1. Introduction
Japan’s medical expenses are increasing every year and will exceed 45 trillion yen in 2021. In contrast, there is a serious shortage of physicians in Japan, and an increasing number of depopulated and mountainous regions are unable to maintain their medical systems [
1]. In this context, telemedicine and health management systems are attracting attention. Although face-to-face medical treatment is the basic medical practice, it has been temporarily relaxed due to Covid19 and transitional care, that is beginning to spread. In many foreign countries, health counseling Chatbot and appointment systems have been deployed before leading to face-to-face medical care [
2,
3]. In Japan, however, the penetration of such tools and culture has been slow, and their diffusion is expected along with the understanding of telemedicine among the public.
In this context, the development of Large Language Models (LLM) has been remarkable. LLM are a mechanism that can provide a wide range of knowledge with high intelligence by using large amounts of training data [
4,
5]. As a result, they have become a useful service in society by incorporating them into interactive systems. However, it is difficult to use cloud systems over external networks in the medical field because they handle sensitive patient information. Therefore, Gunma University Hospital and Center for Advanced Medical Development has developed an on-premise LLM system to promote the use of LLM, and is currently studying the possibility of using it [
6].
Health consultations are used to help patients decide whether or not to visit a hospital and to assess their own health status before and after face-to-face consultations. Currently, the company aims to collect health consultation data in cooperation with health consultations conducted by local governments.
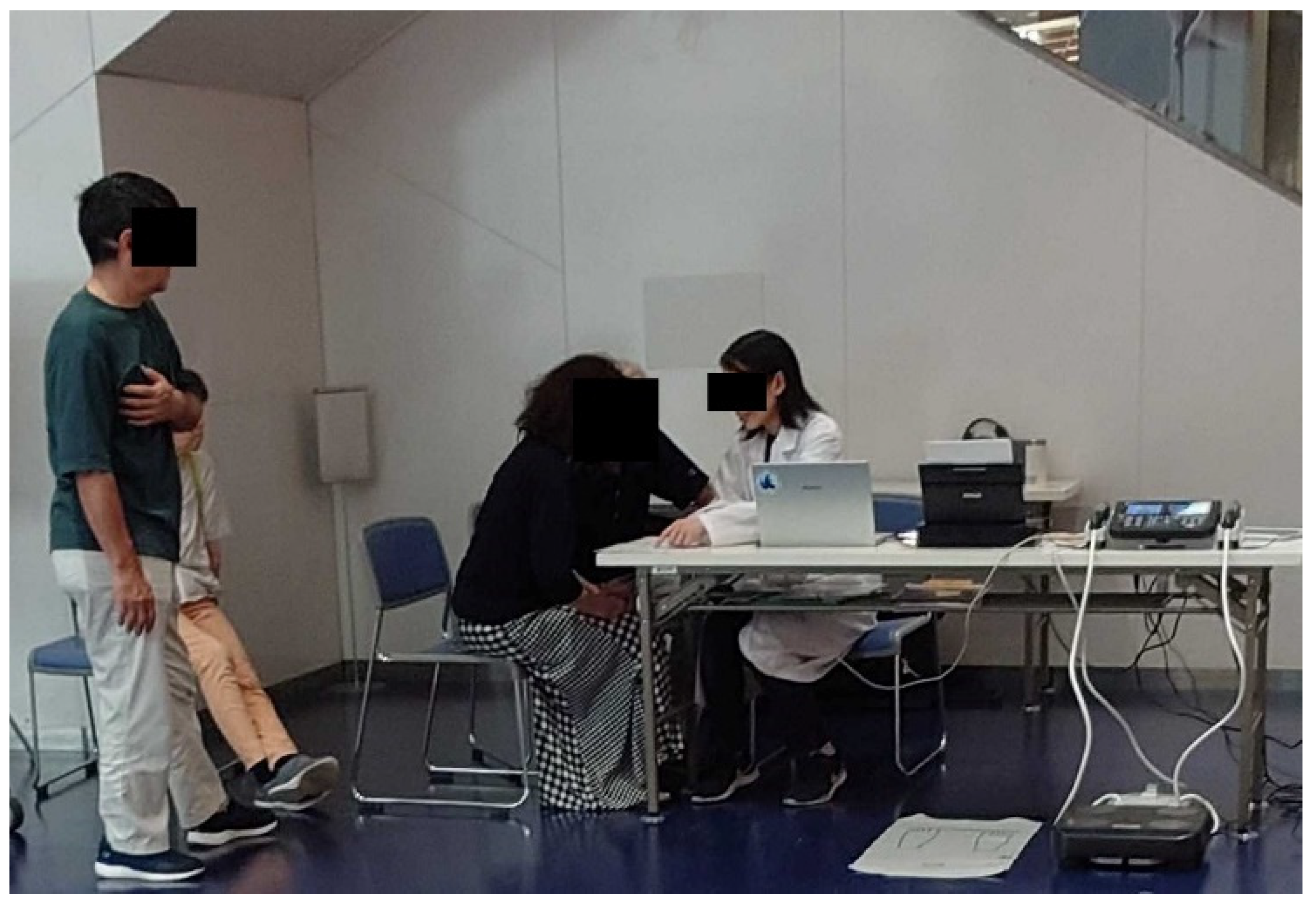
Figure 1 shows a picture of the health consultation we are collaborating with.
If this health consultation can be automated by a system or made into an online service, telemedicine Chatbots like those in other countries may become widespread. In particular, health consultation is highly effective when the patient trusts the other party and speaks interactively, which is highly compatible with technologies that mimic high intelligence, such as LLM. We evaluated the performance of health consultation systems with the Turing test and investigated technologies for health consultation and telemedicine.
2. Related Work
There is a worldwide trend toward applying digital technology to the medical field, and Taiwan has been introducing telemedicine since around 2000 [
7]. According to this report, in areas with few hospitals such as past regions and remote islands, not all medical procedures are performed in person, but only some medical procedures such as follow-up are used [
8].
While all countries emphasize face-to-face medical care, the penetration of telemedicine varies depending on legal and cultural differences [
9,
10]. In particular, electronic medical records, which are medical records, are difficult to share across hospitals, hindering the spread of digital technology in the medical field.
Initiatives to share health information using blockchain and digital technologies have been reported, and although Covid19 has led to the spread of digital technologies in the medical field, the spread of these technologies has been very slow in Japan. There is a personal health record system that manages patients’ health information, and there is also a system that allows patients to manage their own illness and health information by linking with electronic medical records and local government systems [
11]. However, the system is not covered by insurance and has not been widely used in Japan. In Germany, there are reports of PHRs being introduced for cancer patients, but the number of subjects is small 31 [
12]. This is due to challenges in understanding and explaining the benefits to family members.
As digital technology permeates the medical field, there is LLM, which stands for Large Language Models, a system that enables high intelligence and a variety of written expressions, and is rapidly becoming popular in society [
13]. Amin reports that ChatGPT, a representative service of Large Language Models, presents high performance not only in healthcare but also in education and a variety of other services [
14]. Papastratis reported that ChatGPT performed well in providing meal menus and dietary advice to diabetic patients [
15]. Sugiyama uses Large Language Models for interactive robots to establish dialogues with elderly people, and the fact that Large Language Models respond as if they were humans makes it possible to automate the system and improve interactivity [
16]. Large Language Models respond as if they were humans, making it possible to automate the system and improve interactivity.
After surveying medical students using an AI-assisted diagnostic tool called Glass AI, 96% of participants said Glass AI has increased the reliability of their diagnoses, 43% thought Glass AI lacked adequate explanations, and 68% expressed concern about risks to the physician workforce [
17]. Although there are still many challenges, the increasing willingness of patients to search for their symptoms with Large Language Models suggests that it will become more popular and active in the future. These studies and recent services lead us to believe that Large Language Models can be used to provide high-value healthcare online. Of course, there are many concerns about the introduction of Large Language Models into the healthcare system. There have been reports of the use of Large Language Models in medical education, but not in medical practice [
18]. In all reports, it is important to have a system in which a human being monitors the Large Language Models, rather than the Large Language Models themselves making decisions. This is because Large Language Models can make errors in the word “hallucination,” and errors in medical practice are related to the treatment of patients and must be verified by medical professionals. Based on this background, we expect that the relationship between medical professionals and systems in conventional diagnostic imaging will not change [
18,
19]. AI and systems will not take the place of humans in medical practice, but will create a relationship in which AI and systems will support human medical practice, and Large Language Models will play an active role in this relationship.
Against this background, health counseling LLM is highly important as a system to support healthcare professionals, and improving this performance will help reduce the burden on the medical field. However, there is no fixed diagnostic flow for face-to-face diagnosis and health counseling, and in the case of health counseling, counseling is mainly provided or not covered by insurance [
20]. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to propose and evaluate a flow based on past reports.
