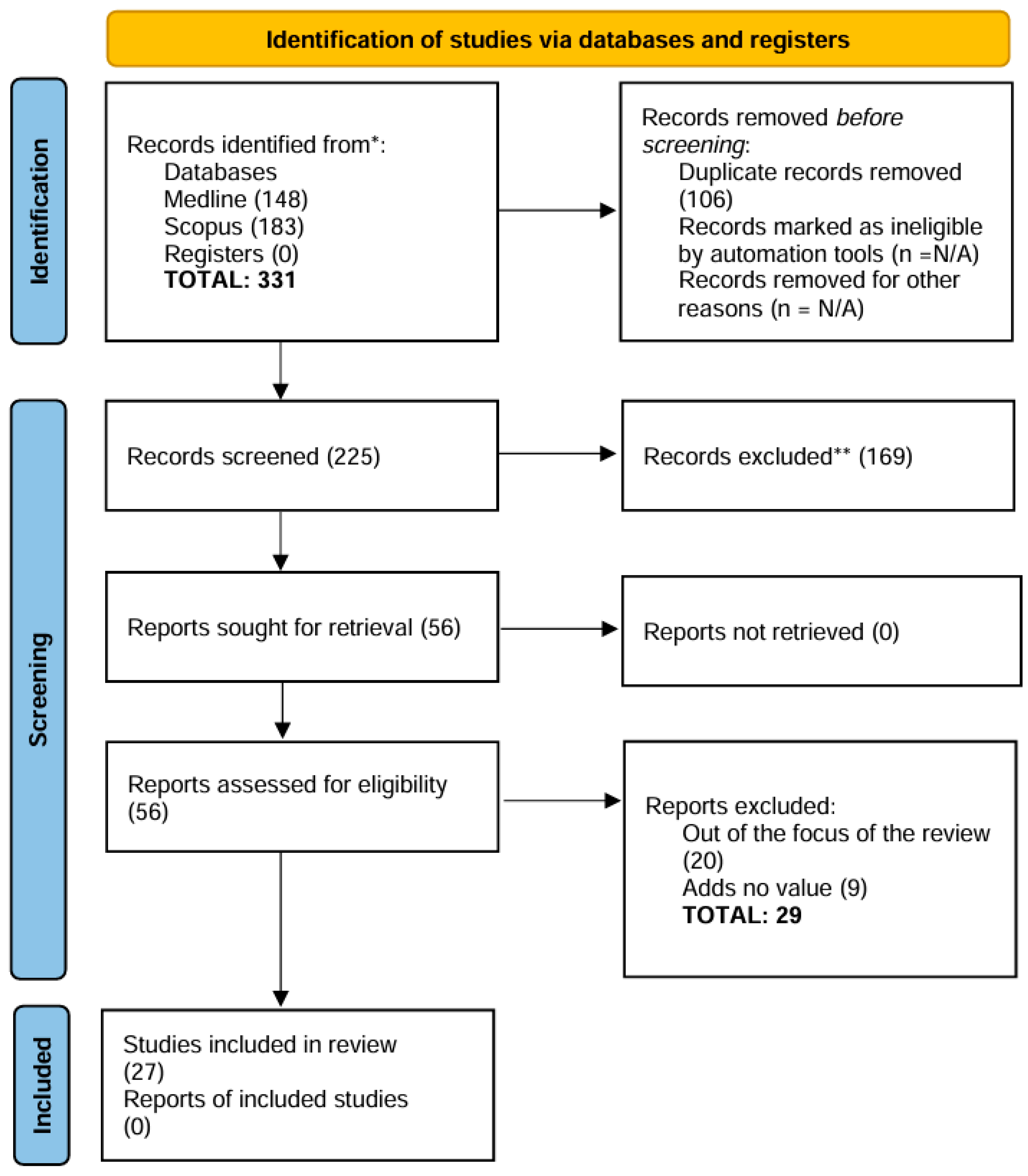
Submitted:
19 August 2024
Posted:
20 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Enamel Regeneration or Repair: Background and Definitions
1.2. Silicon, Silica, and Silicate Toothpastes
1.3. Rationale for the Review – Guiding Question
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pitts, N.B.; Zero, D.T.; Marsh, P.D.; Ekstrand, K.; Weintraub, J.A.; Ramos-Gomez, F.; Tagami, J.; Twetman, S.; Tsakos, G.; Ismail, A. Dental caries. Nature reviews. Disease primers 2017, 3, 17030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, M. Enhancing fluoride: clinical human studies of alternatives or boosters for caries management. Caries Res 2016, 50 Suppl 1, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, F.C.; Bonecker, M.; Paiva, S.M.; Martignon, S.; Ricomini Filho, A.P.; Pozos-Guillen, A.; Oliveira, B.H.; Bullen, M.; Naidu, R.; Guarnizo-Herreno, C.; et al. Dental caries prevalence, prospects, and challenges for Latin America and Caribbean countries: a summary and final recommendations from a Regional Consensus. Braz Oral Res 2021, 35, e056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, N.L.S.; Silva, J.; de Sousa, E.B.G.; D’Alpino, P.H.P.; de Oliveira, A.F.B.; de Jong, E.J.; Sampaio, F.C. Effectiveness of fluoride-containing toothpastes associated with different technologies to remineralize enamel after pH cycling: an in vitro study. BMC oral health 2022, 22, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.S.; Patel, A.N.; Al Botros, R.; Snowden, M.E.; McKelvey, K.; Unwin, P.R.; Ashcroft, A.T.; Carvell, M.; Joiner, A.; Peruffo, M. Measurement of the efficacy of calcium silicate for the protection and repair of dental enamel. J Dent 2014, 42 Suppl 1, S21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, A.; Schäfer, F.; Naeeni, M.M.; Gupta, A.K.; Zero, D.T. Remineralisation effect of a dual-phase calcium silicate/phosphate gel combined with calcium silicate/phosphate toothpaste on acid-challenged enamel in situ. J Dent 2014, 42, S53–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilhena, F.V.; Grecco, S.D.S.; Gonzalez, A.H.M.; D’Alpino, P.H.P. Regenerative and protective effects on dental tissues of a fluoride-silicon-rich toothpaste associated with a calcium booster: an in vitro study. Dent J (Basel) 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, M.; Diekwisch, T.G.H. Enamel biomimetics-fiction or future of dentistry. Int J Oral Sci 2019, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, N. State of the art enamel remineralization systems: the next frontier in caries management. Caries Res 2019, 53, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, J.; Newcombe, R.G.; Matheson, J.R.; Weddell, L.; Edwards, M.; West, N.X. A randomised controlled trial investigating efficacy of a novel toothpaste containing calcium silicate and sodium phosphate in dentine hypersensitivity pain reduction compared to a fluoride control toothpaste. J Dent 2020, 98, 103320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.; Amaechi, B.T.; Fabritius, H.O.; Enax, J. Overview of calcium phosphates used in biomimetic oral care. Open Dent J, 2018, 12, 406–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilhena, F.V.; de Oliveira, S.M.L.; Matochek, M.H.M.; Tomaz, P.L.S.; Oliveira, T.S.; D’Alpino, P.H.P. Biomimetic Mechanism of Action of Fluoridated Toothpaste Containing Proprietary REFIX Technology on the Remineralization and Repair of Demineralized Dental Tissues: An In Vitro Study. Eur J Dent 2021, 15, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Arcos, D. Silicon substituted hydroxyapatites. A method to upgrade calcium phosphate based implants. J Mater Chem 2005, 15, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Cate, J.M.; Buzalaf, M.A.R. Fluoride Mode of Action: Once There Was an Observant Dentist. J Dent Res 2019, 98, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, I.R.; Huang, J.; Best, S.M.; Bonfield, W. Enhanced in vitro cell activity and surface apatite layer formation on novel silicon-substituted hydroxyapatites. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on Ceramics in Medicine, Nam, Japan; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, N.; Best, S.M.; Bonfield, W.; Gibson, I.R.; Hing, K.A.; Damien, E.; Revell, P.A. A comparative study on the in vivo behavior of hydroxyapatite and silicon substituted hydroxyapatite granules. Journal of materials science. Materials in medicine 2002, 13, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhrs, A.K.; Geurtsen, W. The application of silicon and silicates in dentistry: a review. Progress in molecular and subcellular biology 2009, 47, 359–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippert, F. An introduction to toothpaste - its purpose, history and ingredients. Monogr Oral Sci 2013, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thalakiriyawa, D.S.; Dissanayaka, W.L. Advances in Regenerative Dentistry Approaches: An Update. Int Dent J 2024, 74, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Niu, J.; Su, G.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Sun, N. Research progress of biomimetic materials in oral medicine. Journal of biological engineering 2023, 17, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volponi, A.A.; Zaugg, L.K.; Neves, V.; Liu, Y.; Sharpe, P.T. Tooth repair and regeneration. Curr Oral Health Rep 2018, 5, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, S. The biomimetics of enamel: a paradigm for organized biomaterials synthesis. Ciba Foundation symposium 1997, 205, 261–269, discussion 269-274. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, L.C.; Newcomb, C.J.; Kaltz, S.R.; Spoerke, E.D.; Stupp, S.I. Biomimetic systems for hydroxyapatite mineralization inspired by bone and enamel. Chem Rev 2008, 108, 4754–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Yoon, M.; Choi, K.Y. Approaches for Regenerative Healing of Cutaneous Wound with an Emphasis on Strategies Activating the Wnt/beta-Catenin Pathway. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle) 2022, 11, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, R.R.; Habelitz, S. Current developments on enamel and dentin remineralization. Curr Oral Health Rep 2019, 6, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Moradian-Oldak, J.; George, A. Biomineralization of Enamel and Dentin Mediated by Matrix Proteins. J Dent Res 2021, 100, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Veis, A. Phosphorylated proteins and control over apatite nucleation, crystal growth, and inhibition. Chem Rev 2008, 108, 4670–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradian-Oldak, J. Protein-mediated enamel mineralization. Frontiers in bioscience 2012, 17, 1996–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, L.; Fouda, A.; Bourauel, C. Biomimetic approaches and materials in restorative and regenerative dentistry: review article. BMC oral health 2023, 23, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devadiga, D.; Shetty, P.; Hegde, M.N.; Reddy, U. Bioactive remineralization of dentin surface with calcium phosphate-based agents: An in vitro analysis. Journal of conservative dentistry : JCD 2022, 25, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darvell, B.W.; Smith, A.J. Inert to bioactive - A multidimensional spectrum. Dent Mater 2022, 38, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulbert, S.F.; Hench, L.L.; Forbers, D.; Bowman, L.S. History of bioceramics. Ceramics International 1982, 8, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, N.; Mohammed, H.; Al-Hadeethi, Y.; Bakry, A.S.; Umar, A.; Hussein, M.A.; Abbassy, M.A.; Vaidya, K.G.; Al Berakdar, G.; Mkawi, E.M.; et al. Silica-Based Bioactive Glasses and Their Applications in Hard Tissue Regeneration: A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.S.; Pasha, M.B.; Rao, R.N.; Rao, P.V.; Madaboosi, N.; Ozcan, M. A Review on Enhancing the Life of Teeth by Toothpaste Containing Bioactive Glass Particles. Curr Oral Health Rep 2024, 11, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan, D. Bioglass at 50 – A look at Larry Hench’s legacy and bioactive materials. Biomedical Glasses 2019, 5, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.L.; Mei, M.L.; Chu, C.H.; Lo, E.C.M. Mechanisms of Bioactive Glass on Caries Management: A Review. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Wassefy, N.A. Remineralizing effect of cold plasma and/or bioglass on demineralized enamel. Dent Mater J 2017, 36, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadoss, R.; Padmanaban, R.; Subramanian, B. Role of bioglass in enamel remineralization: Existing strategies and future prospects-A narrative review. Journal of biomedical materials research. Part B, Applied biomaterials 2022, 110, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skallevold, H.E.; Rokaya, D.; Khurshid, Z.; Zafar, M.S. Bioactive Glass Applications in Dentistry. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilhena, F.V.; Lonni, A.A.S.G.; D’Alpino, P.H.P. Silicon-enriched hydroxyapatite formed induced by REFIX-based toothpaste on the enamel surface. Braz Dent Sci 2021, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, R.C.B.; Oliveira, L.d.; Silva, J.A.B.; Santos, W.B.B.d.; Ferreira, L.R.d.S.L.; Guiraldo, R.D.; Vilhena, F.V.; D’Alpino, P.H.P. Effectiveness of Bioactive Toothpastes against Dentin Hypersensitivity Using Evaporative and Tactile Analyses: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Oral 2024, 4, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangrando, M.S.R.; Silva, G.F.F.; Bigotto, M.L.B.; Cintra, F.M.R.N.; Damante, C.A.; Sant’Ana, A.C.P.; Vilhena, F.V. Blocking tubules technologies for dentin hypersensitivity in periodontal patients – pilot study. Res Soc Dev 2021, 10, e35101320398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moras, C.G.; Acharya, S.R.; Adarsh, U.K.; Unnikrishnan, V.K. Regenerative biomineralization potential of commercially available remineralizing agents as a preventive treatment approach for tooth erosion - An in vitro laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis. Journal of conservative dentistry : JCD 2023, 26, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, B.; El-Damanhoury, H.M.; Sheela, S.; Ngo, H.C. Effect Of Calcium Silicate, Sodium Phosphate, and Fluoride on Dentinal Tubule Occlusion and Permeability in Comparison to Desensitizing Toothpaste: An In Vitro Study. Operative dentistry 2021, 46, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiadou, D.; Eymael, D.; Hajhamid, B.; Carneiro, K.M.M.; Prakki, A. Chemical and Ultrastructural Characterization of Dentin Treated with Remineralizing Dentifrices. Journal of functional biomaterials 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaz, P.L.S.; Sousa, L.A.; Aguiar, K.F.; Oliveira, T.S.; Matochek, M.H.M.; Polassi, M.R.; D’Alpino, P.H.P. Effects of 1450-ppm fluoride-containing toothpastes associated with boosters on the enamel remineralization and surface roughness after cariogenic challenge. Eur J Dent 2020, 14, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, N.L.S.; Juliellen, L.D.C.; Andressa, F.B.O.; D’Alpino, H.P.P.; Sampaio, C.F. Resistance against erosive challenge of dental enamel treated with 1,450-PPM fluoride toothpastes containing different biomimetic compounds. Eur J Dent 2021, 15, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggio, C.; Gulino, C.; Mirando, M.; Colombo, M.; Pietrocola, G. Preventive effects of different protective agents on dentin erosion: An in vitro investigation. J Clin Exp Dent 2017, 9, e7–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altan, H.; Goztas, Z.; Kahraman, K.; Kus, M.; Tosun, G. Inhibition Effects of Different Toothpastes on Demineralisation of Incipient Enamel Lesions. Oral Health Prev Dent 2019, 17, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Damanhoury, H.M.; Elsahn, N.A.; Sheela, S.; Bastaty, T. In Vitro Enamel Remineralization Efficacy of Calcium Silicate-Sodium Phosphate-Fluoride Salts versus NovaMin Bioactive Glass, Following Tooth Whitening. Eur J Dent 2021, 15, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalas, R.; Wojcik-Checinska, I.; Zamoscinska, J.; Bachanek, T. Assessment of Pain Intensity in Patients with Dentin Hypersensitivity After Application of Prophylaxis Paste Based on Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate Formula. Medical science monitor : international medical journal of experimental and clinical research 2015, 21, 2950–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, P.; Parkinson, C.; Hall, C.; Wang, N.