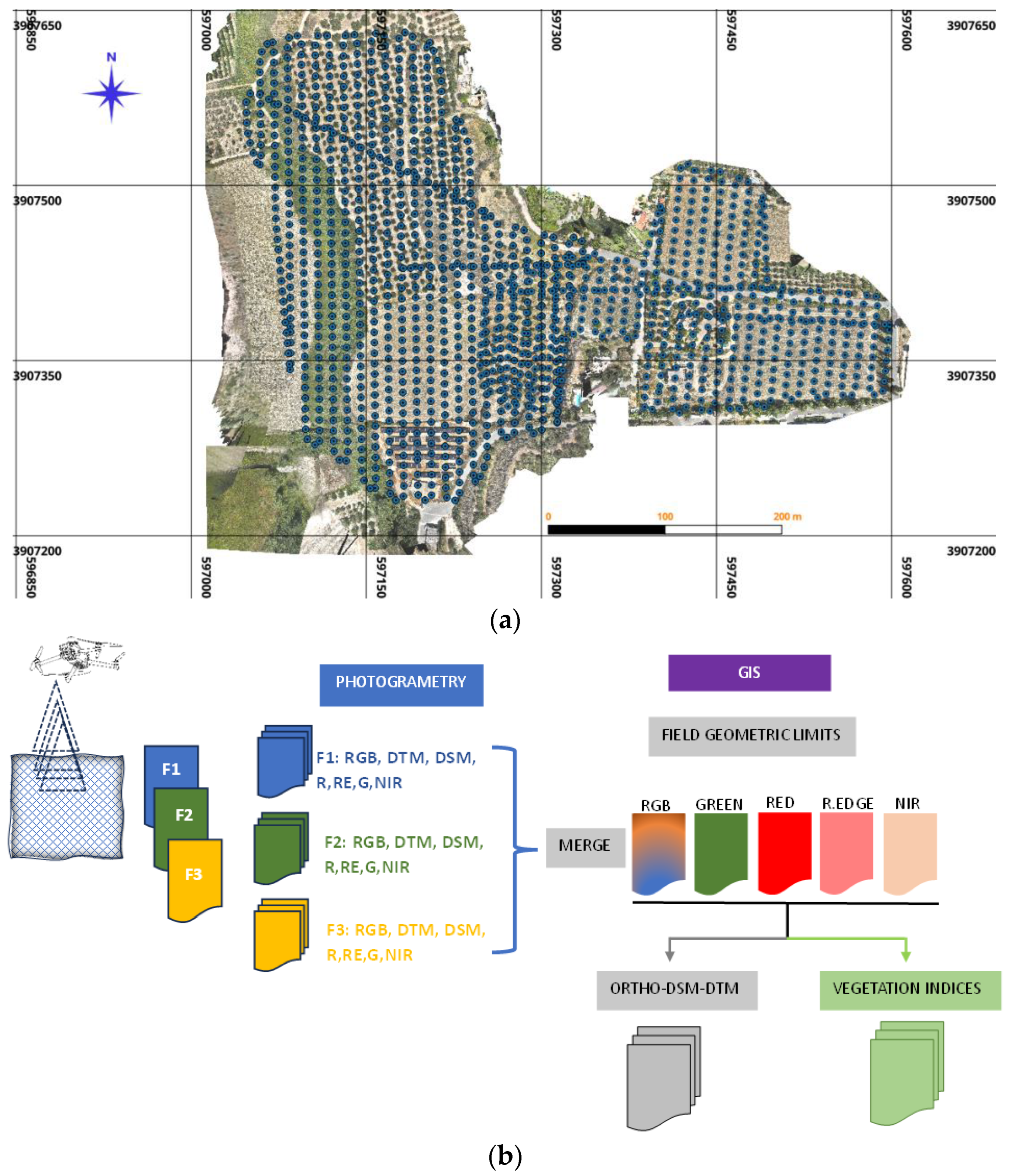
Finally, UAV data (RGB, green, red, red edge, near-infrared) were collected during three flights for the dry period in August 2023 and the wet period in January and March 2024 (
Figure 3a). The UAV data was processed using the Pix4D Mapper software (accessed on 30 June 2024) to obtain the orthomosaic, the digital surface model (DSM), and the digital terrain model (DTM) (
Figure 3b). The products resulting from the photogrammetry were then imported into QGIS (version 3.30.3 Hertogenbosch) for further processing to a) digitize the boundary of the total area (85350.603 m
2), b) digitize the boundaries of the olive and alfalfa plots, c) export the orthomosaic, DTM, DSM (
Figure 1b, c green, red, red edge, near infrared) for each of the three flights, d) merge the products of the 3 flights to generate uniform data backgrounds, e) complete the export for the whole area and f) calculate the vegetation indices together with the terrain attributes (
Figure 3b).
3.2. Geophysical Prospecting
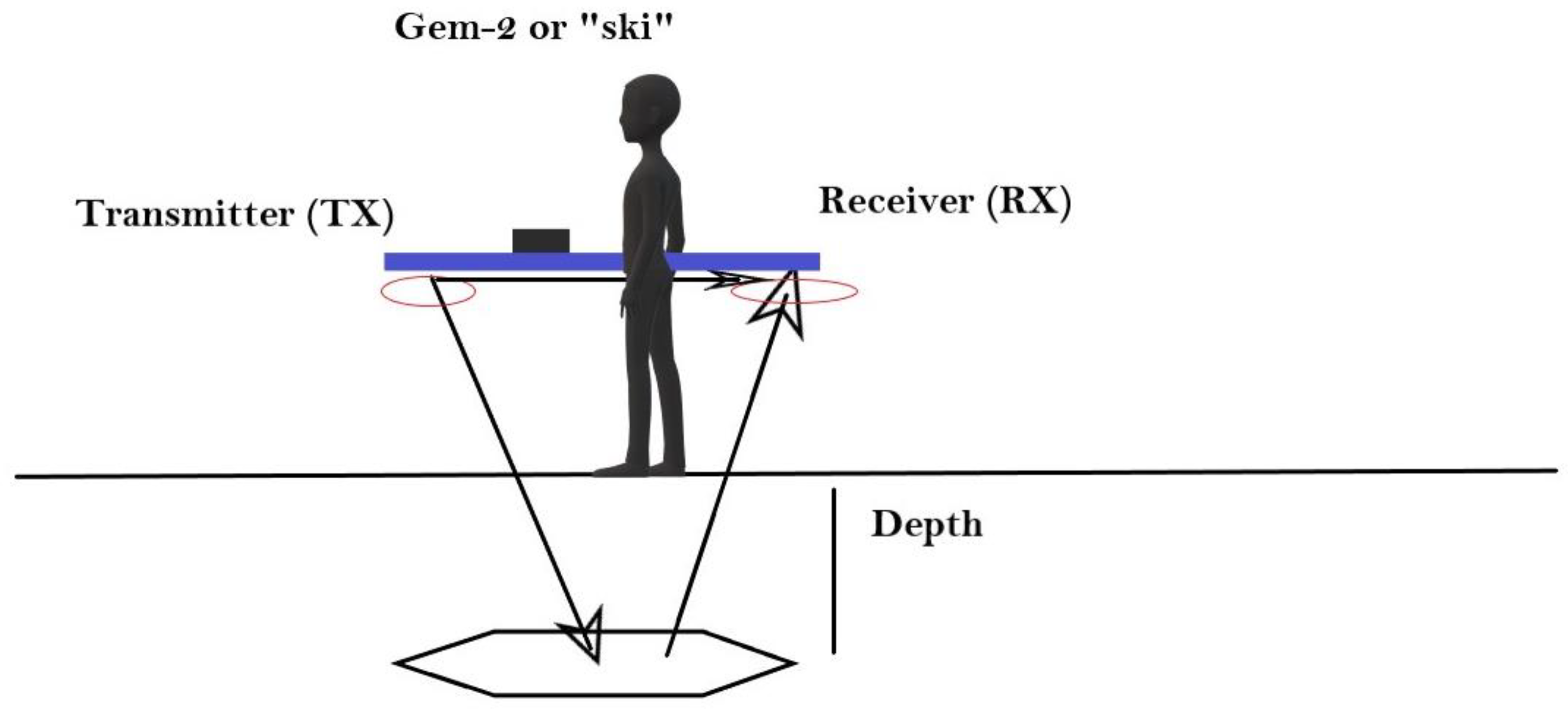
In PA, electromagnetic scanning (
Figure 4) is often used to delineate AMZs because it is a cost-effective, fast and non-invasive method [
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63,
64]. The GEM-2 from Geophex (
https://geophex.com/hand-held-gem-2-ski/), often referred to as a "ski" because of its shape, is a lightweight, portable electromagnetic sensor that was used in the present work. It has a wide frequency bandwidth from 30 Hz to 90000 Hz, allowing the operator to select up to 5 frequencies during the survey. At lower frequencies, the primary electromagnetic field can penetrate deeper, while at higher frequencies shallower. The skin depth monogram [
65] can be used to determine the penetration depth of each frequency. In the present work, GEM-2 was used to map the spatial distribution of soil apparent conductivity (mS/m) in both the olive and alfalfa plots in the wet and dry seasons of 2022 and 2023. The electromagnetic survey was carried out at frequencies close to 90000 Hz, corresponding to a penetration depth of about 1 m - 1.5 m, with the sensor held about 1 m above the ground. The processing of the data to create the colour maps of the apparent electrical conductivity of the soil was carried out according to the specifications of the device manufacturer (
https://pages.mtu.edu/~jdiehl/Homework/GEM2%20Manual.pdf).
