1. Introduction
Cotton produces the majority of natural textile fiber in the world. Cotton fibers are extremely elongated unicellular structures developed from the outermost ovule epidermal cells through four distinct but overlapping stages, initiation, elongation (primary cell wall synthesis), secondary cell wall synthesis and maturation[
1,
2,
3]. The initiation of fibers usually undergoes from -3 days to 3 days post anthesis (DPA), with 20−30% of epidermal cells bulging out and finally differentiating into long fibers or lints [
4]. Once initiated, fiber cells undergo rapid elongation from 0 to 20 DPA and reach the final length at 25−30 DPA. Cellulose begins to deposit at around 16 DPA and continues till 40−50 DPA. At maturation and boll opening, fibers are dehydrated and collapsed with a thick secondary cell wall composed of nearly pure cellulose [
5]. The elongation stage determines the final length of cotton fibers, which is one of the most important indices of cotton fiber. Meanwhile, length is also a determinant of the weight of a single fiber, thus affecting yield. Notably, slowing-down fiber elongation generally is coupled with the onset of the secondary cell wall synthesis stage, and further influences fiber cell wall thickening and final quality [
5,
6].
Cotton fiber is one of the longest plant cells with a length-to-diameter ratio of up to 2000. Fast and polar linear elongation of cotton fiber is characteristic of vigorous expansion of the primary cell wall in the growing tip [
3]. This complex dynamic process comprises the synthesis, transport, and deposition of cell wall components, remodeling of membrane and cell structures, and also redirection of cell metabolism and organization [
7]. Numerous regulatory paths including transcription factors, plant hormones, signaling small molecules, and structural proteins have been reported to play roles in fiber elongation [
7,
8,
9,
10]. For example, two cell wall loosening proteins, GhRDL1 and GhEXP1, promote fiber elongation [
11]. Saturated very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) enhance fiber elongation by activating 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) oxidase (GhACOs) expression and ethylene biosynthesis [
12], and its biosynthesis responses to gibberellin (GA), brassinosteroid (BR) and strigolactone (SL) signals via key β-ketoacyl-CoA synthase (KCS) genes [
9,
13,
14].
Accumulating research reported the essential roles of transcription factors in regulating fiber elongation. Transcription factors generally function as key signaling components of phytohormones and /or direct activators/suppressors to modulate the transcription of structural genes. Transgenic cotton overexpressing BRI1-EMS-SUPPRESSOR1 (BES1), a positive BR-signaling transcription factor, produced significantly longer fiber, while its inhibition resulted in shorter fibers [
14]. GhHOX3 and GhHOX4, two homeodomain-leucine zipper (HD-ZIP) transcription factors, both positively regulate fiber elongation [
8,
15]. Overexpression of PACLOBUTRAZOL RESISTANCE 1 (GhPRE1), a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor, resulted in longer fiber [
16]. Cotton DELLA protein GhSLR1, the major repressor in the GA signaling pathway, inhibited fiber elongation, while its interacted transcription factors GhHOX3, GhZFP8 and GhBLH1promoted fiber elongation [
9,
15]. An appropriate ABA level may promote ethylene biosynthesis and fiber elongation by activating the expression of GhACO3 through the key ABA signaling transcription factor GhbZIP27a, which is preferentially expressed in the elongating fibers [
17]. GhMYB25-silenced cotton altered the timing of fiber elongation, leading to short fibers [
18]. GhMYB109 was important for fiber elongation and silencing GhMYB109 results in shorter fiber [
19]. GhMYB212 directly regulates the expression of sucrose transporter GhSWEET12 transporting sucrose into expanding fibers [
20]. GhWRKY16 participates in fiber elongation by directly regulating the expression of
GhMYB25,
GhHOX3,
GhMYB109 and cellulose synthase gene GhCesA6D-D11 [
4]. Recently, GhMYB86 was found to negatively affect fiber elongation by directly activating a tubulin gene GhTUB7 [
21]. Nevertheless, plenty of transcription factor genes significantly expressed in elongating fibers remained to be functionally characterized, and more work was necessary to comprehensively clarify the molecular network regulating cotton fiber elongation.
In this study, we identified an R2R3-MYB transcription factor (GhMYB201) that is specifically expressed in the cotton fiber rapid elongation stage. Knocking out GhMYB201 significantly decreased the fiber length. Further study revealed that GhMYB201 promoted fiber elongation by directly activating the expression of cell wall loosening genes (GhRDLs), and very-long-chain fatty acid synthase genes (GhKCSs). Our results provide a new insight into the molecular mechanism regulating cotton fiber elongation by revealing the function of GhMYB201, a positive regulator, that plays a vital role in cotton fiber development.
2. Results
2.1. GhMYB201 Is a Transcriptional Activator Preferentially Expressed in Elongating Fibers
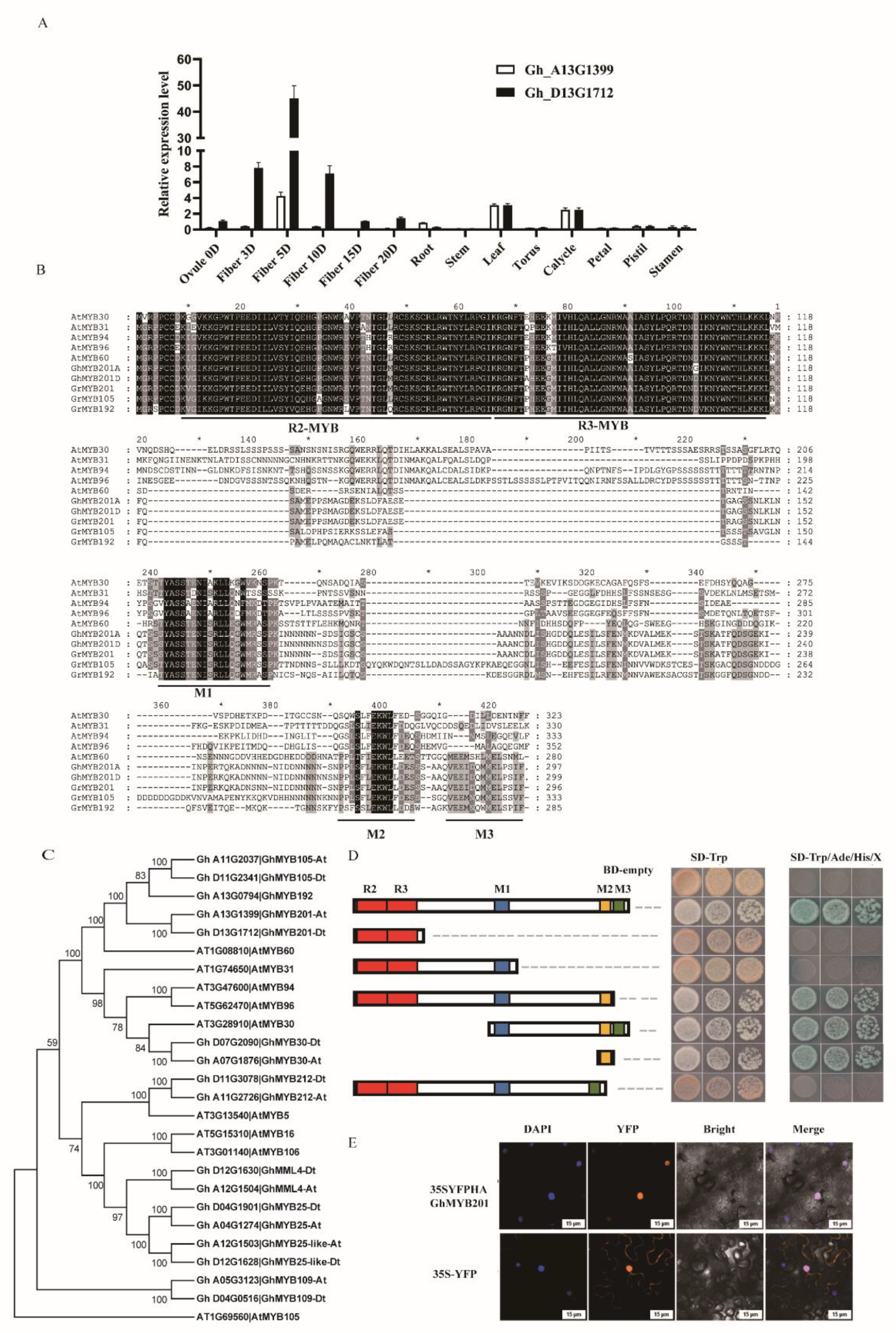
Based on the previously published transcriptomic data [
22], 24 transcription factor genes preferentially expressed in elongating fibers (enrichment fold >3 and enrichment factor > 50) were identified (
Table S1). Among them, two homologous GhMYB201 genes (
Gh_D13G1712 and
Gh_A13G1399, named as
GhMYB201Dt and
At, respectively) had the highest enrichment factors, and qRT-PCR analysis indicated that both GhMYB201 genes were preferentially expressed in elongating fibers, with maximum expression levels in 5 DPA fibers (
Figure 1A,
Figure S1). GhMYB201s shared high similarity with Arabidopsis AtMYB60, with conserved R2 and R3-MYB domains, and M1, M2 and M3 motifs (
Figure 1B). Phylogenetic analysis indicated that GhMYB201s and closely related GhMYB105 and GhMYB192 [
23], were homologous to AtMYB60 (
Figure 1C), different from previously reported R2R3-MYB proteins involved in the regulation of the fiber initiation and growth such as GhMYB25 [
18], GhMYB25-like [
24], GhMYB109 [
19], GhMYB212 [
20] and GhMYB30 [
25].