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Du, M. A Randomized Clinical Trial Investigating the Effect of Particle Size of Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate (CSPS) on the Efficacy of CSPS-containing Dentifrices for the Relief of Dentin Hypersensitivity. J Clin Dent 2016, 27, 54–60. [Google Scholar]
- Sufi, F.; Hall, C.; Mason, S.; Shaw, D.; Milleman, J.; Milleman, K. Efficacy of an experimental toothpaste containing 5% calcium sodium phosphosilicate in the relief of dentin hypersensitivity: An 8-week randomized study (Study 2). Am J Dent 2016, 29, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hall, C.; Mason, S.; Cooke, J. Exploratory randomised controlled clinical study to evaluate the comparative efficacy of two occluding toothpastes - a 5% calcium sodium phosphosilicate toothpaste and an 8% arginine/calcium carbonate toothpaste - for the longer-term relief of dentine hypersensitivity. J Dent 2017, 60, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Sufi, F.; Wang, N.; Young, S.; Feng, X. An Exploratory Randomised Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of an Experimental Occlusion-based Dentifrice in the Relief of Dentin Hypersensitivity. Oral Health Prev Dent 2019, 17, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, E.; Pawar Chandrashekhar, D.; Sharma Hareesha, M. Comparative evaluation of fluorinol and calcium sodium phosphosilicate-containing toothpastes in the treatment of dentin hypersensitivity. Int J Dent Hyg 2021, 19, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, S.; Zaidi, S.J.A.; Farooqui, W.A. Comparative efficacy of BioMin-F, Colgate Sensitive Pro-relief and Sensodyne Rapid Action in relieving dentin hypersensitivity: a randomized controlled trial. BMC oral health 2021, 21, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majji, P.; Murthy, K.R. Clinical efficacy of four interventions in the reduction of dentinal hypersensitivity: A 2-month study. Indian journal of dental research : official publication of Indian Society for Dental Research 2016, 27, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallob, J.; Sufi, F.; Amini, P.; Siddiqi, M.; Mason, S. A randomised exploratory clinical evaluation of dentifrices used as controls in dentinal hypersensitivity studies. J Dent 2017, 64, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salah, R.; Afifi, R.R.; Kehela, H.A.; Aly, N.M.; Rashwan, M.; Hill, R.G. Efficacy of novel bioactive glass in the treatment of enamel white spot lesions: a randomized controlled trial. J Evid Based Dent Pract 2022, 22, 101725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, K.; Hamama, H.H.; Motawea, A.; Fawzy, A.; Mahmoud, S.H. Long-term evaluation of early-enamel lesions treated with novel experimental tricalcium silicate paste: A 2-year randomized clinical trial. Journal of esthetic and restorative dentistry : official publication of the American Academy of Esthetic Dentistry... [et al.] 2022, 34, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollabashi, V.; Heydarpour, M.; Farhadifard, H.; Alafchi, B. DIAGNOdent pen quantification of the synergy of NovaMin(R) in fluoride toothpaste to remineralize white spot lesions in patients with fixed orthodontic appliances: A double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trial. International orthodontics 2022, 20, 100632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, L.; Ebel, M.; Bekes, K.; Klode, C.; Hirsch, C. Influence of caries and molar incisor hypomineralization on oral health-related quality of life in children. Clin Oral Investig 2021, 25, 5205–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerheijm, K.L. Molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH). European journal of paediatric dentistry 2003, 4, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jalevik, B.; Klingberg, G. Treatment outcomes and dental anxiety in 18-year-olds with MIH, comparisons with healthy controls - a longitudinal study. Int J Paediatr Dent 2012, 22, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jälevik, B.; Sabel, N.; Robertson, A. Can molar incisor hypomineralization cause dental fear and anxiety or influence the oral health-related quality of life in children and adolescents?