1. Introduction
The research and development of bacteria-repellent coatings have emerged as a priority to enhance safety in hospital environments.[
1] Microbial fouling can lead to nosocomial infections in patients when bacterial biofilms adhere to medical devices, representing a cause of death among patients [
2,
3,
4]. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus are the most common microorganisms in hospital-acquired infections [
5]. These bacteria pose significant challenges due to their resistance to antimicrobial treatments and ability to persist on surfaces for varying periods, increasing the risk of transmission [
6,
7,
8].
Preventing bacterial adhesion is crucial to avoid infections and ensure safety in clinical settings. While biocides are designed to prevent or control the proliferation of such bacteria, there is a growing concern that their increasingly frequent use may lead to higher bacterial resistance and cross-resistance to clinically important antibiotics, resulting in significant complications [
9,
10]. In this context, developing antibacterial materials based on superhydrophobicity emerges as a promising strategy for maintaining clean and hygienic surfaces and preventing bacterial adhesion [
1,
3,
5,
11,
12]. Research on how Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus interact with superhydrophobic surfaces is essential for developing effective strategies to prevent device-associated infections in healthcare settings [
13,
14,
15].
Superhydrophobic surfaces, characterized by water contact angles (WCA) greater than 150° and sliding angles (WSA) less than 10°, repel water and facilitate a self-cleaning function by removing debris and pathogens [
15,
16]. Various methods and treatments can be employed to achieve this property, including the design of coatings with layers of material that provide this specific function [
17]. Consequently, these superhydrophobic coatings aim to prevent bacterial adhesion, inhibit bacterial growth, and allow for the easy removal of contaminants from surfaces[
1].
Superhydrophobic coatings are based on compounds with low surface energy[
18] and high roughness. Superhydrophobic coatings are based on compounds with low surface energy [
19]. A promising option for obtaining these coatings is the synthesis of modified SiO
2 NPs[
20,
21,
22] and their application via the spray coating method [
23].
SiO
2 NPs are described as a potent group of nanocarriers that have shown antimicrobial properties and drug-delivery capabilities [
24]. Due to their free silanol groups, which allow for modifications, and their porous nature, which enables higher drug loading, they are positioned as a viable alternative for infection treatment. Additionally, the roughness of these nanoparticles can significantly influence their ability to inactivate bacteria, with greater roughness being associated with higher antibacterial effectiveness [
25].
Moreover, the durability and stability of superhydrophobic coatings are crucial under various environmental conditions, including outdoor exposure. Studies have shown that factors such as layer thickness, particle size, and the nature of functional groups play a critical role in determining these properties [
26]. Furthermore, recent research indicates that SiO
2 NPs modified with PFDTES are highly resistant to water abrasion and other environmental factors [
27].
Our research focuses on developing a superhydrophobic coating with antibacterial properties for surfaces using SiO2 NPs smaller than 10 nm modified with PFDTES. To this end, the antibacterial activity was evaluated by applying the coating on glass substrates using the spray coating method, varying the number of layers, and utilizing turbidimetry and inhibition halo measurement techniques against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. Additionally, the durability of the coating was analyzed by exposing it to outdoor conditions for 35 days, and its morphology, composition, and hydrophobic properties were characterized. These findings confirm its effectiveness in preventing bacterial adhesion and growth on surfaces, making it a promising strategy for areas where these bacteria pose a risk.
2. Methodology
2.1. Materials
To synthesize SiO2 nanoparticles (NPs), tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS, Si(OC2H5)4, 98%, Sigma-Aldrich) was utilized as the silica precursor. Ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH, 28-30% NH3, Sigma-Aldrich) was the catalyst agent. Isopropyl alcohol (C3H8O, CEDROSA) and deionized water (18 MΩ·cm) were employed as solvents for the hydrolysis process. For the modification of SiO2 NPs and the preparation of the superhydrophobic coating, 1H,1H,2H,2H-Perfluorodecyltriethoxysilane (PFDTES, C16H19F17O3Si, 97%, Matrix Scientific) was used along with hexane (C6H14, 95%, J.T. Baker) as the solvent. Glass substrates used for the deposition and analysis of the coating were obtained from Fisher Scientific.
2.2. Equipment
The synthesis and characterization of the superhydrophobic coatings were conducted using the following equipment: a laboratory stirrer (PC 410, Corning®) for mixing solutions and a water purification system (Water-Pro PS, Labconco®) for obtaining deionized water. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis was performed using an infrared spectrometer (NICOLET IS50 FT-IR, Thermo Scientific). X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis used a diffractometer (X’Pert Pro, Panalytical). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) characterization was conducted using a transmission electron microscope (JEM-2010, JEOL) with samples deposited on carbon-coated copper grids from Ted Pella Inc. Finally, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was performed using a scanning electron microscope (JSM-7401, JEOL).
2.3. Synthesis and Characterization
The synthesis of SiO
2 nanoparticles (NPs) was performed using the method proposed by Stöber.[
28] To prepare a 100 ml solution of SiO
2 NPs, 95 ml of isopropyl alcohol was mixed at a stirring speed of 300 rpm. Subsequently, 3.65 ml of deionized water, 350 μl of NH
4OH, and 1 ml of TEOS were added. The mixture was maintained at 40°C under continuous stirring for 24 hours. Following this period, 25 ml of hexane was introduced into the solution, the temperature was increased to 60°C, and 500 μl of PFDTES was added. The solution was stirred at 300 rpm for 48 hours, yielding 125 ml of superhydrophobic coating.
For the coating application, 1, 3, 5, and 7 layers of the superhydrophobic coating were deposited onto glass substrates using the spray coating technique. This process was conducted with an air pressure of 30 psi, maintaining a distance of 15 cm between the nozzle and the substrate. The samples were then exposed to outdoor conditions for 35 days to evaluate changes in surface superhydrophobicity. The coating's water contact angle (WCA) and the water sliding angle (WSA) were characterized using custom-built laboratory equipment at room temperature. Deionized water droplets of 4 μl were used for the measurements, and the contact angle was measured five times at different positions on each sample to obtain an average value.
For FTIR and XRD characterization, the solutions were evaporated to obtain the SiO2 NPs and the superhydrophobic coating in powder form. These powders were then deposited onto glass slides for subsequent analysis. For SEM and EDS analysis, glass substrates with varying numbers of layers were examined. For TEM analysis, the colloidal samples were deposited onto carbon-coated copper grids.
2.4. Antibacterial and Bacteriostatic Study
The methodology used to conduct the antibacterial and bacteriostatic study of the superhydrophobic coating involved depositing 1, 3, 5, and 7 layers of the coating onto glass substrates using the spray coating method.
