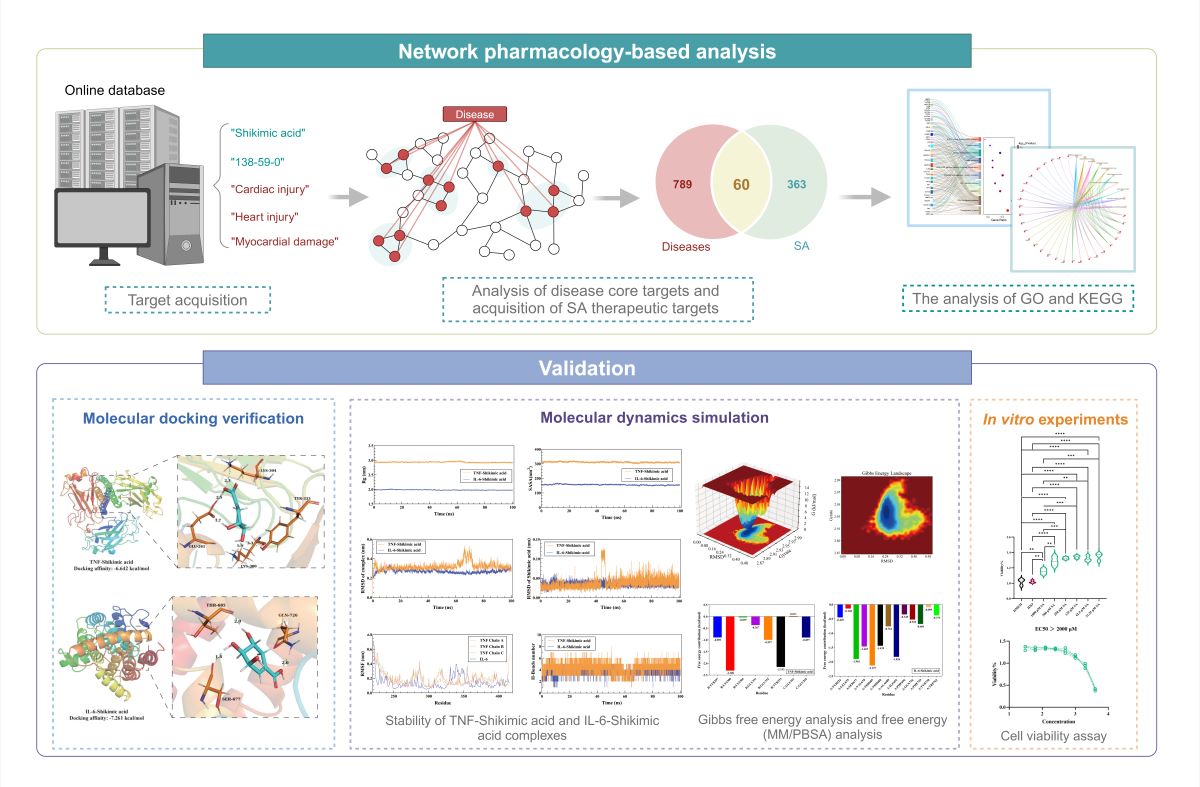
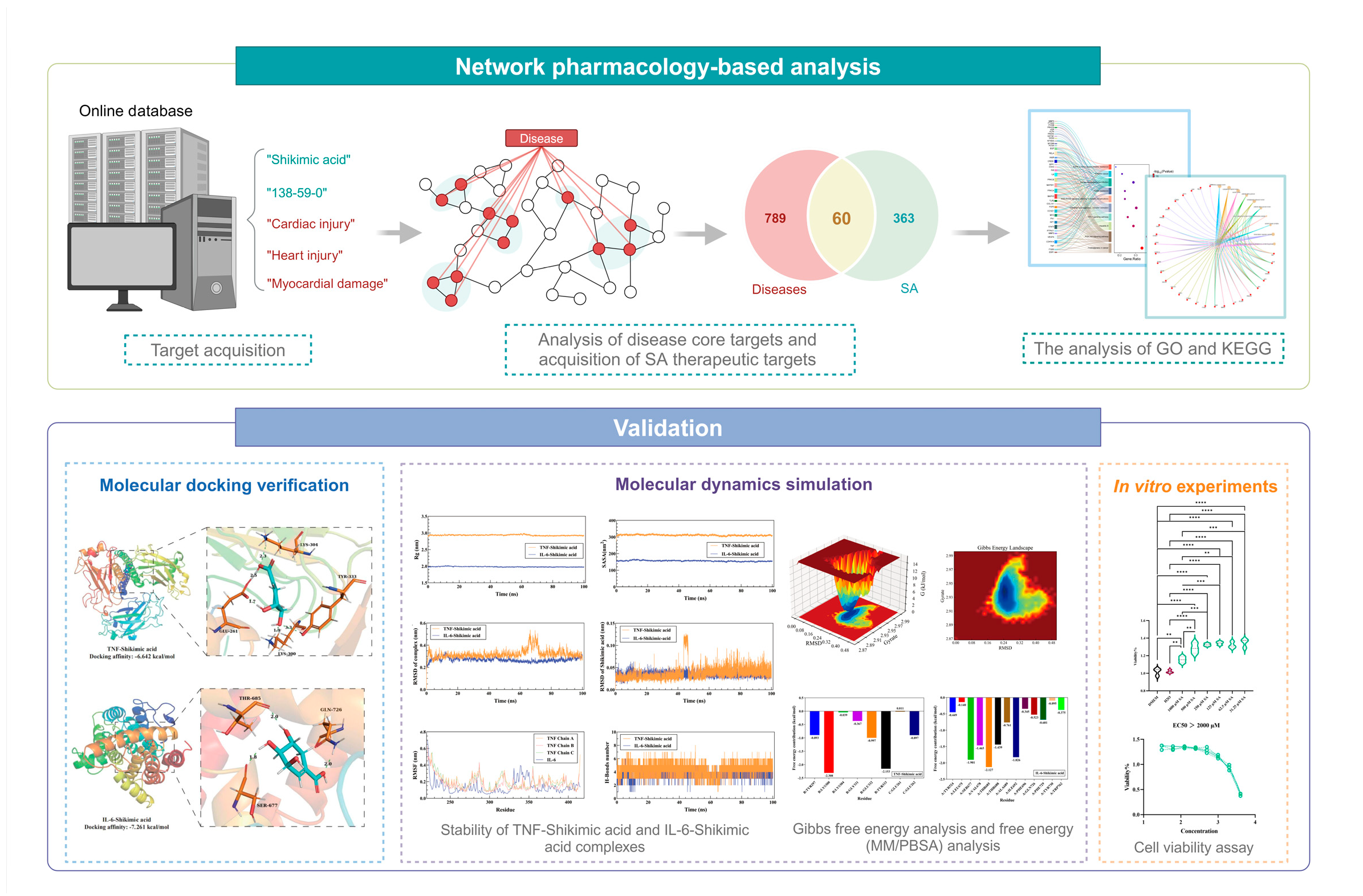
1. Introduction
Climate change poses a substantial threat to humanity in the 21st century, as evidenced by the escalating global surface temperatures and the increasing frequency of extreme heat events [
1,
2]. High temperatures can lead to heat stress (HS) in the body, which particularly endangers vulnerable populations and elevates the risks of cardiovascular mortality among individuals aged 65 and above [
3,
4]. The most dangerous pathological result of cardiovascular disease is myocardial damage, which also plays a significant role in the high death rate associated with cardiovascular disease [
5,
6]. It is important to note that although the mechanism of how HS leads to m
yocardial damage in humans is not yet clear, several pathways have been identified in mouse and rat models. For example, the Akt-Bcl-2 and PKM2-Bcl-2 signaling pathways have been proven to be important in cardiomyocyte death caused by HS in mice [
7]. Currently, many regions worldwide are experiencing population aging trends. Approximately 19% of Europeans and 16% of Americans are over 65 years old, and projections suggest that these figures could double by 2100 [
8]. China, the second-largest economy in the world, is facing an aging population. The elderly population in China is expected to increase significantly by 2050, accounting for about 26.0% of the total population of the country [
9,
10]. Given that HS particularly affects the elderly and can lead to myocardial damage with a high mortality rate, urgent measures must be developed globally to prevent and mitigate these challenges for the elderly worldwide.
