Submitted:
18 August 2024
Posted:
19 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
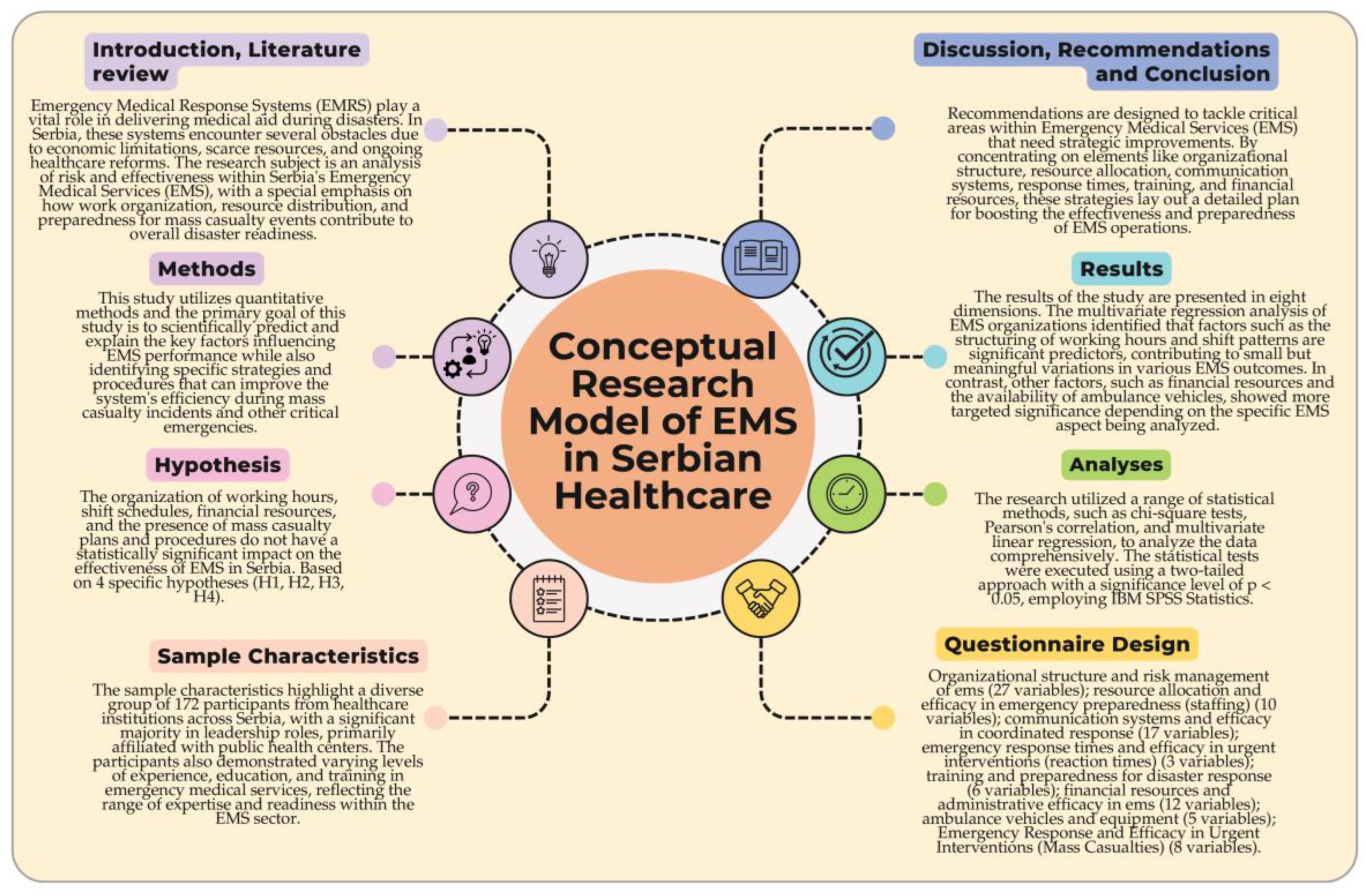
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review
2. Methods
- H₁ − The organization of working hours and shift schedules significantly improves EMS organization and performance in Serbia.
- H₂ − Financial resources allocated to EMS play a critical role in enhancing the system’s preparedness and operational efficiency during disaster response.
- H₃ − The implementation of mass casualty plans and procedures significantly strengthens EMS readiness and response capabilities in large-scale emergencies.
- H₄ − The availability of ambulance vehicles and specialized equipment significantly enhances the overall effectiveness of EMS, particularly in handling mass casualty incidents.
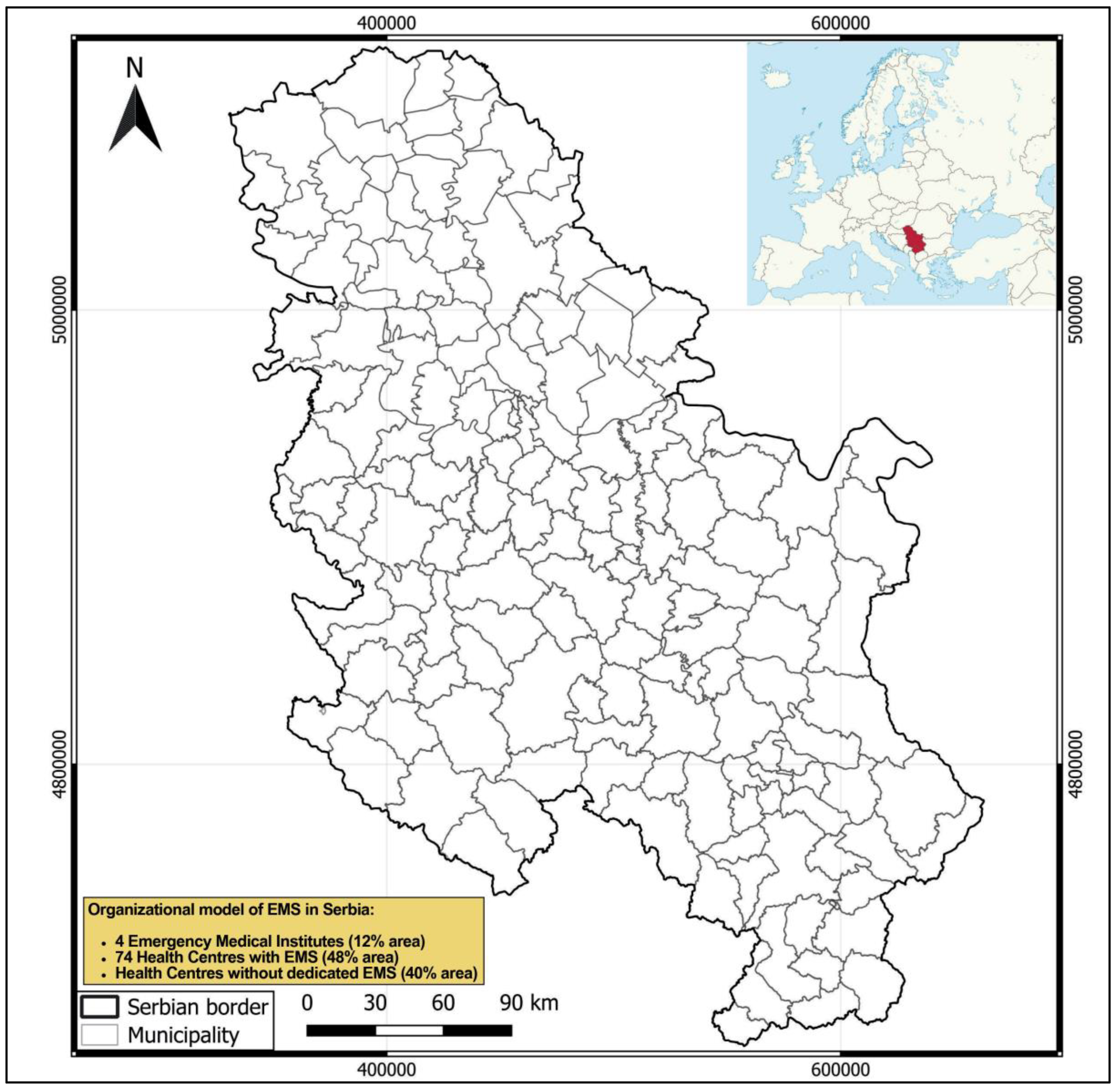
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Characteristics
2.3. Questionnaire Design
2.4. Analyses
3. Results
3.1. The Predictors of Risk and Efficacy Analysis of Emergency Medical Response Systems in Serbian Healthcare
3.2. Correlations and Influences of Demographic and Socioeconomic Factors on the Perception of Risk and Efficacy Analysis of Emergency Medical Response Systems in Serbian Healthcare
3.3. Organizational Structure and Risk Management of Emergency Medical Services (EMS)
3.4. Resource Allocation and Efficacy in Emergency (Disaster) Preparedness
3.5. Communication Systems and Efficacy in Coordinated Response
3.6. Emergency Response Times and Efficacy in Urgent Interventions
3.6. Training and Preparedness for Disaster (Emergency) Response
3.8. Financial Resources and Administrative Efficacy in Emergency Medical Services
4. Discussion
5. Recommendations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A









References
- Cvetković, V.; Tanasić, J.; Ocal, A.; Živković-Šulović, M.; Ćurić, N.; Milojević, S.; Knežević, S. The Assessment of Public Health Capacities at Local Self-Governments in Serbia. Lex localis - Journal of Local Self Government 2023, 21, 1201–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvetković, V.M.; Tanasić, J.; Ocal, A.; Kešetović, Ž.; Nikolić, N.; Dragašević, A. Capacity Development of Local Self-Governments for Disaster Risk Management. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, 10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Liu, J.; Han, Z.; Jiang, J. Stochastic Petri net based modeling of emergency medical rescue processes during earthquakes. Journal of systems science and complexity 2021, 34, 1063–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoro, A.; Mehmood, A.; Rapaport, S.; Ezeigwe, A.K.; Adeyeye, A.; Akinlade, O.; Dias, J.; Barnett, D.J.; Hsu, E.B.; Tower, C. A scoping review of the essential components of emergency medical response systems for mass casualty incidents. Disaster medicine and public health preparedness 2023, 17, e274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billhardt, H.; Lujak, M.; Sánchez-Brunete, V.; Fernández, A.; Ossowski, S. Dynamic coordination of ambulances for emergency medical assistance services. Knowledge-Based Systems 2014, 70, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Quevedo, C.; Bjegovic-Mikanovic, V.; Vasic, M.; Vukovic, D.; Jankovic, J.; Jovic-Vranes, A.; Santric-Milicevic, M.; Terzic-Supic, Z. How accessible is the Serbian health system? Main barriers and challenges ahead. European Journal of Public Health 2020, 30, ckaa166-1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.D.; Simic, S.; Beste, L.; Vukovic, D.; Bjegovic, V.; VanRooyen, M.J. Multimodal assessment of the primary healthcare system of Serbia: a model for evaluating post-conflict health systems. Prehospital and disaster medicine 2003, 18, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacevic, M.; Milicevic, M.S.; Vasic, M.; Horozovic, V.; Milicevic, M.; Milic, N. The relationship between dual practice, intention to work abroad and job satisfaction: A population-based study in the Serbian public healthcare sector. Health Policy 2018, 122, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radović, V.; Ćurčić, L. The opportunities of crises and emergency risk communication in activities of Serbian public health workforce in emergencies. Iranian journal of public health 2012, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tiede, W.; Simon, C. Comparative analysis of the Serbian and German legislation on emergency medical services. SEER Journal for Labour and Social Affairs in Eastern Europe 2010, 12, 263–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavanja, V.A. (81) Reform of the Emergency Medical Services System in Serbia. Prehospital and Disaster Medicine 2007, 22, S48–S49. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, B.D.; Dierberg, K.; Šćepanović, M.; Mitrović, M.; Vuksanović, M.; Milić, L.; VanRooyen, M.J. Integrating quantitative and qualitative methodologies for the assessment of health care systems: emergency medicine in post-conflict Serbia. BMC health services research 2005, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihailovic, N.; Simic-Vukomanovic, I.; Sunjka, M.L.; Zivanovic, S.; Milicic, B.; Milicic, V. Self-Assessment of Health among the Citizens of Serbia in the Transition Period. Iranian Journal of Public Health 2021, 50, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masic, I.; Hadziahmetovic, M.; Donev, D.; Pollhozani, A.; Ramadani, N.; Skopljak, A.; Pasagic, A.; Roshi, E.; Zunic, L.; Zildzic, M. Public health aspects of the family medicine concepts in South eastern europe. Materia socio-medica 2014, 26, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, S.; Milićević, M.Š.; Matejić, B.; Marinković, J.; Adams, O. Do we have primary health care reform? The story of the Republic of Serbia. Health policy 2010, 96, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihailovic, N.M.; Kocic, S.S.; Trajkovic, G.; Jakovljevic, M. Satisfaction with health services among the citizens of Serbia. Frontiers in pharmacology 2017, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstic, K.; Janicijevic, K.; Timofeyev, Y.; Arsentyev, E.V.; Rosic, G.; Bolevich, S.; Reshetnikov, V.; Jakovljevic, M.B. Dynamics of health care financing and spending in Serbia in the XXI Century. Frontiers in public health 2019, 7, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paunović, I.; Apostolopoulos, S.; Miljković, I.B.; Stojanović, M. Sustainable Rural Healthcare Entrepreneurship: A Case Study of Serbia. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmann, J.; Webb, E.; Williams, G.A.; Hernández-Quevedo, C.; Maier, C.B.; Panteli, D. European countries’ responses in ensuring sufficient physical infrastructure and workforce capacity during the first COVID-19 wave. Health Policy 2022, 126, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, B.S.; Stankovic, S.S. Analysis of the Sustainability of Supply Chains and Value Chain Management: Economy in the Republic of Serbia. In Government Impact on Sustainable and Responsible Supply Chain Management; IGI Global, 2023; pp. 282–306. [Google Scholar]
- Djukanovic, V.; Mach, E.P.; World Health, O. Alternative approaches to meeting basic health needs in developing countries: a joint UNICEF/WHO study; World Health Organization, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Vekić, B.; Pilipović, F.; Dragojević-Simić, V.; Živić, R.; Radovanović, D.; Rančić, N. Implementation of the nationwide electronic health record system in Serbia: challenges, lessons learned, and early outcomes. Acta Clinica Croatica 2022, 61, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vucetic, M.; Uzelac, A.; Gligoric, N. E-health transformation model in Serbia: Design, architecture and developing; 2011; pp. 566–573. [Google Scholar]