When transformed into Yeast, GhMYB201 fused with the GAL4 DNA-binding domain exhibited strong transcriptional activation activity on the downstream marker genes (
Figure 1D). The following domain truncation analysis indicated that the transcriptional activation activity was due to the M2 motif conserved in AtMYB60 group and related AtMYB30 group (
Figure 1C, 1D). Furthermore, GhMYB201D was fused to yellow fluorescent protein (YFP), and transiently expressed in tobacco leaves. Based on the overlapping signal of the YFP signal and 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining, the YFP-HA-GhMYB201 protein was exclusively localized in the nucleus (
Figure 1E). Consistent with sequence and expression analysis, these data suggested that GhMYB201s functioned as a transcriptional activator in elongating cotton fibers.
AtMYB60 is involved in the transcriptional regulation of stomatal movements in Arabidopsis and its null mutant (
atmyb60-1) led to a constitutive reduction of stomatal opening [
26,
27]. To explore the biological function of GhMYB201,
GhMYB201 was overexpressed in Arabidopsis (
Figure S2B). Under the same growth condition, the
GhMYB201 overexpressing leaves showed a significant increase in stomatal diameter compared to wild type (WT), in contrast to the
atmyb60-1 mutant (
Figure S2A, C). This observation suggested that
GhMYB201 was a functional homolog of Arabidopsis
AtMYB60.
2.2. GhMYB201 Knockout Negatively Affected Fiber Elongation
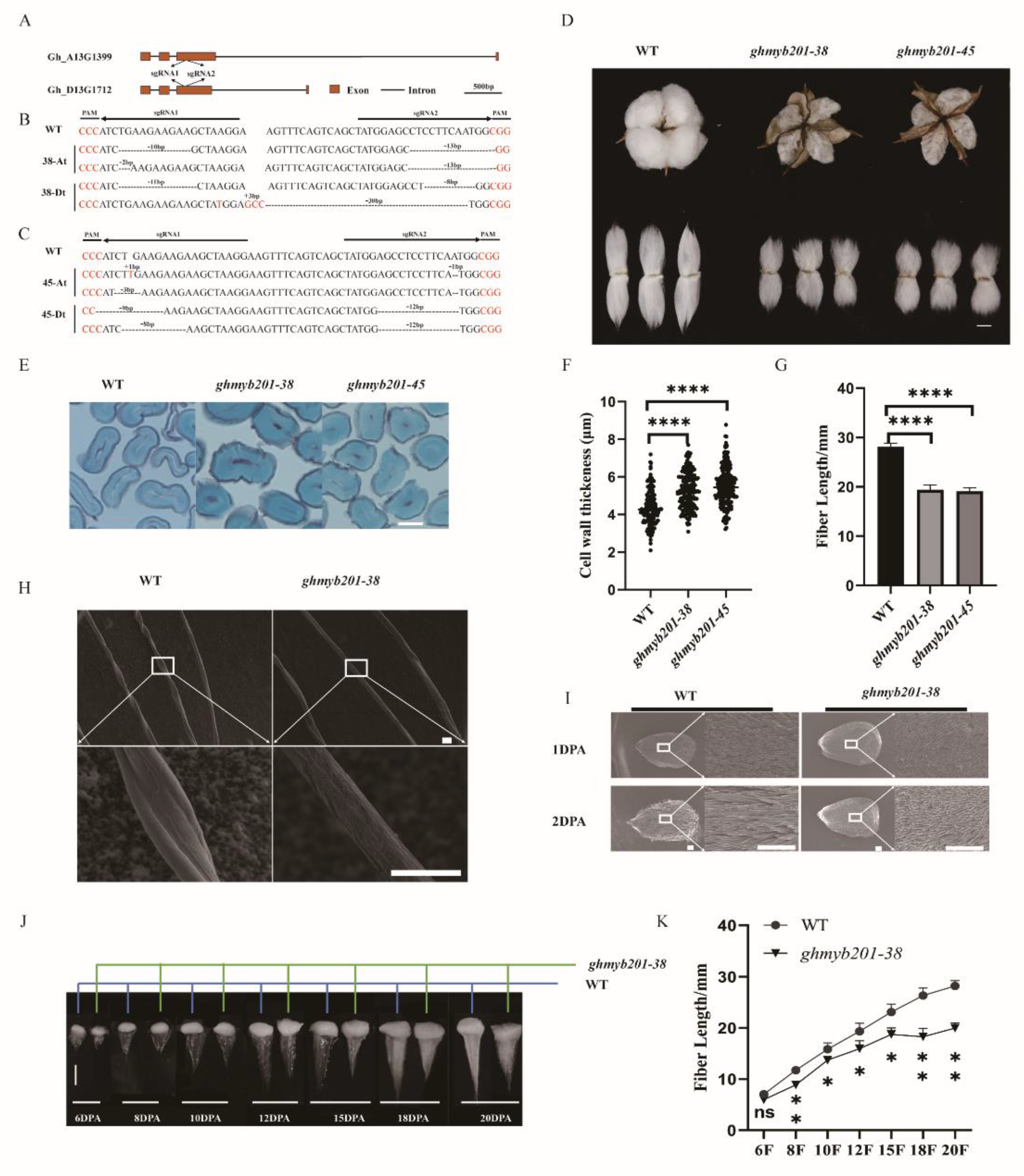
To explore the biological functions of
GhMYB201s in fiber development, we generated stable
GhMYB201 knockout mutants using CRIPSR-Cas9 mediated genome editing. Several independent knockout lines showing similar phenotypic variations were obtained. Two of them (
ghmyb201-38 and
-45) were chosen for full characterization. At the guide RNA-targeted sites located in the third exon of
GhMYB201s, lines #38 and #45 carried mutants in all four chromosomes, causing shifting or Indel (
Figure 2A, B, C,
Figure S4) and probably disrupting all the functional GhMYB201 proteins.
