1. Introduction
Breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in the world, making it a serious public health concern. Age is the most significant risk factor, with older women experiencing the highest incidence rates. Concerning breast cancer types, most cancers are adenocarcinomas, with 85% developing in the breast ducts and 15% in the lobular epithelium [
1,
2]. Early detection of breast cancer is crucial for improving survival rates. Mammography significantly reduces breast cancer-related deaths, but dense breast tissue can make detection challenging. Advanced imaging methods like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), contrast-enhanced mammography, and molecular breast imaging are more sensitive in dense breasts. MRI or ultrasound are used more frequently for individuals with hard-to-image breasts or at high risk, such as women with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations [
3]. Nevertheless, computed tomography (CT) scans and MRIs do not always provide conclusive results for many individuals because they only show structural and anatomical changes at the main cancer site and distant metastases. On the other hand, molecular imaging techniques are more effective in staging and detecting treatment response and recurrence, particularly when structural changes caused by treatment or surgery are present. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) using
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (
18F-FDG) is especially useful for risk stratification, staging, and predicting responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC), but with limited sensitivity and specificity in some subtypes of breast cancer [
4,
5]. In addition to
18F-FDG, many other radiotracers have been developed to complement its diagnostic capabilities. This review aims to elaborate on the role of molecular imaging in the diagnosis of breast cancer and highlight both current and emerging radiotracers and techniques in nuclear imaging of breast cancer.
2. Sources and Selection Criteria
In order to compile the relevant literature for this review on the use of radiotracers in breast cancer imaging, we conducted a comprehensive search using multiple academic databases such as PubMed and Medline. The search strategy included a combination of keywords such as, but not limited to, ‘radiotracers,’ ‘breast cancer,’ ‘positron emission tomography (PET),’ ‘nuclear medicine,’ and ‘molecular imaging.’ We mainly focused on articles published within the last decade to ensure the inclusion of the most recent advancements and research findings. To refine the search results, we applied specific inclusion criteria, such as peer-reviewed articles, studies involving human subjects, and papers published in English. Articles that were not directly related to breast cancer imaging or did not involve radiotracers were excluded. Additionally, we reviewed the references of the selected articles to identify any additional relevant studies. This systematic approach ensured a thorough and relevant selection of literature for the review.
3. Types of Breast Cancer
3.1. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive malignancy of the breast characterized by neoplastic proliferation limited to the breast ducts and without myoepithelial invasion. DCIS is a non-obligate precursor to invasive breast cancer, with 25-60% of cases progressing if left untreated [
6]. DCIS is one of the most common breast cancers, accounting for 20-25% of all diagnosed breast cancers worldwide [
7]. According to estimates by the American Cancer Society, approximately 56,500 new cases of DCIS will be diagnosed in the United States in 2024 [
8]. In the majority of cases with prompt diagnosis and treatment, DCIS has an excellent prognosis and portends a normal life expectancy. In particular, the ten-year overall survival rate is 98% [
7], and the twenty-year cancer-specific mortality rate is 3.3% [
9].
3.2. Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) is an invasive malignancy of the breast characterized by the proliferation of neoplastic luminal epithelial cells and their invasion into the surrounding stromal tissue following the disruption of the myoepithelial cell layer, ductal basement membrane, and ductal wall [
6]. A significant proportion of patients with IDC have an associated DCIS component, with studies reporting the presence of a DCIS component in 30-60% of cases of IDC [
10]. IDC is the most common type of invasive breast cancer, accounting for 70-80% of cases overall [
11]. When detected and treated early, IDC has a good prognosis, with a five-year relative survival rate of 90% [
11,
12].
3.3. Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) is another invasive malignancy of the breast characterized by a discohesive histopathological phenotype with single-file strands of proliferative neoplastic cells lacking epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin) and infiltrating the stromal and adipose tissues [
13]. ILC is the second most common type of invasive breast cancer, accounting for 10-15% of cases worldwide [
11]. The five-year relative survival rate in appropriately treated cases is 93% and does not differ significantly from that of IDC [
11]. However, the long-term outcomes of ILC are equivalent or even inferior to those of IDC, with the prognosis of ILC becoming progressively worse than that of IDC over time [
14].
3.4. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Breast cancers lacking the expression of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) are referred to as triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) [
15,
16]. TNBC typically displays an aggressive clinical course, with a poorer prognosis compared to other types of breast cancer, having a five-year relative survival of only 77% after diagnosis compared to 93% in other breast cancer types, as well as a 30-40% five-year recurrence rate after surgical intervention [
15,
17].
3.5. HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
HER2-positive breast cancers are those with overexpression of the HER2 gene with abnormally elevated levels of the HER2 receptor protein [
18]. The prognosis of having the HER2 gene is a poor one, with survival rates reducing with each additional copy of the gene [
18,
19]. Interestingly, HER2 overexpression was found to inversely correlate with hormone receptor (HR) protein expression levels [
20]. The five-year survival rate of HER2-positive breast cancer when detected and treated early is 91.5% in cases that are also hormone receptor-positive and 85.7% in cases that are hormone receptor-negative [
21]. However, the survival rate decreases to 30% when this aggressive malignancy progresses to more advanced stages [
22].
3.6. Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer (Luminal Subtypes)
Luminal A tumors are defined by the presence of ER and/or PR, the absence of HER2, and low levels of the cell proliferation marker Ki-67; in contrast, Luminal B tumors are typically ER-positive and may lack PR, are characterized by high expression of Ki-67, and are of higher grade and have a poorer prognosis compared to Luminal A [
23]. Approximately 70-75% of invasive breast cancers exhibit notably elevated ER expression. Meanwhile, PR is found in over 50% of patients who are ER-positive but is extremely rare in those with ER-negative breast cancer [
23,
24]. The five-year relative survival percentages of women diagnosed with either subtype is relatively high, with the luminal A subtype being 94.4%, while those with the luminal B subtype having a slightly lower rate at 90.7% [
21].
4. Current Radiotracers in Breast Cancer Imaging
4.1. 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG)
4.1.1. 18F-FDG PET/CT
18F-FDG PET/CT imaging plays an important role in diagnosis, staging, prognosis, assessment of recurrence, treatment planning, and response of breast cancer. FDG is a glucose analog transported through a glucose transporter into the cell and phosphorylated by a hexokinase. FDG follows a similar pathway to glucose, however, it is not entirely metabolized since it does not have a hydroxyl group at the C-2 position. As a result, it becomes confined in tumor cells at a rate proportional to glucose utilization. The fact that malignant cells have higher glucose metabolism and increased glycolytic activity facilitates their detection using
18F-FDG PET/CT imaging [
25].
18F-FDG is not very specific for malignancy since its uptake can be seen in inflammatory or infectious conditions. Many benign breast etiologies also show mild increased
18F-FDG uptake such as fibroadenoma, ductal adenoma, and fibrocystic changes and these can hence be mistaken for malignancy [
26].
4.1.1.1. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Tumors like DCIS are often small in size and show low-to-no
18F-FDG uptake. In addition, the use of
18F-FDG PET/CT to diagnose early-stage breast cancer is limited by its low spatial resolution, which can miss small lesions that are less than 5 mm in size. Therefore,
18F-FDG PET/CT is more useful in invasive breast cancer and metastatic disease [
26]. Accordingly, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology do not recommend the routine use of
18F-FDG PET/CT for early diagnosis of breast cancer [
27]. However,
18F-FDG PET/CT has some utility in cases of DCIS, particularly in predicting the progression of DCIS to invasive cancer. In a study comparing
18F-FDG PET/CT imaging findings with histological results from needle biopsy, maximum standardized uptake (SUV
max, with a cutoff point ≥ 1.9) and tumor size were significant predictors of DCIS upgrade to invasive cancer (p = 0.002 and p = 0.022, respectively) [
28].
4.1.1.2. Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Studies have shown a higher uptake of
18F-FDG in IDC compared to other types of cancer such as DCIS and ILC, with one study for example showing median SUV
max values of 6.6 for IDC and 3.4 for ILC [
29,
30]. In addition to initial diagnosis,
18F-FDG PET/CT plays a crucial role in tumor staging, specifically in invasive breast cancer such as advanced TNBC to assess extra-axillary nodal and distant metastasis. Thus,
18F-FDG PET/CT has a significant role in patients at greater risk of metastatic disease [
31,
32]. Moreover,
18F-FDG PET/CT has good performance in detecting bone metastasis secondary to invasive breast cancer. A systematic review and meta-analysis of 668 patients showed that
18F-FDG PET/CT performed better than bone scintigraphy with a sensitivity of 93% and a specificity of 99% [
33].
18F-FDG PET/CT also plays a major role in assessing prognosis, where
18F-FDG uptake and SUV
max value correlate with tumor invasiveness. A higher SUV
max indicates a poorer prognosis and higher disease recurrence [
34]. A study by Song et al. concluded that the SUV
max value of the primary tumor (pSUV
max) on pretreatment
18F-FDG PET/CT could be used as a good surrogate marker for the prediction of progression in patients with IDC. Meanwhile, patients with a high pSUV
max (more than 6.6) had significantly shorter progression-free survival compared to patients with a low pSUV
max (p < 0.0001) [
35].
18F-FDG PET/CT can predict treatment response with its ability to identify variations in metabolic activity at earlier stages compared to changes in tumor size detected by morphologic imaging. This is especially helpful in the case of targeted therapy, as treatment can inactivate tumor cells without necessarily affecting their size [
25]. Similarly,
18F-FDG PET/CT can also predict breast cancer recurrence. A study concluded that
18F-FDG PET/CT performed better than contrast-enhanced CT alone or combined with bone scan for evaluating disease recurrence. The results showed an area under the receiver operating curve of 0.99 for
18F-FDG PET/CT, 0.84 for contrast-enhanced CT, and 0.86 for combined contrast-enhanced CT and bone scintigraphy [
36].
4.1.1.3. Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Accurate staging of ILC, a subtype of breast cancer, is crucial for successful treatment. While
18F-FDG PET/CT is commonly used for this purpose, its effectiveness varies depending on the histologic subtype. For instance, identifying ILC using
18F-FDG PET/CT is challenging due to its distinctive molecular and clinical characteristics, such as decreased cellular density, receptor expression, and different metastatic patterns. Additionally, the absence of E-cadherin leads to dispersed tumor cells and a low rate of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes [
37]. These unique attributes of ILC diminish the sensitivity of
18F-FDG PET/CT in detecting cancer due to the dispersion of glucose-intensive tumor tissues. Consequently, both primary and metastatic ILC have lower
18F-FDG levels than IDC, limiting the efficacy of
18F-FDG PET/CT for detecting ILC [
38]. Moreover, research has shown that in newly diagnosed stage I-III ILC patients,
18F-FDG PET/CT has a lower impact on systemic staging compared to IDC patients. Additionally, untreated bone metastases in IDC patients tend to have higher
18F-FDG uptake, while non-FDG-avid sclerotic bone metastases are more common in ILC. Therefore, it is recommended to carefully evaluate CT images from PET/CT scans for ILC patients [
39].
When it comes to detecting recurrence,
18F-FDG PET/CT demonstrated usefulness in the surveillance of ILC. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) of PET/CT for predicting recurrence in ILC were 87%, 87%, 95%, and 70%, respectively [
40]. ILC recurrence sites had high SUV
max values, with a mean SUV
max of 6.4. In 40 patients having histopathological data, 30 PET/CT scans yielded true positive results. However, false negatives were reported in cases of local, peritoneal, meningeal, and bladder recurrences [
40]. Moreover, in the first instance of ILC recurrence, the detection of an axillary lymph node using
18F-FDG PET/CT even when
18F-FDG uptake is low, showed an approximate sensitivity of 52%, specificity of 87%, and accuracy of 85%.
18F-FDG PET/CT demonstrated significantly higher specificity compared to MRI with 88% specificity [
41]. Overall,
18F-FDG PET/CT findings influenced treatment plans for 92% of patients [
40].
4.1.1.4. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Advances in
18F-FDG PET/CT have played a revolutionary role in diagnosing, staging, and treating TNBC, a highly aggressive form of breast cancer and thus metastasizes very early on. The use of
18F-FDG PET/CT in tumor staging in breast cancer, notably TNBC, is thus essential. Effective detection of distant metastases is crucial for patient management as it changes management from surgery with or without neoadjuvant systemic therapy to palliative systemic therapy without surgery [
42].
18F-FDG PET/CT provides better predictive stratification than traditional imaging as metabolic uptake varies with tumor phenotype. For instance, in TNBC, high
18F-FDG uptake indicates increased metabolic activity and may predict treatment outcomes. A multivariate regression analysis of TNBC cases showed significant positive correlations between SUV
max and tumor size (p = 0.009) as well as between SUV
max and Ki-67 score (p < 0.001), indicating a wide range of glucose metabolism. This demonstrates that
18F-FDG PET/CT imaging could be used to measure the Ki-67 proliferation index and identify aggressive TNBC cases [
43].
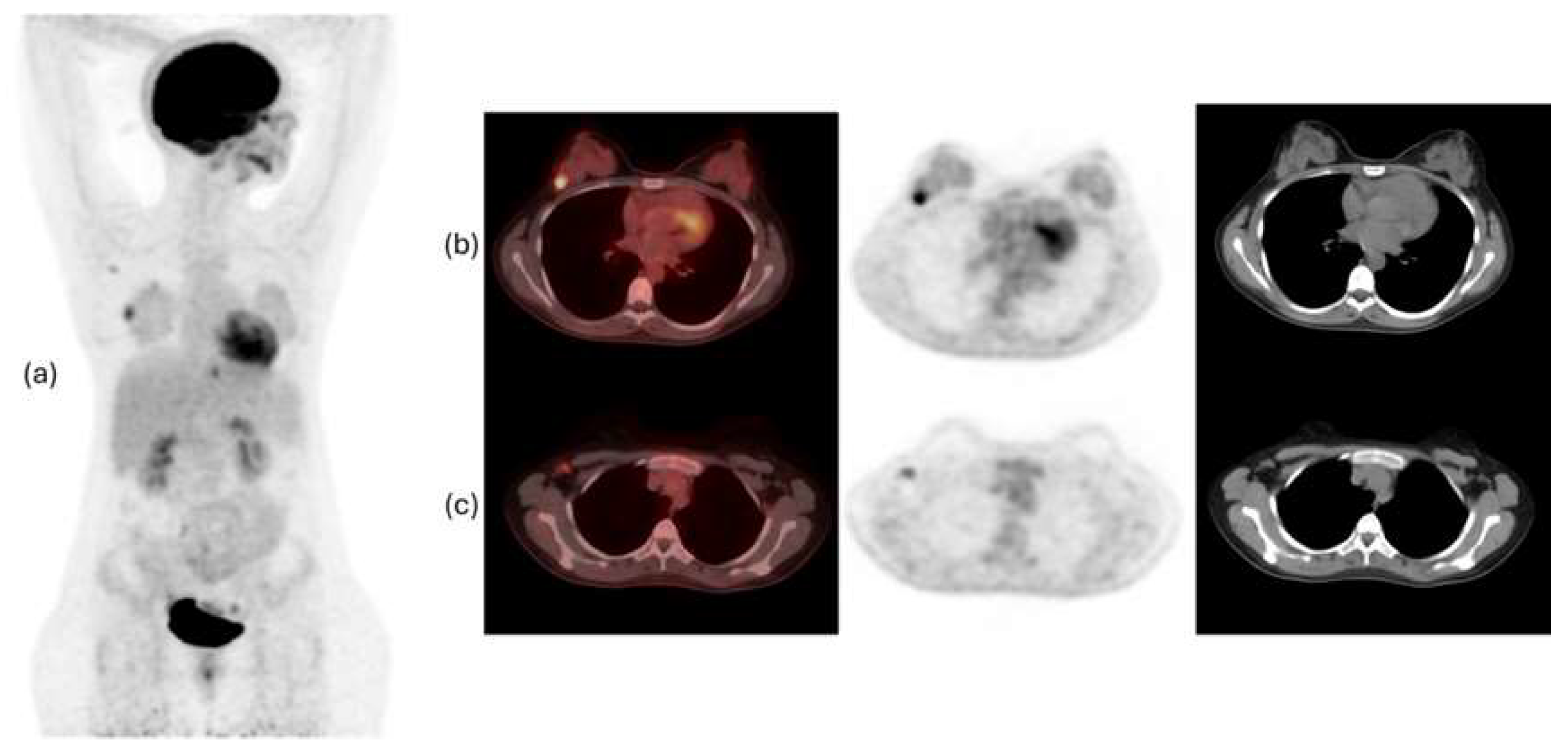
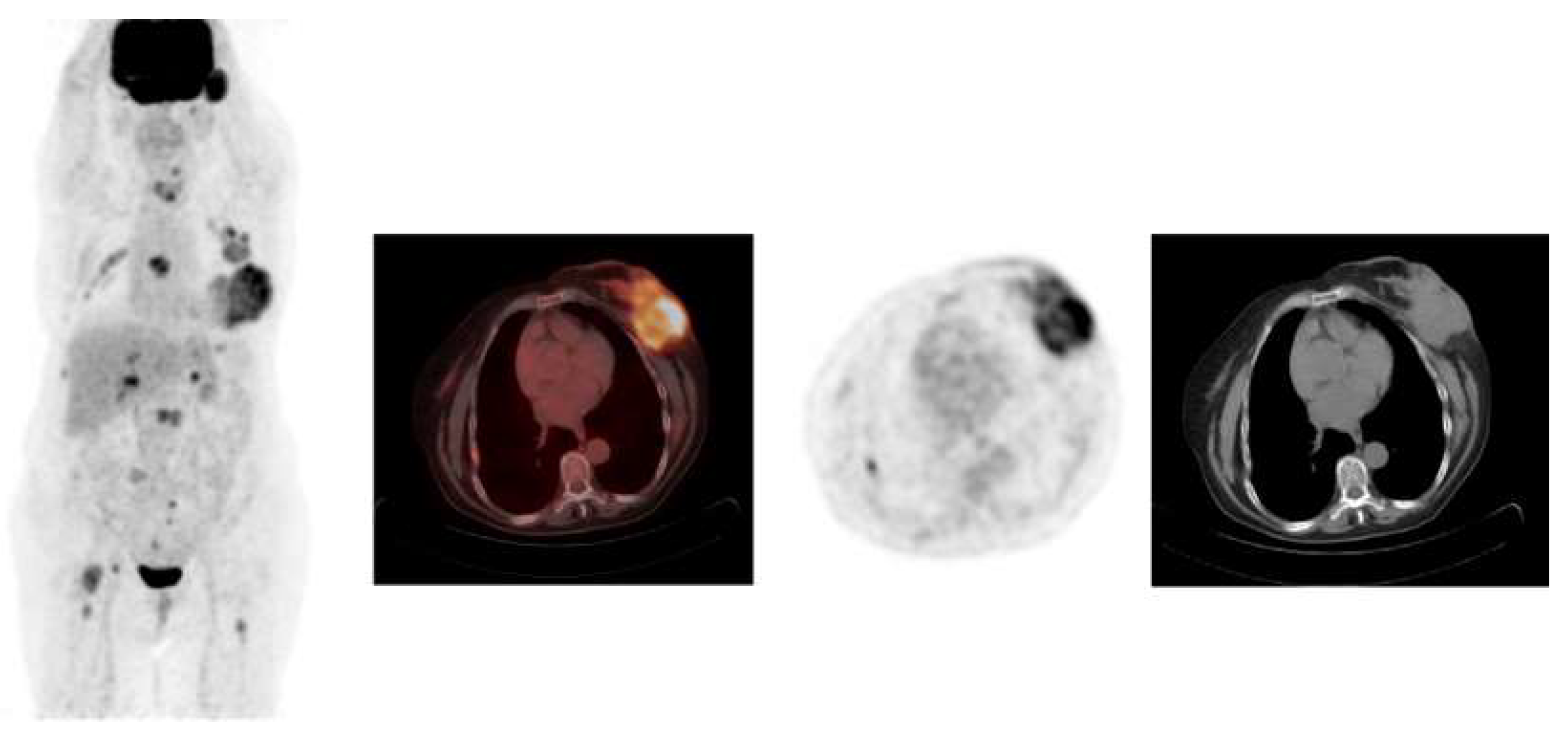
Figure 1 and
Figure 2 show examples of
18F-FDG PET/CT imaging of breast cancer, with the former showing a case of locoregional malignancy and the latter showing a case of metastatic malignancy.
4.1.2. 18F-FDG Positron Emission Mammography (PEM)
As mentioned previously,
18F-FDG PET/CT can be used in clinical settings for staging, re-staging, and assessment of therapeutic response in cases of breast cancer; however, because of its limited spatial resolution especially for sub-centimetric lesions, this technique is not recommended as a means of detecting primary breast cancer or discriminating between benign and malignant breast lesions. These limitations led to the development of different breast imaging devices and nuclear imaging techniques such as positron emission mammography (PEM) to address the shortcomings of
18F-FDG PET/CT. Unlike the whole-body imaging performed in traditional PET/CT scans, PEM is a breast-specific positron imaging system which employs a device that brings the detectors closer to the breast in order to achieve dedicated high-resolution images, with the breast immobilized under gentle compression as the image is being taken. The most common radiotracer employed in PEM is also
18F-FDG. Given that PEM involves imaging the breasts, its utility is mainly in the diagnosis and assessment of primary malignancies rather than distant metastases, which are better evaluated using whole-body PET/CT [
44].
In a study comparing PEM with the standard of X-ray mammography, the sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, PPV, and NPV of PEM in diagnosing various types of breast cancer were 90%, 86%, 88%, 88%, and 88%, respectively (compared with the respective values of 92%, 48%, 71%, 57%, and 84% with convential mammography). In addition, studies have shown that PEM is superior to mammography in several aspects such as distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions, not requiring the use of X-ray radiation, yielding a more rapid diagnosis, offering high-precision information about the location of lesions, and identifying suspicious lesions in the breast [
45,
46]. A preliminary study on breast cancer screening using PEM showed a cancer detection rate of 2.3%, compared with a cancer detection rate of approximately 0.2% using whole-body PET imaging and 0.31% using mammography and physical examination. This result meets the international screening guidelines and shows that PEM may have potential as a screening tool in conjunction with X-ray mammography [
47].
In view of the fact that PEM has a better spatial resolution and takes less time than PET/CT, it may be a useful diagnostic tool and has been investigated for this purpose in comparison with other imaging modalities [
45]. In regard to diagnosis, PEM has shown equivalent sensitivity to MRI with potentially higher specificity for detecting abnormalities. In a pilot study of 25 patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer, PEM detected 96% of malignant index lesions. Despite the small sample size, PEM resulted in fewer false-positive extra lesions than MRI [
48]. Similarly, for preoperative local staging, two prospective studies have shown equivalent sensitivity and superior specificity of PEM in comparison with MRI, with one study reporting that PEM had a sensitivity of 80.5% and specificity of 91.2% compared with the respective values of 80.7% and 86.3% using MRI [
49,
50]. In comparison with PET/CT, PEM has demonstrated superior results in the diagnosis of breast cancer, with a meta-analysis showing higher sensitivity, accuracy, and NPV of PEM, and equivalent specificity and PPV between the two modalities [
45]. PEM has also proven to be more effective than whole-body PET/CT in the detection of residual disease after the completion of NAC. For example, one study using PEM to predict response to NAC showed a sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 77.1%, 83.3%, and 78.7%, respectively, compared with the respective values of 54.3%, 83.3%, and 61.7% using whole-body PET imaging [
51,
52].
