Submitted:
21 August 2024
Posted:
22 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
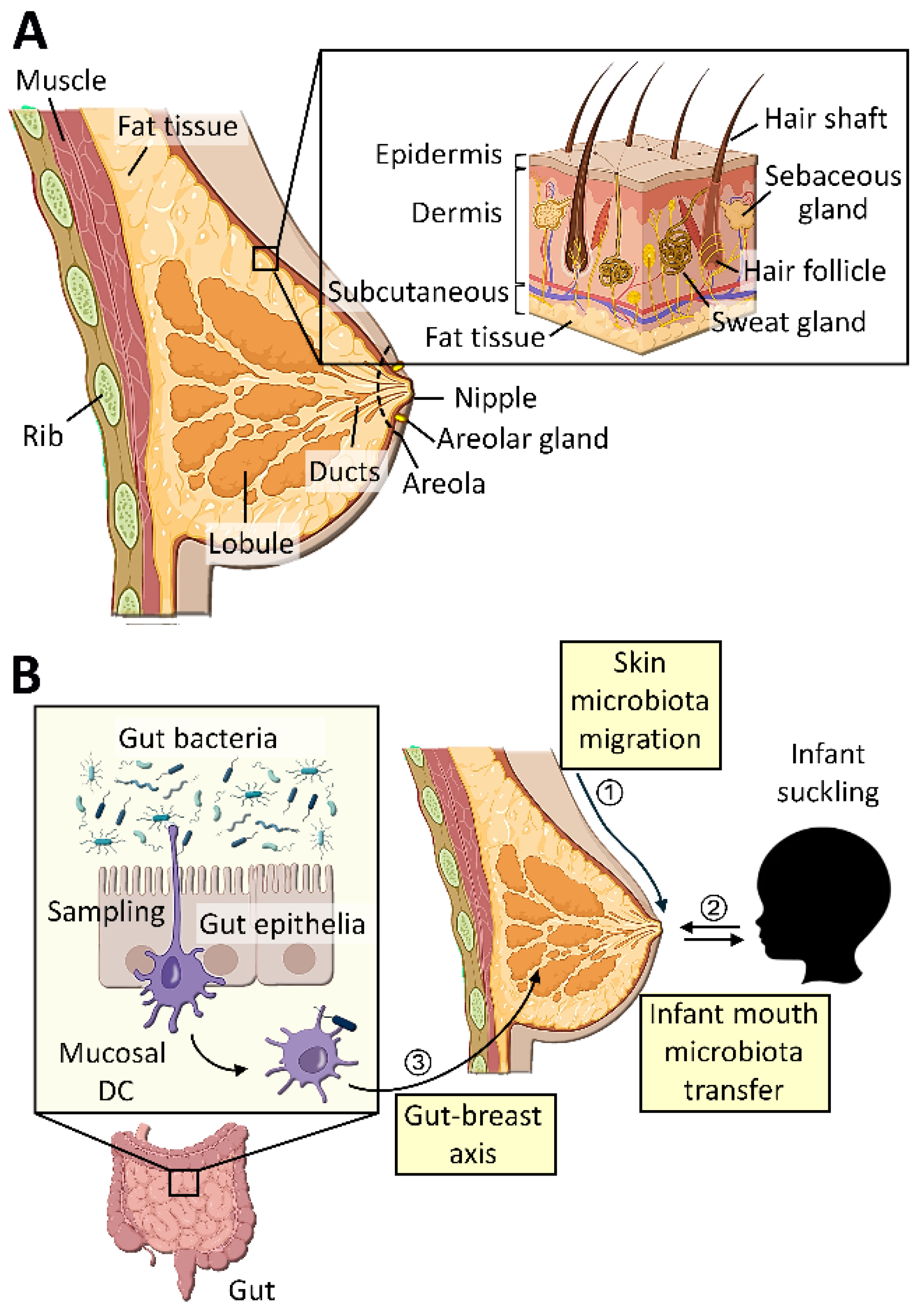
2. Breast Tissue Microbiota
3. Breast Milk Microbiota
4. Breast Tumor Microbiota
4.1. Breast Cancer Subtype-Specific Microbiota
4.2. Race/Ethnicity-Specific Breast Cancer Microbiota
5. Origin of Breast Tissue Microbiota
5.1. Microbial Transfer from Breast Skin
5.2. Microbial Transfer from Nipple
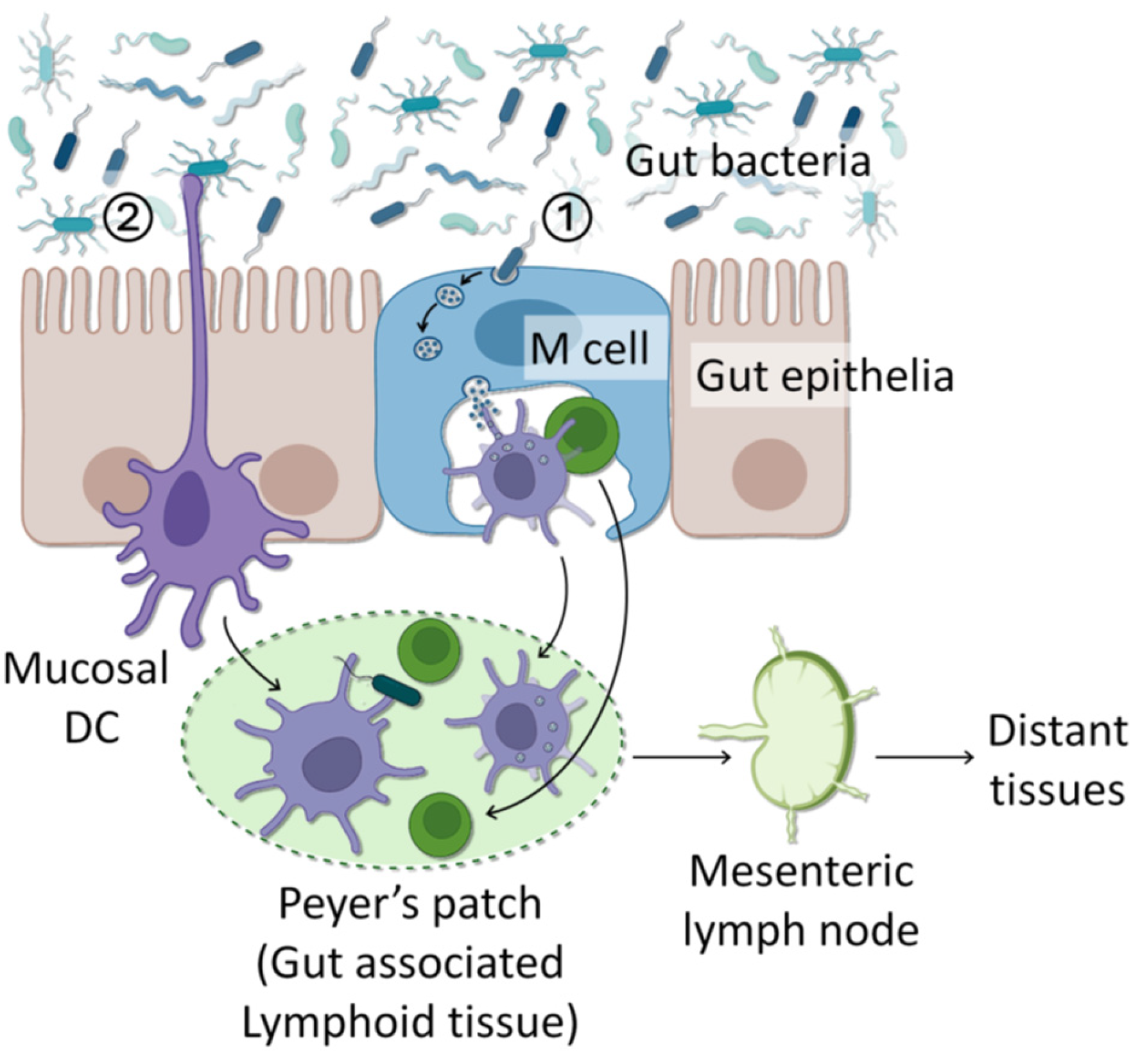
5.3. Microbial Transfer via Gut-Breast Axis or Oro-Breast Axis
6. Mechanisms of Bacterial Translocation
6.1. Internalization into Epithelial Cells
6.2. Sampling and Transportation by Immune Cells
7. Functions of Intracellular Microbiota
8. Bacterially Produced Metabolites
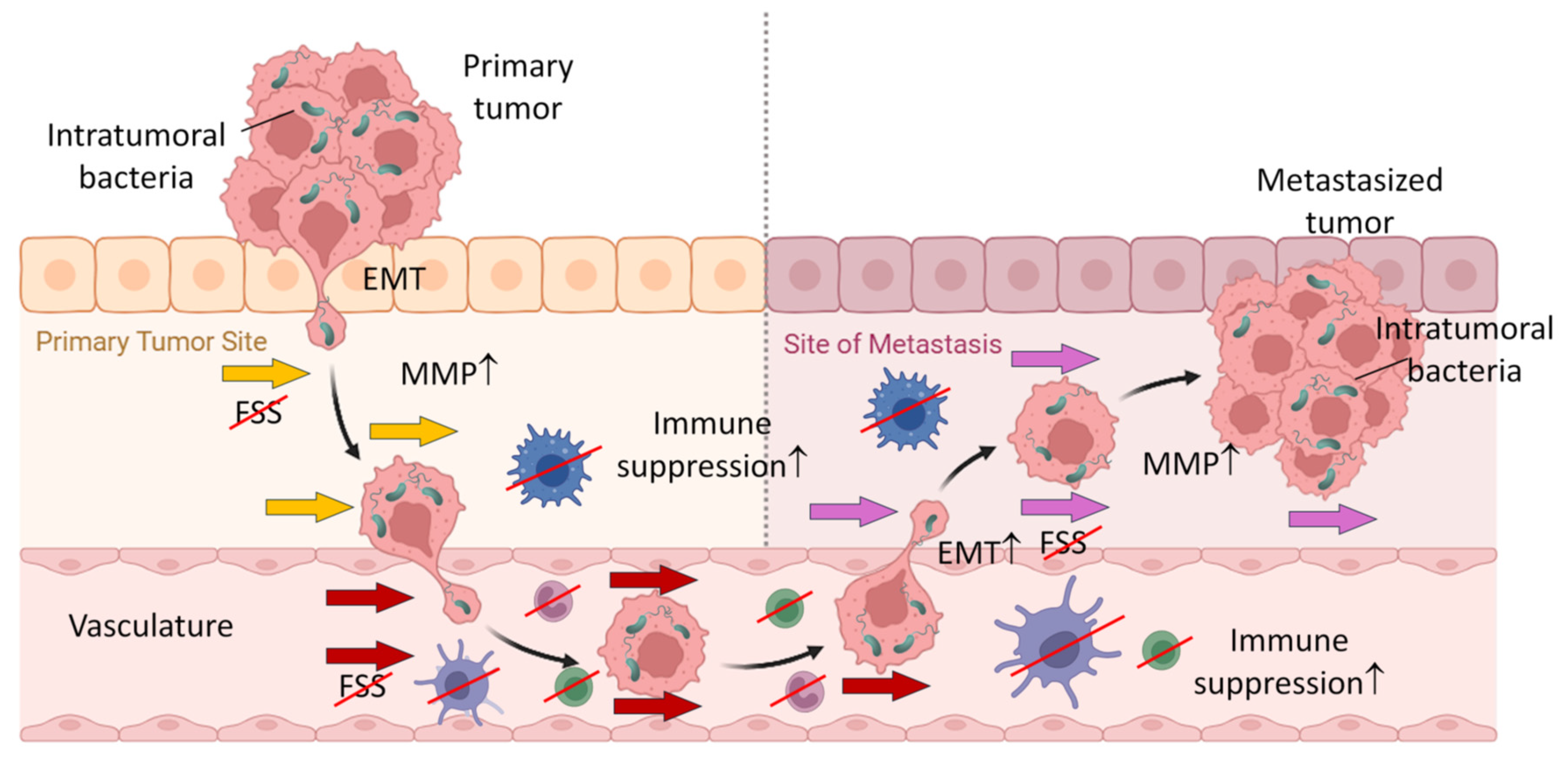
9. Breast Tumor-Associated Bacteria
9.1. Origin of Breast-Tumor Resident Bacteria
9.2. Major Breast-Tumor Resident Bacterial Species
9.2.1. Fusobacterium nucleatum
9.2.2. Streptococcus
9.2.3. Staphylococcus, and Enterobacteriaceae
9.3. Roles of Intracellular Microbes in Breast Tumor Initiation/Development
9.3.1. Genome Instability/Mutation
9.3.2. Tumor Metastasis
10. Discussion
11. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data availability statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Are We Really Vastly Outnumbered? Revisiting the Ratio of Bacterial to Host Cells in Humans. Cell 2016, 164, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, J.K.; Davenport, E.R.; Clark, A.G.; Ley, R.E. The Relationship Between the Human Genome and Microbiome Comes into View. Annu Rev Genet 2017, 51, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.; McCoy, K.D.; Macpherson, A.J. Use of axenic animals in studying the adaptation of mammals to their commensal intestinal microbiota. Semin Immunol 2007, 19, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Research 2020, 30, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesaki, Y.; Setoyama, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Okada, Y. Expansion of alpha beta T-cell receptor-bearing intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes after microbial colonization in germ-free mice and its independence from thymus. Immunology 1993, 79, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hapfelmeier, S.; Lawson, M.A.; Slack, E.; Kirundi, J.K.; Stoel, M.; Heikenwalder, M.; Cahenzli, J.; Velykoredko, Y.; Balmer, M.L.; Endt, K.; et al. Reversible microbial colonization of germ-free mice reveals the dynamics of IgA immune responses. Science 2010, 328, 1705–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.I; Frutos Rde, L.; Manel, N.; Yoshinaga, K.; Rifkin, D.B.; Sartor, R.B.; Finlay, B.B.; Littman, D.R. Specific microbiota direct the differentiation of IL-17-producing T-helper cells in the mucosa of the small intestine. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 4, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Modica, M.; Arlotta, V.; Sfondrini, L.; Tagliabue, E.; Triulzi, T. The Link Between the Microbiota and HER2+ Breast Cancer: The New Challenge of Precision Medicine. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 947188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, A.; Sangwan, N.; Jia, M.; Liu, C.-C.; Keslar, K.S.; Downs-Kelly, E.; Fairchild, R.L.; Al-Hilli, Z.; Grobmyer, S.R.; Eng, C. Human breast microbiome correlates with prognostic features and immunological signatures in breast cancer. Genome Medicine 2021, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodai, B.I.; Nakata, T.E. Breast Cancer: Lifestyle, the Human Gut Microbiota/Microbiome, and Survivorship. Perm J 2020, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Modica, M.; Gargari, G.; Regondi, V.; Bonizzi, A.; Arioli, S.; Belmonte, B.; De Cecco, L.; Fasano, E.; Bianchi, F.; Bertolotti, A.; et al. Gut Microbiota Condition the Therapeutic Efficacy of Trastuzumab in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Res 2021, 81, 2195–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepich-Poore, G.D.; Zitvogel, L.; Straussman, R.; Hasty, J.; Wargo, J.A.; Knight, R. The microbiome and human cancer. Science 2021, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Yadav, H. Bacterial Translocation from the Gut to the Distant Organs: An Overview. Ann Nutr Metab 2017, 71 Suppl 1, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Nakano, K.; Naderi, N.; Bajaj-Elliott, M.; Mosahebi, A. Is the skin microbiota a modifiable risk factor for breast disease?: A systematic review. Breast 2021, 59, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvamani, S.; Dailin, D.J.; Gupta, V.K.; Wahid, M.; Keat, H.C.; Natasya, K.H.; Malek, R.A.; Haque, S.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Abomoelak, B.; et al. An Insight into Probiotics Bio-Route: Translocation from the Mother’s Gut to the Mammary Gland. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.M.; Fernández, L.; Verhasselt, V. The Gut‒Breast Axis: Programming Health for Life. Nutrients 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farache, J.; Koren, I.; Milo, I.; Gurevich, I.; Kim, K.W.; Zigmond, E.; Furtado, G.C.; Lira, S.A.; Shakhar, G. Luminal bacteria recruit CD103+ dendritic cells into the intestinal epithelium to sample bacterial antigens for presentation. Immunity 2013, 38, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Pantoja, D.R.; Gaber, M.; Arnone, A.A.; Bronson, S.M.; Cruz-Diaz, N.; Wilson, A.S.; Clear, K.Y.J.; Ramirez, M.U.; Kucera, G.L.; Levine, E.A.; et al. Diet Alters Entero-Mammary Signaling to Regulate the Breast Microbiome and Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2021, 81, 3890–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Sun, J. Breast and gut microbiome in health and cancer. Genes Dis 2021, 8, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, T.R.; Kuennen, M.R.; Blacker, S.D.; Myers, S.D.; Walker, E.F.; Lee, B.J. The effect of sex, menstrual cycle phase and oral contraceptive use on intestinal permeability and ex-vivo monocyte TNFα release following treatment with lipopolysaccharide and hyperthermia. Cytokine 2022, 158, 155991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atashgaran, V.; Wrin, J.; Barry, S.C.; Dasari, P.; Ingman, W.V. Dissecting the Biology of Menstrual Cycle-Associated Breast Cancer Risk. Front Oncol 2016, 6, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaadt, N.S.; Alfonso, J.C.L.; Schönmeyer, R.; Grote, A.; Forestier, G.; Wemmert, C.; Krönke, N.; Stoeckelhuber, M.; Kreipe, H.H.; Hatzikirou, H.; et al. Image analysis of immune cell patterns in the human mammary gland during the menstrual cycle refines lymphocytic lobulitis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2017, 164, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, J.A.; Lievens, E.; Hummelen, R.; van der Westen, R.; Reid, G.; Petrova, M.I. Women and Their Microbes: The Unexpected Friendship. Trends in Microbiology 2018, 26, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieken, T.J.; Chen, J.; Hoskin, T.L.; Walther-Antonio, M.; Johnson, S.; Ramaker, S.; Xiao, J.; Radisky, D.C.; Knutson, K.L.; Kalari, K.R.; et al. The Microbiome of Aseptically Collected Human Breast Tissue in Benign and Malignant Disease. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 30751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Xin, P.F.; Gao, X.; Li, H.R.; Zhou, C.Y.; Gao, W.M.; Kou, X.X.; Zhang, J.G. Liver Microbiome in Healthy Rats: The Hidden Inhabitants of Hepatocytes. Cellular Microbiology 2023, 2023, 7369034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejman, D.; Livyatan, I.; Fuks, G.; Gavert, N.; Zwang, Y.; Geller, L.T.; Rotter-Maskowitz, A.; Weiser, R.; Mallel, G.; Gigi, E.; et al. The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type-specific intracellular bacteria. Science 2020, 368, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak, C.; Cummins, J.; Brackstone, M.; Macklaim, J.M.; Gloor, G.B.; Baban, C.K.; Scott, L.; O’Hanlon, D.M.; Burton, J.P.; Francis, K.P.; et al. Microbiota of Human Breast Tissue. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2014, 80, 3007–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawani-Luwaji, E.U.; Alade, T. Sphingomonadaceae: Protective against breast cancer? Bulletin of the National Research Centre 2020, 44, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, L.; Alon-Maimon, T.; Sol, A.; Nejman, D.; Shhadeh, A.; Fainsod-Levi, T.; Yajuk, O.; Isaacson, B.; Abed, J.; Maalouf, N.; et al. Breast cancer colonization by Fusobacterium nucleatum accelerates tumor growth and metastatic progression. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, A.; Tangney, M.; Tunney, M.M.; Buckley, N.E. Fusobacterium nucleatum: a novel immune modulator in breast cancer? Expert Rev Mol Med 2023, 25, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, I. Chapter 173—Anaerobic bacteria. In Infectious Diseases (Third Edition), Cohen, J., Opal, S.M., Powderly, W.G., Eds.; Mosby: London, 2010; pp. 1757–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Allali, I.; Delgado, S.; Marron, P.I.; Astudillo, A.; Yeh, J.J.; Ghazal, H.; Amzazi, S.; Keku, T.; Azcarate-Peril, M.A. Gut microbiome compositional and functional differences between tumor and non-tumor adjacent tissues from cohorts from the US and Spain. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Kwon, H.; Kim, Y.J. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio as a Risk Factor of Breast Cancer. J Clin Med 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hieken, T.J.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Johnson, S.; Hoskin, T.L.; Degnim, A.C.; Walther-Antonio, M.R.; Chia, N. The breast tissue microbiome, stroma, immune cells and breast cancer. Neoplasia 2022, 27, 100786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German, R.; Marino, N.; Hemmerich, C.; Podicheti, R.; Rusch, D.B.; Stiemsma, L.T.; Gao, H.; Xuei, X.; Rockey, P.; Storniolo, A.M. Exploring breast tissue microbial composition and the association with breast cancer risk factors. Breast Cancer Res 2023, 25, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Ma, Q.; Cai, Z.; Raza, M.F.; Bai, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H. Similar Shift Patterns in Gut Bacterial and Fungal Communities Across the Life Stages of Bactrocera minax Larvae From Two Field Populations. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaniak, C.; McMillan, A.; Angelini, M.; Gloor, G.B.; Sumarah, M.; Burton, J.P.; Reid, G. Effect of chemotherapy on the microbiota and metabolome of human milk, a case report. Microbiome 2014, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathi, S.; Priya, P.S.; Haridevamuthu, B.; Nayak, S.P.R.R.; Chandrasekar, M.; Arockiaraj, J.; Jia, A.-Q. Expanding germ-organ theory: Understanding non-communicable diseases through enterobacterial translocation. Pharmacological Research 2023, 194, 106856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deplanche, M.; Mouhali, N.; Nguyen, M.-T.; Cauty, C.; Ezan, F.; Diot, A.; Raulin, L.; Dutertre, S.; Langouet, S.; Legembre, P.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus induces DNA damage in host cell. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klann, E.; Williamson, J.M.; Tagliamonte, M.S.; Ukhanova, M.; Asirvatham, J.R.; Chim, H.; Yaghjyan, L.; Mai, V. Microbiota composition in bilateral healthy breast tissue and breast tumors. Cancer Causes Control 2020, 31, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, M.; Dar, S.A.; Jawed, A.; Mandal, R.K.; Akhter, N.; Khan, S.; Khan, F.; Jogaiah, S.; Rai, A.K.; Rattan, R. Microbes in gynecologic cancers: Causes or consequences and therapeutic potential. Seminars in Cancer Biology 2022, 86, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima-Adachi, H.; Tamai, M.; Nakanishi, H.; Hachimura, S. Extracts of Gluconacetobacter hansenii GK-1 induce Foxp3(+)T cells in food-allergic mice by an IL-4-dependent or IL-4-independent mechanism. Biosci Microbiota Food Health 2022, 41, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilian, M.; Rawlynce, B.; Charles, G.; Felix, K. Potential role of rumen bacteria in modulating milk production and composition of admixed dairy cows. Letters in Applied Microbiology 2023, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangeetha, M.; Menakha, M.; Vijayakumar, S. Cryptophycin F—A potential cyanobacterial drug for breast cancer. Biomedicine & Aging Pathology 2014, 4, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fukui, R.; Jia, H.; Kato, H. Amaranth Supplementation Improves Hepatic Lipid Dysmetabolism and Modulates Gut Microbiota in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Foods 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton-Laskibar, I.; Cuevas-Sierra, A.; Portillo, M.P.; Martínez, J.A. Effects of Resveratrol Administration in Liver Injury Prevention as Induced by an Obesogenic Diet: Role of Ruminococcaceae. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaniak, C.; Gloor, G.B.; Brackstone, M.; Scott, L.; Tangney, M.; Reid, G. The Microbiota of Breast Tissue and Its Association with Breast Cancer. Appl Environ Microbiol 2016, 82, 5039–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindels, L.B.; Porporato, P.; Dewulf, E.M.; Verrax, J.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Martin, J.C.; Scott, K.P.; Buc Calderon, P.; Feron, O.; Muccioli, G.G.; et al. Gut microbiota-derived propionate reduces cancer cell proliferation in the liver. British Journal of Cancer 2012, 107, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wei, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, X.; Hou, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, B.; Cao, H. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids regulate gastrointestinal tumor immunity: a novel therapeutic strategy? Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1158200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derqaoui, S.; Oukessou, M.; Attrassi, K.; Elftouhy, F.Z.; Nassik, S. Detection of Sutterella spp. in Broiler Liver and Breast. Front Vet Sci 2022, 9, 859902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Orozco, F.; Thomas-Ahner, J.M.; Galley, J.D.; Bailey, M.T.; Clinton, S.K.; Lesinski, G.B.; Failla, M.L. Intestinal microbial dysbiosis and colonic epithelial cell hyperproliferation by dietary α-mangostin is independent of mouse strain. Nutrients 2015, 7, 764–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, M.S.; Chotirosniramit, K.; Nopsopon, T.; Hirankarn, N.; Pongpirul, K. Human gut, breast, and oral microbiome in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol 2023, 13, 1144021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yu, F.; Li, P. Intratumor microbiota in cancer pathogenesis and immunity: from mechanisms of action to therapeutic opportunities. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1269054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Yu, B.; Rao, B.; Sun, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, D.; Cui, G.; Ren, Z. The effect of the intratumoral microbiome on tumor occurrence, progression, prognosis and treatment. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 1051987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, C.; Li, Y.; Cheng, R.; He, F.; Shen, X. The Effect of Breast Milk Microbiota on the Composition of Infant Gut Microbiota: A Cohort Study. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieleman, S.; Aarnoutse, R.; Ziemons, J.; Kooreman, L.; Boleij, A.; Smidt, M. Exploring the Potential of Breast Microbiota as Biomarker for Breast Cancer and Therapeutic Response. The American Journal of Pathology 2021, 191, 968–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Langa, S.; Martín, V.; Maldonado, A.; Jiménez, E.; Martín, R.; Rodríguez, J.M. The human milk microbiota: Origin and potential roles in health and disease. Pharmacological Research 2013, 69, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gallego, C.; Garcia-Mantrana, I.; Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C. The human milk microbiome and factors influencing its composition and activity. Seminars in Fetal and Neonatal Medicine 2016, 21, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, M.C.; Rautava, S.; Aakko, J.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S. Human gut colonisation may be initiated in utero by distinct microbial communities in the placenta and amniotic fluid. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 23129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favier, C.F.; Vaughan, E.E.; Vos, W.M.D.; Akkermans, A.D.L. Molecular Monitoring of Succession of Bacterial Communities in Human Neonates. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2002, 68, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macia, L.; Mackay, C.R. Dysfunctional microbiota with reduced capacity to produce butyrate as a basis for allergic diseases. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2019, 144, 1513–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, M.P.; Saris, P.E.J. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus by the commensal bacteria of human milk. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2003, 95, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sela, D.A.; Mills, D.A. Nursing our microbiota: molecular linkages between bifidobacteria and milk oligosaccharides. Trends in Microbiology 2010, 18, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benito, D.; Lozano, C.; Jiménez, E.; Albújar, M.; Gómez, A.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Torres, C. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from faeces of healthy neonates and potential mother-to-infant microbial transmission through breastfeeding. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 2015, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, V.; Maldonado-Barragán, A.; Moles, L.; Rodriguez-Baños, M.; Campo, R.d.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Jiménez, E. Sharing of Bacterial Strains Between Breast Milk and Infant Feces. Journal of Human Lactation 2012, 28, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, P.M.; Schoemaker, M.H.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K.; Lambers, T.T.; van Tol, E.A.F.; Acerini, C.L.; Olga, L.; Petry, C.J.; Hughes, I.A.; et al. Human Milk Short-Chain Fatty Acid Composition is Associated with Adiposity Outcomes in Infants. The Journal of Nutrition 2019, 149, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, F.; Wen, L.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, H. Current Understanding of Microbiomes in Cancer Metastasis. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, F.; Zhao, B.; Wang, D.; Tang, D. Intratumoural microbiota: from theory to clinical application. Cell Communication and Signaling 2023, 21, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Kim, E.; Min, H.; Kim, M.G.; Eisenbeis, V.B.; Dutta, A.K.; Pavlovic, I.; Jessen, H.J.; Kim, S.; Seong, R.H. Inositol polyphosphates promote T cell-independent humoral immunity via the regulation of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 12952–12957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S.E.; Sun, L.Y.; Yang, A.L.; Liao, J.; Yang, G.Y. Overview of Inositol and Inositol Phosphates on Chemoprevention of Colitis-Induced Carcinogenesis. Molecules 2021, 26, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marth, J.D.; Grewal, P.K. Mammalian glycosylation in immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2008, 8, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Bin, P.; Yan, W.; Más, D.; Valdivié, M.; Hu, C.A.; Ren, W.; Yin, Y. The role of methionine on metabolism, oxidative stress, and diseases. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 2091–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colbert, L.E.; El Alam, M.B.; Wang, R.; Karpinets, T.; Lo, D.; Lynn, E.J.; Harris, T.A.; Elnaggar, J.H.; Yoshida-Court, K.; Tomasic, K.; et al. Tumor-resident Lactobacillus iners confer chemoradiation resistance through lactate-induced metabolic rewiring. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 1945–1962.e1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.; Yao, B.; Dong, T.; Chen, Y.; Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Bai, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Tumor-resident intracellular microbiota promotes metastatic colonization in breast cancer. Cell 2022, 185, 1356–1372.e1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullman, S.