1. Introduction
The modern automotive electrical and electronic (E/E) architecture is unable to manage the increasing demands being placed on it in the 21st century [
26]. This arise as we witnessed the automotive technology move from a solely mechanically controlled device to a digitally connected system in the last 4 decades. These digital systems primarily consist of automotive electronic control units (ECU), which are small, often-bespoke embedded systems, that monitor and control the basic operations of the vehicle as well as provide safety, efficiency, comfort and infotainment functions and services [
1]. The first single function ECU was introduced in the late 1970s [
6], and today many high-end vehicles incorporate in excess of 100 ECUs.
Current increased ECU numbers is fueled through technological advancements together with increased demand for new consumer features and functions for occupant/vehicle interaction as well as increased safety and vehicle operational efficiency. Increasing computerisation of the automobile requires complex computing hardware, application and operating software as well as multiple in-vehicle networking solutions, enabling communication between often disparate sub-systems. Together with the number of ECUs and interconnection hardware, an exponential increase has been seen in the number of peripheral components including sensors and actuators [
30].
Non-standard ad-hoc inclusion of new features packaged as niche ECU’s together with the requirement of safety and reliability, has resulted in the evolution of a more distributed vehicular software architecture. Such a distributed architecture though provided its benefits during early development phase, have now evolved into a complex and intricate mesh of ECUs incurring a number of disadvantages. These include:
Increased cost: there is a marked increase in cost and overheads with each new addition of hardware and its associated software from development to maintenance [
7].
Increased complexity: the complexity of the modern automotive E/E architecture has arisen from the ever-increasing interactions between various components parts. The introduction of multiple in-vehicle networking solutions such as CANBus, LIN, Flexray has aided in overall system complexity. As more automotive functions require data across multiple automotive domains of responsibility [
2,
7].
Reduced scalability: embedded systems are not inherently scalable by design. They are bespoke pieces of hardware which have been highly optimized on an architectural level to ensure that only the necessary components are included [
16]
2. Virtualisation in the Automotive Domain
The automotive E/E architecture has evolved very similarly to the traditional datacentre. Clients access services and systems from dedicated servers within a datacentre. Drawing parallel within the E/E architecture, sensors and actuators are the clients, accessing services, data and systems from the ECUs, which are analogous to servers. Similar to the automotive E/E architecture, the traditional datacentre has evolved through the need of new business functions being met by a new dedicated server, creating the issue of ever-increasing numbers of underutilised hardware [
32,
33]. Hence, conventional datacentres had suffered from issues, such as hardware decentralisation, rising hardware implementation and operational costs, space constraints and increasing complexity. The datacentre community, successfully addressed these issues through the adoption of the virtualisation technology.
To address the disadvantages highlighted in section within the automotive sector, there has been a move in recent years towards a more centralized automotive E/E architecture. To promote system consolidation, multiple independent automotive functions need to merge with fewer hardware devices. Given the parallels with the traditional data centres, virtualization has been seen as one of the mechanisms of achieving a centralised and streamlined architecture [
17]. Virtualisation has been proven to be highly effective within client/server architectures, data storage and cloud computing environments, especially in hardware consolidation and overall cost reduction [
27,
28]. Hardware consolidation promotes reducing infrastructure costs and hardware expenditure, however higher system redundancy levels, increased productivity and security through isolation are additional benefits of virtualization [
29]. Architectural centralization and virtualization combine a group of physically separate hardware resources such as ECUs to facilitate the execution of multiple applications simultaneously on a single system. Such ECU consolidation, gives the impression of several separate physical systems or user environments.
One of the major benefits of virtualization is its ability for enormous cost savings as well as lowered power consumption through ECU consolidation. Furthermore, virtualization allows dynamic load balancing and improved throughput and continuity, particularly necessary for system critical applications. Another one of the key advantages is temporal and spatial separation [
18]. However, full system virtualisation and hypervisors can incur considerable system resource overheads [
8]. To overcome such limitations, virtualisation technology has gained traction towards more lightweight solutions, namely containers [
25,
31].
Operating system virtualisation also known as containers offers a number of benefits to the automotive E/E architecture. Containerised applications can start almost instantly. With full system virtualization a single hardware platform running multiple virtual machines requires an operating system for each virtual machine to support installed applications. In contrast, containers run within a single operating system environment with each container sharing parts of the OS kernel. A containerised application includes in a single package all required dependencies; libraries, binaries and configuration files for that program to run. Containers offer a much-reduced footprint of megabytes rather than gigabytes. Similar to full system virtualisation each containers’ available resource is in isolation from other containers on the same host system. This resource isolation is achieved through Linux kernel namespaces enabling different processes to utilise global system resources as though they were their own isolated set of resources.
An ECU utilizing containers can operate in a “just in time” (JIT) mode where it is activated as and when needed and then shut down when they are no longer required freeing up the hosts resources. Containers enable high modularity; large monolithic applications can be broken up into separate modules and run within their own individual containers. This microservice approach can facilitate changes to different parts of the application without having to rebuild the entire application. Containers are ideally suited to over the air (OtA) software updates which could provide new and upgraded automotive software without the need to return the vehicle to an authorised mechanic or dealership [
9,
15,
22].
3. Related Work
There have been a number of studies and articles relating specifically to ECU virtualization. [
17,
19] discuss automotive E/E architecture scalability utilizing virtualization and the AUTOSAR standard. Embedded hypervisors are being introduced into the automotive arena to promote safety [
19]. [
10] looks at where virtualization could be used within the motor car, focusing on less critical solutions such as the vehicle head unit and passenger infotainment functionality. To promote system consolidation, [
11] investigates the reduction in overall cost and weight by dedicating specific cores to various virtualised automotive systems, including infotainment and telematic information. Containers have shown potential in non-automotive sectors that need both high performance [
23] and embedded [
24,
25] in nature, hence holding promise for the E/E architecture.
Building on the work done by Soltesz et. all. [
12] and Feltes et. all. [
20], containers are a viable alternative to hypervisor technology that can provide increased scalability and higher performance workloads. Kugele et. all.[
21] proposed a data-centric service-oriented automotive E/E architecture to facilitate (among other higher-level goals) common messages needed by several functions in several ECUs as services and to address issue around high bus load as a result of messages that have no receivers. Kugele et al. l.[
21], the primary contribution is in the area of using a shared middleware layer to provide a data-centric publish-subscribe service-oriented architecture. The architecture uses docker based containerisation to harness its layered architecture approach to allow sharing and reusing layers among containers towards the higher-level goal of providing service-oriented architecture. The proposed architecture by Kugele et. all.[
21] assumes lower layers do not change, while our proposed architecture is rooted in the fact that updates will be required throughout the software-firmware layers thus allowing much needed adaptability.
There has been very little published work or research regarding the use of container-based virtualization within the automotive E/E architecture. Examining containers and what they offer could have major benefits to the modern motor car, which is not just limited to infotainment features and functions but adds to the entire automotive E/E. Given the aforementioned, an important direction for this research is to evaluate the performance of a container-based ECU environment whilst in the execution of an automotive function. In this paper we evaluate the overall performance of various ECU based containers. Our evaluation was performed on a bespoke hardware test bed which modelled a number of different automotive ECUs that provided the automotive function of a vehicle central locking/unlocking mechanism.
To fully test a container-based automotive architecture it was decided that a mix of real and non-real time systems would be required to represent a distributed automotive function. Several potential possibilities were researched which culminated in a vehicle door central locking mechanism being selected as the test system. There are many different types of vehicle door central locking mechanisms on all manner of vehicle makes and models and a central locking mechanism which incorporated real and non-real time inputs would more accurately simulate an actual implemented central locking system. A central locking mechanism is a simple vehicle-related function that locks and unlocks either all doors or selected doors based on some form of trigger mechanism.
4. Design of a Container Based ECU
The automotive architecture has evolved historically in response to functional and customer needs, without a holistic blueprint, leading to a complex and error-prone architecture. Academia and industry have responded in recent times with possible standardised approaches to address these issues and we present them within this section as appropriate in the context of the proposed work.