Overall, PEM is a breast-specific molecular imaging modality that has great potential as a tool for specific uses such as local staging, evaluation of the response to neoadjuvant treatment, and detection of local disease recurrence [
44], in addition to its utility as a diagnostic tool and perhaps even as a screening tool. PEM is also advantageous in that it can be used to biopsy specific lesions, and a PEM-guided biopsy system is available in the market that employs a stereotactic method for targeting lesions [
53]. However, the radiation exposure involved in PEM must be taken into consideration. In comparison with X-ray mammography, PEM is associated with a 15-fold increase in the risk of cancer induction and a 25-fold increase in the overall risk of cancer-related mortality. This relates to the fact that only the fibroglandular breast tissue is exposed to significant amounts of ionizing radiation in X-ray mammography, resulting in a risk of induce breast cancer, whereas PEM involves the use of radionuclides which can induce malignancy in any radiosensitive organs. In particular, the bladder has the highest radiation dose and risk of cancer induction in PEM [
54].
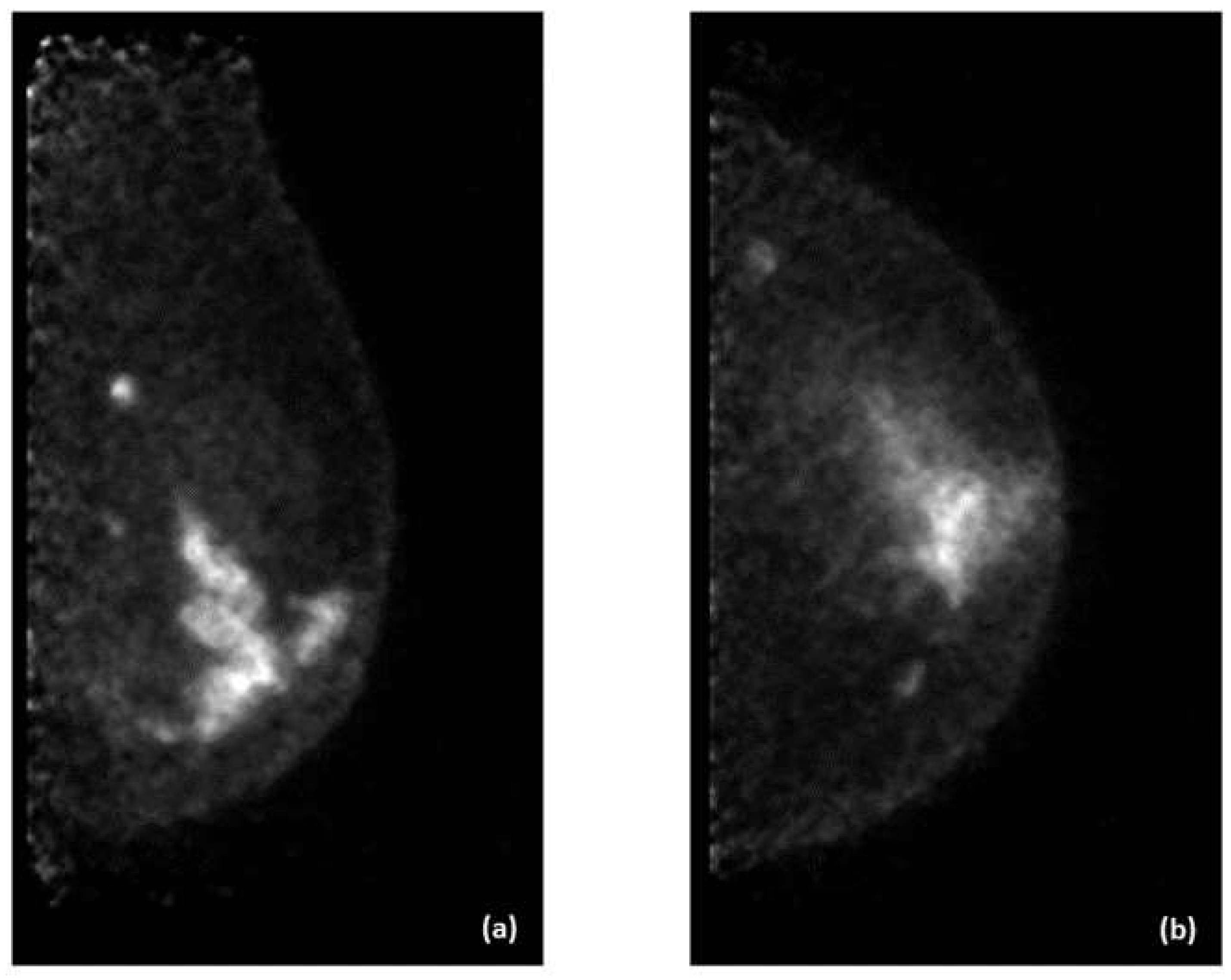
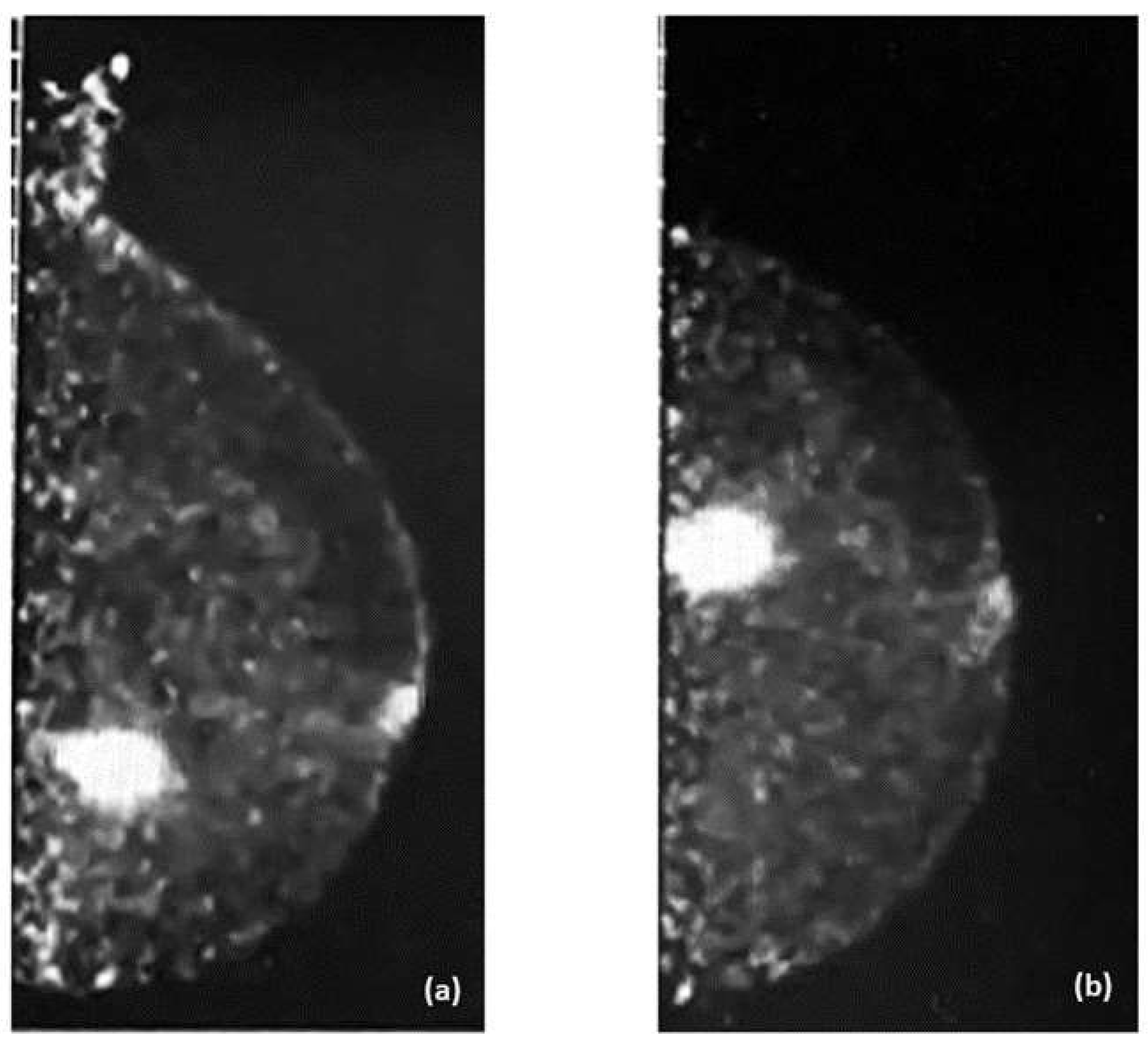
Examples of PEM images of breast cancer are shown in
Figure 3 and
Figure 4, with the former showing PEM using 3′-deoxy-3′-[
18F]-fluorothymidine (
18F-FLT) and the latter showing PEM using
68Ga-Trivehexin.
4.1.3. 18F-FDG PET/MRI
There is great potential for integrating PET with MRI. In a prospective study by Moy et al. with 36 women with confirmed or suspected breast cancer, researchers found that while breast MRI alone was highly sensitive (96%), combining it with prone-position [¹⁸F]FDG-PET/CT data increased the PPV from 77% to 98% and the specificity from 53% to 97%. The overall accuracy also improved from 78% with MRI alone to 89% with the fused PET/MRI [
55]. In a study by Botsikas et al., in the lesion-per-lesion analysis, the sensitivity of PET/MR compared to PET/CT for detecting bone metastases, other metastases, axillary and internal mammary nodes, and contralateral tumors combined was 89% vs. 77% (p = 0.0013); Meanwhile, the corresponding specificity was 96% vs. 98% (p = 0.0075) [
56]. A meta-analysis done by Zhang et al. has shown that PET/MRI has higher accuracy in the distant staging of breast cancer compared to PET/CT, with a sensitivity of 95% vs. 87%, all the while having comparable specificities of 96% vs. 94% [
57].
PET/MRI has been investigated for its role in diagnosing, staging, and phenotyping breast cancer, as well as assessing prognosis and treatment response. It offers a comprehensive evaluation for newly diagnosed patients by identifying disease spread throughout the body; it can also provide critical information that influences clinical management and exposes patients to significantly less radiation than PET/CT. However, the studies are limited by their sample sizes. For now, PET/MRI is most suitable to be done in patients that will need a PET/CT and MRI done for disease evaluation, where PET/MRI is a two-in-one option [
56,
58].
4.2. Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI)
Another important radiotracer is the fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI). Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) is a type II transmembrane serine protease. Its expression is increased in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) which induces tumor proliferation and worsens the survival of cancer patients. Cancer-associated fibroblasts have FAP as a target which is highly specific to tumor expression.
68Ga-FAPI and
18F-FAPI are among the many FAP-targeting radiotracers developed that play a significant role in tumor detection. However,
68Ga has a short half-life of 68 minutes and a lower image resolution compared to
18F which has a longer half-life of 110 minutes as well as a higher image resolution [
25,
59].
When comparing
68Ga-FAPI to
18F-FDG in diagnosing breast cancer, studies have shown that
68Ga-FAPI had a higher overall tumor uptake in breast cancer and a higher metastatic detection rate than
18F-FDG specifically when metastasis was in the bone and peritoneum [
60,
61,
62,
63]. One of the disadvantages of
18F-FDG is its low specificity since benign conditions such as infection, fibroadenoma, ductal adenoma, inflammatory granulomatous mastitis, and fibrocystic changes are also FDG-avid [
33]. In such cases, using
68Ga-FAPI might be a better choice in breast cancer staging since it is more specific and has a decreased uptake in the brain, liver, and oral mucosa [
64].
Studies have also demonstrated that
68Ga-FAPI PET/CT is superior to
18F-FDG PET/CT in ILC by showing higher tumoral activity and tumor-to-background uptake ratios, and by detecting more primary tumors, axillary lymph node metastases, and additional foci, including multicentric cancer. Furthermore,
68Ga-FAPI PET/CT detected more bone and liver metastases, and a positive association was made between the peritumoral lymphocyte ratio and
68Ga-FAPI PET/CT-to-
18F-FDG PET/CT uptake ratios [
38].
68Ga-FAPI PET/CT showed increased effectiveness in detecting lesions in the breast, lymph nodes, lung, liver, and bone [
65,
66]. Moreover, compared to CT alone,
68Ga-FAPI PET/CT detected more lesions, especially in infiltrative soft tissue and serosal locations [
65]. However, larger cohorts are needed to assess these findings further.
