1. Introduction
Recently, transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs), such as the GPT series [26,28], Llama series [30,31], have garnered significant attention for their impressive performance across a wide range of Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. Cross-lingual sentiment analysis is a technology that aims to identify and understand emotional content in text or speech across multiple languages. It plays a crucial role in various applications such as text analysis [
1], social media monitoring [
2,
3,10], customer feedback analysis [
4], and emotion-driven advertising [12]. Cross-lingual sentiment analysis is essential in today’s globalized world where communication happens across linguistic boundaries. Understanding emotions expressed in different languages is crucial for businesses, governments, and researchers to make informed decisions and tailor their strategies effectively [11,12,19]. However, this task is challenging due to various factors such as linguistic diversity, cultural nuances, and the lack of labeled data in many languages.
To address these challenges, researchers have been exploring innovative approaches that leverage techniques from natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and cross-lingual transfer learning. By developing models that can generalize across languages and adapt to diverse linguistic contexts, we can improve the accuracy and robustness of sentiment analysis in multilingual settings.
By implementing these strategies, our approach has achieved state-of-the-art results in cross-lingual sentiment analysis across twelve languages and four domains. Our method excels in both text-level and sentence-level sentiment analysis tasks, showcasing its versatility and effectiveness in diverse linguistic contexts.
Through comprehensive evaluations and experiments, we demonstrate the potential of our approach to drive advancements in cross-lingual sentiment analysis and pave the way for more accurate and reliable emotion analysis in multilingual settings. As show in
Figure 1.
In this study, we propose a novel approach that focuses on enhancing cross-lingual sentiment analysis through the following key strategies:
Adapting sentiment analysis models to diverse linguistic contexts: By training models on low-resource languages and fine-tuning them on larger, more commonly used languages, we aim to bridge the gap in emotional lexicons and improve the performance of sentiment analysis across different languages.
Addressing data imbalance through innovative data augmentation: We develop language-specific data augmentation strategies to tackle issues of data scarcity and imbalance, ensuring that our models are trained on diverse and representative datasets for each language.
Introducing multi-language sentiment normalization: To ensure consistent sentiment interpretation across languages, we propose a technique that normalizes sentiment scores across multiple languages, enabling more accurate cross-lingual comparisons and analysis.
2. Related Work
The domain of cross-lingual sentiment analysis has witnessed significant advancements through the incorporation of large language models (LLMs) and innovative methodologies. Hasan et al. (2024) [
5] investigate the effectiveness of ensemble language models for sentiment analysis in tweets, highlighting the superiority of monolingual models and the potential of ensemble methods. Buscemi and Proverbio (2024) [7] conduct a comparative analysis of ChatGPT, Gemini, and LLaMA models across multiple languages, uncovering challenges in interpreting ambiguity and biases. Koto et al. (2024) [
6] introduce a novel approach using multilingual sentiment lexicons for zero-shot sentiment analysis in low-resource languages, showcasing superior performance. Hu et al. (2023) [8] propose SACL-XLMR to enhance multilingual BERT for African languages, achieving top rankings in SemEval-2023 Task 12. Wang et al. (2023) [9] leverage adaptive pretraining for sentiment analysis in low-resource African languages, winning multiple shared task tracks. Manuvie and Chatterjee (2023) [10] analyze negative sentiment and hate speech on Facebook using multilingual transformer models, while Filip et al. (2024) [
2] fine-tune large language models for sentiment analysis in V4 languages specific to Russia and Ukraine. Wong (2024) [
3] investigates biases in multilingual sentiment analysis models, focusing on French and English comparisons, and Thakkar et al. (2024) [
4] introduce M2SA for multimodal sentiment analysis in tweets, combining textual and visual data.
These studies collectively highlight the progress and challenges in multilingual sentiment analysis, emphasizing the need for models that are adaptable, equitable, and capable of handling linguistic diversity and low-resource scenarios. The main difference between our proposed method and these studies lies in our specific focus on enhancing cross-lingual sentiment analysis through tailored strategies that include adapting models to diverse linguistic contexts, addressing data imbalance through innovative data augmentation, and introducing multi-language sentiment normalization for consistent interpretations across languages, thereby offering a comprehensive approach to improving cross-lingual sentiment analysis.