For the antibacterial test, the turbidimetry technique was employed using 1:1 solutions (culture broth-phosphate buffer solution) with Escherichia coli (ATCC® 11229™) and Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC® 6538™). The tests were conducted by adding the bacterial solution to tubes containing the coated samples, which were then incubated for 24 hours at 37°C in a Fisher Scientific Low-Temperature Incubator. After the incubation period, the solutions were measured using UV-visible light spectroscopy (Genesys2, Thermo Spectronic) at a wavelength of 450 nm. Negative controls (bacterial solution without sample) and positive controls (buffer solution with sample) were included, and the analysis was performed in triplicate.
For the bacteriostatic characterization, all samples were sterilized using UV light within a laminar flow hood (Labconco) for 15 minutes on each side before testing. In a sterile environment, standard solutions of approximately 1.5 × 10⁸ CFU/ml of Escherichia coli (ATCC® 11229™) and Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC® 6538™) were prepared. These solutions were then separately plated on Petri dishes containing nutrient agar (Difco 21300). The coated samples were placed on the inoculated agar, and the Petri dishes were incubated at 37°C for 24 and 48 hours to observe the inhibition halos.
3. Results
3.1. WCA
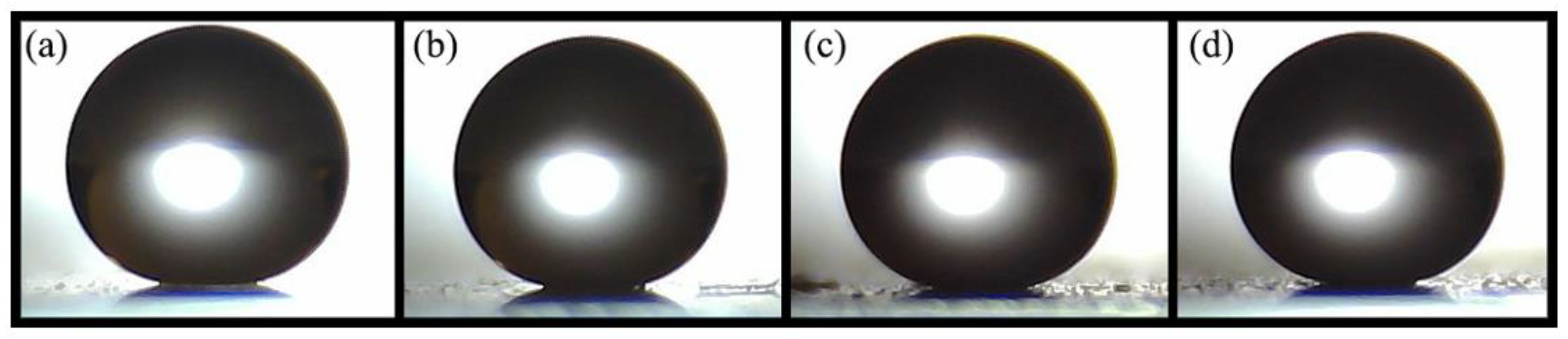
The manufactured coating exhibits water contact angles (WCA) ≥150° and water sliding angles (WSA) ≤10°.
Figure 1 presents photographs of water droplets deposited on glass substrates with varying numbers of coating layers.
Table 1 provides the contact and sliding angle values measured initially and after 35 days of exposure to outdoor conditions.
Initially, as the number of layers increases, the WCA also increases. At the same time, the WSA remains below 3°, demonstrating the necessary characteristics for superhydrophobicity. After 35 days, the coating retains contact angles ≥150° and sliding angles ≤10°. Although slight changes are observed in both angles, the coating maintains its superhydrophobic properties.
3.2. SEM
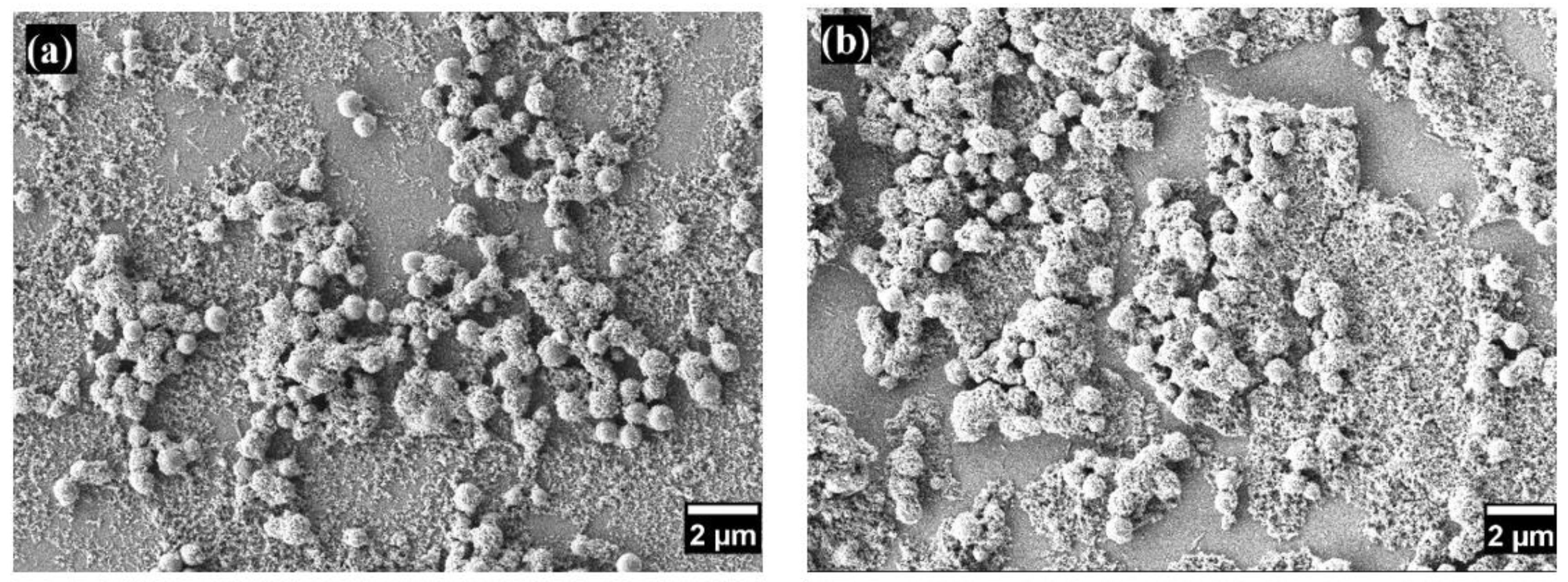
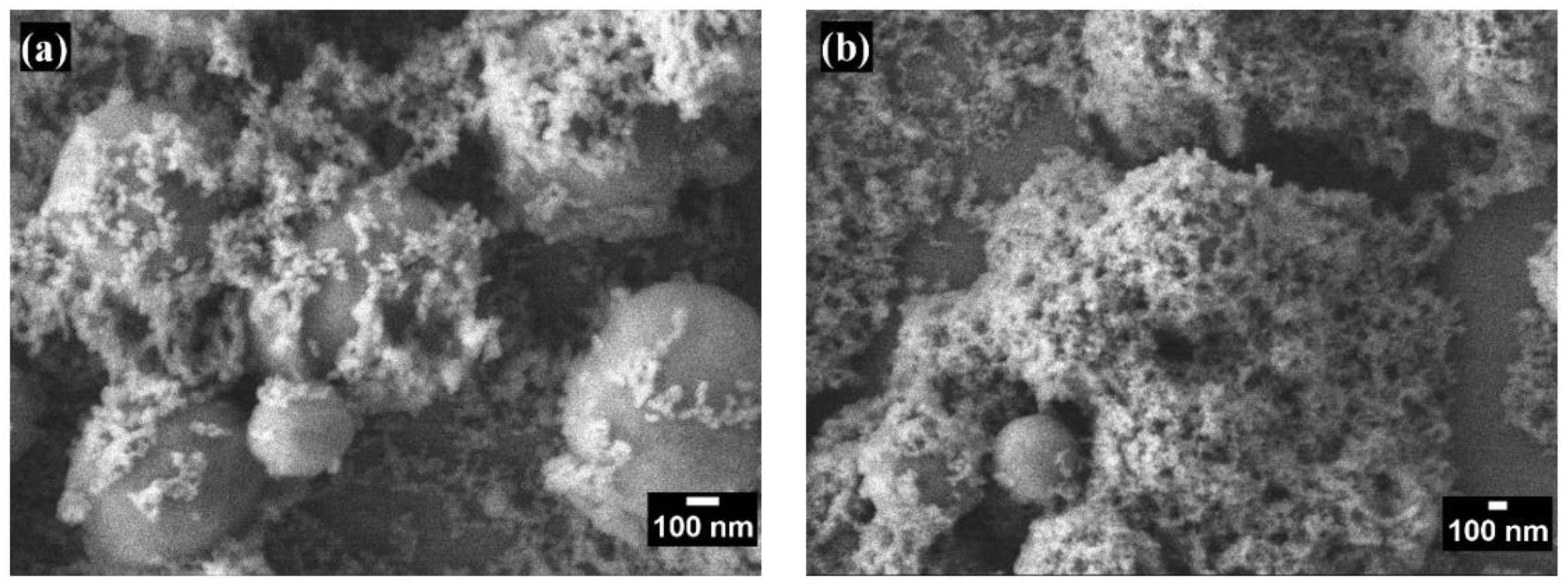
Figure 2 and
Figure 3 show the morphology of the coatings on glass substrates with varying numbers of layers. Scanning electron microscopy observations in both figures reveal surfaces with a hierarchical structure composed of nano- and microscale particles with diameters ranging from 733.5 ± 116.9 nm to 20.046 ± 3.69 nm. This multiscale roughness is advantageous for superhydrophobic coatings, enhancing superhydrophobicity, durability, and self-cleaning properties [
19].
Figure 3 provides a detailed view of the increased porosity corresponding to the increment in coating layers. This enhanced porosity allows for more effective air trapping beneath water droplets, significantly contributing to the surface's superhydrophobic properties.
3.3. TEM
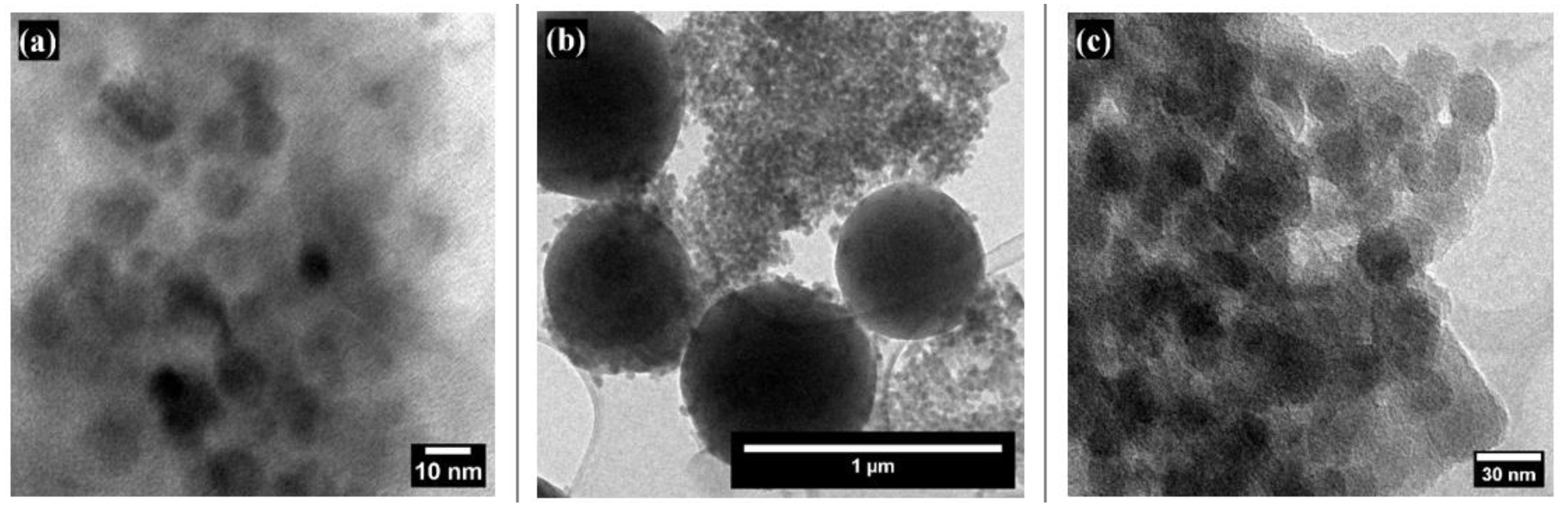
TEM images of the colloids are presented in
Figure 4. Image (a) shows bare SiO
2 NPs, which are spherical, well-dispersed, and relatively uniform, with an average size of 6.309 ± 1.891 nm. In contrast, images (b) and (c) display the superhydrophobic coating at different magnifications. These images reveal a hierarchical structure of the material, confirming the presence of particles at both the micro- and nanoscale with diameters ranging from 658 ± 89.5 nm to 17.49 ± 4.83 nm.