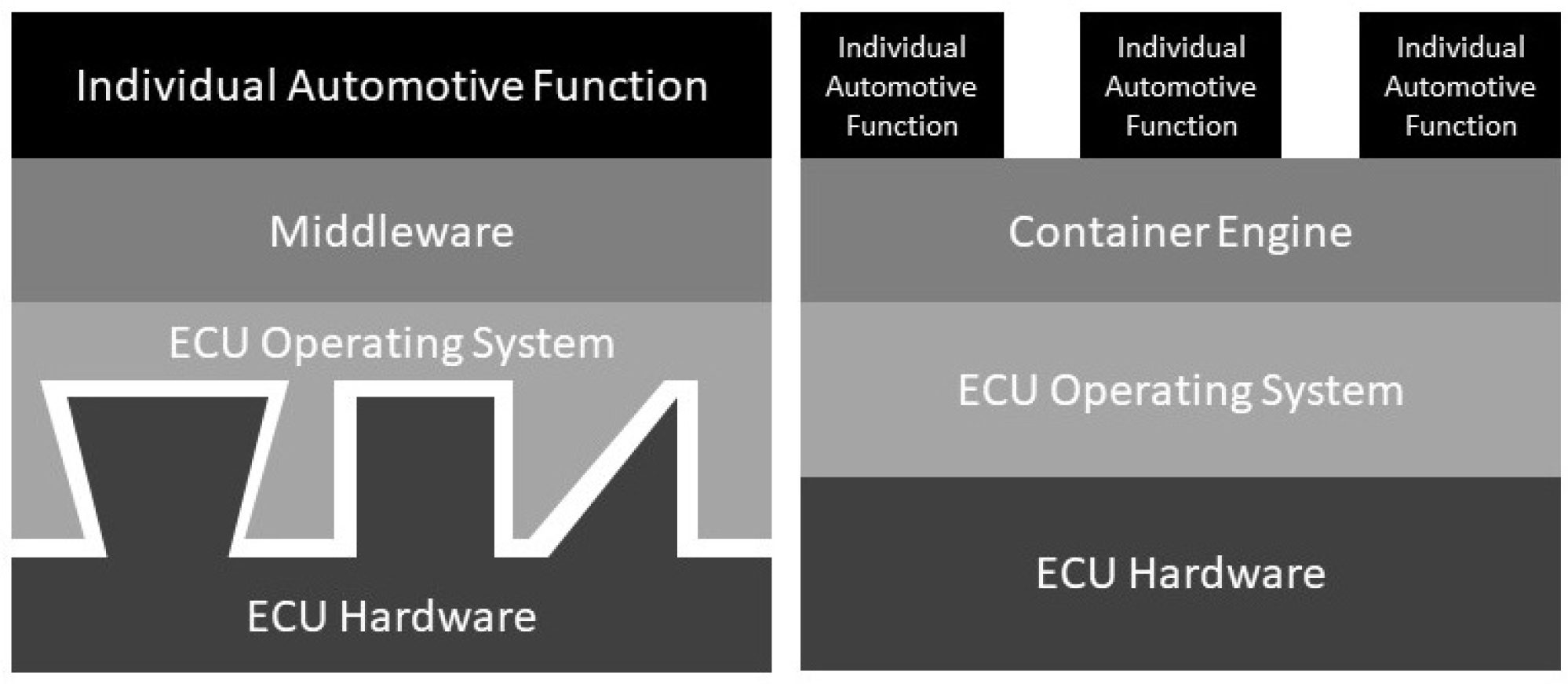
Automotive ECUs are generally simple computing devices where power consumption, speed of operation and efficiency are key aspects to their design. ECU hardware architectures are finely tuned to the software function they have been designed for as observed in
Figure 1. Their rigid design has little to no capacity for additional lines of code or functionality in any future software update. A crucial feature of an ECU is the microprocessor which are usually ARM (Advanced RISC Machine) based microprocessors. ARM-based ECUs integrate many additional peripherals within its architecture which keeps the number of additional required components to complete a given function or task to a minimum. This type of architecture is ideal for an automotive ECU.
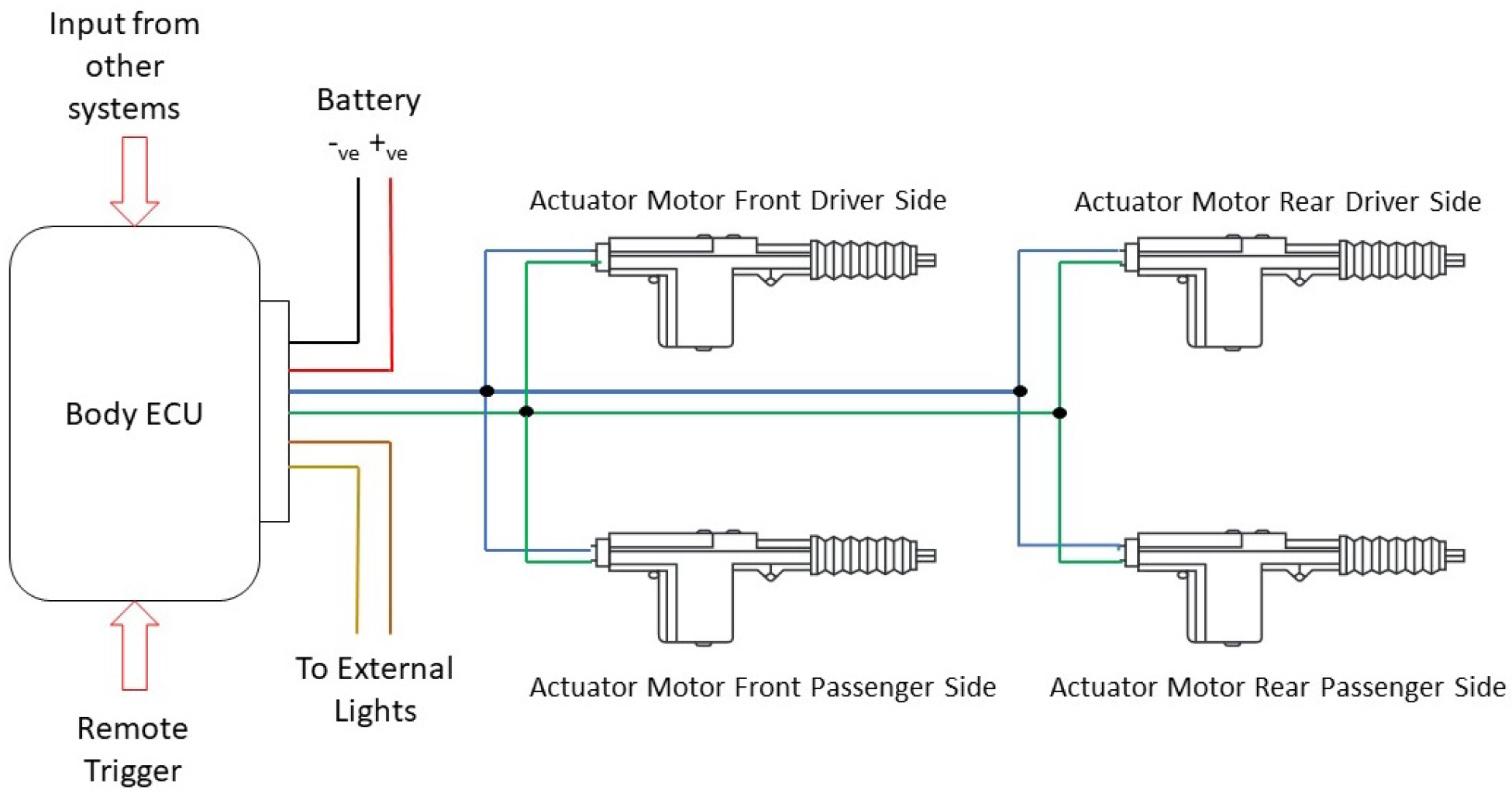
4.1. Automotive Central Locking Function
Figure 2 is an example of a classic door central locking/unlocking function. For this research the modelled central locking function incorporated both real and non-real time conditions which triggered the central locking mechanism including several visual outputs when the system was activated. The central locking mechanism was activated via the following triggers:
Infrared Remote (Simulated remote key fob)
Transmission - Selection of a specific gear
Vehicle Speed - When vehicle achieves a specific speed
4.2. Test Bed- ECU and Sensor Hardware
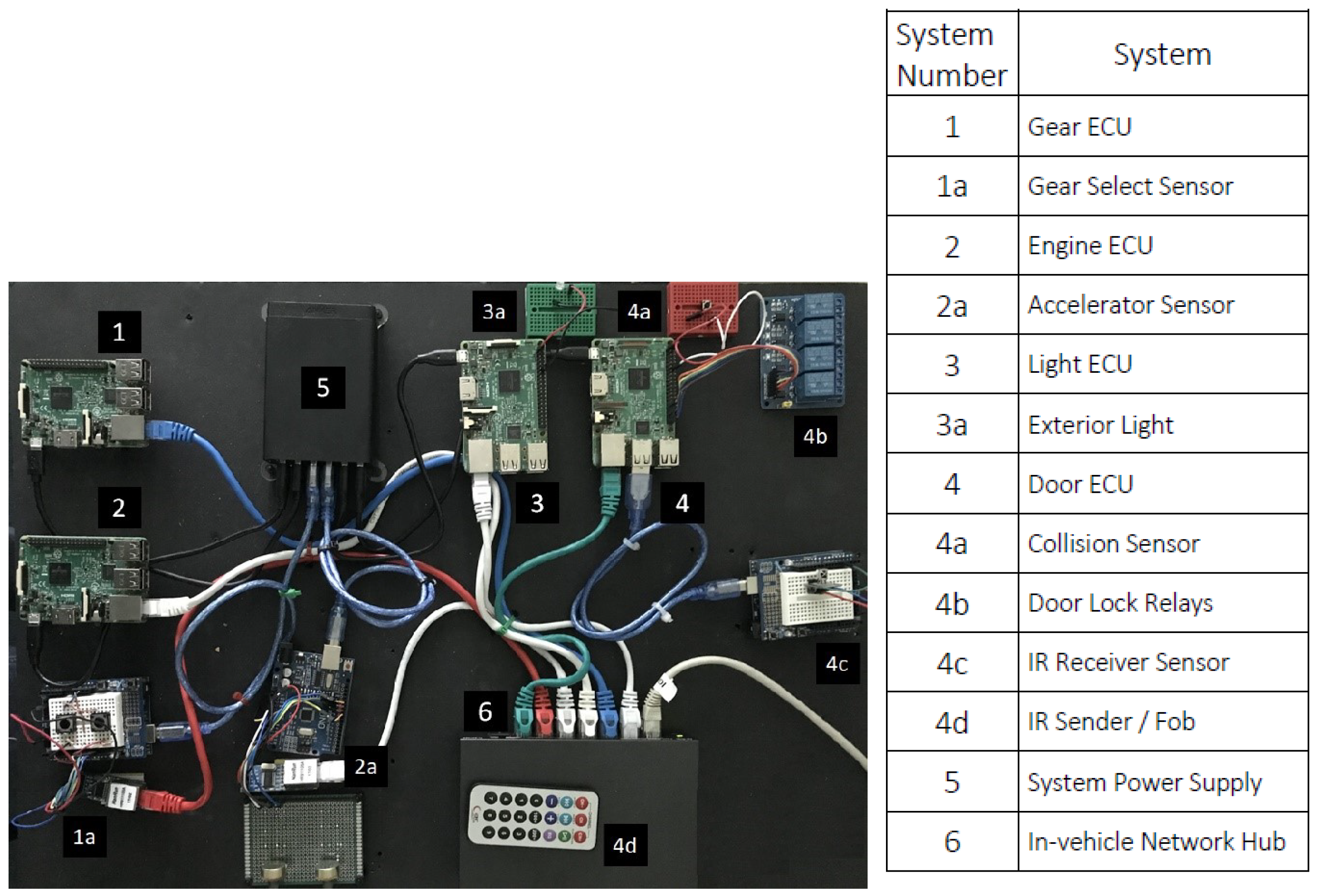
To assess the suitability of containers within an automotive context an experimental test system was required to model an ECU/vehicle function utilising a more generic type of ARM based hardware to accomplish this task. For the experimental test system, the ARM based Raspberry Pi 3B was chosen as a generic hardware platform to model an automotive ECU as can be seen in
Figure 3. Similar to an ECU, the Raspberry Pi has many available GPIO pins and through these the Raspberry Pi can interact directly with externally connected hardware as well as other ECUs. Although the Raspberry Pi has limited potential within a commercial environment it is ideally placed as a platform for research purposes [
13].
