1. Introduction
The importance of the Colorado River in the Western region of the United States cannot be overstated, as it serves as a vital resource for seven basin states (Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming). These states rely on the river for various purposes such as water supply, hydropower generation, recreational activities, preservation of fish and wildlife habitats, and other essential benefits. While agricultural activities consume 70 percent of the river’s water, approximately 35 to 40 million individuals depend on it for at least some, if not all, of their municipal water needs [
1]. During the 21st century, it is forecasted that the snowpack in basin headwaters will increase. However, warmer conditions at lower elevations are expected to lead to a shift from snowfall to rainfall, resulting in increased runoff from December to March and decreased runoff from April to July. Reductions in spring and early summer runoff could lead to decreased water availability for irrigation purposes and potentially disrupt hydropower operations at reservoirs.
Similarly, the Mississippi River serves as a crucial resource for water supply, navigation, agricultural irrigation, recreation, and the preservation of fish and wildlife habitats. It spans 31 states and supports a significant portion of the U.S. agricultural output, with 92% of the nationâs agricultural exports and 78% of the worldâs feed grains and soybeans [
2]. Additionally, over 18 million people rely on the river for drinking water. Given their extensive reach and the multitude of services they provide, the Colorado and Mississippi River Basins are critical to the overall water resilience and resource management in the United States. Implementing sustainable water practices in these basins is crucial and offers opportunities to create a positive climate impact.
In the broader context of water resource management, the energy system plays a critical role, being responsible for significant freshwater withdrawals [
3]. In the United States alone, the energy sector accounts for approximately 40% of total freshwater withdrawals, primarily for cooling processes in thermoelectric power plants [
4]. Moreover, water management practices contribute to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions through various processes, such as water treatment, transport, and the decomposition of wastewater. For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that water and wastewater systems account for approximately 2% of U.S. energy use, resulting in the emission of over 45 million tons of GHGs annually (EPA, 2017). It is clear that there are linkages between the water sector, climate change, and the economy. Nevertheless, recognizing and managing water as a form of natural capital poses considerable difficulties. Its mobility, weight, non-rivalrous nature, multiple uses, and time- and place-dependent value complicate these efforts [
5] and have constrained the development of water management markets. Climate finance mechanisms, such as the voluntary carbon market (VCM), address these challenges by creating new, recurring revenue sources that establish sustainable, performance-based funding streams, thereby incentivizing safe water services globally. Private sector climate financing offers an opportunity to support dependable and sustainable water systems [
6]. Many companies are interested in purchasing carbon credits through the VCM to offset a portion of their remaining emissions, achieve sustainability targets linked to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, or contribute to global net zero goals. High-integrity carbon markets must ensure that credits represent genuine, verified emission reductions, uphold strict environmental and social safeguards, complement corporate decarbonization efforts, and are supported by credible claims.
A voluntary carbon credit, valued at approximately
$10 for many nature-based projects [
7] and over
$1,000 for some direct air capture projects [
8], represents the reduction or removal of one tonne of carbon dioxide. While the global market for carbon credits is substantial and growing, water has traditionally not been as easily traded due to its inherently local natureâconserving water in Louisiana, for example, does not address water insecurity in Colorado. This localization makes it challenging to develop effective financing and trading mechanisms for water, limiting the value, transactability, and liquidity of water credits, such as those created under the US Clean Water Act [
7]. However, when a carbon credit incentivizes actions like water conservation in Colorado or coastal wetland restoration in Louisiana, it can access a liquid market, be traded, and generate revenue, thus encouraging water security efforts.
Given these complexities, this paper aims to explore how leveraging the VCM can enhance water resilience in the Colorado and Mississippi River Basins. We will examine existing and potential water-related carbon credit programs, estimate the potential carbon credits and financial returns, and highlight policy and programmatic innovations to strengthen the VCMâs role in supporting water resilience projects.
4. Discussion
4.1. Challenges
Multiple Stakeholders. The Colorado and Mississippi River basins present significant challenges for water resiliency projects due to their vast size and complexity. These basins encompass diverse ecosystems and a wide range of water needs, making project implementation and coordination highly intricate. The involvement of multiple stakeholders, including federal, state, and local governments, private landowners, and indigenous communities, further complicates decision-making and project execution. The necessity to harmonize the interests and priorities of such a varied group of stakeholders adds a layer of complexity that can impede the timely and efficient progress of water resiliency initiatives.