- Rajković, P.; Janković, D.; Milenković, A. Developing and deploying medical information systems for Serbian public healthcare: Challenges, lessons learned and guidelines. Computer Science and Information Systems 2013, 10, 1429–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjegovic-Mikanovic, V.; Vasic, M.; Vukovic, D.; Jankovic, J.; Jovic-Vranes, A.; Santric-Milicevic, M.; Terzic-Supic, Z.; Hernández-Quevedo, C.; World Health, O. Serbia: Health system review. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Veličković, J.; Lutovac, M.; Jokić, M. Integrated health information system in the Republic of Serbia. Annals of Nursing 2023, 2, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzoni, L.I.; Dorner, S.C.; Ajayi, T. Community paramedicine—addressing questions as programs expand. New England Journal of Medicine 2016, 374, 1107–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gligorovic, P.; Knezevic, V.; Stojanovic, Z.; Pavicevic, D.; Karlicic, I.S. International models of emergency psychiatric care: the Republic of Serbia. Models of Emergency Psychiatric Services That Work 2020, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Zabuha, Y.Y.; Mykhailichenko, T.О.; Morochkovska, O.V. Overview and analysis of occupational risks in healthcare of eastern europe countries. Wiadomości Lekarskie 2019, 72, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mihic, M.M.; Obradovic, V.L.; Todorovic, M.L.; Petrovic, D.C. Analysis of implementation of the strategic management concept in the healthcare system of Serbia. HealthMED 2012, 6, 34–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanović, R.; Lozanović, D.; Milovančević, M.P.; Jovanović, L.S. The child health care system of Serbia. The Journal of Pediatrics 2016, 177, S156–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasković-Marković, Z.; Bjegović, V.; Janković, S.; Kocev, N.; Laaser, U.; Marinković, J.; Marković-Denić, L.; Pejin-Stokić, L.; Penev, G.; Stanisavljević, D. The burden of disease and injury in Serbia; Ministry of health of the Republic of Serbia: Belgrade, Serbia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, H.K.; Bhusal, S.; Barone-Adesi, F.; Hubloue, I. Prehospital emergency care in low-and middle-income countries: a systematic review. Prehospital and Disaster Medicine 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakovljevic, M.; Jovanovic, M.; Lazic, Z.; Jakovljevic, V.; Radovanovic-Velickovic, R.; Antunovic, M. Current efforts and proposals to reduce healthcare costs in Serbia. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetković, V.; Šišović, V. Understanding the Sustainable Development of Community (Social) Disaster Resilience in Serbia: Demographic and Socio-Economic Impacts. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.; Nikolić, N.; Lukić, T. Exploring Students’ and Teachers’ Insights on School-Based Disaster Risk Reduction and Safety: A Case Study of Western Morava Basin, Serbia. Safety 2024, 10, 2024040472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.M. In-Depth Analysis of Disaster (Risk) Management System in Serbia: A Critical Examination of Systemic Strengths and Weaknesses. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sudar, S.; Cvetković, V.; Ivanov, A. Harmonization of Soft Power and Institutional Skills: Montenegro’s Path to Accession to the European Union in the Environmental Sector. International Journal of Disaster Risk Management 2024, 6, 41–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V. Disaster Risk Management; Scientific-Professional Society for Disaster Risk Management. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tanasić, J.; Cvetković, V. The Efficiency of Disaster and Crisis Management Policy at the Local Level: Lessons from Serbia; Scientific-Professional Society for Disaster Risk Management: Belgrade, Serbia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lončar, D.; Stojanović, F. Gap analysis of the health system in Serbia compared to the developed health systems in Europe. Ekonomika preduzeća 2017, 65, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch Mejsner, S.; Eklund Karlsson, L. Informal payments and health system governance in serbia: A pilot study. Sage Open 2017, 7, 2158244017728322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.M.; Radovanović, M.P.; Milašinović, S.M. Disaster risk communication: Attitudes of Serbian citizens. Sociološki pregled 2021, 55, 1610–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.M.; Radovanović, M. Disaster risk communication: attitudes of Serbian citizens-Komunikacija o rizicima od katastrofa: stavovi građana Srbije.
- Ebben, R.H.A.; Siqeca, F.; Madsen, U.R.; Vloet, L.C.M.; Van Achterberg, T. Effectiveness of implementation strategies for the improvement of guideline and protocol adherence in emergency care: a systematic review. BMJ open 2018, 8, e017572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gačić, J.; Jović, S.J.; Terzić, N.S.; Cvetković, V.M.; Terzić, M.T.; Stojanović, D.G.; Stojanović, G.R. Gender differences in stress intensity and coping strategies among students, future emergency relief specialists. Vojnosanitetski pregled 2021, 78, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.; Aksentijević, V.; Ivović, M. Uloga službe hitne medicinske pomoći u vanrednim situacijama izazvanim terorističkim aktima - The role of emergency medical service in disaster caused by terrorism. 2015; 355–367. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetković, V. Essential Tactics for Disaster Protection and Resque. Belgrade: Scientific-Professional Society for Disaster Risk Management 2022, 1–794. [Google Scholar]
- Hopp, W.J.; Lovejoy, W.S. Hospital operations: Principles of high efficiency health care; FT Press, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hick, J.L.; Hanfling, D.; Wynia, M.K.; Pavia, A.T. Duty to plan: health care, crisis standards of care, and novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Nam Perspectives 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hick, J.L.; Hanfling, D.; Cantrill, S.V. Allocating scarce resources in disasters: emergency department principles. Annals of emergency medicine 2012, 59, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, L.; Kaiyou, Y. Research on Smart Warehouse of Emergency Supplies Based on Cloud Computing and IoT. 2022; 693–697. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, M.A.; Gayer, M.; Ryan, M.J.; Salama, P.; Spiegel, P.; Heymann, D.L. Communicable diseases in complex emergencies: impact and challenges. The Lancet 2004, 364, 1974–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee on the Future of Emergency Care in the United States Health, S. Hospital-based emergency care: at the breaking point; National Academies Press, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, P.A.; Gabbe, B.J.; Smith, K.; Mitra, B. Triaging the right patient to the right place in the shortest time. British journal of anaesthesia 2014, 113, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butkus, R.; Serchen, J.; Moyer, D.V.; Bornstein, S.S.; Hingle, S.T.; Health; Public Policy Committee of the American College of, P. Achieving gender equity in physician compensation and career advancement: a position paper of the American College of Physicians. Annals of internal medicine 2018, 168, 721–723.