The sensors attached to the Raspberry Pi provide the initial simulated automotive data. Actuators provide the door locking mechanism and LEDs simulate the vehicle lights. The modelled system described above requires specific peripheral hardware including:
Central door locking mechanism - provided by a four-channel relay module. Each relay represents a particular vehicle door. The vehicle doors are locked when the relay corresponding to it is in the closed position.
Remote door lock trigger - manual door states are affected via a remote IR transmitter device. The IR transmitter sends one of three selectable door commands to an IR receiver. This particular functionality is suspended if the current transmission state is in any gear other than neutral.
External lighting - an LED simulates the vehicle headlights, which illuminates according to the received door state.
Gear position – the current selected gear is represented by a series of depressions on one of two push-button sensors that either increase or decrease the gear.
Vehicle acceleration – the simulated engine r/min is selected by a potentiometer position setting with a data range of 0–1024.
The collision sensor – a push-button sensor simulates the deployment of an airbag or activation of a collision sensor and when pressed, activates the overriding safety mechanism.
Several system peripheral devices are directly connected via the GPIO pins of a particular ECU. Other peripheral devices are connected via Arduino programmable circuit boards where raw sensor data is collected, processed and subsequently transmitted to the relevant ECU via a simulated in-vehicle network.
5. Implementation
To test containers accurately within an automotive E/E architecture context, the modelled central door locking function must closely replicate an existing automotive system. Several dedicated ECU hardware platforms are required to separate the individual and independent ECU functions across several different automotive domains. The modelled system requires four control systems and associated transactions, these included:
Transmission ECU - part of the transmission domain
Acceleration ECU - part of the engine domain
Door Control ECU - part of the body domain
Light Control ECU - part of the body domain
Each of the identified ECU functions was hosted on its own individual Raspberry Pi hardware platform and was connected via a network to model cross-domain functionality. Each Raspberry Pi was responsible for specific data collection and subsequent processing.
Figure 3 depicts the testbed layout of the ECU hardware and attached peripherals.
Raspbian Lite was the chosen OS as it includes components needed to run a container environment, the network stack as well as the performance monitoring tools.
6. Evaluation
The evaluation was initially performed in native mode (as defined below) where the software was executed within the ECU OS. This provided a set of base line results that the subsequent container evaluation tests were compared against. The CPU and memory resources required and consumed by an ECU function are predictable and determined during the design and testing stages. This research proposed a container-based ECU architecture which in implementation requires additional software and a level of abstraction between the application software and underlying hardware. By measuring the specific system resource use, an understanding can be gained of how additional resources are required to support a container-based automotive architecture when compared with current ECU configurations.
6.1. System Performance Metrics
In supporting a server environment, the Utilisation, Saturation and Errors (USE) methodology can investigate performance issues and potential bottlenecks [
3,
14]. The Rate, Errors and Duration (RED) method can also be used to monitor microservices [
4,
5]. A combination of these two methods provides an ideal methodology for monitoring the specific resources to support native and container-based ECU execution. By combining elements of the USE and RED methods, a new methodology was developed and adopted. This new methodology focused on the Utilisation, Saturation and Duration (USD) components to identify performance across the target system CPU and memory. The critical metrics for this research includes:
Utilisation – the percentage of time a resource is busy compared to when that resource is available over a given time interval.
Saturation – the amount of work that is queued or waiting for an available resource, often expressed as a queue length.
Duration – the amount of time spent serving a request.
6.2. ECU Test Mode of Operation
To determine the additional resources necessary for a container based system, a series of test comparisons was performed against three identified system operational modes. These test modes included:
Base system test mode - This initial test mode establishes a baseline benchmark of the system resources used when the modelled ECU is in an idle state. Any system overhead introduced by the ECU software across subsequent test modes can be compared to this baseline set of results to determine the overheads when the ECU functional software is executed natively and within a container.
Native system test mode - This test mode generally mirrors current automotive E/E architectures and ECU function operations. During this test mode, the results will show specific increases in system resource use when each ECU functional software is in execution compared with the base system test.
Container system test mode - This test mode measures any other system resources or resource overhead required to run the ECU software within a container when compared with native operation.
A set of test criteria was defined to ensure the same conditions were applied across all resource tests during the three test modes. Best practice for data capture involves evaluating each specified metric over multiple data collection instances and time frames, to fully understand the specific system resource usage. Specific test times were divided into three distinct time frames (60-second, 600-second and 1200-second duration), as described below:
time_60 = 60-second sample run - some tests investigate specific resource use required during ECU software initialisation. Thus, only the first few initial seconds were required for analysis. A 60-second test run was a sufficient time to allow for an initial warm-up period before script execution.
time_600 = 600-second sample run – these tests investigated the functional software’s entire life cycle from initialisation to termination. These time frame tests included a system idle warm-up period of 30 seconds, which eliminated spikes in specific resources associated with the initial stages of software execution. Script execution time for these timed tests was 500 seconds, at which point the script terminated, with the final 30 seconds of the test being the cool-down period. CPU and memory resource levels after script execution were a crucial area of investigation. They revealed whether the system returned to a similar state before the script was executed. It was important to understand the level of resources which were not released back to the system after execution, particularly ECU systems that only activate periodically to accomplish a specific task or function.
time_1200 = 1200-second sample run – this test period investigated resource use trends over an extended time to understand if there were specific increases during long execution cycles. However, to display this information, the published results must be a cross-section of the entire 1200-second test, especially where test results showed little to no observable activity.
7. Software Tools
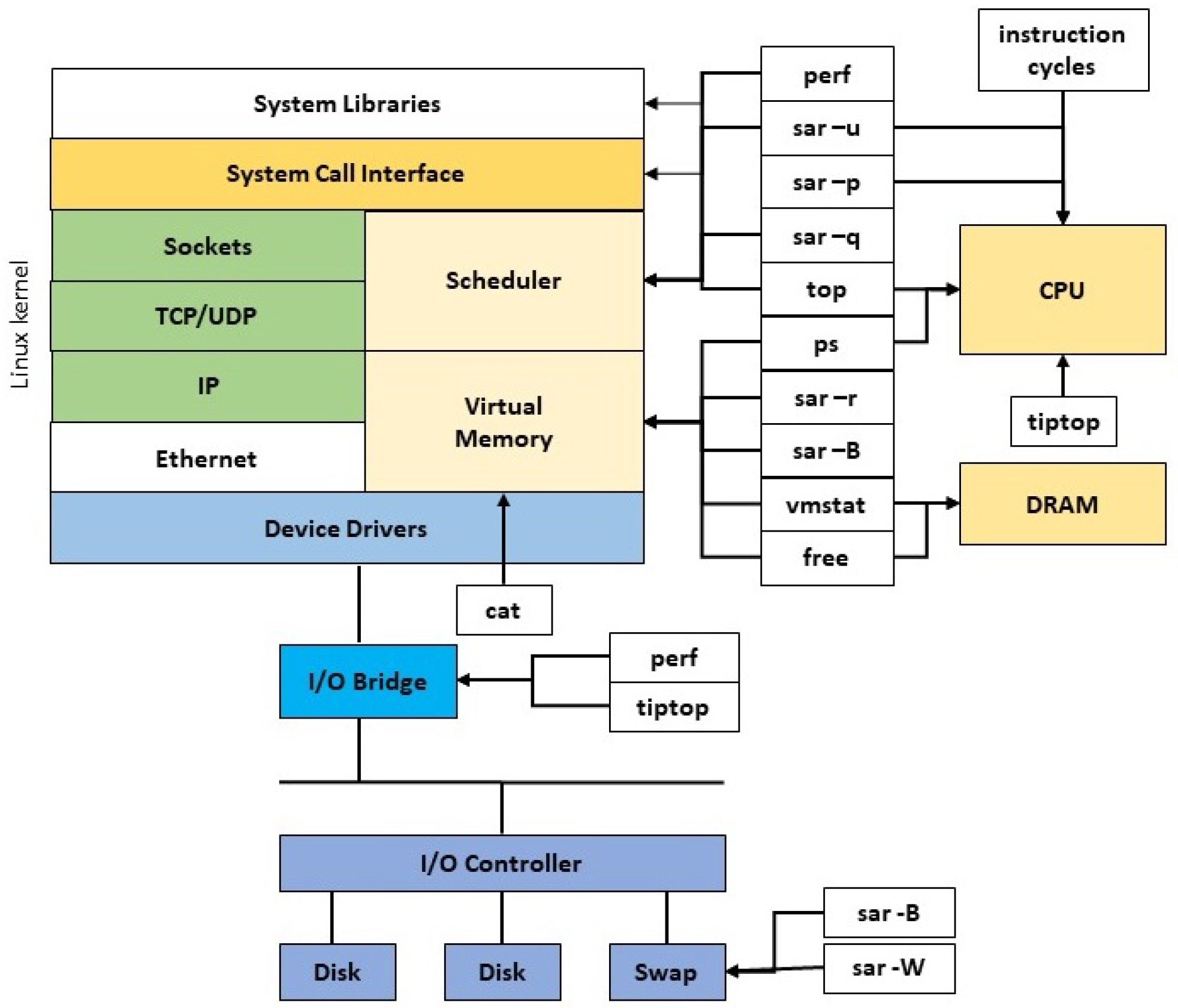
Numerous software monitoring tools that measure key CPU and memory metrics across all four ECUs were required, the specific areas of research within each system and the associated tools can be seen in
Figure 4. In turn, these specific resources were observed by applying the USD methodology to each ECU. The following software tools were used to monitor and record CPU and memory utilisation, saturation and duration for each modelled ECU when the ECU was in an idle state and when the automotive function was running in both native and container operational modes.