—a systematic review. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 2022, 23, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, F.; de Carvalho Rodrigues, Ana C.; Lia, Érica N.; Leal, Soraya C. Prevalence of Hypersensitivity in Teeth Affected by Molar-Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH). Caries Res 2019, 53, 424–430. [CrossRef]
- Rodd, H.D.; Graham, A.; Tajmehr, N.; Timms, L.; Hasmun, N. Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation: Current Knowledge and Practice. Int Dent J 2021, 71, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author (Year) | Title | Study aim | Outcome Measurement | Sample Size (SS), Follow-Up (FU) | Material(s) or Technology (ies) Used |
Active agent(s) | Primary results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poggio et al. (2017) | Preventive effects of different protective agents on dentin erosion: An in vitro investigation | To evaluate the preventive effects of different protective agents on dentin erosion caused by soft drinks | Percent weight loss, SEM imaging | SS: 70 human dentin specimens; FU: 32 minutes total immersion in Coca-Cola | Remin Pro, MI Paste Plus, Tooth Mousse, Biorepair, Biorepair Plus, Regenerate | Hydroxyapatite, CPP-ACP, CPP-ACPF, zinc hydroxyapatite, calcium silicate, sodium phosphate, sodium monofluorophosphate (1450 ppm fluoride) | Biorepair and Regenerate significantly reduced dentin weight loss, showing greater resistance to acid erosion compared to other agents. Remin Pro and MI Paste Plus showed results similar to the control group, while Tooth Mousse and Biorepair Plus increased dentin demineralization |
| Altan et al. (2019) | Inhibition effects of different toothpastes on demineralisation of incipient enamel lesions | To Evaluate the inhibitory effects of different toothpastes on demineralisation of incipient enamel lesions using a toothbrush simulator | Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDX) with weight percentage of mineral changes (Ca, P, Na, Si) | 50 Human enamel blocks (n=10 per group) 5 days pH cycling |
Toothpaste with Arginine, Fluoride, CPP-ACP, and Bioactive Glass (NovaMin) | Arginine, Sodium Monofluorophosphate (Fluoride), CPP-ACP, Bioactive Glass (NovaMin) | All toothpaste groups showed a statistically significant increase in Ca and P compared to the control group (p < 0.05). CPP-ACP showed the highest increase in Ca and P. NovaMin increased Na and Si significantly |
| Vilhena et al. (2020) |
Biomimetic Mechanism of Action of Fluoridated Toothpaste Containing Proprietary REFIX Technology on the Remineralization and Repair of Demineralized Dental Tissues: An in vitro Study |
Characterize the mineral content and surface and cross-sectional morphology of enamel and dentin tissues treated with a 1450 ppm fluoride-containing toothpaste with REFIX technology. |
The surface and cross-sectional micromorphology were assessed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The ele- mental analyses (weight%) were determined with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectros- copy (EDS). |
Bovine enamel blocks (n=5) 7 days of pH cycling |
REFIX technology | Fluoride sodium, tetrasodium pyrophosphate |
REFIX technology remineralized and repaired the surface enamel effectively. Enamel with the toothpaste formed a silicon-enriched mineral layer on the enamel surface. The results were also consistent in the dentin, where the dentinal tubules were progressively occluded until there was complete occlusion after 7 days. |
| Tomaz et al. (2020) |
Effects of 1450-ppm Fluoride-containing Toothpastes Associated with Boosters on the Enamel Remineralization and Surface Roughness after Cariogenic Challenge |