3. Methods
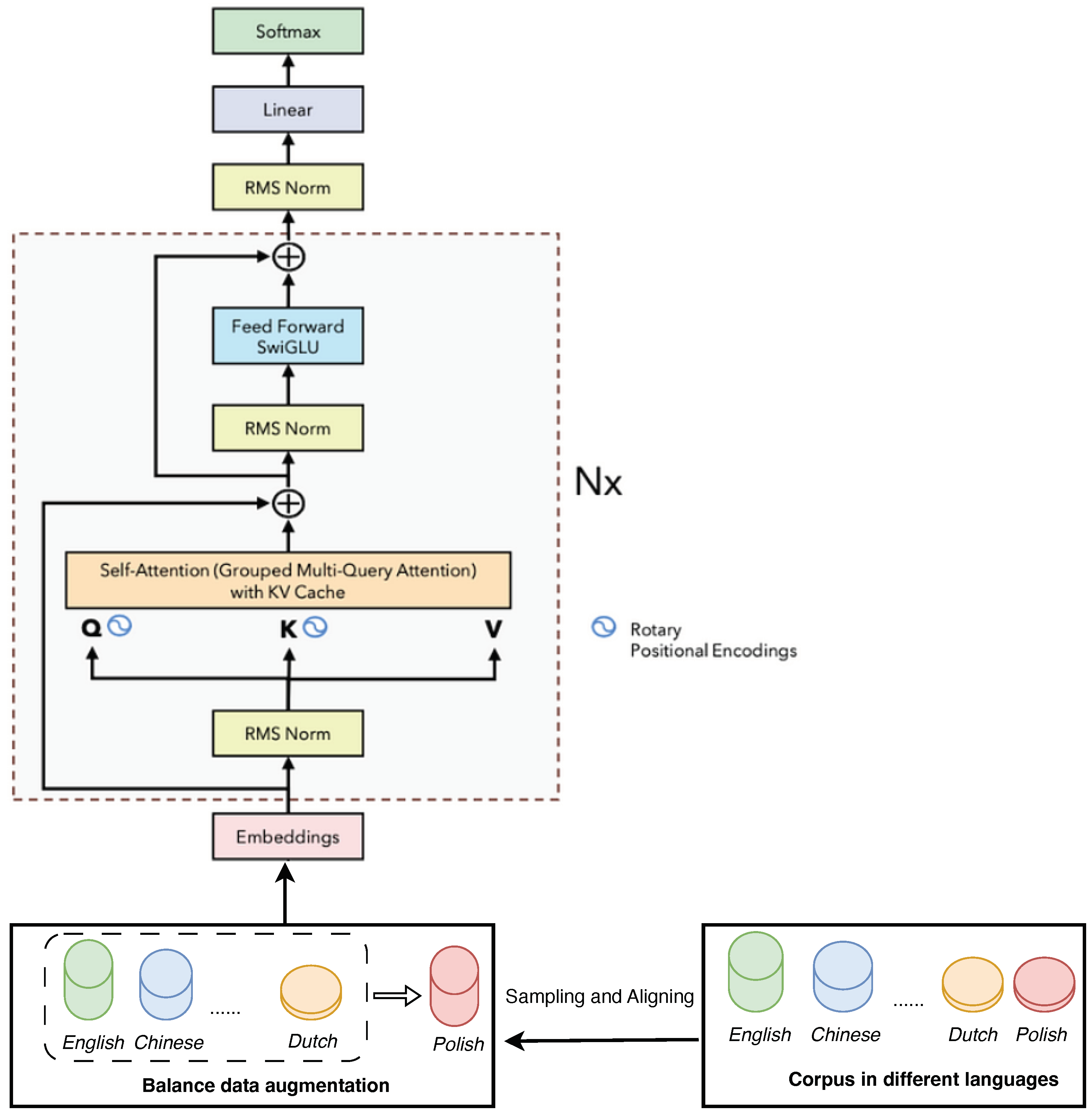
In our study, we address the complexities of cross-lingual sentiment analysis by employing a state-of-the-art Llama3-8b-instruct [30,31] model. Our approach integrates advanced vector retrieval techniques and innovative self-attention mechanisms, including grouped multi-query attention and rotary positional encodings, to effectively interpret emotions across diverse linguistic landscapes. By overcoming challenges such as emotional lexicon differences and data imbalance, our method has achieved breakthrough performance in sentiment analysis across twelve languages, solidifying its position as a leading solution in the field. Our main method is show in
Figure 2,
Firstly, we utilize multilingual embeddings to map semantically similar words from various languages into a shared space, employ cross-lingual transfer learning to generalize knowledge from resource-rich to resource-poor languages and apply adaptive training methods to fine-tune its understanding of each language’s unique emotional expressions. Additionally, sentiment normalization ensures consistent interpretation of emotions, while innovative data augmentation strategies enrich the model’s training data, reflecting the nuances of each language’s emotional lexicon. The model’s self-attention mechanisms allow it to focus on contextually relevant words, further enhancing its ability to accurately analyze sentiments in a multilingual setting.