Instead of fluffy fibers observed in wild-type opening bolls, mature fibers of the GhMYB201 knockout mutants were tightly attached around seeds, somewhat like dead locule (
Figure 2D). Unlike the traditional dead locule, e.g. immature fiber mutant [
28], resulted from incomplete development of secondary cell wall, GhMYB201 knockout fibers had thicker secondary wall (
Figure 2E, F) and significantly increased microware value (
Table 1), compared to wild type. In addition, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observation indicated that
GhMYB201 knockout fibers had more round and rough appearance and less conversion (
Figure 2H). Finally, mature fiber length was significantly decreased in
GhMYB201 knockout lines compared with the wild type (
Figure 2D, G,
Table 1). We further compared the development dynamics between the
GhMYB201 knockout line and wild type cotton. It was found that the fiber length of
GhMYB201 knockout line was significantly shorter than that of the wild type form 2 DPA through 20 DPA (
Figure 2I, J, K), suggesting a lower elongation rate in the knockout fibers. We also observed that fast fiber elongation ceased at 15 DPA in the
GhMYB201 knockout line, 3 days earlier than that in the wild type (18 DPA) (Fig 2I, J, K). Consistently, the birefringence of fiber walls was observed in the
GhMYB201 knockout line at 13 DPA (
Figure S3), indicating an earlier onset of secondary wall deposition in the knockout fibers. Therefore, the knock-out of
GhMYB201 led to impaired fiber elongation and final length by decreasing the rate and also the duration of fiber elongation.
2.3. GhMYB201 Transcriptionally Activates Cell Wall Loosening Related Genes
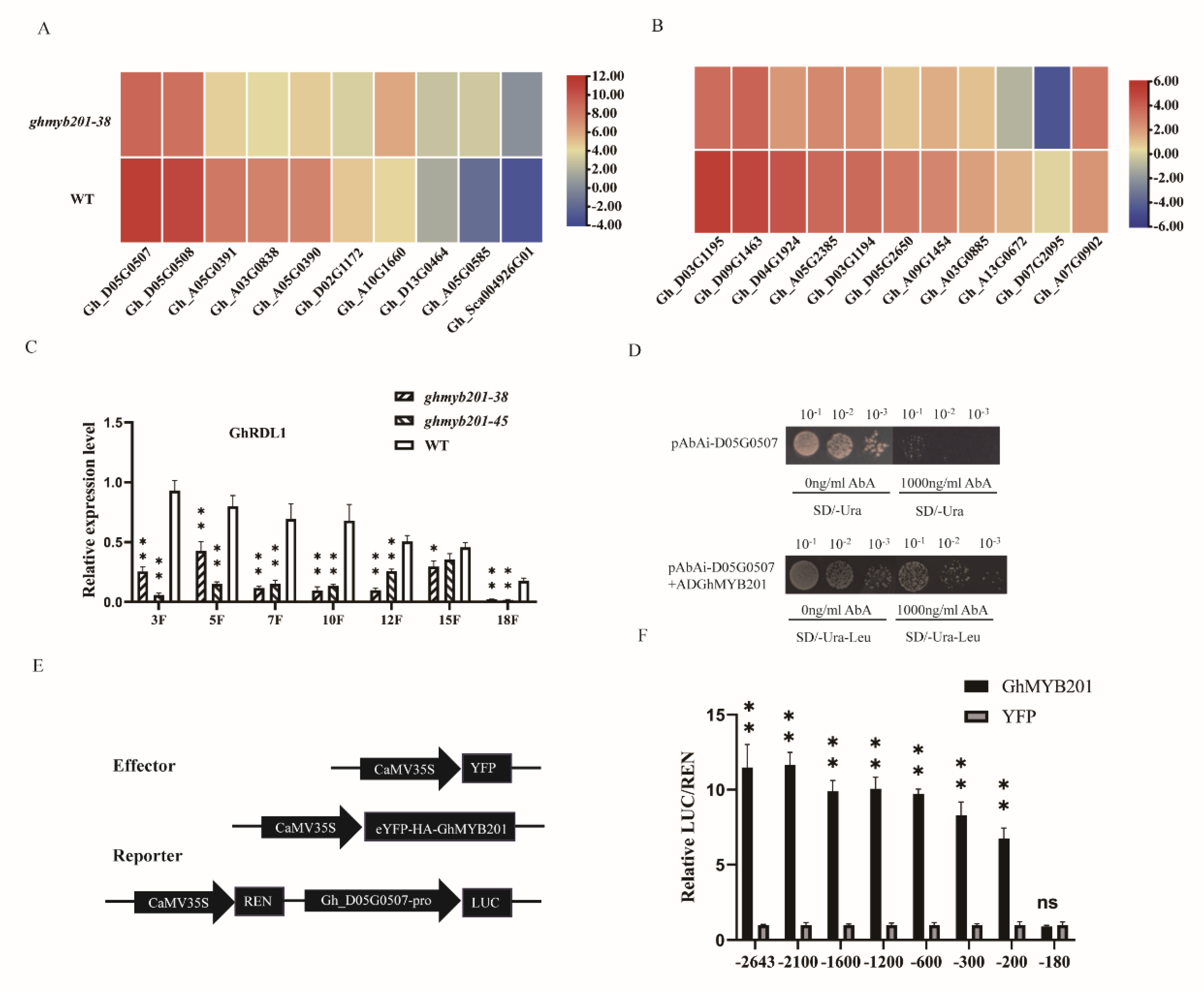
To identify GhMYB201-regulated genes in elongating fibers, we performed transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis of 7 DPA fibers from wild-type and
GhMYB201 knockout line (
ghmyb201-38). A total of 5762 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), including 1674 downregulated and 4088 upregulated genes were identified in knockout elongation fibers (
Figure S5). In the significantly downregulated DEGs (i.e. GhMYB201 activated genes in wild-type fibers), we recognized a series of cell wall loosening related genes (
Figure 3A, B), especially BURP domain protein (RDL, AtRD22-Like) and expansin genes [
11].
Further, GhRDL1 (
Gh_D05G0507) with a high expression level in elongating fibers was selected to analyze whether it could be transcriptionally activated by GhMYB201. qRT-PCR analysis showed that
GhRDL1 transcript levels in elongating fiber of 3−18 DPA were significantly decreased in GhMYB201 knockout lines compared with WT (
Figure 3C). In Yeast-one-hybrid (Y1H) assay, yeast cells harbored with pGADT7-GhMYB201 and pAbAi containing promoter regions of
GhRDL1 survived on selective medium containing aureobasidin A (AbA; 1000 ng/mL), suggesting that GhMYB201 interacted with the promoter of
GhRDL1 in yeast (
Figure 3D). Dual-luciferase (LUC) fluorescence assay was performed to detect the transcriptional activation activity of GhMYB201 on the
GhRDL1 promoters of various length. As shown in
Figure 3E and F, GhMYB201 could bind the
GhRDL1 promoter and activate the expression of the downstream reporter gene (firefly luciferase, LUC), and further, the binding site was located in a 20-bp fragment (-200 bp and -180 bp upstream of ATG). These results collectively demonstrated that GhMYB201 activated the expression of cell wall loosening genes in elongating cotton fibers.