- Bogdan, G.M.; Scherger, D.L.; Keller, D.; Wruk, K.M.; Peterson, J.; Swanson, B.S.N.D.D.; Ammon, K.; Daley, D.W.; Dart, R.C.; Gabow, P.A. Health Emergency Assistance Line and Triage Hub (HEALTH) Model. Prepared by Denver Health—Rocky Mountain Poison and Drug Center under Contract 2005, 5–0040. [Google Scholar]
- Besciu, C.D. The Paradoxes of European Medical System Regarding the Performance Management. International Journal of Economic Practices & Theories 2015, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Beamon, B.M.; Kotleba, S.A. Inventory modelling for complex emergencies in humanitarian relief operations. International Journal of Logistics: research and applications 2006, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriball, L.; Bremner, J.; Buchan, J.; Craveiro, I.; Dieleman, M.; Dix, O.; Dussault, G.; Jansen, C.; Kroezen, M.; Rafferty, A.M. Recruitment and retention of the health workforce in Europe; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Aringhieri, R.; Bruni, M.E.; Khodaparasti, S.; van Essen, J.T. Emergency medical services and beyond: Addressing new challenges through a wide literature review. Computers & Operations Research 2017, 78, 349–368. [Google Scholar]
- Anđelić, S.; Vidanović, V.; Milutinović, O. View on health care system of the Republic of Serbia. Annals of Nursing 2023, 2, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboueljinane, L.; Sahin, E.; Jemai, Z. A review on simulation models applied to emergency medical service operations. Computers & Industrial Engineering 2013, 66, 734–750. [Google Scholar]
- Abella, M. Policies and best practices for management of temporary migration. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wennlund, K.T. Emergency medical dispatching: protocols, experiences and priorities; Karolinska Institutet (Sweden). 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Snow, R.C.; Asabir, K.; Mutumba, M.; Koomson, E.; Gyan, K.; Dzodzomenyo, M.; Kruk, M.; Kwansah, J. Key factors leading to reduced recruitment and retention of health professionals in remote areas of Ghana: a qualitative study and proposed policy solutions. Human resources for health 2011, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchison-Krupat, J.; Kavadias, S. Strategic resource allocation: Top-down, bottom-up, and the value of strategic buckets. Management Science 2015, 61, 391–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, C.-A.; Singh, D. From staff-mix to skill-mix and beyond: towards a systemic approach to health workforce management. Human resources for health 2009, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, J.E.; Tannenbaum, S.I.; Salas, E. Influences of individual and situational characteristics on measures of training effectiveness. Academy of management journal 1992, 35, 828–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, I.C. Improving public safety emergency response efficiency amid uncertainty through crisis leadership training. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetković, V.M.; Öcal, A.; Ivanov, A. Young adults’ fear of disasters: A case study of residents from Turkey, Serbia and Macedonia. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.M.; Dragašević, A.; Protić, D.; Janković, B.; Nikolić, N.; Milošević, P. Fire safety behavior model for residential buildings: Implications for disaster risk reduction. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M. Governing the health care state: a comparative study of the United Kingdom, the United States, and Germany. Manchester University Press, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlmann, E.; Allsop, J.; Saks, M. Professional governance and public control: a comparison of healthcare in the United Kingdom and Germany. Current Sociology 2009, 57, 511–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.; Andrić, K. Comparative Analysis of Disaster Risk Management Systems in Germany, USA, Russia and China. Preprints 2023, arXiv:2023020267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, M.; Zuzan, O. EMS systems in Germany. Resuscitation 2006, 68, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyworth, J. Emergency medicine—quality indicators: the United Kingdom perspective. Academic emergency medicine 2011, 18, 1239–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S. Keynote address: United Kingdom experiences of evaluating performance and quality in emergency medicine. Academic Emergency Medicine 2011, 18, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavalankar, D.V.; Ramani, K.V.; Patel, A.; Sankar, P. Building the Infrastructure to Reach and Care for the Poor: Trends, Obstacles and Strategies to overcome them. 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Committee on the Future of Emergency Care in the United States Health, S. Emergency medical services: at the crossroads; National Academies Press, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pozner, C.N.; Zane, R.; Nelson, S.J.; Levine, M. International EMS systems: The United States: past, present, and future. Resuscitation 2004, 60, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, L.G.; Williams, C.A.; Byrne, C.L.; McCauley, D. Planning for organization development in operations control centers; United States. Office of Aerospace Medicine, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Alanazy, A.R.M.; Wark, S.; Fraser, J.; Nagle, A. Factors impacting patient outcomes associated with use of emergency medical services operating in urban versus rural areas: a systematic review. International journal of environmental research and public health 2019, 16, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutilier, J.J. Emergency Medical Services Response Optimization; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Oostlander, S.A.; Bournival, V.; O’Sullivan, T.L. The roles of emergency managers and emergency social services directors to support disaster risk reduction in Canada. International journal of disaster risk reduction 2020, 51, 101925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, P.; Arii, M.; Kayden, S. Learning from Japan: Strengthening US emergency care and disaster response. Health Affairs 2013, 32, 2172–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgington, D.W. Local Government Emergency Response Following the Great East Japan Earthquake Disaster. JAPAN: Facing Major Natural and International Challenges in the 21st Century, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, E.; Naidoo, M.R.; Prakaschandra, D.R. Preparedness of Western Cape ALS providers to provide clinical stabilisation and intensive care for neonates during the patient journey. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Geisler, E.; Wickramasinghe, N. The role and use of wireless technology in the management and monitoring of chronic diseases. IBM Center for The Business of Government, Tech. Rep 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.-Y.; Park, Y.-T.; Jo, E.C.; Kim, S.-M. Current status and progress of telemedicine in Korea and other countries. Healthcare Informatics Research 2015, 21, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langhelle, A.; Lossius, H.M.; Silfvast, T.; Björnsson, H.M.; Lippert, F.K.; Ersson, A.; Søreide, E. International EMS systems: the Nordic countries. Resuscitation 2004, 61, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawhari, B.; Ludwick, D.; Keenan, L.; Zakus, D.; Hayward, R. Benefits and challenges of EMR implementations in low resource settings: a state-of-the-art review. BMC medical informatics and decision making 2016, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.L.; Poggioli, S. A81 Emergency Transport experiences from Sub-Saharan Africa: public involvement in transport innovations to improve access to healthcare. Journal of Transport & Health 2015, 2, S47. [Google Scholar]
- Apiratwarakul, K.; Suzuki, T.; Celebi, I.; Tiamkao, S.; Bhudhisawasdi, V.; Pearkao, C.; Ienghong, K. “Motorcycle Ambulance” policy to promote health and sustainable development in large cities. Prehospital and Disaster Medicine 2022, 37, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaiman, T.; Filmalter, C.J.; Heyns, T. Important factors for planning nurse staffing in the emergency department: a consensus study. International Emergency Nursing 2021, 56, 100979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abimbola, S.; Baatiema, L.; Bigdeli, M. The impacts of decentralization on health system equity, efficiency and resilience: a realist synthesis of the evidence. Health policy and planning 2019, 34, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, D.; Refsgaard, K. Institutional development and scale matching in disaster response management. Ecological Economics 2007, 63, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapčević, Z.; Mandić-Rajčević, S.; Lepić, M.; Jovanović, M. Evaluating a primary healthcare centre’s preparedness for disasters using the hospital safety index: lessons learned from the 2014 floods in Obrenovac, Serbia. International journal of disaster risk reduction 2019, 34, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank, GFDRR. Serbia – Ready 2 Respond: Emergency Preparredness and Response Assesment - Country Report. 2022. Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/099350008252228932/pdf/P16537706f45a60ba0898302ebcf92314b2.pdf?_gl=1*14k0evo*_gcl_au*MjExOTU3MDcwMC4xNzE2ODkxNzE0.
- GHS Index. "2021 GHS Index Country Profile for Serbia". 2021. Available online: https://ghsindex.org/country/serbia/.
- Nguyen, H.T.H. Disclosable Restructuring Paper-Serbia Emergency COVID-19 Response Project-P173892. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vukosavljević, I.; Vukosavljević, I.; Milutinović, S.; Krivokapić, L.; Cvetković-Jovanović, M.; Ivanović, S. Analysis of the health care system in the Republic of Serbia: Cross-sectional study for the year 2021. Medicinski pregled 2023, 76, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.M.; Nikolić, N.; Radovanović Nenadić, U.; Öcal, A.; K Noji, E.; Zečević, M. Preparedness and Preventive Behaviors for a Pandemic Disaster Caused by COVID-19 in Serbia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, 17, 4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, M.V. The impact fo demographic factors on the expetation of assistance from the police inn natural disaster. Serbian Science Today 2016, 1, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetković, V.; Andrejević, T. Qualitative research on the readiness of citizens to respond to natural disasters. Serbian Science Today 2016, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetković, V.; Kevin, R.; Shaw, R.; Filipović, M.; Mano, R.; Gačić, J.; Jakovljević, V. Household earthquake preparedness in Serbia – a study from selected municipalities. Acta Geographica 2019, 59, In. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetković, V.; Roder, G.; Öcal, A.; Tarolli, P.; Dragićević, S. The Role of Gender in Preparedness and Response Behaviors towards Flood Risk in Serbia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2018, 15, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V. Essential Tactics for Disaster Protection and Resque. Scientific-Professional Society for Disaster Risk Management, Belgrade: 2024.
- Cvetković, V.M.; Gačić, J.; Jakovljević, V. Geospatial and temporal distribution of forest fires as natural disasters. Vojno delo 2016, 68, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.; Renner, R.; Lukić, T.; Aleksova, B. Geospatial and Temporal Patterns of Natural and Man-made (Technological) Disasters (1900-2024): Insights from Different Perspectives. Preprints 2024, 2024080175. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetković, V.; Stojković, D. Analysis of geospatial and temporal distribution of storms as a natural disaster. In International scientific conference - Criminalistic education, situation and perspectives 20 years after Vodinelic, Faculty of security, University St. Kliment Ohridski - Bitola in collaboration with Faculty of detectives and security, FON University: Skopje, 2015.
- Cvetković, V.; Milojković, B.; Stojković, D. Analysis of geospatial and temporal distribution of earthquakes as natural disasters. Vojno delo 2014, 66, 166–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V. The relationship between educational level and citizen preparedness for responding to natural disasters. Journal of the Geographical Institute “Jovan Cvijić” SASA 2016, 66, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.; Gačić, J.; Babić, S. Religiousness level and citizen preparedness for natural disasters. Vojno delo 2017, 69, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.; Janković, B. Private security preparedness for disasters caused by natural and anthropogenic hazards. International Journal of Disaster Risk Management 2020, 2, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.; Roder, G.; Tarolli, P.; Öcal, A.; Ronan, K.; Dragićević, S. Flood risk perception and preparedness: a gendered perspective in Serbia. Disasters 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cvetković, V.; Roder, G.O.A.; Tarolli, P.; Dragićević, S. The Role of Gender in Preparedness and Response Behaviors towards Flood Risk in Serbia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Nam, M.-Y.; Choi, J.; Kirlik, A.; Sha, L.; Berlin, R.B. Supporting emergency medical care teams with an integrated status display providing real-time access to medical best practices, workflow tracking, and patient data. Journal of medical systems 2017, 41, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risser, D.T.; Rice, M.M.; Salisbury, M.L.; Simon, R.; Jay, G.D.; Berns, S.D.; MedTeams Research, C. The potential for improved teamwork to reduce medical errors in the emergency department. Annals of emergency medicine 1999, 34, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKelvie, S.E. Clinical decision making in uncertainty; an ethnography of a complex intervention in the ambulatory emergency care setting. 2021.
- Gowing, J.R.; Walker, K.N.; Elmer, S.L.; Cummings, E.A. Disaster preparedness among health professionals and support staff: what is effective? An integrative literature review. Prehospital and disaster medicine 2017, 32, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, K.; Arbon, P. Are nurses ready?: Disaster preparedness in the acute setting. Australasian Emergency Nursing Journal 2008, 11, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Ding, D.; Hao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Kang, Z.; Jiao, M.; Liang, L.; Ferrier, A. How prepared are hospitals’ emergency management capacity? Factors influencing efficiency of disaster rescue. Disaster medicine and public health preparedness 2018, 12, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waugh Jr, W.L.; Streib, G. Collaboration and leadership for effective emergency management. Public administration review 2006, 66, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, J.; Noon, C. The definitive guide to emergency department operational improvement: employing lean principles with current ED best practices to create the “no wait” department; Productivity Press: 2019.