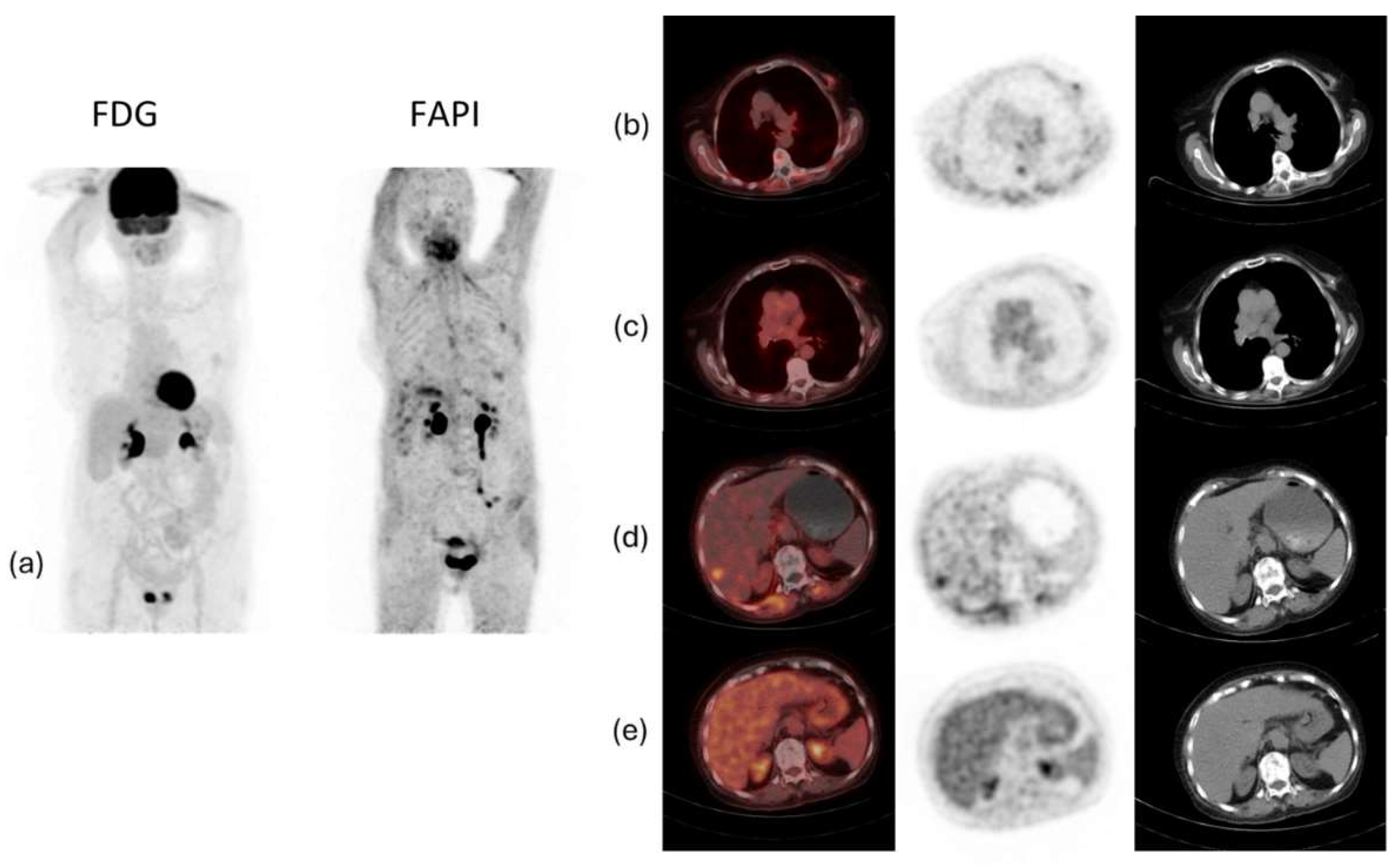
Figure 5 shows an example of a case of metastatic ILC with comparison between
18F-FDG PET/CT and
68Ga-FAPI PET/CT, demonstrating that the latter was better able to detect the primary malignancy as well as the metastatic lesions.
4.3. 16α-[18F]fluoroestradiol (FES)
Estrogen receptors are elevated in 70-75% of breast cancers, making estrogen receptor radiotracers highly valuable in both disease prognosis and prediction [
23,
24]. 16α-[
18F]fluoroestradiol (FES) is a radiotracer for estrogen receptors in breast cancer and is regarded as the first PET imaging agent used for a receptor target in cancer, discovered in 1984 and Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved in May 2020 [
67,
68].
Since most breast cancers are estrogen receptor-positive (ER+), making hormonal therapy important, there is only a 30-40% response rate in metastatic cases. PET imaging using FES can identify candidates for antiestrogen therapy by assessing receptor function. Increased tumor uptake of FES predicts responsiveness to antiestrogen therapy, while a lack of FES uptake indicates potential hormone resistance. A study by Martimer et al. aimed to determine if
18F-FDG and FES can detect hormone-induced changes in tumor metabolism and ER levels before and after tamoxifen treatment, and if these PET findings could predict hormonally responsive breast cancer. Forty women with advanced ER-positive breast cancer underwent PET scans with
18F-FDG and FES before and 7 to 10 days after starting tamoxifen therapy, evaluating seventy lesions using the mean standardized uptake value (SUV
mean). Responders showed a 28.4% increase in tumor
18F-FDG uptake after tamoxifen, with only five exhibiting a clinical flare reaction, while non-responders had no significant change in tumor
18F-FDG uptake. Responders had higher baseline FES uptake (SUV
mean 4.3) compared to non-responders (SUV
mean 1.8). All patients showed ER blockade after tamoxifen initiation, with a greater degree in responders (54.8% decrease) than in non-responders (19.4% decrease) [
69].
This concludes that a decrease in FES uptake after tamoxifen treatment suggests effective ER binding and is in agreement with other similar studies [
69,
70,
71,
72]. Baseline SUV
mean for FES and changes post-therapy can help identify hormone responsiveness in breast cancer [
69,
70]. With an SUV
mean cutoff of 2.0 for baseline FES-PET, the PPV is 79% and the NPV is 88%; this suggests that FES-PET offers much greater predictive values for hormone therapy responsiveness compared to standard clinical measurement of ER by IHC, which has a predictive value of only 50% in ER-positive patients [
67].
FES-PET imaging can also provide prognostic information. Kurland et al. evaluated progression-free survival in 84 patients with ER-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer receiving endocrine therapy, using lesion uptake from
18F-FDG and FES-PET. Patients were divided into three groups: low
18F-FDG uptake (29%), FDG-avid tumors with high FES uptake (59%), and FDG-avid tumors with low FES uptake (12%). The median progression-free survival for these groups was 26.1 months, 7.9 months, and 3.3 months, respectively. The study indicated that
18F-FDG PET and FES-PET might provide important prognostic information, helping identify patients with indolent disease and aiding in the selection of targeted and/or cytotoxic chemotherapy [
73].
Moreover, metastatic breast tumors may become heterogeneous, affecting responsiveness to treatment [
74]. In a study conducted by Gennari et al., eligible patients underwent an
18F-FES PET/CT at baseline, with those having SUV
mean ≥ 2 receiving single-agent endocrine therapy until disease progression, and those with SUV
mean < 2 being randomized to either endocrine therapy or chemotherapy to compare the activity of first-line endocrine therapy versus chemotherapy in patients with SUV
mean < 2. One hundred and seventeen received ET and 30 were randomized to endocrine therapy or chemotherapy. After a median follow-up of 62.4 months, 73.2% experienced disease progression and 37.3% died. Median progression-free survival was 12.4 months for patients with SUV
mean < 2 who took endocrine therapy and 23.0 months for those who took chemotherapy, while median progression-free survival was 18.0 months for patients with SUV
mean ≥ 2 on endocrine therapy. The ET-FES trial showed that ER+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer patients have varying levels of endocrine responsiveness based on
18F-FES PET/CT SUV
mean [
75]. When evaluating the impact of FES-PET on staging, a study done by Gupta et al. on 12 patients with 154 disease lesions found that
18F-FES PET-CT provided better characterization of lesions and influenced management decisions in 20% of patients [
76].
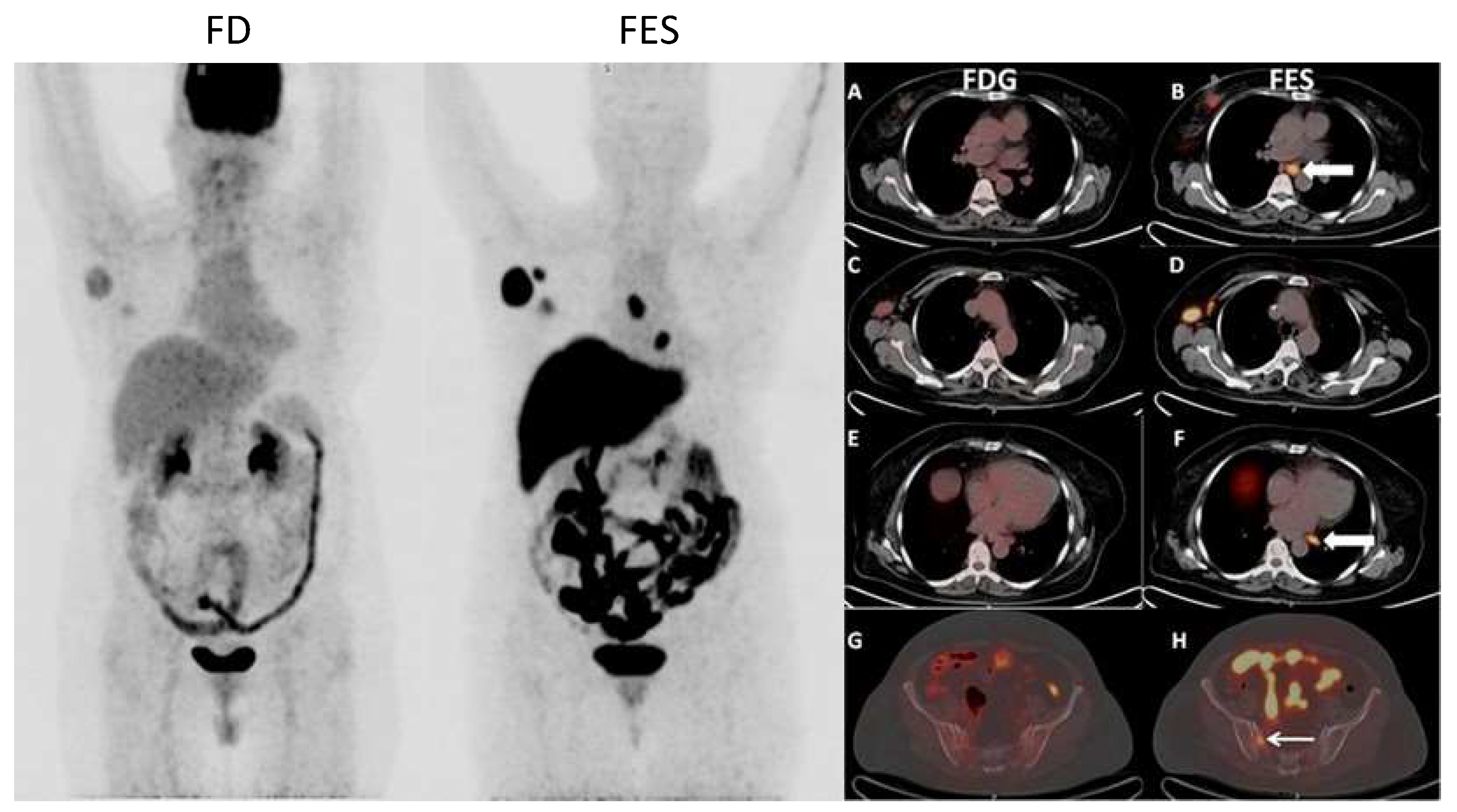
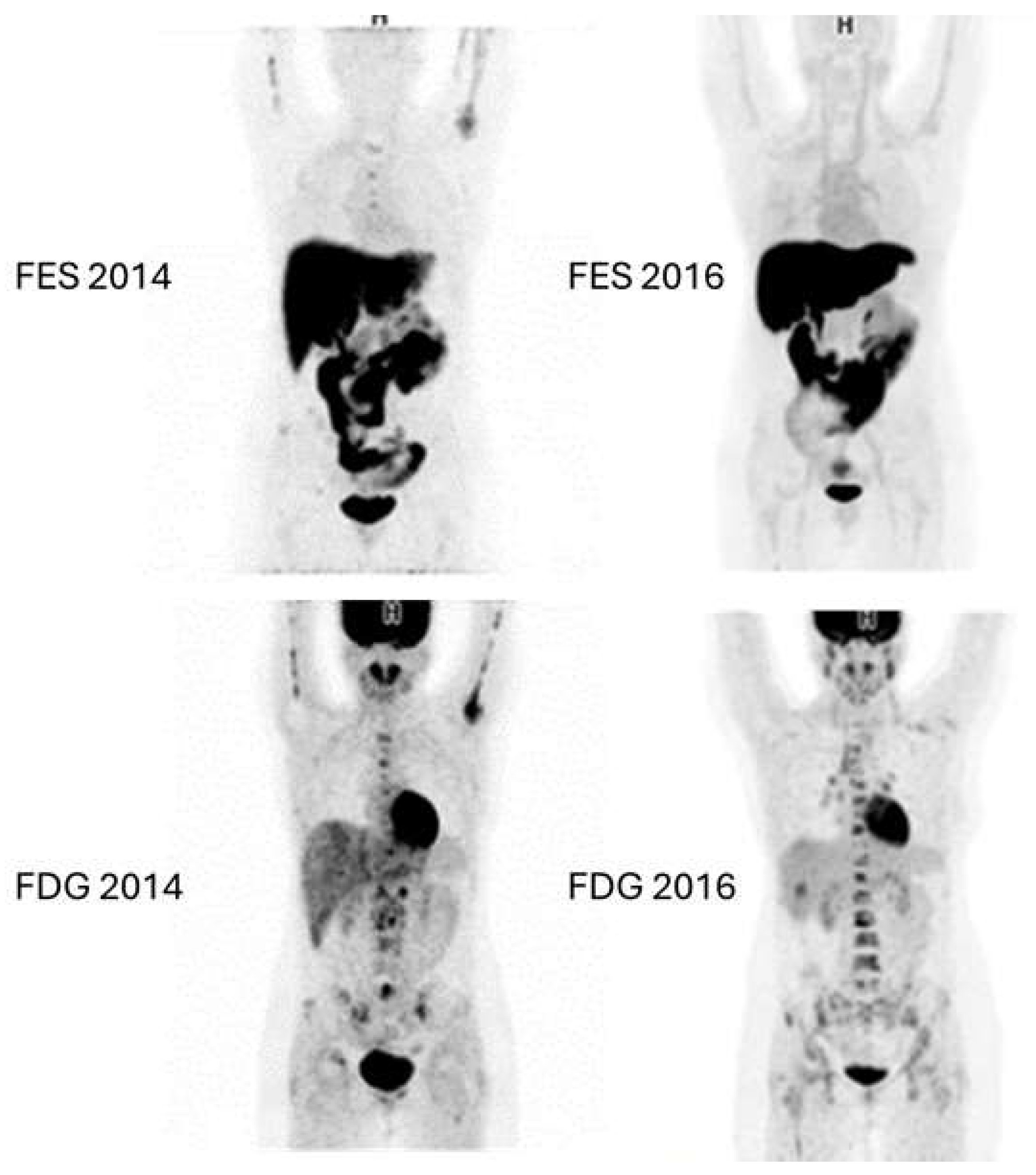
Figure 6 and
Figure 7 show examples of images of breast cancer obtained using FES PET/CT.
4.4. 4-Fluoro-11β-Methoxy-16α-18F-Fluoroestradiol (18F-4FMFES)
As previously shown,
18F-FES is extremely useful for whole-body monitoring of estrogen receptor status in both breast and gynecologic cancers; However, it does come with some shortcomings.
18F-FES is quickly metabolized in the liver, creating low-affinity radio metabolites that increase nonspecific background activity, especially in the mediastinal region, reducing image quality.
18F-FES is a steroid-based tracer, hence it has high hepatic uptake and biliary excretion; This leads to high background activity in the liver and intestines, making lesion detection difficult. Additionally,
18F-FES binds to plasma globulins, such as sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin. The level of SHBG inversely affects tumoral
18F-FES uptake, as globulin-bound
18F-FES cannot target receptors, contributing to the blood pool [
77].
To improve
18F-FES, researchers modified the parent estradiol molecule. Several 11b-methoxy or A-ring fluorine-substituted
18F-FES derivatives were synthesized. Among these, 4-fluoro-11β-methoxy-16α-
18F-FES (
18F-4FMFES) showed the highest uterine and brain uptake as well as best uterus-to-blood ratios in female rats as well as a lower affinity for plasma globulins [
78,
79,
80]. Further studies in tumor-bearing mice revealed that
18F-4FMFES had the best in vivo ER1 tumor uptake and image contrast [
78]. A phase I clinical study in healthy women showed substantial uterine uptake and retention, faster blood clearance, and lower nonspecific organ uptake compared to
18F-FES [
79].
Paquette et al. conducted a phase II study on newly diagnosed ER1 breast cancer patients to compare the performance of
18F-4FMFES PET with
18F-FES PET. The study included time-dependent blood metabolite analysis and static PET imaging using both tracers within a 7-day interval. The study demonstrated that
18F-4FMFES PET provides a lower nonspecific signal and better tumor contrast compared to
18F-4FMFES PET, resulting in improved diagnostic confidence and fewer false-negative diagnoses [
81].
4.5. 21-18F-fluoro-16α,17α-[(R)-(1′-α-furylmethylidene)dioxy]-19-norpregn-4-ene-3,20-dione (FFNP)
21-
18F-fluoro-16α,17α-[(R)-(1′-α-furylmethylidene)dioxy]-19-norpregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, also known simply as
18F-FFNP, is a radiotracer with high affinity and selectivity for the PR [
82]. Out of several progestin derivatives,
18F-FFNP was shown to be the most successful for PET imaging based on preclinical studies, designed to be stable against defluorination, resulting in low bone uptake studies. Importantly, due to its relatively low lipophilicity, it accumulates minimally in the liver and fat, leading to low nonspecific binding in vivo [