2.4. GhMYB201 Activates the Expression of GhKCSs and Changes the VLCFA Contents
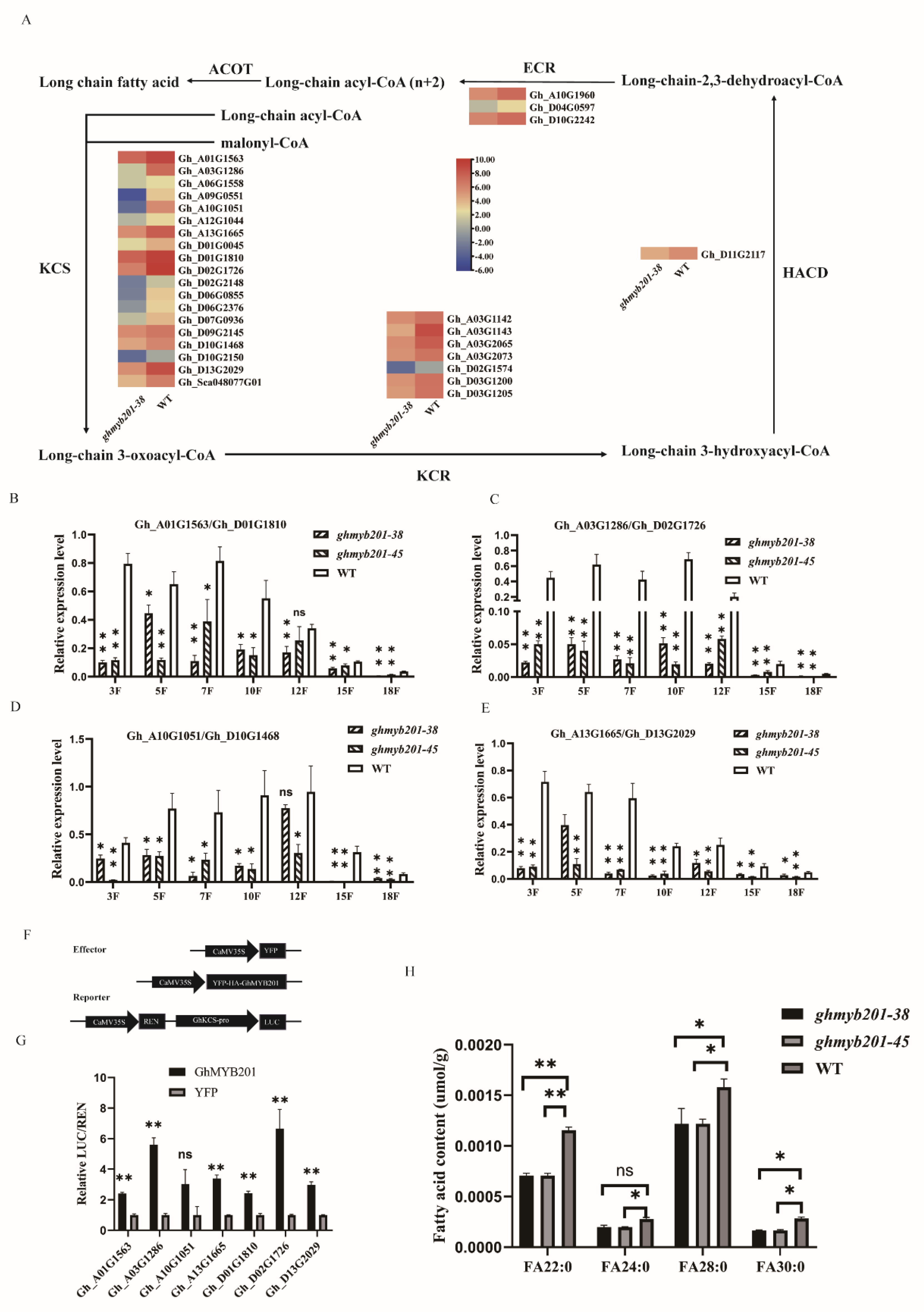
KEGG and GO enrichment analysis of the downregulated DEGs showed that multiple VLCFA-related processes including fatty acid elongation, fatty acid biosynthesis, biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acid degradation, and fatty acid metabolic process were significantly enriched (
Figure S4B and C). VLCFAs, synthesized via the fatty acid elongation pathway, are important components that promote cotton fiber elongation [
9,
12,
14]. Further analysis indicated that four out of five enzymes in the fatty acid elongation pathway, namely 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase (KCS), very-long-chain 3-oxoacyl-CoA reductase (KCR), very-long-chain (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratase (HACD) and very-long-chain enoyl-CoA reductase (ECR) were downregulated in
GhMYB201 knockout line compared with the wild type (
Figure 4A). qRT-PCR analyses consistently indicated that the expression level of the 8
GhKCSs in elongating fibers of 3−18 DPA was significantly decreased in knockout lines compared with the wild type (
Figure 4 B-E). Furthermore, the contents of saturated VLCFAs (C22:0, C24:0, C28:0, and C30:0) in
GhMYB201 knockout 10 DPA fibers were significantly lower than those of WT (
Figure 4H). Finally, the Dual-luciferase assay showed that GhMYB201 could strongly activate the expression of the downstream firefly luciferase gene (
Figure 4F and G), suggesting that GhMYB201 could bind to the promoter of
GhKCSs and activate their transcription. These data indicated that GhMYB201 promoted VLCFA biosynthesis in elongating fibers via activating VLCFA synthase genes.