High costs in the US. High costs represent another substantial challenge in these regions. The costs of water, energy, and labor in the United States are notably higher compared to global averages, which escalates the overall expenditure required for large-scale infrastructure projects. The significant upfront capital investment needed to initiate and sustain these projects poses a barrier to their implementation, particularly in the context of the high financial outlays associated with advanced technological solutions and extensive construction efforts. This financial burden is often a deterrent for potential investors and can stall the progress of crucial water management projects.
Complex Regulatory and Policy Landscape. Regulatory and policy barriers also hinder the advancement of water resiliency projects in the Colorado and Mississippi River basins. The complex web of regulations and policies at federal, state, and local levels creates a cumbersome and time-consuming environment for regional project development. Additionally, the potential for future policy changes adds an element of uncertainty that can affect the long-term viability of carbon-financed projects. These regulatory challenges necessitate ongoing navigation and compliance, which can divert resources and focus away from the core objectives of water resiliency initiatives.
Integrity of Monitoring and Verification. Accurate monitoring and verification of carbon and water benefits are critical yet challenging aspects of water resiliency projects. These tasks require sophisticated technology and consistent oversight to ensure reliability and credibility. Implementing advanced technologies, such as internet-of-things (IoT) and machine learning for project verification involves high costs and technical challenges. The financial and operational demands of these technologies can be prohibitive, further complicating the management and reporting of project outcomes.
Market Fluctuations. Market uncertainties compound the difficulties faced in these regions. Fluctuations in carbon credit prices and demand can significantly impact the financial stability of water resiliency projects. The volatile nature of the carbon market introduces risks that can deter investment and undermine the sustainability of projects. Additionally, uncertain future regulations regarding carbon markets contribute to investor hesitancy, making it challenging to secure consistent funding and support. These market dynamics require careful consideration and strategic planning to mitigate risks and ensure the long-term success of water resiliency efforts.
4.2. Opportunities
Urgent Need for Water Resiliency Projects. The increasing incidence of droughts, floods, and algae blooms in the Colorado and Mississippi River basins highlights the urgent ecological need for water resiliency projects. These critical water basins possess high ecological value, and preserving and restoring them can significantly enhance environmental sustainability. Addressing these ecological challenges underscores the urgent need for developing comprehensive water management and carbon sequestration projects to alleviate the negative impacts of climate change and environmental degradation.
Proximity to Local Carbon Credit Investors. Proximity to major corporations with significant carbon footprints presents a unique opportunity for investment in local carbon credits. Corporations located near these basins are likely to invest in region-specific carbon credits to meet their sustainability goals and reduce their carbon footprints. This proximity also offers marketing benefits, as companies can demonstrate their commitment to local environmental stewardship and community support. Region-specific carbon credits can appeal to corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives and attract substantial investments from businesses aiming to achieve net-zero emissions.
Availability of Federal and State Funding. Federal and state funding programs provide valuable support for water resiliency and climate adaptation projects in these basins. The availability of federal grant money and state-level funding initiatives can be leveraged to supplement carbon finance mechanisms, making projects more financially viable. Additionally, the growing interest in innovative financing mechanisms, such as blended finance models that combine public, private, and philanthropic capital, can fund large-scale projects. Developing new financial instruments tailored to the needs of water and carbon markets can attract diverse investment sources and enhance project sustainability.
Using Private Project Developers to Manage Complexity. In other global contexts, carbon credit project developers bring critical expertise that could address the challenges of stakeholder coordination and regulatory complexities in the Colorado and Mississippi River basins. Their experience can facilitate more efficient decision-making and project implementation. Additionally, these developers’ understanding of complex regulatory landscapes allows them to navigate compliance and adapt to policy changes effectively. Similar to how mitigation bankers operate at scale in the US, well-focused private developers can accelerate project progress and impact.
Rising Public Awareness and Technological Advancements. Increasing public awareness and support for climate action and sustainable water management is another significant opportunity. Public engagement can drive demand for voluntary carbon market (VCM) projects, fostering community involvement and co-benefits such as job creation and local economic development. Technological advancements in IoT, remote sensing, and machine learning can further improve project efficiency and verification processes. Innovations in water management and carbon sequestration technologies can enhance the impact and viability of these projects, making them more attractive to investors and stakeholders.
Synergy with Existing Water Management and Conservation Initiatives. Finally, there is considerable potential for synergy with existing water management, conservation, and restoration initiatives. Aligning VCM projects with ongoing efforts can create integrated solutions that address both carbon and water challenges simultaneously. By building on existing initiatives, new projects can leverage established networks, resources, and expertise, thereby enhancing their effectiveness and scalability. This integrated approach can maximize environmental benefits and contribute to long-term water and carbon sustainability in the Colorado and Mississippi River basins.