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Sicinska, E.; Clancy, T.E.; Zhang, X.; Cai, D.; Neuberg, D.; Huang, K.; Guevara, F.; Nelson, T.; et al. Analysis of Fusobacterium persistence and antibiotic response in colorectal cancer. Science 2017, 358, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skibinski, A.; Kuperwasser, C. The origin of breast tumor heterogeneity. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5309–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappelletti, V.; Iorio, E.; Miodini, P.; Silvestri, M.; Dugo, M.; Daidone, M.G. Metabolic Footprints and Molecular Subtypes in Breast Cancer. Dis Markers 2017, 2017, 7687851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Pierre, J.F.; Makowski, L.; Tolley, E.; Lyn-Cook, B.; Lu, L.; Vidal, G.; Starlard-Davenport, A. Distinct microbial communities that differ by race, stage, or breast-tumor subtype in breast tissues of non-Hispanic Black and non-Hispanic White women. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Altemus, J.; Niazi, F.; Green, H.; Calhoun, B.C.; Sturgis, C.; Grobmyer, S.R.; Eng, C. Breast tissue, oral and urinary microbiomes in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 88122–88138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzega, D.; Minarik, G.; Karaba, M.; Kalavska, K.; Benca, J.; Ciernikova, S.; Sedlackova, T.; Nemcova, P.; Bohac, M.; Pindak, D.; et al. Uncovering Microbial Composition in Human Breast Cancer Primary Tumour Tissue Using Transcriptomic RNA-seq. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, A.; Sangwan, N.; Jia, M.; Liu, C.C.; Keslar, K.S.; Downs-Kelly, E.; Fairchild, R.L.; Al-Hilli, Z.; Grobmyer, S.R.; Eng, C. Human breast microbiome correlates with prognostic features and immunological signatures in breast cancer. Genome Med 2021, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Wei, Z.; Tan, F.; Peck, K.N.; Shih, N.; Feldman, M.; Rebbeck, T.R.; Alwine, J.C.; Robertson, E.S. Distinct microbiological signatures associated with triple negative breast cancer. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 15162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.J.; Ingle, J.N.; Tang, X.; Chia, N.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Walther-Antonio, M.R.; Kandimalla, K.K.; Johnson, S.; Yao, J.Z.; Harrington, S.C.; et al. A comprehensive analysis of breast cancer microbiota and host gene expression. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0188873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chng, K.R.; Chan, S.H.; Ng, A.H.Q.; Li, C.; Jusakul, A.; Bertrand, D.; Wilm, A.; Choo, S.P.; Tan, D.M.Y.; Lim, K.H.; et al. Tissue Microbiome Profiling Identifies an Enrichment of Specific Enteric Bacteria in Opisthorchis viverrini Associated Cholangiocarcinoma. EBioMedicine 2016, 8, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audirac-Chalifour, A.; Torres-Poveda, K.; Bahena-Román, M.; Téllez-Sosa, J.; Martínez-Barnetche, J.; Cortina-Ceballos, B.; López-Estrada, G.; Delgado-Romero, K.; Burguete-García, A.I.; Cantú, D.; et al. Cervical Microbiome and Cytokine Profile at Various Stages of Cervical Cancer: A Pilot Study. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0153274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łaniewski, P.; Barnes, D.; Goulder, A.; Cui, H.; Roe, D.J.; Chase, D.M.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. Linking cervicovaginal immune signatures, HPV and microbiota composition in cervical carcinogenesis in non-Hispanic and Hispanic women. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 7593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejea, C.M.; Fathi, P.; Craig, J.M.; Boleij, A.; Taddese, R.; Geis, A.L.; Wu, X.; DeStefano Shields, C.E.; Hechenbleikner, E.M.; Huso, D.L.; et al. Patients with familial adenomatous polyposis harbor colonic biofilms containing tumorigenic bacteria. Science 2018, 359, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Guo, L.; Liu, J.J.; Zhao, H.P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.H. Alteration of the esophageal microbiota in Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2019, 25, 2149–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Castaño-Rodríguez, N.; Man, S.M.; Mitchell, H.M. Is Campylobacter to esophageal adenocarcinoma as Helicobacter is to gastric adenocarcinoma? Trends Microbiol 2015, 23, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Li, S.; Ma, Z.; Liang, S.; Shan, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, G.; Zhou, F.; et al. Presence of Porphyromonas gingivalis in esophagus and its association with the clinicopathological characteristics and survival in patients with esophageal cancer. Infect Agent Cancer 2016, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés-Jiménez, F.; Guitron, A.; Segura-López, F.; Méndez-Tenorio, A.; Iwai, S.; Hernández-Guerrero, A.; Torres, J. Microbiota studies in the bile duct strongly suggest a role for <em>Helicobacter pylori</em> in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2016, 22, 178.e111–178.e122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, Y.; Loza, E.; Villa-Gomez, G.; Trujillo, C.C.; Baez, S.; Asai, T.; Ikoma, T.; Endoh, K.; Nakamura, K. Metagenomics of Microbial Communities in Gallbladder Bile from Patients with Gallbladder Cancer or Cholelithiasis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2018, 19, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buti, L.; Spooner, E.; Van der Veen, A.G.; Rappuoli, R.; Covacci, A.; Ploegh, H.L. Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) subverts the apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 (ASPP2) tumor suppressor pathway of the host. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 9238–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Geng, F.; Shi, X.; Li, Q.; Lu, Z.; Pan, Y. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transiton through regulation of the lncRNA MIR4435-2HG/miR-296-5p/Akt2/SNAI1 signaling pathway. Febs j 2020, 287, 4032–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, M.; Avenaud, P.; Ménard, A.; Le Bail, B.; Balabaud, C.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; de Magalhães Queiroz, D.M.; Mégraud, F. Association of Helicobacter species with hepatitis C cirrhosis with or without hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2005, 54, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greathouse, K.L.; White, J.R.; Vargas, A.J.; Bliskovsky, V.V.; Beck, J.A.; von Muhlinen, N.; Polley, E.C.; Bowman, E.D.; Khan, M.A.; Robles, A.I.; et al. Interaction between the microbiome and TP53 in human lung cancer. Genome Biology 2018, 19, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Gail, M.H.; Consonni, D.; Carugno, M.; Humphrys, M.; Pesatori, A.C.; Caporaso, N.E.; Goedert, J.J.; Ravel, J.; Landi, M.T. Characterizing human lung tissue microbiota and its relationship to epidemiological and clinical features. Genome Biology 2016, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, B.L.; Kuczynski, J.; Bhattacharya, A.; Huey, B.; Corby, P.M.; Queiroz, E.L.; Nightingale, K.; Kerr, A.R.; DeLacure, M.D.; Veeramachaneni, R.; et al. Changes in abundance of oral microbiota associated with oral cancer. PLoS One 2014, 9, e98741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.J.; Seraj, I.M.; Kalugdan, T.H.; King, A. Prevalence of mycoplasma conserved DNA in malignant ovarian cancer detected using sensitive PCR-ELISA. Gynecol Oncol 1996, 63, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, L.T.; Barzily-Rokni, M.; Danino, T.; Jonas, O.H.; Shental, N.; Nejman, D.; Gavert, N.; Zwang, Y.; Cooper, Z.A.; Shee, K.; et al. Potential role of intratumor bacteria in mediating tumor resistance to the chemotherapeutic drug gemcitabine. Science 2017, 357, 1156–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushalkar, S.; Hundeyin, M.; Daley, D.; Zambirinis, C.P.; Kurz, E.; Mishra, A.; Mohan, N.; Aykut, B.; Usyk, M.; Torres, L.E.; et al. The Pancreatic Cancer Microbiome Promotes Oncogenesis by Induction of Innate and Adaptive Immune Suppression. Cancer Discov 2018, 8, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykut, B.; Pushalkar, S.; Chen, R.; Li, Q.; Abengozar, R.; Kim, J.I.; Shadaloey, S.A.; Wu, D.; Preiss, P.; Verma, N.; et al. The fungal mycobiome promotes pancreatic oncogenesis via activation of MBL. Nature 2019, 574, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavarretta, I.; Ferrarese, R.; Cazzaniga, W.; Saita, D.; Lucianò, R.; Ceresola, E.R.; Locatelli, I.; Visconti, L.; Lavorgna, G.; Briganti, A.; et al. The Microbiome of the Prostate Tumor Microenvironment. Eur Urol 2017, 72, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.J.; Shannon, B.A.; McNeal, J.E.; Shannon, T.; Garrett, K.L. Propionibacterium acnes associated with inflammation in radical prostatectomy specimens: a possible link to cancer evolution? J Urol 2005, 173, 1969–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Baba, Y.; Ishimoto, T.; Tsutsuki, H.; Zhang, T.; Nomoto, D.; Okadome, K.; Yamamura, K.; Harada, K.; Eto, K.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum confers chemoresistance by modulating autophagy in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 2021, 124, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, C.; Shamonki, J.M.; Chung, A.; Dinome, M.L.; Chung, M.; Sieling, P.A.; Lee, D.J. Microbial dysbiosis is associated with human breast cancer. PLoS One 2014, 9, e83744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, G.; Le Noci, V.; Di Modica, M.; Montanari, E.; Triulzi, T.; Pupa, S.M.; Tagliabue, E.; Sommariva, M.; Sfondrini, L. The Emerging Role of the Microbiota in Breast Cancer Progression. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, S.; Siddharth, S.; Xia, Y.; Sharma, D. Concomitant analyses of intratumoral microbiota and genomic features reveal distinct racial differences in breast cancer. npj Breast Cancer 2023, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyagarajan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Thapa, S.; Allen, M.S.; Phillips, N.; Chaudhary, P.; Kashyap, M.V.; Vishwanatha, J.K. Comparative analysis of racial differences in breast tumor microbiome. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 14116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Leeds, J.A.; Meredith, T.C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa directly shunts β-oxidation degradation intermediates into de novo fatty acid biosynthesis. J Bacteriol 2012, 194, 5185–5196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Choi, W.S.; Yoon, Y.; Jung, G.H.; Lee, C.K.; Ahn, S.H.; Wonsuck, Y.; Yoo, Y. Breast abscess caused by Staphylococcus aureus in 2 adolescent girls with atopic dermatitis. Korean J Pediatr 2018, 61, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, A.; Bawaneh, A.; Velazquez, C.; Clear, K.Y.J.; Wilson, A.S.; Howard-McNatt, M.; Levine, E.A.; Levi-Polyachenko, N.; Yates-Alston, S.A.; Diggle, S.P.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Shifts Breast Tumor Microbiota Populations to Regulate Drug Responsiveness and the Development of Metastasis. Molecular Cancer Research 2020, 18, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotland, N.; Uhre, M.L.; Sandholdt, H.; Mejer, N.; Lundbo, L.F.; Petersen, A.; Larsen, A.R.; Benfield, T. Increased risk of incident primary cancer after Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A matched cohort study. Medicine 2020, 99, e19984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullander, J.; Forslund, O.; Dillner, J. Staphylococcus aureus and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2009, 18, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, E.A.; Segre, J.A. The skin microbiome. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2011, 9, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-j.; Deng, H.; Ma, J.; Huang, S.-j.; Yang, J.-m.; Huang, Y.-f.; Mu, X.-p.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q. Clinical metagenomic analysis of bacterial communities in breast abscesses of granulomatous mastitis. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2016, 53, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Li, F.; Xu, H.; Yu, X.; Liu, L.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Etiology of granulomatous lobular mastitis based on metagenomic next-generation sequencing. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2021, 113, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal, J.; Carvajal, M.; Hernández, G. Back to Basics: Could the Preoperative Skin Antiseptic Agent Help Prevent Biofilm-Related Capsular Contracture? Aesthet Surg J 2019, 39, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachour, Y.; Poort, L.; Verweij, S.P.; van Selms, G.; Winters, H.A.H.; Ritt, M.J.P.F.; Niessen, F.B.; Budding, A.E. PCR Characterization of Microbiota on Contracted and Non-Contracted Breast Capsules. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery 2019, 43, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, U.M.; Mesina, J.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Haug, M.; Frey, H.P.; Pico, R.; Frei, R.; Pierer, G.; Lüscher, N.J.; Trampuz, A. Bacterial biofilms and capsular contracture in patients with breast implants. British Journal of Surgery 2013, 100, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Johani, K.; Almatroudi, A.; Vickery, K.; Van Natta, B.; Kadin, M.E.; Brody, G.; Clemens, M.; Cheah, C.Y.; Lade, S.; et al. Bacterial Biofilm Infection Detected in Breast Implant–Associated Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2016, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.N.; Hanson, B.M.; Pinkner, C.L.; Simar, S.R.; Pinkner, J.S.; Parikh, R.; Clemens, M.W.; Hultgren, S.J.; Myckatyn, T.M. Insights into the Microbiome of Breast Implants and Periprosthetic Tissue in Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 10393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, S.M.; Barsky, S.H. Anatomy of the nipple and breast ducts revisited. Cancer 2004, 101, 1947–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, P.A.; Hewitt, J.H.; Murphy, O.M. Influence of methods of collection and storage on the bacteriology of human milk. The Journal of applied bacteriology 1979, 46 2, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.A.; Bashir, M.; Rivas, M.N.; Duvall, K.; Sieling, P.A.; Pieber, T.R.; Vaishampayan, P.A.; Love, S.M.; Lee, D.J. Characterization of the microbiome of nipple aspirate fluid of breast cancer survivors. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 28061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, D.T.; Kent, J.C.; Owens, R.A.; Hartmann, P.E. Ultrasound Imaging of Milk Ejection in the Breast of Lactating Women. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, R.D. Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tract. Adv Exp Med Biol 1999, 473, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedman, P.C.; Macfie, J.; Sagar, P.; Mitchell, C.J.; May, J.; Mancey-Jones, B.; Johnstone, D. The prevalence of gut translocation in humans. Gastroenterology 1994, 107, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.V.; Baigorí, M.D.; Alvarez, S.; Castro, G.R.; Oliver, G. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity in Lactobacillus rhamnosus with capacity to translocate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2001, 204, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, R.D. Bacterial translocation from the gastrointestinal tract. Trends Microbiol 1995, 3, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, P.F.; Doré, J.l.; Leclerc, M.; Levenez, F.; Benyacoub, J.; Serrant, P.; Segura-Roggero, I.; Schiffrin, E.J.; Donnet-Hughes, A. Bacterial Imprinting of the Neonatal Immune System: Lessons From Maternal Cells? Pediatrics 2007, 119, e724–e732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, M.; Morrissey, D.; Rajendran, S.; El Mashad, S.M.; van Sinderen, D.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; Tangney, M. Orally administered bifidobacteria as vehicles for delivery of agents to systemic tumors. Mol Ther 2010, 18, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danino, T.; Prindle, A.; Kwong, G.A.; Skalak, M.; Li, H.; Allen, K.; Hasty, J.; Bhatia, S.N. Programmable probiotics for detection of cancer in urine. Sci Transl Med 2015, 7, 289ra284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, A.; Rodríguez, J. Prebiotics and Probiotics in Human Milk. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg, P. The mucosal immune system and its integration with the mammary glands. J Pediatr 2010, 156, S8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, A.S.; Goldblum, R.M. Transfer of maternal leukocytes to the infant by human milk. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 1997, 222, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trend, S.; de Jong, E.; Lloyd, M.L.; Kok, C.H.; Richmond, P.; Doherty, D.A.; Simmer, K.; Kakulas, F.; Strunk, T.; Currie, A. Leukocyte Populations in Human Preterm and Term Breast Milk Identified by Multicolour Flow Cytometry. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0135580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuaillon, E.; Valea, D.; Becquart, P.; Al Tabaa, Y.; Meda, N.; Bollore, K.; Van de Perre, P.; Vendrell, J.P. Human milk-derived B cells: a highly activated switched memory cell population primed to secrete antibodies. J Immunol 2009, 182, 7155–7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabinian, A.; Sinsimer, D.; Tang, M.; Zumba, O.; Mehta, H.; Toma, A.; Sant’Angelo, D.; Laouar, Y.; Laouar, A. Transfer of Maternal Immune Cells by Breastfeeding: Maternal Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Present in Breast Milk Localize in the Peyer’s Patches of the Nursed Infant. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0156762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, K.A. Adaptation of the maternal intestine during lactation. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 1997, 2, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosalbes, M.J.; Compte, J.; Moriano-Gutierrez, S.; Vallès, Y.; Jiménez-Hernández, N.; Pons, X.; Artacho, A.; Francino, M.P. Metabolic adaptation in the human gut microbiota during pregnancy and the first year of life. EBioMedicine 2019, 39, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, E.; Fernández, L.; Maldonado, A.; Martín, R.; Olivares, M.; Xaus, J.; Rodríguez, J.M. Oral Administration of <i>Lactobacillus</i> Strains Isolated from Breast Milk as an Alternative for the Treatment of Infectious Mastitis during Lactation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2008, 74, 4650–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, R.; Martín, V.; Maldonado, A.; Jiménez, E.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M. Treatment of Infectious Mastitis during Lactation: Antibiotics versus Oral Administration of Lactobacilli Isolated from Breast Milk. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2010, 50, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moossavi, S.; Azad, M.B. Origins of human milk microbiota: new evidence and arising questions. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1667722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, M.; Lei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Xiang, X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Q. Oral Microbiota and Tumor-A New Perspective of Tumor Pathogenesis. Microorganisms 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petris, C.K.; Golomb, M.; Phillips, T.E. Bacterial Transcytosis across Conjunctival M Cells. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 2007, 48, 2172–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, M.D.; Leaphart, C.; Levy, R.; Prince, J.; Billiar, T.R.; Watkins, S.; Li, J.; Cetin, S.; Ford, H.; Schreiber, A.; et al. Enterocyte TLR4 mediates phagocytosis and translocation of bacteria across the intestinal barrier. J Immunol 2006, 176, 3070–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Moniri, N.H.; Ozawa, K.; Stamler, J.S.; Daaka, Y. Nitric oxide regulates endocytosis by S-nitrosylation of dynamin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, C.L.; VandeWesterlo, E.M.; Jechorek, R.P.; Erlandsen, S.L. Effect of hypoxia on enterocyte endocytosis of enteric bacteria. