1. Introduction
Acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is amongst the leading causes of death worldwide with a permanently high mortality rate despite high quality treatment on stroke-wards [
1]. According to 2023 data, it could reach 10% in the first 30 days and up to 40% by the end of the year [
2]. Intravenous thrombolysis significantly increases the rate of good functional outcome in acute ischemic stroke, but still, a considerable proportion of patients undergoing thrombolysis won’t survive [
3]. The rate of body and brain autopsies is decreasing worldwide, even though only autopsies can clarify the real frequencies of complications leading to death, undiagnosed tumors in the clinical phase, thromboembolic events and so on [
4]. According to the retrospective analysis of 1112 patients, cardiovascular diseases notably influence disparities between ante- and post-mortem diagnoses (61,7%), underlying the importance of autopsy [
5]. As no observation carried out on high number of previously thrombolysed, deceased patients undergoing body and brain autopsy is available in the literature, we aimed to investigate the clinical and pathological data of our lost patients undergoing intravenous thrombolysis and autopsy. We aimed to find answers to the following:
- 1./
The frequency of hemorrhagic transformation (HT) observed in the autopsies of thrombolysed AIS patients.
- 2./
The link between HT and thrombolysis treatment (i.e. whether HT develops within a day after the treatment or later)
- 3./
The postmortem clinical differences between HT positive and HT negative patients
- 4./
Whether the direct causes of death can be attributed to HT (such as herniation) or to a complication (such as pneumonia).
- 5./
Potential predictive markers of HT (clinical or laboratory parameters) at admission of patients
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
We involved patients undergoing intravenous thrombolysis at the Department of Neurology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Debrecen between 2007-2017 (neither thrombectomy not intraarterial thrombolysis was carried out in patients). 1426 intravenous thrombolysis were performed in this time period. Thrombolysis was carried out according to the protocol of the American Stroke Association (ASA) and European Stroke Initiative [
6], and the European Stroke Organisation (ESO)[
7]. Briefly: patients arriving within the 3 and 4.5 hours time window complying to the ASA and European criteria were directly transferred to the CT laboratory. Following the CT and neurological examination, blood sampling was performed and the 1-hour rt-PA infusion was administered according to the protocol. No antithrombotic treatment was initiated within 24 hours after the thrombolysis, when a control cranial CT was performed to exclude HT. The presence or absence of intracranial bleeding was confirmed by a neuroradiologist (HT positive and HT negative group). Patients after the thrombolysis were transferred to the stroke ward where multiparametric monitoring (blood pressure, blood oxygen saturation, transcranial ultrasound, arterial blood gas and so on) was carried out. Patients received antipyretics, antibiotics and antithrombotics (deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis) if needed. The average time of hospitalization was 16,71±16,36 days at our department before death. The in-hospital mortality of the 1426 patients who underwent intravenous thrombolysis was 11.7%. We had the chance to compare the body and brain autopsy results with the clinical data in 98 cases (59%) out of the 167 deceased patients (
Figure 1). The body autopsy was carried out the following day after death, brain autopsy took place after one week formalin fixation of the brain. The latter was performed by a neuropathologist. Although HT is divided into further subgroups by previous reports [
8], we did not use this grouping for the evaluation of either the cranial CT scans or the autopsy results [
9]. Irrespective of the size of the bleeding, its presence was considered as HT. We consider both small parenchymal and large confluent hemorrhages to hold back the initiation of a potential antithrombotic treatment, promote complications and poor outcome.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Stata v13 software, the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS, Version 26.0, Chicago, IL), and GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad Prism Inc., La Jolla, CA). Normality of data was studied using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Student’s t test or Mann–Whitney U test was performed for independent two-group analyses. Differences between categorical variables were assessed by χ2 test or by Fisher’s exact where appropriate. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were built by plotting sensitivity vs. 1-specificity and calculating the area under the curve (AUC). Youden’s J statistics were used to calculated optimal threshold values. Sensitivity, specificity, positive (PPV), and negative predictive values (NPV) were calculated using contingency tables and χ2 test or Fisher’s exact at statistically optimal threshold values. Binary backward logistic regression models were used to determine independent predictors of HT in the studied cohort. Adjustments of the models were based on the results of univariate statistical analyses of baseline characteristics between groups. Results of the logistic regression analysis were expressed as odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics and Cause of Death Detected in Autopsied Stroke Cases with or without HT
In a ten-year period between 2007-2017, 1426 AIS patients received intravenous thrombolysis in our center. The in-hospital mortality of these patients was 11.7 % (n=167 patients). More than half of these patients had an autopsy at our center, which gave us the opportunity to analyze 98 cases. HT was found in nearly half of the cases (47%, 46 HT positive vs. 52 HT negative cases) (
Table 1). Interestingly, less than half of HT cases occurred within a day after thrombolysis (42%), while the majority of HT events developed later, between day 1 and the event of death.