- MacDonald, S.; Winner, B.; Smith, L.; Juillerat, J.; Belknap, S. Bridging the rural efficiency gap: expanding access to energy efficiency upgrades in remote and high energy cost communities. Energy Efficiency 2020, 13, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, E.P.; Powers, T.L. Volume flexible strategies in health services: A research framework. Production and Operations Management 2004, 13, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Folkard, S.; Tucker, P.; Macdonald, I. Work shift duration: a review comparing eight hour and 12 hour shift systems. Occupational and environmental medicine 1998, 55, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimpfel, A.W.; Sloane, D.M.; Aiken, L.H. The longer the shifts for hospital nurses, the higher the levels of burnout and patient dissatisfaction. Health affairs 2012, 31, 2501–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton-Fairley, D.; Coakley, J.; Moss, F. Hospital at night: an organizational design that provides safer care at night. BMC Medical Education 2014, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, D.L.; Korzenowski, A.L.; Alvarado, M.M.; Sperafico, J.H.; Ackermann, A.E.F.; Mareth, T.; Scavarda, A.J. A systematic review on lean applications’ in emergency departments. 2021; p. 763.
- Dolinskaya, I.; Besiou, M.; Guerrero-Garcia, S. Humanitarian medical supply chain in disaster response. Journal of Humanitarian Logistics and Supply Chain Management 2018, 8, 199–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, J.; Ye, M.; She, D.; Yu, J. Multi-coverage optimal location model for emergency medical service (EMS) facilities under various disaster scenarios: a case study of urban fluvial floods in the Minhang district of Shanghai, China. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences 2020, 20, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakali, S. Assessment of Pre-Hospital Emergency Medical Services Using a Systemic Approach. 2023.
- Cvetković, V.; Nikolić, A. The Role of Social Media in the Process of Informing the Public About Disaster Risks. Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V. A Predictive Model of Community Disaster Resilience based on Social Identity Influences. Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetkovic, V.; Ivanov, A. Knowledge and perceptions of students of the Academy of criminalistic and police studies about natural disasters. 2015; pp. 181-195.
- Cvetković, V.; Ivković, T. Social Resilience to Flood Disasters: Demographic, Socio-economic and Psychological Factors of Impact. 2022.
- Grozdanić, G.; Cvetković, V.; Lukić, T.; Ivanov, A. Sustainable Earthquake Preparedness: A Cross-Cultural Comparative Analysis in Montenegro, North Macedonia, and Serbia. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carla S, R.G. School-community collaboration: disaster preparedness towards building resilient communities. International Journal of Disaster Risk Management 2019, 1, 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Mano, R.; A, K.; Rapaport, C. Earthquake preparedness: A Social Media Fit perspective to accessing and disseminating earthquake information. International Journal of Disaster Risk Management 2019, 1, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Scott, D.; Hall, C.M. Pandemics, tourism and global change: a rapid assessment of COVID-19. Journal of sustainable tourism 2020, 29, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter-Oppermann, M.; van den Berg, P.L.; Vile, J.L. Logistics for emergency medical service systems. Health Systems 2017, 6, 187–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, D.; Miner, K. Outcome-based workforce development and education in public health. Annual Review of Public Health 2010, 31, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.M.; Šišović, V. Capacity Building in Serbia for Disaster and Climate Risk Education. Available at SSRN 4575350 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.D.D.; Ormilla, R.C.G. Disaster Risk Reduction Management Implementation in the Public Elementary Schools of the Department of Education, Philippines. International Journal of Disaster Risk Management 2022, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.; Tarolli, P.; Roder, G.; Ivanov, A.; Ronan, K.; Ocam, A.; Kutub, R. Citizens education about floods: a Serbian case study. Proceedings of the VII International scientific conference Archibald Reiss days; p. In press.
- Bickel, J. Gender equity in undergraduate medical education: a status report. Journal of women’s health & gender-based medicine 2001, 10, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Bickel, J.; Brown, A.J. Generation X: Implications for faculty recruitment and development in academic health centers. Academic Medicine 2005, 80, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health, O.; Netherlands Institute for Health Services, R. Evaluation of structure and provision of primary care in Romania: a survey-based project; World Health Organization. Regional Office for Europe: 2012.
- Aunger, J.; Ross Millar, P.; Greenhalgh, J.; Russell Mannion, P.; Rafferty, A.M.; Faulks, M.D.; McLeod, H. How, Why, and When Do Inter-Organisational Collaborations in Healthcare Improve Performance? A Realist Evaluation. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bruggen, V.; Barendrecht, P.; Geense, A.; Van Dijk, E.; Achilleos, M.; Saris, I.; Meijer, M.; Deijkers, A.; Verwoerd, G.; Taks, M. Continuously improving patient safety by a rapid response system. Critical Care 2010, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clawson, J.J. EMS dispatch. Emergency medical services: clinical practice and systems oversight 2015, 94–112. [Google Scholar]
- Taneja, A. Better Elective Waiting Times For The Surgical Outpatient Clinic. 2017.
- Prince, A.W.; Armstrong, E. Empowering nurses to help reduce the rate of primary cesarean births. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing 2015, 44, S23. [Google Scholar]
- Eitel, D.R.; Rudkin, S.E.; Malvehy, M.A.; Killeen, J.P.; Pines, J.M. Improving service quality by understanding emergency department flow: a White Paper and position statement prepared for the American Academy of Emergency Medicine. The Journal of emergency medicine 2010, 38, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V. Innovative solutions for disaster early warning and alert systems: a literary review. Proceedings of XI International scientific conference Archibald Reiss days, November 9-10, 2021At: Belgrade, University of Criminal Investigation and Police Studies 2021.
- Vladimir, C.M. Policija i prirodne katastrofe - Police and natural disasters. Beograd: Zadužbina Andrejević: 2016.
- Cvetković, V.M.; Milojković, B. The influence of demographic factors on the level of citizen awareness of police responsibilities in natural disasters. Bezbednost, Beograd 2016, 58, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, K. Sharing Information between Public Safety and Transportation Agencies for Traffic Incident Management; Transportation Research Board: 2004; Vol. 520.
- Cvetković, V.; Filipović, M. Information systems and disaster risk management. Proceedings of International scientific and professional conference – 40 years of higher education in the field of security – Theory and Practice, Skopje, Republic of Macedonia; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Svrdlin, M.; Cvetković, V.J.V.d. Mobilni komunikacioni sistemi i aplikacije od značaja za integrisano upravljanje katastrofama -Mobile communications systems and relevant applications for integrated disaster risk management. 2019, In press.
- Cvetković, V.; Nikolić, M. The role of social networks in disaster risk reduction: a case study Belgrade - Uloga društvenih mreža u smanjenju rizika od katastrofa: studija slučaja Beograd. Bezbednost 2021, 61, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.M.; Filipović, M.; Dragićević, S.; Novković, I. The role of social networks in disaster risk reduction. 2018; pp. 311-321.
- Cvetković, V. First aid disaster kit for a family: a case study of Serbia - Porodični pribor za pružanje prve pomoći u katastrofama: studija slučaja Srbije. In Proceedings of the IX International scientic conference Archibald Reiss days November 6-7, 2019. University of Criminal Investigation and Police Studies, Belgrade 2019.
- Cvetković, V.M. First aid disaster kit for a family: A case study of Serbia. Archibald Reiss Days 2019, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Lanyero, B.; Edea, Z.A.; Musa, E.O.; Watare, S.H.; Mandalia, M.L.; Livinus, M.C.; Ebrahim, F.K.; Girmay, A.; Bategereza, A.K.; Abayneh, A. Readiness and early response to COVID-19: achievements, challenges and lessons learnt in Ethiopia. BMJ global health 2021, 6, e005581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.R.; Wang, W.; Wei, C.-P.; Hsu, S.H.-Y.; Chiu, H.-C. Service innovation readiness: Dimensions and performance outcome. Decision Support Systems 2012, 53, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, J.T. From Crash to Care: A Road Towards Improved Safety and Efficiency of Emergency Medical Response. 2024.
- McKinnon, A. The impact of Traffic congestion on logistical efficiency; Citeseer: 1998.
- Nichol, G.; Detsky, A.S.; Stiell, I.G.; O’Rourke, K.; Wells, G.; Laupacis, A. Effectiveness of emergency medical services for victims of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a metaanalysis. Annals of emergency medicine 1996, 27, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elamir, H. Improving Patient Flow in the Emergency Department of a General Hospital Providing Secondary Healthcare Services. 2015.
- Cvetković, V.M. Crises: Readiness of state, local community and citizens. Vojno delo 2017, 69, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, V.M. Prepreke unapređenju spremnosti za reagovanje u prirodnim katastrofama - Obstacles to improving readiness for responding in natural disasters. Vojno delo 2017, 69, 132–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, B.J. A theory of organizational readiness for change. In Handbook on implementation science, Edward Elgar Publishing: 2020; pp. 215-232.
- Meyer, J.P.; Becker, T.E.; Vandenberghe, C. Employee commitment and motivation: a conceptual analysis and integrative model. Journal of applied psychology 2004, 89, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latman, N.S.; Wooley, K. Knowledge and skill retention of emergency care attendants, EMT-As, and EMT-Ps. Annals of emergency medicine 1980, 9, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostin, L.O.; Hanfling, D.; Hanson, S.L.; Stroud, C.; Altevogt, B.M. Guidance for establishing crisis standards of care for use in disaster situations: a letter report. 2009.