Supplementation with specific food components on a daily basis may present a promising strategy to counteract heat stress-induced damage to the heart. A monomeric compound known as shikimic acid (SA) is extracted from the seeds of the Chinese star anise plant (
Illicium verum) [
11,
12], exhibits various beneficial biological activities for the body[
13]. It has been reported that SA can inhibit the expression of TNF-α in vivo due to various pathological factors [
14,
15,
16]. Interestingly, TNF-α is also a marker of HS [
17], especially in older adults, those who experienced nine hours of heat exposure had 1.5 times more TNF-α expression than younger adults [
17]. Additionally, SA has been demonstrated to inhibit P-selectin expression on activated platelets, resulting in an anti-cardiovascular embolic effect [
13]. In summary, although the specific treat HS-induced myocardial damage effect of SA has not been conclusively demonstrated, its pharmacological effect is highly relevant to the symptoms of patients caused by heat stress, particularly in the HS-induced myocardial damage. Hence, SA may be a promising candidate for alleviating myocardial symptoms and complications in heat-stressed patients.
By integrating network biology and polypharmacology, network pharmacology can predict the mechanisms and pathways underlying various drug actions and directly identify drug and disease targets from a large amount of data [
18]. Molecular docking, a well-known silicon-based technique widely utilized in contemporary drug design, can predict the interactions between ligands and proteins, evaluate binding free energy, and define structure-activity relationships [
19]. The study of conformational changes in proteins brought about by ligand binding and unbinding, as well as the connection between protein structure and function, is made easier by molecular dynamics (MD) simulation [
20]. The objective of this research was to employ network pharmacology to determine putative molecular targets and signaling pathways associated with SA's potential therapeutic effect on HS-induced myocardial damage. Molecular docking, MD simulation and
In vitro experiments were utilized to verify the reliability of the analysis.
Figure 1 depicts the process of this study.
2. Results
2.1. Network pharmacological analysis
2.1.1. Targets acquisition of disease
The number of targets retrieved based on keywords in each database is presented in
Supplementary Table 1. A total of 2011 targets were obtained using cardiac injury as the keyword, while 3373 targets were collected with heart injury as the keyword. Additionally, 2000 targets were retrieved using myocardial damage as the keyword, and a total of 2850 targets were collected based on heat stress as the keyword. The Venn analysis results indicated that there were 849 common targets between HS and myocardial damage, as well as Heart injury and Cardiac injury (
Figure 2A).
2.1.2. PPI network construction
Disease-related targets were added to string 12.0, with the species restricted to Homo sapiens and the interaction score more than 0.9. A PPI network of disease-associated targets with 4015 edges and 740 nodes was created (
Figure 2B). After importing the disease-related target PPI network into Cytoscape 3.9.1, four algorithms (Betweenness, Closeness, Degree, Eigenvector) in CytoNCA of Cytoscape 3.10.0 were used to analyze the core targets in the disease-related target PPI network. The top 10 core targets in the disease's PPI network were determined by the four algorithms to be TP53, SRC, TNF, FN1, STAT3, AKT1, MAPK1, IL6, EGFR, and CTNNB1 (
Figure 2C). As shown in
Figure 2D, six clusters received scores greater than 4. By using the jVenn tool to analyze the shared targets between the illness and SA, 60 common targets were identified (
Figure 2E).
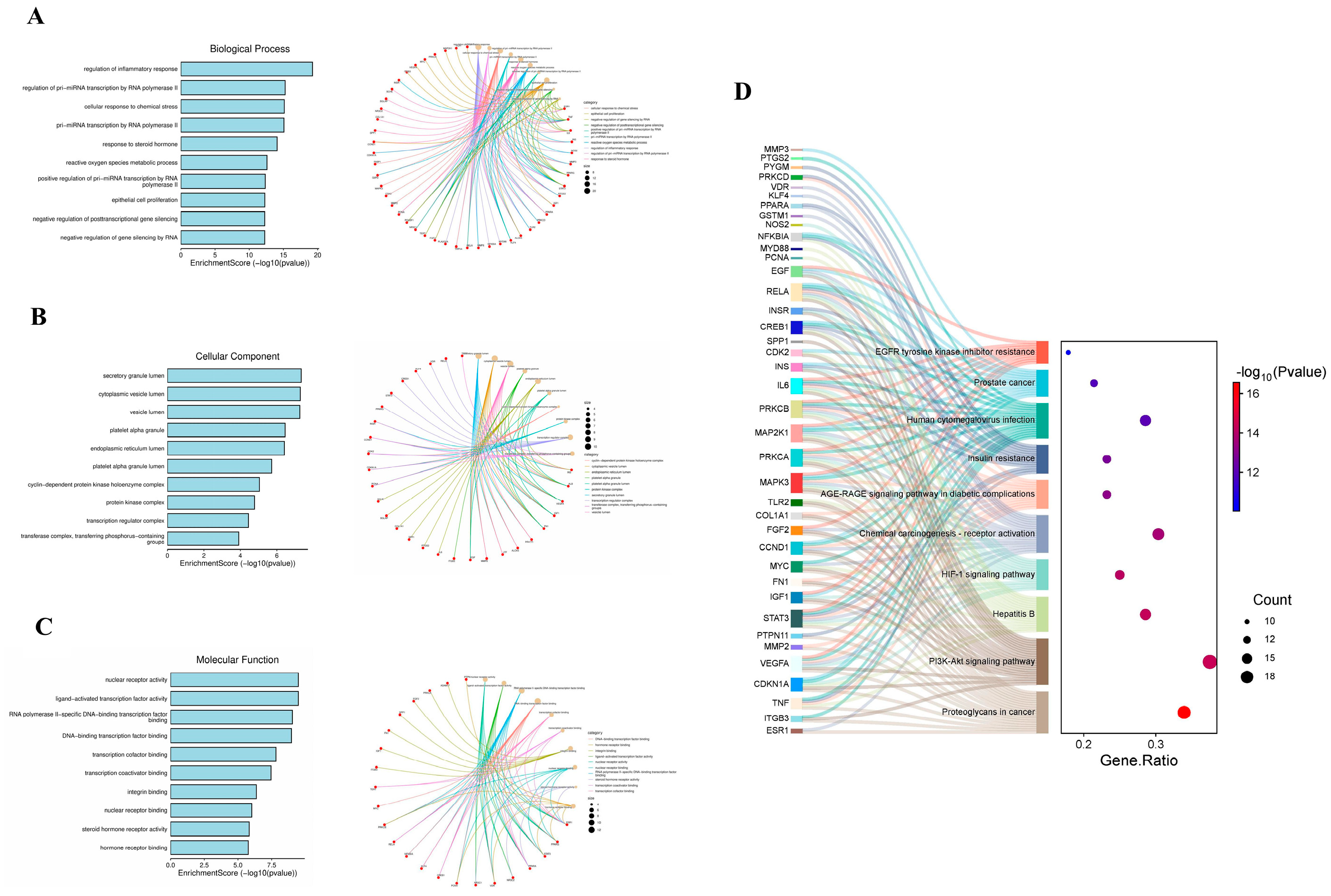
2.1.3. GO and KEGG analysis
We utilized the bioinformatics tool DAVID to conduct the analysis of the GO and KEGG. In the GO analysis, 76 BP, 25 CC, and 33 MF items were derived from the analysis of 869 disease-related targets. The lowest p-value was employed to visualize the top 10 items for CC, MF, and BP. Significant biological terms encompass the control of RNA polymerase II over primiRNA transcription, regulation of the inflammatory response, cellular stress response, and steroid hormone response (
Figure 3A). Prominent categories in CC include the endoplasmic tube lumen, platelet alpha granule, vesicular lumen, cytoplasmic vesicular lumen, and secretory granule lumen (
Figure 3B). Key terms for the MF class include DNA-binding transcription factor binding specific to RNA polymerase II, nuclear receptor activity, ligand-activated transcription factor activity, and DNA-binding transcription factor binding (
Figure 3C).