3.4. EDS
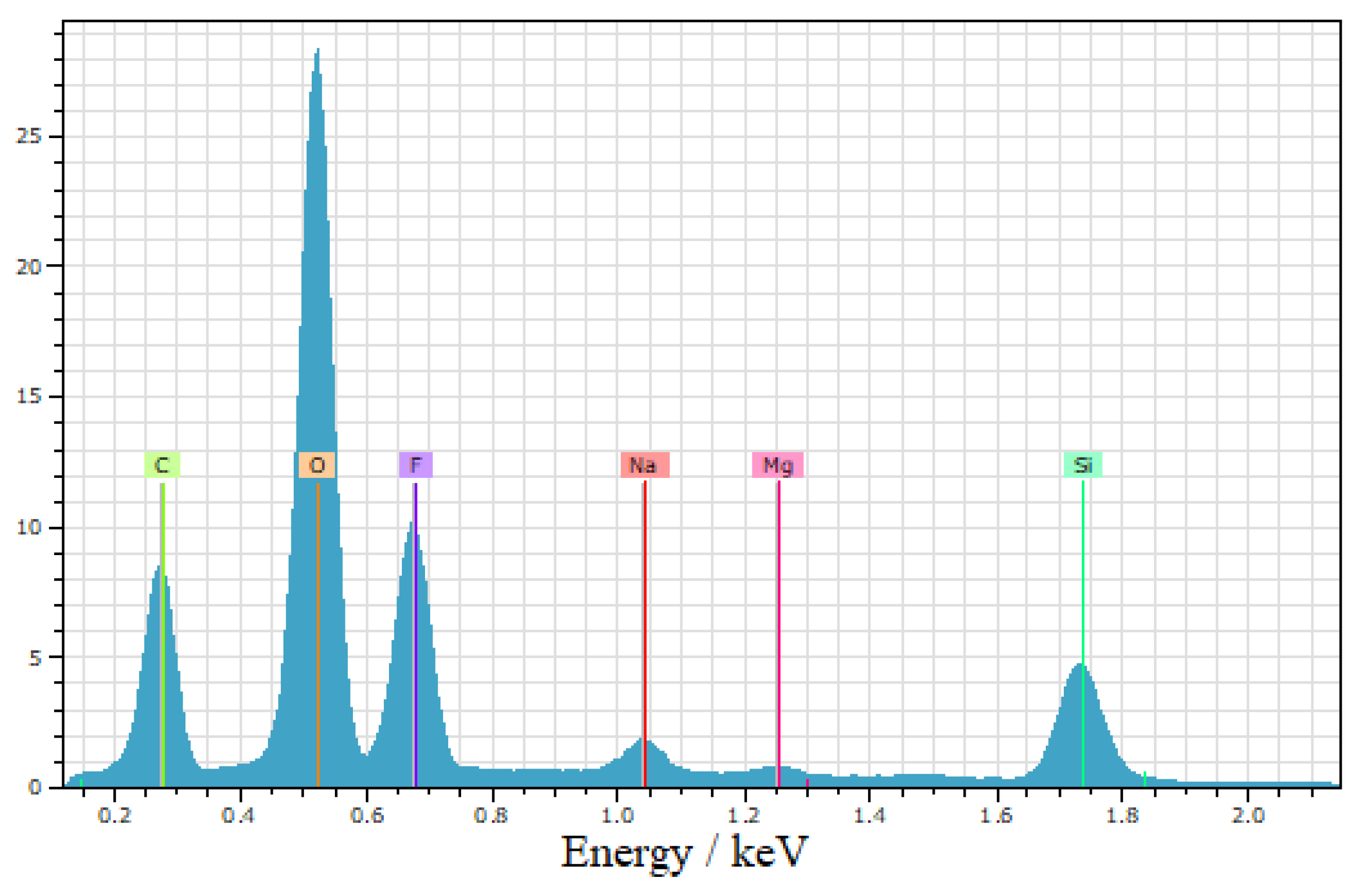
The energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analysis in
Figure 5 confirmed the presence of fluorine and carbon, indicating the successful modification of the nanoparticles with trifluoromethyl (CF
3) groups. These findings verify the incorporation of the desired functional groups on the surface of the silica nanoparticles, thereby supporting the functionalization and effectiveness of the superhydrophobic coating.
3.5. FTIR Spectroscopy
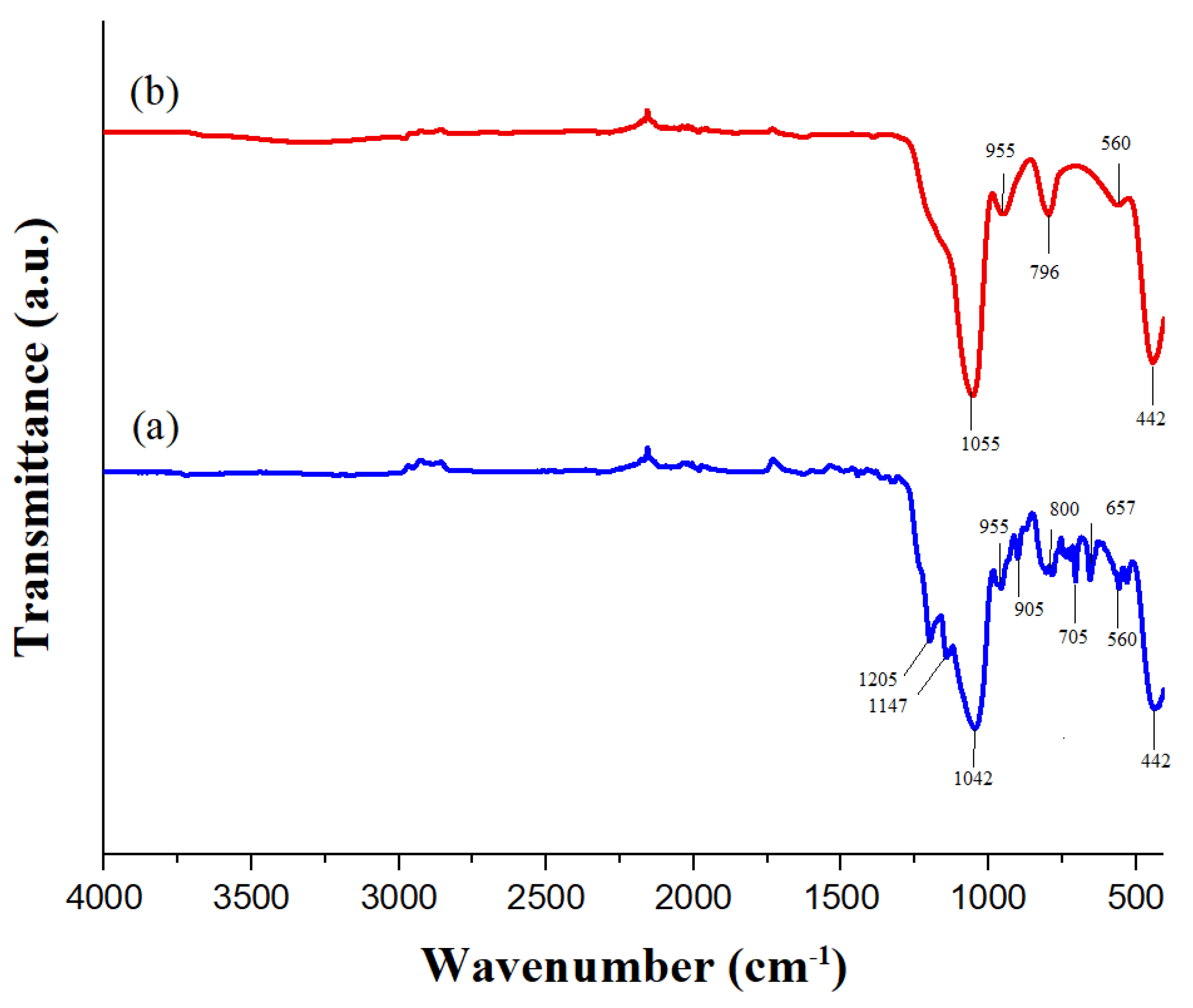
Figure 6 shows the infrared spectra of SiO
2 NPs and the superhydrophobic coating. The infrared spectrum of the SiO
2 NPs exhibits peaks at 1055 cm⁻¹, 955 cm⁻¹, and 796 cm⁻¹, corresponding to the fingerprint region of silica.[
29] Both spectra also display signals at 442 cm⁻¹ and 560 cm⁻¹ attributed to the bending vibrations of O-Si-O, which are typical in amorphous silica.[
30]
The FTIR spectrum of the coating reveals additional peaks, such as those at 1205 cm⁻¹ and 1147 cm⁻¹, which are likely indicative of C-F [
31,
32] they are stretching vibrations. The peak at 1042 cm⁻¹ confirms the presence of SiO
2, while the peaks at 905 cm⁻¹, 800 cm⁻¹, 705 cm⁻¹, and 657 cm⁻¹ are assigned to the symmetric stretching vibrations of Si-O-Si due to functionalization.[
33] These functional groups are essential for ensuring the superhydrophobicity of the nanoparticles and confirming successful nanoparticle functionalization.
3.6. DRX