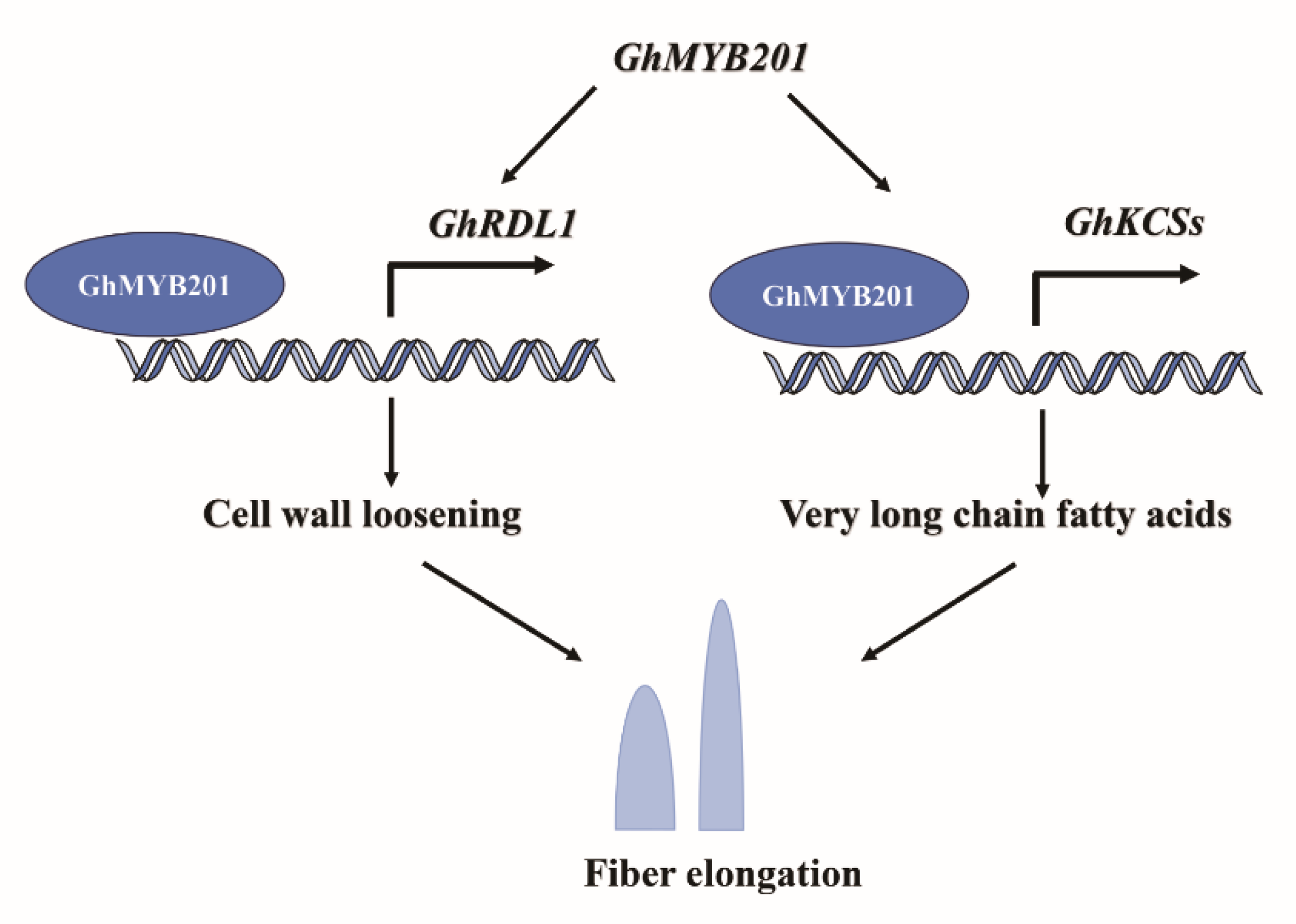
Taken together, our results support the function of GhMYB201 in fiber elongation. GhMYB201 promotes cell wall loosening via activating the expression of
GhRDLs and increases the very-long-chain fatty acid (VLCFA) levels by upregulating the β-ketoacyl-CoA synthase genes (
GhKCSs), which results in elongated fibers (
Figure 5). Our results provide a new insight into the molecular mechanism regulating cotton fiber elongation by revealing the function of GhMYB201 in cotton fiber development and contribute to improving fiber quality through GhMYB201 gene manipulation.
3. Discussion
Transcription factors play essential role in regulating the elongation or primary cell wall synthesis of cotton fiber. A series of transcription factors have been reported to promote fiber elongation via activating structural genes and/or responding to various stimuli, including phytohormone signals. Nevertheless, a lot of transcription factors still need to be functionally dissected to understand the regulatory mechanism of fiber elongation comprehensively. In this study, an R2R3-MYB transcription factor gene GhMYB201, preferentially expressed in elongating fibers, was characterized and functionally verified via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing. GhMYB201s was homologous to Arabidopsis AtMYB60, and characterized as a typical transcription factor with nuclear location in tobacco and transactivation activity in yeast (Fig, 1D, E). Knocking-out of GhMYB201s significantly reduced the rate and duration of fiber elongating, and the final length of mature fibers. Furthermore, we demonstrated that GhMYB201 can bind to the promoter and activate the transcription of cell wall loosening genes (e.g., GhRDLs), and VLCFA synthase genes (i.e., GhKCSs), thereby enhancing VLCFA levels in elongating fibers. Taken together, we revealed the functions and possible mechanism of a new transcription factor GhMYB201 in promoting fiber elongation, which added new clues to establish a complete regulatory network of cotton fiber elongation.
AtMYB60 was firstly identified as an R2R3-MYB transcription factor regulating stomatal movement and drought tolerance, which is expressed exclusively in guard cells of all epidermal tissues in Arabidopsis [
26]. It was further indicated that AtMYB60 plays dual roles under drought stress by controlling stomatal movement and root growth. At the initial stage of drought stress,
AtMYB60 expression is induced by low-level ABA to enhance root growth for increased water uptake, while severe drought stress inhibits the expression of the
AtMYB60 gene, resulting in stomatal closure and root growth inhibition [
27]. In addition, over-expression of
AtMYB60 represses anthocyanin biosynthesis in lettuce leaves [
29]. In cotton, 3 and 5-6 AtMYB60 homologs were identified in diploid and tetraploid species (
Figure 1C and S1), respectively. Previously, Xu et al [
23] reported that drought-induced
GbMYB60 (homologous to
GhMYB192,
Ghi_A13G07006/Ghi_D13G05886) was expressed in the vascular tissue and meristems, and its overexpression negatively regulates salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. GhMYB201 shared high sequence similarity with AtMYB60 (
Figure 1A), and the overexpression of
GhMYB201 promoted stomatal opening in Arabidopsis (
Figure S4), suggesting similar function of
GhMYB201 as
AtMYB60 to regulate stomatal movement. However,
GhMYB201 was specifically expressed in the elongating fiber stage, and knockout of
GhMYB201 led to significantly shorter cotton fibers (
Figure 2D), indicating that GhMYB201 functioned as a positive regulator of the rapid elongation of fiber cells. Taken together, in addition to stomatal movement, the AtMYB60 family might be involved in regulating multiple physiological processes, including root growth, secondary metabolism and cell elongation.
Cotton fiber is one of the longest plant cells and is regarded as an excellent model to explore cell growth [
3,
30]. Cotton fiber cells elongate through a combination of tip growth and diffuse-growth modes, which require repeated cell wall loosening and integration of new components into the wall. Cell wall loosening proteins, including BURP domain protein (e.g., GhRDL1), expansin (e.g., GhEXPA1) and xyloglucan endotransglycosylase/hydrolase, play important roles in promoting cotton fiber elongation [
11,
31]. Both
GhRDL1 and
GhEXPA1 are direct targets of the fiber elongation-promoting transcription factor GhHOX3; meanwhile, GA repressor GhSLR1 interacts with GhHOX3 to inhibit its transcriptional activation activity on
GhRDL1 and
GhEXPA1 [
15]. Therefore, cell wall loosening mediated by GhRDL1 and GhEXPA1 is a part of GA signaling to promote fiber cell elongation. In this study, we demonstrated that GhMYB201 can directly bind to the promoter and activate the expression of
GhRDL1, and possibly other
GhRDLs and
GhEXPAs, suggesting that GhMYB201 promoted fiber elongation via GhRDLs and GhEXPAs mediated cell wall loosening. Considering that GhMYB201 did not interact with GhHOX3 (data not shown), the GhMYB201 regulation of cell wall loosening and fiber elongation might be independent of GA signaling. Furthermore, we found that GhMYB201 might transcriptionally activate more efficiently than GhHOX3 (
Figure S6), indicating the importance of the GhMYB201 pathway to regulate fiber elongation.