The direct causes of death in these cases were frequently attributed to the HT event itself or its consequences. Based on the results of body and brain autopsy, a direct CNS complication, herniation was responsible for the death in 29 cases (30% of the total cohort, a borderline tendency for being more frequent in the HT positive group), while pneumonia, pulmonary embolism and cardiorespiratory failure were the causes of death in the remaining cases. Two cases of malignant cancers were discovered (pancreatic adenocarcinoma, neuroendocrine tumor) during the autopsies that had not been diagnosed previously due to subtle symptoms only.
The investigated baseline clinical and laboratory parameters in the HT positive and HT negative cases are presented in
Table 2. Interestingly, only few clinical and laboratory parameters showed difference between the two groups at admission. HT positive patients had significantly higher lactate dehydrogenase (LD) levels at admission as compared to HT negative patients (median: 272, IQR: 217-444 vs. 204, IQR: 176-264 U/L, p: 0.0011). In addition, significantly lower platelet count was observed in HT positive vs. HT negative patients before thrombolysis (median: 184, IQR: 150-227 vs. 223, IQR: 171-264 G/L, p: 0.0106), together with significantly longer prothrombin time (PT) and higher INR values (median: 1.1, IQR: 0.9-1.1 vs. 0.9, IQR: 0.9-1.0, p: 0.0429).
We investigated whether the antithrombotic treatment used before and after the onset of ischemic stroke influenced the risk of hemorrhagic transformation of the developing ischemic lesion. Concerning the use of different antithrombotic therapy combinations before thrombolysis (antiplatelets and/or anticoagulants), no significant difference was observed between the HT positive and HT negative group (2 test: p:0.089), but it is to be noted that a hemorrhagic tendency was present among those anticoagulated. After the event of stroke, no significant difference was observed between the group receiving therapeutic or prophylactic anticoagulant therapy in terms of HT rates (p=0.808). However, it is important to note of the 98 cases included, HT had been already clinically detected in 20 cases on day 1, therefore more patients received prophylactic anticoagulants for DVT prophylaxis in the HT negative group. Looking separately at the 26 cases (treated as pure ischemic lesions during clinical course) with clinically not recognized HT at brain autopsy compared to the 52 cases without bleeding at brain autopsy, there was no significant association between antithrombotic therapy and bleeding (2 test p=0.945).
3.2. Independent Predictors of HT in the Studied Autopsied Cohort
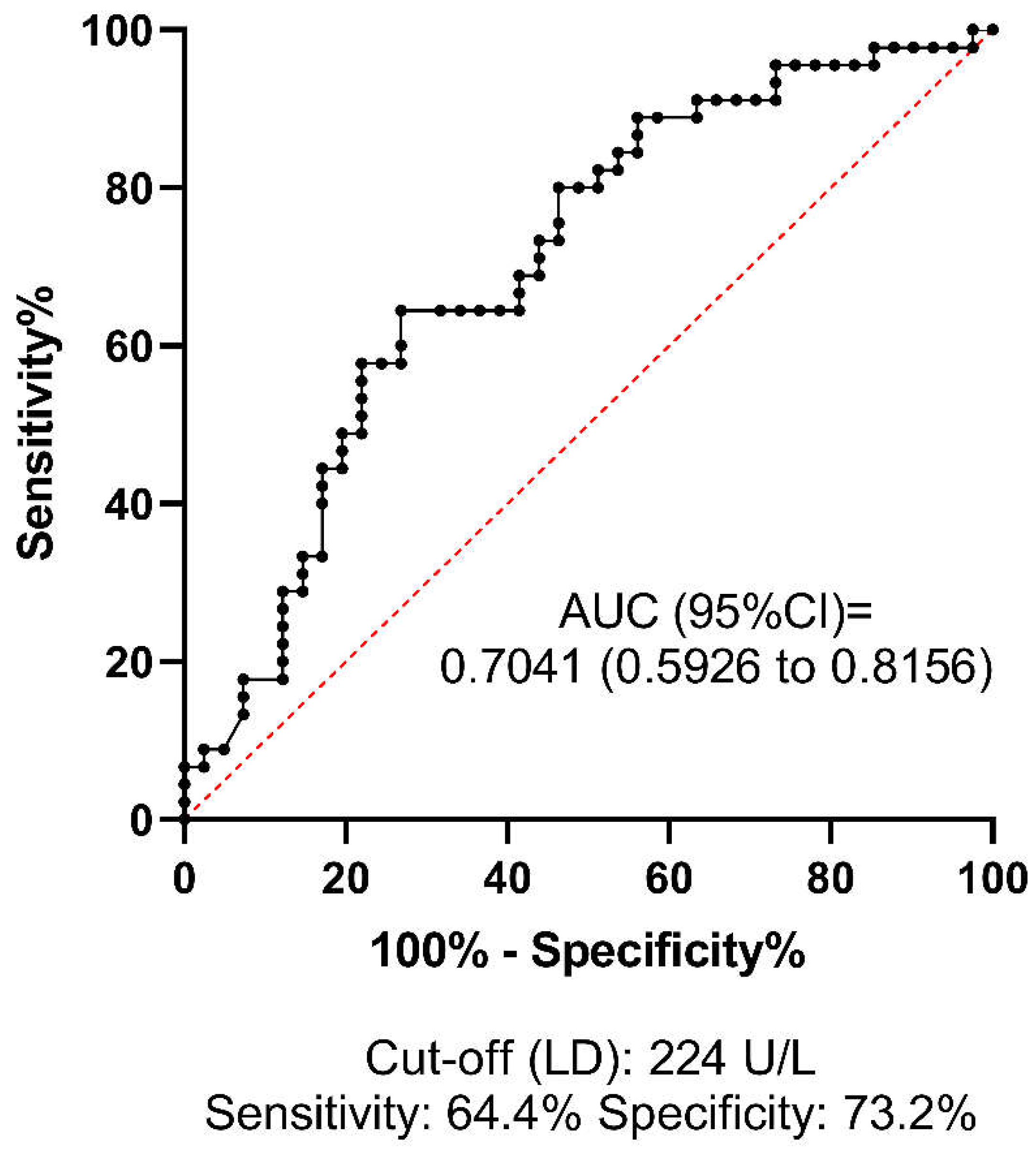
ROC analysis was performed to investigate the predictive value and diagnostic efficacy of all baseline test parameters that differed significantly between groups according to univariate statistical analyses. The best AUC of ROC for predicting HT was 0.7041 (95%CI: 0.5926-0.8156) for LD, at the optimal statistical threshold of 224 U/L (sensitivity: 64.4%, specificity: 73%) (