7.1. Vmstat
Used to identify potential resource bottlenecks and corroborates the data collected from several other monitoring tools. The metrics monitored included:
The number of processes/tasks waiting runtime (R state)
The number of processes/tasks waiting in an uninterruptible sleep (D state)
The amount of free or idle system memory
Memory swap information
CPU statistics including %us, %sy and %id.
7.2. Free (Free and Used Memory)
This tool displays various memory statistics, including the total available free memory, used swap and physical memory. Other observed metrics from this software monitoring tool include the buffers column that reports the amount of allocated memory in use. The cache column reports the amount of allocated memory swapped to disk or unallocated if other tasks require that resource.
7.3. Schedstat (Scheduler Statistics)
OS kernel schedule statistics regarding individual processes. The values obtained are a snapshot of the average time totals a process has spent on the CPU or waiting for an available time slot on the CPU at the point when the schedstat command is run. schedstat describes three statistics which define overall scheduling latency:
The sum of time spent running processes in the processor.
The sum of time spent waiting to run a task (often measured in jiffies).
The number of time slices or voluntary and involuntary switches running on the CPU.
Automotive ECUs often have real-time operational requirements which habitually relate to system safety. Understanding the overall scheduling latency between the native/bare metal and container ECU operational modes is a crucial factor of this research.
7.4. Sar (System Activity Reporter)
The sar monitoring tool is used extensively throughout this research. It is vital for monitoring ECU resource use for both CPU and memory saturation and utilisation. The following configuration flags can be applied to this tool to monitor and record specific CPU and memory saturation and utilisation metrics:
sar -B - reported system paging statistics.
sar -q – monitors CPU load, run queue and process list lengths.
sar -R - monitors general memory statistics.
sar -r - reports on the percentage of system memory used.
sar -W - monitors swap in and swap out rates.
7.5. Perf (Performance Analysis)
perf is a software tool that provides system-wide statistical profiling information for analysing the performance of an application in execution. perf enhances understanding of the system scheduler properties (sched latency and sched timehist) that measure latencies at the task/process level and latency events, including the sched-in count, total run time, and average run time per sched-in count.
7.6. Pidstat (Process Statistics)
Monitors individual kernel tasks and corresponding child processes. The metrics displayed relate to the time spent by a task executing at the user and system level.
7.7. Top / htop / nmon
These are all dynamic software monitoring tools providing real-time data regarding numerous aspects of the host system, including CPU, memory and processes. They provide a real-time monitor for ECU functional software in execution at the process and thread-level and report any other processes invoked during the native and container test modes. These tools were used to validate the accuracy of the results obtained from the other more specialised tools.
8. System Saturation
CPU saturation is the amount of extra work that cannot be serviced by the CPU and has to be queued, thus adding latency [
14]. CPU saturation is a crucial metric in determining overall system performance. A CPU is considered saturated when the system load average increases to a value above the number of system processors/cores and maintains that value for an extended period of time. In this instance, CPU load is calculated as the sum of processes in execution or waiting for execution at any given time. A system which is over saturated experiences:
A longer wait for a process in an idle or wait state.
An increase in overall request-response times.
A subsequent increase in CPU utilisation.
Therefore, CPU saturation also refers to the number of processes, either queued or blocked awaiting CPU time. If the number of instructions to be processed is more than the processor can accommodate due to its speed, the program in execution is considered CPU bound. An example of a CPU bound process is an algorithm which requires a large number of calculations that hold the CPU for as long as the scheduler allows. The saturation tests conducted as part of this research use the standard inbuilt OS scheduler (SCHED_OTHER), a conventional timed-shared process.
8.1. System Load
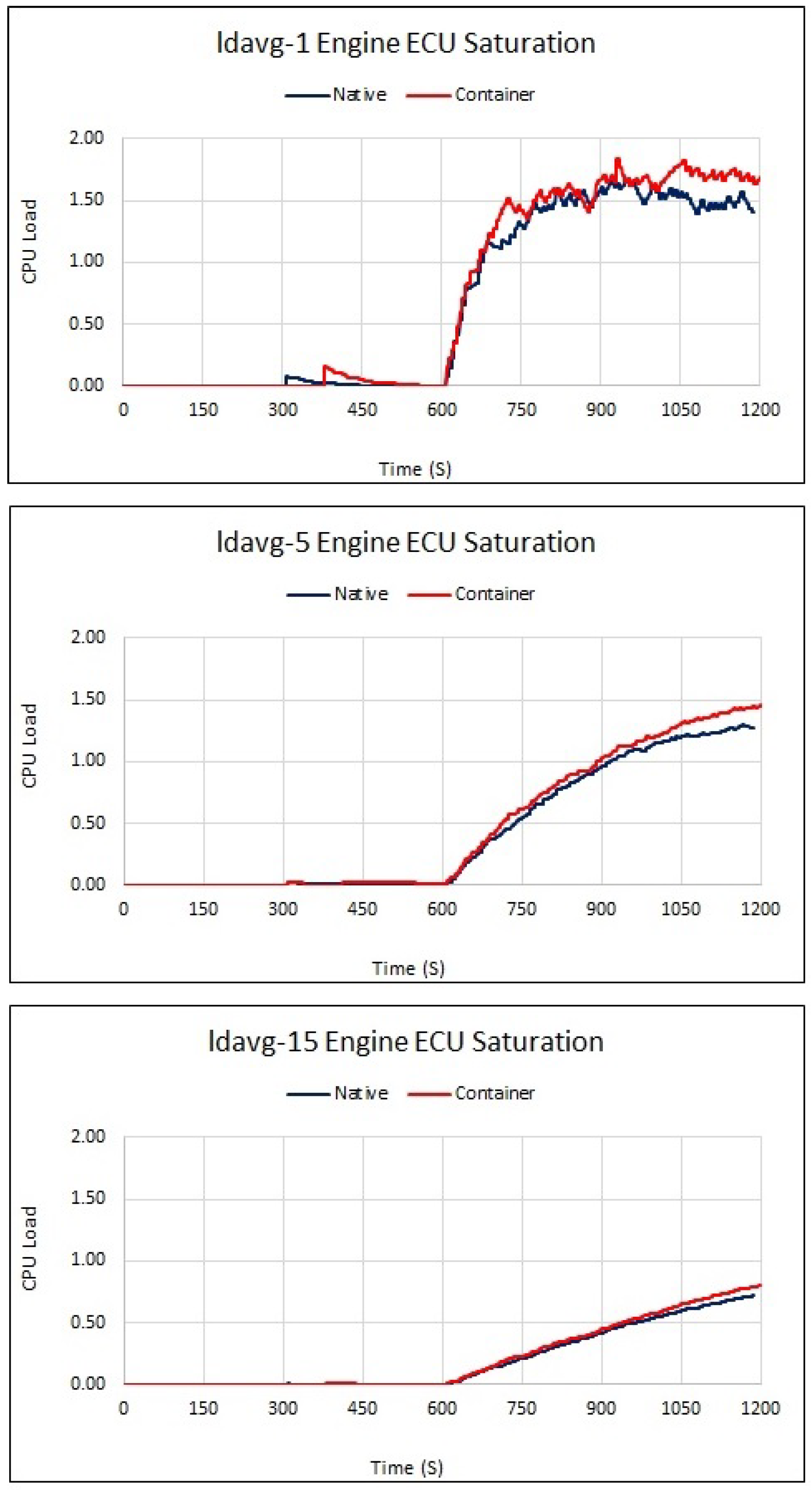
System load is calculated as the average number of processes/tasks running (R state) and the number of processes/tasks in uninterruptible sleep (D state). The ldavg-1 metric gives the total number of processes in both D and R states over a 60-second time frame. Both ldavg-5 and ldavg-15 are extended sampled time frames over 300 and 900 seconds and not the repeated average of the ldavg-1 results. Below is a clarification of how each load average is related:
If the average is 0.00, the system is regarded as being in an idling state
If the 5 or 15-minute average is higher than the 1-minute average, overall system load is increasing
If the 5 or 15-minute average is lower than the 1-minute average, overall system load is decreasing
If the load average in any ldavg triplet result is greater than the number of system CPUs (cores), it may affect overall system performance. Excessive load on the ldavg-1 metric would indicate, for example, short spikes in resource use due to program execution or excessive paging to disk and as such gives a brief snapshot of the most recent system activity. Suppose the ldavg-15 metric is consistently higher than the CPU/core count. In that case, it generally indicates a prolonged increase in the number of R and D state processes. It potentially represents a more persistent and protracted problem with overall system performance.
The results of system load average can be seen in
Figure 5. All CPU load averages across the base test run experienced a minimum load of zero for extended periods with a ldavg-1 peaking periodically at 0.17 (17%). The ldavg-5 and 15 results were lower than expected at 0.11 (11%) and 0.05 (5%) respectively. The average load across the entire base test run was 0.02 (2%). The ldavg-5 and 15 showed a decreasing trend over the test run, consistent with a CPU principally in an idle state.