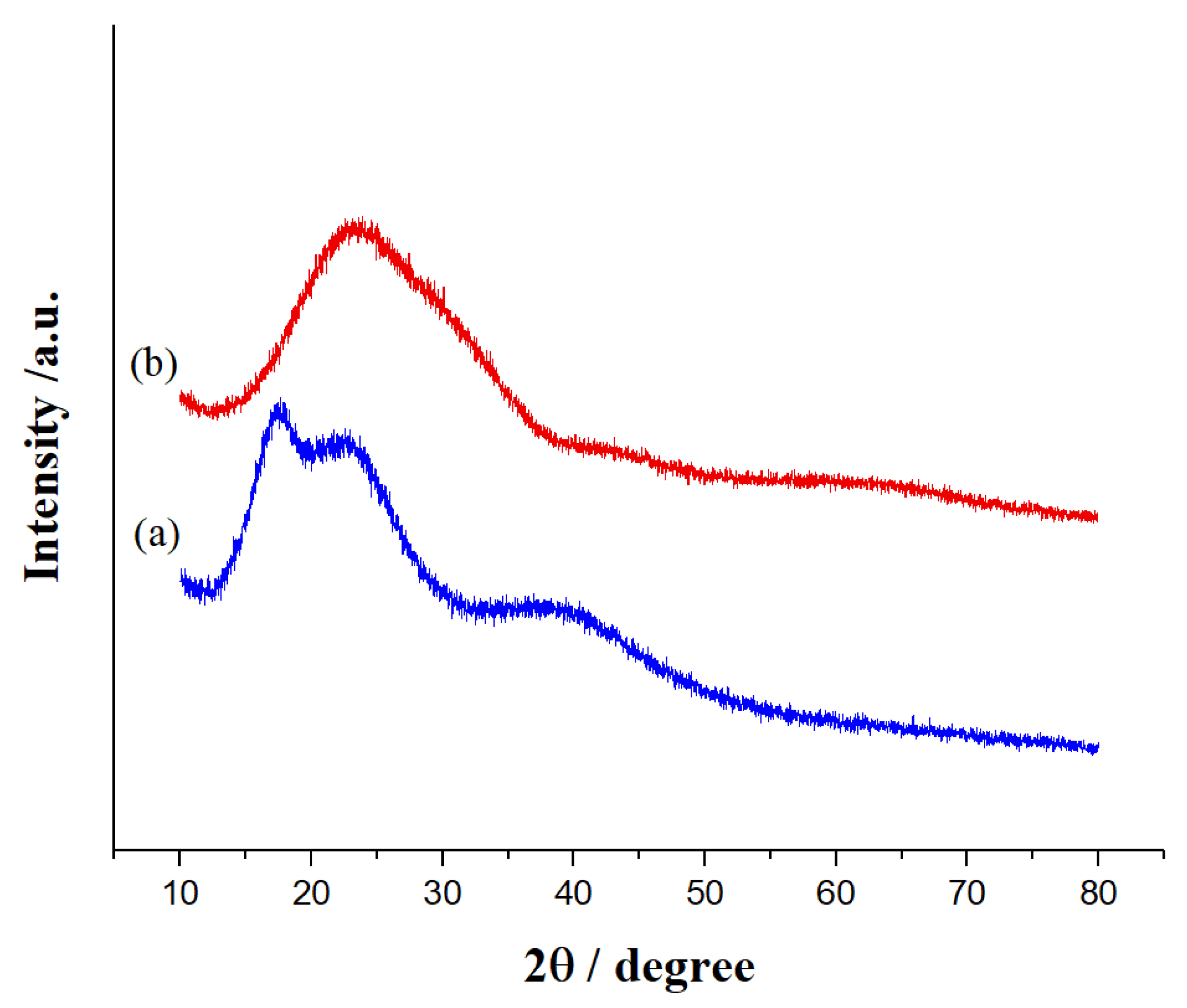
As shown in
Figure 7, the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of the SiO
2 NPs exhibits an amorphous structure consistent with the JCPDS file 00-083-2467. The broad peak observed at a Bragg angle of 2θ = 23.37° is characteristic of amorphous materials, including amorphous silica.[
34]
Post-functionalization, the XRD pattern reveals the persistence of the amorphous nature of SiO
2 along with the emergence of three new peaks at 2θ = 17.67°, 22.72°, and 39.44°. These new peaks suggest the formation of a new crystalline phase or a structural change due to the functionalization process. Such changes can result from compressive or expansive stresses within the material, affecting the diffraction angles. Additionally, introducing C-F groups on the surface of SiO
2 can alter the local atomic environment, leading to variations in peak intensities, the emergence of new peaks, or shifts in existing peaks.[
31]
Furthermore, the hydrophobic nature of the C-F groups can reduce interactions with surrounding water molecules, potentially causing changes in the structure of the nanoparticles. This may lead to potential aggregation or changes in particle morphology.[
35] Furthermore, the hydrophobic nature of the C-F groups can reduce interactions with surrounding water molecules, potentially causing changes in the structure of the nanoparticles. This may lead to potential aggregation or changes in particle morphology.