Figure 2). The AUC of ROC for platelet count was 0.6579 (95%CI: 0.5437-0.7720), at the optimal statistical threshold of 196 G/L (sensitivity: 66.6%, specificity: 65.1%) (
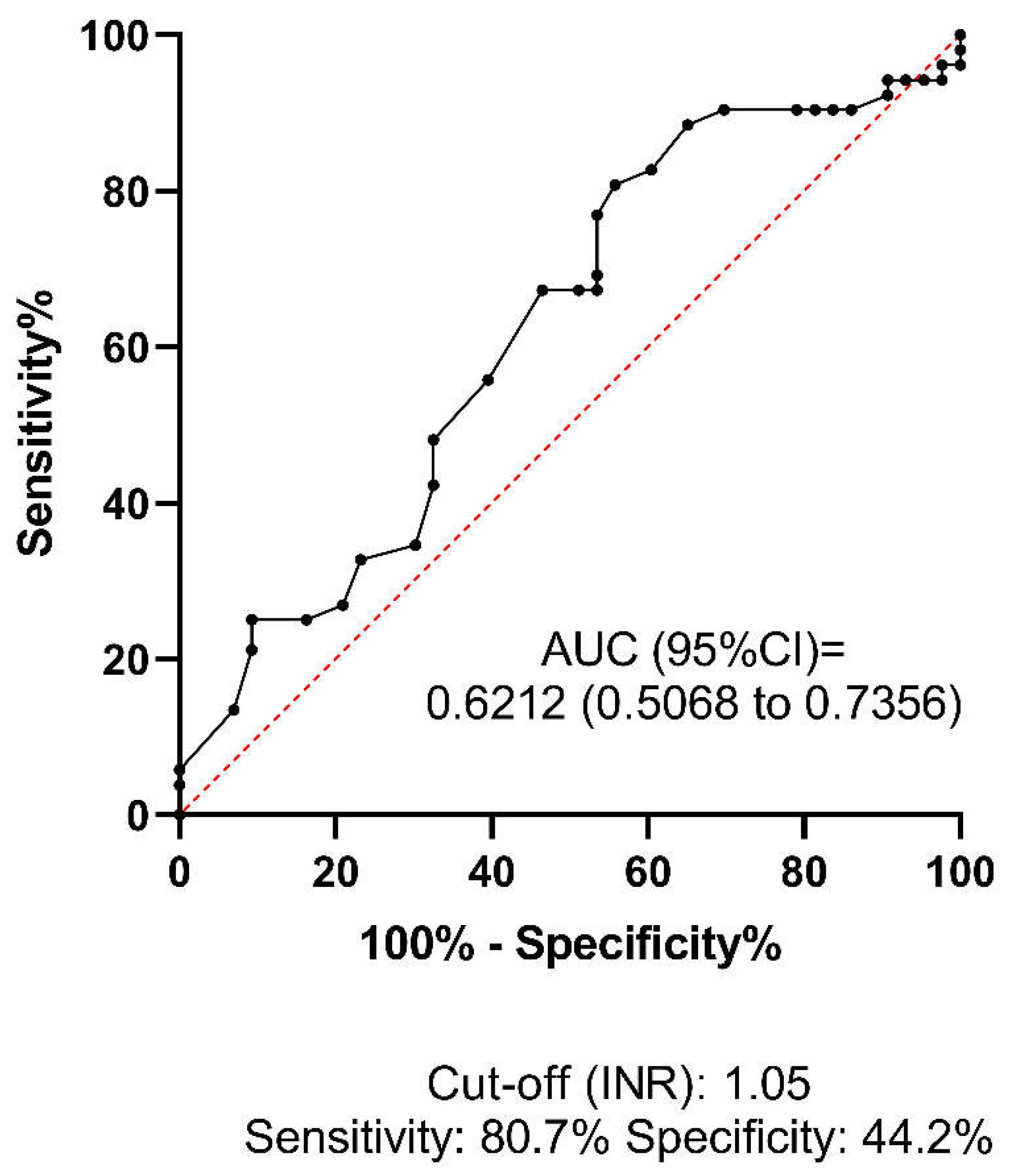
Figure 3). This result suggests that a relatively low platelet count (<196 G/L), despite being within the reference range (150-400 G/L), may increase the risk of HT in AIS patients receiving thrombolysis. Based on the optimal threshold value as defined by the Youden index (INR: 1.05), the best sensitivity was provided by the INR parameter (80.7%,
Figure 4), although the low AUC value suggests poor overall test performance.