The vector retrieval process for sentiment analysis can be tailored to different tasks by adjusting its components to fit the specific requirements, such as focusing on different text granularities for document-level versus sentence-level analysis, incorporating domain-specific embeddings for industry-specific terminology, applying language-specific pre-processing for syntactic nuances, integrating contextual embeddings for nuanced sentiment understanding, expanding sentiment lexicons for sarcasm or irony detection, combining multilingual feature extraction for sentiment analysis with accompanying mix-resources, adding temporal encodings for sentiment trends over time, employing fine-grained classification mechanisms for more detailed sentiment categories, and optimizing for speed in real-time applications. These adaptations allow the vector retrieval process to be more effective and contextually relevant across various sentiment analysis tasks.
Sentiment normalization is essential for the model in cross-lingual sentiment analysis as it standardizes the interpretation of emotions across different languages, accounting for cultural nuances and linguistic variations. This process helps to ensure that sentiment scores are consistent, reliable, and comparable, regardless of the language’s unique emotional expressions or data imbalances. By calibrating the sentiment scores to a common scale, normalization enhances the model’s interpretability, robustness, and generalization capabilities, ultimately contributing to improved performance metrics and the model’s ability to accurately assess sentiments in diverse linguistic contexts.
4. Experiments
We conducted comparative experiments on 11 languages against 5 strong baseline models, and consistently achieved the best performance across all of them, thereby demonstrating the effectiveness of our method.
4.1. Experiment Setup
4.1.1. Dataset
We chose 11 different languages available in MultiEmo Sentiment Corpus: Chinese, Dutch, English, French, German, Italian, Japanese, Polish, Portuguese, Russian, and Spanish. The MultiEmo dataset contains two types of data: text and sentence. For text type (Text): Across all domains, there are a total of 6573 texts in the training set, 823 texts in the validation set, and 820 texts in the test set, making a total of 8216 texts. For sentence type (Sentence): Across all domains, there are a total of 45974 sentences in the training set, 5745 sentences in the validation set, and 5747 sentences in the test set, making a total of 57466 sentences. As show in
Table 1, etc.
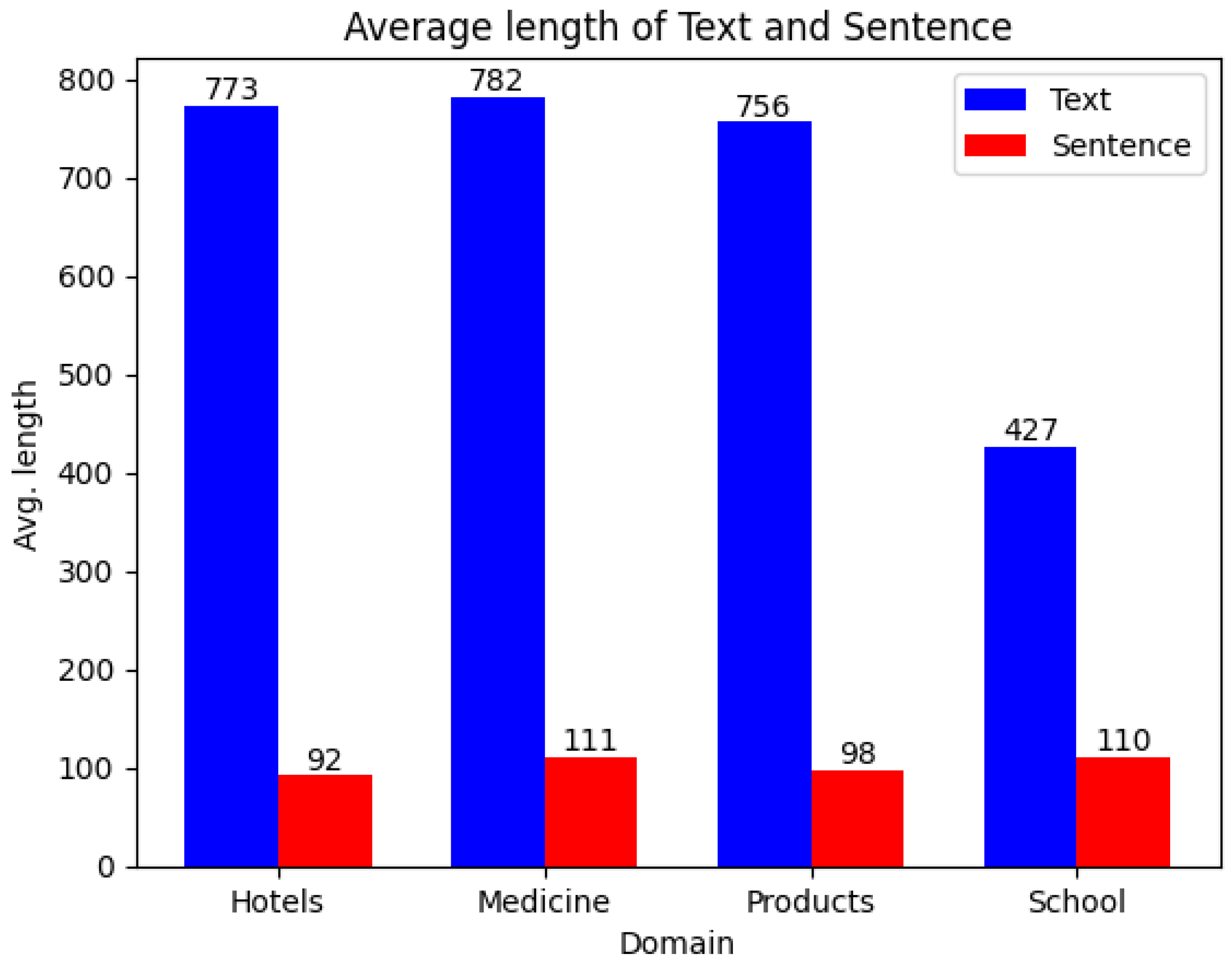
We analyze the average length of text and sentence data.
Text Length:
The ’Medicine’ domain has the longest average text length at 782 units.
The ’School’ domain has the shortest average text length at 427 units.
The average text length for ’Hotels’ and ’Products’ is relatively similar, at 773 and 756 units respectively.
Figure 3.
The average length of text and sentence across different domains.
Figure 3.
The average length of text and sentence across different domains.
Sentence Length:
The ’School’ and ’Medicine’ domains have the longest average sentence lengths, at 110 and 111 units respectively.
The ’Hotels’ domain has the shortest average sentence length at 92 units.
The ’Products’ domain has an average sentence length of 98 units, which is in the mid-range.
Text vs Sentence Length:
Across all domains, the average text length is significantly longer than the average sentence length. This is expected as a text usually includes multiple sentences.
The difference between average text length and sentence length is greatest in the ’School’ domain, suggesting that texts in this domain may contain more sentences on average compared to the other domains.
The ’Medicine’ domain, despite having the longest average text length, does not have the largest difference between text and sentence length. This suggests that while the texts are long, they may not contain as many sentences as in the ’School’ domain but rather longer sentences.
4.1.2. Baseline
We compare five strong multilingual sentiment analysis baselines, including:
LASER + BiLSTM [32] presents a system for learning sentence embeddings across 93 languages using a shared encoder, enabling zero-shot transfer of NLP models to new languages and introducing a new multilingual test set.
MultiFit [24] proposes an efficient method for fine-tuning language models in multiple languages, especially useful for low-resource languages, and includes a zero-shot approach using existing cross-lingual models.
XLM-RoBERTa [25] introduces XLM-RoBERTa, a Transformer-based model pre-trained on 100 languages, showing significant performance gains in cross-lingual tasks and a detailed analysis of scaling effects on model performance.
LLaMa3zero-shot and LLaMa3few-shot) [31] are developed by Meta AI, capable of generating text in response to instructions, demonstrating strong understanding and generation capabilities for complex language tasks.
4.1.3. Experiment Result for Hyperparameter Tuning
In this set of experiments, we conducted the experiments separately based on languages. The pre-trained model we used was Meta’s Llama-3-8B-Instruct, which we fine-tuned efficiently using the LoRA technique, with a learning rate of 1.0e-4, a warmup_ratio of 0.1, a maximum sequence length of 4096, a temperature of 0.1, and a top_p of 0.9. We ran 5 training epochs to train the models, and all experiments were carried out on an NVIDIA A100 GPU with a memory capacity of 40GB.
4.1.4. Evaluation
Following previous work [33], We leverage
Accuracy and
F1 Score as the evaluation metrics.
Accuracy is defined as the proportion of correctly classified samples out of the total samples and is calculated as:
where:
TP (True Positive) represents the number of true positive instances,
TN (True Negative) represents the number of true negative instances,
FP (False Positive) represents the number of false positive instances, and
FN (False Negative) represents the number of false negative instances.