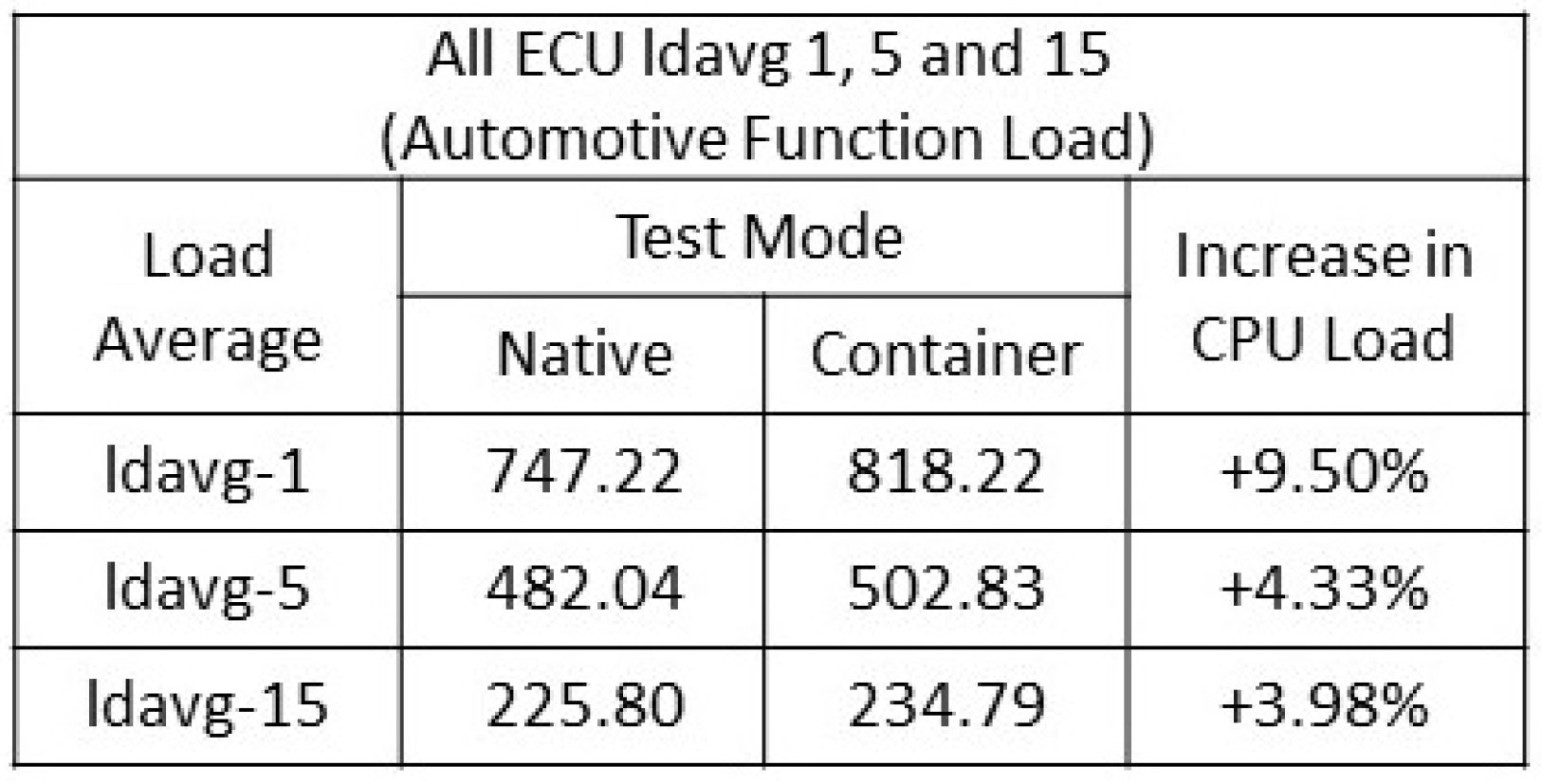
Figure 6 details the results obtained from native and container CPU load averages. The total observed function load - the combination of all the ECU CPU ldavg-1,5 and 15 load averages was observed at +9.50%, +4.33% and +3.98% respectively.
8.2. Scheduler Statistics
The scheduler must decide which process will run and which will be temporarily suspended and subsequently placed in a queue (runqueue). Enforcing process suspension is accomplished through preemptive multitasking. Upon creation, each process is provided with a portion of execution time known as a time slice, representing the amount of processor time allocated to that particular process. The two metrics monitored were time spent on CPU and time spent waiting on the runqueue.
During the container test mode, the software spent more time in execution than when in the native test mode. In the native test mode, the functional software spent a long time on the runqueue compared with the container test. As is standard in container operation, the software reserves an amount of CPU time specifically for execution. To replicate this effect during native execution, the native process priority level must be elevated to enable the native task more time on the CPU, which can have a detrimental impact on other processes running on the same system.
The two tables in
Figure 7 show the time spent on CPU as well as how long a task was waiting for available CPU allocation. The increase in overall CPU saturation when all the ECUs were executing within containers did not create excessive numbers of new tasks/processes nor did it add large numbers of processes on the process list or place an unreasonable or a disproportionate load on the CPU. Notably, with the automotive function in container operation, the average overall CPU load across all ECUs was 9.44% higher than with native execution mode. These tests demonstrate that CPU saturation did not occur on any individual ECU whilst the automotive function executed within a container environment.
9. System Resource Utilisation
CPU saturation refers to the amount of work or load that is waiting to be serviced, whereas CPU utilisation is the measurement of the requirement divided by the capacity. High CPU utilisation can indicate poor application performance where processes must remain in the processor queue for other processes to complete execution. The principle CPU metrics monitored during these series of tests were:
%user - percentage of CPU utilisation while executing processes at the application (user) level and pertains to kernel activities such as servicing interrupts and resource management.
%system - percentage of CPU utilisation while running processes at the system (kernel) level.
%idle - percentage of time the CPU was inactive with no outstanding disk I/O requests.
%nice - percentage of CPU utilisation executing higher-level processes at the user level. It must also be considered when examining overall CPU utilisation - a positive value indicates higher priority user-level processes which can affect overall CPU utilisation.
%iowait - percentage of time the CPU was idle with outstanding disk I/O requests.
If the %user + %nice + %system total is equal to 100% CPU utilisation, then the workload is considered CPU bound. A constant or long-term high level of CPU utilisation can result in several adverse factors, including:
High temperatures can reduce the CPU’s operational lifetime or can cause premature failure.
An increase in overall power consumption (an essential factor in automotive systems).
A subsequent increase in CPU utilisation.
9.1. Overall CPU Utilisation
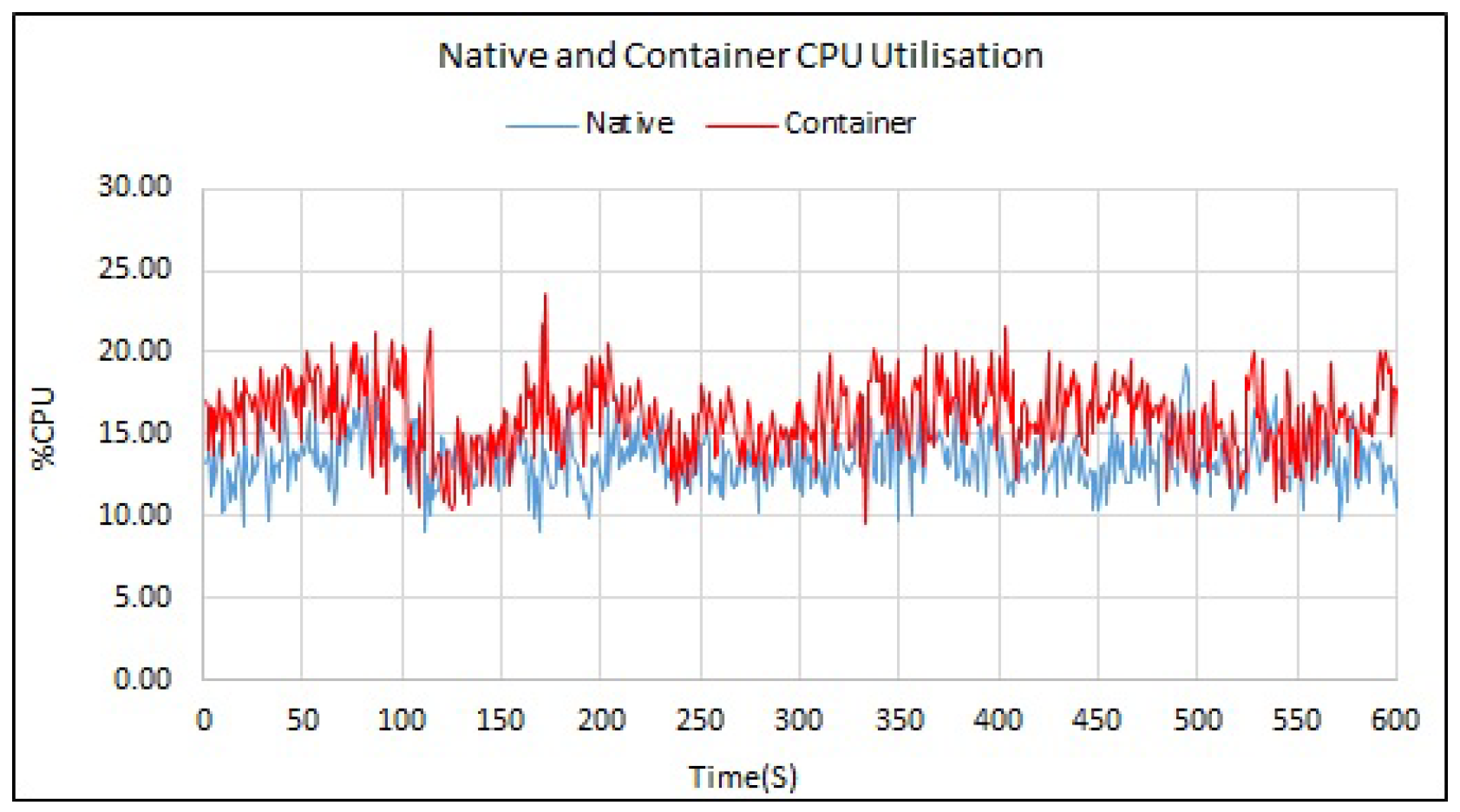
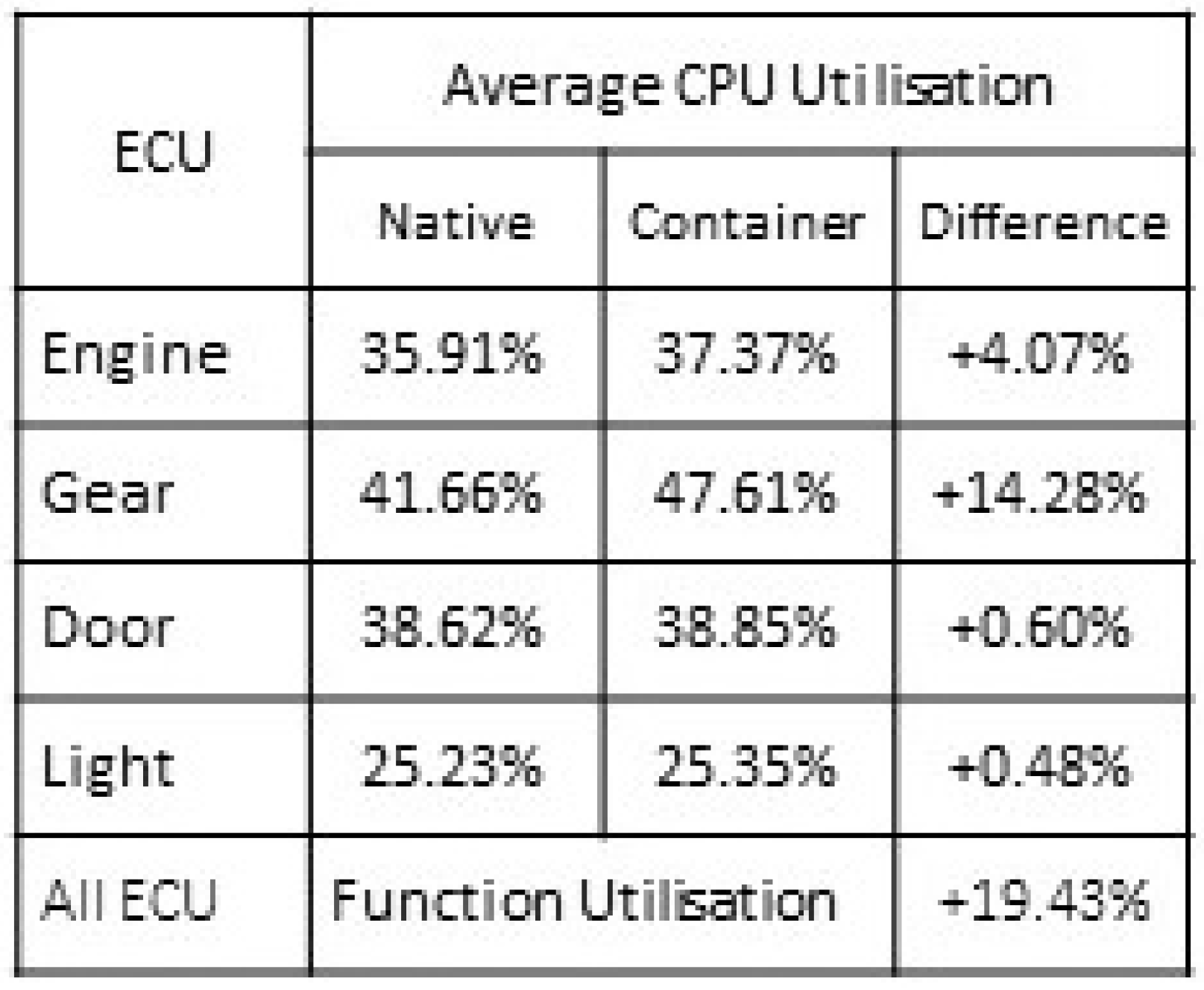
The output data from the monitoring tools iostat, mpstat, vmstat and sar all provided similar output results and were used to ensure data correctness and consistency across the modelled ECU CPU cores. The monitored metrics involved with these tools were %user, %system and % idle.
Similar to CPU saturation baseline, tests exhibited minimal amounts of recorded overall CPU utilisation, observed in
Figure 8 and
Figure 9. The %user average increase was measured at +4.01% when the script executed within the container. The %system utilisation container results show the additional required processes/tasks needed to support the container. These additions include the container shim, docker and containerd processes. The container %system utilisation represented an overall average system function increase of 7.75%. The total additional %user and %system required to support the entire modelled central locking system was 4.86% compared with the native mode of operation.
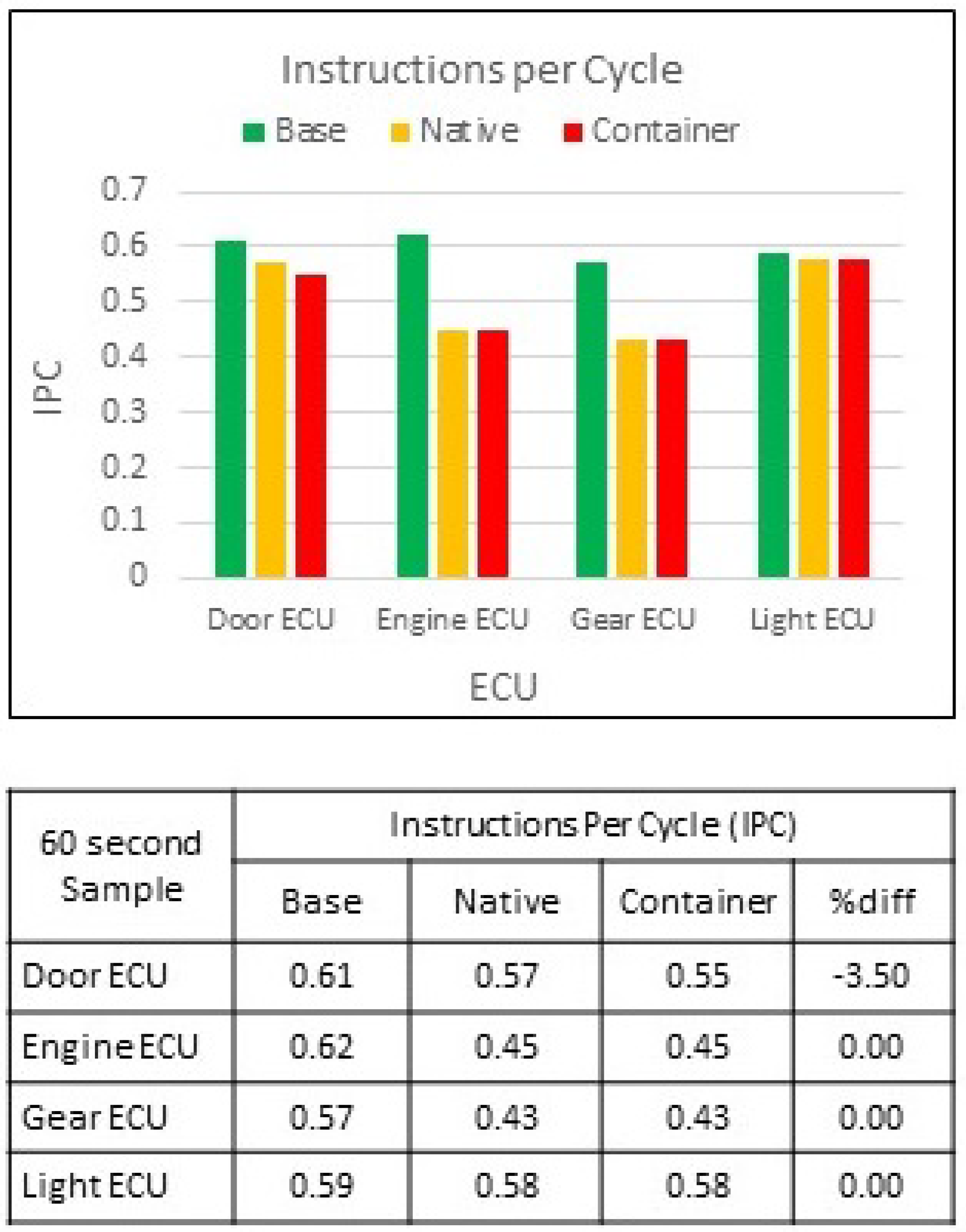
9.2. Instructions per Cycle
IPC measure how many instructions are completed during each CPU clock cycle. The modelled ECUs used for this research incorporate a quad-core ARM Cortex-A53 processor. The stated IPC value for the ARM Cortex-A53 processor is 2.0. This IPC value represents the total number of instructions that the CPU can be executed per clock cycle. The ARM Cortex-A53 IPC value was used as a benchmark during the three test modes to provide an overall value in understanding CPU utilisation concerning IPC, the results of which are shown in
Figure 10.
As the load on the CPU increases, it affects the overall IPC value. The maximum stated Cortex-A53 CPU IPC value is documented at 2.0. However, when recorded during the base operation test mode, the base level IPC value was between 0.57 and 0.62 across all four modelled ECUs. The results obtained from the native and container test modes revealed that there was very little difference between the two test mode IPC values. The Door ECU showed a slight decrease in the IPC value of -3.50% when executing within the container. The results of this particular test highlight that regardless of ECU functional operation mode, there was little to no drop in the number of instructions per second executed on the ECU processor.