Using a binary backward logistic regression model (including age, sex, NIHSS on admission, hypertension, INR≥1.05, LD≥224 U/L, platelet count≥196 G/L, ASAT, ALT, GGT, creatine kinase, hsCRP, creatinine), only LD and INR remained as significant, independent predictors of HT in the studied autopsied cohort (OR: 4.68, 95%CI: 1.57-14.00, p=0.006 and OR: 6.23, 95%CI: 1.55-25.13, p=0.010, respectively,
Table 3).
Last step of backward multiple regression analysis is provided. Backward multiple regression model included age, sex, NIHSS on admission, INR≥1.05, LD≥224 U/L, platelet count≥196 G/L, ASAT, ALT, GGT, creatine kinase, hsCRP, creatinine.
95%CI, 95% confidence interval; INR, International normalised ratio; LD, Lactate dehydrogenase; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; OR, odds ratio.
4. Discussion
HT is a (symptomatic or asymptomatic) complication in case of acute ischemic stroke, that may occur spontaneously but can be a considerable consequence of intravenous thrombolysis. According to Jensen et al. intravenous thrombolysis approximately doubled the frequency of HT (HR: 2.08 [95% CI, 1.28–3.40]) [
10]. Pande et al. followed the frequency of hemorrhagic complications in thrombolysed patients by imaging techniques and found it to be 36.6% [
11]. In the ECASS II study (thrombolysed patients) the rate of hemorrhagic transformation was 35.6% [
12].The actual frequency of HT in the above mentioned studies was probably even higher as justification of HT was based on the results of the 24-hour control and a further cranial CT performed only in case of clinical deterioration. Therefore, in asymptomatic HT patients – unless a second cranial CT scan was done for any reason – the hemorrhagic complication remained unnoticed. However, brain autopsy of the patients suffering from ischemic stroke provides reliable information on the actual frequency of hemorrhagic transformation. Our working group had previously investigated the brain autopsy results of ischemic stroke patients who did not undergo intravenous thrombolysis, and the rate of hemorrhagic transformation was 29-38% [4, 13, 14]. Rt-PA has been shown to disrupt blood and brain barrier (BBB) integrity via several ways, including LDL receptor-related protein (LRP) expression on the endothelial cells, microglia, and astrocytes [
15], increasing plasma kallikrein [
16] and platelet-derived growth factor-CC (PDGF-CC) activation [
17]. Shi et al. demonstrated that rt-PA also mobilizes immune cells exacerbating HT after ischemic stroke [
18].
In our current study the frequency of HT was only 20% on the control cranial CT performed 24 hours after the intravenous thrombolysis, while it was 47% based on the brain autopsy of the same patient group. The 20% of HT detected on the first day does not significantly differ from the observation the co-workers of the ECASS-I study made: they found some kind of HT in 48 cases out of 264 acute ischemic (not thrombolysed) stroke patients (18%) [
8]. According to a recent multicenter retrospective study (32375 patients) the rate of symptomatic and asymptomatic intracranial hemorrhage after intravenous thrombolysis is 17.5% (95% CI, 17.0-18.0) [
19]. The meta-analysis of Honig et al systematically reviewed the incidence, predictors, and outcomes of hemorrhagic transformation (HT) in 65 studies with 17,259 patients with acute ischemic stroke using ECASS-II criteria [
20]. The overall prevalence of HT was 27%, with 32% occurring in patients receiving IV-tPA compared to 20% in those who did not receive it. This result is particularly important because HT increased the chance of unfavorable 90-day outcome (mRS 5-6), regardless of the type of hemorrhage (HI or PH).