Numerous studies reported that saturated very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) are involved in promoting fiber elongation [
9,
12,
13,
14,
32]. Overexpression of the key VLCFA synthase gene Gh KCS10_At (GhKCS6) significantly increases fiber length, while suppression of Gh KCS10_At leads to a decrease in fiber length [
14,
32]. VLCFAs activate ACC oxidase genes (GhACOs) expression and ethylene biosynthesis [
12]. Meanwhile, its synthase genes (especially KCSs) are up-regulated in responses to GA, BR, and SL signals [
9,
13,
14]. Biochemical and RNA-Seq analyses revealed that VLCFA biosynthesis pathways were significantly decreased in
ghmyb201 knockout fibers (Fig 4A-G). These observations indicated that VLCFA biosynthesis genes might be the direct target of GhMYB201. Besides as signaling molecules, VLCFA were also precursors of sphingolipids, seed triacylglycerols, suberins, and cuticular waxes [
3]. The mature fibers of GhMYB201 knockout cotton cohered to each other and the seed (
Figure 1D) with a coarse appearance, in contrast to the smooth appearance of the wild-type fibers (
Figure 1H). We envision that this phenotypic variation might be attributed to disturbed cuticular wax biosynthesis due to insufficient VLCFA precursor in elongating fibers, although more detailed works is still ongoing.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification and Cloning of GhMYB201s
Using the previously published transcriptomic data [
22], of 20 tissues (fibers of 5, 10, 20, and 25 DPA, ovules of -3, -1, 0, 1, 3, 5, 10, 20, 25, and 35 DPA, roots, stems, leaves, petals stamens, and pistils), we calculated the enrichment fold and the enrichment factors of all genes. The enrichment fold was calculated as the average FPKM (Fragments Per Kilobase of exon model per Million mapped fragments) in elongating fiber of 5 and 10 DPA/average FPKM in all tissues, and the enrichment factor as the enrichment fold multiply the average FPKM of elongating fibers. The transcription factor genes preferentially expressed in elongating fibers were identified with the cutoff (enrichment fold >3 and enrichment factor > 50,
Table S1).
GhMYB201s (
Gh_D13G1712 and
Gh_A13G1399) owns the highest enrichment fold and enrichment factor.
The 5 DPA fiber cDNA was used as the template to amplify
Gh_D13G1712 coding sequences with PrimeSTAR
®Max DNA Polymerase (TaKaRa, Dalian, China). The coding sequences of Gh_D13G1712 were cloned into pLGN vector linearized with
EcoRI and
BcuI to construct the pro35S-GhMYB201 vector using the ClonExpress II One Step Cloning Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). The cloned fragment was confirmed by Sanger sequencing in Tsingke (Beijing, China). Primers used in this assay are listed in
Supplementary Table S3.
4.2. Total RNA Isolation, qRT-PCR Analysis and Transcriptome Analysis
Total RNAs were extracted from various cotton tissues using the RNA Easy Fast Plant Tissue Kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China) according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer. First-strand cDNA was reverse-transcribed using a PrimeScriptTM RT reagent kit (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) with a gDNA eraser. Quantitative PCRs (qRT-PCR) were performed with SYBR-Green PCR MasterMix (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). qRT-PCR assays were performed using a CFX96 real-time PCR system (Bio-Rad, California, United States). The parameters of the qRT-PCR assay were as follows: 95 °C for 1min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s and 60 °C for 30 s. Specific primers of
GhMYB201,
GhRDL1 and
GhKCSs were designed. Cotton GhUBQ14 and GhActin2 were used as internal controls to normalize the transcript levels of target genes. Primers used in this assay are listed in
Supplementary Table S3.
Total RNAs were extracted from 7 DPA fibers of knockout line #38 and the wild type, and were detected and sequenced by Shanghai Majorbio Bio-pharm Technology Co., Ltd (
www.majorbio.com). After filtration, paired-end clean reads were assembled to genome assembly of
G. hirsutum (
https://mascotton.njau.edu.cn/Data.htm) using HISAT2 [
33,
34]. The number of fragments per kilobase per million mapped reads (FPKM) was used to normalize and calculate the expression level of each gene. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified with the cutoffs: |log2(fold change)| ≥ 1 and FDR (false discovery rate) < 0.05. The Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis was performed using topGO and KOBAS 3.0 respectively [
35,
36].
4.3. Generation of Knockout Cottons
The specific guide RNA (sgRNA) sequences targeting
Gh_D13G1712 and
Gh_A13G1399 were designed on the website (
http://crispr.hzau.edu.cn/CRISPR/) [
37]. Two sgRNA sequences (5’CCTTAGCTTCTTCTTCAGAT3’ and 5’TATGGAGCCTCCTTCAATGG3’) and tRNA fusion were amplified through PCR using the pUC-sgRNA-tRNA vector as a template and then cloned into pRGEB32-GhU6.9 expression vector digested with the
Eco31I [
38]. The pRGEB-
ghmyb201 construct was transferred into
Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain LBA4404. The Agrobacterium-mediated transformation was performed according to the previously described method [
39]. Cotton plants (
G. hirsutum cv Jimian14, and transgenic
ghmyb201 knockout lines) were grown in the greenhouse at Southwest University, Chongqing, China. On the day of anthesis, the flowers and bolls were marked as 0 DPA. Primers used in this assay are listed in
Supplementary Table S3.
4.4. Observation of Cotton Fiber Phenotype
Cotton bolls of
ghmyb201 knockout lines and wild type on similar fruit branches under the same growing conditions were harvested. The fiber length was combed and measured manually. The 6, 8, 10,1 2, 15, 18, and 20 DPA cottons were harvested. The ovules with fibers were boiled in 30% acetic acid. Then, the fiber length was measured manually. The fresh ovules and mature fibers of transgenic plants and wild-type plants were collected and observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (SU 3500, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). Cross-sections of mature fibers were performed and observed as described [
40]. The cell wall thickness of fiber transverse sections was measured by ImageJ (
https://imagej.net/software/fiji/).
About 15 grams of mature fibers for each sample were collected. The mature fibers were tested by the Center of Cotton Fiber Quality Inspection and Testing, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (Henan, China). Fiber length, strength, micronaire, and uniformity were measured with a high-volume fiber test system (Premier HFT 9000, Premier, India).
4.5. Arabidopsis Growth and Transformation
Arabidopsis thaliana, ecotype Columbia (Col-0) was used in this study. The mutant line (SALK_148646C) was obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (ABRC) (
https://abrc.osu.edu/). Seeds were surface sterilized with ethanol (75%), followed by washing 3 times with sterile water. Arabidopsis seeds were germinated and grown at 22 °C with a 16 h light/8 h dark cycle at a relative humidity of 70% following 2 days of stratification at 4 °C. The plants were transferred to soil and grown in a greenhouse after 2 weeks. The pro35S-GhMYB201 construct was introduced into
A. tumefaciens strain GV3101 by electroporation (MicroPulser, Bio-Rad, California, United States). The overexpression of GhMYB201 in Arabidopsis was transformed using floral dip [
41]. Transformed seeds were determined by PCR using the specific primers. The expression level of GhMYB201 was examined by qRT-PCR using the rosette leaf cDNA as a template. Arabidopsis AtActin2 was used as an internal control to normalize the transcript levels of target genes. Primers used in this assay are listed in
Supplementary Table S3.
Leaves of 5-week-old seedlings were used in the stomatal aperture assays. Fully expanded leaves were detached and submerged in an opening solution (5 mM KCl, 50 mM CaCl2, and 10 mM MES buffer, pH 5.6) for 2 hours. Leaf peels were prepared and observed with an optical microscope (Olympus IX81, Olympus, Japan).
4.6. Transactivation Activity Assay in Yeast and Yeast One-Hybrid Assay
To investigate the transcriptional activity of GhMYB201, the full-length or truncated coding sequence (CDS) of GhMYB201 was amplified and inserted into the pGBKT7 with
EcoRI and
BamHI restriction sites using the ClonExpress II One Step Cloning Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). The pGBKT7 bait vector was transferred into yeast strain Y2H using the high-efficiency lithium acetate transformation, and plated on a minimal synthetic defined (SD) base supplemented with -Trp medium for 3 days at 30 °C. The transcriptional activity was detected on SD/-Trp-His-Ade medium with X-α-Gal. Primers used in this assay are listed in
Supplementary Table S3.