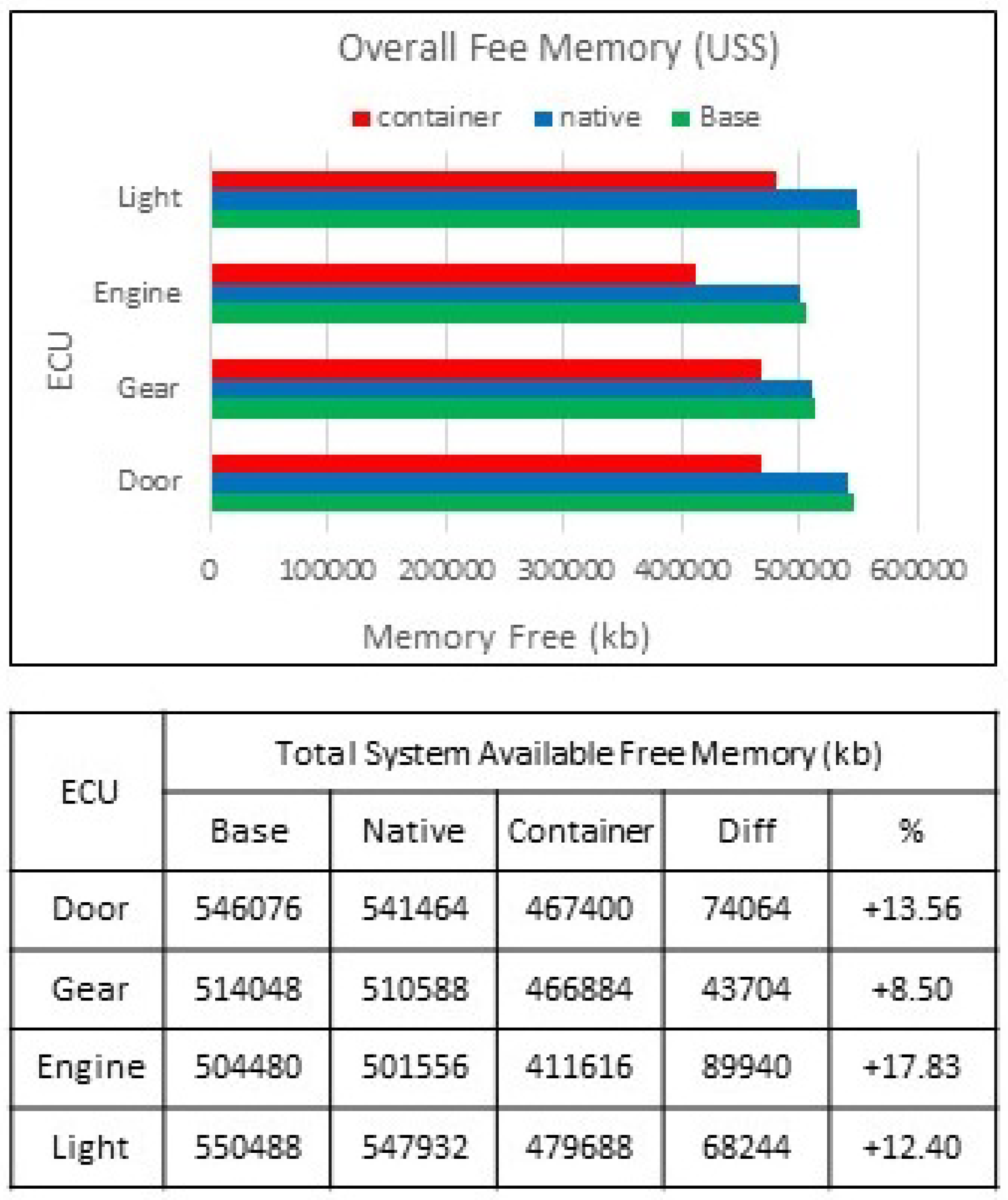
9.3. Memory Unique Set Size
Traditional memory monitoring tools focus on Resident Set Size (RSS). The RSS is the amount of physical memory occupied by a process. However, the RSS is often an overestimation of process memory use and shows little information on any memory pages shared between processes. The Proportional Set Size (PSS) details the amount of main memory allocated to a process, which includes memory allocated for the sole use of that process and the proportion of memory shared with other processes. It is essential to understand how much memory is being used proportionally and exclusively by comparing memory use between native and container test modes. The Unique Set Size (USS) is the amount of private, unshared memory allocated solely to a specific process and is a true reflection of how much memory the kernel assigns to an individual process.
The USS (
Figure 11) reveals the amount of process allocated memory. The USS test results showed that the functional software script requires considerably more memory when executing within a container environment. To support the container ECU functional script required an average of 70.93% more available system memory than native operation across all four ECUs. However, when factoring additional memory needed for container-specific processes, this average memory use is observed at 13.07%. Therefore virtualisation, regardless of the method or type, requires more available memory to accommodate each virtual instance, but this is not excessive.
10. Evaluation of Container Specific Resource Consumption
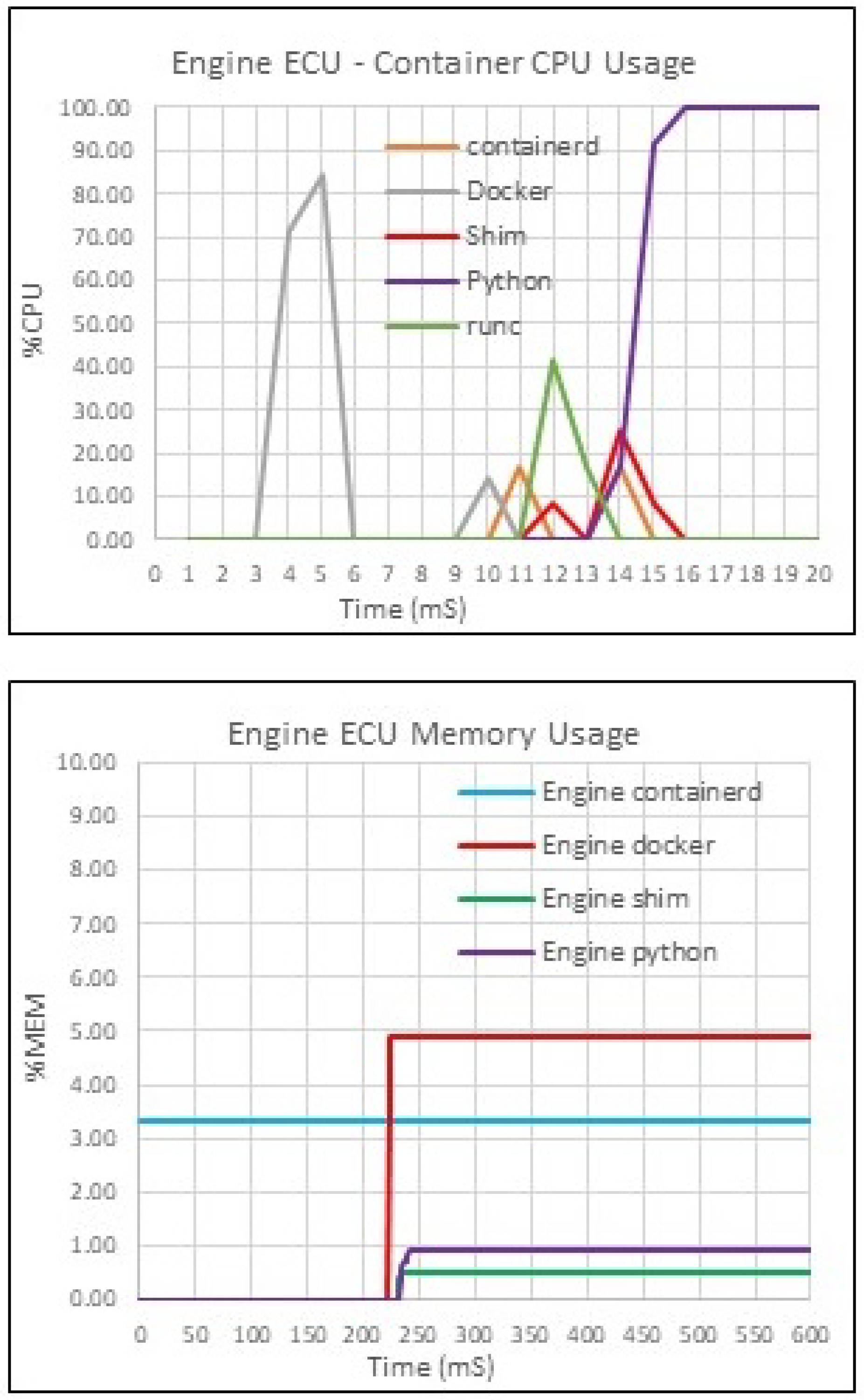
To port ECU functional software into a container-based environment, several subprocesses initiate and run in the background. Each container is an isolated and immutable client supported by the container daemon, which acts as the server. Each container is constructed from an image consisting of several layers representing process configuration and required software to support the container encased function.
Upon execution of the container software, the docker process is the first process to consume CPU resources which initiates the process of starting the container. The runc process is a lightweight container runtime process, which incorporates code that interacts with dedicated OS features related to container virtualisation execution. The runc process initialises the container and once initialisation is complete, the container is then handed over to the shim. The container shim is a process that manages the corresponding container. Once the runc and container shim have completed handover, the Python script is automatically executed.
The shim and runc processes consume negligible CPU resources, as reflected in the previous CPU utilisation section. The overall additional CPU utilisation to support the container environment was minimal. The observed container process-specific memory use is relatively static once the container is initialised and under container shim management. The containerd process is a constant process initiated during system start-up and is a continuous level from system initialisation to system shutdown. The containerd process manages the container lifecycle and is often referred to as an executor of containers.
Figure 12 highlights specific CPU and memory use by individual container process. The container daemon and shim processes are initiated to manage and maintain the container shell’s memory requirements from the start of container initialisation. The container daemon listens for API requests and manages other container configuration functions, including images, networking and volumes, so the overall memory use is notably higher. Once the shim has completed its initialisation, the python script executes and allocated memory accordingly.
11. Conclusion and Future Work
Historically, vehicle manufacturers have generally responded to increased demand for new consumer features and functions, by increasing the number of ECUs. The research presented in this text moves away from these current practices and identifies many similarities between the data centre and the automotive E/E architecture, arguing that virtualisation technologies, which have provided many benefits to the data centre, can be replicated within an automotive context. Specifically, container virtualisation offers many advantages to the automotive E/E architecture. Notably, containerisation can promote ECU consolidation and in turn, reduce overall costs as well as enhance vehicle efficiency.