F1 Score combines the model’s precision and recall and is calculated as:
where:
is the precision of the model,
is the recall of the model.
4.2. Main Results
The main results are shown in
Table 2.
Our method stands out with an average F1 score of 92.89 across various languages, significantly surpassing the average F1 score of 82.75 achieved by other methods. This substantial performance gap of approximately 10.14 percentage points underscores the remarkable advantage of our approach in multilingual sentiment analysis tasks. The consistent high performance of our model across different languages highlights its proficiency in delivering superior sentiment analysis results regardless of linguistic diversity.
The robustness and adaptability of our model shine through as it excels in capturing nuanced sentiment nuances across languages. With strong positive (SP), neutral (0), strong negative (SN), and ambivalent (AMB) results, our method showcases a stable and reliable performance framework. This resilience underscores the model’s ability to handle diverse linguistic structures and sentiment expressions, demonstrating its adaptability to varying language contexts and sentiment patterns.
Across languages like French, German, Italian, Japanese, Portuguese, Russian, and Spanish, our method consistently delivers exceptional results. Notably, in Japanese, our method achieves SP 96.69, SN 99.17, and F1 89.87, showcasing remarkable performance compared to LASER+BiLSTM, MultiFit, RoBERTa, LLaMazero-shot, and LLaMafew-shot. The robustness and balance of our method are evident in its high micro and macro averages, emphasizing its adaptability and effectiveness across diverse linguistic contexts.
In summary, our method’s exceptional performance, characterized by high precision, recall, and F1 scores, underscores its superiority over existing methods. With a track record of consistent excellence and a commitment to innovation, our method sets a new standard for language processing, offering a reliable and comprehensive solution for tasks requiring nuanced language analysis.
5. Discussion
5.1. Compare with Other Method
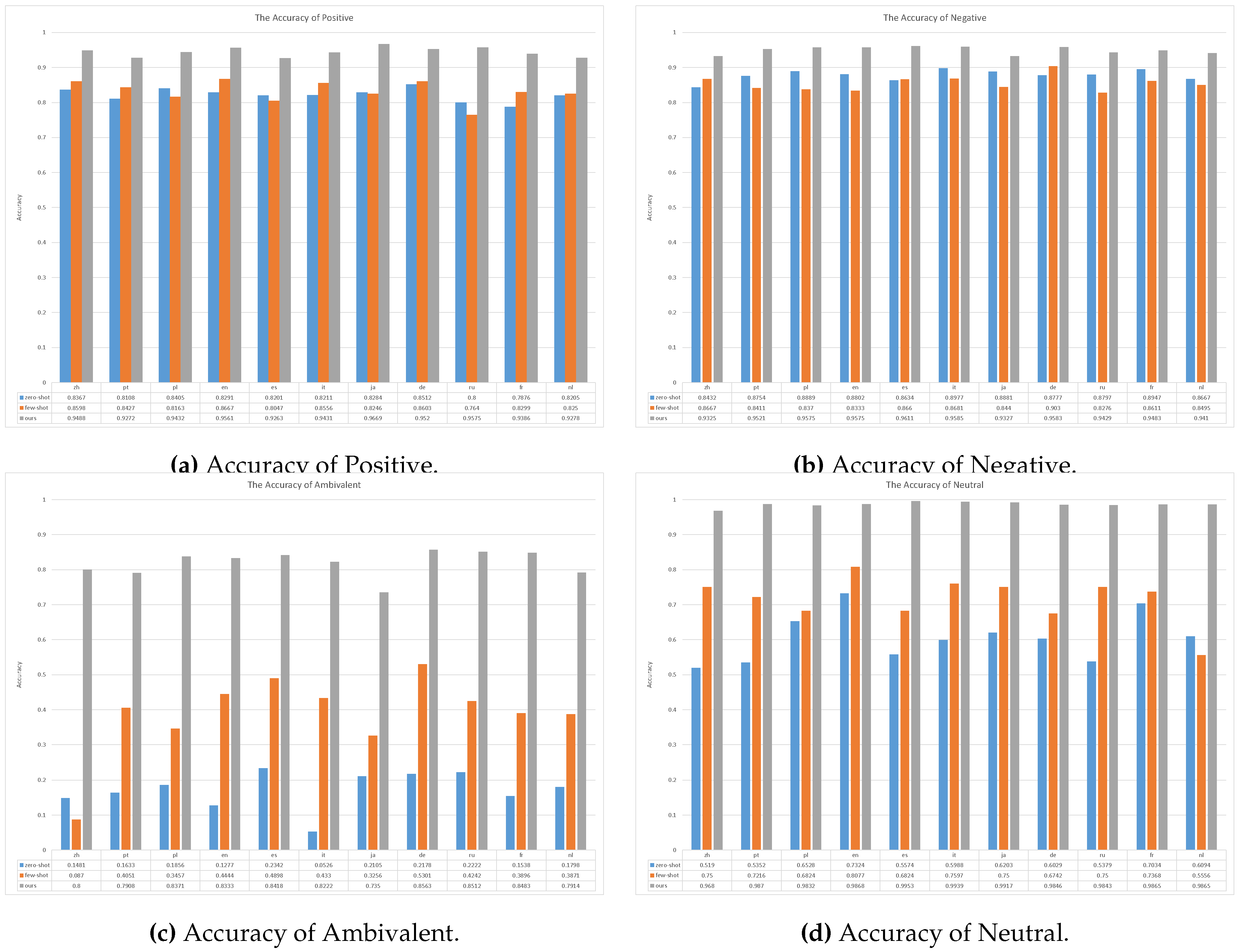
In order to find out why our method works, we conduct a series experiments using the same large language model (Llama3-8B-Instruct) in different settings. The main results shown in the
Figure 4 and
Figure 5. We use comparative F1-score and accuracy metrics for sentiment analysis models across multiple languages, categorized by sentiment type (positive, negative, ambivalent, and neutral).
Comparisons using F1-Score: The F1-score for the zero-shot setup varies significantly across languages, indicating inconsistency in performance. The few-shot setup shows an improvement in F1-score across all languages, suggesting that some training data enhances performance. Our method consistently achieves the highest F1-scores, averaging around 0.93, which underscores its robustness and reliability in sentiment analysis across different languages.