- Takahashi, T.; Nakamura, M. The impact of operational characteristics on firms’ EMS decisions: strategic adoption of ISO 14001 certifications. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management 2010, 17, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.D. Medical direction in emergency medical services: the role of the physician. Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America 1987, 5, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiya, T.; Mazenda, A.; Davids, Y.D. Effective public participation in municipal service delivery. Administratio publica 2019, 27, 27–47. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, S.M.; Prybutok, V. The Era of Artificial Intelligence Deception: Unraveling the Complexities of False Realities and Emerging Threats of Misinformation. Information 2024, 15, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, C.; Alexander, J.; Morlock, L.; Lyles, A.C. Does the hospital board need a doctor?: The influence of physician board participation on hospital financial performance. Medical care 1995, 33, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelen, G.D.; Wolfe, R.; D’Onofrio, G.; Mills, A.M.; Diercks, D.; Stern, S.A.; Wadman, M.C.; Sokolove, P.E. Emergency department crowding: the canary in the health care system. NEJM Catalyst Innovations in Care Delivery 2021, 2. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Function in EMS | Medical personnel | 23 | 13.37 |
| Leadership positions within a medical institution | 140 | 81.4 | |
| Administrative medical personnel | 7 | 4.07 | |
| Operational medical personnel | 2 | 1.16 | |
| Type of Institution EMS | Public Health Center | 122 | 70.93 |
| Hospital | 11 | 6.40 | |
| Private Healthcare Facility | 39 | 22.67 | |
| Experience in EMS | Less than 5 years | 45 | 26.16 |
| 5-10 years | 85 | 49.42 | |
| More than 10 years | 42 | 24.42 | |
| Gender | Male | 95 | 55.23 |
| Female | 77 | 44.77 | |
| Education Level | High School | 30 | 17.44 |
| Bachelor’s Degree | 100 | 58.14 | |
| Master’s Degree | 42 | 24.42 | |
| Participation in Training | No participation in training | 50 | 29.07 |
| Participated in one or more training sessions | 122 | 70.93 | |
| Emergency Response Role | First responder | 50 | 29.07 |
| Coordinator | 80 | 46.51 | |
| Support staff | 42 | 24.42 | |
| Mass Casualty Plans/Procedures | Yes, institution has a plan | 110 | 63.95 |
| No, institution does not have a plan | 62 | 36.05 | |
| Total | 172 | 100 |
| Predictor Variable |
Organization of EMS | Number of EMS points performed | Service area coverage | EMS doctors |
Plan/procedures mass casualty | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | β | B | SE | β | B | SE | β | B | SE | β | B | SE | β | |
| Organization of working hours |
0.03 | 0.01 | 0.035* | −0.032 | 0.011 | −0.037* | 0.029 | 0.012 | 0.032 | 0.038 | 0.012 | 0.042 | 0.041 | 0.013 | 0.045 |
| Organization of shift work |
0.04 | 0.012 | 0.042* | −0.041 | 0.013 | −0.045* | 0.039 | 0.014 | 0.043* | 0.047 | 0.015 | 0.048 | 0.049 | 0.016 | 0.051 |
| Organization of work in shifts |
0.027 | 0.009 | 0.029 | −0.028 | 0.01 | −0.031* | 0.026 | 0.011 | 0.028 | 0.034 | 0.011 | 0.035 | 0.036 | 0.012 | 0.037 |
| EMS team working only in the clinic |
0.065 | 0.015 | 0.062 | −0.065 | 0.016 | −0.063 | 0.067 | 0.017 | 0.064 | 0.072 | 0.018 | 0.07* | 0.075 | 0.019 | 0.073 |
| Teams per day shift for amb. tran. |
0.058 | 0.014 | 0.058 | −0.062 | 0.015 | 0.059 | 0.061 | 0.016 | 0.06 | 0.066 | 0.017 | 0.065* | 0.07 | 0.018 | 0.069 |
| Teams per night shift for amb. tran. |
0.049 | 0.013 | 0.053 | −0.051 | 0.014 | −0.055 | 0.05 | 0.015 | 0.054 | 0.055 | 0.016 | 0.057 | 0.059 | 0.017 | 0.061 |
| Teams per shift during weekends |
0.034 | 0.01 | 0.038 | −0.036 | 0.011 | −0.039 | 0.035 | 0.012 | 0.037 | 0.041 | 0.012 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.013 | 0.046 |
| Financial resources for the healthcare |
0.023 | 0.009 | 0.029 | −0.026 | 0.01 | −0.028 | 0.025 | 0.011 | 0.027 | 0.031 | 0.012 | 0.031 | 0.033 | 0.013 | 0.033 |
| Ambulance vehicles | 0.06 | 0.012 | 0.06 | −0.065 | 0.013 | −0.065 | 0.067 | 0.014 | 0.067 | 0.072 | 0.015 | 0.072* | 0.075 | 0.016 | 0.075 |
| Vehicle for mass casualties (disasters) |
0.044 | 0.011 | 0.041 | −0.048 | 0.012 | −0.046 | 0.047 | 0.013 | 0.045 | 0.052 | 0.014 | 0.05 | 0.055 | 0.015 | 0.053 |
| Plan/procedures | 0.071 | 0.016 | 0.073 | −0.071 | 0.017 | -0.074 | 0.073 | 0.018 | 0.075 | 0.078 | 0.019 | 0.078 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.08 |
| 0.019 (0.006) | 0.020 (0.008) | 0.027 (0.015) | 0.035 (0.022) | 0.041 (0.030) | |||||||||||
| Variables | Organization of EMS | Number of EMS points performed |
Service area coverage |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sig. | r | Sig. | r | Sig. | r | |
| Average time spent by medical teams (minutes) | 0.817 | −0.020 | −0.057 | 0.597 | 0.232 | 0.654 |
| Average time spent by transport teams (minutes) | 0.732 | −0.030 | −0.060 | 0.582 | 0.338 | −0.549 |
| Total number of EMS doctors | 0.000** | −0.340 | 0.139 | 0.199 | 0.190 | −0.698 |
| EMS doctors specialized in emergency medicine | 0.000** | −0.424 | 0.135 | 0.213 | 0.909 | 0.072 |
| EMS doctors in emergency medicine training | 0.000** | −0.430 | 0.139 | 0.203 | 0.857 | 0.112 |
| EMS doctors specialized in general medicine | 0.161 | −0.125 | 0.042 | 0.702 | 0.750 | 0.197 |
| EMS doctors practicing general medicine | 0.001** | −0.286 | 0.140 | 0.199 | 0.874 | −0.126 |
| Permanent EMS ambulance drivers | 0.000** | −0.344 | 0.128 | 0.244 | 0.905 | 0.074 |
| Doctors with verified limited working capacity | 0.068 | −0.162 | 0.033* | 0.762 | 0.981 | 0.015 |
| Day shift teams on weekdays | 0.000** | −0.326 | 0.115 | 0.297 | 0.942 | 0.046 |
| Night shift teams on weekdays | 0.000** | −0.409 | 0.124 | 0.257 | 0.992 | 0.006 |
| Standby readiness for doctors | 0.059 | 0.164 | 0.120 | 0.269 | 0.892 | 0.007 |
| Standby readiness for nurses-techn | 0.088 | 0.149 | 0.113 | 0.299 | 0.321 | 0.08 |
| Maximum diameter of the EMS service area | 0.423 | 0.147 | 0.366 | 0.112 | 0.213 | 0.09 |
| Max distance EMC to hospital | 0.002** | 0.275 | 0.132 | 0.228 | 0.163 | 0.837 |
| Gender distribution of male doctors | 0.000** | −0.346 | 0.079 | 0.472 | 0.995 | 0.004 |
| Gender distribution of female doctors | 0.009** | −0.231 | 0.103 | 0.343 | 0.866 | 0.105 |
| Male emergency medicine specialists | 0.000** | −0.473 | 0.072 | 0.505 | 0.919 | 0.063 |
| Female emergency medicine specialists | 0.000** | −0.338 | 0.066 | 0.404 | 0.435 | 0.460 |
| Variable | Organization of EMS |
Employees (EMS) training |
Plan/procedures mass casualty |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | X2 | p | X2 | |||
| Conducting EMS Activities | 0.001** | 190.38 | 0.001** | 126.64 | 0.001** | 110.05 |
| Number of points EMS | 0.005** | 86.99 | 0.107 | 25.68 | 0.526 | 16.56 |
| Organization of working hours | 0.000** | 194.06 | 0.002** | 134.01 | 0.000** | 113.90 |
| Organization of shift work | 0.001** | 76.13 | 0.001** | 34.58 | 0.055 | 14.49 |
| Organization of work in shifts | 0.006** | 85.40 | 0.065 | 23.13 | 0.000** | 42.14 |
| EMS team working only in the clinic | 0.004** | 165.43 | 0.005** | 147.07 | 0.060 | 18.23 |
| Teams per day shift for amb. transport | 0.001** | 265.23 | 0.001** | 154.02 | 0.000** | 140.43 |
| Teams per night shift for amb. transport | 0.000** | 185.06 | 0.003** | 127.23 | 0.000** | 126.24 |
| Teams per shift during weekends | 0.000** | 223.92 | 0.001** | 143.07 | 0.000** | 124.43 |
| Ambulance transport team | 0.001** | 142.18 | 0.056 | 16.98 | 0.000** | 133.37 |
| On-call duty, leave the territory | 0.003** | 154.18 | 0.001** | 142.88 | 0.000** | 123.21 |
| Regular shift workload | 0.001** | 140.29 | 0.006** | 153.06 | 0.000** | 131.61 |
| Number of doctors in EMC | 0.006** | 236.17 | 0.007** | 160.02 | 0.000** | 138.07 |
| Systematic medical examinations | 0.002** | 126.85 | 0.285 | 53.05 | 0.313 | 52.24 |
| Verified limited work capacity | 0.005** | 115.26 | 0.320 | 68.18 | 0.000** | 148.73 |
| Number of ambulance drivers | 0.000** | 211.04 | 0.160 | 34.30 | 0.909 | 9.128 |
| Separate phone number for amb. transport | 0.007** | 129.06 | 0.000** | 179.29 | 0.875 | 35.75 |
| Call identification capability | 0.018* | 159.62 | 0.004** | 175.19 | 0.453 | 28.07 |
| Protocol/procedure for receiving calls | 0.023* | 116.4 | 0.000** | 176.43 | 0.000** | 154.63 |
| Presence of a call recorder | 0.003* | 169.14 | 0.001** | 174.02 | 0.000** | 150.10 |
| Recording conversations | 0.001** | 153.06 | 0.065 | 43.65 | 0.232 | 46.01 |
| Communication with teams in the field | 0.005** | 151.13 | 0.001** | 179.06 | 0.000** | 152.96 |
| Presence of radio stations in ambulances | 0.001** | 124.43 | 0.003** | 172.02 | 0.000** | 148.92 |
| Condition of radio repeaters | 0.008** | 134.18 | 0.204 | 34.01 | 0.000** | 18.56 |
| Power supply device for the radio system | 0.001** | 123.02 | 0.001** | 183.02 | 0.000** | 145.05 |
| Dedicated communication: police | 0.005** | 127.01 | 0.000** | 172.14 | 0.001** | 124.04 |
| Monitoring reaction time of interventions | 0.001** | 174.44 | 0.000** | 185.93 | 0.005** | 162.87 |
| Dedicated communication firefighers | 0.003** | 119.02 | 0.002** | 172.14 | 0.003** | 148.73 |
| Training for emergency medicine doctors | 0.004** | 105.01 | 0.001** | 187.01 | 0.005** | 139.01 |
| Training for emergency medicine nurses | 0.003** | 102.07 | 0.002** | 175.01 | 0.001** | 23.08 |
| Financial resources for the healthcare | 0.001** | 156.07 | 0.003* | 165.45 | 0.000** | 211.76 |
| Ambulance vehicles | 0.765 | 15.06 | 0.001** | 197.32 | 0.005** | 175.20 |
