Submitted:
18 August 2024
Posted:
19 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Review of Literature
2.1. Financial Development and Environmental Quality
2.2. Green Technological Innovation and Environmental Quality
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Data
3.2. Empirical Model
3.3. Econometric Methodology
3.3.1. The Slope Homogeneity Test
3.3.2. The Cross-Section Dependence Test
3.3.3. Unit Root Test
3.3.4. Co-Integration Test
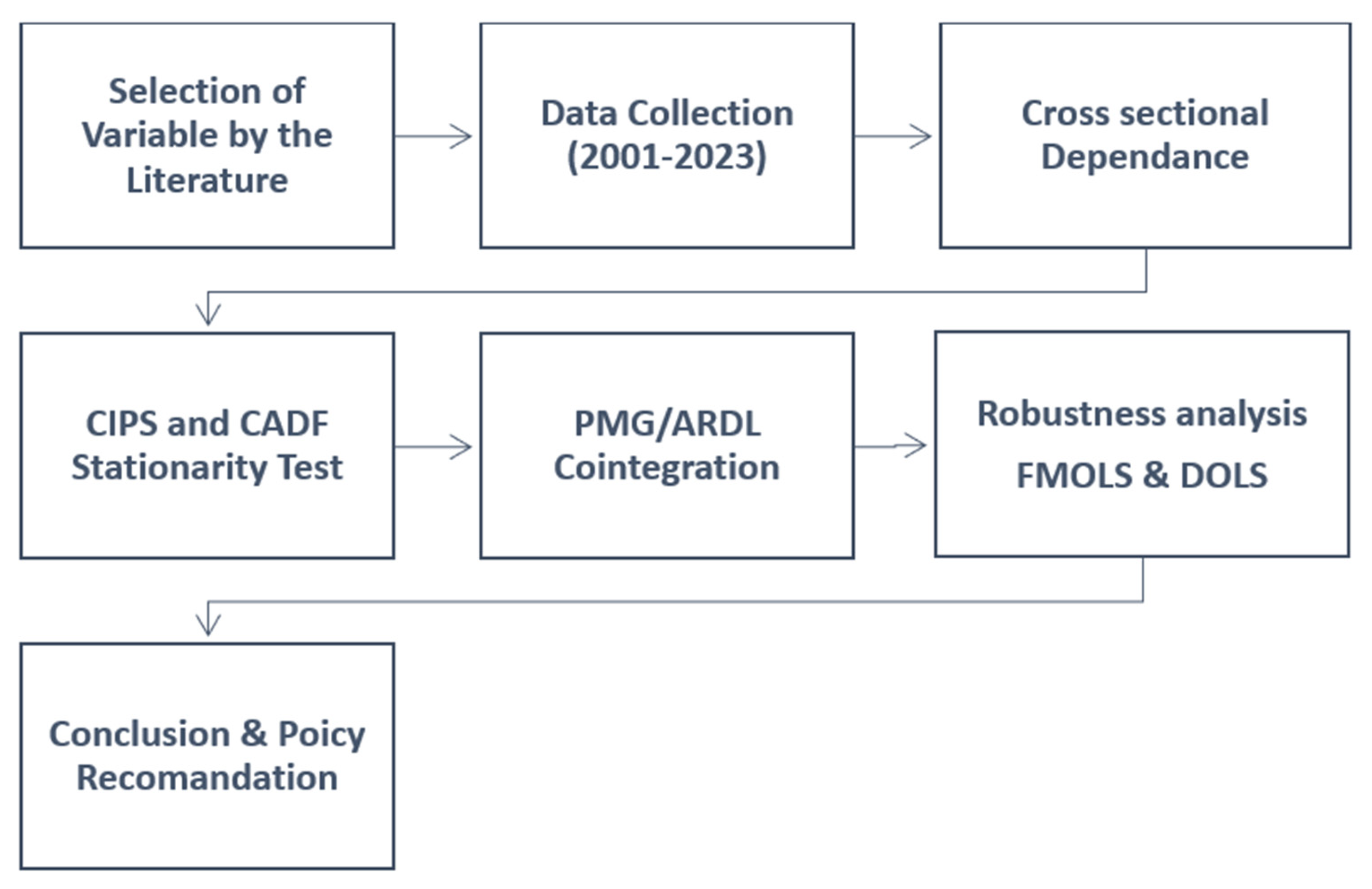
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Statistics on Study Variables
4.2. Correlation between Variables
4.3. The Slope of Heterogeneity Test
| Cross Section ally Augmented IPS (CIPS) | |||||
| Level | First Difference | ||||
| Variable | Statistics | Prob. | Statistics | Prob. | Decision |
| LCO2 | 1.58 | 0.94 | -3.37*** | 0.00 | I(0) |
| LBM | 0.11 | 0.54 | -8.26*** | 0.00 | I(I) |
| LDCPS | -1.73** | 0.04 | -10.99*** | 0.00 | I(0) |
| LFDI | -2.20 | 0.01 | -6.96*** | 0.00 | I(I) |
| LGTI | 1.21 | 0.11 | -3.91*** | 0.00 | I(I) |
| Cross Section ally Augmented CADF (CADF) | |||||
| Level | First Difference | ||||
| Variable | Statistics | Prob. | Statistics | Prob. | Decision |
| LCO2 | 3.55 | 0.96 | 31.20*** | 0.00 | I(0) |
| LBM | 9.20 | 0.90 | 92.51*** | 0.00 | I(I) |
| LDCPS | 22.93 | 0.01 | 35.11*** | 0.00 | I(0) |
| LFDI | 20.86 | 0.02 | 60.77*** | 0.00 | I(I) |
| LGTI | 15.60 | 0.10 | 37.21*** | 0.00 | I(I) |
| Cross Section Levin et al. (2002) | |||||
| Level | First Difference | ||||
| Variable | Statistics | Prob. | Statistics | Prob. | Decision |
| LCO2 | 0.69 | 0.75 | -2.43*** | 0.00 | I(I) |
| LBM | -1.84 | 0.03 | -5.09*** | 0.00 | I(I) |