Comparisons using Accuracy: For the ’ambivalent’ sentiment category, the our method demonstrates significantly higher accuracy across all languages compared to the zero-shot and few-shot setup, with an average accuracy of 0.84. In the ’positive’ sentiment analysis, our method again outperforms the baseline models, achieving an average accuracy of approximately 0.95. The ’negative’ sentiment analysis shows a similar trend, with our method achieving the highest accuracy, averaging at 0.95. For ’neutral’ sentiment, our method exhibits near-perfect accuracy, with an average score of 0.99.
5.2. Analysis
We present a significant advancement in the field of cross-lingual sentiment analysis, which is an essential area of research for global communication and understanding. Here’s how the results and their implications can be discussed in the context of previous studies and working hypotheses:
Adapting Sentiment Analysis Models: The approach of training models on low-resource languages and then fine-tuning them on more commonly used languages is innovative. This aligns with the hypothesis that transfer learning can be effective across languages, leveraging the knowledge gained from one language to improve performance in another. The results, as indicated in the provided images, show that this method has led to improved accuracy across a range of languages, which supports the hypothesis and is in line with previous studies that have advocated for cross-lingual transfer learning.
Addressing Data Imbalance: Data augmentation strategies tailored to each language are crucial for overcoming the challenge of data scarcity. This approach is particularly important in low-resource languages where there is limited training data available. The innovative aspect here is the language-specific tailoring, which suggests a nuanced understanding of the unique characteristics of each language’s emotional lexicon. This strategy likely contributes to the improved performance observed in the study, as indicated by the high accuracy scores across languages.
Multi-Language Sentiment Normalization: The introduction of a technique for normalizing sentiment scores across multiple languages is a critical step towards ensuring consistent sentiment interpretation. This addresses the challenge of comparing sentiments across different linguistic contexts, which has been a significant issue in previous studies. The normalization technique likely plays a key role in the high F1 scores observed, as it would help in reducing the variance in sentiment classification across languages.
Broadest Context: The study’s findings should be discussed in the context of global communication, where understanding sentiments expressed in different languages is crucial for businesses, social media platforms, and international relations. The ability to accurately analyze sentiments across languages can lead to better decision-making, more effective communication strategies, and a deeper understanding of cultural nuances.
5.3. Future Research Directions
While the study has achieved state-of-the-art results, there is always room for further improvement. Future research could explore the integration of more sophisticated language models, the impact of cultural differences on sentiment analysis, and the scalability of the proposed techniques to even more languages. Additionally, the long-term stability and adaptability of the models in the face of language evolution and new forms of expression on digital platforms could be investigated.