83,
84,
85,
86]. As mentioned earlier, decreases in FES uptake after starting ER antagonist therapy, such as tamoxifen or fulvestrant, confirm that the drug effectively targets the receptor, as the antagonist occupies the receptor-ligand binding pocket over FES. However, antagonist binding does not ensure complete inhibition of ER transcriptional function, especially with ESR1 gene mutations [
86]. This has led to exploring imaging of estrogen-regulated target genes, like PR, to monitor therapy response. In a study conducted by Dehdashti et al.,
18F-FFNP PET was shown to be effective in assessing the PR status of individual breast cancer lesions, with the potential to noninvasively and repeatedly evaluate the PR positivity of lesions, aiding in the decision-making for antiestrogen therapy before or after endocrine treatment [
88]. In another study by Dehdashti et al., they demonstrated that the estradiol-challenge test using FFNP-PET effectively predicts response to endocrine therapy (ET) in advanced ER+ breast cancer patients, with a > 6.7% increase in FFNP uptake accurately identifying responders, with 100% PPV and NPV. This method outperforms
18F-FDG PET in heavily pretreated subjects and offers a rapid, reliable prediction of ET benefit within 2 days, showing significant separation between responders and non-responders. Additionally, it correlates with longer overall survival in responders and efficiently identifies non-responders in patients receiving CDK4/6 inhibitor/ET therapy [
89].
4.6. 89Zr-Trastuzumab
Numerous radiotracers targeting HER2-positive malignancies have been reported in the literature, with the strongest evidence supporting the use of
89Zr-trastuzumab. Zirconium-89 is a positron-emitting radiometal with a long and favorable half-life of 78.4 hours, making it compatible with the half-life of trastuzumab in vivo and hence a suitable radionuclide for use in this setting.
89Zr-labeled antibodies can be visualized for up to seven days after injection; however, optimal PET scanning should be done 4-5 days after injection.
89Zr-trastuzumab is subject to high uptake in regions of high perfusion and vascularity, thereby making it particularly suited for the imaging of metastatic lesions characterized by vigorous angiogenesis. In one study, HER2-positive metastatic lesions demonstrated significant radiotracer uptake, and previously unknown brain metastases were detected [
90]. In other studies, HER2-positive metastatic lesions were detected in patients with HER2-negative primary malignancies and vice versa, highlighting the potential utility of
89Zr-trastuzumab as a tool to investigate the heterogeneity between primary and metastatic lesions [
42,
91]. Another study showed that
89Zr-trastuzumab PET/CT had a PPV of 88% and a NPV of 72% in the prediction of morphological response of metastatic breast cancer to treatment with trastuzumab emtansine, compared with 83% and 96% respectively for
18F-FDG PET/CT. The combination of
89Zr-trastuzumab PET/CT and
18F-FDG PET/CT yielded a PPV and NPV of 100%, accurately predicting morphological response to treatment [
92].
4.7. 64Cu-DOTA-Trastuzumab
A similar radiotracer is
64Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab, which has a half-life of 12.7 hours and can therefore achieve high-resolution imaging with lower radiation exposure and in a shorter time frame. An early study in 2013 showed that
64Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab PET/CT imaging was successful in detecting HER2-positive primary malignant lesions. In addition, brain metastases were detected in some patients, indicating adequate infiltration via the blood-brain barrier [
93]. Another study showed that
64Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab PET/CT had a sensitivity of 89% when imaging was done at day 2 post-injection, which was comparable to the sensitivity of 93% achieved using traditional
18F-FDG PET imaging. This study showed that the ideal imaging time should be 48 hours after the injection of the radiotracer and that
64Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab is highly sensitive for the detection of HER2-positive malignancies and the surveillance of disseminated disease. Furthermore, some patients were pre-treated with trastuzumab prior to imaging, which improved the biodistribution of the radiotracer and the imaging quality by reducing liver uptake by 75% without affecting tumor uptake [
94]. A third study further confirmed the effectiveness of
64Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab PET/CT imaging in detecting primary lesions with a strong correlation with histopathological HER2 status, and also showed notable uptake in metastatic liver lesions and was able to detect these metastases. However, in this study, significant variability in SUV
max was detected within and among HER2-positive patients, and an overlap was seen between HER2-positive and HER2-negative patients [
95]. Interestingly, a recent study investigated the use of
64Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab PET imaging to predict disease response to treatment with trastuzumab emtansine. Patients with HER2-positive metastatic disease were enrolled and underwent
64Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab PET imaging on days 1 and 2 preceding treatment. Favorable response to treatment was correlated with specific SUV
max values, specifically the day 2 minimum SUV
max value [
96].
4.8. 89Zr-Pertuzumab
Alongside trastuzumab, pertuzumab is another monoclonal antibody often used for the treatment of metastatic HER2-positive breast malignancies. Accordingly, a radiolabeled tracer employing pertuzumab tagged with zirconium-89 has been developed and is under study in the literature. The first human study in 2018 showed that the optimal time for imaging is 5-8 days after administration of
89Zr-pertuzumab, which allowed sufficient time for the elevated background radioactivity in the liver and blood to decrease. In all patients with HER2-positive primary malignancies, the primary lesions showed avid uptake of
89Zr-pertuzumab. In addition, metastatic brain lesions showed avid uptake of
89Zr-pertuzumab. Similarly,
89Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT imaging detected a HER2-positive metastatic lesion in the chest. However, other metastatic lesions were not detected; for instance, lung and nodal metastases only showed mild avidity, and liver metastases did not show significant avidity. Interestingly,
89Zr-pertuzumab also showed utility in the investigation of heterogeneity in HER2 status and was able to distinguish between HER2-positive and HER2-negative lesions within the same patient [
97]. Another study further investigated the use of
89Zr-pertuzumab in patients with heterogeneous lesions and showed that it was able to detect some HER2-positive metastatic lesions in patients with HER2-negative primary malignancies [
98]. A site specifically-labeled conjugate known as
89Zr-site-specific (ss)-pertuzumab has also been investigated. A recent study showed that
89Zr-ss-pertuzumab yields improved lesion detection owing to increased tracer avidity, but again failed to detect significant metastases in the liver, bones, lungs, and other sites; its utility in detecting brain metastases is yet to be studied. The study also showed that radiotracer imaging can directly impact therapeutic considerations; one patient enrolled with a HER2-positive primary malignancy and diffuse osseous and hepatic metastases had minimal foci of avid
89Zr-pertuzumab uptake and was thus switched to chemotherapy with doxorubicin instead of HER2-targeted therapy [
99].
5. Investigational Radiotracers in Breast Cancer Imaging
5.1. [18F]PSMA-1007
Patients with TNBC have limited treatment options because their tumors do not have human epidermal growth factor receptors, progesterone receptors, or estrogen receptors. Thus, understanding the TNBC microenvironment and identifying molecular subgroups can provide immunotherapy benefits. Recent studies have shown increased levels of prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) in tumor-associated neovascularizations and metastases, indicating potential for both therapy and diagnosis [
100]. For instance, a prospective cohort study limited by the small number of patients demonstrated that TNBC lesions can be successfully detected using [
18F]PSMA-1007 PET/CT [
101]. Moreover, compared to standard
18F-FDG PET/CT, [
18F]PSMA-1007 demonstrated higher accumulation in distant metastases, especially in the brain, potentially providing benefits in detecting distant metastases. In addition to that, the high presence of PSMA in TNBC, as revealed by immunohistochemical investigations, suggests that it could be a target for treatment. PSMA-based imaging is promising, especially for TNBC patients, despite
18F-FDG PET/CT still being more sensitive [
100]. Further research is necessary to fully assess these results, as PSMA-based radiopharmaceuticals may enhance TNBC diagnostic imaging and potentially open up new treatment possibilities.
5.2. 68Ga-ABY-025
A recently emerging radiotracer is
68Ga-ABY-025, which consists of the biopharmaceutical HER2-binding Affibody molecule ABY-025 tagged with gallium-68. A study showed that
68Ga-ABY-025 PET/CT imaging was able to detect HER2-positive primary malignancies effectively. In regard to metastatic lesions,
68Ga-ABY-025 imaging was most effective in detecting liver metastases which showed more avid uptake than any other metastatic lesions [
102]. A subsequent study investigated the use of
68Ga-ABY-025 imaging to predict metabolic response to treatment. The results showed a significant negative correlation between
68Ga-ABY-025 SUV
max and the change in tumor lesion glycolysis (Δ-TLG). This shows that
68Ga-ABY-025 imaging may be useful as an adjunct tool to estimate the level of HER2 expression needed to induce metabolic remission using HER2-targeted therapies [
103]. In a recent study in 2024, some patients had avid uptake in 2-5 mm lymph nodes that had not shown radioactivity on
18F-FDG PET/CT scans, which led to re-staging and a change in treatment regimen. This indicates the potential utility of
68Ga-ABY-025 imaging in accurate disease staging. In addition,
68Ga-ABY-025 imaging reduced false positive results; patients who had recently received the COVID-19 vaccine had avid uptake of
18F-FDG in lymph nodes ipsilateral to the vaccination site, whereas no uptake of
68Ga-ABY-025 was seen in these benign inflammatory lesions [
104].
5.3. 68Ga-NOTA-Fab-Trastuzumab
A study in 2022 showed that the molecule
68Ga-NOTA-Fab-trastuzumab had a favorable pharmacokinetic profile, with decreased non-specific binding and a relatively low uptake in the liver and non-tumoral regions. Notably,
68Ga-NOTA-Fab-trastuzumab PET/CT imaging showed avid uptake in HER2-positive primary lesions as well as in metastatic lesions in the axillary lymph nodes. However, because of the elevated physiological uptake in the blood pool and liver, metastatic lesions in the mediastinal lymph nodes near the heart as well as in the liver could not be detected [
105,
106]. A recent study in 2023 investigated the utility of
68Ga-DFO-Fab-trastuzumab-M74, a similar radiotracer using DFO instead of NOTA as a chelating agent and with the addition of a methionine residue M74. In vitro cell studies and in vivo mouse studies showed that the M74-conjugated radiotracer had a better pharmacokinetic profile with higher affinity to HER2-expressing cells, resulting in more rapid blood clearance, less liver uptake, and more tumor uptake [
107].
5.4. 89Zr∙Df-HER2-Fab-PAS200
An emerging radiotracer that has been preliminarily tested is
89Zr∙Df-HER2-Fab-PAS200. This molecule consists of a PASylated antibody fragment tagged with zirconium-89. In particular, PASylation is a process of genetic fusion that produces functional proteins with attached sequences of proline (P), alanine (A), and serine (S) amino acids; this technique increases the size of the fusion protein and hinders its clearance, thereby resulting in a prolonged half-life and enhanced, longer-lasting activity. In the first human study, a 67-year-old woman with HER2-positive breast cancer metastatic to the axillary lymph nodes and brain underwent
89Zr∙Df-HER2-Fab-PAS200 PET/CT imaging. The radiotracer showed strong uptake and signal in the primary malignant lesion and the sites of lymph node metastasis. However, in contrast with other radionuclides such as
89Zr-trastuzumab, no radioactivity was seen in the metastatic brain lesions, possibly owing to the fact that the patient had been pre-treated with dexamethasone which may have stabilized the blood-brain barrier and prevented the penetration of
89Zr∙Df-HER2-Fab-PAS200 [
108].
5.5. 68Ga-HER2-Nanobody
An additional radiotracer that is currently being studied is
68Ga-HER2-Nanobody, also known as
68Ga-NOTA-anti-HER2-sdAb. Nanobodies are antigen-specific single-domain antibodies (sdAb) that consist of a monomeric variable domain derived from heavy-chain antibodies. An initial study in 2016 showed that
68Ga-HER2-Nanobody is characterized by accelerated blood clearance, which is advantageous and allows for rapid same-day imaging of patients. Additionally, the results showed avid uptake in most metastatic lesions, including those in axillary, hilar, and mediastinal lymph nodes and in the pelvic region among other sites. However, the primary lesions showed a heterogeneous uptake pattern, indicating that this radiotracer may be more suited for the assessment of metastatic lesions and not ideal for detecting HER2 expression in primary breast lesions [
109]. In a follow-up study in 2024,
68Ga-NOTA-anti-HER2-sdAb PET imaging was better able to detect inter-lesional heterogeneity than
18F-FDG PET imaging and showed uptake in some malignant lesions with low proliferation and metabolic activity which had not shown
18F-FDG uptake. In addition, avid uptake of
68Ga-NOTA-anti-HER2-sdAb in the lymph nodes and bones of several patients revealed additional metastases that had not been detected using
18F-FDG [
110].
5.6. 68Ga-NOTA-MAL-Cys-MZHER2:342
Another emerging radiotracer for the detection of HER2-positive malignancy is
68Ga-NOTA-MAL-Cys-MZHER
2:342, which consists of the HER2-targeting antibody ZHER
2:342 conjugated with NOTA-MAL and radiolabeled with gallium-68. An initial study showed avid in vitro uptake of the radiotracer in HER2-positive cell lines and avid in vivo uptake in mice xenografted with HER2-positive tissues. The authors also enrolled two human patients with primary breast cancer for an initial in-human investigation of
68Ga-NOTA-MAL-Cys-MZHER
2:342 PET imaging, one with HER2-positive disease and another with HER2-negative disease. The former patient had significantly more avid uptake of the radiotracer. In addition, the low background radioactivity observed with this radiotracer may prove useful for detecting metastatic lesions in the future, particularly those in the liver [
111].
5.7. 18F-Labeled 1-Amino-3-Fluorocyclobutane-1-Carboxylic Acid (18F-Fluciclovine)
The positron emitter
18F-labeled 1-amino-3-fluorocyclobutane-1-carboxylic acid (
18F-fluciclovine) is being investigated as an imaging agent for various cancers. This radiotracer has been FDA-approved for use in PET imaging of men with suspected recurrence of prostate cancer after initial treatment [
112]. Initial trials in breast cancer, particularly ILC, have shown promising results, suggesting that
18F-fluciclovine may be more effective than
18F-FDG in diagnosing ILC. Although the number of ILC patients studied so far has been small, preliminary evidence indicates that changes in the corrected SUV
max of
18F-fluciclovine PET/CT are associated with ILC tumor response [
113].
5.8. 3′-Deoxy-3′-[18F]-Fluorothymidine (18F-FLT) and 18F-DPA-714
18F-FLT is an imaging agent that indicates the level of cell proliferation. Ma et al. conducted a preclinical study that was the first trial to employ
18F-FLT PET/CT to forecast early responses to CDK4/6 inhibitors in TNBC [
114]. The study found that
18F-FLT PET/CT can successfully track early treatment responses shown by a significant decrease in
18F-FLT uptake and tumor volume in MDA-MB-231 cells after therapy. In addition to that,
18F-DPA-714 is a second-generation translocator protein 18 kDa (TSPO) tracer that is also being investigated in TNBC. TSPO is a sensitive macrophage marker with potential applications in TNBC classification. A preliminary study showed
18F-DPA-714 uptake with different kinetic patterns potentially linked to TSPO polymorphism status [
115].
5.9. Others
Other tracers have also been studied in breast cancer. They are less commonly used and more studies are needed to evaluate their potential role in tumor detection. Such tracers include
68Ga-PSMA-HBED-CC, 16β-[
18F]fluoro-5α-dihydrotestosterone (
18F-FDHT), and
68Ga-RM2, which have been studied primarily in prostate cancer [
116,
117,
118], as well as
68Ga-Pentixafor which has been studied primarily in hematological malignancies [
34].
6. Future Directions
Theranostics is an emerging field which integrates diagnostic imaging and therapeutic interventions and has become a promising approach to personalized medicine, especially in the treatment of cancer. In regard to nuclear imaging of breast cancer, theranostics may involve the use of radiolabeled therapeutic molecules such as monoclonal antibodies and peptides. Numerous targeted radionuclide therapies have shown potential, including for example
177Lu-trastuzumab for HER2-positive breast cancer, and
90Y-FAPI-04 and
177Lu-FAPI-46 for advanced stage malignancies and metastatic breast cancer [
119]. In addition, new techniques that incorporate nanotechnology have emerged and have proven particularly effective in TNBC [
120]. Several trials and phase 1 or phase 2 studies are also ongoing for the development of new radionuclide-based treatments for breast cancer [
121]. Although the treatment of breast cancer has progressed significantly in recent years, many patients still fail the currently available therapeutic modalities and are left with minimal options. Theranostic approaches represent a potential option for such patients in the future and have the potential to greatly improve the diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes of breast cancer. However, limited evidence is available and primarily focuses on compassionate use for pain management and palliative therapy rather than treatment. Further studies are needed to investigate new molecules and applications and expand this promising field [
119].