3.7. Antimicrobial Activity
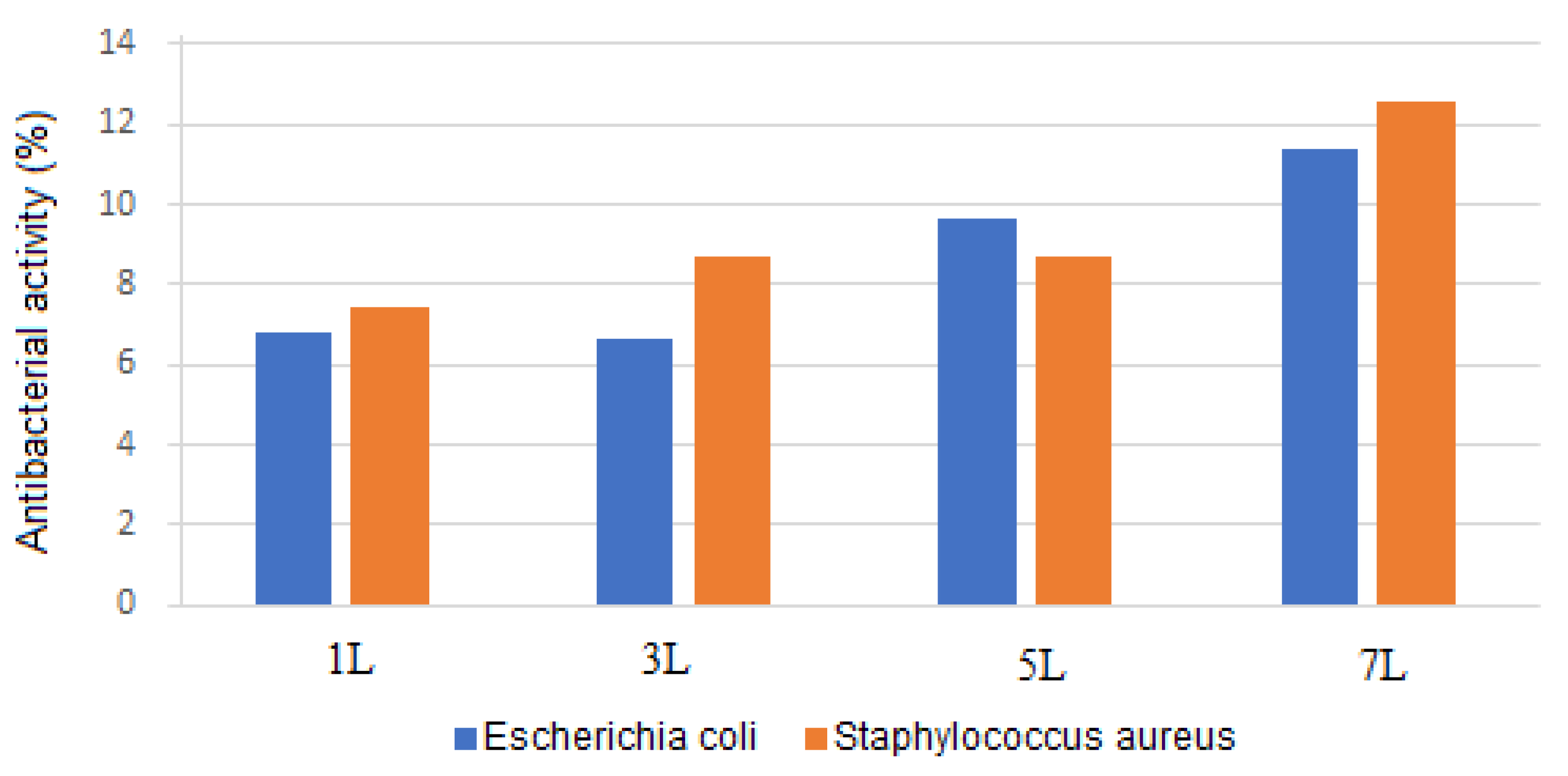
Figure 8 presents the measurement of the antibacterial activity of various samples using the turbidimetry technique. The data show that the percentage of antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus increased with the number of layers, reaching 11.37% and 12.58%, respectively. Escherichia coli, a Gram-negative bacterium, has two membranes. In contrast, Staphylococcus aureus, a Gram-positive bacterium, has a thick cell wall, contributing to its resistance mechanisms against antibacterial substances. Nevertheless, the coating exhibited antibacterial activity against both types of bacteria, with the highest activity observed against Gram-positive bacteria.