Our observation is that the 20% HT-rate 24 hours after thrombolysis increased to 47% upon brain autopsy, which cannot be attributed either to the immediate action of rt-PA (half-life is 4-6 minutes) or to the prolonged activation of the plasminogen-plasmin system, which can last several hours. [21, 22]. Therefore, other factors also play an important role in the development of HT between the 24-hour control cranial CT and death. According to our results, low platelet count and prolonged PT are factors provoking HT and unfavorable clinical outcome. Our statements are supported by other researchers as well, for example Cheng et al. reported that low platelet levels were independently associated with HT in non-AF patients [
23]. Domingo et al. found that patients with low platelet counts had increased mortality compared with patients with normal platelet counts following desobliteration for large vessel occlusion [
24]. Mustanoja at el. investigated 636 young patients (median age was 42.9 year) and found no significant correlation with gender, age, prehospital oral anticoagulant, antiplatelet or statin therapy and blood glucose level upon admission but the probability of HT increased with – among others – low platelet count [
25]. Prodan et al. reported that the lower levels of coated-platelets are associated with the presence of early HT in patients with non-lacunar ischemic stroke [
26]. On the other hand, using a binary backward regression model, only LD and INR remained in the statistical model as independent predictors of HT- which reflects that although the balance of hemostasis is most likely an important contributor to HT occurrence, other potential contributing factors might play key roles.
As – according to our observation – the vast majority of the HT develops between the 24-hour control cranial CT and death, we suggest performing a further cranial CT before discharging the patient independent of their neurological status to exclude HT as its presence may influence the initiation of an antithrombotic or antiplatelet therapy. The current European guideline does not contain strong recommendation concerning the regular checking of platelet count in case of acute ischemic stroke or after thrombolysis. However, our findings suggest the importance of decreased platelet count to be even higher than previously thought. Platelet count is to be checked more often after thrombolysis and medications decreasing it should be avoided. Multicenter prospective studies can verify our suggestions.
Two malignant tumors were detected upon body autopsy, that remained unnoticed during the clinical phase due to lack of symptoms. Systemic tumors can provoke cerebral ischemia by affecting/influencing the coagulation cascade. According to previous observations, 3%–5% of patients were diagnosed with a malignancy after suffering an ischemic stroke [
27]. The most common tumors in patients who had a stroke are lung, gastrointestinal and breast tumors [
28].
Thrombolytic therapy can provoke not only space occupying HT but also malignant brain edema and herniation, leading to death [
29]. According to our observations HT was the direct cause of death only in 30% of the patients (via herniation), the rest of our patients were lost due to other complications, mainly pneumonia. The considerable role of pneumonia as a cause of death is supported by the observations of Katzan et al., who investigated more than 11.000 acute ischemic stroke patients and found that pneumonia conferred a threefold increased risk of 30-day death [
30]. According to an American study, 47% of critically ill patients who had a stroke developed pneumonia [
31].
Similarly to all retrospective clinical investigations, results of this study should be interpreted in the context of its strengths and limitations. A major limitation of the study is that it was restricted to a single center, which limited sample size, however this assured unified patient care and autopsy practices. A second limitation is that 41% of the deceased patients did not undergo autopsy in our center on the basis of the request of the relatives. The data was collected over a 10-year period (2007-2017) in which the study focused exclusively on patients who received intravenous thrombolysis, excluding those who underwent thrombectomy or intra-arterial thrombolysis. Changes in stroke management protocols, thrombolysis techniques, and supportive care over this period might have influenced the outcomes, making it difficult to attribute findings to a consistent treatment approach. Lastly, the study did not perform a detailed subgroup analysis based on the severity or subtypes of hemorrhagic transformation. Grouping all types of HT together might have masked specific factors relevant to different HT subtypes.