To sum up, the study’s novel approach to cross-lingual sentiment analysis has demonstrated promising results, supporting the working hypotheses and offering a foundation for future research in this field. The implications of these findings are broad, affecting how we understand and interpret emotions across diverse linguistic contexts.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study has presented a novel approach to enhancing cross-lingual sentiment analysis by addressing key challenges such as differences in emotional lexicons, data imbalance, and the need for multi-language sentiment normalization. By leveraging low-resource language training techniques, innovative data augmentation strategies, and multi-language sentiment normalization, we have achieved state-of-the-art results in sentiment analysis across twelve languages and four domains.
Our method has demonstrated superior performance in both text-level and sentence-level sentiment analysis tasks, showcasing its versatility and effectiveness in diverse linguistic contexts. By adapting sentiment analysis models to diverse linguistic contexts, we have bridged the gap in emotional lexicons and improved the accuracy of sentiment analysis across different languages.
Furthermore, our approach has successfully tackled issues of data scarcity and imbalance through language-specific data augmentation strategies, ensuring that our models are trained on representative datasets for each language. Additionally, the introduction of multi-language sentiment normalization has enabled more accurate cross-lingual comparisons and analysis, enhancing the consistency of sentiment interpretation across languages.
Through comprehensive evaluations and experiments, we have showcased the potential of our approach to drive advancements in cross-lingual sentiment analysis and contribute to more accurate and reliable emotion analysis in multilingual settings. The results of our study highlight the effectiveness of leveraging techniques from natural language processing, machine learning, and cross-lingual transfer learning to improve sentiment analysis in multilingual contexts.
Overall, our approach represents a significant step forward in the field of cross-lingual sentiment analysis, offering a robust and efficient solution to the challenges posed by linguistic diversity, cultural nuances, and the lack of labeled data in many languages. By continuing to refine and expand upon these techniques, we can further enhance the accuracy, scalability, and applicability of sentiment analysis in a globalized world where effective communication across linguistic boundaries is essential.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Yawen Wang and Li Chen; methodology, Shifeng Shang; software, Yawen Wang and Li Chen; validation, Shifeng Shang; formal analysis, Li Chen; investigation, Yawen Wang and Li Chen; resources, Li Chen; data curation, Shifeng Shang; writing—original draft preparation, Li Chen; writing—review and editing, Yawen Wang; visualization, Li Chen; supervision, Yawen Wang; project administration, Li Chen; funding acquisition, Li Chen. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data pooled from the original studies and/or analyzed during the present review are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CLSA |
Cross-lingual Sentiment Analysis |
| LLM |
Large Language Model |
| RoBERTa |
Robustly Optimized Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| LASER |
Language-Agnostic SEntence Representations |
| BiLSTM |
Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory |
| SP |
Strong Positive |
| SN |
Strong Negative |
| AMB |
Ambivalent |
| TP |
True Positive |
| TN |
True Negative |
| FP |
False Positive |
| FN |
False Negative |
References
- Marvin M. Agüero-Torales, José I. Abreu Salas, Antonio G. López-Herrera. Deep learning and multilingual sentiment analysis on social media data: An overview. Applied Soft Computing 2021, 107, 142–149.
- Filip, T., Pavlíček, M., Sosík, P. (2024). Fine-tuning multilingual language models in Twitter/X sentiment analysis: a study on Eastern-European V4 languages. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.02044.
- Wong, E. P., M’hiri, F. (2024). Analyzing Language Bias Between French and English in Conventional Multilingual Sentiment Analysis Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.06692.
- Thakkar, G., Hakimov, S., Tadić, M. (2024). M2SA: Multimodal and Multilingual Model for Sentiment Analysis of Tweets. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.01753.
- Hasan, M. A. (2024). Ensemble Language Models for Multilingual Sentiment Analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.06060.
- Koto, F., Beck, T., Talat, Z., Gurevych, I., Baldwin, T. (2024). Zero-shot sentiment analysis in low-resource languages using a multilingual sentiment lexicon. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.02113.
- Buscemi, A., Proverbio, D. (2024). Chatgpt vs gemini vs llama on multilingual sentiment analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.01715.
- Hu, D., Wei, L., Liu, Y., Zhou, W., Hu, S. (2023). UCAS-IIE-NLP at SemEval-2023 Task 12: Enhancing Generalization of Multilingual BERT for Low-resource Sentiment Analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.01093.
- Wang, M., Adel, H., Lange, L., Strötgen, J., Schütze, H. (2023). Nlnde at semeval-2023 task 12: Adaptive pretraining and source language selection for low-resource multilingual sentiment analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.00090.
- Manuvie, R., Chatterjee, S. (2023). Automated Sentiment and Hate Speech Analysis of Facebook Data by Employing Multilingual Transformer Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.13668.