11.1. Key Findings
Whilst small spikes are observed when ECU functional software is initially started, the total additional CPU load in container execution is observed at only 6.73% across all triplets and ECUs. Similarly, the results obtained from the CPU utilisation tests across both native and container test modes reveal little variance. The results obtained reveal that the average increase across all ECUs in required memory is approximately 13.07%. This is not excessive and equates in this series of tests to an overall average of 275kb of memory, which is approximately 68kb per container. This research demonstrates that containers do not have any significant detrimental impact on CPU memory and resources when running automotive software within a container. It also shows that either CPU bound or memory bound processes, or a combination of the two, are suited ideally for ECU consolidation when utilising container-based ECUs.
11.2. In Summary
The findings from this research are of significance for both the automotive industry and industries that utilise embedded systems, more broadly. Firstly, the research demonstrates that multiple ECU functionality can be incorporated into individual containers on a single hardware platform, thus consolidating individual bespoke embedded hardware and associated software. This results in a reduction of both physical hardware and overall weight, which has a direct positive impact on the fuel economy and operational range of the vehicle. Furthermore, containers offer several significant cost-savings to the automotive industry. For example, savings can be achieved through a reduction in hardware development costs – this could have a substantial impact when considering that costs related to bespoke ECU hardware development have increased by 75% since 2000 and are expected to double by 2030. Savings can also be realised through a reduction in individual ECU hardware components. In addition, by reducing costs for the manufacturer, savings can be passed onto the consumer.
11.3. Going Forward
The conducted research used standard OS and container software. However, a more optimised and efficient container-based ECU could be obtained from the use of potentially more optimised OS and container platforms, specifically through kernel scheduling algorithms. Future work will delve deeper into this aspect. Further, thorough investigation and development of container virtualisation security must be conducted, as in its present form it may not be as secure as full system virtualisation. It is primarily because isolation in containers is provided within the OS kernel rather than through separate virtual machines. Another direction of future research will be to study data transfer rates and associated benefits of container-based ECU consolidation, as it has the potential to reduce the requirement for in-car networking, which can reduce associated hardware, weight and complexity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.A.. and L.D.; methodology, N.A.; software, N.A.; validation, N.A., L.D. and D.P.; formal analysis, N.A.; investigation, N.A.; resources, N.A. , L.D. and D.P.; data curation, N.A.; writing—original draft preparation, N.A.; writing—review and editing, N.A., L.D. and D.P.; visualization, N.A..; supervision, L.D. and D.P.; project administration, L.D. and D.P.; funding acquisition, L.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
The work was part of PhD studies of the first author. The Phd studenship was funded by De Montfort University. We are thankful for the support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MDPI |
Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| ND |
Nicholas Ayres |
| LD |
Lipika Deka |
| DP |
Daniel Paluszczyszyn |
References
- H. Takada, "Introduction to Automotive Embedded Systems, Nagoya: Nagoya University" [Online] Available at: https://cse.buffalo.edu/~bina/cse321/fall2015/Automotive-embedded-systems.pdf [Accessed 16 August 2024].
- T. Nolte, H. Hansson, and L. L. Bello, "Automotive communications-past, current and future", in IEEE Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, 2005, pp. 8. [CrossRef]
- H. Hartmann, System Monitoring with the USE Dashboard. 2017. [Online] Available at: https://www.circonus.com/2017/08/system-monitoring-with-the-use-dashboard/ [Accessed 16 August 2024].
- J. Jackson, The RED Method: A New Approach to Monitoring Microservices. 2018 [Online] Available at: https://thenewstack.io/monitoring-microservices-red-method/ [Accessed 16 August 2024].
- T. Wilke, The RED Method: Key metrics for microservices architecture. 2017 [Online] Available at: https://www.weave.works/blog/the-red-method-key-metrics-for-microservices-architecture/ [Accessed 16 August 2024].
- J. Bereisa, "Applications of microcomputers in automotive electronics," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 2, pp. 87-96. [CrossRef]
- C. P. Quigley, R. McMurran, R. P. Jones, and P. T. Faithfull, " An Investigation into Cost Modelling for Design of Distributed Automotive Electrical Architectures", in 3rd Institution of Engineering and Technology Conference on Automotive Electronics, 2007, pp. 1-9.
- B. Bermejo, and C. Juiz, "Virtual machine consolidation: A systematic review of its overhead influencing factors" The Journal of Supercomputing, 2020, vol 76, issue 1, pp. 324-361. [CrossRef]
- S. Halder, A. Ghosal, and M. Conti, "Secure over-the-air software updates in connected vehicles: A survey", Computer Networks, 2020, vol. 178, Issue C. [CrossRef]
- J. Pelzl, M. Wolf, and T. Wollinger, "Virtualization Technologies for Cars: Solutions to increase safety and security of vehicular ECUs", Proceedings of embedded world conference. Nuremberg, Germany, 2008, [Online].Available: http://www.escrypt.com.
- H. Dakroub, A. Shaout, and A. Awajan, "Connected Car Architecture and Virtualization", SAE International Journal of Passenger Cars - Electronic and Electrical Systems, 2016, vol. 9, pp. 153-159. [CrossRef]
- S. Soltesz, P. Herbert, M. E. Fiuczynski, A. Bavier and L. Peterson, "Container-based operating system virtualization: A scalable, high-performance alternative to hypervisors", in Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGOPS/EuroSys European conference on computer systems, 2007, pp. 275-287. [CrossRef]
- J. Walter, M. Fakih, and K. Grüttner, "Hardware-based real-time simulation on the Raspberry pi", in 2nd. Workshop on High performance and Real-time Embedded Systems, 2014.
- B. Gregg, "Thinking methodically about performance", Communications of the ACM, 2013, vol. 56, pp. 45-51. [CrossRef]
- N. Ayres, L. Deka, and D. Paluszczyszyn, "Continuous Automotive Software Updates through Container Image Layers", Electronics, 2021, vol. 10, pp. 739. . [CrossRef]
- M. Broy, "Challenges in automotive software engineering", in Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Software Engineering, 2006, pp 33-42. [CrossRef]
- D. Reinhardt, and M. Kucera, "Domain controlled architecture", in Proceedings 3rd International Conference on Pervasive and Embedded Computing and Communication Systems (PECCS 2013), Barcelona.
- G. Heiser, "Hypervisors for consumer electronics", in 6th IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference, 2009, pp. 1-5. [CrossRef]
- D. Reinhardt, and G. Morgan, "An embedded hypervisor for safety-relevant automotive E/E-systems", in Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Embedded Systems (SIES 2014), 2014, pp. 189-198. [CrossRef]
- Felter, W., Ferreira, A., Rajamony, R. and Rubio, J., 2015, March. An updated performance comparison of virtual machines and linux containers. In 2015 IEEE international symposium on performance analysis of systems and software (ISPASS) (pp. 171-172). IEEE. [CrossRef]
- S. Kugele, D. Hettler, and J. Peter, "Data-Centric Communication and Containerization for Future Automotive Software Architectures", in IEEE International Conference on Software Architecture (ICSA), Seattle, WA, 2018, pp. 65-69. [CrossRef]
- N. Ayres, L. Deka, and B. Passow, "Virtualisation as a Means for Dynamic Software Update within the Automotive E/E Architecture", in 2019 IEEE SmartWorld, Ubiquitous Intelligence and Computing, Advanced and Trusted Computing, Scalable Computing and Communications, Cloud and Big Data Computing, Internet of People and Smart City Innovation, Leicester, United Kingdom, 2019, pp. 154-157. [CrossRef]
- M. G. Xavier, M. V. Neves, F. D. Rossi, T. C. Ferreto, and C. A. F. De Rose, "Performance Evaluation of Container-Based Virtualization for High Performance Computing Environments", in 21st Euromicro International Conference on Parallel, Distributed, and Network-Based Processing, 2013, pp. 233-240. [CrossRef]
- R. Morabito, "A performance evaluation of container technologies on Internet of Things devices", in IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), 2016, pp. 999-1000. [CrossRef]
- V. Noronha, E. Lang, M. Riegel, and T. Bauschert, "Performance Evaluation of Container Based Virtualization on Embedded Microprocessors", in 30th International Teletraffic Congress (ITC 30), 2018, pp. 79-84. [CrossRef]
- S. Saidi, S. Steinhorst, A. Hamann, D. Ziegenbein, and M. Wolf, "Future automotive systems design: Research challenges and opportunities", in Proceedings of the International Conference on Hardware/Software Codesign and System Synthesis, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Chebiyyam, R. Malviya, S. K. Bose, and S. Sundarrajan, "Server consolidation: Leveraging the benefits of virtualization". Infosys Research, SETLabs Briefings, vol. 7, pp. 65-75.
- L. Malhotra, D. Agarwal, and A. Jaiswal, "Virtualization in cloud computing". Journal of Information Technology and Software Engineering, 2014, Vol. 4, pp. 1-3. [CrossRef]
- F. Lombardi, and R. Di Pietro, "Secure virtualization for cloud computing", Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 34, pp. 1113-1122. [CrossRef]
- D. Breitschwerdt, A. Cornet, S. Kempf, L. Michor, and M. Schmidt, "The changing aftermarket game and how automotive suppliers can benefit from arising opportunities". McKinsey.
- R. Morabito, "Virtualization on Internet of Things Edge Devices With Container Technologies: A Performance Evaluation", in IEEE Access, 2017, vol. 5, pp. 8835-8850. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Scheepers, "Virtualization and containerisation of application infrastructure: A comparison", in 21st Twente Student Conference on IT, 2014, Enschede, The Netherlands. Vol. 21.
- O. Rolik, E. Zharikov, S. Telenyk, V. Samotyy, "Dynamic virtual machine allocation based on adaptive genetic algorithm", in Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Cloud Computing, GRIDs, and Virtualization, Athens, Greece, 2017, pp. 108–114.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).