| LDCPS | -2.95** | 0.00 | -4.91*** | 0.00 | I(0) |
| LFDI | -1.38 | 0.08 | -3.55*** | 0.00 | I(I) |
| LGTI | -3.74 | 0.00 | -2.85*** | 0.00 | I(I) |
4.4. Pooled Mean Group Autoregressive Distributed Lag (PMG- ARDL) Analysis
| Null hypothesis | W-Stat | Zbar-Stat. | Prob. | Direction of causality |
| LBM LCO2 | 7.91 | 4.76 | 2.01 | Non-directional causality between REC and LGDP |
| LCO2 LBM | 1.78 | -0.42 | 0.67 | |
| LDCPS LCO2 | 2.55 | 0.22 | 0.82 | Non -directional causality between TI and GDP |
| LCO2 LDCPS | 7.74 | 4.62 | 4.E | |
| LFDI LCO2 | 2.01 | -0.23 | 0.93 | Non -directional causality between GDP and ED |
| LCO2 LFDI | 1.95** | -028 | 0.02 | |
| LGTI LCO2 | 5.38 | 2.62 | 1.23 | Uni-directional causality between FS and GDP |
| LCO2 LGTI | 2.32 | 0.03 | 0.97 |
4.5. Panel Causality Test Results
Conclusions and Policy Recommendation
References
- Grossman, Gene M., and Alan B. Krueger. “Economic growth and the environment.” The quarterly journal of economics 110.2 (1995): 353-377. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X., Huang, S., Haizhong, A., Vigne, S., & Lucey, B. M. (2021). The influence pathways of financial development on environmental quality: New evidence from smooth transition regression models. In SSRN Electronic Journal. Elsevier BV. [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, H. E., & Lotfalipour, M. R. (2014). The environmental issues and forecasting threshold of income and pollution emissions in Iran economy. International Journal of Resistive Economics, 2(2), 72..
- Majeed, M. T., & Mazhar, M. (2019). Financial development and ecological footprint: a global panel data analysis. Pakistan Journal of Commerce and Social Sciences (PJCSS), 13(2), 487-514.