| Vehicle for mass casualties (disasters) | 0.005** | 130.52 | 0.001** | 159.67 | 0.000** | 172.45 |
| Plan/procedure: mass casualties | 0.001** | 110.30 | 0.005** | 149.32 | 0.000** | 215.65 |
| Triage tags | 0.003** | 118.01 | 0.002** | 150.2 | 0.045 | 35.53 |
| Exercises for responding to mass casualties | 0.001** | 103.32 | 0.001** | 149.01 | 0.000** | 178.34 |
| Joint exercises with other first responders | 0.003** | 109.11 | 0.005** | 139.04 | 0.000** | 160.14 |
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organization of EMS in Facility | No organized emergency medical service | 2 | 1.44 |
| Special institution – Institute for Emergency Medical Services | 5 | 3.60 | |
| Within a special Emergency Medical Service department of a health center | 64 | 46.04 | |
| Within the general medical service (through regular work and duty of doctors and other health workers) | 47 | 33.81 | |
| Within the general medical service, as a separate organizational unit for emergency medical services | 21 | 15.11 | |
| Conducting EMS Activities | From a single location | 46 | 26.7 |
| Within a healthcare facility | 78 | 45.3 | |
| From multiple dislocated points | 13 | 7.6 | |
| Number of points where EMS activities are conducted | From 0 to 2 points | 80 | 88.89 |
| From 3 to 5 points | 4 | 4.44 | |
| From 6 to 10 points | 4 | 4.44 | |
| From 11 to 50 points | 1 | 1.11 | |
| From 51+ points | 1 | 1.11 | |
| Organization of working hours | Shift work | 95 | 55.2 |
| Rotating shifts | 77 | 44.8 | |
| Organization of shift work | In shifts of 12 hours | 138 | 80.2 |
| Other | 14 | 8.1 | |
| In shifts of 8 hours | 20 | 11.6 | |
| Organization of work in shifts | Day shift - 24h off – night shift - 48h off | 33 | 24.44 |
| Day shift – 24h off – night shift – 72h off | 70 | 51.85 | |
| Day shift – 48h off – night shift - 48h off | 32 | 23.70 | |
| Team configurations during daytime shifts on weekdays | 1 team (all variations) | 87 | 50.6 |
| 2 teams (all variations) | 29 | 16.9 | |
| 3 or more teams | 6 | 3.5 | |
| Special configurations | 48 | 27.9 | |
| Team configurations during nighttime shifts on weekdays | 0 teams | 2 | 1.2 |
| 1 team (all variations) | 83 | 48.3 | |
| 2 teams (all variations) | 28 | 16.3 | |
| 3 or more teams | 19 | 11.0 | |
| Special configurations | 40 | 23.2 | |
| Healthcare Management Plan have a team that only works in the clinic | Yes | 49 | 28.5 |
| N/A | 38 | 22.1 | |
| No | 85 | 49.4 | |
| Teams in the clinic during the daytime on weekdays | 1 team (including various descriptions) | 110 | 64.0 |
| 2 teams | 14 | 8.1 | |
| 3 or more teams (special configurations) | 12 | 7.0 | |
| Teams in the clinic during the nighttime on weekdays | 0 teams | 26 | 15.1 |
| 1 team (including various descriptions) | 124 | 72.1 | |
| Transport by a team of medical nurse-technician and driver | 33 | 19.2 |
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical transport teams during daytime shifts on weekdays | No teams reported | 9 | 5.2 |
| 1 team configurations | 106 | 43.0 | |
| 2 teams configurations | 39 | 14.0 | |
| 3 teams configurations | 7 | 4.1 | |
| 4 teams configurations | 7 | 4.1 | |
| 5 teams configurations | 2 | 1.2 | |
| More than 5 teams configurations | 3 | 1.7 | |
| Medical transport teams during nighttime shifts on weekdays | No teams reported | 34 | 19.8 |
| 1 team (including all 1 team variations) | 126 | 47.7 | |
| 2 teams (including all 2 teams variations) | 10 | 5.8 | |
| Composition of medical transport teams | Nurse-technician and vehicle driver | 67 | 29.7 |
| Other | 31 | 13.4 | |
| Vehicle driver | 74 | 33.1 | |
| Medical transport team configurations | Standard team (doctor, nurse/technician, driver) | 65 | 37.8 |
| Driver only or driver with occasional medical staff | 29 | 16.9 | |
| Teams formed based on specific needs | 24 | 14.0 | |
| No specific team required for transport only | 17 | 9.9 | |
| Variable teams depending on patient condition | 36 | 20.9 | |
| Other unspecified configurations | 1 | 0.6 | |
| Organization of preparedness for medical teams | Yes | 74 | 43.0 |
| No | 98 | 57.0 | |
| Organization of preparedness for vehicle drivers | Yes | 83 | 48.3 |
| No | 89 | 51.7 | |
| Average holding time of medical teams (in minutes) | 0 - 10 | 27 | 15.7 |
| 11 - 30 | 25 | 14.5 | |
| 31 - 60 | 27 | 15.7 | |
| 61 - 120 | 31 | 18.0 | |
| 121 - 240 | 22 | 12.8 | |
| 241 mins and above | 16 | 9.3 | |
| Average Holding Time of Transport Teams (in minutes) | Under 10 | 19 | 11.0 |
| 10 - 30 | 26 | 15.1 | |
| 31 - 60 | 32 | 18.6 | |
| 61 - 120 | 30 | 17.4 | |
| 121 - 240 | 19 | 11.0 | |
| 241 mins and above | 6 | 3.5 | |
| Area covered by health services (HMP) | Less than 100 km² | 12 | 7.0 |
| 100 – 200 km² | 18 | 10.5 | |
| 200 – 300 km² | 18 | 10.5 | |
| 300 – 400 km² | 35 | 20.3 | |
| 400 – 500 km² | 18 | 10.5 | |
| 500 – 600 km² | 14 | 8.1 | |
| 600 – 700 km² | 14 | 8.1 | |
| 700 – 800 km² | 13 | 7.6 | |
| 800 – 900 km² | 10 | 5.8 | |
| 900 – 1000 km² | 1 | 0.6 | |
| 1000 – 1100 km² | 9 | 5.2 | |
| Other | 8 | 4.7 | |
| The largest diameter of territory covered by health services (HMP) | Under 30 km | 32 | 18.6 |
| 30 - 60 km | 104 | 60.5 | |
| Over 60 km | 37 | 21.5 | |
| Maximum distance from HMP headquarters to corresponding hospital | 0 - 25 km | 50 | 29 |
| 25 - 50 km | 53 | 31 | |
| 50 - 75 km | 28 | 16 | |
| Over 75 km | 41 | 24 | |
| Maximum distance from HMP headquarters to the corresponding tertiary healthcare center | Under 30 km | 27 | 15.7 |
| 30 to 60 km | 39 | 22.7 | |
| 60 to 90 km | 41 | 23.8 | |
| Over 90 km | 49 | 28.5 | |
| Institution cover part of the highway | Yes | 45 | 26.2 |
| N/A | 41 | 23.8 | |
| No | 86 | 50.0 | |
| Distances that institutions cover part of a highway | Under 25 km | 40 | 23.3 |
| 25 to 50 km | 35 | 20.3 | |
| 50 to 75 km | 30 | 17.4 | |
| Over 75 km | 22 | 12.8 | |
| Seasonal variations in the population numbers within the HMP’s jurisdiction | Yes | 84 | 48.8% |
| N/A | 41 | 23.8% | |
| No | 47 | 27.3% | |
| Specific population increases reported during seasonal variations within the HMP’s jurisdiction | Under 1,000 | 70 | 40.7% |
| 1,000 to 5,000 | 64 | 37.2% | |
| 5,001 to 10,000 | 18 | 10.5% | |
| 10,001 to 30,000 | 33 | 19.2% | |
| Over 30,000 | 7 | 4.1% | |
| Seasonal population increases reported by institutions | Short-Term (1-3 months) | 92 | 53.5 |
| Mid-Term (4-5 months) | 41 | 23.8 | |
| Long-Term (6 months) | 39 | 22.7 | |
| Reasons for the increase in the population or users of HMP services | Seasonal Tourism and Migration | 65 | 37.8 |
| Returnees and Temporary Residents | 34 | 19.8 | |
| Local Events and Activities | 25 | 14.5 | |
| Migrants | 11 | 6.4 | |
| Regional Center | 5 | 2.9 | |
| Tourist Center | 32 | 18.6 | |
| Regular shift’s workload, beyond the scope of managing urgent care, includes additional activities | Yes | 112 | 65.1 |
| N/A | 41 | 23.8 | |
| No | 19 | 11.0 | |
| Extent of Additional Activities by Staff Type | From On-Call Duty | 43 | 25.0 |
| From Regular Staff | 129 | 75.0 | |
| Organization of transport teams during the night shift for urgent medical care | Transport by a team of medical nurse-technician and driver | 33 | 19.2 |
| Transport by a complete medical team (doctor, nurse-technician, driver) | 127 | 73.8 | |
| Transport by a medical vehicle driver only | 12 | 7.0 | |
| Transport by a team of medical nurse-technician and driver | 33 | 19.2 |
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Doctors in emergency medical services | 0-2 doctors | 20 | 11.63 |
| 3-5 doctors | 44 | 25.58 | |
| 6-8 doctors | 31 | 18.02 | |
| 9-11 doctors | 31 | 18.02 | |
| 12-15 doctors | 19 | 11.05 | |
| More than 15 doctors | 15 | 8.72 | |
| Specialists in emergency medical services | 0-2 doctors | 89 | 51.74 |
| 3-5 doctors | 27 | 15.70 | |
| 6-8 doctors | 7 | 4.07 | |
| 9-11 doctors | 3 | 1.74 | |
| 12-15 doctors | 2 | 1.16 | |
| More than 15 doctors | 4 | 2.33 | |
| Doctors in emergency medical services (EMS) specialists who are in training for emergency medicine | 0-2 doctors | 116 | 67.44 |
| 3-5 doctors | 8 | 4.65 | |
| 6-8 doctors | 2 | 1.16 | |
| 9-11 doctors | 1 | 0.58 | |
| 12-15 doctors | 1 | 0.58 | |
| More than 15 doctors | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Doctors in emergency medical services (EMS) who are specialists in general medicine | 0-2 doctors | 100 | 58.14 |
| 3-5 doctors | 23 | 13.37 | |
| 6-10 doctors | 4 | 2.33 | |
| More than 10 doctors | 1 | 0.58 | |
| General medicine doctors in emergency medical services (EMS) | 0-4 doctors | 74 | 43.02 |
| 5-9 doctors | 42 | 24.42 | |
| 10-19 doctors | 11 | 6.40 | |
| 20 or more doctors | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Institutions have other specialties | Yes | 94 | 54.7 |
| Not Applicable | 43 | 25.0 | |
| No | 35 | 20.3 | |
| Medical specialties in institutions | General medicine (general practitioners) | 30 | 17.4 |
| Specialized medicine (all specialized fields like gynecology, pediatrics, etc.) | 85 | 49.4 | |
| Diagnostics and lab (radiology, biochemistry, etc.) | 40 | 23.3 | |
| Surgical specialties (surgery-related fields) | 10 | 5.8 | |
| Other specialties (less common specialties) | 7 | 4.1 |
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender distribution of male doctors | 0-5 doctors | 71 | 41.3 |
| 6-10 doctors | 27 | 15.7 | |
| 11-20 doctors | 21 | 12.2 | |
| 21-30 doctors | 4 | 2.3 | |
| More than 30 doctors | 5 | 2.9 | |
| Gender distribution of female doctors | 0-5 Doctors | 52 | 30.2 |
| 6-10 Doctors | 33 | 19.2 | |
| 11-20 Doctors | 30 | 17.4 | |
| 21-30 Doctors | 7 | 4.1 | |
| More than 30 Doctors | 6 | 3.5 | |