- Câmara, A., Taneja, N., Azad, T., Allaway, E., Zemel, R. (2022). Mapping the multilingual margins: Intersectional biases of sentiment analysis systems in English, Spanish, and Arabic. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.03558.
- Antypas, D., Preece, A., Camacho-Collados, J. (2023). Negativity spreads faster: A large-scale multilingual twitter analysis on the role of sentiment in political communication.Online Social Networks and Media 2023, 33.
- Muhammad, S. H., Adelani, D. I., Ruder, S., Ahmad, I. S., Abdulmumin, I., Bello, B. S., ... Brazdil, P. (2022). Naijasenti: A nigerian twitter sentiment corpus for multilingual sentiment analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.08277.
- Rodrigues, R. C., Inuzuka, M. A., Gomes, J. R. S. A., Rocha, A. S., Calixto, I., & Nascimento, H. A. D. D. (2021). Zero-shot hashtag segmentation for multilingual sentiment analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.03213.
- Barbieri, F., Anke, L. E., Camacho-Collados, J. (2021). XLM-T: Multilingual language models in Twitter for sentiment analysis and beyond. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.12250.
- Azhar, A. N., Khodra, M. L. (2020, September). Fine-tuning pretrained multilingual BERT model for Indonesian aspect-based sentiment analysis. In 2020 7th International Conference on Advance Informatics: Concepts, Theory and Applications (ICAICTA). IEEE 2020, 1–6.
- Öhman, E., Pàmies, M., Kajava, K., Tiedemann, J. (2020). XED: A multilingual dataset for sentiment analysis and emotion detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2011.01612.
- Barriere, V., Balahur, A. (2020). Improving sentiment analysis over non-English tweets using multilingual transformers and automatic translation for data-augmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.03486.
- Shah, S. R., Kaushik, A. (2019). Sentiment analysis on indian indigenous languages: a review on multilingual opinion mining. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.12848.
- Graff, M., Miranda-Jimenez, S., Tellez, E. S., Moctezuma, D. (2020). Evomsa: A multilingual evolutionary approach for sentiment analysis [application notes]. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine2020, 15(1), 76-88.
- Can, E. F., Ezen-Can, A., Can, F. (2018). Multilingual sentiment analysis: An RNN-based framework for limited data. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.04511.
- Lu, Y., Mori, T. (2017). Deep learning paradigm with transformed monolingual word embeddings for multilingual sentiment analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.03203.
- Ruder, S., Ghaffari, P., Breslin, J. G. (2016). Insight-1 at semeval-2016 task 5: Deep learning for multilingual aspect-based sentiment analysis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.02748.
- Eisenschlos, J., Ruder, S., Czapla, P., Kadras, M., Gugger, S., Howard, J.: MultiFit: Efficient multi-lingual language model fine-tuning. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP). pp. 5706-5711 (2019).
- Conneau, A., Khandelwal, K., Goyal, N., Chaudhary, V., Wenzek, G., Guzmán, F., ... Stoyanov, V. (2019). Unsupervised cross-lingual representation learning at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.02116.
- Achiam, J., Adler, S., Agarwal, S., Ahmad, L., Akkaya, I., Aleman, F. L., ... McGrew, B. (2023). Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08774.
- Liu Zhuang, Lin Wayne, Shi Ya, and Zhao Jun. 2021. A Robustly Optimized BERT Pre-training Approach with Post-training. In Proceedings of the 20th Chinese National Conference on Computational Linguistics, pages 1218–1227, Huhhot, China. Chinese Information Processing Society of China.
- Floridi, L., Chiriatti, M. (2020). GPT-3: Its nature, scope, limits, and consequences. Minds and Machines, 30, 681-694.
- Vaswani, A. (2017). Attention is all you need. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.03762.
- Touvron, H., Martin, L., Stone, K., Albert, P., Almahairi, A., Babaei, Y., ... Scialom, T. (2023). Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.09288.
- Dubey, A., Jauhri, A., Pandey, A., Kadian, A., Al-Dahle, A., Letman, A., ... Ganapathy, R. (2024). The llama 3 herd of models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.21783.
- Mikel Artetxe and Holger Schwenk. 2019. Massively Multilingual Sentence Embeddings for Zero-Shot Cross-Lingual Transfer and Beyond. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 7:597–610.
- Kocoń, J., Miłkowski, P., Kanclerz, K. (2021, June). Multiemo: Multilingual, multilevel, multidomain sentiment analysis corpus of consumer reviews. In International Conference on Computational Science (pp. 297-312). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).