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, radiotracers have significantly enhanced breast cancer imaging, with current techniques like PET using tracers such as 18F-FDG and FAPI proving invaluable in clinical practice. These methods improve tumor detection, characterization, and treatment monitoring. Future advancements, including novel tracers targeting specific molecular pathways like HER2 and ER, hybrid imaging technologies such as PET/MRI, and radionuclide-based treatments promise even greater precision and personalization in breast cancer care. Ongoing research and clinical trials are crucial to validate these innovations, which hold the potential to further improve early detection, treatment planning, and patient outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H., J.R., O.E.S., N.E.G., N.O., A.A.G.; methodology, M.H., J.R., O.E.S., N.E.G., N.O., A.A.G.; software, not applicable; validation, M.H., A.A.G., G.B., L.N., A.T., H.M., P.C., A.S., H.D., F.M., N.S.; formal analysis, not applicable; investigation, M.H., A.A.G., G.B., L.N., A.T., H.M., P.C., A.S., H.D., F.M., J.R., O.E.S., N.E.G., N.O., Z.H.; resources, M.H., N.S., P.C., A.S., H.D., F.M., A.T., H.M.; data curation, N.S., P.C., A.S., H.D., F.M., Z.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.R., O.E.S., N.E.G., N.O., Z.H.; writing—review and editing, M.H., A.A.G., G.B., L.N., A.T., H.M., J.R., O.E.S.; visualization, J.R., O.E.S., N.S., Z.H., H.D., A.S., F.M., P.C.; supervision, M.H., A.A.G., G.B., L.N., A.T., H.M.; project administration, M.H., A.A.G., G.B., L.N.; funding acquisition, not applicable. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
All subjects gave their informed consent for the inclusion of images in this manuscript as per protocol RAD.MH.04 approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the American University of Beirut.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to Diala Jazra for her contributions to this manuscript. We deeply appreciate her support and commitment throughout the process.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wilkinson, L. and T. Gathani, Understanding breast cancer as a global health concern. Br J Radiol, 2022. 95(1130): p. 20211033. [CrossRef]
- Katsura, C., et al., Breast cancer: presentation, investigation and management. Br J Hosp Med (Lond), 2022. 83(2): p. 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Tollens, F., et al., Economic potential of abbreviated breast MRI for screening women with dense breast tissue for breast cancer. Eur Radiol, 2022. 32(11): p. 7409-7419. [CrossRef]
- Lebron, L., D. Greenspan, and N. Pandit-Taskar, PET imaging of breast cancer: role in patient management. PET Clin, 2015. 10(2): p. 159-95. [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.M. and S.Y. Cho, PET imaging for breast cancer. Radiol Clin North Am, 2021. 59(5): p. 725-735. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., et al., Progression from ductal carcinoma in situ to invasive breast cancer: molecular features and clinical significance. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2024. 9(1): p. 83. [CrossRef]
- van Seijen, M., et al., Ductal carcinoma in situ: to treat or not to treat, that is the question. Br J Cancer, 2019. 121(4): p. 285-292. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L., A.N. Giaquinto, and A. Jemal, Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024. 74(1): p. 12-49. [CrossRef]
- Narod, S.A., et al., Breast cancer mortality after a diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ. JAMA Oncol, 2015. 1(7): p. 888-96. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.G., et al., Prognostic value of ductal carcinoma in situ component in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: a Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database analysis. Cancer Manag Res, 2018. 10: p. 527-534. [CrossRef]
- Chamalidou, C., et al., Survival patterns of invasive lobular and invasive ductal breast cancer in a large population-based cohort with two decades of follow up. Breast, 2021. 59: p. 294-300. [CrossRef]
- Kole, A.J., et al., Overall survival is improved when DCIS accompanies invasive breast cancer. Sci Rep, 2019. 9(1): p. 9934. [CrossRef]
- Grabenstetter, A., et al., E-cadherin immunohistochemical expression in invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast: correlation with morphology and CDH1 somatic alterations. Hum Pathol, 2020. 102: p. 44-53. [CrossRef]
- Yang, C., et al., Comparison of overall survival between invasive lobular breast carcinoma and invasive ductal breast carcinoma: a propensity score matching study based on SEER database. Front Oncol, 2020. 10: p. 590643. [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, F. and J.S. Reis-Filho, Pathogenesis of triple-negative breast cancer. Annu Rev Pathol: Mechanisms of Disease, 2022. 17(Volume 17, 2022): p. 181-204. [CrossRef]
- Borri, F. and A. Granaglia, Pathology of triple negative breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol, 2021. 72: p. 136-145. [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, C., et al., Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2008. 26(8): p. 1275-1281. [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.J., et al., Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science, 1989. 244(4905): p. 707-712. [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.J., et al., Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science, 1987. 235(4785): p. 177-182. [CrossRef]
- Konecny, G., et al., Quantitative association between HER-2/neu and steroid hormone receptors in hormone receptor-positive primary breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2003. 95(2): p. 142-153. [CrossRef]
-
Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer Subtypes. [cited 2024 7/15/2024]; Available from: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast-subtypes.html.
- Gupta, R., et al., Therapeutic landscape of advanced HER2-positive breast cancer in 2022. Med Oncol, 2022. 39(12): p. 258. [CrossRef]
- Harvey N. Mayrovitz, P., Department of Medical Education, Dr. Kiran C. Patel and N.S.U. College of Allopathic Medicine, FL, USA, eds. Breast Cancer. 2022, Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia.
- Sørlie, T., et al., Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2001. 98(19): p. 10869-10874. [CrossRef]
- Hadebe, B., et al., The role of PET/CT in breast cancer. Diagnostics (Basel), 2023. 13(4). [CrossRef]
- Paydary, K., et al., The evolving role of FDG-PET/CT in the diagnosis, staging, and treatment of breast cancer. Mol Imaging Biol, 2019. 21(1): p. 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Gradishar, W.J., et al., Breast Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2022. 20(6): p. 691-722. [CrossRef]
- Jung, N.Y., et al., Role of FDG-PET/CT in identification of histological upgrade of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) in needle biopsy. I J Radiol, 2021. 18(3): p. e113862. [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A., PET/CT for patients with breast cancer: where is the clinical impact? AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2019. 213(2): p. 254-265. [CrossRef]
- Dashevsky, B.Z., et al., Appearance of untreated bone metastases from breast cancer on FDG PET/CT: importance of histologic subtype. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2015. 42(11): p. 1666-1673. [CrossRef]
- Groheux, D., et al., Early assessment with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography can help predict the outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple negative breast cancer. Eur J Cancer, 2014. 50(11): p. 1864-71. [CrossRef]
- Park, H.L., et al., Prognostic impact of 18F-FDG PET/CT in pathologic stage II invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: re-illuminating the value of PET/CT in intermediate-risk breast cancer. Cancer Imaging, 2023. 23(1): p. 2. [CrossRef]
- Kitajima, K. and Y. Miyoshi, Present and future role of FDG-PET/CT imaging in the management of breast cancer. Jpn J Radiol, 2016. 34(3): p. 167-180. [CrossRef]
- Vag, T., et al., PET imaging of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in patients with primary and recurrent breast carcinoma. EJNMMI Res, 2018. 8(1): p. 90. [CrossRef]
- Song, B.I., et al., Prognostic value of primary tumor uptake on F-18 FDG PET/CT in patients with invasive ductal breast cancer. Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2011. 45(2): p. 117-24. [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, M.G., et al., [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) in suspected recurrent breast cancer: a prospective comparative study of dual-time-point FDG-PET/CT, contrast-enhanced CT, and bone scintigraphy. J Clin Oncol, 2016. 34(16): p. 1889-1897. [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y., et al., The E-cadherin and N-cadherin switch in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: signaling, therapeutic implications, and challenges. Cells, 2019. 8(10). [CrossRef]
- Sahin, E., et al., 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT as an alternative to 18F-FDG PET/CT in the imaging of invasive lobular breast carcinoma. J Nucl Med, 2024. 65(4): p. 512-519. [CrossRef]
- Gilardi, L., et al., FDG and Non-FDG radiopharmaceuticals for PET imaging in invasive lobular breast carcinoma. Biomedicines, 2023. 11(5). [CrossRef]
- Bonnin, D., et al., Performance of [18F]FDG-PET/CT imaging in first recurrence of invasive lobular carcinoma. J Clin Med, 2023. 12(8). [CrossRef]
- Park, H.L., et al., Clinical utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT in low 18F-FDG-avidity breast cancer subtypes: comparison with breast US and MRI. Nucl Med Commun, 2018. 39(1): p. 35-43. [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A., et al., (18)F-FDG-PET/CT for systemic staging of newly diagnosed triple-negative breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2016. 43(11): p. 1937-44. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J., et al., 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake on PET/computed tomography in association with androgen receptor expression and other clinicopathologic factors in surgically resected triple-negative breast cancer. Nucl Med Commun, 2021. 42(1): p. 101-106. [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.M., et al., Molecular breast imaging and positron emission mammography. PET Clin, 2023. 18(4): p. 487-501. [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, K., et al., Positron Emission Mammography (PEM) in the diagnosis of breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Med J Islam Repub Iran, 2020. 34: p. 100. [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.A., et al., High-resolution fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography with compression (“positron emission mammography”) is highly accurate in depicting primary breast cancer. Breast J, 2006. 12(4): p. 309-23. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y., et al., A preliminary report of breast cancer screening by positron emission mammography. Ann Nucl Med, 2016. 30(2): p. 130-7. [CrossRef]
- Freitas, V., et al., Breast cancer detection using a low-dose positron emission digital mammography system. Radiol Imaging Cancer, 2024. 6(2): p. e230020. [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K., et al., Positron emission mammography in breast cancer presurgical planning: comparisons with magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2011. 38(1): p. 23-36. [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.A., et al., Breast cancer: comparative effectiveness of positron emission mammography and MR imaging in presurgical planning for the ipsilateral breast. Radiology, 2011. 258(1): p. 59-72. [CrossRef]
- Koyasu, H., et al., The feasibility of dedicated breast PET for the assessment of residual tumor after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Jpn J Radiol, 2019. 37(1): p. 81-87. [CrossRef]
- Sasada, S., et al., Dedicated breast PET for detecting residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in operable breast cancer: a prospective cohort study. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2018. 44(4): p. 444-448. [CrossRef]
- Argus, A. and M.C. Mahoney, Positron emission mammography: diagnostic imaging and biopsy on the same day. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2014. 202(1): p. 216-22. [CrossRef]
- Hendrick, R.E., Radiation doses and cancer risks from breast imaging studies. Radiology, 2010. 257(1): p. 246-53. [CrossRef]
- Moy, L., et al., Role of fusion of prone FDG-PET and magnetic resonance imaging of the breasts in the evaluation of breast cancer. Breast J, 2010. 16(4): p. 369-76. [CrossRef]
- Botsikas, D., et al., What is the diagnostic performance of 18-FDG-PET/MR compared to PET/CT for the N- and M- staging of breast cancer? Eur Radiol, 2019. 29(4): p. 1787-1798. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C., et al., Comparison of whole-body 18F-FDG PET/CT and PET/MRI for distant metastases in patients with malignant tumors: a meta-analysis. BMC Cancer, 2023. 23(1): p. 37. [CrossRef]
- Fowler, A.M. and R.M. Strigel, Clinical advances in PET-MRI for breast cancer. Lancet Oncol, 2022. 23(1): p. e32-e43. [CrossRef]
- Lindner, T., et al., Development of quinoline-based theranostic ligands for the targeting of fibroblast activation protein. J Nucl Med, 2018. 59(9): p. 1415-1422. [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y., L. Zhao, and H. Chen, 68Ga-FAPI outperforms 18F-FDG PET/CT in identifying bone metastasis and peritoneal carcinomatosis in a patient with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Nucl Med, 2020. 45(11): p. 913-915. [CrossRef]