- Khan, H., Dong, Y., Nuţă, F. M., & Khan, I. (2023). Eco-innovations, green growth, and environmental taxes in EU countries: A panel quantile regression approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(49), 108005-108022. [CrossRef]
- Li, L., Zhai, Z., Liu, J., & Hu, J. (2015). Estimating industrial and domestic environmental releases of perfluorooctanoic acid and its salts in China from 2004 to 2012. Chemosphere, 129, 100-109. [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M., Shahzad, S. J. H., Ahmad, N., & Alam, S. (2016). Financial development and environmental quality: the way forward. Energy policy, 98, 353-364. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. J. (2011). The impact of financial development on carbon emissions: An empirical analysis in China. Energy policy, 39(4), 2197-2203. [CrossRef]
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). (2020). Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2019. Retrieved from https://www.irena.org/publications/2020/Jun/Renewable-Power-Generation-Costs-in-2019.
- Jednak, S., Minović, J., & Kragulj, D. (2020). A review of economic and environment indicators and energy efficiency: Evidence from the EU and Serbia. Economic themes, 58(4), 459-477. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T. K. L., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W., Nghiem, L. D., Qian, G., Liu, Q., ... & Mainali, B. (2021). Assessing the environmental impacts and greenhouse gas emissions from the common municipal wastewater treatment systems. Science of the Total Environment, 801, 149676. [CrossRef]
- Ruza, C., & Caro-Carretero, R. (2022). The non-linear impact of financial development on environmental quality and sustainability: evidence from G7 countries. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(14), 8382. [CrossRef]
- Xu, W., Xie, Y., Cai, Y., Ji, L., Wang, B., & Yang, Z. (2021). Environmentally-extended input-output and ecological network analysis for Energy-Water-CO2 metabolic system in China. Science of the Total Environment, 758, 143931. [CrossRef]
- Sharif, T., Uddin, M. M. M., & Alexiou, C. (2022). Testing the moderating role of trade openness on the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a novel approach. Annals of Operations Research, 1-39. [CrossRef]
- Yasin, I., Aslam, A., Siddik, A. B., Abbass, K., & Murshed, M. (2023). Offshoring the scarring causes and effects of environmental challenges faced by the advanced world: an empirical evidence. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(32), 79335-79345. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N., Hamid, Z., Rehman, K. U., Senkus, P., Khan, N. A., Wysokińska-Senkus, A., & Hadryjańska, B. (2023). Environmental regulation, fiscal decentralization, and agricultural carbon intensity: a challenge to ecological sustainability policies in the United States. Sustainability, 15(6), 5145. [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, A., Fatima, T., & Murshed, M. (2023). Asymmetric effects of tourism development and green innovation on economic growth and carbon emissions in Top 10 GDP Countries. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, 66(3), 471-500. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M. M., Shahbaz, M., Sultana, T., Wang, Z., Sohag, K., & Abbas, S. (2023). Changes in environmental degradation parameters in Bangladesh: the role of net savings, natural resource depletion, technological innovation, and democracy. Journal of Environmental Management, 343, 118-190. [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, C., Infante, D., & Smirnova, J. (2012). Rule of law and the environmental Kuznets curve: evidence for carbon emissions. International Journal of Sustainable Economy, 4(3), 254-269. [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N., & Payne, J. E. (2017). Per capita carbon dioxide emissions across US states by sector and fossil fuel source: evidence from club convergence tests. Energy Economics, 63, 365-372. [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M., Haouas, I., & Van Hoang, T. H. (2019). Economic growth and environmental degradation in Vietnam: is the environmental Kuznets curve a complete picture?. Emerging Markets Review, 38, 197-218. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Sun, M., Yang, R., Li, X., Zhang, L., & Li, M. (2021). Decoupling water environment pressures from economic growth in the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Ecological Indicators, 122, 107314. [CrossRef]