3. Method
Develop LLM infrastructure for health counseling and conduct Turing tests with interactive avatars. The Turing test is a test to determine whether an AI can speak like a human by hiding whether the interactive partner is human or AI. A comparative study will be conducted between the developed health counseling LLM infrastructure and general LLM. In the Turing test, three volunteers provided three minutes of health counseling and a nurse tested the system’s conversation.
3.1. Health Consultation LLM Basis System
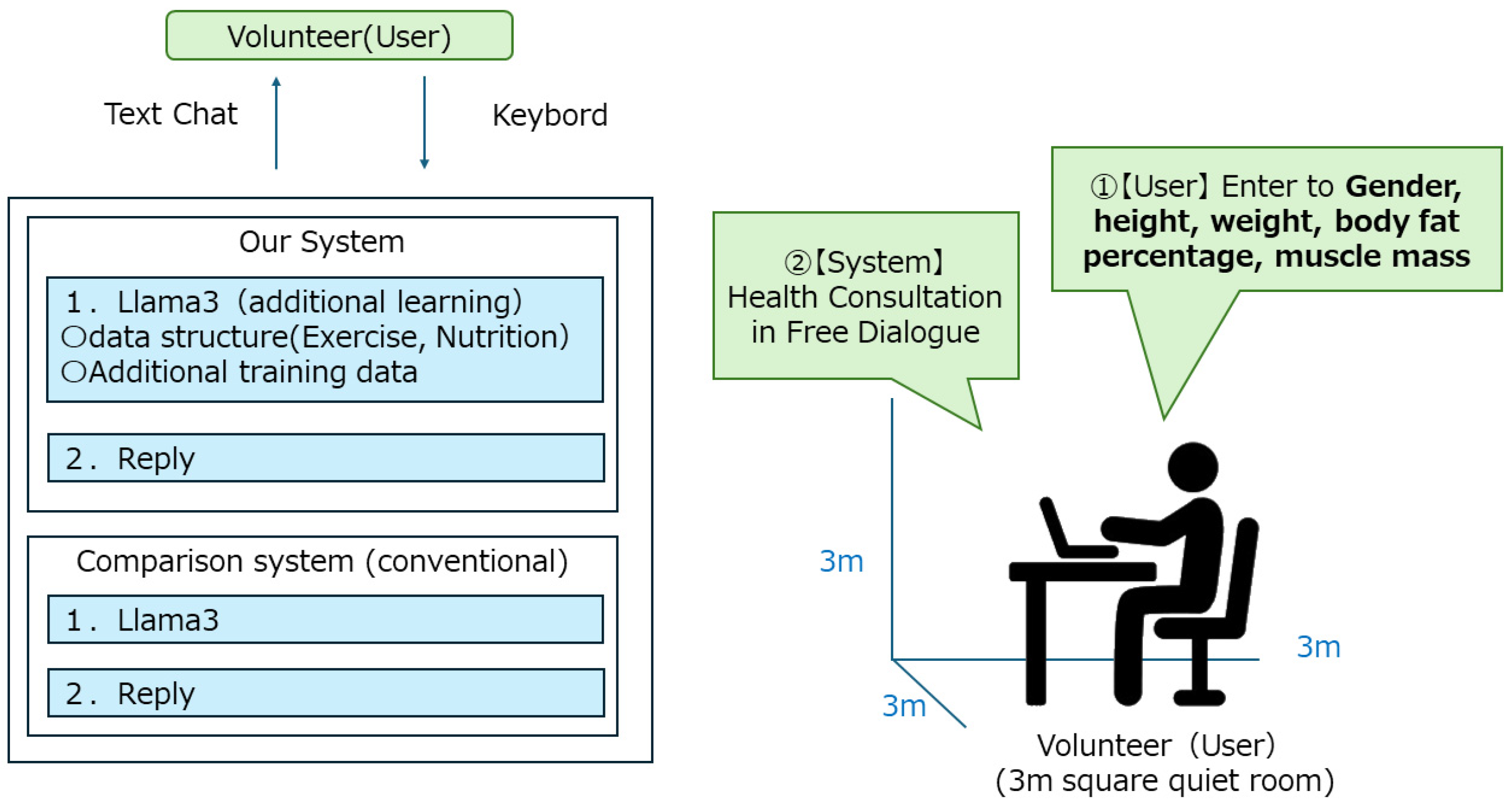
Health counseling mainly consists of exercise and nutritional guidance. In this study, we focused on exercise guidance, and the LLM analysis items were [gender, height, weight, body fat percentage, and muscle mass]. Since it would be costly to create all LLM data, we proceeded with development based on learned model. For the dialogue system, a VRAM-based dialogue console was built to generate an infinite number of facial expressions in response to replies [
22].
Figure 2 shows the system flow of the health counseling LLM infrastructure, and
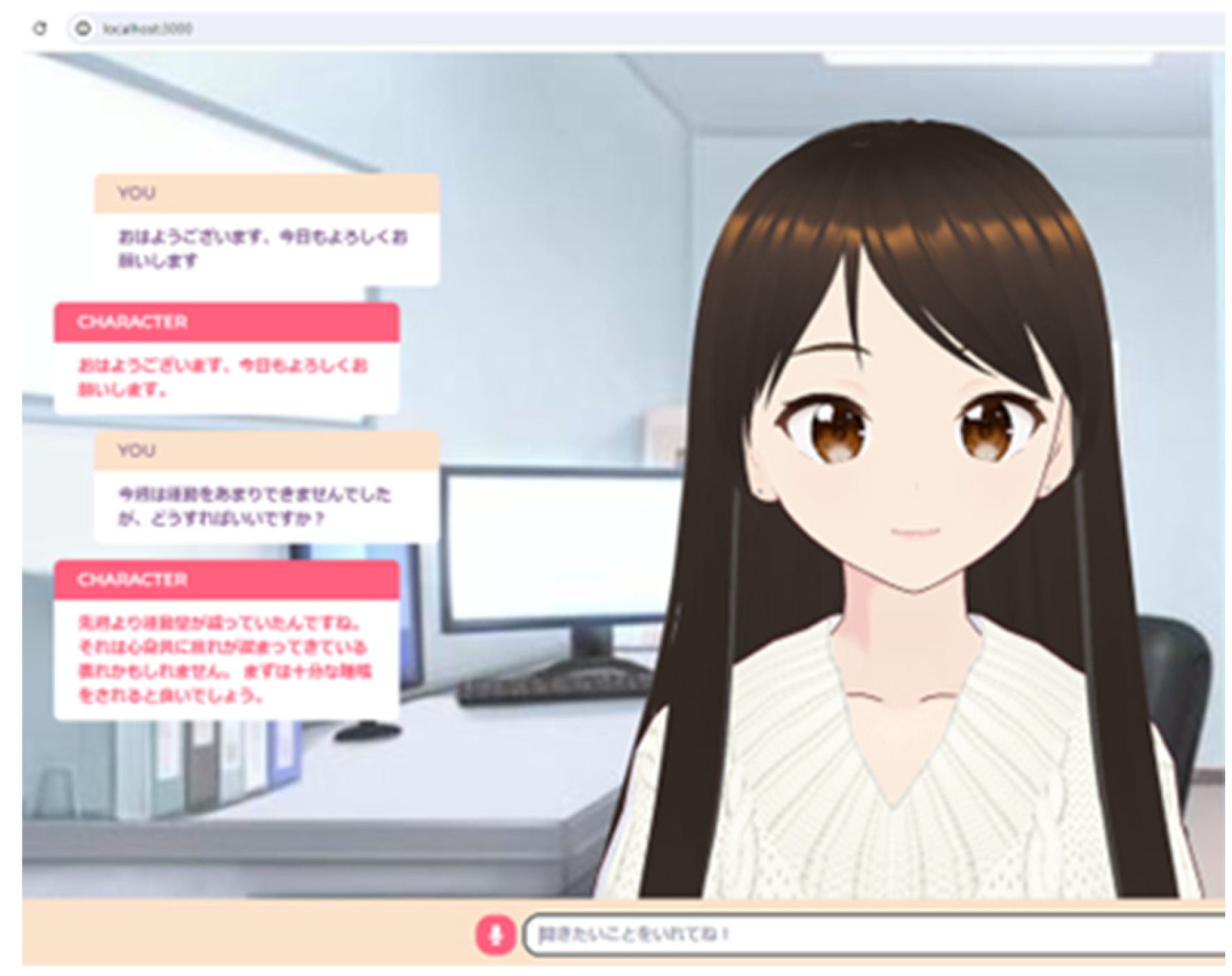
Figure 3 shows the health counseling LLM screen.
The LLM infrastructure we have developed this time uses an LLM model that is additionally trained to Llama3 [
23]. One of the features of this system is that the conversational data of the health consultation conducted so far is converted to text and additional learning is performed. The health consultations are systematized in the following order, (1) patient hearing, (2) dietary guidance, and (3) nutritional guidance. By conducting this additional learning, regularity was observed in the replies of the LLM base, and it became possible to make more regular replies than in the previous LLM base. We implemented this system on a 13-inch laptop computer and installed it in a 3 m square quiet room.