| Male specialists in emergency medicine | 0-2 doctors | 107 | 62.2 |
| 3-5 doctors | 16 | 9.3 | |
| 6-10 doctors | 5 | 2.9 | |
| 11-15 doctors | 1 | 0.6 | |
| more than 15 doctors | 1 | 0.6 | |
| Female specialists in emergency medicine | 0-2 doctors | 113 | 65.7 |
| 3-5 doctors | 10 | 5.8 | |
| 6-10 doctors | 2 | 1.2 | |
| 11-20 doctors | 1 | 0.6 | |
| more than 20 doctors | 1 | 0.6 | |
| Male doctors in specialization for emergency medicine | 0 doctors | 97 | 56.4 |
| 1-2 doctors | 24 | 14.0 | |
| 3-5 doctors | 6 | 3.5 | |
| Female doctors in specialization for emergency medicine | 0 doctors | 93 | 54.1 |
| 1-2 doctors | 28 | 16.3 | |
| 3 or more doctors | 5 | 2.9 | |
| Male general medicine specialists | 0 doctors | 77 | 44.8 |
| 1-2 doctors | 42 | 24.4 | |
| 3 or more doctors | 8 | 4.7 | |
| Female general medicine specialists | 0 doctors | 61 | 35.5 |
| 1-2 doctors | 41 | 23.8 | |
| 3-5 doctors | 17 | 9.9 | |
| 6 or more doctors | 7 | 4.1 | |
| Male general medicine doctors | 0-2 doctors | 84 | 48.8 |
| 3-5 doctors | 33 | 19.2 | |
| 6-10 doctors | 9 | 5.2 | |
| more than 10 doctors | 1 | 0.6 | |
| Female general medicine doctors | 0-2 doctors | 50 | 29.1 |
| 3-5 doctors | 35 | 20.3 | |
| 6-10 doctors | 24 | 14.0 | |
| 11 or more doctors | 17 | 9.9 | |
| Male nursing staff with higher education | 0-1 | 104 | 60.5 |
| 2-4 | 17 | 9.9 | |
| 5 or more | 5 | 2.9 | |
| Female nursing staff with higher education | 0-2 | 95 | 55.2 |
| 3-5 | 16 | 9.3 | |
| 6 or more | 16 | 9.3 | |
| Male nursing technicians with secondary education | 0-5 | 76 | 44.2 |
| 6-10 | 22 | 12.8 | |
| 11-20 | 13 | 7.6 | |
| 21 or more | 16 | 9.3 | |
| 0-5 | 76 | 44.2 | |
| Female nursing technicians with secondary education | 0-5 | 35 | 20.3 |
| 6-10 | 41 | 23.8 | |
| 11-20 | 35 | 20.3 | |
| 21-30 | 11 | 6.4 | |
| 31 or more | 5 | 2.9 |
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age structure data for doctors under the age of 30 | 0-1 | 105 | 61.0 |
| 2-5 | 19 | 11.0 | |
| 6 or more | 2 | 1.2 | |
| Doctors aged 30-55 | 0-5 | 39 | 22.7 |
| 6-10 | 39 | 22.7 | |
| 11-20 | 48 | 27.9 | |
| 21-30 | 14 | 8.1 | |
| 31 or more | 7 | 4.1 | |
| Doctors over the age of 55 | 0-5 | 85 | 49.4 |
| 6-10 | 19 | 11.0 | |
| 11 or more | 23 | 13.4 | |
| Nursing technicians under the age of 30 with secondary education | 0-1 | 89 | 51.7 |
| 2-4 | 27 | 15.7 | |
| 5 or more | 10 | 5.8 | |
| Nursing technicians aged 30-55 | 0-5 | 29 | 16.9 |
| 6-10 | 33 | 19.2 | |
| 11-15 | 24 | 14.0 | |
| 16-20 | 11 | 6.4 | |
| 21 or more | 30 | 17.4 | |
| Nursing technicians over the age of 55 | 0-2 | 60 | 34.9 |
| 3-5 | 37 | 21.5 | |
| 6-10 | 18 | 10.5 | |
| 11 or more | 11 | 6.4 | |
| Doctors with verified limited work capacity | No limitation | 106 | 61.6 |
| Minor limitation | 18 | 10.5 | |
| Significant limitation | 3 | 1.7 | |
| Doctors comply with the legal requirement to undergo annual systematic medical examinations | Yes | 81 | 47.1 |
| No | 46 | 26.7 | |
| Medical nurses and technicians comply with the legal requirement for annual systematic examinations | Yes | 78 | 45.3 |
| No | 49 | 28.5 | |
| Ambulance drivers regarding compliance with the legal requirement for annual systematic examinations | Yes | 111 | 64.5 |
| No | 16 | 9.3 | |
| Medical nurses and technicians with verified limited work capacity | No Limitation | 92 | 53.5 |
| Minor Limitation | 31 | 18.0 | |
| Significant Limitation | 4 | 2.3 | |
| Ambulance drivers per vehicle in the Emergency Medical Service (HMP) | 0-5 | 77 | 44.77 |
| 6-15 | 34 | 19.77 | |
| 16-30 | 10 | 5.81 | |
| 31-70 | 5 | 2.91 | |
| 71+ | 1 | 0.58 | |
| Ambulance drivers in HMP service (permanent employees) | 0-16 | 115 | 66.9 |
| 17-33 | 11 | 6.4 | |
| 34-66 | 1 | 0.6 | |
| Ambulance drivers in the Emergency Medical Service by contract type (Fixed-term Employees) | 0–1 | 89 | 51.7 |
| 2–3 | 26 | 15.1 | |
| 4–10 | 11 | 6.4 | |
| Ambulance drivers on fixed-term contracts with secondary education | 0–1 | 97 | 56.4 |
| 2–6 | 25 | 14.5 | |
| 8–20 | 5 | 2.9 | |
| Ambulance drivers based on their shifts per month with completed traffic school education | 0 | 115 | 66.9 |
| 1–3 | 10 | 5.8 | |
| 10 | 1 | 0.6 | |
| Ambulance drivers who have undergone special training under the National Emergency Medicine Education Program in the past two years | 0 | 104 | 60.5 |
| 1–6 | 16 | 9.3 | |
| 8–71 | 7 | 4.1 | |
| Male ambulance drivers | 0–9 | 98 | 57.0 |
| 10–29 | 24 | 14.0 | |
| 30–69 | 5 | 2.9 | |
| 70 and above | 1 | 0.6 | |
| Female ambulance drivers | 0 | 123 | 71.5 |
| 1–2 | 2 | 1.2 | |
| 6 | 1 | 0.6 | |
| Ambulance drivers under the age of 30 | 0 | 86 | 50.0 |
| 1–2 | 30 | 17.4 | |
| 3–6 | 9 | 5.2 | |
| 20 | 1 | 0.6 | |
| Ambulance drivers aged 30 to 55 | 0–5 | 82 | 47.7 |
| 6–15 | 33 | 19.2 | |
| 17–33 | 10 | 5.8 | |
| 50 and above | 3 | 1.7 | |
| Ambulance drivers over the age of 55 | 0–3 | 109 | 63.4 |
| 4–10 | 15 | 8.7 | |
| 12 and above | 3 | 1.7 | |
| Ambulance drivers with verified limited work capability | 0 | 119 | 69.2 |
| 1–3 | 7 | 4.1 | |
| 6 | 1 | 0.6 |
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phone number to call (from the territory under your HMP jurisdiction) in case of intervention | 194 | 59 | 34.3% |
| Other | 68 | 39.5% | |
| The specific phone number for registering for ambulance transport? | Yes | 40 | 23.3% |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2% | |
| No | 87 | 50.6% | |
| Capability to identify incoming calls | Yes | 78 | 45.3% |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2% | |
| No | 49 | 28.5% | |
| Who receives calls | Doctor | 24 | 14.0% |
| Nurse/Technician | 24 | 14.0% | |
| Nurse/Technician only with doctor consultation | 18 | 10.5% | |
| Mixed model (nurse, doctor) | 61 | 35.5% | |
| Protocol/procedure for receiving calls | Yes | 93 | 54.1% |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2% | |
| No | 34 | 19.8% |
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Presence and condition of a dictation machine | Yes, functional | 61 | 35.5% |
| Yes, non-functional | 16 | 9.3% | |
| No | 50 | 29.1% | |
| Phone conversations with patients are recorded on a dictation machine | Yes | 71 | 41.3% |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2% | |
| No | 56 | 32.6% | |
| Radio communications recorded on a dictation machine | Yes | 15 | 8.7% |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2% | |
| No | 112 | 65.1% | |
| Special direct telephone line for communication with the police | Yes | 21 | 12.2% |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2% | |
| No | 106 | 61.6% | |
| Direct line for communication with the Alert and Notification Center | Yes | 20 | 11.6% |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2% | |
| No | 107 | 62.2% | |
| Communication conducted with teams in the field | Both methods | 14 | 8.1% |
| Via mobile phone | 107 | 62.2% | |
| Via radio | 6 | 3.5% | |
| Ambulance vehicles have a radio station | Yes | 27 | 15.7% |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2% | |
| No | 100 | 58.1% | |
| Ambulance Vehicles Without a Radio Station | 0-5 | 64 | 37.2% |
| 6-10 | 11 | 6.4% | |
| 11-15 | 1 | 0.6% | |
| 16-20 | 24 | 13.9% | |
| Condition of the radio repeaters | Operational | 29 | 16.9% |
| Not Operational | 98 | 57.0% | |
| Device to power the radio communication system in case of a power outage | Yes | 30 | 17.4% |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2% | |
| No | 97 | 56.4% | |
| Special radio communication channel for direct communication with the police | Yes | 3 | 1.7% |
| No | 124 | 72.1% | |
| Special radio communication channel for direct communication with firefighters-rescuers | Yes | 3 | 1.7% |
| No | 124 | 72.1% | |
| Reaction time monitored during first-order emergency interventions | Yes | 68 | 39.5% |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2% | |
| No | 59 | 34.3% |
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activation times | 0 to 1 hour | 35 | 20.3 |
| >1 to 3 hours | 11 | 6.4 | |
| >3 to 10 hours | 7 | 4.1 | |
| >10 hours | 15 | 8.7 | |
| Reaction time | 0 to 1 hour | 15 | 8.7 |
| >1 to 10 hours | 40 | 23.3 | |
| >10 to 20 hours | 10 | 5.8 | |
| >20 hours | 3 | 1.7 | |
| Prehospital intervention time results | 0 to 10 hours | 27 | 15.7 |
| 10 to 30 hours | 28 | 16.3 | |
| 30 to 60 hours | 9 | 5.2 | |
| More than 60 hours | 4 | 2.3 | |
| A written plan/procedure known to workers in case of disasters | Yes | 84 | 48.8 |
| N/A | 50 | 29.1 | |
| No | 38 | 22.1 | |
| Vehicle for mass casualty incidents equipped with stretchers and medical supplies? | Yes | 10 | 5.8 |
| N/A | 50 | 29.1 | |
| No | 112 | 65.1 | |
| Availability of triage cards (either in vehicles or bags) | Yes | 16 | 9.3 |
| N/A | 50 | 29.1 | |
| No | 106 | 61.6 | |
| Mass casualty response drills in the last 2 years at your institution | Yes | 24 | 14.0 |
| N/A | 50 | 29.1 | |
| No | 98 | 57.0 | |
| Frequently drills for mass casualty incidents | One time per year or less | 20 | 80.0 |
| Twice a year | 4 | 16.0 | |
| More than twice a year | 1 | 4.0 | |
| Joint drills with other emergency services in the last 2 years? | Yes | 27 | 15.7 |
| N/A | 50 | 29.1 | |
| No | 95 | 55.2 |
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Newly hired employee doctors undergone special training in emergency medicine | Yes | 55 | 32.0 |
| No | 72 | 41.9 | |
| Newly hired employee nursing technician undergone special training in emergency medicine | Yes | 53 | 30.8 |
| No | 74 | 43.0 | |
| Employees in EMS service undergone training at any of the existing training centers | Yes | 73 | 42.4 |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2 | |
| No | 54 | 31.4 | |