3.3. IRRIGOPTIMAL® System
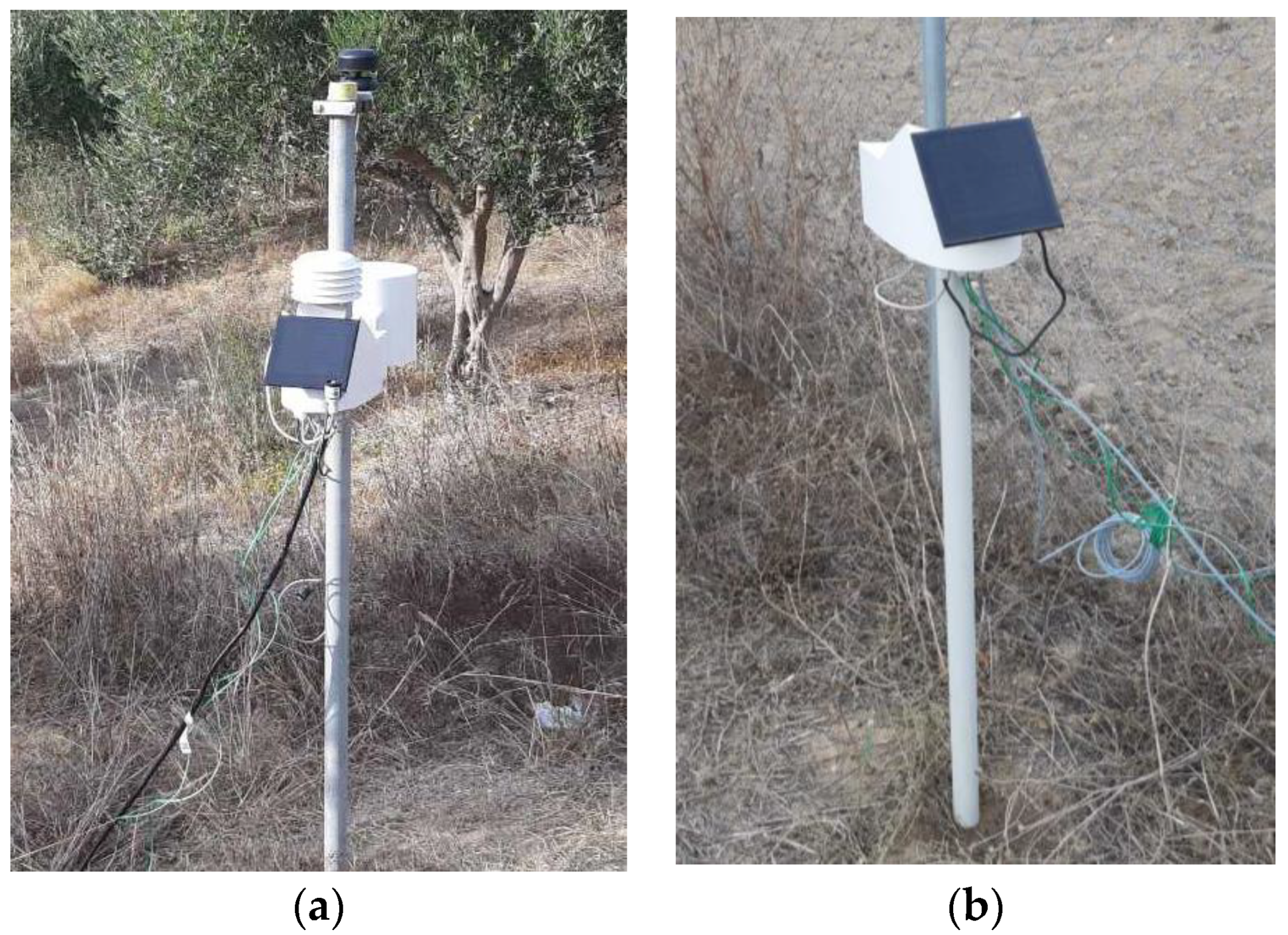
IRRIGOPTIMAL® is an integrated system designed, developed and patented by the Maltese company WES TRADE LTD to support agricultural processes such as predicting water requirements in the coming days, predicting diseases and pests and monitoring the harvest. Prediction integrates a variety of agronomic, soil, sensor and weather data to provide a comprehensive prediction of crop water needs. The system's data processing methodology for predicting irrigation needs includes two main machine learning (ML) models that work in parallel to ensure high accuracy in predicting irrigation. The system starts by collecting detailed agronomic data for the crop being grown. This includes information on plant growth stages, stage-specific water requirements and drought sensitivity, as well as plant coefficient (kc) values. In addition, soil properties such as the proportion of silt, clay and sand, as well as critical soil properties such as saturation point, wilting point and bulk density are considered. This agronomic and soil data is then combined with real-time sensor data from the field and weather data from local stations and forecasts. The sensor (
Figure 5a, b) data includes measurements of soil moisture, soil tension, humidity, temperature, soil temperature, precipitation, wind direction and wind speed. These inputs are crucial for accurately estimating the plants' current and future water requirements. The first ML model works daily, while the second ML model processes data on an hourly basis. The first model compares these sensor readings with total crop evapotranspiration (ETc) values calculated from solar radiation data to estimate daily water consumption. The second model combines the hourly sensor data with weather forecast data to predict soil moisture dynamics for the next three days. This short-term prediction helps to accurately adjust irrigation schedules and ensures optimal water utilisation and plant health. By integrating these two models, the IRRIGOPTIMAL® system can provide irrigation recommendations three days in advance, significantly increasing water management efficiency and crop yield. The IRRIGOPTIMAL® system can be flexibly configured so that the settings can be adjusted as required. In this study, sensors (
Figure 5a, b) were placed in olive trees (3 m away to minimise the influence of the root system) and alfalfa to measure precipitation, solar radiation, air temperature, soil temperature at six depths, soil moisture, relative humidity, wind speed and wind direction. The measurements were carried out from December 2023 to May 2024, while the alfalfa harvest took place at the beginning of May 2024.
3.4. Machine Learning
Machine learning has so far proven to be indispensable in PA [
66,
67,
68,
69,
70,
71,
72,
73,
74,
75]. In this work, our machine learning pipeline (
Figure 6) consists of several structured steps to ensure a thorough evaluation and selection of the most effective model for predicting soil electrical conductivity (EC) based on salinity indices from satellite data (Sentinel-2, on 1 September 2023 and 2 September 2023) and mapping of the apparent electrical conductivity of an alfalfa plot (performed on 1 September 2023,
Figure 1b). The data set from 1 September 2023 was used to train and select the best model, while the data set from 2 September 2023 was used to test the model's ability to fit new data. The pipeline starts with the data from the first partition (on 1 September 2023), which is split 80/20 into training and test datasets. This split allows us to train the models and then evaluate their performance on an unknown portion of the data to ensure that the results are not biased by overfitting. The next step is to fit the data from the training set to the selected models. We explored three different algorithms: Linear Regression (LR), Random Forest (RF) and XGBoost (XGB). For each of these models, we performed extensive parameter fine-tuning and cross-validation to determine the best combination of hyperparameters. Cross-validation not only helps in selecting optimal parameters, but also provides a robust assessment of the generalization ability of the model by splitting the training data into multiple folds and evaluating the performance across these folds. Following parameter optimization, we evaluated the performance of each model using key metrics such as the coefficient of determination (R2) and the mean squared error (MSE). The R2 metric provides insight into how well the model explains the variability of the response data, while MSE provides a quantitative measure of predictive accuracy by averaging the squared differences between predicted and actual values.
4. Results
4.1. Remote Sensing Imagery
To check the soil's ability to retain moisture, Sentinel-1 data were used for both the olive and alfalfa plots. An example of the distribution of median soil moisture from January 2024 to June 2024 is shown in
Figure 7a. The surface soil moisture ranges from 36% to 70% for both the olive and alfalfa plots. The lowest moisture values (36% - 55%) are observed in the north-western part and in the centre of both the olive and alfalfa plots. In addition, the Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI), which is used to assess water content in crops with possible water stress, among others, shows values above 0.64 for both the olive and alfalfa plots in our study, indicating a high canopy cover and no water stress. The altitudinal difference (
Figure 1c) seems to affect the NDMI’s distribution. An example of the distribution of mean NDMI from January 2024 to June 2024 for the olive grove is shown in
Figure 7b.
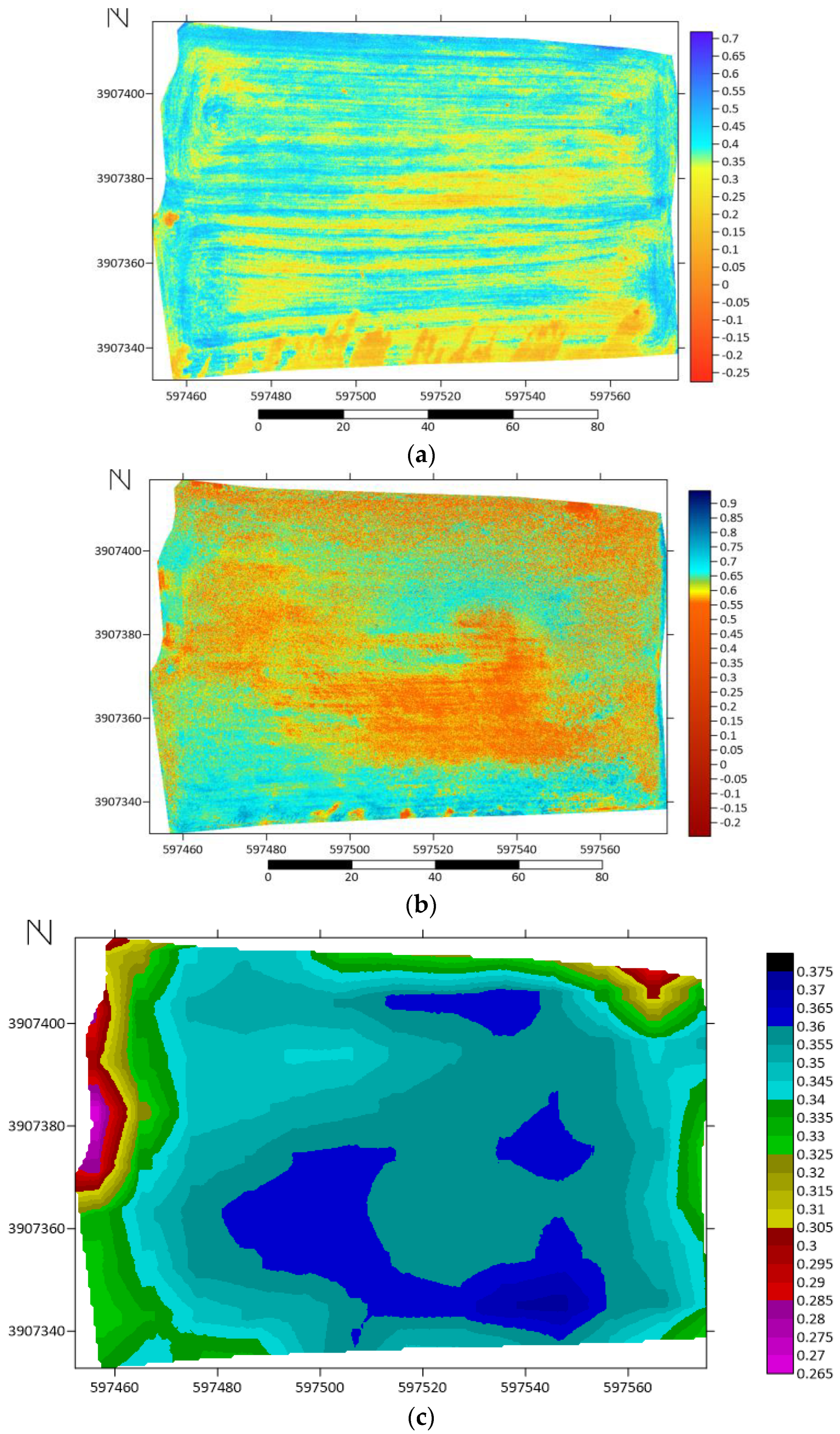
Next, we present the spatial distribution of the Green Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (GNDVI) of the alfalfa plot (
Figure A2a, b,
Appendix A) for two UAV flights on 25 January 2024 and 22 March 2024 (
Figure 8a, b) and a more general distribution of the GNDVI based on Sentinel-2 data for the period April to June 2024 (
Figure 8c). The GNDVI index, which varies between -1 and 1, is related to the “greenness" or photosynthetic activity of plants and is often used to determine water and nitrogen uptake [
53]. GNDVI values between -1 and 0 are associated with the presence of water or bare soil, while GNDVI values above 0 are associated with more vigorous vegetation and vegetation cover. The spatial distribution of the GNDVI (-0.25 – 0.7) regarding the UAV flight on 25 January 2024 is clearly influenced by the furrows created by ploughing to plant the alfalfa (
Figure 8a). On the other hand, the spatial distribution of the GNDVI (-0.25 – 0.9) for the UAV flight on 22 March 2024 indicates the presence of low (-0.25 – 0.33), moderate (0.34 – 0.66) and vigorous (0.67 – 0.99) vegetation cover (
Figure 8b). The presence of this GNDVI zonation (
Figure 8ab) is also confirmed by the calculation of the mean GNDVI (0.265 – 0.375) based on Sentinel-2 data for the period April to June 2024 (
Figure 8c).