3.2. Turing Test
A Turing test is a test of system evaluation and is conducted with the opponent concealed as either a human or an AI (system). The results are used to evaluate whether the AI maintains a certain level of performance [
24].
A Turing test was conducted using health information [gender, height, weight, body fat percentage, and muscle mass] of 200 people collected in collaboration with local authorities. Three volunteer health professionals were asked to give health advice to two LLM infrastructures using the health information of 200 people, and were asked to speak and respond as if they were human beings, and the results were evaluated. We also tested whether there was a breakdown in conversation for the two LLM infrastructures’ replies using a public health nurse who has been providing health advice for more than 3 years. The input items were [gender, height, weight, body fat percentage, and muscle mass], and the data was entered in a chat format using a keyboard. Comparative experiments were conducted using the LLM platform developed in this study and lla-ma3.
4. Result
200 health information [gender, height, weight, body fat percentage, and muscle mass] were prepared, and three volunteers (users) conducted a health consultation via text chat with their respective health information. The health counseling text chat was conducted using our LLM platform and a conventional LLM platform, but the three volunteers (users) were asked to conceal whether the other party was an AI or a human in a Turing test. If they were AI or if the conversation broke down, the health counseling session was interrupted. The text of the LLM infrastructure was always checked by a health professional familiar with health counseling and interrupted for the same reason as above.
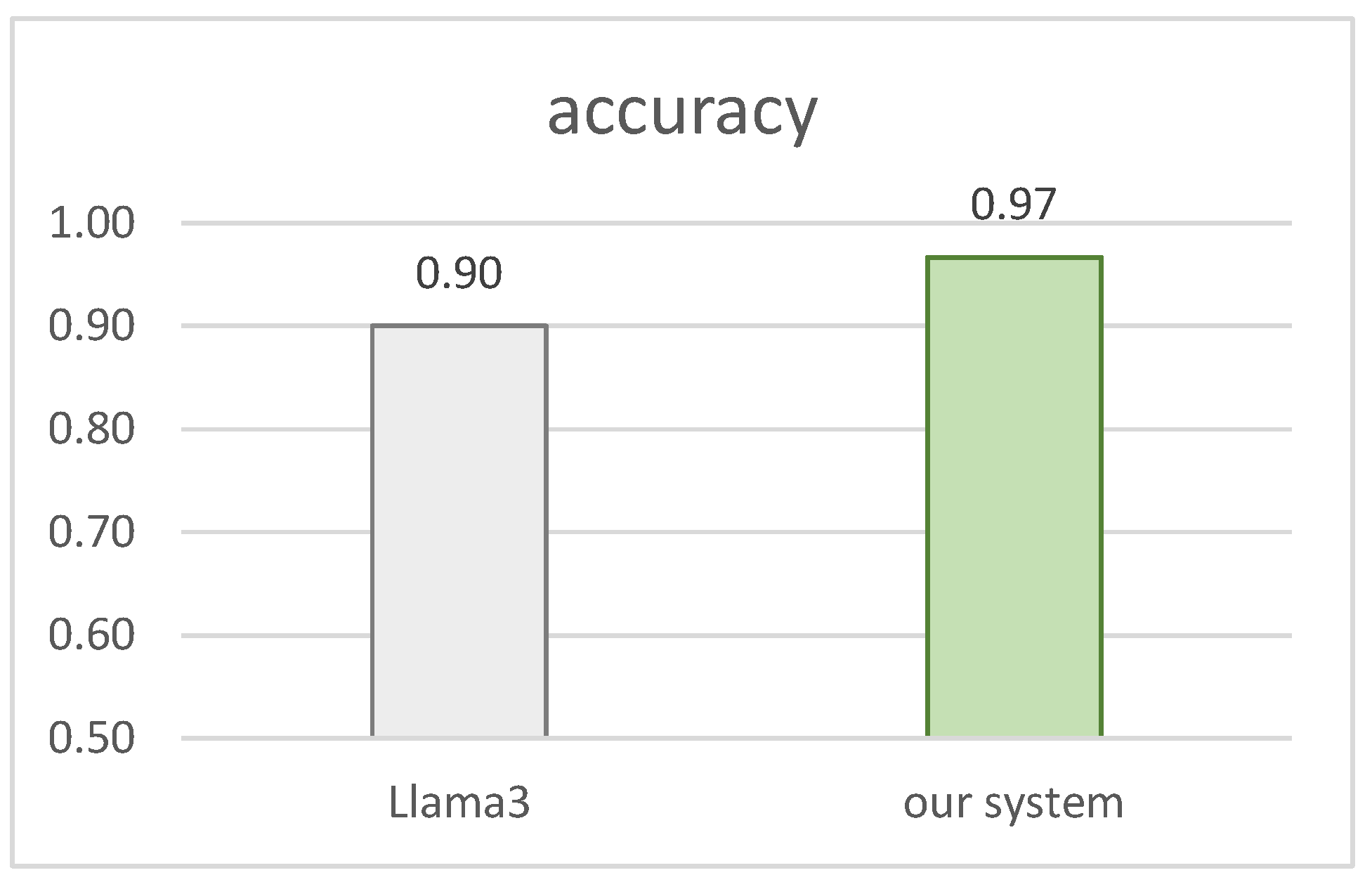
The result of the health worker’s confirmation test was 97.0% in our system, compared to 90.0% in the conventional system. Three volunteers (users) averaged 87.5% in the conventional system, but 93.1% in our system.
Figure 4 and
Table 1 show the results, respectively.
5. Discussion
Looking at the cases where the Turing test failed, the two systems had something in common. When a human (volunteer) asked or returned the same question, the LLM infrastructure tended to change its opinion. For example, when asked the question, “Do you gain weight from drinking alcohol or smoking cigarettes?” at first they would answer that they gain weight or that it is harmful to their health, but when asked the opposite question, in some cases they reversed their opinion and answered that it is good for their health if the right amount is observed. This may be because the culture in Japan is such that the opinion of the medical professional is absolute, and people tend to be skeptical when there are two points of attitude of the medical professional. We also interviewed the subjects (volunteers) and found that most of the cases that failed the Turing Test followed this pattern. When the LLM base was asked about the amount of exercise they were getting, albeit in solitude, for their age, most of them often answered “more than 6,000 steps per day”. This was attributed to municipal and government guidelines for exercise instruction, but the Turing test was failed because of the weak age-specific responses. Looking at the conventional system alone, there were many cases where the Turing test failed due to overlapping themes and consultation topics. In this respect, the system we developed this time had fewer such failures because the flow of dialogue was established.
6. Conclusions
In this study, we structured the dialogue flow and data by performing additional learning on the LLM infrastructure and obtained high accuracy in the health counseling LLM infrastructure. In health counseling, the dialogue is based on multiple items, each item has a priority, and complex conditional branching exists. In addition, because it is a free dialogue, it is difficult to envision the future of the conversation. In this context, the additional learning with the use of teacher data, in which the flow of the dialogue is organized, triggered high accuracy. We believe that by extracting the items in advance, we were able to clarify the perspective of the health consultation.
Telemedicine and health consultation systems using chatbots are not widespread in Japan, but services such as those using LLM have become popular overseas [
25]. In Japan, health consultation and medical treatment are separated from each other, making it difficult for such services to spread, but we believe that if telemedicine, PHR, and health consultation services spread, they could support physicians before and after face-to-face medical treatment. From this perspective, our study is significant in two ways. First, the development cost is low. LLMs require significant power from development to operation [
26], and a single LLM infrastructure can cost several thousand dollars, but we have succeeded in significantly lowering that cost by adding additional learning to existing models. We have successfully lowered that cost significantly by adding additional learning to existing models. For this additional learning and operation, we used the expensive but generally available GeForce RTX 4080 SUPER. Second, the data used in the development was structured. the LLM infrastructure is based on the ability to interactively regenerate sentences, but there are many situations in medicine where the accuracy and reproducibility of the generated sentences is required. It should be noted that by clarifying the flow of the system, we were able to prevent loops and breakdowns in the dialogue. The above two points can be used for applications other than health counseling. For example, if additional learning data can be added and data can be structured, the system can be used for nutritional guidance and education. Therefore, this study has high potential for use in fields other than health counseling. In the future, Llama3 will be used as the LLM foundation, but LLM models will continue to be developed and released around the world. In the meantime, changing to a model other than Llama3 can improve accuracy and conform to AI research around the world.
In this study, we used the Turing test to evaluate our dialogue system. However, although LLM evaluation packages have been developed, various Japanese and medical-specific models are in widespread use. In Japan, evaluation scales for medical LLM have also been published, but have only just begun to spread [
27,
28]. Although we did not test using these evaluation models in this study, we would like to use them in the future for quantitative evaluation and approaches.