4.3. Strategies for Enhancing Demand for Colorado and Mississippi Generated Carbon Credits
Improving Messaging on Environmental Benefits. Improved messaging is crucial for enhancing the demand for carbon credits generated from the Colorado and Mississippi River basins. Emphasizing the direct environmental benefits of these projects, such as mitigating local droughts, floods, and water quality issues, can significantly increase their appeal. Highlighting success stories and case studies that showcase tangible improvements in these regions will help potential buyers understand the real-world impact of their investments. This localized approach not only underscores the immediate environmental benefits but also demonstrates the broader value of supporting regional carbon projects.
Highlighting Socio-Economic Impacts. Promoting the positive socio-economic impacts of carbon credit projects is another effective strategy. Emphasizing benefits such as job creation, community resilience, and local economic development can attract a wider audience. Featuring testimonials from local stakeholders, including residents, businesses, and policymakers, adds credibility and relatability to the messaging. These personal accounts can resonate with potential investors by illustrating how carbon projects directly contribute to the well-being of local communities, thereby fostering stronger support and engagement.
Leveraging the Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Benefits. Leveraging the CSR benefits is also key to enhancing demand. The proximity of major corporations to the Colorado and Mississippi River basins provides a unique opportunity to align carbon projects with corporate sustainability goals. By emphasizing how these credits contribute to broader environmental and social objectives, companies can be encouraged to invest in local carbon projects. Additionally, connecting the importance of water quality and availability to public health outcomes underscores the health and wellness benefits of these initiatives. Highlighting how improved water quality can enhance community health and well-being can further motivate corporate and individual investments in regional carbon credits.
Developing and Promoting Region-Specific Methodologies. To further enhance demand for carbon credits generated from the Colorado and Mississippi River basins, it is essential to develop and promote region-specific methodologies. These methodologies should be tailored to the unique environmental and socio-economic conditions of these areas. Collaborating with local experts and stakeholders ensures that the methodologies are not only practical and effective but also widely accepted by the community. This localized approach can improve the relevance and impact of carbon credit projects, making them more attractive to potential buyers who seek region-specific solutions.
Promoting Diverse Project Development. Encouraging the development of diverse project types can also drive demand for carbon credits. Projects such as wetland restoration, sustainable agriculture, reforestation, and water efficiency improvements offer multiple environmental and social co-benefits. Piloting innovative approaches that integrate carbon sequestration with water management can further enhance the overall impact of these projects. By showcasing a variety of project types, stakeholders can appeal to a broader audience with different interests and priorities, thereby increasing the market for carbon credits.
Rigorous Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification. Ensuring transparency and accountability is crucial for building trust with credit buyers. Implementing rigorous monitoring, reporting, and verification (MRV) protocols helps maintain high standards of integrity and transparency. Using third-party certification bodies to validate project outcomes further reinforces the credibility of the projects. This level of scrutiny and accountability can reassure potential investors about the legitimacy and effectiveness of the carbon credits they purchase. By upholding stringent standards, stakeholders can foster a trustworthy market environment that attracts long-term investments in carbon credits from the Colorado and Mississippi River basins.
Targeted Marketing Campaigns. To effectively engage the market and boost demand for carbon credits generated from the Colorado and Mississippi River basins, it is crucial to implement targeted marketing campaigns. These campaigns should focus on key sectors such as agriculture, energy, manufacturing, and finance, which have a significant presence in these regions. Utilizing a mix of digital marketing, social media, and traditional media channels can help reach a broad audience and raise awareness of the benefits associated with purchasing regional carbon credits. Messages that highlight the environmental, social, and economic advantages of these projects can attract diverse stakeholders and increase market penetration.
Establishing Strategic Partnerships. Strategic partnerships are essential for co-promoting and supporting carbon projects. Alliances with local governments, non-profits, industry associations, and academic institutions can amplify efforts to enhance the credibility and reach of carbon credit initiatives. Collaborating with major corporations and investors to secure long-term purchase agreements and funding commitments can provide the financial stability necessary for the success of these projects. These partnerships can also facilitate knowledge exchange and resource sharing, further strengthening the implementation and impact of carbon credit projects in the river basins.
Engaging with policymakers. Policy advocacy plays a vital role in creating a supportive environment for carbon credit generation and purchase. Engaging with policymakers to develop regulatory frameworks and incentives can drive the adoption of carbon credits. Advocacy efforts should aim to integrate carbon credits into regional and state-level sustainability and climate action plans. By influencing policy, stakeholders can ensure that carbon credits become a recognized and valuable component of broader environmental and economic strategies. Support from policymakers can increase the appeal of carbon credits to investors and buyers, helping to build a strong market for these environmental assets.
Promoting Co-Benefits. Emphasizing the co-benefits of climate-financed water projects could boost demand for these initiatives. Research indicates that projects likely to deliver the most significant co-benefits received a 30.4% higher valuation compared to those with the fewest co-benefits [
29]. Although this trend pertains to international development projects within the compliance carbon market, it demonstrates that carbon markets do value co-benefits, even if this doesn’t always lead to a price premium. In the Colorado and Mississippi River basins, it would be beneficial to establish a framework that places greater emphasis on delivering co-benefits to communities.
4.4. Recommendations
This paper identifies specific opportunities at the intersection of water security programs and the Voluntary Carbon Market (VCM) within the Colorado River and Mississippi River regions. Leaders and stakeholders in both the VCM and the water sector can take several steps to realize this potential, addressing the unique challenges and opportunities of these regions.
-
Articulate and Promote the VCM-Water Relationship: Stakeholders should actively communicate the critical link between existing VCM methodologies and water-related programs in the Colorado and Mississippi River basins. Public awareness of the carbon impacts of water treatment and conveyance to regional greenhouse gas emissions is low, and the potential for nature-based practices that improve water quality and quantity outcomes while also sequestering carbon or avoiding future emissions is high. Promoting this relationship and the benefits of integrating carbon credits with water programs can support market growth and attract investments, particularly highlighting chronic issues like the depletion of the Colorado River and nutrient pollution in the Mississippi River.
Regulators, utility staff, and watershed stakeholders should collaborate with watershed carbon project developers and VCM standards body staff to explore innovative approaches for attracting catalytic capital from the VCM to establish a more scalable framework for improving water quality issues. It is crucial for project developers to ensure that local community stakeholders and landowners receive adequate education about the operations of the carbon market and how they can equitably participate. Furthermore, local elected officials and water sector leaders should actively communicate the economic and ecological co-benefits of these projects to State and Federal regulators, advocating for broader VCM connectivity and acceptance. This will help to expand the implementation of these restoration projects beyond individual communities.
-
Encourage Methodology Innovation: Standards bodies governing the VCM should actively lead or promote the development of innovative methodologies specifically designed for the unique environmental conditions of the Colorado and Mississippi River basins. While recent critiques of the VCM have driven a shift towards more standardized approaches, it is essential that registries and standards bodies maintain a space for methodological and project development innovation within the water sector. This is particularly important given the lack of published methodologies for many potential water-related projects.
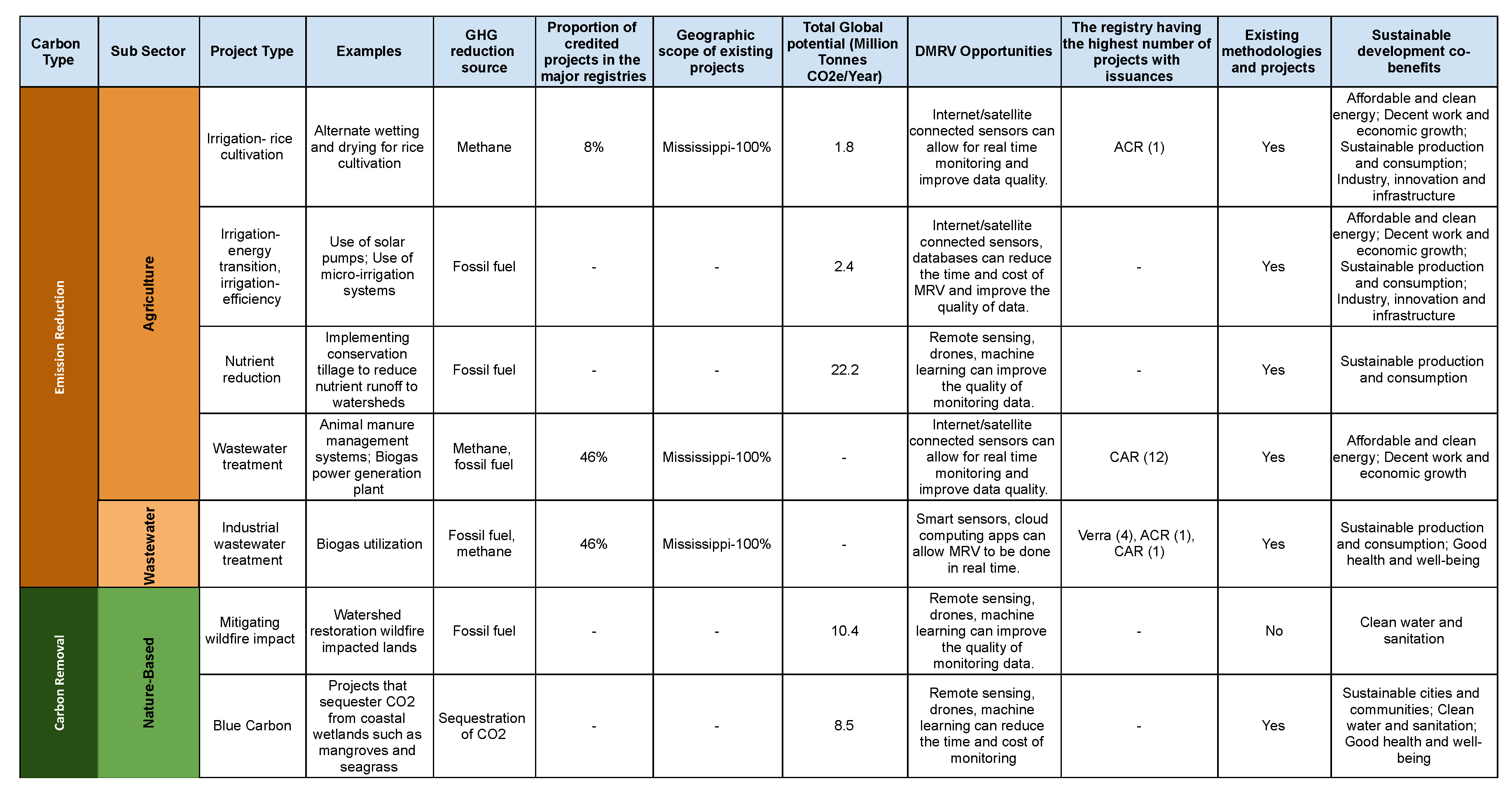