4.2. Electromagnetic Mapping
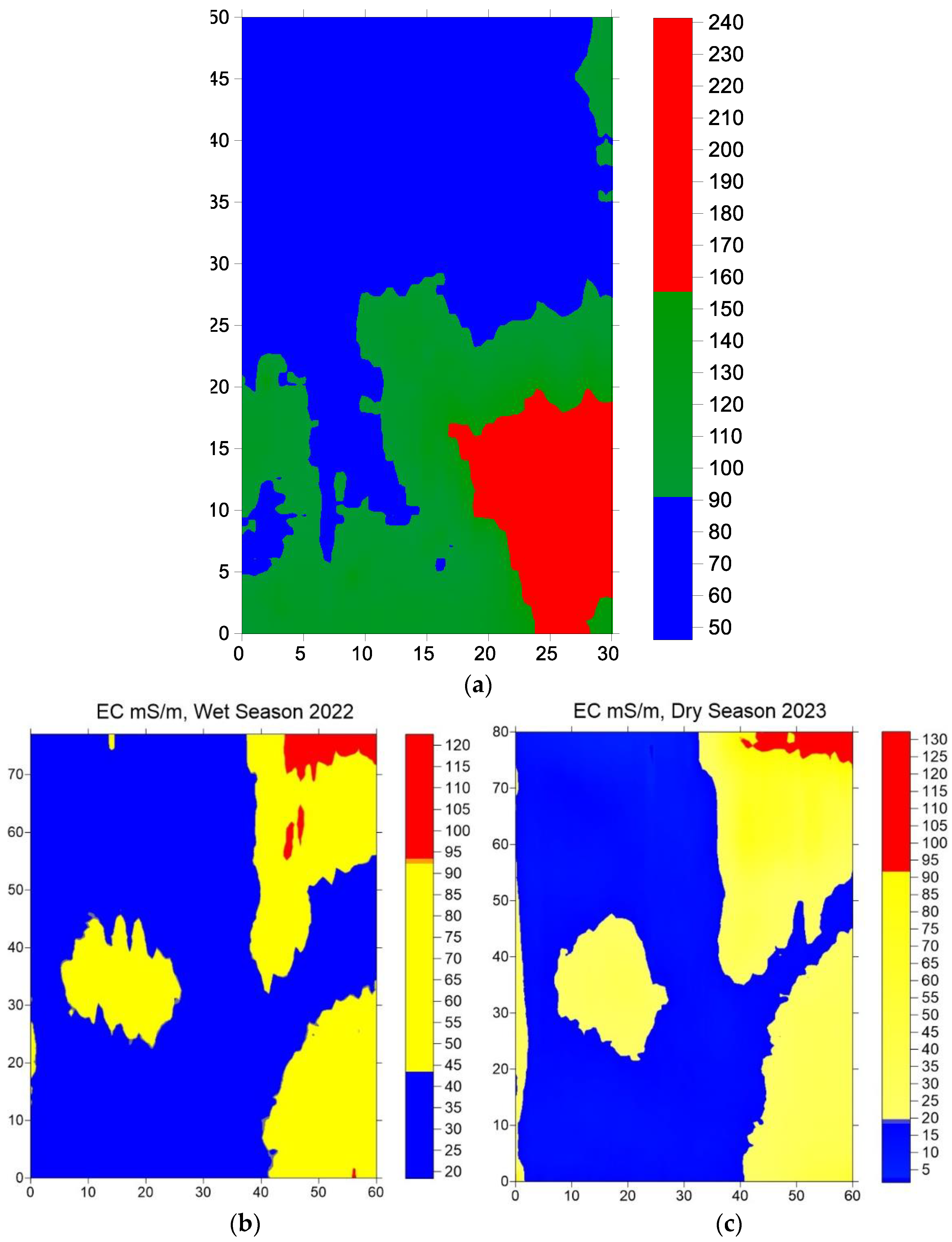
Figure 9 shows examples of the intra-plot soil zones for the olive (
Figure 9a) and the alfalfa plots (
Figure 9b, c) based on the mapping of apparent electrical conductivity (mS/m) with GEM-2 [
29].
The apparent conductivity of the soil in the olive plot measured in the 2022 wet season ranges from 50 mS/m to 240 mS/m (
Figure 9a) exhibiting three zones, namely the low apparent conductivity zone (50 mS/m – 90 mS/m), the moderate apparent conductivity zone (91 mS/m – 155 mS/m) and the high apparent conductivity zone (151 mS/m – 240 mS/m). The plot corresponding to the alfalfa was also mapped in the 2022 wet season, before the alfalfa was planted. Within the plot, two main soil zones were identified based on the apparent conductivity of the soil, namely the low apparent conductivity zone (20 mS/m – 43 mS/m) and the moderate apparent conductivity zone (44 mS/m – 93 mS/m), while the high apparent conductivity zone (94 mS/m – 120 mS/m) has a very small spatial extent in the north-east. The same alfalfa plot was also mapped in the 2023 dry season (
Figure 9c). Both the spatial extent and the range of apparent conductivity values showed the same distribution of soil zones within the alfalfa plot (
Figure 9b, c). The fact that the soil zones are stable in both the wet and dry seasons confirms the robustness of the apparent conductivity mapping to define the soil zones with high accuracy (
Figure 9b, c).
4.3. Soil Temperature and Moisture for the Olive Grove and Alfalfa Plots
Of the soil parameters recorded by the IRRIGOPTIMAL® sensors, we selected the temperature and moisture records for this work as they are closely related to the remote sensing and geophysical data collected for this same area.
Soil Temperature
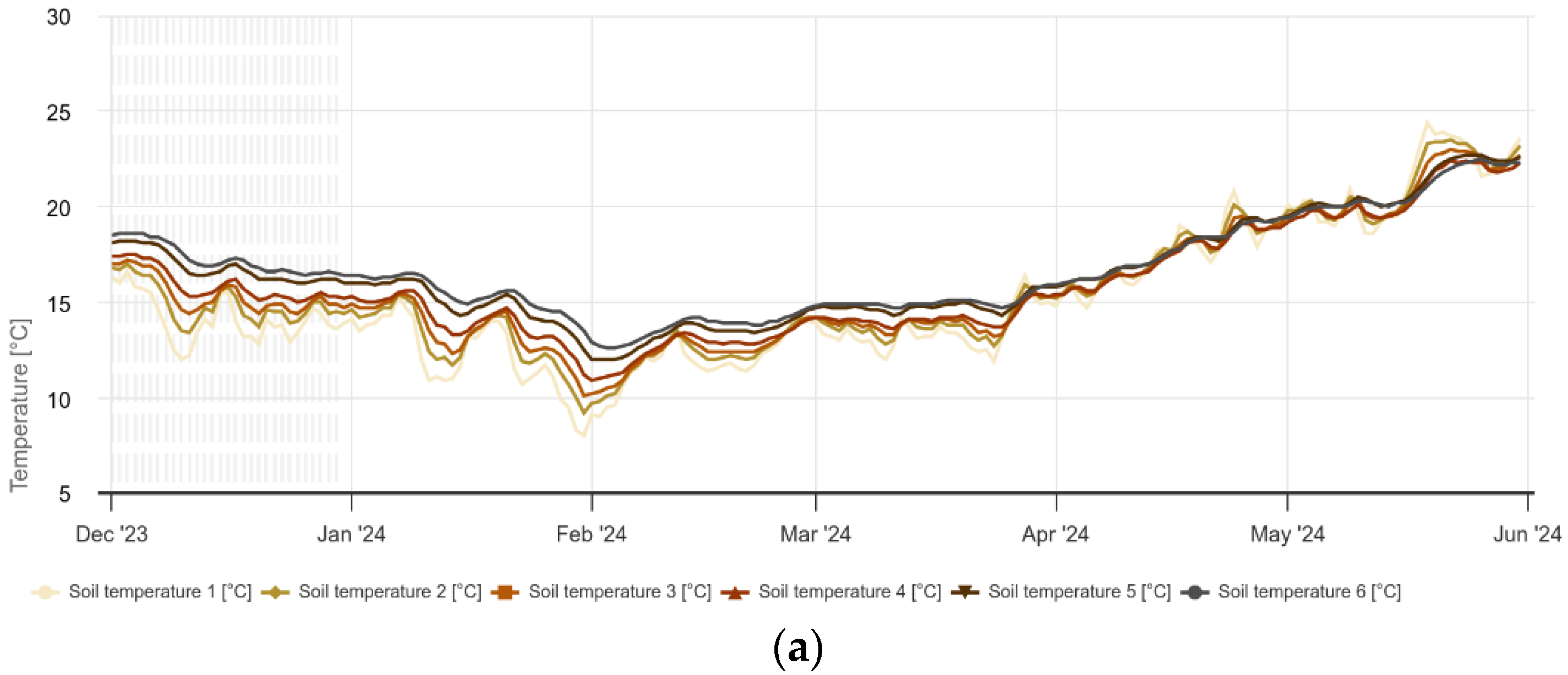
Figure 10a shows the distribution of soil temperature in the olive plot measured at different soil depths (10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 50 cm, 60 cm) from the beginning of December 2023 to the end of May 2024. More specifically, soil temperature 1 (
oC) corresponds to 10 cm, soil temperature 2 (
oC) to 20 cm and so on. As expected, the temperature variations were more pronounced at shallower depths. Thus, the temperatures in the olive plot at a depth of 10 cm ranged from a minimum of 8°C to a maximum of 24.4°C, with an average of 15°C and a fluctuation of 13.2°C. At a greater depth (60 cm), the average temperature was 16.7°C ranging from a minimum of 12.6°C to a maximum of 22.5°C, with a smaller fluctuation of 6.1°C. This indicates that temperatures remain relatively stable at greater soil depths. At intermediate depths, slight fluctuations were observed, possibly due to the heterogeneity of the soil or the distribution of plant roots. In general, temperatures show less fluctuation at depths greater than 40 cm. At the end of February 2024, for example, the soil temperature did not fall below 12°C at a depth of 60 cm, while it reached 8°C at shallower soil depths. These temperature fluctuations could have a significant impact on plant health, particularly by affecting the circulation of fluids in the root system.
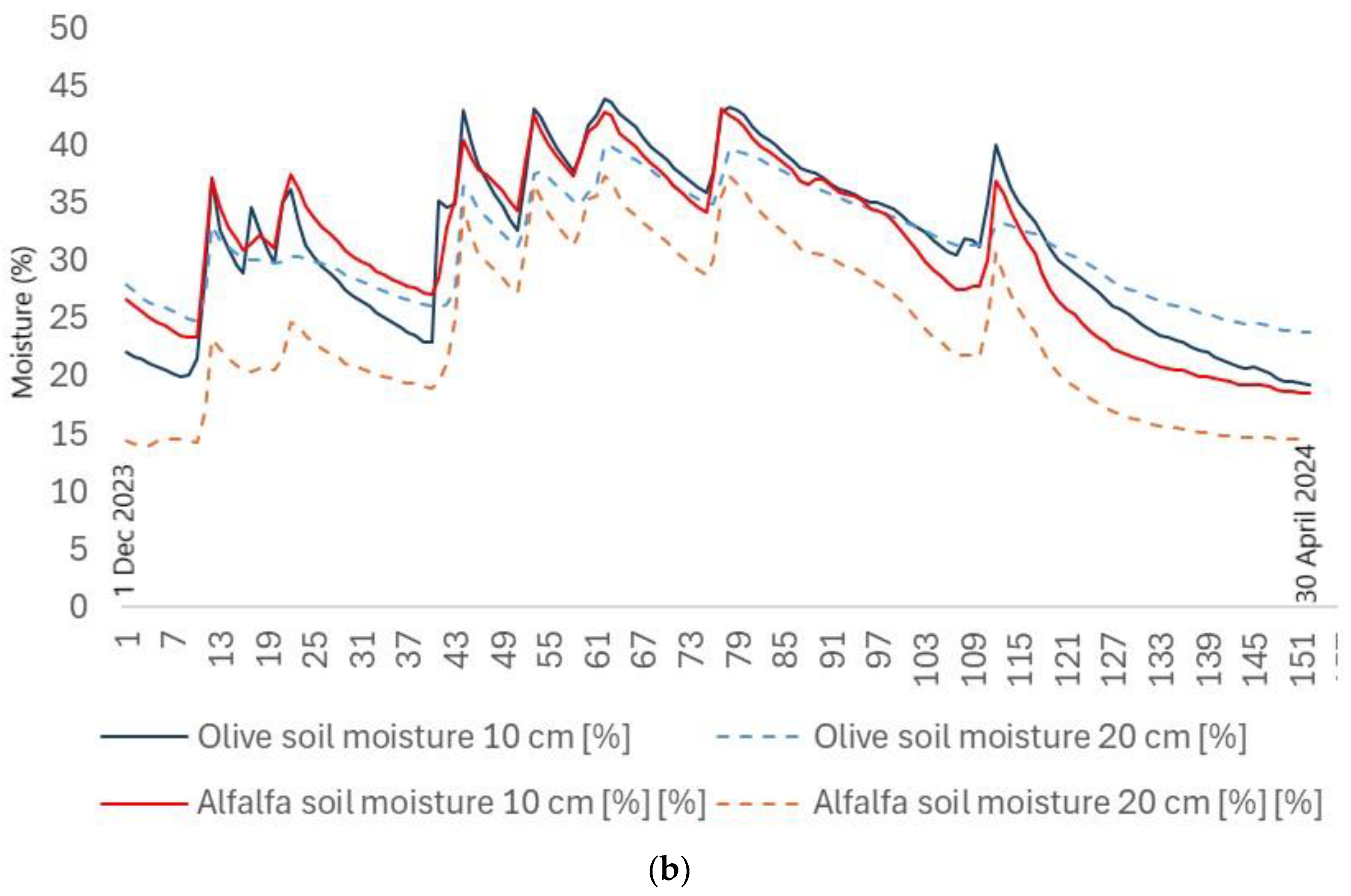
Figure 10b shows the comparison of soil temperatures for the olive and alfalfa plots up to 20 cm soil depth from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 April 2024. The distribution of temperatures for the olive grove and alfalfa plots shows a similar pattern with slight deviations until 21 February 2024. After 21 February 2024, the soil temperature distribution of the alfalfa plot up to a depth of 20 cm tends to increase faster than the soil temperature distribution of the olive grove. This difference could be due to local factors such as shading by the olive tree canopy, the ability of the olive root system to retain moisture and the relief slope.
Soil Moisture
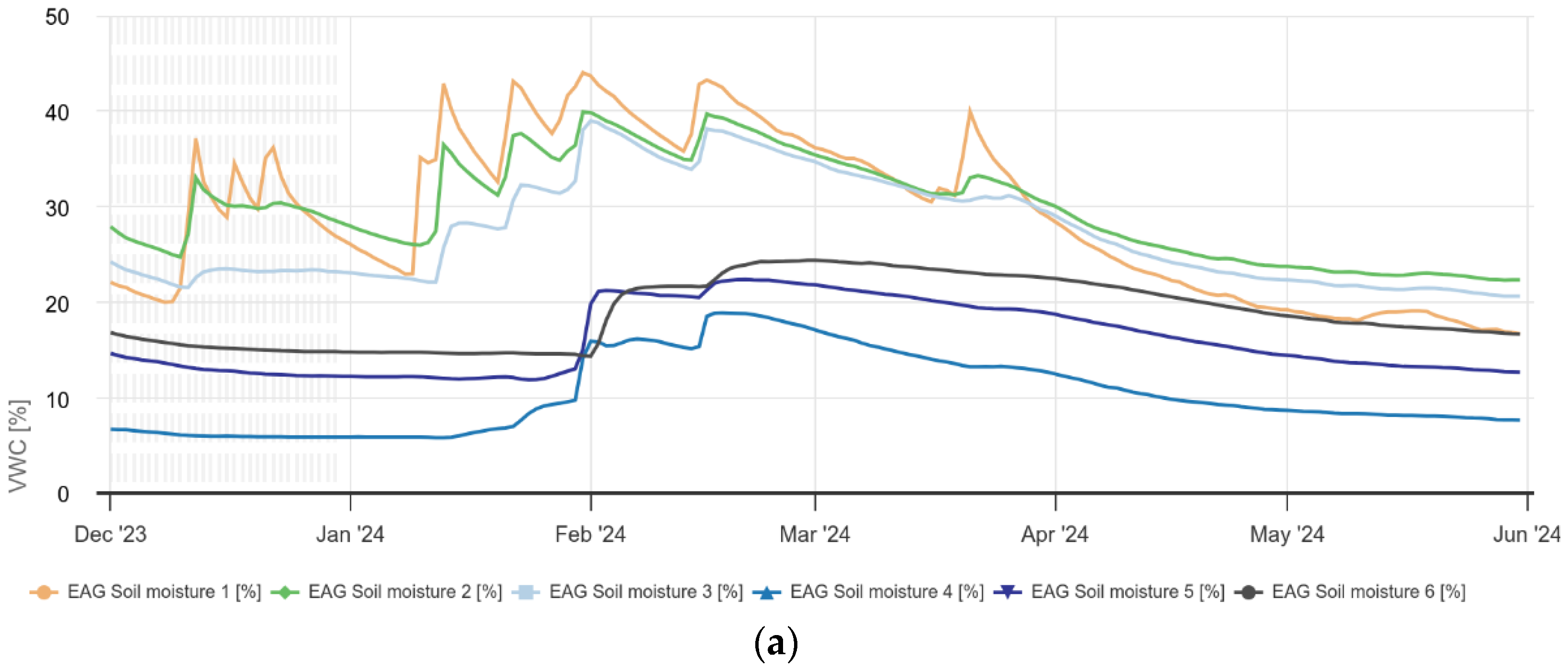
Figure 11a shows the distribution of soil moisture in the olive grove, measured at different soil depths (10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 50 cm, 60 cm) from the beginning of December 2023 to the end of May 2024. More precisely, soil moisture 1 (%) corresponds to 10 cm, soil moisture 2 (%) to 20 cm and so on. In general, the soil at a depth of more than 30 cm tends to keep the moisture content relatively stable, while the moisture at a depth of less than 30 cm is subject to strong fluctuations. In addition, the increase in precipitation in January 2024 to 174 mm (
Figure 2b) contributed to the increase in moisture at all depths (
Figure 10a).
Figure 11b shows the comparison of soil moisture for the olive and alfalfa plots up to 20 cm soil depth from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 April 2024. The distribution of soil moisture up to 20 cm depth in the olive grove is generally more stable than the moisture in the alfalfa plot.
4.4. Machine Learning for Predicting Soil Electrical Conductivity
Machine learning is an emerging field with numerous potential applications in agriculture [
66,
67,
68,
69,
70,
71,
72,
73,
74,
75]. The results of the model evaluation phase summarized in
Table 1, which are based on the test set, show significant differences in model performance. As expected, the linear regression model had difficulty capturing the relationships between the salinity indices and the electrical conductivity (EC) of the soil, which is reflected in its high mean square error (MSE). The Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) were also remarkably high at 26.79 and 18.99, respectively, indicating poor predictive accuracy and significant deviation from the actual EC values. In contrast, both ensemble methods,Random Forest and XGBoost showcased strong and comparable performance. Random Forest, achieving an R2 value of 0.97, indicating an excellent ability to explain variability in the data set. The MSE for Random Forest was significantly lower at 27.97, with corresponding RMSE and MAE values of 5.28 and 3.0, respectively. These results indicate that the Random Forest model provides more accurate predictions with fewer errors. The XGBoost model also performed well, with an R2 of 0.97 and an MSE of 26.21. The RMSE and MAE values for XGBoost were 5.12 and 3.22, respectively, suggesting that it was also a strong predictor,as accurate as Random Forest. Despite the fact that Random Forest and XGboost display similar performance, we are going to select Random Forest as the best model, because it’s simpler and more suited to the data in this implementation. These results emphasize the superior performance of ensemble methods, particularly Random Forest, over simpler models such as linear regression for this particular case. The higher accuracy and lower error rates of Random Forest make it the most suitable model for predicting the EC value of soils based on salinity indices and thus a reliable tool for the further development of precision agriculture techniques.
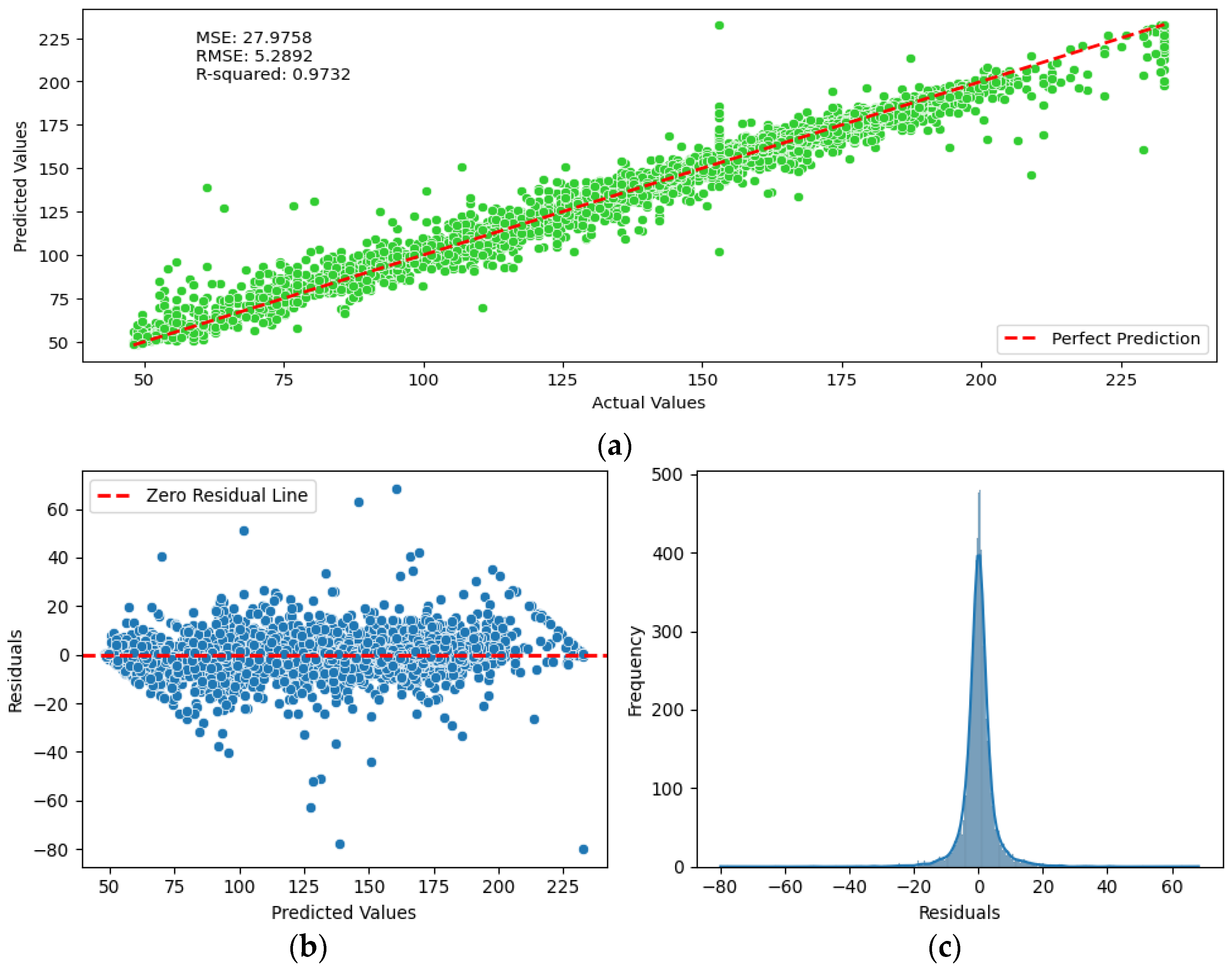
When analyzing the performance of the Random Forest model, the visualization of actual versus predicted values in
Figure 12a shows that the data points are closely aligned with the perfect prediction line. This alignment indicates that the model predicts the target values well and deviates only minimally from the ideal scenario, where the predicted values correspond exactly to the actual values. Furthermore, the presentation of the residuals in
Figure 12b complements this observation. It shows that the residuals —the differences between the observed and predicted values — are scattered around the value zero without any recognisable pattern. This random distribution of the residuals indicates that the errors of the model are unbiased and consistent over the entire range of predicted values. The plot of the distribution of the residuals in
Figure 12c underlines this result by showing a distribution centered around zero, which is a further indication that the predictions of the model are reliable and the errors are normally distributed. Overall, these plots confirm that the Random Forest model effectively captures the underlying patterns in the data and provides robust predictive performance.
After selecting the Random Forest model as the best model based on these evaluation metrics, we used the second partition (on 2 September 2023) for a final evaluation. This step ensures that our chosen model maintains its predictive accuracy in a fully independent dataset, further confirming its robustness and applicability. With this rigorous methodology, we aimed to develop a reliable soil EC prediction model that utilises satellite-based salinity indices to modify agricultural practises with more efficient and scalable soil monitoring methods.
To assess the adaptability of our model, we extended the evaluation beyond the initial training data. After demonstrating strong predictive capability on the training and validation datasets, the model was tested on new data from the following day, on 2 September 2023. This temporal test was performed under the assumption that soil electrical conductivity (EC) does not show significant fluctuations within a single day and thus provides a reliable basis for evaluating the model. The evaluation of the new data resulted in a mean EC error of 25.16, indicating that the predictive power of the model remains consistent even under slightly varying conditions. This small margin of error indicates that the model accurately captures the underlying relationships in the data and can be relied upon for practical applications.
Further experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of feature selection on model performance. Using the Random Forest model, which had proven to be the best performing model in the first phase of testing, we systematically reduced the number of features to investigate how this reduction affected the predictive accuracy and efficiency of the model (
Table 2). In the experiments, we varied the number of features, considering sets with the 27, 20, 15 and 10 most important features as well as a separate set with 8 features - indices that can be derived from UAV data. The original training dataset was used for this purpose. The results showed that the Random Forest model maintained a high level of accuracy with minimal performance degradation when the number of features was reduced from 27 to 15. Remarkably, the R² of the model remained relatively high, around 0.97 (
Table 2), for 20 and 15 features, while the MSE increased only slightly, indicating a strong resilience to feature reduction. In fact, there was a slight increase in performance when reducing from 27 to 15 features, as evidenced by the improvement in R
2 and a decrease in MSE and RMSE, indicating that the model became more efficient without compromising accuracy. However, a significant drop in performance was observed when the number of features was further reduced to 10, with the R² dropping to 0.91 (
Table 2) and the MSE increasing to 87.51 (
Table 2). This trend continued for UAV-derived features, where the R² decreased to 0.7 (
Table 2) and the MSE increased to 266.6 (
Table 2). These results emphasise the importance of feature selection and highlight that although a smaller subset of features can be computationally efficient, there is a trade-off in prediction accuracy, especially when the feature set becomes limited.
5. Discussion
Site-specific farming systems promise to increase the efficiency of agriculture by attempting to optimise the AMZs that are uniform in their soil, weather and water supply patterns [
8,
9,
21,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
31]. As an example of the temporal distribution of water patterns, we show in
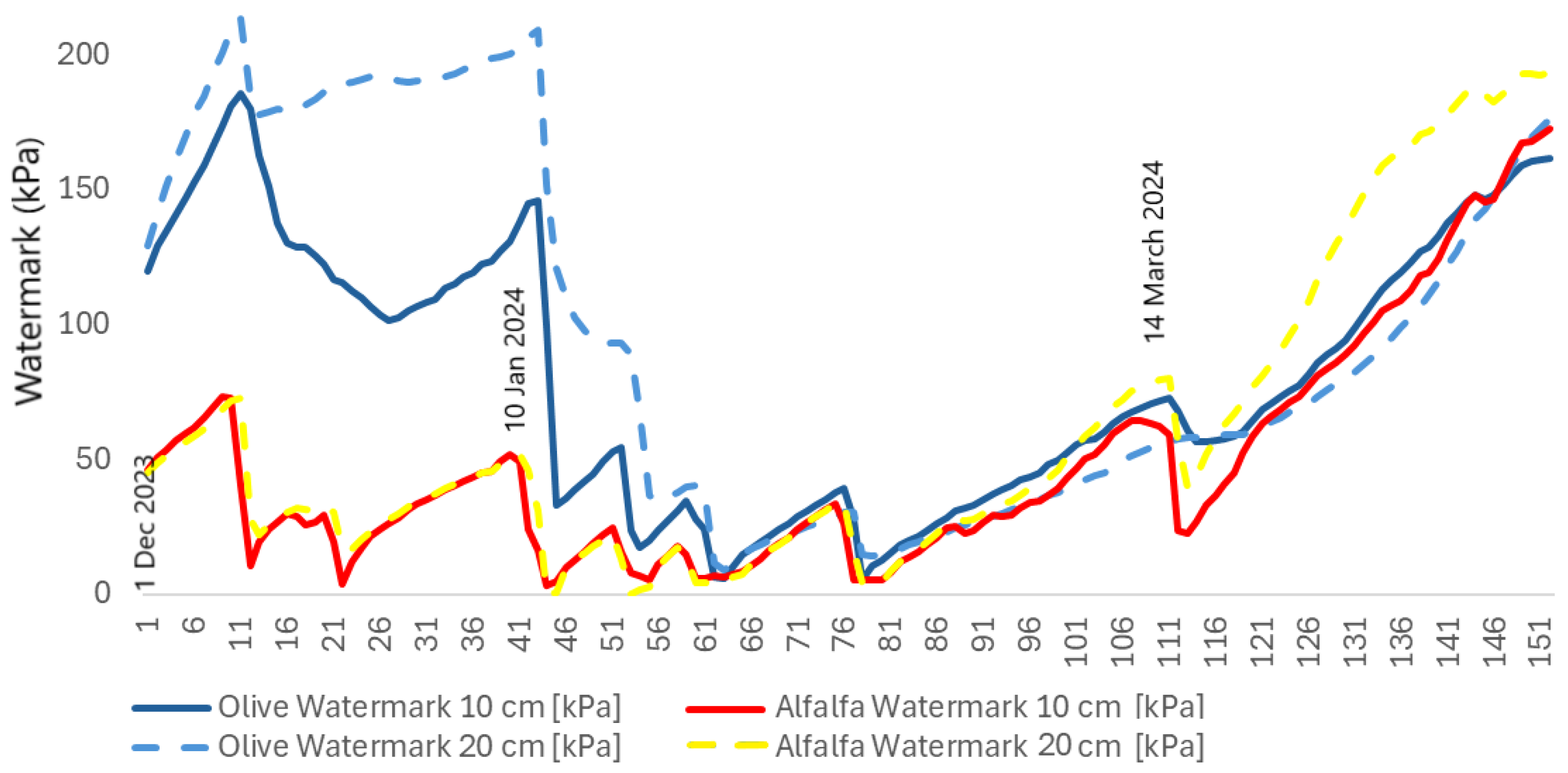
Figure 13 the comparison of watermarks (kPa) for the olive grove and alfalfa plots of the study area up to 20 cm soil depth from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 April 2024. A watermark value above 30 kPa means that the soil is starting to dry out and the plants must therefore make more effort to extract water from the soil. In addition, the water requirement of the olive grove is higher than that of the alfalfa until 10 January 2024.
The benefits and challenges of AMZs delineation are related to the techniques and methods used [
76,
77,
78,
79,
80,
81,
82,
83,
84]. In situ and laboratory soil analyses can provide very accurate data, but they are expensive and time-consuming, especially when large-scale experiments are carried out, for which an RS system is usually available (
Figure 7a, b and
Figure 8a, b, c). In contrast, geophysical methods focussing on agricultural fields [
29,
85,
86], namely electromagnetic mapping in the present case (
Figure 9a, b, c), are time-saving and provide non-destructive data [
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63,
64]. They allow the user to collect data with high spatial resolution over relatively large areas. These methods are a very useful option for obtaining data on physical soil properties [
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63,
64]. Finally, machine learning [
87,
88,
89,
90,
91,
92] is the optimal and cost-effective technique to make reliable predictions about selected soil properties.
Detailed mapping of soil variability and delineation of AMZs [
76,
77,
78,
79,
80,
81,
82,
83,
84] is even more necessary nowadays as climate change is present worldwide and farms need to become sustainable while protecting the environment. The first step in formulating a site-specific management system requires the subdivision of the field into AMZs that are as uniform as possible in terms of soil properties (
Figure 8a, b, c and
Figure 9a, b, c). Managing the spatial variability of fields through the development of AMZs can be successfully applied to many site-specific agricultural management practises. The process of developing AMZs usually involves three main steps: preliminary observations, characterization of the spatial and temporal distribution of soil properties, and validation of the proposed management zones. In this work, we present a flexible and adaptable protocol for Mediterranean areas to delineate AMZs based on satellite remote sensing (Sentinel-1 and 2) for pre-observation, electromagnetic mapping (GEM-2) and UAV flights to characterize the spatial and temporal soil structure, machine learning and targeted soil analysis for validation and real-time recording (IRRIGOPTIMAL® system) of different soil parameters to determine soil and crop requirements. The proposed protocol can a) define temporally and spatially stable AMZs, b) promote targeted soil sampling for further soil analyses to accurately determine cropping practises, and c) define water patterns (
Figure 11a, b and
Figure 13).
6. Conclusions
In this work, satellite-based and unmanned aerial systems together with geophysical prospection, machine learning and real-time monitoring of weather and soil parameters with the IRRIGOPTIMAL® system for the period 2022-2024 were combined for olive and alfalfa plots to establish a protocol regarding the robust delineation of agricultural management zones. This protocol could be important nowadays and, in the future, as it can contribute significantly to the rational use of cultivation inputs and the establishment of optimal irrigation systems. The ability to know the spatial variability of the soil within the field and the associated crop response through monitoring technologies and/or spatial and temporal analyses requires the correct functional use of these observations in terms of solving management system problems in the field. In conclusion:
• Satellite data (Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2) and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) data were used to calculate a) the median soil moisture, b) the Normalized Difference Moisture Index, c) the Green Normalized Difference Vegetation Index, d) terrain attributes and e) vegetation indices for olive and alfalfa plots, comprising the first crucial phase in the delineation of agricultural management zones.
• Spatial and temporal electromagnetic scanning of the plots proved to be ideal for determining the distribution of the apparent conductivity of the soil to a) determine the exact boundaries of the soil management zones and b) define the locations for soil sampling and subsequent soil analyses.
• Real-time monitoring of weather parameters (air temperature, dew point, solar radiation, vapor pressure, relative humidity, precipitation and delta T) and soil parameters (temperature, moisture, watermark) at different soil depths down to 60 cm ensures the rational use of inputs (water, pesticides, fertilizers) and the planning of optimal irrigation considering agricultural management zones.
• Random Forest model of machine learning for predicting the electrical conductivity of the soil performs well and deviates only minimally from the ideal scenario. It shows a strong predictive ability in the training and validation datasets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.K., and D.C.; methodology, E.K., D.C., N.K., I.K., A.B., and M.D.; software, E.K., D.C., N.K., I.K., and M.D.; validation, E.K., D.C., N.K., and I.K.; formal analysis, D.C., and E.K.; investigation, E.K., D.C., N.K., I.K., A.B., and M.D.; resources, E.K., and A.B.; data curation, E.K., D.C., N.K., and I.K.; writing—original draft preparation, E.K., D.C., N.K., I.K., A.B., and M.D. writing—review and editing, E.K., D.C., N.K., I.K., A.B., and M.D.; visualization, E.K., and D.C., N.K., I.K.; supervision, E.K.; project administration, E.K; funding acquisition, E.K, and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been has been supported by internal funding in the context of Ph.D. Studies and the momerantum of understanding between the Hellenic Mediterranean University (HMU) and WES TRADE LTD.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the editor, assistant editor, and the anonymous reviewers for their critical review and constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
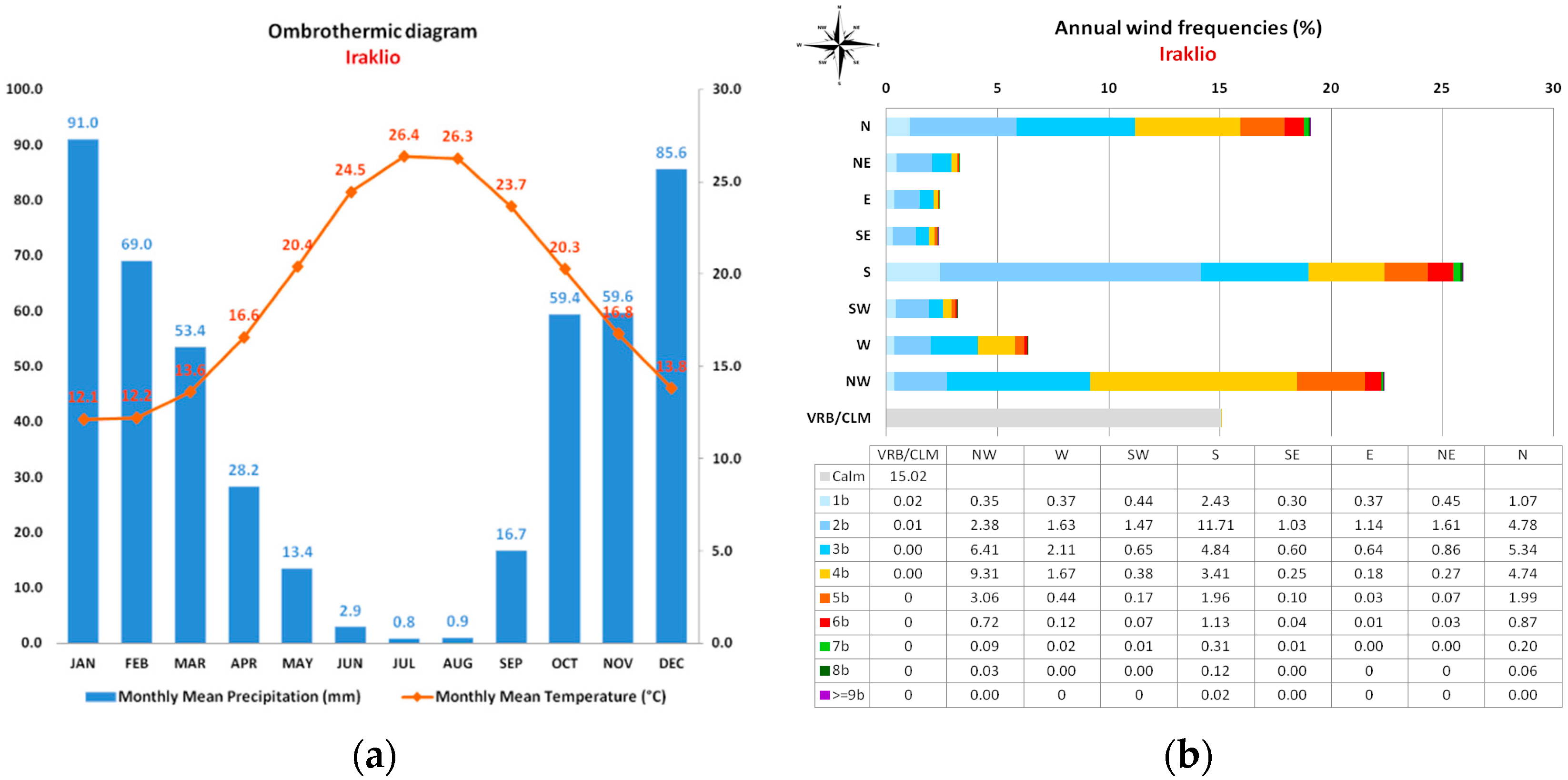
Figure A1.
MeteoroMetereological conditions in Heraklion according to stations installed by the Region of Crete and the Hellenic National Meteorological Service, (a) the ombrothermic diagram shows the normal values of temperature and precipitation for the period 1955-2010. Two climatic seasons are clearly visible: a dry season with high temperatures and a wet season with low temperatures, (b) wind intensity and direction for the period 1955-2010.
Figure A1.
MeteoroMetereological conditions in Heraklion according to stations installed by the Region of Crete and the Hellenic National Meteorological Service, (a) the ombrothermic diagram shows the normal values of temperature and precipitation for the period 1955-2010. Two climatic seasons are clearly visible: a dry season with high temperatures and a wet season with low temperatures, (b) wind intensity and direction for the period 1955-2010.
Figure A2.
(a) 25 January 2024 alfalfa, orthomosaic view, 2.0cm/px, (b) 22 March 2024 orthomosaic view, 2.0cm/px.
Figure A2.
(a) 25 January 2024 alfalfa, orthomosaic view, 2.0cm/px, (b) 22 March 2024 orthomosaic view, 2.0cm/px.
Table A1.
Average monthly values of meteorological parameters for the study area.
Table A1.
Average monthly values of meteorological parameters for the study area.
| Month |
Air
Temperature
OC
|
Dew Point
OC
|
VPD |
Solar
Radiation
w/m2
|
Precipitation
(total)
mm
|
Precipitation
(average)
mm
|
Precipitation
days
|
| December 23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 14.7 |
9.5 |
0.52 |
96.2 |
53,2 |
1.7 |
11 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| January 24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 12.1 |
6.7 |
0.52 |
88.7 |
174 |
5.6 |
12 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| February 24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 12.2 |
7.7 |
0.49 |
126.9 |
71 |
2.4 |
14 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| March 24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 13.6 |
7.8 |
0.67 |
181,0 |
38.4 |
1.2 |
12 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| April 24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 16.6 |
8.6 |
1,13 |
248,0 |
1.6 |
0.1 |
4 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| May 24 |
20.4 |
11.5 |
1,17 |
278.1 |
15.2 |
0.5 |
7 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| min |
7.6 |
0.9 |
|
8,0 |
|
0 |
|
| max |
26.8 |
16.8 |
|
354.0 |
Total=353.4 |
33 |
Total=60 |
| mean |
15.6 |
8.6 |
|
169.8 |
58.9 |
3.83 |
|
References
- Strickland, R.M.; Ess, D.R.; Parsons, S.D. Precision Farming and Precision Pest Management: The Power of New Crop Production Technologies. J. Nematol. 1998, 30, 431–435. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K. Precision Farming. Water Technology Centre, IARI, New Delhi 2010.
- Shibusawa, S. Precision Farming Approaches for Small Scale Farms. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2001, 34, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, P.C. Precision Agriculture: A Challenge for Crop Nutrition Management. Plant Soil 2002, 247, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, M.; Wang, N. Precision Agriculture - A Worldwide Overview. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2002, 36, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, M.Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, M.H. Yield Mapping In Precision Farming Development Of Hardware. Springer 2008, 259, 1407–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, S.B.; Aruna, M.S.; Bairagi, S.G.D. A Review : The Application of Remote Sensing, GIS and GPS in Precision Agriculture. Internarional J. Adv. Technol. Enginering Res. 2012, 2, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Heege, H.J. Precision in Crop Farming: Site Specific Concepts and Sensing Methods: Applications and Results; Springer Netherlands, 2013; ISBN, 9789400767607. [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S. Precision Farming for Small Agricultural Farm: Indian Scenario. Am. J. Exp. Agric. 2013, 3, 200–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zude-Sasse, M.; Fountas, S.; Gemtos, T.A.; Abu-Khalaf, N. Applications of Precision Agriculture in Horticultural Crops. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 2016, 81, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balafoutis, A.; Beck, B.; Fountas, S.; Vangeyte, J.; Wal, T.V.d.; Soto, I.; Gómez-Barbero, M.; Barnes, A.; Eory, V. Precision Agriculture Technologies Positively Contributing to GHG Emissions Mitigation, Farm Productivity and Economics. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paustian, M.; Theuvsen, L. Adoption of Precision Agriculture Technologies by German Crop Farmers. Precis. Agric. 2017, 18, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallottino, F.; Biocca, M.; Nardi, P.; Figorilli, S.; Menesatti, P.; Costa, C. Science Mapping Approach to Analyze the Research Evolution on Precision Agriculture: World, EU and Italian Situation. Precis. Agric. 2018, 19, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, J.; Hawkins, E.; Taylor, R.; Franzen, A. Yield Monitoring and Mapping. In Precision Agriculture Basics; Shannon, D.K., Clay, D.E., Kitchen, N.R., Eds.; ASA, CSSA, SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 2018; pp. 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, U.; Mumtaz, R.; García-nieto, J.; Hassan, S.A. Precision Agriculture Techniques and Practices : From Considerations to Applications. Sensors 2019, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, R.; Swinton, S.M.; El Benni, N.; Walter, A. Precision Farming at the Nexus of Agricultural Production and the Environment. Annu. Rev. Resour. Econ. 2019, 11, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, B.R.; Dudwal, B. . L. Precision Farming; Their Tools and Techniques. Just Agric. Multidiscip. e-Newsletter 2021, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Rimpika; Anushi; Manasa, S.; Anusha, K.N.; Sharma, S.; Thakur, A.; Shilpa; Sood, A. An Overview of Precision Farming. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.R.; Durairaj, C.D.; Woods, S.; Sullivan, M. Potential Application of Electrical Conductivity (EC) Map for Variable Rate Seeding. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR Ejournal 2005, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hörbe, T.A.N.; Amado, T.J.C.; Ferreira, A.O.; Alba, P.J. Optimization of Corn Plant Population According to Management Zones in Southern Brazil. Precis. Agric. 2013, 14, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridgen, J.; Fraisse, C.; Kitchen, N.; Sudduth, K. Delineation and Analysis of Site-Specific Management Zones. Precis. Agric. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Peralta, N.R.; Costa, J.L.; Balzarini, M.; Castro Franco, M.; Córdoba, M.; Bullock, D. Delineation of Management Zones to Improve Nitrogen Management of Wheat. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 110, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobryk, C.W.; Myers, D.B.; Kitchen, N.R.; Shanahan, J.F.; Sudduth, K.A.; Drummond, S.T.; Gunzenhauser, B.; Gomez Raboteaux, N.N. Validating a Digital Soil Map with Corn Yield Data for Precision Agriculture Decision Support. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, F.S.; Corstanje, R.; Halcro, G.; Mulla, D.; Mouazen, A.M. Delineation of Soil Management Zones for Variable-Rate Fertilization : A Review. Adv. Agron. 2017, 143, 175–245. [Google Scholar]
- Leroux, C.; Jones, H.; Clenet, A.; Tisseyre, B. A New Approach for Zoning Irregularly-Spaced, within-Field Data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 141, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Franco, M.; Córdoba, M.A.; Balzarini, M.G.; Costa, J.L. A Pedometric Technique to Delimitate Soil-Specific Zones at Field Scale. Geoderma 2018, 322, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajili, A.; Cambouris, A.N.; Chokmani, K.; Duchemin, M.; Perron, I.; Zebarth, B.J.; Biswas, A.; Adamchuk, V.I. Analysis of Four Delineation Methods to Identify Potential Management Zones in a Commercial Potato Field in Eastern Canada. Agronomy 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Rondelli, V.; Martelli, R.; Falsone, G.; Lupia, F.; Barbanti, L. Management Zones Delineation through Clustering Techniques Based on Soils Traits, NDVI Data, and Multiple Year Crop Yields. Agric. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzidavid, D.; Kokinou, E.; Kokolakis, S.; Karagiannidou, M. Integrating Earth Observation with Stream Health and Agricultural Activity. Remote Sens. 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Jacob, F.; Duveiller, G. Remote Sensing for Agricultural Applications: A Meta-Review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, P.J.; Hatfield, J.L.; Barnes, E.M.; Schepers, J.S.; Moran, S.M.; Daughtry, C.; Upchurch, D. Remote Sensing for Crop Management Management. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing. 2003, 69(3), 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomarasca, M.A. Basic of Geomatics; Gomarasca, M.A., 1st ed.; Springer, 2009; Vol. 53; ISBN 9788578110796.
- Ravelo, A.C.; Abril, E.G. Applied Agrometeorology; Kees Stigter, Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, 2010; pp. 1–1100 ISBN 9783540746973. [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.; Bills, C. Visualisation, Imagery, and the Development of Geometrical Reasoning. Proceeding Br. Res. into Learn. Math. 1998, 18, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kingra, P.K.; Majumder, D.; Singh, S.P. Application of Remote Sensing and Gis in Agriculture and Natural Resource Management Under Changing Climatic Conditions. Agric. Res. J. 2016, 53, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, J.K.; Varghese, A.O. Remote Sensing and GIS in Agriculture and Forest Resource Monitoring. In Geospatial Technologies in Land Resources Mapping,Monitoring and Management; Springer International Publishing, 2018 ISBN 9783319787114. [CrossRef]
- Shanmugapriya, P.; Rathika, S.; Ramesh, T.; Janaki, P. Applications of Remote Sensing in Agriculture-A Review. Appl. Remote Sens. Agric. 1990, 8, 2270–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Thomasson, J.A.; Sui, R. Remote Sensing of Soil Properties in Precision Agriculture : A Review. Front. Earth Sci. 2011, 5, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourgialas, N.N.; Psarras, G.; Morianou, G.; Pisinaras, V.; Koubouris, G.; Digalaki, N.; Malliaraki, S.; Aggelaki, K.; Motakis, G.; Arampatzis, G. Good Agricultural Practices Related to Water and Soil as a Means of Adaptation of Mediterranean Olive Growing to Extreme Climate-Water Conditions. Sustainability. 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourgialas, N.N.; Anastopoulos, I.; Stefanakis, A. Adapting Water and Soil Management to Climate Change. Sustainability. 2024, 16, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrochidou, A.E.K.; Tsanis, I.K. Assessing Precipitation Distribution Impacts on Droughts on the Island of Crete. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapoglou, E.; Vozinaki, A.-E.E.; Tsanis, I. Climate Change Impact on the Frequency of Hydrometeorological Extremes in the Island of Crete. Water 2019, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.R.; Gregorich, E.G. Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis; 2nd ed.; CRC PRESS: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; ISBN 9781420005271. [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; National, M.; Forecast, C.; Panigrahy, S. Use of high resolution remote sensing data for generating site-specific soil management plan. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Congress Technical Commission VII Symposioum, Instanbul, Turkey, 12–23 July 2004; pp. 127. [Google Scholar]
- Douaoui, A.E.K.; Nicolas, H.; Walter, C. Detecting Salinity Hazards within a Semiarid Context by Means of Combining Soil and Remote-Sensing Data. Geoderma 2006, 134, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allbed, A.; Kumar, L. Soil Salinity Mapping and Monitoring in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions Using Remote Sensing Technology: A Review. Adv. Remote Sens. 2013, 02, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawley, V.; Lewis, M.; Clarke, K.; Ostendorf, B. Site-Based and Remote Sensing Methods for Monitoring Indicators of Vegetation Condition: An Australian Review. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.; Ntakos, G.; Nielsen, J.; Svensgaard, J.; Poulsen, R.N.; Christensen, S. Are Vegetation Indices Derived from Consumer-Grade Cameras Mounted on UAVs Sufficiently Reliable for Assessing Experimental Plots? Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 74, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, H.; Ceddia, M.B.; Vasques, G.M.; Mulder, V.L.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Oliveira, R.P.; Brandão, Z.N.; Morais, J.P.S.; Neves, M.L.; Tavares, S.R.L. Remote Sensing and Kriging with External Drift to Improve Sparse Proximal Soil Sensing Data and Define Management Zones in Precision Agriculture. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 2326–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliff, C.; Gobbett, D.; Bramley, R.G.V. PAT - Precision Agriculture Tools. CSIRO.V3 Software 2020, 2020–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congedo, L. Semi-Automatic Classification Plugin: A Python Tool for the Download and Processing of Remote Sensing Images in QGIS. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C. NDWI?A Normalized Difference Water Index for Remote Sensing of Vegetation Liquid Water from Space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, C.; Nagel, E. In Vivo Spectroscopy and Internal Optics of Leaves as Basis for Remote Sensing of Vegetation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudduth, K.A.; Kitchen, N.R.; Bollero, G.A.; Bullock, D.G.; Wiebold, W.J. Comparison of Electromagnetic Induction and Direct Sensing of Soil Electrical Conductivity. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.A.; Dampney, P.M.R.; Lark, R.M.; Wheeler, H.C.; Bradley, R.I.; Mayr, T.R. Mapping Potential Crop Management Zones within Fields: Use of Yield-Map Series and Patterns of Soil Physical Properties Identified by Electromagnetic Induction Sensing. Precis. Agric. 2005, 6, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domsch, H.; Giebel, A. Estimation of Soil Textural Features from Soil Electrical Conductivity Recorded Using the EM38. Precis. Agric. 2004, 5, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Characterizing Soil Spatial Variability with Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity: I. Survey Protocols. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 103–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambouris, A.N.; Nolin, M.C.; Zebarth, B.J.; Laverdière, M.R. Soil Management Zones Delineated by Electrical Conductivity to Characterize Spatial and Temporal Variations in Potato Yield and in Soil Properties. Am. J. Potato Res. 2006, 83, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral García, F.J.; Terrón, J.M.; Marques Da Silva, J. Delineation of Management Zones Using Mobile Measurements of Soil Electrical Conductivity and Multivariate Geostatistical Techniques. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 106, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J.; Shahidian, S.; da Silva, J.M. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Apparent Electrical Conductivity: DUALEM vs. Veris Sensors for Monitoring Soil Properties. Sensors (Switzerland) 2014, 14, 10024–10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, W.N.; de Queiroz, D.M.; Valente, D.S.M.; Pinto, F. D. A.; Melo, C.A.D. The Temporal Stability of the Variability in Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity. Biosci. J. 2016, 32, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J.; Shahidian, S.; Paixão, L.; Marques da Silva, J.; Moral, F. Management Zones in Pastures Based on Soil Apparent Electrical Conductivity and Altitude: NDVI, Soil and Biomass Sampling Validation. Agronomy 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J.; Mau, V.; Rodrigues, R.; Paixão, L.; Shahidian, S.; Marques da Silva, J.; Paniagua, L.L.; Moral, F.J. Definition and Validation of Vineyard Management Zones Based on Soil Apparent Electrical Conductivity and Altimetric Survey. Environ. - MDPI 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottega, E.L.; Marin, C.K.; Oliveira, Z.B. de; Lamb, C. de C.; Amado, T.J.C. Soil Density Characterization in Management Zones Based on Apparent Soil Electrical Conductivity in Two Field Systems: Rainfeed and Center-Pivot Irrigation. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, I.J. A Wide-Bank Electromagnetic Exploration Method - Some Theoretical and Experimental Results. Geophysics 1980, 45, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraisse, C.W.; Sudduth, K.A.; Kitchen, N.R.; Fridgen, J.J. Use of Unsupervised Clustering Algorithms for Delineating Within-Field Management Zones. In Proceedings of the 1999 ASAE/CSAE-SCGR Annual International Meeting: Emerging Technologies for the 21st Century, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, 18–21 July 1999. Paper No. 993043. [Google Scholar]