Author Contributions
Dr. Miyagawa was in charge of organizing and constructing the additional learning model, Dr. Tatsuoka was in charge of constructing the LLM model, Dr. Oyama was in charge of experimental and research design, and Dr. Miyagawa, Dr. Ishii and Dr. Onishi were in charge of Turing test support.
Funding
This research was supported by two grants. First, we received a grant for “Practical Foundations of Law, Medicine, and Care, Ethnomethodology of Bodies and Norms and Conversation Analysis” (Grant No. JP24H00151, Fundamental Research A) for information and literature review from the perspectives of medicine and HCI, and a grant for information and literature review from the perspective of PHRs and LLM for “Investigation of Issues on the Part of Patients and Health Care Professionals in the Diffusion, Continuation, and Use of PHR Applications in Diabetes Care. A survey of the issues that patients and health care providers have in the diffusion, continuity, and utilization of PHR applications in diabetes care” as an information and literature survey from the perspective of PHRs and LLM. (Grant No. D22-ST-0009, Toyota Foundation 2022).
Acknowledgments
We are deeply grateful to Dr. Keiichi Yamazaki, Saitama University, and Dr. Akiko Yamazaki, Tokyo University of Technology, for their advice in carrying out this study and for their contributions on par with those of the co-authors. We would also like to express our deepest gratitude to the ICT Community Development Common Platform Promotion Organization for their cooperation in the demonstration experiment.
References
- Matsumoto M.; Inoue K.; Kajii E.; Takeuchi K.; Retention of physicians in rural Japan: concerted efforts of the government, prefectures, municipalities and medical schools. Rural Remote Health. 2010, vol.10(2), pp.1432. [CrossRef]
- Elia Grassini.; Marina Buzzi.; Barbara Leporini.; Alina Vozna.; A systematic review of chatbots in inclusive healthcare: insights from the last 5 years. Univ Access Inf Soc. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Maia E.; Vieira P.; Praça I.; Empowering Preventive Care with GECA Chatbot. Healthcare (Basel). 2023, Sep, vol.13;11(18):2532. [CrossRef]
- Goh E.; Gallo R.; Hom J.; Strong E.; Weng Y.; Kerman H.; Cool J.; Kanjee Z.; Parsons AS.; Ahuja N.; Horvitz E.; Yang D.; Milstein A.; Olson APJ.; Rodman A.; Chen JH,; Influence of a Large Language Model on Diagnostic Reasoning: A Randomized Clinical Vignette Study. medRxiv. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Jun Zhao.; Zhihao Zhang.; Luhui Gao.; Qi Zhang.; Tao Gui.; Xuanjing Huang,; LLaMA Beyond English: An Empirical Study on Language Capability Transfer,Computation and Language (cs.CL). 2024. [CrossRef]
- Kenji Nakamura.; Yoshiaki Ohyama,; ChatGPT-4V Application in Hospitals—Potential of Multimodal AI, Cyber Symposium on Online Education and Digital Transformation in Universities, November, 2023.
- Wang, L.M.; Huang, Y.T.; Chern, C.H.; Lo, H.C.; Lee, C.H.; Tang, D.D.; Ho, L.T. Tele-emergency medicine: the evaluation of Taipei Veterans General Hospital and Kinmen-Granite Hospital in Taiwan. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2001, vol.64, pp.621-628.