It is critical to rapidly develop new methodologies to address water quality, water quantity, and carbon sequestration, such as protocols for wetland restoration in the Mississippi River Basin and forest management in the Colorado River Basin. Emerging protocols, like Regen Networkâs âWatershed Nature-Based and Green Infrastructure Water Methodology,â represent progress in quantifying emission reductions through improved instream water quality [
21]. A particular focus should be placed on the ’Big 4’ VCM registriesâVerra, the Gold Standard, the American Carbon Registry, and the Climate Action Reserve. These leading registries should prioritize incorporating water sector into their frameworks. Moreover, existing protocols, such as the Climate Action Reserve’s "Soil Enrichment Protocol" and Verra’s "Methodology for Improved Agricultural Land Management", which address soil carbon, should be expanded to explicitly include water quality metrics [
29,
30]. Both registries already offer broader methodologies for emission reductions through improved agricultural land management, providing a foundation upon which to build.
Pilot Programs and Demonstration Projects: However possible, regional stakeholders should develop regional pilot programs and demonstration projects in collaboration with leading corporations to showcase the feasibility and benefits of investing in high-priced, high-quality carbon credits. Use these projects to generate data, success stories, and best practices that can be shared with a broader corporate audience to build trust and momentum. Emphasize the co-benefits of water-related carbon credits, such as improved water security, ecosystem health, and community resilience, which can contribute to a companyâs overall sustainability goals. Highlight the potential return on investment (ROI) through enhanced corporate reputation, regulatory compliance, and long-term environmental impact.
Invest in Digital Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (DMRV): Investment in DMRV technologies can significantly enhance the credibility and scalability of water projects generating carbon credits. Implementing a common architecture of DMRV technologies, including sensors, remote sensing, and statistical tools, can support both carbon credit verification and the direct operation of water programs. This is particularly relevant for monitoring water flow and quality in the Colorado River and sediment control in the Mississippi River.
Conduct High-Resolution, Localized Analysis: Future work should include higher resolution and more localized analysis of the carbon credit potential in the water sector. Developing precise estimates of emission reductions and the associated costs for specific projects or regions within the Colorado and Mississippi River basins can increase accuracy and support targeted investments. For example, focusing on specific areas of need like the Lower Colorado River Basin and the Mississippi Alluvial Plain can provide more actionable insights for stakeholders.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.T., J.E. and A.J.; methodology, J.E. and E.T.; software, J.E..; validation, E.T.; formal analysis, J.E. and A.J.; investigation, J.E. and A.J.; resources, E.T. and A.J.; data curation, J.E.; writing—original draft preparation, J.E., A.J. and T.L. ; writing—review and editing, J.E., A.J., E.T. and T.L.; visualization, J.E.; supervision, A.J. and E.T.; project administration, A.J.; funding acquisition, A.J. and E.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.