By using KEGG enrichment items, 230 disease-related targets were identified. The top 10 pathways, including the HIF-1 signaling pathway, hepatitis B, proteoglycan in cancer, and the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, were selected based on the lowest P-value (
Figure 3D).
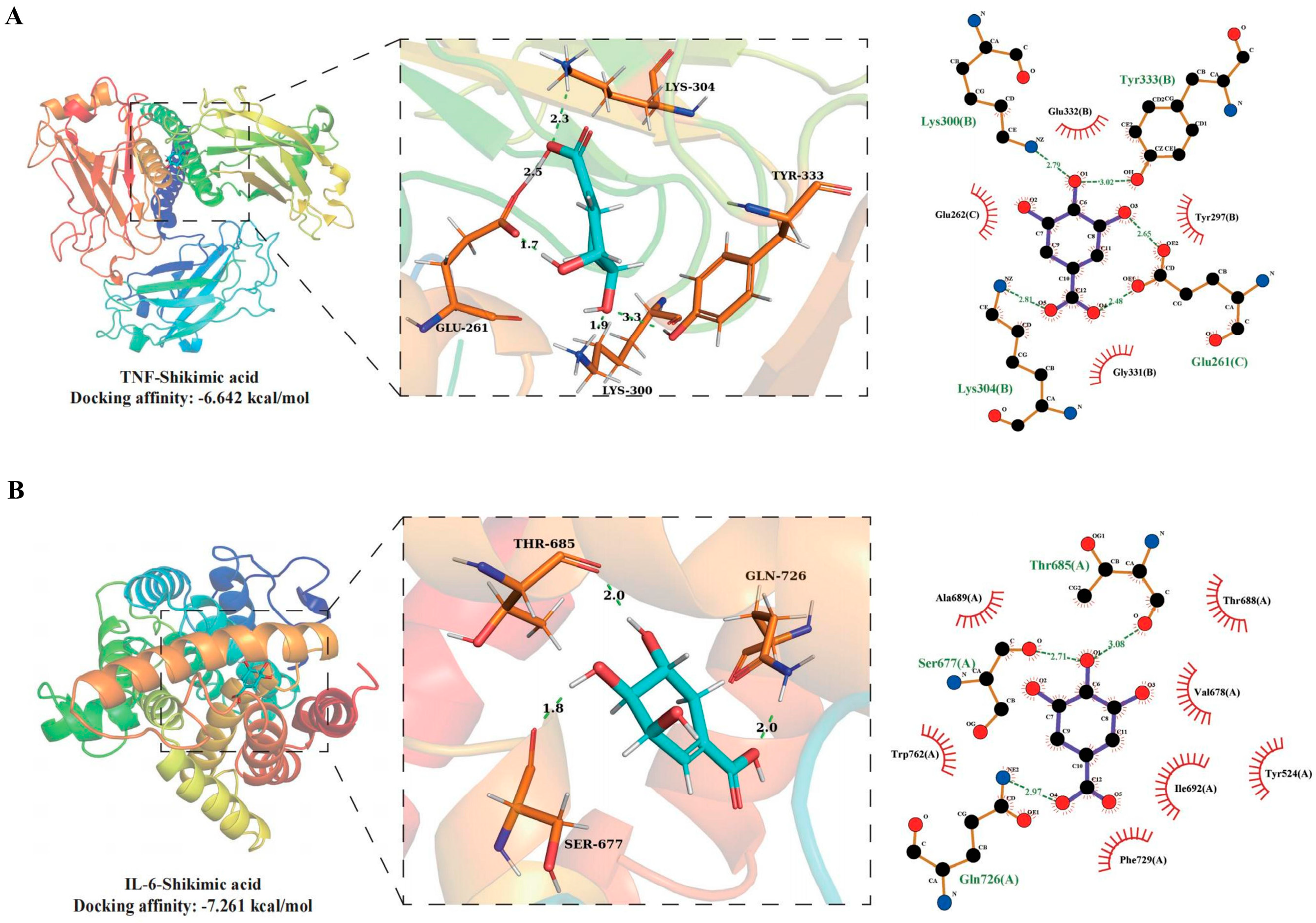
2.2. Molecular docking
To confirm whether SA can interfere with the pathogenic targets of HS-induced myocardial damage, IL-6 and TNF were selected for molecular docking with SA due to IL-6 and TNF are the core targets for SA against on disease. The results of molecular docking demonstrated that SA (Pubchem ID: 8742) can stably bind to the disease protein targets TNF (PDB ID: 5E1T) and IL-6 (PDB ID: 5SFK), with docking affinities of -6.642 kcal/mol and -7.261 kcal/mol, respectively (
Figure 4A to 4B). In addition, SA can form H-bonds with the amino acid residues of TNF LYS304, GLU261, LYS300, and TYR333, and hydrophobic interactions with surrounding cogwheel amino acids (
Figure 4A). SA can form H-bonds with the THR685, GLN726, and SER677 amino acid residues of IL-6, and hydrophobic interactions with the surrounding gear amino acids (
Figure 4B).