- Dong, L., Tong, X., Li, X., Zhou, J., Wang, S., & Liu, B. (2019). Some developments and new insights of environmental problems and deep mining strategy for cleaner production in mines. Journal of Cleaner Production, 210, 1562-1578. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A. (2019). Corporate environmental performance evaluation: A cross-country appraisal. Journal of cleaner production, 237, 117607. [CrossRef]
- Khan, A., Muhammad, F., Chenggang, Y., Hussain, J., Bano, S., & Khan, M. A. (2020). The impression of technological innovations and natural resources in energy-growth-environment nexus: a new look into BRICS economies. Science of The Total Environment, 727, 138265. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., Pei, Y., Zhao, S., Xiao, R., Sang, X., & Zhang, C. (2020). A review of remote sensing for environmental monitoring in China. Remote Sensing, 12(7), 1130. [CrossRef]
- Aluko, O. A., & Obalade, A. A. (2020). Financial development and environmental quality in sub-Saharan Africa: Is there a technology effect?. Science of the Total Environment, 747, 141515. [CrossRef]
- Nosheen, F., Imran, M., Anjum, S., & Kouser, R. (2021). Economic growth, environmental efficiency, and industrial transfer demonstration zones of China: A way forward for CPEC. Review of Applied Management and Social Sciences, 4(2), 357-370. [CrossRef]
- Odhiambo, N. M. (2020). Financial development, income inequality and carbon emissions in Sub-Saharan African countries: a panel data analysis. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 38(5), 1914-1931. [CrossRef]
- Raghutla, C., Malik, M. N., Hameed, A., & Chittedi, K. R. (2024). Impact of public-private partnerships investment and FDI on CO2 emissions: A study of six global investment countries. Journal of Environmental Management, 360, 121213. [CrossRef]
- Umar, M., Ji, X., Kirikkaleli, D., & Xu, Q. (2020). COP21 Roadmap: Do innovation, financial development, and transportation infrastructure matter for environmental sustainability in China?. Journal of environmental management, 271, 111026. [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M. A., Canh, N. P., & Le, T. N. L. (2021). Environmental degradation & role of financialisation, economic development, industrialisation and trade liberalisation. Journal of environmental management, 277, 111471. [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Herránz, A., Balsalobre, D., Cantos, J. M., & Shahbaz, M. (2017). Energy innovations-GHG emissions nexus: fresh empirical evidence from OECD countries. Energy Policy, 101, 90-100. [CrossRef]
- Duque-Grisales, E., Aguilera-Caracuel, J., Guerrero-Villegas, J., & García-Sánchez, E. (2020). Can proactive environmental strategy improve Multilatinas’ level of internationalization? The moderating role of board independence. Business Strategy and the Environment, 29(1), 291-305. [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, B., Tzeremes, P. G., & Tzeremes, N. G. (2020). Energy consumption, economic growth and environmental degradation in OECD countries. Economic Modelling, 84, 203-213. [CrossRef]
- Birdsall, N., & Wheeler, D. (1993). Trade policy and industrial pollution in Latin America: where are the pollution havens?. The Journal of Environment & Development, 2(1), 137-149. [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, F., & Riaz, K. (2016). CO2 emissions and financial development in an emerging economy: an augmented VAR approach. Energy policy, 90, 102-114. [CrossRef]
- Law, B. E., Hudiburg, T. W., Berner, L. T., Kent, J. J., Buotte, P. C., & Harmon, M. E. (2018). Land use strategies to mitigate climate change in carbon dense temperate forests. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(14), 3663-3668. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J. (1996). Chlorophenols in the terrestrial environment. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology: Continuation of Residue Reviews, 25-51.
- Ogbeifun, L., & Shobande, O. A. (2022). A reevaluation of human capital accumulation and economic growth in OECD. Journal of Public Affairs, 22(4), e2602. [CrossRef]
- Singhania, M., & Gandhi, G. (2015). Social and environmental disclosure index: Perspectives from Indian corporate sector. Journal of Advances in Management Research, 12(2), 192-208. [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, V. S. (2023). Financial development, economic growth, globalisation and environmental quality in BRICS economies: evidence from ARDL bounds test approach. Economic Change and Restructuring, 56(3), 1651-1682. [CrossRef]
- Pantelopoulos, G. (2023). Human capital, gender equality and foreign direct investment: Evidence from OECD countries. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Popp, D. (2019). Environmental policy and innovation: A decade of research. Environmental and Resource Economics. https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w25631/w25631.pdf.