Investigated the remineralization potential of 1450 ppm, fluoride-containing toothpastes containing different active remineralization agents after cariogenic challenge with pH cycling. |
Mean and percentage of surface hardness recovery (% SHR) were calculated. Surface enamel roughness (Ra) was also evaluated. The pH, %weight of particles, zeta potential, and polydispersity index of toothpaste slurries were also evaluated. |
Bovine enamel blocks (n=8/ per group) 7 days of pH cycling |
REFIX, NR-5, Candida Professional, Colgate Total 12 Daily Repair, Bianco Pro Clinical, Elmex Sensitive |
Sodium fluoride, Tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP), Sodium Monofuoro-phosphate, Oligopeptide-104, Calcium glycerophosphate, Triclosan, Arginine, Tetrasodium pyrophosphate, Calcium silicate and sodium phosphate |
The enamel subsurface was more effectively remineralized when treated with Bianco Pro Clinical, Elmex Sensitive, and Refix. The surface roughness was higher when the demineralized third was treated with Refix, and NR-5 and after the cariogenic challenge. |
| El-Damanhouryet al. (2021) | In Vitro Enamel Remineralization Efficacy of Calcium Silicate-Sodium Phosphate-Fluoride Salts versus NovaMin Bioactive Glass, Following Tooth Whitening | To evaluate the effect of in-office bleaching on enamel surface and compare the efficacy of Calcium Silicate-Sodium Phosphate-Fluoride (CS) and NovaMin bioactive glass (NM) in remineralizing bleached enamel | Surface Microhardness (Knoop Hardness Number (KHN), Surface Roughness, SEM/EDX Elemental Analysis | 40 human premolars (n=10) 7 days pH cycling |
Toothpaste with Novamin Bioactive Glass (NM), NR-5 (CS) and additional treatment with NR-5 boosting serum (CS+NR-5), |
silica, calcium sodium phosphosilicate (Novamin), sodium monofluorophosphate Calcium Silicate-Sodium Phosphate with Sodium Monofluorophosphate, hydrated silica (NR-5) |
CS and CS+NR-5 showed superior remineralization compared to NM. All remineralization agents increased hardness and decreased surface roughness after bleaching, but NM had a significantly higher surface roughness. CS and CS+NR-5 were more effective in restoring hardness and smoothness. |
| Fernandes et al. (2021) |
Resistance against Erosive Challenge of Dental Enamel Treated with 1,450-PPM Fluoride Toothpastes Containing Different Biomimetic Compounds |
This in vitro study aimed to characterize the superficial and subsurface morphology of dental enamel treated with fluoridated gels containing different bio- mimetic compounds after erosive challenge. |
The surface and cross-sectional micromorphology were assessed using scanning electron microscope (SEM). The elemental analyses (weight percent- age) were determined with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). |
Bovine enamel blocks (n=5/ per group) 6 days of pH cycling |
NR-5, REFIX, Novamin. |
Fluoride sodium, triclosan, arginine, tetrasodium pyrophosphate Sodium monofuorophosphate, calcium silicate and sodium phosphate Calcium sodium phosphosilicate 5% |
Enamel treated with the product containing REFIX technology presented a smoother surface morphology compared to the other treatments. The higher resis- tance to the erosive challenge can be attributed to a silicon-enriched mineral layer formed on the enamel induced by the REFIX-based toothpaste. |
| Rahman et al. (2021) | Effect of Calcium Silicate, Sodium Phosphate, and Fluoride on Dentinal Tubule Occlusion and Permeability in Comparison to Desensitizing Toothpaste: An In Vitro Study | To compare the efficacy of a calcium silicate-, sodium phosphate-, and fluoride-based (CSSPF)toothpaste in promoting dentinal tubule occlusion and reducing dentin permeability against other commercial desensitizing toothpastes | Dye Percolation (DP%) test, SEM microphotographs, EDS elemental analysis | SS: 78 human dentin discs; FU: 7 days | Calcium silicate, sodium phosphate, fluoride (Regenerate Advanced); Bioactive Glass (NovaMin - Sensodyne Repair and Protect); Potassium Nitrate (Signal