2.3. MD simulation
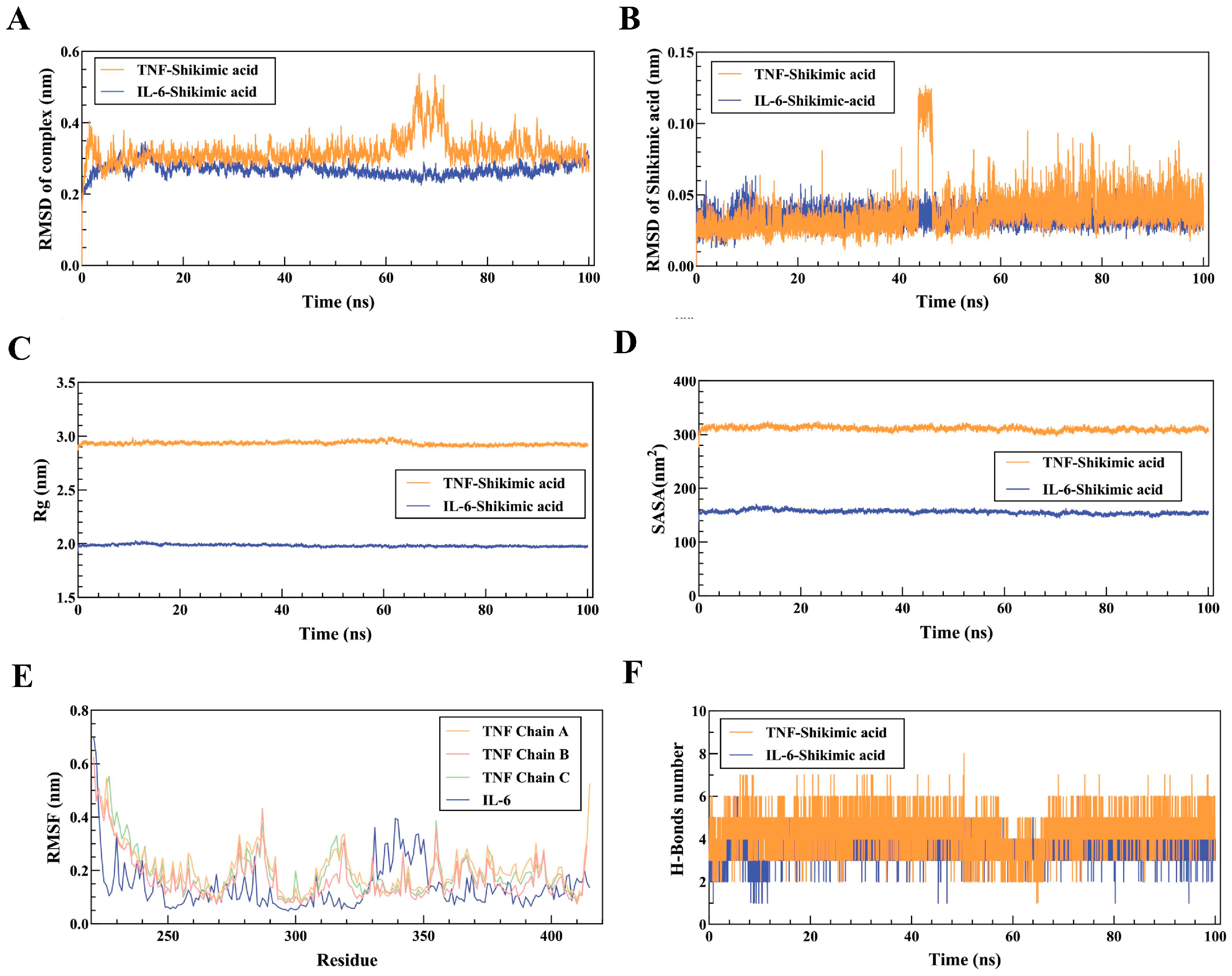
2.3.1. Stability of TNF-Shikimic acid and IL-6-Shikimic acid complexes
MD simulation analysis was utilized to ascertain the stability of complexes formed by SA with TNF or IL-6 in 100 ns, in order to further assess the impact of SA on IL-6 and TNF proteins. The RMSD curve of the TNF-Shikimic acid complex manifests considerable oscillations in the 60 - 70 ns stage but sustains equilibrium in other stages, with an RMSD mean of 0.3 nm (
Figure 5A). The RMSD curve of the IL-6-Shikimic acid complex attains equilibrium after 20 ns, with an RMSD mean of 0.26 nm (
Figure 4A). The essentially unchanged RMSD curve of SA in TNF during the 100 ns simulation indicates the stability of the site where SA binds to TNF. Concurrently, the RMSD curve of SA in IL-6 undergoes a slight fluctuation between 45 and 50 ns before reverting to normal (
Figure 5B). The TNF- and IL-6-Shikimic acid Rg curves maintain equilibrium, with Rg means of 2.9 nm and 2.0 nm, respectively (
Figure 5C). Moreover, the SASA curves of TNF-Shikimic acid and IL-6-Shikimic acid persist in equilibrium, with SASA means of 310 nm2 and 160 nm2, respectively (
Figure 5D). RMSF analysis reveals no substantial difference in amino acid flexibility in the TNF-Shikimic acid complex system, while amino acids in the IL-6-Shikimic acid complex system exhibit greater flexibility in the 330 - 350 region (
Figure 5E). To delve deeper into the h-bond variations in these complexes, the H-bonds formed between the TNF-Shikimic acid and IL-6-Shikimic acid complexes during the 100 ns molecular simulation were inspected. The TNF-Shikimic acid and IL-6-Shikimic acid complexes form between one and eight and between one and six H-bonds, respectively (
Figure 5F).