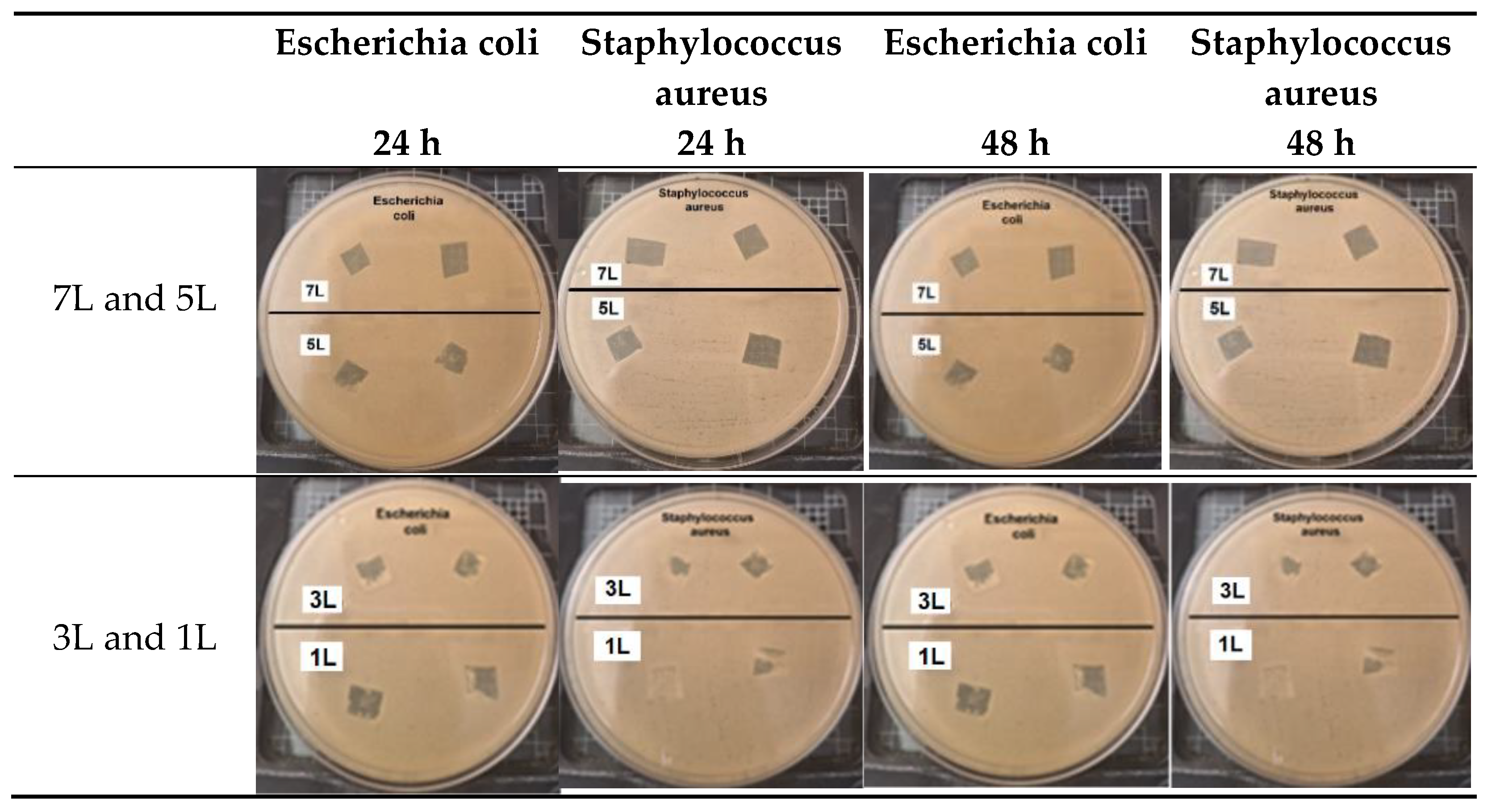
Table 2 presents the results of antibacterial activity measured by the inhibition halo. No inhibition halos were formed in any of the samples. However, the samples exhibited bacteriostatic activity, successfully inhibiting bacterial growth on the coating's surface. This effect is attributed to the coating's ability to interfere with bacterial DNA replication and cellular metabolism [
36]. Notably, samples with seven layers (7L) and five layers (5L) demonstrated higher bacteriostatic activity, indicating that the concentration of the coating layers influences bacteriostatic efficacy.
4. Discussion
The water contact angle (WTC) results presented values from 156 to 159° when the coating was not exposed outdoors. The value increased when the number of layers was bigger. Different research presented results from 125° to 160° when the coating was based on silicones. The values obtained in this research are inside of specs. The increase of WCA when exposed after 35 days is due to the hydrophobic membrane generating a possible chemical polymerization of coating [
16,
21,
22,
24,
28,
33].
The hierarchical structure in our coating helps keep the water droplets in place [
37]. One important point in developing a good hydrophobic coating is to generate hierarchical structures and modify the rough surface. The 35 days of exposure modified the coating roughness, generating a more hydrophobic layer [
38].
Authors have used 1H, 1H, 2H, and 2H-Perfluorodecyltriethoxysilane (PFDTES) with a nano hierarchical structure to suppress the bacteria addition [
38]. The presence of a nano hierarchical structure made it easier to avoid the proliferation of bacteria according to the size of the structure, which was 6.309 ± 1.891 nm and also 658 ± 89.5 nm to 17.49 ± 4.83 nm according to the TEM results [
8,
10,
11,
22,
24,
33,
34,
39,
40,41].
5. Conclusions
The developed superhydrophobic coating has demonstrated significant antibacterial activity, particularly against Gram-positive bacteria. Additionally, all samples exhibited bacteriostatic activity, indicating the coating's effectiveness in inhibiting bacterial growth on the treated surface. The antibacterial activity of the coating was shown to be influenced by the number of layers, with samples containing a higher concentration of layers displaying greater effectiveness.
Morphological and structural characterization revealed a hierarchical structure in the coating with nano- and microscale particles contributing to its roughness and superhydrophobicity, evidenced by contact angles ≥150° and sliding angles ≤10°. The successful functionalization of silica nanoparticles with trifluoromethyl (CF3) groups in the coating confirms the efficacy of the functionalization and the coating's ability to repel water and resist biofilm formation.