Sensitive Expert) | Sodium monofluorophosphate (1450 ppm fluoride), calcium silicate, trisodium phosphate, hydrated silica (Regenerate); Sodium monofluorophosphate (Sensodyne); Potassium nitrate, Sodium fluoride (Signal) | The Regenerate demonstrated the highest dentinal tubule occlusion and calcium deposition, significantly reducing dentin permeability. Novamin also showed effective tubule occlusion but with less calcium deposition compared to Regenerate. Signal Sensitive Expert, using potassium nitrate, showed effective tubule occlusion and permeability reduction, but was less effective overall compared to both Regenerate and Sensodyne in terms of calcium deposition and tubule occlusion. |
| Vilhena et al. (2021) |
Silicon-enriched hydroxyapatite formed induced by REFIX-based toothpaste on the enamel surface |
At characterizing the mineral content and filler particle morphology of a fluoridated toothpaste containing REFIX technology and the mineral content and the morphology of the enamel surface treated with this product. |
The surface morphology was assessed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The elemental analyses were performed using an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS). |
Bovine enamel blocks (n=5) 7 days of pH cycling |
REFIX technology | Fluoride sodium, tetrasodium pyrophosphate |
Elemental analysis of the toothpaste’s formulation demonstrated the presence of Si (silicon), Na (sodium), P (phosphorus), and F (fluorine), among others. We also detected a mineral layer that had formed on the treated enamel surface; the layer had a consistent uniform thickness of ~14 μm. |
| Fernandes et al. (2022) |
Efectiveness of fuoride-containing toothpastes associated with diferent technologies to remineralize enamel after pH cycling: an in vitro study |
To evaluate the efcacy of fuoride-containing toothpastes with diferent technologies to remineralize artifcial caries lesions in enamel. |
Surface microhardness recovery (%SMHR) and the fuorescence recovery (ΔFRE) with quantitative light-induced fuores- cence. The cross-sectional micromorphology of the enamel surface was also assessed using scanning electron micros- copy. Elemental analyses (weight%) were determined with an energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS). |
Bovine enamel blocks (n=12/ per group) 6 days of pH cycling |
REFIX, NR-5, and NOVAMIN. |
Fluoride sodium, triclosan, arginine, tetrasodium pyrophosphate Sodium monofuorophosphate, calcium silicate and sodium phosphate Calcium sodium phosphosilicate 5% |
The Refix to recover the surface microhardness with a signifcantly lower mean of ΔFRE. Only Refix was able to promote the formation of a mineralized layer on the surface of enamel enriched with silicon on the surface. |
| Moras et al. (2023) | Regenerative Biomineralization Potential of Commercially Available Remineralizing Agents as a Preventive Treatment Approach for Tooth Erosion – An In Vitro Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Analysis | To evaluate and compare the surface remineralization potential of SAP P11-4 (self-assembling peptide) and CSSP (calcium silicate plus sodium phosphate) on intact and demineralized enamel | Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) to measure changes in Ca and P levels | SS:32 human enamel samples (16 intact, 16 demineralized) 30 days pH cycling |
SAP P11-4 (CURODONT™ PROTECT), CSSP (REGENERATE™ Enamel Science™ Advanced Toothpaste and Serum) | SAP P11-4, calcium silicate, sodium phosphate, fluoride | Both SAP P11-4 and CSSP significantly increased Ca and P levels in demineralized enamel. No significant difference in remineralization potential was observed between the two agents on intact and demineralized enamel. |
| Vilhena et al. (2023) | Regenerative and Protective Effects on Dental Tissues of a Fluoride–Silicon-Rich Toothpaste Associated with a Calcium Booster: An In Vitro Study | To characterize the regenerative and protective effects of a fluoride-silicon-rich toothpaste combined with a calcium booster on dental tissues | SEM imaging, Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS), Elemental analysis (weight %) | SS: 5 bovine enamel and 5 bovine dentin blocks; FU: Immediate and after 5 days |