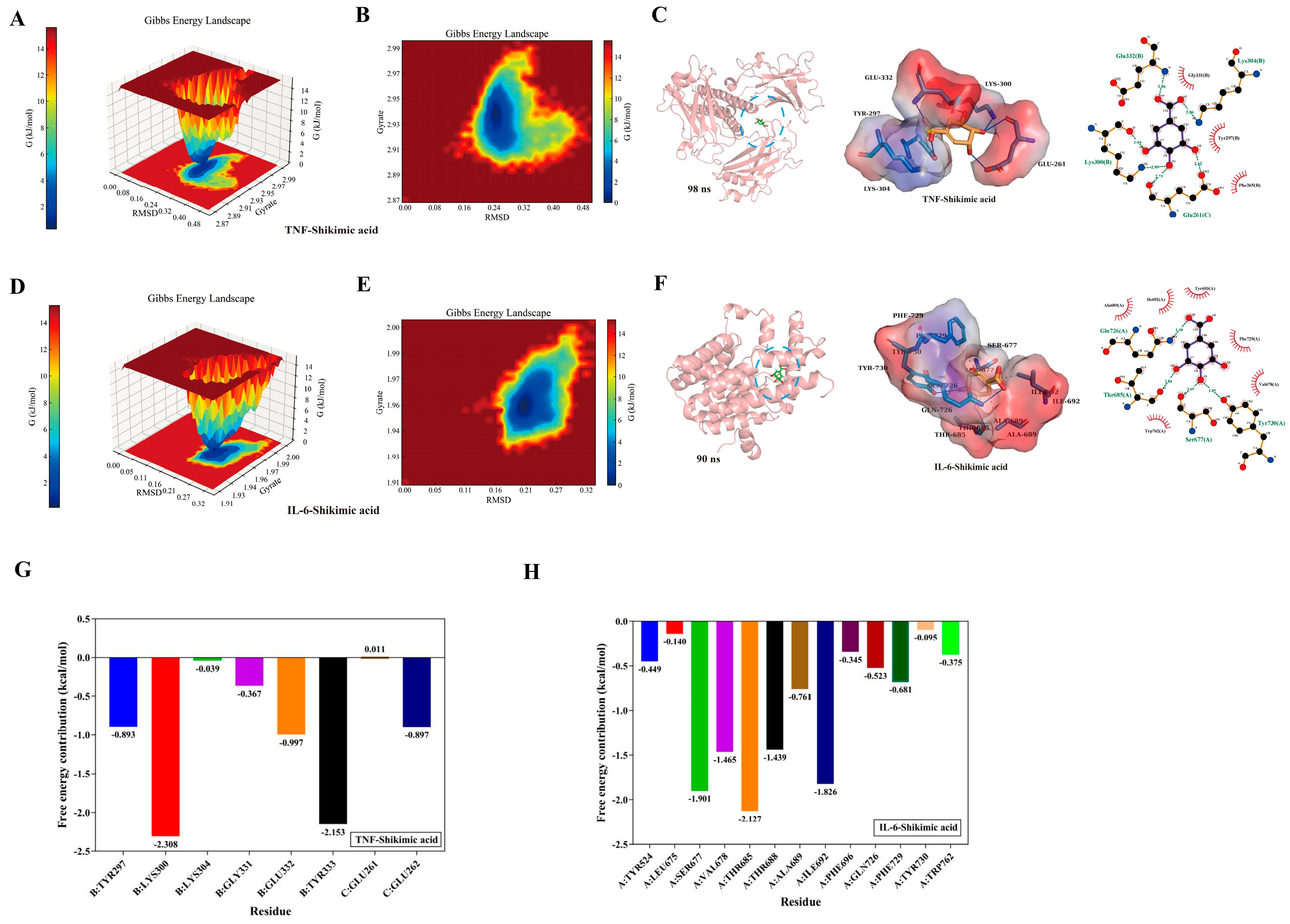
2.3.2. Gibbs free energy analysis and free energy (MM/PBSA) analysis
The "g_sham" and "xpm2txt.py" built-in scripts of Gromacs 2022.03 were utilized in this study to calculate the Gibbs free energy in relation to the RMSD and Rg values of the IL-6 and TNF complexes. The Gibbs free energy diagram was used to clarify the stability of receptor-ligand pairings. The lowest free energy region, represented by the blue and purple areas, is where the stable conformation of the complex is most noticeably visible at lower energies. Multiple minimum energy clusters with rough surfaces will be visible on the free energy landscape map if the interaction between the protein and ligand is weak or unstable. Conversely, strong and stable interactions can lead to the formation of nearly single, smooth energy clusters. The two-dimensional (
Figure 6A) and three-dimensional (
Figure 6B) morphologies of the TNF-shikimic acid complex both exhibited a single, distinct minimum energy region, according to the results of the Gibbs free energy calculation. Furthermore,
Figure 6C presents the visualization of the lowest Gibbs energy region of the TNF-shikimic acid complex based on the results of the Gibbs free energy calculation. A single, distinct minimum energy region could also be observed in the 3D (
Figure 6D) and 2D (
Figure 6E) morphologies of the IL-6-shikimic acid complex.
Figure 6F shows the visualization of the lowest Gibbs energy region of the IL-6-shikimic acid complex based on the results of the Gibbs free energy calculation. Additionally, the stability of free energy between complexes is quantitatively determined by free energy (MM/PBSA) analysis. The TNF-Shikimic acid complex had a total binding free energy of -21.79 ± 1.08 kJ/mol, while the IL-6-Shikimic acid complex had a total binding free energy of -18.67 ± 2.88 kJ/mol. Further details are provided in
Table 1. The present study employed decomposition analysis on the amino acids in the binding pocket of the TNF-Shikimic acid and IL-6-Shikimic acid complexes to identify the residues that contribute the most to the binding free energy. It was found that a total of 8 and 13 residues were significant for the TNF- and IL-6-Shikimic acid complexes, respectively (Figures 6G to 6H). For the TNF-Shikimic acid complex, it was found that LYS300 (B chain) and TYR333 (B chain) contributed the most (
Figure 6G), while for the IL-6-Shikimic acid complex, it was found that SER677 (A chain), VAL678 (A chain), THR685 (A chain), THR688 (A chain), and ILE692 (A chain) contributed the most (
Figure 6H).
2.4. In vitro experimental validation
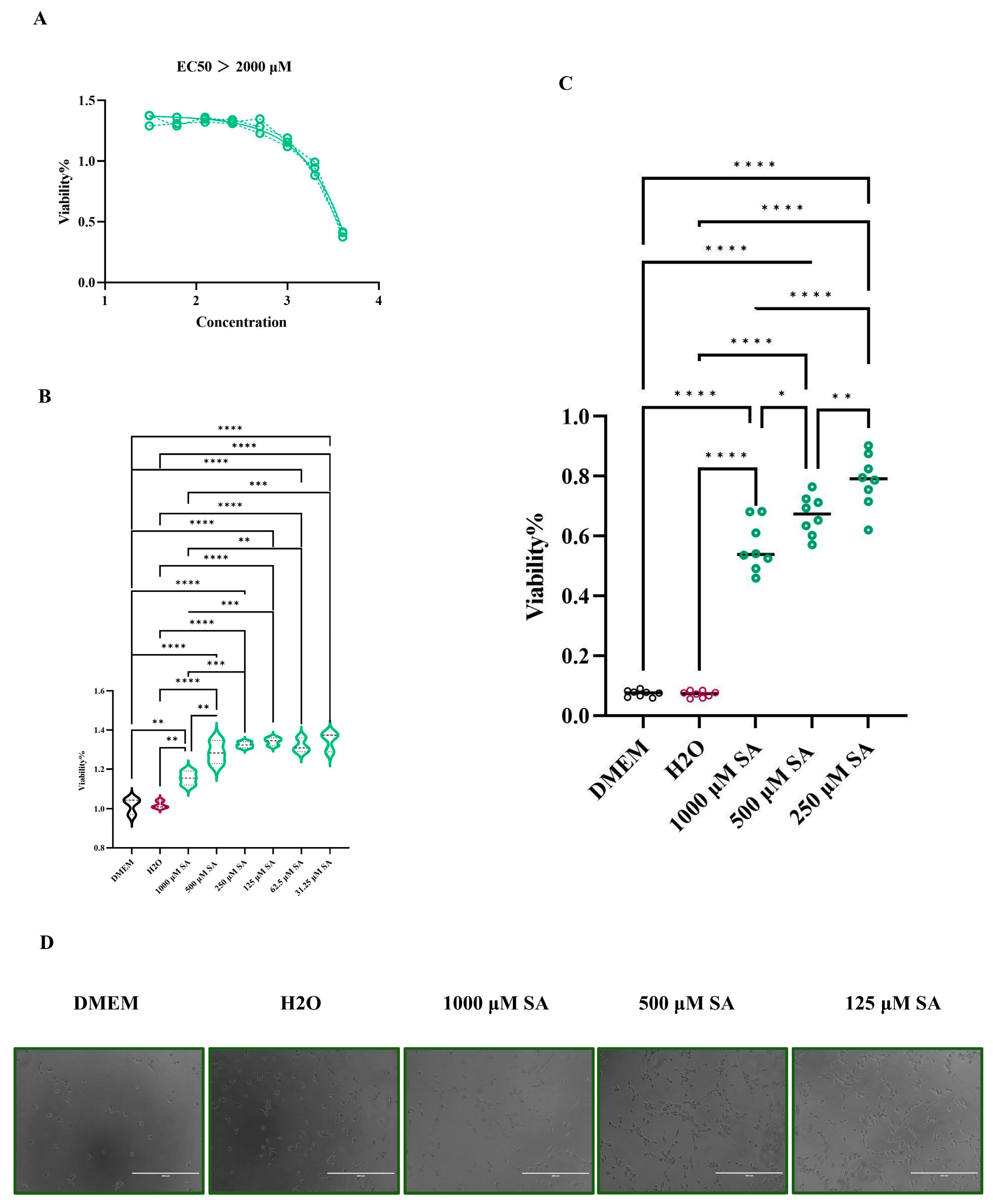
To explore the concentration of cytotoxicity 0% of SA in HL-1 cells, the cells cultured in 96-plates were exposed to 4000 μM, 2000 μM, 1000 μM, 500 μM, 125 μM, 62.5 μM, and 31.25 μM of SA, respectively. CCK-8 was utilized to measure the viability of HL-1 cells after 6 different concentrations of SA at 24 h. The results indicated that 1000 μM is the maximum safe concentration of SA in HL-1 cells, and the CC50 of SA in HL-1 cells is greater than 2000 μM (
Figure 7A). Additionally, the CCK-8 results demonstrated that SA can promote the proliferation of HL-1 cells, yet it is not dose-dependent (
Figure 7B). To assess the protective effect of SA on HL-1 cells subjected to HS, the CCK-8 was employed to measure the viability of HL-1 cells treated at 43°C for 2 h. The results showed that SA can aid HL-1 cells in resisting the damage caused by HS. Interestingly, 250 μM SA is more beneficial in helping cells resist HS than 1000 μM SA (
Figure 7C). The microscope (100×) results are presented in (
Figure 7D).