- Jaffe, A. B., & Stavins, R. N. (1995). Dynamic incentives of environmental regulations: The effects of alternative policy instruments on technology diffusion. Journal of environmental economics and management, 29(3), S43-S63. [CrossRef]
- Horbach, J. (2016). Empirical determinants of eco-innovation in European countries using the community innovation survey. Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions, 19, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y., Gao, P., Tian, W., & Guan, W. (2023). Green innovation for resource efficiency and sustainability: Empirical analysis and policy. Resources Policy, 81, 103369. [CrossRef]
- He, W., & Wang, B. (2024). Environmental jurisdiction and energy efficiency: Evidence from China’s establishment of environmental courts. Energy Economics, 131, 107358. [CrossRef]
- Li, L., & Li, W. (2022). The promoting effect of green technology innovations on sustainable supply chain development: evidence from China’s transport sector. Sustainability, 14(8), 4673. [CrossRef]
- Chishti, M. Z., & Sinha, A. (2022). Do the shocks in technological and financial innovation influence the environmental quality? Evidence from BRICS economies. Technology in Society, 68, 101828. [CrossRef]
- Chishti, M. Z., Arfaoui, N., & Cheong, C. W. (2023). Exploring the time-varying asymmetric effects of environmental regulation policies and human capital on sustainable development efficiency: a province level evidence from China. Energy Economics, 126, 106922. [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S., Mody, A., Roy, S., & Wheeler, D. (2001). Environmental regulation and development: A cross-country empirical analysis. Oxford development studies, 29(2), 173-187.
- Zhang, J., Ouyang, Y., Ballesteros-Pérez, P., Li, H., Philbin, S. P., Li, Z., & Skitmore, M. (2021). Understanding the impact of environmental regulations on green technology innovation efficiency in the construction industry. Sustainable Cities and Society, 65, 102647. [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M. T., & Mazhar, M. (2019). Financial development and ecological footprint: a global panel data analysis. Pakistan Journal of Commerce and Social Sciences (PJCSS), 13(2), 487-514.
- Shahbaz, M., Haouas, I., & Van Hoang, T. H. (2019). Economic growth and environmental degradation in Vietnam: is the environmental Kuznets curve a complete picture?. Emerging Markets Review, 38, 197-218. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W., & Li, G. (2020). Environmental decentralization, environmental protection investment, and green technology innovation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1-16.
- Dong, Z., He, Y., Wang, H., & Wang, L. (2020). Is there a ripple effect in environmental regulation in China?–Evidence from the local-neighborhood green technology innovation perspective. Ecological Indicators, 118, 106773. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A., Nand, A., & Castka, P. (2019). Lean-green integration and its impact on sustainability performance: A critical review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 236, 117697. [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M. H., & Yamagata, T. (2008). Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. Journal of econometrics, 142(1), 50-93. [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M. H. (2007). A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. Journal of applied econometrics, 22(2), 265-312. [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, J. (2008). Panel cointegration tests of the Fisher effect. Journal of applied econometrics, 23(2), 193-233. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z., Ahmad, M., Rjoub, H., Kalugina, O. A., & Hussain, N. (2022). Economic growth, renewable energy consumption, and ecological footprint: Exploring the role of environmental regulations and democracy in sustainable development. Sustainable Development, 30(4), 595-605. [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, E. I., & Hurlin, C. (2012). Testing for Granger non-causality in heterogeneous panels. Economic modelling, 29(4), 1450-1460. [CrossRef]
- Im, K. S., Pesaran, M. H., & Shin, Y. (2003). Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. Journal of econometrics, 115(1), 53-74. [CrossRef]
- Dickey, D. A., & Fuller, W. A. (1979). Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. Journal of the American statistical association, 74(366a), 427-431.
- Farooq, S. A., Mukhtar, S. H., Raina, A., Haq, M. I. U., Siddiqui, M. I. H., Naveed, N., & Dobrota, D. (2024). Effect of TiB2 on the mechanical and tribological properties of marine grade Aluminum Alloy 5052: An experimental investigation. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 29, 3749-3758. [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M. (2009). A reassessment of finance-growth nexus for Pakistan: under the investigation of FMOLS and DOLS techniques. IUP Journal of Applied Economics, 8(1), 65.