These findings suggest that the superhydrophobic coating holds significant promise for applications requiring clean surfaces, resistance to biofilm formation, and effective antibacterial properties.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.S-S, D.C-M, and I.O-A; Methodology, D.C-M and A.V-M; Software, Not applicable; Validation, J.S.A-CA, I.O-A, and D.C-M; Formal analysis, D.C-M.; Investigation, E.A.M-G, J.S.A-C, E.O-C, and J.O.D-R; Resources, E.A.M-G; Data curation, B.S-S, D.C-M; Writing—original draft preparation, B.S-S; Writing—review and editing, J.M.J-M and D. C-M; Visualization, B.S-S; Supervision, I.O-A; Project administration, D.C-M;
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
References
- Privett, B.J.; Youn, J.; Hong, S.A.; Lee, J.; Han, J.; Shin, J.H.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Antibacterial Fluorinated Silica Colloid Superhydrophobic Surfaces. Langmuir 2011, 27, 9597–9601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.G.; Attaway, H.H.; Sharpe, P.A.; John, J.J.; Sepkowitz, K.A.; Morgan, A.; Fairey, S.E.; Singh, S.; Steed, L.L.; Cantey, J.R.; et al. Sustained Reduction of Microbial Burden on Common Hospital Surfaces through Introduction of Copper. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, D.; Taheri, M.; Garg, P.; Webb, D.; Parajuli, P.; Wang, Y.; Funnell, B.; Taylor, B.; Tscharke, D.C.; Tsuzuki, T.; et al. Shielding Surfaces from Viruses and Bacteria with a Multiscale Coating. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarb, P.; Coignard, B.; Griskeviciene, J.; Muller, A.; Vankerckhoven, V.; Weist, K.; Goossens, M.M.; Vaerenberg, S.; Hopkins, S.; Catry, B.; et al. The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) Pilot Point Prevalence Survey of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Use. Eurosurveillance 2012, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, D.; Cheeseman, S.; Wang, Y.; Funnell, B.; Leung, S.F.; Tricoli, A.; Nisbet, D. Superhydrophobic Surfaces to Combat Bacterial Surface Colonization. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlan, R.M. Biofilms: Microbial Life on Surfaces. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokare, C.R.; Chakraborty, S.; Khopade, A.N.; Mahadik, K.R. Biofilm: Importance and Applications. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, P.S.; Costerton, J.W. Antibiotic Resistance of Bacteria in Biofilms. Lancet 2001, 358, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, K. Mechanisms of Bacterial Biocide and Antibiotic Resistance. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 55S–64S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Levänen, E. Superhydrophobic Surfaces for the Reduction of Bacterial Adhesion. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12003–12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falde, E.J.; Yohe, S.T.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Superhydrophobic Materials for Biomedical Applications. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendjchi, A.; Khajavi, R.; Yazdanshenas, M.E. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic and Antibacterial Surface on Cotton Fabric by Doped Silica-Based Sols with Nanoparticles of Copper. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crick, C.R.; Ismail, S.; Pratten, J.; Parkin, I.P. An Investigation into Bacterial Attachment to an Elastomeric Superhydrophobic Surface Prepared via Aerosol Assisted Deposition. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 3722–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A. Superhydrophobicity Fundamentals: Implications to Biofouling Prevention. Biofouling 2006, 22, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciasca, G.; Papi, M.; Businaro, L.; Campi, G.; Ortolani, M.; Palmieri, V.; Cedola, A.; De Ninno, A.; Gerardino, A.; Maulucci, G.; et al. Recent Advances in Superhydrophobic Surfaces and Their Relevance to Biology and Medicine. Bioinspiration and Biomimetics 2016, 11, 11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbil, H.Y. Practical Applications of Superhydrophobic Materials and Coatings: Problems and Perspectives. Langmuir 2020, 36, 2493–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreekantan, S.; Hassan, M.; Murthe, S.S.; Seeni, A. Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity Study of Polydimethylsiloxane (Pdms) and Palm Oil Fuel Ash (Pofa) Sustainable Super-Hydrophobic Coating for Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadik, S.A.; Pedraza, F.; Mahadik, S.S.; Relekar, B.P.; Thorat, S.S. Biocompatible Superhydrophobic Coating Material for Biomedical Applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.L.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L. Superhydrophobic Surfaces: From Natural to Artificial. Adv. Mater. 2002, 1857–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Geng, M.; Dong, B.; Zhao, L.; Wang, S. Transparent and Robust SiO2/PDMS Composite Coatings with Self-Cleaning. Surf. Eng. 2020, 36, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huo, M.; Huo, J.; Zhan, P.; Shao, X.; Zhang, X. Preparation of Silica-Epoxy Superhydrophobic Coating with Mechanical Stability and Multifunctional Performance via One-Step Approach. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 653, 129957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.; Liu, W.; Wang, K.; Rao, Y.; Jiang, C.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Ultrasonic Assisted Rapid Preparation of Superhydrophobic Stainless Steel Surface and Its Application in Oil/Water Separation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 81, 105848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, H. Constructing Fluorine-Free and Cost-Effective Superhydrophobic Surface with Normal-Alcohol-Modified Hydrophobic SiO(2) Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M.; Thomas, S.; Sreedharan, M. Micro Nano Bio Aspects Modification of Silica Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Activities: Mechanism of Action. Micro Nano Bio Asp. 2022, 2022, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Pi, J.; Song, F.; Feng, R.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z. A Superhydrophobic Coating to Create Multi-Functional Materials with Mechanical/Chemical/Physical Robustness. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 381, 122539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Shi, X.; Bai, W.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L. Enhanced Durability and Versatile Superhydrophobic Coatings via Facile One-Step Spraying Technique. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 640, 128411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Wang, L. Preparation of Durable Superhydrophobic Coatings Based on Discrete Adhesives. Coatings 2024, 14, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled Growth of Monodisperse Silica Spheres in the Micron Size Range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, B.H. Infrared Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications. Infrared Spectrosc. Fundam. Appl. 2005, 8, 1–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravlev, L.T. The Surface Chemistry of Amorphous Silica. Zhuravlev Model. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 173, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-Inspired Surface Chemistry for Multifunctional Coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Suk, J.W.; Potts, J.R.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene and Graphene Oxide: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of Infrared Spectra, A Practical Approach. Encycl. Anal. Chem. 2000, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musić, S.; Filipović-Vinceković, N.; Sekovanić, L. Precipitation of Amorphous SiO2 Particles and Their Properties. Brazilian J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 28, 89–94, B.D. & Stock, S.R.C. Elements of X-Ray Diffraction; 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Ganguly, S.; Bose, M.; Mondal, S.; Choudhary, S.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Das, A.K.; Banerjee, S.; Das, N.C. Zinc and Nitrogen Ornamented Bluish White Luminescent Carbon Dots for Engrossing Bacteriostatic Activity and Fenton Based Bio-Sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 88, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Xing, Q.; Chen, Z.; Jin, M.; Xing, Q.; Chen, Z. A Review: Natural Superhydrophobic Surfaces and Applications. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 11, 110–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Cui, Z.; Ge, F.; Man, C.; Lei, L.; Wang, X. Fabrication of Durable and Roughness-Regeneration Superhydrophobic Composite Materials by Hot Pressing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 179, 107431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.K.; Farzaneh, M.; Paynter, R.W. Superhydrophobic Properties of Ultrathin Rf-Sputtered Teflon Films Coated Etched Aluminum Surfaces. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 1226–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Kharraz, J.A.; Choi, P.J.; Guo, J.; Deka, B.J.; An, A.K. Superhydrophobic Membrane by Hierarchically Structured PDMS-POSS Electrospray Coating with Cauliflower-Shaped Beads for Enhanced MD Performance. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 597, 117638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Li, X. Fabrication of TiO2/SiO2 Superhydrophobic Coating for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).