3. Discussion
It has been demonstrated that HS can lead to myocardial damage, and myocardial infarction is one of the most frequent causes of death among patients with HS [
22,
23]. Patients with HS-induced myocardial damage have considerably higher expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6, FN1, and IL-1β [
24,
25,
26]. Notably, in this study, we constructed a heat stress PPI network and analyzed the four algorithms in Cytoscape 3.10, revealing that TNF, IL-6, and IL-1β were also significant TOP 20 core targets of myocardial damage caused by heat stress in patients, and these targets are mainly in the same disease gene subcluster 2, suggesting that gene subcluster 2 may be the principal gene cluster in heat stress-induced myocardial damage. According to the Jvenn analysis results, there were 60 common targets between HS-induced myocardial damage and SA, including many core targets of HS myocardial damage, such as TNF, IL-6, STAT3, FN1, and IL-1B. We performed on GO and KEGG enrichment analyses on 60 common targets to further investigate the mechanism of SA resistance to HS-induced myocardial damage. Based on the outcomes of the GO enrichment analysis, SA is capable of modulating a variety of disordered biological processes, encompassing the regulation of the inflammatory response, the regulation of pri-miRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II, and the cellular response to chemical stress. SA can also restore aberrant molecular functions in the heart myocardial damage resulting from HS, such as nuclear receptor activity, ligand-activated transcription factor activity, and RNA polymerase l-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding. Moreover, SA can assist in the recovery of the body's cell components, including the lumen of secretory granules, cytoplasmic vesicles, and vesicles.
To validate the results of network pharmacological analysis suggesting that SA can suppress myocardial inflammation induced by HS and assist the host in alleviating myocardial damage, the interaction between SA and key inflammatory factors in myocardial injury caused by HS was verified through molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. In the analysis of this study, TNF and IL-6 were identified as the main targets in HS-induced myocardial injury, and these two targets are also crucial for SA's intervention in the disease. The molecular docking results of this study indicated that SA can bind to the disease protein targets TNF and IL-6 with docking affinities of -6.642 kcal/mol and -7.261 kcal/mol, respectively. It has been proven in a previous study that curcuma can reduce TNF and IL-6. However, the molecular docking results of the compound with TNF and IL-6 were only -3.9 kcal/mol and -3.6 kcal/mol, respectively [
27]. According to the principle that the binding energy of a complex decreases as its stability increases [
28], by comparing the molecular docking results of this experiment with those of previous experimental studies, it can be demonstrated that SA can stably bind to IL-6 and TNF, respectively. The results of MD simulation further verified the reliability of the above conclusions. RMSD is crucial in ascertaining system stability, as it gauges the accuracy of protein structure prediction [
29]. In a previous study, 0.3 nm variations in RMSD had no impact on complex stability [
30]. Here, the average RMSD for TNF-Shikimic acid and IL-6-Shikimic acid in MD analysis were 0.3 nm and 0.26 nm, both less than 0.3. In addition, in 100 ns, RMSF analysis in MD showed that there were no significant variations in the TNF-Shikimic acid and IL-6-Shikimic acid complex [
31]. Based on the results of molecular docking and MD simulation, we can infer that SA can have stable interactions with TNF and IL-6.
According to the results of network pharmacological analysis in this study, HS-induced myocardial injury is mainly caused by the regulation of inflammatory factors such as TNF, IL1B and IL-6. it has been proven that these inflammatory factors can stimulate cell apoptosis [
32,
33,
34]. Therefore, it is reasonable to speculate that SA can protect cells by inhibiting the expression of inflammatory factors and reducing apoptosis. To validate this speculation, we established an in vitro HS-induced myocardial injury model using HL-1 cells, and subsequently carried out the SA drug intervention experiment. The results demonstrated that SA not only can effectively elevate the survival rate of HL-1 cells under HS, but also promote the proliferation of healthy HL-1 cells.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell lines and Compound
Mouse cardiomyocytes (HL-1) procured from the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 units/mL of penicillin, and 100 mg/mL of streptomycin at 37°C in a 5% CO2 environment.
Shikimic acid (SA) with a purity ≥ 99.15% was purchased from MedChemExpress (CAS No.: 138-59-0) and diluted in H2O to achieve a final concentration of 100 mM.
4.2. Network pharmacology analysis
4.2.1. Prediction of the SA pharmacological target
4.2.2. Collection of HS-induced myocardial damage related targets
We collected HS targets from four databases: CTD (
http://ctdbase.org), Disgenet (
https://www.disgenet.org/), OMIM (
https://omim.org/), and Genecards (
https://www.genecards.org/), limited to Homo sapiens organisms, to identify the targets of HS-induced myocardial damage [
21]. Then, we found targets related to myocardial damage in multiple databases by using the keywords "Myocardial damage," "Heart injury," and "Cardiac injury." Based on the priority relevance ranking of the raw data, the top 2,000 targets were selected, and duplicates were removed by keyword mergers. Finally, the targets of HS-induced myocardial damage were obtained by using JVenn (
https://jvenn.toulouse.inrae.fr/app/example.html) to extract the common targets of HS-related targets and myocardial damage-related targets.
4.2.3. PPI Network Analysis
To acquire the Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Network of HS-induced myocardial damage for the subsequent identification of core targets, we imported the obtained HS-related targets into STRING 12.0, with Homo sapiens designated as the organism. The confidence level for the interaction score was set to ≥ 0.9. We then employed Cytoscape 3.9.1 to construct the PPI network diagram. The CytoNCA plugin in Cytoscape 3.9.1 was utilized to analyze the disease-related targets and identify the core targets using four algorithms: Betweenness, Closeness, Degree, and Eigenvector. Subsequently, the Molecular Complex Detection (MCODE) tool was applied for cluster analysis, with default parameters used and the MCODE score set to 4. After the analysis, the modules were visualized in a diagram according to the MCODE score.