- Priyankara, H. P. R., Luo, F., Saeed, A., Nubuor, S. A., & Jayasuriya, M. P. F. (2018). How does leader’s support for environment promote organizational citizenship behaviour for environment? A multi-theory perspective. Sustainability, 10(1), 271. [CrossRef]
- Khan, I., Saeed, K., & Khan, I. (2019). Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arabian journal of chemistry, 12(7), 908-931.
- Olofin, R. E. (2019). Strengthening civil-military relations in Nigeria for improved national security: Lessons from the field. Deepening Civil Military Relations for Effective Peacebuilding and Democratic Governance in Nigeria. Ni.
- Olorogun, L. A. (2023). Modelling Financial Development in the Private Sector, FDI, and Sustainable Economic Growth in sub-Saharan Africa: ARDL Bound Test-FMOLS, DOLS Robust Analysis. Journal of the Knowledge Economy, 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J., Carrico, R., Wilde, A., Junkins, A., Furmanek, S., Chandler, T., ... & Begier, E. (2023). Diagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus in adults substantially increases when adding sputum, saliva, and serology testing to nasopharyngeal swab RT–PCR. Infectious Diseases and Therapy, 12(6), 1593-1603. [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, J., & Hosseinkouchack, M. (2016). Modified CADF and CIPS panel unit root statistics with standard chi-squared and normal limiting distributions. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics, 78(3), 347-364. [CrossRef]
- Batool, M., Jehan, Y., & Hayat, N. (2020). Effect of financial development and institutional quality on the environmental degradation in developed and developing countries. Int J Hum Capital Urban Manage, 5(2), 111-124.
- Gök, A. (2020). The role of financial development on carbon emissions: a meta regression analysis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(11), 11618-11636. [CrossRef]
- Neog, Y., & Yadava, A. K. (2020). Nexus among CO2 emissions, remittances, and financial development: a NARDL approach for India. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(35), 44470-44481. [CrossRef]
- Ali, M., Raza, S. A. A., Puah, C. H., & Samdani, S. (2021). How financial development and economic growth influence human capital in low-income countries. International Journal of Social Economics, 48(10), 1393-1407. [CrossRef]
- Jianguo, D., Ali, K., Alnori, F., & Ullah, S. (2022). The nexus of financial development, technological innovation, institutional quality, and environmental quality: evidence from OECD economies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(38), 58179-58200. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C., Zhang, F., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Revisiting financial opening and financial development: A regulation heterogeneity perspective. Economic Analysis and Policy, 80, 181-197. [CrossRef]
- Pao, H. T., & Tsai, C. M. (2011). Multivariate Granger causality between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, FDI (foreign direct investment) and GDP (gross domestic product): evidence from a panel of BRIC (Brazil, Russian Federation, India, and China) countries. Energy, 36(1), 685-693. [CrossRef]
- Cole, M. A., Elliott, R. J., Okubo, T., & Zhang, L. (2021). Importing, outsourcing and pollution offshoring. Energy Economics, 103, 105562. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, P. T., Postel-Vinay, G., & Rosenthal, J. L. (2015). Entry, information, and financial development: A century of competition between French banks and notaries. Explorations in Economic History, 55, 39-57. [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M., Rehman, I. U., & Muzaffar, A. T. (2015). Re-Visiting Financial Development and Economic Growth Nexus: The Role of Capitalization in B angladesh. South African Journal of Economics, 83(3), 452-471.
- Tang, C. F., & Tan, B. W. (2014). The linkages among energy consumption, economic growth, relative price, foreign direct investment, and financial development in Malaysia. Quality & Quantity, 48, 781-797. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y. (2021). [Retracted] Financial Development and Carbon Emissions: Analyzing the Role of Financial Risk, Renewable Energy Electricity, and Human Capital for China. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, 2021(1), 1025669.