- Li, T., et al., Case Report: (68)Ga-FAPI PET/CT, a more advantageous detection mean of gastric, peritoneal, and ovarian metastases from breast cancer. Front Oncol, 2022. 12: p. 1013066. [CrossRef]
- Elboga, U., et al., Superiority of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT scan in detecting additional lesions compared to 18FDG PET/CT scan in breast cancer. Ann Nucl Med, 2021. 35(12): p. 1321-1331. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H., et al., Comparison of [(68)Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [(18)F] FDG PET/CT for the diagnosis of primary and metastatic lesions in patients with various types of cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2020. 47(8): p. 1820-1832. [CrossRef]
- Giesel, F.L., et al., Head-to-head intra-individual comparison of biodistribution and tumor uptake of (68)Ga-FAPI and (18)F-FDG PET/CT in cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2021. 48(13): p. 4377-4385. [CrossRef]
- Eshet, Y., et al., The role of 68 Ga-FAPI PET/CT in detection of metastatic lobular breast cancer. Clin Nucl Med, 2023. 48(3): p. 228-232. [CrossRef]
- Ballal, S., et al., Head-to-head comparison between [(68)Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi and [(18)F]F-FDG PET/CT imaging in patients with breast cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel), 2023. 16(4). [CrossRef]
- Katzenellenbogen, J.A., The quest for improving the management of breast cancer by functional imaging: the discovery and development of 16α-[18F]fluoroestradiol (FES), a PET radiotracer for the estrogen receptor, a historical review. Nucl Med Biol, 2021. 92: p. 24-37. [CrossRef]
- Katal, S., M.J. McKay, and K. Taubman, PET molecular imaging in breast cancer: current applications and future perspectives. J Clin Med, 2024. 13(12): p. 3459. [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, J.E., et al., Metabolic flare: indicator of hormone responsiveness in advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2001. 19(11): p. 2797-2803. [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.M., et al., A phase 2 study of 16α-[18F]-fluoro-17β-estradiol positron emission tomography (FES-PET) as a marker of hormone sensitivity in metastatic breast cancer (MBC). Mol Imaging Biol, 2014. 16(3): p. 431-440. [CrossRef]
- Dehdashti, F., et al., Positron emission tomographic assessment of “metabolic flare” to predict response of metastatic breast cancer to antiestrogen therapy. Eur J Nucl Med, 1999. 26(1): p. 51-56. [CrossRef]
- van Kruchten, M., et al., Positron emission tomography of tumour [18F]fluoroestradiol uptake in patients with acquired hormone-resistant metastatic breast cancer prior to oestradiol therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2015. 42(11): p. 1674-1681. [CrossRef]
- Kurland, B.F., et al., Estrogen receptor binding (18F-FES PET) and glycolytic activity (18F-FDG PET) predict progression-free survival on endocrine therapy in patients with ER+ breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 2017. 23(2): p. 407-415. [CrossRef]
- Hao, W., et al., Heterogeneity of estrogen receptor based on 18F-FES PET imaging in breast cancer patients. Clin Transl Imaging, 2021. 9(6): p. 599-607. [CrossRef]
- Gennari, A., et al., Early prediction of endocrine responsiveness in ER+/HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer (MBC): pilot study with 18F-fluoroestradiol (18F-FES) CT/PET. Ann Oncol, 2024. 35(6): p. 549-558. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M., et al., Can 18F-fluoroestradiol positron emission tomography become a new imaging standard in the estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patient: a prospective comparative study with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography? World J Nucl Med. 2017 Apr-Jun;16(2):133-139. [CrossRef]
- Mankoff, D.A., T.J. Tewson, and J.F. Eary, Analysis of blood clearance and labeled metabolites for the estrogen receptor tracer [F-18]-16α-Fluorestradiol (FES). Nucl Med Biol, 1997. 24(4): p. 341-348. [CrossRef]
- Bénard, F., et al., [18F]Fluorinated estradiol derivatives for oestrogen receptor imaging: impact of substituents, formulation and specific activity on the biodistribution in breast tumour-bearing mice. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2008. 35(8): p. 1473-1479. [CrossRef]
- Beauregard, J.M., et al., Assessment of human biodistribution and dosimetry of 4-fluoro-11beta-methoxy-16alpha-18F-fluoroestradiol using serial whole-body PET/CT. J Nucl Med, 2009. 50(1): p. 100-7. [CrossRef]
- Paquette, M., et al., Cross-species physiological assessment of brain estrogen receptor expression using (18)F-FES and (18)F-4FMFES PET imaging. Mol Imaging Biol, 2020. 22(5): p. 1403-1413. [CrossRef]
- Paquette, M., et al., Improved estrogen receptor assessment by PET using the novel radiotracer (18)F-4FMFES in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients: an ongoing phase II clinical trial. J Nucl Med, 2018. 59(2): p. 197-203. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H., et al., Development of [F-18]fluorine-substituted Tanaproget as a progesterone receptor imaging agent for positron emission tomography. Bioconjug Chem, 2010. 21(6): p. 1096-104. [CrossRef]
- Kochanny, M.J., et al., Fluorine-18-labeled progestin ketals: synthesis and target tissue uptake selectivity of potential imaging agents for receptor-positive breast tumors. J Med Chem, 1993. 36(9): p. 1120-7. [CrossRef]
- Buckman, B.O., et al., Fluorine-18-labeled progestin 16 alpha, 17 alpha-dioxolanes: development of high-affinity ligands for the progesterone receptor with high in vivo target site selectivity. J Med Chem, 1995. 38(2): p. 328-37. [CrossRef]
- Kym, P.R., K.E. Carlson, and J.A. Katzenellenbogen, Progestin 16 alpha, 17 alpha-dioxolane ketals as molecular probes for the progesterone receptor: synthesis, binding affinity, and photochemical evaluation. J Med Chem, 1993. 36(9): p. 1111-9. [CrossRef]
- Vijaykumar, D., et al., An efficient route for the preparation of a 21-fluoro progestin-16 alpha,17 alpha-dioxolane, a high-affinity ligand for PET imaging of the progesterone receptor. J Org Chem, 2002. 67(14): p. 4904-10. [CrossRef]
- Jeselsohn, R., et al., Emergence of constitutively active estrogen receptor-α mutations in pretreated advanced estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 2014. 20(7): p. 1757-1767. [CrossRef]
- Dehdashti, F., et al., Assessment of progesterone receptors in breast carcinoma by PET with 21-18F-fluoro-16α,17α-[(R)-(1’-α-furylmethylidene)dioxy]-19-norpregn-4-ene-3,20-dione. J Nucl Med, 2012. 53(3): p. 363-70. [CrossRef]
- Dehdashti, F., et al., Association of PET-based estradiol-challenge test for breast cancer progesterone receptors with response to endocrine therapy. Nat Commun, 2021. 12(1): p. 733. [CrossRef]
- Dijkers, E.C., et al., Biodistribution of 89Zr-trastuzumab and PET imaging of HER2-positive lesions in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2010. 87(5): p. 586-92. [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A., et al., 89Zr-trastuzumab PET/CT for detection of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastases in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative primary breast cancer. Clin Nucl Med, 2017. 42(12): p. 912-917. [CrossRef]
- Gebhart, G., et al., Molecular imaging as a tool to investigate heterogeneity of advanced HER2-positive breast cancer and to predict patient outcome under trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1): the ZEPHIR trial. Ann Oncol, 2016. 27(4): p. 619-24. [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K., et al., 64Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab PET imaging in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. J Nucl Med, 2013. 54(11): p. 1869-75. [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, J.E., et al., Functional imaging of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer using (64)Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab PET. J Nucl Med, 2014. 55(1): p. 23-9. [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, J.E., et al., Tumor uptake of (64)Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab in patients with metastatic breast cancer. J Nucl Med, 2018. 59(1): p. 38-43. [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, J.E., et al., Use of (64)Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab PET to predict response and outcome of patients receiving trastuzumab emtansine for metastatic breast cancer: a pilot study. J Nucl Med, 2022. 63(8): p. 1145-1148. [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A., et al., First-in-human human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-targeted imaging using (89)Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT: dosimetry and clinical application in patients with breast cancer. J Nucl Med, 2018. 59(6): p. 900-906. [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A., et al., Identification of HER2-positive metastases in patients with HER2-negative primary breast cancer by using HER2-targeted (89)Zr-pertuzumab PET/CT. Radiology, 2020. 296(2): p. 370-378. [CrossRef]
- Yeh, R., et al., First-in-human evaluation of site-specifically labeled (89)Zr-pertuzumab in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. J Nucl Med, 2024. 65(3): p. 386-393. [CrossRef]
- Arslan, E., et al., The roles of 68 Ga-PSMA PET/CT and 18 F-FDG PET/CT imaging in patients with triple-negative breast cancer and the association of tissue PSMA and claudin 1, 4, and 7 levels with PET findings. Nucl Med Commun, 2023. 44(4): p. 284-290. [CrossRef]
- Andryszak, N., et al., Head-to-head comparison of [(18)F]PSMA-1007 and [(18)F]FDG PET/CT in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Cancers (Basel), 2024. 16(3). [CrossRef]
- Sörensen, J., et al., Measuring HER2-receptor expression in metastatic breast cancer using [68Ga]ABY-025 Affibody PET/CT. Theranostics, 2016. 6(2): p. 262-71. [CrossRef]
- Alhuseinalkhudhur, A., et al., Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-targeting [(68)Ga]Ga-ABY-025 PET/CT predicts early metabolic response in metastatic breast cancer. J Nucl Med, 2023. 64(9): p. 1364-1370. [CrossRef]
- Alhuseinalkhudhur, A., et al., [68Ga]Ga-ABY-025 PET in HER2-positive breast cancer: benefits and pitfalls in staging of axillary disease. J Clin Onc, 2024. 42(16_suppl): p. 1035-1035. [CrossRef]
- Rathore, Y., et al., Development 68Ga trastuzumab Fab and bioevaluation by PET imaging in HER2/neu expressing breast cancer patients. Nucl Med Commun, 2022. 43(4): p. 458-467. [CrossRef]
- Rathore, Y., et al., Clinical evaluation of Ga-68 NOTA-Fab in HER2 expressing breast cancer patients. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 2019. 60(supplement 1): p. 1228-1228.
- Yue, T.T.C., et al., Site-specific (68)Ga radiolabeling of trastuzumab Fab via methionine for immunoPET imaging. Bioconjug Chem, 2023. 34(10): p. 1802-1810. [CrossRef]
- Richter, A., et al., First in-human medical imaging with a PASylated (89)Zr-labeled anti-HER2 Fab-fragment in a patient with metastatic breast cancer. Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2020. 54(2): p. 114-119. [CrossRef]
- Keyaerts, M., et al., Phase I study of 68Ga-HER2-Nanobody for PET/CT assessment of HER2 expression in breast carcinoma. J Nucl Med, 2016. 57(1): p. 27-33. [CrossRef]
- Gondry, O., et al., Phase II trial assessing the repeatability and tumor uptake of [(68)Ga]Ga-HER2 single-domain antibody PET/CT in patients with breast carcinoma. J Nucl Med, 2024. 65(2): p. 178-184. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y., et al., PET imaging of a (68)Ga labeled modified HER2 affibody in breast cancers: from xenografts to patients. Br J Radiol, 2019. 92(1104): p. 20190425. [CrossRef]
- Savir-Baruch, B. and D.M. Schuster, Prostate cancer imaging with 18F-fluciclovine. PET Clin, 2022. 17(4): p. 607-620. [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A., et al., Prospective clinical trial of (18)F-fluciclovine PET/CT for determining the response to neoadjuvant therapy in invasive ductal and invasive lobular breast cancers. J Nucl Med, 2017. 58(7): p. 1037-1042. [CrossRef]
- Ma, G., et al., (18)F-FLT PET/CT imaging for early monitoring response to CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy in triple negative breast cancer. Ann Nucl Med, 2021. 35(5): p. 600-607. [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, C., et al., Pilot feasibility study: 18 F-DPA-714 PET/CT macrophage imaging in triple-negative breast cancers (EITHICS). Clin Nucl Med, 2024. 49(8): p. 701-708. [CrossRef]
- Sathekge, M., et al., (68)Ga-PSMA-HBED-CC PET imaging in breast carcinoma patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2017. 44(4): p. 689-694. [CrossRef]
- Venema, C.M., et al., Androgen and estrogen receptor imaging in metastatic breast cancer patients as a surrogate for tissue biopsies. J Nucl Med, 2017. 58(12): p. 1906. [CrossRef]
- Stoykow, C., et al., Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor imaging in breast cancer using the receptor antagonist (68)Ga-RM2 and PET. Theranostics, 2016. 6(10): p. 1641-50. [CrossRef]
- Vorster, M., B.P. Hadebe, and M.M. Sathekge, Theranostics in breast cancer. Front Nucl Med, 2023. 3. [CrossRef]
- Choi, H. and K. Kim, Theranostics for triple-negative breast cancer. Diagnostics (Basel), 2023. 13(2): p. 272. [CrossRef]
- Altena, R., et al., Current status of contemporary diagnostic radiotracers in the management of breast cancer: first steps toward theranostic applications. EJNMMI Res, 2023. 13(1): p. 43. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).