5. Conclusions
Our results highlight the importance of postmortem investigations as the results of the autopsies of our patients confirm the high rate of HT after intravenous thrombolysis. Our data indicate that the development of HT can only be attributed to the acute effect of rt-PA in a small number of cases, while in the vast majority of HT cases, other contributing factors (low platelet count, prolonged PT) may be important. According to our observations made by brain autopsies, only 30% of mortality is caused directly by HT (via herniation), 70% of the patients died of other complications. Of the routinely assessed clinical and laboratory parameters at admission only LD and INR were found to be independent predictors of HT in the autopsied studied cohort.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.C., L.O., and L.H.; methodology, L.C., L.O., and L.H.; data curation and preparation, L.H., V.B., Z.F., B.B. and B.P-K.; statistical analysis, A.N., Z.B. and I.S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.H. L.C., L.L. P., H.P-P., K.B.K., R.O-K. and L.O.; writing—review and editing, Z.B., I.S., L.H.; L.C. and L.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported by the MTA-DE Lendület “Momentum” Hemostasis and Stroke Research Group of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Hungarian Research Network (HUN-REN-DE), the Lendület and OTKA Bridging Fund of the University of Debrecen. H.P. is supported by National Academy of Scientist Education program.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by University of Debrecen Ethics Committee permission (no. H.0265–2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Not required.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon reasonable request. All data relevant to the study are included in the article. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, L.C. (University of Debrecen Faculty of Medicine Department of Neurology, csiba@med.unideb.hu), upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Collaborators GBDS. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(10):795-820. Epub 20210903. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moraes MA, Jesus PAP, Muniz LS, Costa GA, Pereira LV, Nascimento LM, et al. Ischemic stroke mortality and time for hospital arrival: analysis of the first 90 days. Rev Esc Enferm USP. 2023;57:e20220309. Epub 20230414. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, von Kummer R, Davalos A, Meier D, et al. Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of thrombolytic therapy with intravenous alteplase in acute ischaemic stroke (ECASS II). Second European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study Investigators. Lancet. 1998;352(9136):1245-51. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudak L, Nagy AC, Molnar S, Mehes G, Nagy KE, Olah L, et al. Discrepancies between clinical and autopsy findings in patients who had an acute stroke. Stroke Vasc Neurol. 2022;7(3):215-21. Epub 20220131. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kurz SD, Sido V, Herbst H, Ulm B, Salkic E, Ruschinski TM, et al. Discrepancies between clinical diagnosis and hospital autopsy: A comparative retrospective analysis of 1,112 cases. PLoS One. 2021;16(8):e0255490. Epub 20210813. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Klijn CJ, Hankey GJ, American Stroke A, European Stroke I. Management of acute ischaemic stroke: new guidelines from the American Stroke Association and European Stroke Initiative. Lancet Neurol. 2003;2(11):698-701. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Stroke Organisation Executive C, Committee ESOW. Guidelines for management of ischaemic stroke and transient ischaemic attack 2008. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008;25(5):457-507. Epub 20080506. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorelli M, Bastianello S, von Kummer R, del Zoppo GJ, Larrue V, Lesaffre E, et al. Hemorrhagic transformation within 36 hours of a cerebral infarct: relationships with early clinical deterioration and 3-month outcome in the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study I (ECASS I) cohort. Stroke. 1999;30(11):2280-4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harker P, Aziz YN, Vranic J, Chulluncuy-Rivas R, Previtera M, Yaghi S, et al. Asymptomatic Intracerebral Hemorrhage Following Endovascular Stroke Therapy Is Not Benign: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024;13(4):e031749. Epub 20240213. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jensen M, Schlemm E, Cheng B, Lettow I, Quandt F, Boutitie F, et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcome of Patients With Hemorrhagic Transformation After Intravenous Thrombolysis in the WAKE-UP Trial. Front Neurol. 2020;11:957. Epub 20200828. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pande SD, Win MM, Khine AA, Zaw EM, Manoharraj N, Lolong L, et al. Haemorrhagic transformation following ischaemic stroke: A retrospective study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):5319. Epub 20200324. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Larrue V, von Kummer RR, Muller A, Bluhmki E. Risk factors for severe hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke patients treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator: a secondary analysis of the European-Australasian Acute Stroke Study (ECASS II). Stroke. 2001;32(2):438-41. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szepesi R, Csokonay A, Murnyak B, Kouhsari MC, Hofgart G, Csiba L, et al. Haemorrhagic transformation in ischaemic stroke is more frequent than clinically suspected - A neuropathological study. J Neurol Sci. 2016;368:4-10. Epub 20160625. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerenyi L, Kardos L, Szasz J, Szatmari S, Bereczki D, Hegedus K, et al. Factors influencing hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke: a clinicopathological comparison. Eur J Neurol. 2006;13(11):1251-5. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yepes M, Sandkvist M, Moore EG, Bugge TH, Strickland DK, Lawrence DA. Tissue-type plasminogen activator induces opening of the blood-brain barrier via the LDL receptor-related protein. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(10):1533-40. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Simao F, Ustunkaya T, Clermont AC, Feener EP. Plasma kallikrein mediates brain hemorrhage and edema caused by tissue plasminogen activator therapy in mice after stroke. Blood. 2017;129(16):2280-90. Epub 20170127. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Su EJ, Fredriksson L, Geyer M, Folestad E, Cale J, Andrae J, et al. Activation of PDGF-CC by tissue plasminogen activator impairs blood-brain barrier integrity during ischemic stroke. Nat Med. 2008;14(7):731-7. Epub 20080622. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shi K, Zou M, Jia DM, Shi S, Yang X, Liu Q, et al. tPA Mobilizes Immune Cells That Exacerbate Hemorrhagic Transformation in Stroke. Circ Res. 2021;128(1):62-75. Epub 20201019. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinel TR, Wilson D, Gensicke H, Scheitz JF, Ringleb P, Goganau I, et al. Intravenous Thrombolysis in Patients With Ischemic Stroke and Recent Ingestion of Direct Oral Anticoagulants. JAMA Neurol. 2023;80(3):233-43. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Honig A, Percy J, Sepehry AA, Gomez AG, Field TS, Benavente OR. Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Quantitative Systematic Review. J Clin Med. 2022;11(5). Epub 20220222. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- An J, Haile WB, Wu F, Torre E, Yepes M. Tissue-type plasminogen activator mediates neuroglial coupling in the central nervous system. Neuroscience. 2014;257:41-8. Epub 20131104. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grotta JC. Intravenous Thrombolysis for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2023;29(2):425-42. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng HR, Chen YB, Zeng YY, Ruan YT, Yuan CX, Cheng QQ, et al. Hemostasis functions are associated with hemorrhagic transformation in non-atrial fibrillation patients: a case-control study. BMC Neurol. 2021;21(1):36. Epub 20210126. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Domingo RA, Tripathi S, Perez-Vega C, Martinez J, Suarez Meade P, Ramos-Fresnedo A, et al. Influence of Platelet Count on Procedure-Related Outcomes After Mechanical Thrombectomy for Large Vessel Occlusion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2022;157:187-92 e1. Epub 20211012. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustanoja S, Haapaniemi E, Putaala J, Strbian D, Kaste M, Tatlisumak T. Haemorrhagic transformation of ischaemic stroke in young adults. Int J Stroke. 2014;9 Suppl A100:85-92. Epub 20120927. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodan CI, Stoner JA, Cowan LD, Dale GL. Lower coated-platelet levels are associated with early hemorrhagic transformation in patients with non-lacunar brain infarction. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8(6):1185-90. Epub 20100309. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocho D, Gendre J, Boltes A, Espinosa J, Ricciardi AC, Pons J, et al. Predictors of occult cancer in acute ischemic stroke patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2015;24(6):1324-8. Epub 20150413. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navi BB, Iadecola C. Ischemic stroke in cancer patients: A review of an underappreciated pathology. Ann Neurol. 2018;83(5):873-83. Epub 20180430. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Han SW, Kim SH, Shin HY, Choi HY, Park CH, Kim JK, et al. Paradoxically accelerated fatal brain herniation following thrombolytic therapy in acute ischemic stroke. Neurocrit Care. 2006;5(1):35-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzan IL, Cebul RD, Husak SH, Dawson NV, Baker DW. The effect of pneumonia on mortality among patients hospitalized for acute stroke. Neurology. 2003;60(4):620-5. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadya A, Thorevska N, Sena KN, Manthous C, Amoateng-Adjepong Y. Predictors and consequences of pneumonia in critically ill patients with stroke. J Crit Care. 2004;19(1):16-22. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).