- Shan, S., Ahmad, M., Tan, Z., Adebayo, T. S., Li, R. Y. M., & Kirikkaleli, D. (2021). The role of energy prices and non-linear fiscal decentralization in limiting carbon emissions: tracking environmental sustainability. Energy, 234, 121243. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X., Shang, Y., Ma, X., Xia, P., & Shahzad, U. (2022). Does carbon trading lead to green technology innovation: recent evidence from Chinese companies in resource-based industries. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 71, 2506-2523. [CrossRef]
- Bakhsh, S., Yin, H., & Shabir, M. (2021). Foreign investment and CO2 emissions: do technological innovation and institutional quality matter? Evidence from system GMM approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(15), 19424-19438. [CrossRef]
| Types | Acronym | Variable Titles | Measurements and Data Sources | Data Availability |
| Outcome | CO2 | Corbon Emission | CO2 emissions (kg per 2021 PPP $ of GDP) | 2001-2023 |
| Input | FSD | Broad Money | Broad money (% of GDP) | 2001-2023 |
| DCPS | Domestic Credit to private Sector | Domestic credit to private sector (% of GDP) | 2001-2023 | |
| FDI | Foreign Direct Investment | Foreign direct investment, net inflows (% of GDP) | 2001-2023 | |
|
GTI |
Green Technological Innovation | Green technological Innovation Patent applications, (residents & non-resident) | 2001-2023 |
| LCO2 | LBM | LDCPS | LFDI | LGTI | |
| Mean | -1.55 | 4.38 | 4.09 | 0.42 | 9.45 |
| Median | -1.35 | 4.29 | 4.04 | 0.51 | 9.13 |
| Maximum | -0.32 | 5.43 | 5.27 | 2.27 | 14.17 |
| Minimum | -3.91 | 3.17 | 2.82 | -1.58 | 6.30 |
| Std. Dev. | 0.97 | 0.48 | 0.51 | 0.72 | 2.14 |
| Skewness | -0.54 | 0.41 | 0.33 | -0.32 | 0.68 |
| Kurtosis | 2.09 | 3.02 | 3.17 | 2.72 | 2.85 |
| Correlation | |||||
| LCO2 | LBM | LDCPS | LFDI | LGTI | |
| LCO2 | 1 | 0.55 | 0.56 | -0.45 | -0.01 |