Yeast one-hybrid (Y1H) assay was performed with the Match-maker™ Gold Yeast One-Hybrid System (Clontech). The promoter fragments of
Gh_D05G0507 were amplified and cloned into the pAbAi vectors with
HindIII and
XhoI restriction sites. The pAbAi vector was linearized with
BstBI, then transformed into Y1H Gold strain to generate a specific reporter strain and plated on SD/-Ura media supplemented with appropriate concentrations of Aureobasidin A (AbA). The full-length CDS sequences of GhMYB201 were cloned into the modified pGADT7 vector digested with
EcoRI and
BcuI. The plasmid was transformed into Y1H Gold strains containing
Gh_D05G0507-pAbAi and plated on SD/-Leu-Ura media supplemented with AbA. All strains were cultured at 30 °C for 2 to 3 days. Primers used in this assay are listed in
Supplementary Table S3.
4.7. Transient Assays in Nicotiana Benthamiana
N. benthamiana plants were grown in the growth chamber at 23 °C and 16 h light/8 h dark cycles. The
YFP and
YFP-HA-GhMYB201 fusion genes were amplified and cloned into a pLGN vector linearized with
EcoRI and
BcuI. The pro35S-YFP-HA-GhMYB201 plasmid and pro35S-YFP plasmid were introduced into
A. tumefaciens strain GV3101 by electroporation (MicroPulser, Bio-Rad, California, United States). The transformed Agrobacterium colony containing pro35S-YFP-HA-GhMYB201/ pro35S-YFP was grown overnight at 28 °C in an antibiotic selection medium containing rifampicin and kanamycin 50 mg/L. The cells were collected (5000rpm, 10min) when cultured to OD
600 of 0.8-1.0, and then resuspended in infiltration solution (10mM MgCl2, 10mM MES and 100 μM acetosyringone). The resuspended cells were injected into 5-week-old
N. benthamiana leaves. Two days later, the leaves were stained by 4,6-diamino-2-phenyl indole (DAPI, 5 μg/mL) for 10 minutes and then washed with ddH
2O 3 times. YFP fluorescence signal was excited at 514 nm by laser confocal microscope (SP8, Leica, Germany). Primers used in this assay are listed in
Supplementary Table S3.
About 2000bp of
GhRDL1, and
GhKCSs promoters were amplified from
G. hirsutum cv Jimian14 gDNA and inserted into the pGreen0800 vector with
NcoI and
KpnI restriction enzyme sites. The successfully constructed vectors were transferred into
A. tumefaciens strain GV3101 along with pSOUP vector. The pro35S-YFP-HA-GhMYB201 or pro35S-YFP were used as the effectors. The Agrobacteria harboring reporter and effectors were coinfiltrated into 5-week-old
N. benthamiana leaves as described above. The leaf discs at the infiltrated areas were collected two days later, and ground into powder in liquid nitrogen. The measurement of LUC activity was detected using a dual luciferase assay system (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). Primers used in this assay are listed in
Supplementary Table S3.
4.8. Fatty Acid Extractions
Ten DPA fibers of
ghmyb201 knockout lines and wild type were collected and ground into powder in liquid nitrogen. 100 mg samples were inactivated with hot isopropanol (75°C) using a protocol previously described [
42]. Following inactivation, 1.2mL of Extraction solvent containing chloroform : methanol: 300 mM ammonium acetate (30:41.5:3.5) (v/v/v) was added to the samples followed by incubating at room temperature for 24 h at 150 rpm. After incubation, samples were centrifuged (12000g, 10min) and clear supernatant was transferred to fresh tubes. The inactivation and extraction steps were repeated once and lipid extracts from both rounds of extraction were pooled and dried in a SpeedVac (Genevac, UK). The dried extract was resuspended in 150μL methanol and derivatized using 50mM 3-Nitrophenylhdyrazine [
43]. Metabolites were analyzed on a Jasper HPLC coupled to the Sciex 4500 MD system. In brief, individual metabolites were separated on a Phenomenex Kinetex C18 column (100 x 2.1 mm, 2.6 μm) using 0.05% formic acid in acetonitrile: water (1:9) as mobile phase A and 0.05% formic acid and 2mM ammonium acetate in acetonitrile: methanol: isopropanol (1:2:2) as mobile phase B. VLCFAs were quantitated using d31-16:0 (Sigma-Aldrich) and d8-20:4 (Cayman Chemicals) as internal standards.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we characterized an R2R3 transcription factor GhMYB201, which was localized in the nucleus. qRT-PCR analysis revealed that GhMYB201 was dominantly expressed in rapid elongation fibers. Knock out of ghmyb201 resulted in shorter fibers compared with the wild type, due to decreased expression of cell wall loosening genes (GhRDLs) and β-ketoacyl-CoA synthase genes (GhKCSs). Our findings suggest that GhMYB201 is crucial for promoting fiber elongation and provides a new genetic resour5ce for improving fiber quality.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.S. and Y.X.; methodology, Q.S., N.F., Y.W., J.Z., W.Y., and F.Y.; software, Q.S., N.F., Y.W.; validation, Q.S., J.Z., Y.L., J. C. and A.L.; formal analysis and investigation, Q.S., N.F., F.Y., and X.Z.; resources, Y.X.; data curation, Q.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.S. and Y.X.; writing—review and editing, Q.S., J.K., and Y.X.; visualization, Q.S. and N.F.; supervision, Y.X; project administration, Y.X.; funding acquisition, Y.X. and Y.W. All authors performed the experiments. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number (U2003209 to Y.X. and 32201859 to Y.W.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Haigler, C.H.; Betancur, L.; Stiff, M.R.; Tuttle, J.R. Cotton fiber: a powerful single-cell model for cell wall and cellulose research. Frontiers in plant science 2012, 3, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Woodward, A.W.; Chen, Z.J. Gene expression changes and early events in cotton fibre development. Ann Bot 2007, 100, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.M.; Zhu, Y.X. How cotton fibers elongate: a tale of linear cell-growth mode. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2011, 14, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.N.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Lu, R.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.B. Phosphorylation of WRKY16 by MPK3-1 is essential for its transcriptional activity during fiber initiation and elongation in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Plant Cell 2021, 33, 2736–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.F.; Zhao, B.; Huang, C.C.; Chen, Z.W.; Zhao, T.; Liu, H.R.; Hu, G.J.; Shangguan, X.X.; Shan, C.M.; Wang, L.J.; et al. The miR319-Targeted GhTCP4 Promotes the Transition from Cell Elongation to Wall Thickening in Cotton Fiber. Mol Plant 2020, 13, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Zeng, J.; Huang, L.; Xiong, L.; Song, S.; Zhao, J.; Hou, L.; Wang, F.; et al. Sucrose enhanced reactive oxygen species generation promotes cotton fibre initiation and secondary cell wall deposition. Plant Biotechnol J 2021, 19, 1092–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Jin, S.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Saeed, S.; et al. A comprehensive overview of cotton genomics, biotechnology and molecular biological studies. Sci China Life Sci 2023, 66, 2214–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.N.; Ni, P.; Wei, Y.L.; Hu, R.; Li, Y.; Li, X.B.; Zheng, Y. Phosphatidic acid interacts with an HD-ZIP transcription factor GhHOX4 to influence its function in fiber elongation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Plant J 2024, 118, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, P.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Jiang, B.; Wang, H.; Xiao, G. Gibberellic acid promotes single-celled fiber elongation through the activation of two signaling cascades in cotton. Dev Cell 2024, 59, 723–739 e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; He, S.P.; Xu, S.W.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.B. The transcription factor ERF108 interacts with AUXIN RESPONSE FACTORs to mediate cotton fiber secondary cell wall biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 4133–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Gou, J.Y.; Li, F.G.; Shangguan, X.X.; Zhao, B.; Yang, C.Q.; Wang, L.J.; Yuan, S.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, X.Y. A cotton BURP domain protein interacts with alpha-expansin and their co-expression promotes plant growth and fruit production. Mol Plant 2013, 6, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.M.; Hu, C.Y.; Pang, Y.; Kastaniotis, A.J.; Hiltunen, J.K.; Zhu, Y.X. Saturated very-long-chain fatty acids promote cotton fiber and Arabidopsis cell elongation by activating ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3692–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, B.; Wang, H.; Gao, R.; Friml, J.; Xiao, G. Strigolactones act downstream of gibberellins to regulate fiber cell elongation and cell wall thickness in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum). Plant Cell 2022, 34, 4816–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ge, X.; Lu, L.; Qin, W.; Qanmber, G.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, F. Brassinosteroids regulate cotton fiber elongation by modulating very-long-chain fatty acid biosynthesis. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 2114–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.M.; Shangguan, X.X.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.F.; Chao, L.M.; Yang, C.Q.; Wang, L.J.; Zhu, H.Y.; Zeng, Y.D.; Guo, W.Z.; et al. Control of cotton fibre elongation by a homeodomain transcription factor GhHOX3. Nat Commun 2014, 5, 5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Cao, J.F.; Hu, G.J.; Chen, Z.W.; Wang, L.Y.; Shangguan, X.X.; Wang, L.J.; Mao, Y.B.; Zhang, T.Z.; Wendel, J.F.; et al. Core cis-element variation confers subgenome-biased expression of a transcription factor that functions in cotton fiber elongation. New Phytol 2018, 218, 1061–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Yao, D.; Luo, M.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Ye, S. e.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Fiber-specific increase of carotenoid content promotes cotton fiber elongation by increasing abscisic acid and ethylene biosynthesis. The Crop Journal 2023, 11, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Dennis, E.S. The MYB transcription factor GhMYB25 regulates early fibre and trichome development. Plant J 2009, 59, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, L.; Li, Q.; Fan, X.; Yang, W.; Xue, Y. The R2R3 MYB transcription factor GhMYB109 is required for cotton fiber development. Genetics 2008, 180, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, M.; Wang, J.; Luo, M.; Zuo, K. Cotton fiber elongation requires the transcription factor GhMYB212 to regulate sucrose transportation into expanding fibers. New Phytol 2019, 222, 864–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, G.; He, S.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yan, X.; Hu, Y.; Tian, H.; Luo, M. Sphingolipid inhibitor response gene GhMYB86 controls fiber elongation by regulating microtubule arrangement. J Integr Plant Biol 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Fang, L.; Guan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Saski, C.A.; Scheffler, B.E.; Stelly, D.M.; et al. Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat Biotechnol 2015, 33, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.C.; Liu, H.L.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhao, J.R.; Guo, Y.W.; Long, L.; Gao, W.; Song, C.P. Heterogeneous expression of the cotton R2R3-MYB transcription factor GbMYB60 increases salt sensitivity in transgenic. Plant Cell Tiss Org 2018, 133, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walford, S.A.; Wu, Y.; Llewellyn, D.J.; Dennis, E.S. GhMYB25-like: a key factor in early cotton fibre development. Plant J 2011, 65, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Lian, B.; Hao, P.; Fu, X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, J.; Ma, L.; Yu, S.; Wei, H.; Wang, H. GhMYB30-GhMUR3 affects fiber elongation and secondary wall thickening in cotton. Plant J 2024, 117, 694–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cominelli, E.; Galbiati, M.; Vavasseur, A.; Conti, L.; Sala, T.; Vuylsteke, M.; Leonhardt, N.; Dellaporta, S.L.; Tonelli, C. A guard-cell-specific MYB transcription factor regulates stomatal movements and plant drought tolerance. Curr Biol 2005, 15, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.E.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Noh, H.; Hong, S.W.; Lee, H. A dual role for MYB60 in stomatal regulation and root growth of Arabidopsis thaliana under drought stress. Plant Mol Biol 2011, 77, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lv, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhang, T.; Guo, W. Aberrant phenotype and transcriptome expression during fiber cell wall thickening caused by the mutation of the Im gene in immature fiber (im) mutant in Gossypium hirsutum L. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Kim, J.B.; Cho, K.J.; Cheon, C.I.; Sung, M.K.; Choung, M.G.; Roh, K.H. Arabidopsis R2R3-MYB transcription factor AtMYB60 functions as a transcriptional repressor of anthocyanin biosynthesis in lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Plant Cell Rep 2008, 27, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Triplett, B.A. Cotton Fiber Growth in Planta and in Vitro. Models for Plant Cell Elongation and Cell Wall Biogenesis. Plant Physiology 2001, 127, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Burns, T.H.; Light, G.; Sun, Y.; Fokar, M.; Kasukabe, Y.; Fujisawa, K.; Maekawa, Y.; Allen, R.D. Xyloglucan endotransglycosylase/hydrolase genes in cotton and their role in fiber elongation. Planta 2010, 232, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Wu, Z.; Percy, R.G.; Bai, M.; Li, Y.; Frelichowski, J.E.; Hu, J.; Wang, K.; Yu, J.Z.; Zhu, Y. Genome sequence of Gossypium herbaceum and genome updates of Gossypium arboreum and Gossypium hirsutum provide insights into cotton A-genome evolution. Nat Genet 2020, 52, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, X.; Chen, S.; Zhou, B.; et al. Genomic analyses in cotton identify signatures of selection and loci associated with fiber quality and yield traits. Nat Genet 2017, 49, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibar, S.; Fontanillo, C.; Droste, C.; De Las Rivas, J. Functional Gene Networks: R/Bioc package to generate and analyse gene networks derived from functional enrichment and clustering. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1686–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, D.; Luo, H.; Huo, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; He, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; et al. KOBAS-i: intelligent prioritization and exploratory visualization of biological functions for gene enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, W317–W325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Lu, L.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, S.; Xing, F.; Chen, L.L. CRISPR-P: a web tool for synthetic single-guide RNA design of CRISPR-system in plants. Mol Plant 2014, 7, 1494–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Ma, Y.; Xu, J.; Liang, S.; Deng, J.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tu, L.; et al. High efficient multisites genome editing in allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) using CRISPR/Cas9 system. Plant Biotechnol J 2018, 16, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Xiao, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Deng, W.; Li, D.; Hou, L.; Hu, M.; Li, Y.; Pei, Y. GhDET2, a steroid 5alpha-reductase, plays an important role in cotton fiber cell initiation and elongation. Plant J 2007, 51, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Luo, M.; Liu, D.; Song, W.; et al. Up-regulation of GhTT2-3A in cotton fibres during secondary wall thickening results in brown fibres with improved quality. Plant Biotechnol J 2018, 16, 1735–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welti, R.; Li, W.; Li, M.; Sang, Y.; Biesiada, H.; Zhou, H.E.; Rajashekar, C.B.; Williams, T.D.; Wang, X. Profiling membrane lipids in plant stress responses. Role of phospholipase D alpha in freezing-induced lipid changes in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 31994–32002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Lam, S.M.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Niu, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Microbiota Depletion Impairs Thermogenesis of Brown Adipose Tissue and Browning of White Adipose Tissue. Cell Rep 2019, 26, 2720–2737 e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).