Fluoride-silicon-rich toothpaste with calcium booster - REFIX technology | Sodium Fluoride (1450 ppm), Silicon-rich compounds, Calcium Carbonate, Tricalcium Phosphate | The treatment formed a mineralized layer on enamel and dentin surfaces. After 5 days, the enamel had a 4-5 µm layer and dentin had a 7 µm layer. The calcium and silicon signals increased after immediate treatment, showing significant remineralization and occlusion of dentin tubules. |
| Athanasiadou et al. (2024) |
Chemical and Ultrastructural Characterization of Dentin Treated with Remineralizing Dentifrices |
Investigate dentin chemical and ultrastructural changes upon exposure to remineralizing dentifrices. | Atomic force microscopy (AFM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and selected area electron diffraction (SAED). |
12 human dentin blocks (n= 3 per group) 14 days of toothbrushing |
REFIX, REFIX + Booster and Novamin | Fluoride sodium, tetrasodium pyrophosphate Calcium |
All evaluated dentifrices led to successful formation of hydroxyapatite and increased dentin stiffness. |
| Author (Year) | Title | Study design | Study aim | Outcome Measurement | Sample Size (SS), Follow-Up (FU) | Material(s) or Technology(ies) Used | Active agent(s) | Primary results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chalas (2015) | Assessment of Pain Intensity in Patients with Dentin Hypersensitivity After Application of Prophylaxis Paste Based on Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate Formula |
Longitudinal study | The clinical evaluation of the effectiveness in eliminating dentin hypersensitivity after a single application | The pain reaction of exposed dentine was induced by tactile and dehydrating stimuli, asking patients to assess the severity of pain on the VAS scale |
SS: 92 teeth with hypersensitivity FU: baseline and after 1 week |
NUPRO® Sensodyne® Prophylaxis Paste, Dentsply (NovaMin Formula) |
Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate (CSPS) | In-office use of professional prophylactic paste with NovaMin formula noticeably reduces dentin hypersensitivity 1 week after application |
| Zang (2016) | A Randomized Clinical Trial Investigating the Effect of Particle Size of Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate (CSPS) on the Efficacy of CSPS-containing Dentifrices for the Relief of Dentin Hypersensitivity |
Randomized clinical trial | To compare the efficacy in dentin hypersensitivity relief | The hypersensitivity was measured by tactile stimulus (Yeaple probe) and evaporative (air) stimulus (Schiff Sensitivity Scale, visual analogue scale) | SS: 133 subjects FU: baseline and after 1, 2, 4 and 8 weeks |
Vitryxx® (NaF and < 5% CSPS) NovaMin® (NaF or SMFP and 5% CSPS) Regular fluoride toothpaste |
Sodium fluoride and Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate (CSPS) Sodium mono fluorophosphate (SMFP) and CSPS Fluoride |
The apparent absence of a positive treatment effect for the CSPS-containing dentifrices compared to the regular fluoride dentifrice is inconsistent with other previously reported efficacy studies for CSPS dentifrices |
| Majji (2016) | Clinical efficacy of four interventions in the reduction of dentinal hypersensitivity: A 2-month study | Randomized clinical trial | To compare the efficacy in reduction of dentinal hypersensitivity |
The patients’ dentin hypersensitivity scores for tactile, thermal, and evaporative stimuli were recorded on a visual analog scale | SS: 160 subjects FU: baseline, after 2 weeks and after 1 and 2 months |
Toothpaste with 5% potassium nitrate NovaMin toothpaste (calcium sodium phosphosilicate) Toothpaste with |
Potassium Nitrate Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate (CSPS) Strontium chloride |
The four desensitizing kinds of toothpaste containing different active agents were effective in relieving dentinal hypersensitivity. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