- Lamichhane, S.; Kumar, L.; Wilson, B. Digital Soil Mapping Algorithms and Covariates for Soil Organic Carbon Mapping and Their Implications: A Review. Geoderma 2019, 352, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeraatpisheh, M.; Bakhshandeh, E.; Emadi, M.; Li, T.; Xu, M. Integration of PCA and Fuzzy Clustering for Delineation of Soil Management Zones and Cost-Efficiency Analysis in a Citrus Plantation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Nabiollahi, K.; Rasoli, L.; Kerry, R.; Scholten, T. Land Suitability Assessment and Agricultural Production Sustainability Using Machine Learning Models. Agronomy 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadi, M.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Cherati, A.; Danesh, M.; Mosavi, A.; Scholten, T. Predicting and Mapping of Soil Organic Carbon Using Machine Learning Algorithms in Northern Iran. Remote Sens. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaledian, Y.; Miller, B.A. Selecting Appropriate Machine Learning Methods for Digital Soil Mapping. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 81, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makungwe, M.; Chabala, L.M.; Chishala, B.H.; Lark, R.M. Performance of Linear Mixed Models and Random Forests for Spatial Prediction of Soil PH. Geoderma 2021, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wu, T.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, G.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Pu, L. Comparison of Random Forest and Multiple Linear Regression Models for Estimation of Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities in Agricultural Reclaimed Coastal Saline Land. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashikumar, B.N.S.; Justin, K.K.; Abhishek, G.; Singh, K. Soil Variability Mapping and Delineation of Site - Specific Management Zones Using Fuzzy Clustering Analysis in a Mid - Himalayan Watershed, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 8539–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.; Karimi, A.; Mousavi, A.; Kerry, R.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R. Delineation of Soil Management Zone Maps at the Regional Scale Using Machine Learning. Agronomy 2023, 13, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, A.; Shanahan, J.; Liebig, M.; Schepers, J..; Johnson, S.; Jr, L. Appropriateness of Management Zones for Characterizing Spatial Variability of Soil Properties and Irrigated Corn Yields across Years. Agron. J. 2004, 96. [CrossRef]
- Vitharana, U.W.A.; Meirvenne, M. Van; Simpson, D. Key Soil and Topographic Properties to Delineate Potential Management Classes for Precision Agriculture in the European Loess Area. Geoderma 2008, 143, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaddad, S.M.; Buttafuoco, G.; Elrys, A.; Castrignanò, A. Site-Specific Management of Salt Affected Soils: A Case Study from Egypt. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loures, L.; Chamizo, A.; Ferreira, P.; Loures, A.; Castanho, R.; Panagopoulos, T. Assessing the Effectiveness of Precision Agriculture Management Systems in Mediterranean Small Farms. Sustainability. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambilla, M.; Romano, E.; Toscano, P.; Cutini, M.; Biocca, M.; Ferré, C.; Comolli, R.; Bisaglia, C. From Conventional to Precision Fertilization: A Case Study on the Transition for a Small-Medium Farm. AgriEngineering 2021, 3, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerry, R.; Ingram, B.; Oliver, M. Sampling Needs to Establish Effective Management Zones for Plant Nutrients in Precision Agriculture. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Precision Agriculture (ECPA), Budapest, Hungary, 19–22 July 2021; pp. 653–660. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Shi, B.; Yost, R.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Cao, Q. Optimization of Management Zone Delineation for Precision Crop Management in an Intensive Farming System. Plants 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeraatpisheh, M.; Bottega, E.L.; Bakhshandeh, E.; Owliaie, H.R.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Kerry, R.; Scholten, T.; Xu, M. Spatial Variability of Soil Quality within Management Zones: Homogeneity and Purity of Delineated Zones. Catena 2022, 209, 105835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, E.A.; Naime, J.M.; Vaz, C.M.P.; Santos, J.C.F.; Inamasu, R.Y.; Lopes, I. O.N.; Queirós, L.R.; Rabelo, L.M.; Jorge, L.A.C.; Chagas, S.; et al. Delineating Management Zones with Different Yield Potentials in Soybean–Corn and Soybean–Cotton Production Systems. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 1481–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritikakis, G.; Kokkinou, E.; Economou, N.; Andronikidis, N.; Brintakis, J.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Kourgialas, N.; Pavlaki, A.; Fasarakis, G.; Markakis, N.; et al. Estimating Soil Clay Content Using an Agrogeophysical and Agrogeological Approach: A Case Study in Chania Plain, Greece. Water 2022, 14, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou, N.; Brintakis, J.; Andronikidis, N.; Kritikakis, G.; Kokkinou, E.; Papadopoulos, N.; Kourgialas, N.; Vafidis, A. GPR Data Migration Velocity Estimation Using a Local Diffraction Multi-Focusing Criterion. In Proceedings of the 11th Congress of the Balkan Geophysical Society, Online, 10–14 October 2021; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Bunnik, The Netherlands; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, W.; Sun, D. Prediction Model of Soil Electrical Conductivity Based on ELM Optimized by Bald Eagle Search Algorithm. Electronics 2021, 25, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Samadianfard, S.; Darbandi, S.; Nabipour, N.; Qasem, S.N.; Salwana, E.; S. Band, S. Predicting Soil Electrical Conductivity Using Multi-Layer Perceptron Integrated with Grey Wolf Optimizer. J. Geochemical Explor. 2021, 220, 106639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.G.; Shubha, C.; Sushma, S.A. Random Forest Algorithm for Soil Fertility Prediction and Grading Using Machine Learning. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 9, 1301–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Hamzehpour, N. Quantitative Remote Sensing of Soil Electrical Conductivity Using ETM+ and Ground Measured Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 38, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Du, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wu, Y.; Guo, J.; Peng, Y. Combination of Hyperspectral and Machine Learning to Invert Soil Electrical Conductivity. Remote Sens. 2022, 14(11), 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Li, H.; Yin, C.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H. Soil Salinity Mapping Using Machine Learning Algorithms with the Sentinel-2 MSI in Arid Areas, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
a) Map of Greece showing the location of this study, coordinates in Greek Geodetic Reference System 1987, b) orthomosaic of the study area showing the two plots (in red colour) cultivated with alfalfa while purple colour corresponds to the plot of olive trees. In addition, S1 and S2 show the locations where IRRIGOPTIMAL® sensors have been installed, c) the corresponding Digital Surface Model (DSM).
Figure 1.
a) Map of Greece showing the location of this study, coordinates in Greek Geodetic Reference System 1987, b) orthomosaic of the study area showing the two plots (in red colour) cultivated with alfalfa while purple colour corresponds to the plot of olive trees. In addition, S1 and S2 show the locations where IRRIGOPTIMAL® sensors have been installed, c) the corresponding Digital Surface Model (DSM).
Figure 2.
Weather data for the study area according to recordings from IRRIGOPTIMAL® sensors. a) air temperature (oC), dew point (oC), c) solar radiation (W/m²), d) vapor pressure deficit (VPD) in kPa, e) relative humidity (%), f) precipitation (mm), and g) delta T (oC).
Figure 2.
Weather data for the study area according to recordings from IRRIGOPTIMAL® sensors. a) air temperature (oC), dew point (oC), c) solar radiation (W/m²), d) vapor pressure deficit (VPD) in kPa, e) relative humidity (%), f) precipitation (mm), and g) delta T (oC).
Figure 3.
UAS data (a) Initial image position acquired by the DJI Mavic 3M, (b) basic processing flow of the UAV data.
Figure 3.
UAS data (a) Initial image position acquired by the DJI Mavic 3M, (b) basic processing flow of the UAV data.
Figure 4.
GEM-2 operation principle.
Figure 4.
GEM-2 operation principle.
Figure 5.
The sensors (imetos) installed in the field on 20/11/22023. (a) the autonomous meteorological station that was installed in the olive grove (Imetos IMT280-USW). The solar panel and the cables connected to the ground sensors are visible. (b) sensor installed in the alfalfa plot prior cultivation. The solar panel and cables connected to the ground sensors are visible (Imetos-IMT200).
Figure 5.
The sensors (imetos) installed in the field on 20/11/22023. (a) the autonomous meteorological station that was installed in the olive grove (Imetos IMT280-USW). The solar panel and the cables connected to the ground sensors are visible. (b) sensor installed in the alfalfa plot prior cultivation. The solar panel and cables connected to the ground sensors are visible (Imetos-IMT200).
Figure 6.
Machine learning flow chart.
Figure 6.
Machine learning flow chart.
Figure 7.
Distribution of (a) soil moisture based on Sentinel-1 data for the time January – June 2024 for both olive and alfalfa plots, (b) mean Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI) of the olive grove based on Sentinel-2 L2A (cloud cover<= 5%) for the time January – June 2024.
Figure 7.
Distribution of (a) soil moisture based on Sentinel-1 data for the time January – June 2024 for both olive and alfalfa plots, (b) mean Normalized Difference Moisture Index (NDMI) of the olive grove based on Sentinel-2 L2A (cloud cover<= 5%) for the time January – June 2024.
Figure 8.
Distribution of Green Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (GNDVI) of the alfalfa plot (
Figure A2a, b,
Appendix A) for (a) and (b) two UAV flights on 25 January 2024 and 22 March 2024, and (c) Sentinel-2 based data for the time April to June 2024.
Figure 8.
Distribution of Green Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (GNDVI) of the alfalfa plot (
Figure A2a, b,
Appendix A) for (a) and (b) two UAV flights on 25 January 2024 and 22 March 2024, and (c) Sentinel-2 based data for the time April to June 2024.
Figure 9.
Electomagnetic response of GEM-2 corresponding to apparent conductivity (mS/m) of the soil for (a) the olive grove in the wet season 2022, (b) the alfalfa plot (prior the cultivation) in the wet season 2022 (left) and dry season 2023 (right).
Figure 9.
Electomagnetic response of GEM-2 corresponding to apparent conductivity (mS/m) of the soil for (a) the olive grove in the wet season 2022, (b) the alfalfa plot (prior the cultivation) in the wet season 2022 (left) and dry season 2023 (right).
Figure 10.
Temperature (oC) distribution a) at different soil depths (10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 50 cm, 60 cm) for the olive grove from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 May 2024, (b) for the olive grove and alfalfa plots up to 20 cm soil depth from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 April 2024.
Figure 10.
Temperature (oC) distribution a) at different soil depths (10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 50 cm, 60 cm) for the olive grove from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 May 2024, (b) for the olive grove and alfalfa plots up to 20 cm soil depth from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 April 2024.
Figure 11.
Moisture (%) distribution a) at different soil depths (10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 50 cm, 60 cm) for the olive grove from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 May 2024, (b) for the olive and alfalfa plots up to 20 cm soil depth from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 April 2024.
Figure 11.
Moisture (%) distribution a) at different soil depths (10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 50 cm, 60 cm) for the olive grove from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 May 2024, (b) for the olive and alfalfa plots up to 20 cm soil depth from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 April 2024.
Figure 12.
Visualization of the Random Forest model results, a) actual vs predicted EC values as depicted from the Random Forest model, b) residuals from the model, c) the distribution of the residuals of the model.
Figure 12.
Visualization of the Random Forest model results, a) actual vs predicted EC values as depicted from the Random Forest model, b) residuals from the model, c) the distribution of the residuals of the model.
Figure 13.
Watermark (kPa) distribution for the olive grove and alfalfa plots up to 20 cm soil depth from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 April 2024.
Figure 13.
Watermark (kPa) distribution for the olive grove and alfalfa plots up to 20 cm soil depth from the beginning of December 2023 to 30 April 2024.
Table 1.
Evaluation of Linear Regression, Random Forest and XGBoost model, based on the test set.
Table 1.
Evaluation of Linear Regression, Random Forest and XGBoost model, based on the test set.
| Model |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
MAE |
MAPE |
| LR |
0.31 |
717.87 |
26.79 |
18.99 |
16.43 |
| RF |
0.97 |
27.97 |
5.28 |
3.0 |
2.39 |
| XGB |
0.97 |
26.21 |
5.12 |
3.22 |
2.48 |
Table 2.
Results revealed by the application of Random Forest model.
Table 2.
Results revealed by the application of Random Forest model.
| #Features |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
MAE |
MAPE |
Time(s) |
| 27 |
0.9732 |
27.97 |
5.28 |
3.0 |
2.39 |
97 |
| 20 |
0.9786 |
22.37 |
4.72 |
2.65 |
2.09 |
67 |
| 15 |
0.9799 |
20.95 |
4.57 |
2.53 |
2.00 |
54 |
| 10 |
0.9161 |
87.51 |
9.35 |
5.2 |
4.08 |
37 |
| Drone (8) |
0.7094 |
266.6 |
16.32 |
9.49 |
7.97 |
31.19 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).