| LBM | 0.55 | 1.00 | 0.93 | -0.27 | 0.63 |
| LDCPS | 0.56 | 0.93 | 1.00 | -0.31 | 0.58 |
| LFDI | -0.45 | -0.27 | -0.31 | 1.00 | -0.17 |
| LGTI | -0.01 | 0.63 | 0.58 | -0.17 | 1.00 |
| Test statistics | Statistics | p-value |
| ∆test | 2.13** | 0.00 |
| ∆ adj | 4.11** | 0.00 |
| Variables | CD statistics | p-value | Decisions |
| LCO2 | 5.13*** | 0.00 | Cross sectional dependency |
| LBM | 13.02*** | 0.00 | Cross sectional dependency |
| LDCPS | 7.93*** | 0.00 | Cross sectional dependency |
| LFDI | 1.75*** | 0.07 | Cross sectional dependency |
| LGTI | 1.63*** | 0.10 | Cross sectional dependency |
| Statistics | Value | Z-value | P- Value | Outcomes |
| Gt | 4.02*** | 3.05*** | 0.00 | Co-integration |
| Ga | -2.04*** | -3.60** | 0.05 | Co-integration |
| Pt | -3.12*** | -4.32*** | 0.00 | Co-integration |
| Pa | -1.08** | -1.40* | 0.09 | Co-integration |
| Long Run Equation | Short Run Equation | |||||||
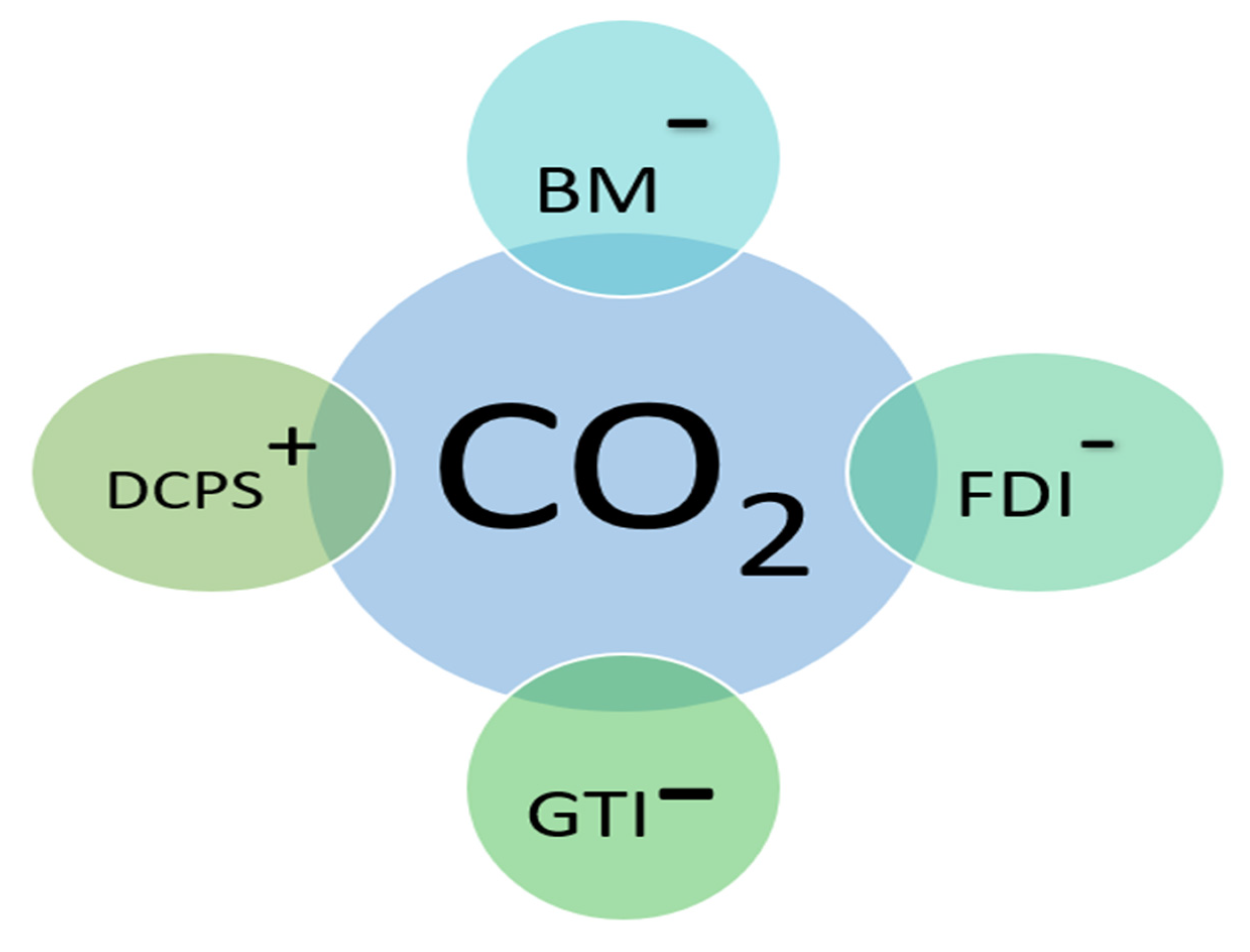
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob.* | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob.* |
| LBM | -2.88 | 1.33 | -2.17 | 0.03 | -0.15 | 0.09 | -1.63 | 0.11 |
| LDCPS | 3.53 | 1.86 | 1.90 | 0.06 | -0.10 | 0.08 | -1.34 | 0.18 |
| LFDI | -0.74 | 0.29 | -2.53 | 0.01 | -0.01 | 0.02 | -0.51 | 0.61 |
| LGTI | -0.29 | 0.24 | -1.20 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 1.86 | 0.07 |
| COINTEQ01 | -0.02 | 0.01 | -1.53 | 0.13 | ||||
| FOLS | DOLS | |||||||
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob. | Coefficient | Std. Error | t-Statistic | Prob. |
| LBM | -0.26 | 0.00 | -66.03 | 0.00 | -0.86 | 0.58 | -1.49 | 0.14 |
| LDCPS | 0.41 | 0.01 | 73.80 | 0.00 | 0.96 | 0.55 | 1.76 | 0.09 |
| LFDI | -0.72 | 0.00 | -194.40 | 0.00 | -0.69 | 0.17 | -4.13 | 0.00 |
| LGTI | -0.22 | 0.00 | -53.98 | 0.00 | -0.14 | 0.08 | -1.69 | 0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