4.2.4. GO and KEGG analyses
To investigate the molecular function (MF), biological process (BP), cellular component (CC) and pathway of common targets, we used DAVID Bioinformatics (
https://david.ncifcrf.gov/tools.jsp) to perform Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia Gene and Genome analysis (KEGG). Using bioinformatics (
http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/), the p-value is the lowest in the first 10 terms.
4.3. Molecular docking
To determine if SA could block the pathogenic target of HS-induced myocardial damage, it was molecularly docked with IL-6 and TNF. The three-dimensional (3D) structure of the target protein, specific to Homo sapiens, was obtained from the PDB (
https://www.rcsb.org/). The two-dimensional structure (2D) of SA was determined using PubChem (
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Following the AutoDock v1.2.3 docking procedure, the binding affinity (kcal/mol) was determined. The docking box configurations were Z: 50A, Y: 50A, and X: 50A. The ligand-receptor interaction was thoroughly examined using PyMol v2.6 and LigPlot+ v2.2.8 software, and both 2D and 3D maps of the interaction were generated.
4.4. MD simulation
MD simulations were used to further explore the stability and binding sites of the SA complex after docking with IL-6 and TNF. In this study, 100 ns MD simulations of the complexes obtained from molecular docking were conducted using Gromacs v2022.03 with the CHARMM36 force field. The specific steps include converting the "pdb" format to "gro" format, adding the GAFF force field, dissolving the complex with TIP3P solvent, performing energy minimization, heating and equilibration, and finally performing 100 ns MD simulations and saving the trajectory for analysis. Based on the obtained results, we computed the RMSD, RMSF, SASA, Rg, and H-bonds. Furthermore, we employed the "g_sham" and "xpm2txt.py" scripts in conjunction with the "MMPBSA.py v.16.0" script to determine the thermodynamic stability.
4.5. In vitro experimental validation
4.5.1. Determination of cytotoxic concentration of 50% (CC50)
To determine the concentration of cytotoxicity 50% (CC50) and concentration of cytotoxicity 0% (CC0) of SA on HL-1 cellscells were plated in 96-well plates at a density of 1 × 104 cells per well. Subsequently, HL-1 cells were exposed to 8 different concentrations of SA (2000 μM, 1000 μM, 500 μM, 250 μM, 125 μM, 62.5 μM, 31.25 μM, 15.625 μM, 7.8125 μM) prepared in DMEM supplemented with 2% FBS. A control group treated with the solvent was used for comparison. After a 24-h incubation period, cell viability was assessed using the CCK-8 (Cell Counting Kit-8) assay (Vazyme, A311-01, China). All procedures were performed in triplicate to ensure reproducibility. The CC50 value corresponding to each SA concentration was determined based on the assay results. GraphPad Prism 9.5 software was used for data analysis.
4.5.2. SA protects HL-1 cells against HS in a dose-dependent
The anti-HS activities of SA in HL-1 cells were investigated using dose-dependent treatments. In brief, HL-1 cells were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 1 × 104 cells per well. Subsequently, different concentrations of the SA are added to the 96 Wells at 100 μL/well (1000 μM, 500 μM, 250 μM). In addition, a healthy cell group and mock treatment group were set up. The cells were heat treated at 42℃ for 2 h, and then CCK-8 was used to evaluate the protective effect of SA on HL-1 cells.
4.5.3. Statistical analysis
One-way ANOVA in GraphPad Prism 9.5 was used to determine significant differences (P < 0.05) across all experiments.
5. Conclusions
In this study, network pharmacology was used to explore the therapeutic potential of SA in treating HS-induced myocardial damage. Molecular docking, MD simulation and In vitro experiments were employed to validate the obtained results. However, our study has some limitations, In vivo experiments is required for the specific treatment of HS-induced myocardial damage with SA.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org: Table S1: The number of targets collected by each database
Author Contributions
Writing-original draft,Y.G. and J.Z.; Writing-review and editing, Y.G., Y.H. and J.X.; Data curation, Y.G., J.Z., M.Z. and Y.Q.; Formal analysis, M.Z. and Y.Q.; Methodology, H.Z.; Supervision, Y.H. and J.X.; Resources, Y.H.
Funding
This work was supported by Science and Technology Support Program of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 2015SZ0201) & Major Science and Technology Projects of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 2020YFS0337).
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts OF Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest regarding the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethics Statement
This study did not involve the collection of clinical samples from humans or animals, and no animal experiments were conducted. As a result, there are no ethical or moral issues associated with this study.
References
- Costello, A., Abbas, M., Allen, A., Ball, S., Bell, S., Bellamy, R., Friel, S., Groce, N., Johnson, A., Kett, M., Lee, M., Levy, C., Maslin, M., McCoy, D., McGuire, B., Montgomery, H., Napier, D., Pagel, C., Patel, J., de Oliveira, J. A., Patterson, C. (2009). Managing the health effects of climate change: Lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. Lancet (London, England), 373(9676), 1693–1733. [CrossRef]
- Meehl, G. A., & Tebaldi, C. (2004). More intense, more frequent, and longer lasting heat waves in the 21st century. Science (New York, N.Y.), 305(5686), 994–997. [CrossRef]
- Basu, R., & Samet, J. M. (2002). Relation between elevated ambient temperature and mortality: a review of the epidemiologic evidence. Epidemiologic reviews, 24(2), 190–202. [CrossRef]
- Vandentorren, S., Bretin, P., Zeghnoun, A., Mandereau-Bruno, L., Croisier, A., Cochet, C., Ribéron, J., Siberan, I., Declercq, B., & Ledrans, M. (2006). August 2003 heat wave in France: risk factors for death of elderly people living at home. European journal of public health, 16(6), 583–591. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, C., Nishina, N., & Kawai, C. (2015). Stress-induced cardiomyopathy accompanied by heat stroke. Journal of cardiology cases, 12(1), 16–19. [CrossRef]
- Li, A. L., Lian, L., Chen, X. N., Cai, W. H., Fan, X. B., Fan, Y. J., Li, T. T., Xie, Y. Y., & Zhang, J. P. (2023). The role of mitochondria in myocardial damage caused by energy metabolism disorders: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Free radical biology & medicine, 208, 236–251. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. H., Wu, J. X., Sha, J. Z., Yang, B., Sun, J. R., & Bao, E. D. (2020). Heat shock protein 90 relieves heat stress damage of myocardial cells by regulating Akt and PKM2 signaling in vivo. International journal of molecular medicine, 45(6), 1888–1908. [CrossRef]
- Gerland, P., Raftery, A. E., Sevčíková, H., Li, N., Gu, D., Spoorenberg, T., Alkema, L., Fosdick, B. K., Chunn, J., Lalic, N., Bay, G., Buettner, T., Heilig, G. K., & Wilmoth, J. (2014). World population stabilization unlikely this century. Science (New York, N.Y.), 346(6206), 234–237. [CrossRef]
- Zeng Y. (2012). Towards Deeper Research and Better Policy for Healthy Aging --Using the Unique Data of Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey. China economic journal, 5(2-3), 131–149. [CrossRef]
- Lobanov-Rostovsky, S., He, Q., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., Wu, Y., Liu, Y., Venkatraman, T., French, E., Curry, N., Hemmings, N., Bandosz, P., Chan, W. K., Liao, J., & Brunner, E. J. (2023). Growing old in China in socioeconomic and epidemiological context: systematic review of social care policy for older people. BMC public health, 23(1), 1272. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Pan, C., Gong, J., Liu, X., & Li, H. (2016). Enhancing the Enrichment of Pharmacophore-Based Target Prediction for the Polypharmacological Profiles of Drugs. Journal of chemical information and modeling, 56(6), 1175–1183. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Shen, Y., Wang, S., Li, S., Zhang, W., Liu, X., Lai, L., Pei, J., & Li, H. (2017). PharmMapper 2017 update: a web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database. Nucleic acids research, 45(W1), W356–W360. [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z. Z., Xu, Q. P., & Sun, J. N. (2001). Effects and mechanisms of triacetylshikimic acid on platelet adhesion to neutrophils induced by thrombin and reperfusion after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Acta pharmacologica Sinica, 22(8), 679–684.
- Li, X., Mo, K., Tian, G., Zhou, J., Gong, J., Li, L., & Huang, X. (2023). Shikimic Acid Regulates the NF-κB/MAPK Signaling Pathway and Gut Microbiota to Ameliorate DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 71(23), 8906–8914. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X., Li, X., Zhai, X., Zhi, X., Cao, L., Qin, L., & Su, J. (2018). Shikimic Acid Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis in Vivo and in Vitro by Blocking RANK/TRAF6 Association and Suppressing NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Cellular physiology and biochemistry : international journal of experimental cellular physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology, 51(6), 2858–2871. [CrossRef]
- Rabelo, T. K., Guimarães, A. G., Oliveira, M. A., Gasparotto, J., Serafini, M. R., de Souza Araújo, A. A., Quintans-Júnior, L. J., Moreira, J. C. F., & Gelain, D. P. (2016). Shikimic acid inhibits LPS-induced cellular pro-inflammatory cytokines and attenuates mechanical hyperalgesia in mice. International immunopharmacology, 39, 97–105. [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J. J., Meade, R. D., King, K. E., Notley, S. R., Akerman, A. P., McGarr, G. W., Richards, B. J., McCourt, E. R., Boulay, P., Sigal, R. J., & Kenny, G. P. (2023). Physiological responses to 9 hours of heat exposure in young and older adults. Part II: Autophagy and the acute cellular stress response. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 135(3), 688–695. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z., Chen, B., Chen, S., Lin, M., Chen, Y., Jin, S., Chen, W., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Applications of Network Pharmacology in Traditional Chinese Medicine Research. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2020, 1646905. [CrossRef]
- Pinzi, L., & Rastelli, G. (2019). Molecular Docking: Shifting Paradigms in Drug Discovery. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(18), 4331. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X., Xu, L. Y., Li, E. M., & Dong, G. (2022). Application of molecular dynamics simulation in biomedicine. Chemical biology & drug design, 99(5), 789–800. [CrossRef]
- Liao, X., Xin, J., Yu, Z., Yan, W., Li, C., Cao, L., Zhang, H., & Wang, W. (2024). Unlocking the antiviral potential of rosmarinic acid against chikungunya virus via IL-17 signaling pathway. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology, 14, 1396279. [CrossRef]
- Dematte, J. E., O'Mara, K., Buescher, J., Whitney, C. G., Forsythe, S., McNamee, T., Adiga, R. B., & Ndukwu, I. M. (1998). Near-fatal heat stroke during the 1995 heat wave in Chicago. Annals of internal medicine, 129(3), 173–181. [CrossRef]
- KNOCHEL, J. P., BEISEL, W. R., HERNDON, E. G., Jr, GERARD, E. S., & BARRY, K. G. (1961). The renal, cardiovascular, hematologic and serum electrolyte abnormalities of heat stroke. The American journal of medicine, 30, 299–309. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C. C., Wu, H. H., Chang, C. P., Lin, C. H., & Yang, H. H. (2019). Calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside reduces myocardial injury in heat stroke rats. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association = Taiwan yi zhi, 118(3), 730–738. [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J. J., Meade, R. D., King, K. E., Notley, S. R., Akerman, A. P., McGarr, G. W., Richards, B. J., McCourt, E. R., Boulay, P., Sigal, R. J., & Kenny, G. P. (2023). Physiological responses to 9 hours of heat exposure in young and older adults. Part II: Autophagy and the acute cellular stress response. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985), 135(3), 688–695. [CrossRef]
- Matozaki, M., Saito, Y., Yasutake, R., Munira, S., Kaibori, Y., Yukawa, A., Tada, M., & Nakayama, Y. (2019). Involvement of Stat3 phosphorylation in mild heat shock-induced thermotolerance. Experimental cell research, 377(1-2), 67–74. [CrossRef]
- Peng, H., Jiang, X., Cui, L., Zhu, Y., Ye, Z., & Zhang, Z. (2022). Mechanistic Investigation of Curcuma Protection against Oral Submucous Fibrosis. Evidence-based complementary and alternative medicine : eCAM, 2022, 3891598. [CrossRef]
- Costello, A., Abbas, M., Allen, A., Ball, S., Bell, S., Bellamy, R., Friel, S., Groce, N., Johnson, A., Kett, M., Lee, M., Levy, C., Maslin, M., McCoy, D., McGuire, B., Montgomery, H., Napier, D., Pagel, C., Patel, J., de Oliveira, J. A., … Patterson, C. (2009). Managing the health effects of climate change: Lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. Lancet (London, England), 373(9676), 1693–1733. [CrossRef]
- Brüschweiler R. (2003). Efficient RMSD measures for the comparison of two molecular ensembles. Root-mean-square deviation. Proteins, 50(1), 26–34. [CrossRef]
- Liao, F., Yousif, M., Huang, R., Qiao, Y., & Hu, Y. (2023). Network pharmacology- and molecular docking-based analyses of the antihypertensive mechanism of Ilex kudingcha. Frontiers in endocrinology, 14, 1216086. [CrossRef]
- Baskin L. S. (1968). Electric conductance and pH measurements of isoionic salt-free bovine mercaptalbumin solutions. An evaluation of root-mean-square proton fluctuations. The Journal of physical chemistry, 72(8), 2958–2962. [CrossRef]
- Minchenko, O. H., Tsymbal, D. O., Minchenko, D. O., & Ratushna, O. O. (2016). The role of the TNF receptors and apoptosis inducing ligands in tumor growth. Ukrainian biochemical journal, 88(5), 18–37. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Duan, C., Wu, S., Ma, J., Liu, Y., Li, W., Wang, T., Yang, L., Cheng, K., & Zhuang, R. (2022). Knockout of IL-6 mitigates cold water-immersion restraint stress-induced intestinal epithelial injury and apoptosis. Frontiers in immunology, 13, 936689. [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y., Dong, B., Geng, Z., & Xu, L. (2022). Excess Uric Acid Induces Gouty Nephropathy Through Crystal Formation: A Review of Recent Insights. Frontiers in endocrinology, 13, 911968. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).