- Tilahun, B.; Gashu, K.D.; Mekonnen, Z.A.; Endehabtu, B.F.; Angaw, D.A. Mapping the Role of Digital Health Technologies in Prevention and Control of COVID-19 Pandemic: Review of the Literature. Yearb Med Inform. 2021, vol.30, pp.26-37. [CrossRef]
- Hawig, D.; Zhou, C.; Fuhrhop, S.; Fialho, A.S.; Ramachandran, N. Designing a Distributed Ledger Technology System for Interoperable and General Data Protection Regulation-Compliant Health Data Exchange: A Use Case in Blood Glucose Data. J Med Internet Res. 2019, vol.21, e13665. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Prinz, A.; Riegler, M.A.; Das, J. A systematic review and knowledge mapping on ICT-based remote and automatic COVID-19 patient monitoring and care. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023, vol.23, 1047. [CrossRef]
- Ose, D.; Baudendistel, I.; Pohlmann, S.; Winkler, E.C.; Kunz, A.; Szecsenyi, J. Persönliche Patientenakten im Internet. Ein narrativer Review zu Einstellungen, Erwartungen, Nutzung und Effekten [Personal health records on the Internet. A narrative review of attitudes, expectations, utilization and effects on health outcomes. Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundhwes. 2017, vol.122, pp.9-21. [CrossRef]
- Weis, A.; Pohlmann, S.; Poss-Doering, R.; Strauss, B.; Ullrich, C.; Hofmann, H.; Ose, D.; Winkler, E.C.; Szecsenyi, J.; Wensing, M. Caregivers’ role in using a personal electronic health record: a qualitative study of cancer patients and caregivers in Germany. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020, vol.20, 158. [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, M.; Kaplan, G.; Malkin, D.; Dror, R.; Shahaf, D.; Stanovsky, G. State of What Art? A Call for Multi-Prompt LLM Evaluation. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2024, vol.12, pp.933-949. [CrossRef]
- Amin, K.S.; Mayes, L.C.; Khosla, P.; Doshi, R.H. Assessing the Efficacy of Large Language Models in Health Literacy: A Comprehensive Cross-Sectional Study. Yale J Biol Med 2024, vol.97, pp.17-27. [CrossRef]
- Papastratis, I.; Stergioulas, A.; Konstantinidis, D.; Daras, P.; Dimitropoulos, K. Can ChatGPT provide appropriate meal plans for NCD patients? Nutrition. 2024, vol.121, 112291. [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, H.; Nakamura, K. Temporary improvement of cognitive and behavioral scales for Dementia elderly by Shiritori word game with a dialogue robot: A pilot study. Front Robot AI. 2022, vol.9, 941056. [CrossRef]
- Robleto, E.; Habashi, A.; Kaplan, M.B.; Riley, R.L.; Zhang, C.; Bianchi, L.; Shehadeh, L.A. Medical students’ perceptions of an artificial intelligence (AI) assisted diagnosing program. Med Teach. 2024, pp.1-7. [CrossRef]
- Templin, T.; Perez, M.W.; Sylvia, S.; Leek, J.; Sinnott-Armstrong, N. Addressing 6 challenges in generative AI for digital health: A scoping review. PLOS Digit Health. 2024, vol.3, e0000503. [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.K. Biomedical image processing. Crit Rev Bioeng. 1981, vol.5, pp.185-271.
- Abdulkareem, M.; Petersen, S.E. The Promise of AI in Detection, Diagnosis, and Epidemiology for Combating COVID-19: Beyond the Hype. Front Artif Intell. 2021, vol.4, 652669. [CrossRef]
- Sterland J. Shaping the stress consultation in Occupational Health. Occup Med (Lond). 2023, vol.73(9), pp.523-524. [CrossRef]
- Isozaki, N.; Ishima, S.; Yamada, Y.; Obuchi, Y.; Sato, R.; Shimizu, N. VRoid studio: a tool for making anime-like 3D characters using your imagination. In SIGGRAPH Asia 2021 Real-Time Live!; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Articleno 9, pp. 1.
- Huang, W.; Zheng, X.; Ma, X.; Qin, H.; Lv, C.; Chen, H.; Luo, J.; Qi, X.; Liu, X.; Magno, M. An Empirical Study of LLaMA3.
- Quantization: From LLMs to MLLMs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.14047. [CrossRef]
- Halpern, M. The Trouble with the Turing Test. 2023, vol.11, pp.42–63.
- Ganguli, D.; Hernandez, D.; Lovitt, L.; Askell, A.; Bai, Y.; Chen, A.; Conerly, T.; Dassarma, N.; Drain, D.; Elhage, N.; El Showk, S.; Fort, S.; Hatfield-Dodds, Z.; Henighan, T.; Johnston, S.; Jones, A.; Joseph, N.; Kernian, J.; Kravec, S.; Mann, B.; Nanda, N.; Ndousse, K.; Olsson, C.; Amodei, D.; Brown, T.; Kaplan, J.; McCandlish, S.; Olah, C.; Amodei, D.; Clark, J. Predictability and Surprise in Large Generative Models. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022, pp.1747-1764.
- Parmar, P.; Ryu, J.; Pandya, S.; et al. Health-focused conversational agents in person-centered care: a review of apps. npj Digit. Med. 2022, vol.5, 21. [CrossRef]
- Nara Institute of Science and Technology. JMED-LLM: Japanese Medical LLM Evaluation Dataset. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/llm-jp/awesome-japanese-llm (accessed on 2024.7.25).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).