| Additional training is necessary for all employees in the EMS | Yes | 117 | 68.0 |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2 | |
| No | 10 | 5.8 | |
| Importance of who needs training the most | Doctor | 98 | 57.0 |
| Nursing Technician | 9 | 5.2 | |
| Ambulance Driver | 9 | 5.2 | |
| Categories of training needs | CPR and Trauma Management (Cardiopulmonary resuscitation, trauma management, polytrauma handling) | 45 | 26.2% |
| Urgent Medical Conditions (Emergency response, urgent medical and pediatric care) | 35 | 20.3% | |
| Emergency Protocols and Equipment (Equipment use, triage, protocols, communication) | 32 | 18.6% | |
| Safety and Operational Training (Safety protocols, personal safety, psychological support) | 30 | 17.4% | |
| Specialized Medical Training (Obstetrics, toxicology, neurology, cardiology) | 30 | 17.4% | |
| Specification of norms for operations (equipment, staff, space, vehicles, education, etc.) as key area for enhancing EMC services | Yes | 98 | 57.0 |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2 | |
| No | 29 | 16.9 | |
| Implementation and adherence to standards and procedures as key area for enhancing emc services | Yes | 81 | 47.1 |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2 | |
| No | 46 | 26.7 | |
| Continuous education as key area for enhancing EMC services | Yes | 97 | 56.4 |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2 | |
| No | 30 | 17.4 | |
| Establishing new training centers as key area for enhancing EMC services | Yes | 59 | 34.3 |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2 | |
| No | 68 | 39.5 | |
| Equipment renewal as key area for enhancing EMC services | Yes | 106 | 61.6 |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2 | |
| No | 21 | 12.2 | |
| Additional Staff as key area for enhancing EMC services | Yes | 102 | 59.3 |
| N/A | 45 | 26.2 | |
| No | 25 | 14.5 |
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| National health insurance fund (RFZO) resources: source of funding EMS | Yes | 119 | 69.2 |
| N/A | 46 | 26.7 | |
| No | 7 | 4.1 | |
| Municipal/City Budget Resources: source of funding EMS | Yes | 67 | 39.0 |
| N/A | 46 | 26.7 | |
| No | 59 | 34.3 | |
| Own Revenue: source of funding EMS | Yes | 42 | 24.4 |
| N/A | 46 | 26.7 | |
| No | 84 | 48.8 | |
| Donations: source of funding EMS | Yes | 35 | 20.3 |
| N/A | 46 | 26.7 | |
| No | 91 | 52.9 | |
| Healthcare institution receive additional financial resources from local government to employ additional staff | Yes | 70 | 40.7 |
| N/A | 47 | 27.3 | |
| No | 55 | 32.0 | |
| Doctors in Emergency Medical Services | 0-5 | 86 | 50.0% |
| 6-10 | 14 | 8.1% | |
| 11-15 | 8 | 4.7% | |
| 16-20 | 8 | 4.7% | |
| 21+ | 9 | 5.2% | |
| Medical Nursing Technicians in Emergency Medical Services | 0-5 | 83 | 48.3% |
| 6-10 | 18 | 10.5% | |
| 11-15 | 11 | 6.4% | |
| 16-20 | 8 | 4.7% | |
| 21+ | 5 | 2.9% | |
| Ambulance Drivers in Emergency Medical Services | 0-5 | 84 | 48.8% |
| 6-10 | 16 | 9.3% | |
| 11-20 | 15 | 8.7% | |
| 21-30 | 7 | 4.1% | |
| 30+ | 3 | 1.7% | |
| Doctors in Emergency Medical Services have credited service years | Yes | 56 | 32.6 |
| No | 66 | 38.4 | |
| Undecided | 3 | 1.7 | |
| Doctors in Emergency Medical Services have paid night shifts? | Yes | 120 | 69.8 |
| No | 2 | 1.2 | |
| Undecided | 3 | 1.7 | |
| Doctors in Emergency Medical Services have paid work on Sundays? | Yes | 120 | 69.8 |
| No | 5 | 2.9 | |
| Medical technicians/nurses in Emergency Medical Services and ambulance transport have credited service years? | Yes | 57 | 33.1 |
| No | 66 | 38.4 | |
| Undecided | 2 | 1.2 | |
| Medical technicians/nurses in Emergency Medical Services and ambulance transport have paid night shifts? | Yes | 120 | 69.8 |
| No | 2 | 1.2 | |
| Medical technicians/nurses in Emergency Medical Services and ambulance transport have paid work on Sundays | Yes | 120 | 69.8 |
| No | 5 | 2.9 |
| Variables | Category | n | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ambulance Vehicles by Year of Manufacture | 1989-2000 | 11 | 6.4% |
| 2001-2005 | 19 | 11.0% | |
| 2006-2010 | 21 | 12.2% | |
| 2011-2015 | 32 | 18.6% | |
| 2016-2018 | 20 | 11.6% | |
| Medical Vehicles - number of kilometers traveled | 0 - 57,200 | 21 | 20.2 |
| 57,200 - 125,354 | 19 | 18.3 | |
| 125,354 - 285,564 | 20 | 19.2 | |
| 285,564 - 400,000 | 21 | 20.2 | |
| 400,000 - 1,000,000 | 23 | 22.1 | |
| Presence of radio stations in medical vehicles | Yes | 38 | 22.0 |
| No | 70 | 40.7 | |
| Functionality of EKG machines for activities within the healthcare service | Does not exist | 2 | 1.2 |
| Exists | 122 | 70.9 | |
| Biphasic defibrillators with monitors for activities within the healthcare service | Does not exist | 13 | 7.6 |
| Exists | 110 | 64.0 | |
| Functionality of portable aspirators for activities within the healthcare service | Does not exist | 17 | 9.9 |
| Exists | 106 | 61.6 | |
| Portable Mechanical Respirator with Oxygen Tank Functionality in HMP Activities | Does not exist | 59 | 34.3 |
| Exists | 64 | 37.2 | |
| Functionality of portable mechanical respirators with oxygen tanks that have the CPAP mode | Does not exist | 104 | 60.5 |
| Exists | 19 | 11.0 | |
| Availability of cardiopulmonary resuscitation sets | Does not exist | 17 | 9.9 |
| Exists | 106 | 61.6 | |
| Availability of 10-liter oxygen bottles for activities within the healthcare service | Does not exist | 5 | 2.9 |
| Exists | 118 | 68.6 | |
| Vacuum mattresses for activities within the healthcare service | Does not exist | 66 | 38.4 |
| Exists | 57 | 33.1 | |
| Cervical collars for spinal immobilization | Does not exist | 15 | 8.7 |
| Exists | 108 | 62.8 | |
| Kramer splints for activities within the healthcare service | Does not exist | 39 | 22.7 |
| Exists | 84 | 48.8 | |
| Infusion Solution Heater Functionality in HMP Activities | Does not exist | 122 | 70.9 |
| Exists | 1 | 0.6 | |
| Medications for thrombolytic therapy | Does not exist | 115 | 66.9 |
| Exists | 8 | 4.7 | |
| Emergency cricothyrotomy kits | Does not exist | 108 | 62.8 |
| Exists | 15 | 8.7 | |
| Availability of childbirth kits | Does not exist | 38 | 22.1 |
| Exists | 85 | 49.4 | |
| Protective Helmets with Lamps Availability in HMP Activities | Does not exist | 122 | 70.9 |
| Exists | 1 | 0.6 | |
| Fixed Radio Station Availability in Ambulance | Does not exist | 80 | 46.5 |
| Exists | 43 | 25.0 | |
| Handheld Radio Availability | Does not exist | 107 | 62.2 |
| Exists | 16 | 9.3 | |
| Ultrasound Device Availability | Does not exist | 112 | 65.1 |
| Exists | 11 | 6.4 |
| Aspect | Recommendations | Term | Feasibility | Cost | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organizational Structure and Risk Management | Standardize risk assessments across all EMS units. | Short | High | Low | High |
| Introduce dynamic updating protocols for emergency response strategies. | Short | High | Medium | High | |
| Establish a centralized authority for EMS management. | Long | Medium | Medium | High | |
| Integrate new technology platforms for real-time risk management. | Long | Low | High | High | |
| Develop inter-agency agreements for risk management best practices. | Long | Medium | Medium | Medium | |
| Resource Allocation and Efficacy | Conduct targeted resource audits in high-demand locations. | Short | High | Low | High |
| Deploy mobile resource units in underserved areas. | Short | Medium | High | High | |
| Establish a fund for state-of-the-art EMS equipment. | Long | Medium | High | Medium | |
| Develop partnerships with technology providers. | Long | Low | High | Medium | |
| Implement a resource sharing protocol among EMS agencies. | Long | High | Low | Low | |
| Communication Systems and Efficacy | Upgrade to digital radio systems and secure networks. | Short | High | Medium | High |
| Establish regional communication centers. | Short | Medium | High | High | |
| Create redundant communication channels. | Long | Medium | High | High | |
| Launch training programs for communication technologies. | Long | Medium | Medium | Medium | |
| Invest in AI-driven communication tools. | Long | Low | High | Medium | |
| Emergency Response Times and Efficacy | Enhance GPS and dispatch technologies. | Short | High | Medium | High |
| Develop rapid deployment strategies. | Short | Medium | High | High | |
| Invest in infrastructure improvements at EMS stations. | Long | Medium | High | High | |
| Expand the network of emergency medical facilities. | Long | Low | High | Medium | |
| Implement performance tracking for response times. | Long | High | Medium | Medium | |
| Training and Preparedness for Disaster Response | Increase frequency and complexity of disaster response simulations. | Short | High | Medium | High |
| Develop specialized units for specific disaster scenarios. | Short | High | Medium | High | |
| Collaborate with international disaster response agencies. | Long | Medium | High | Medium | |
| Create a digital training hub for disaster response. | Long | Medium | Medium | High | |
| Mandate disaster preparedness certifications. | Long | High | Medium | High | |
| Financial Resources and Administrative Efficacy | Optimize financial planning for high-priority needs. | Short | High | Low | High |
| Streamline administrative processes to reduce overhead. | Short | High | Low | High | |
| Develop strategic financial partnerships. | Long | Medium | Low | Medium | |
| Use big data analytics for predictive funding needs. | Long | Medium | Medium | Low | |
| Lobby for increased governmental and international funding. | Long | Low | Low | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





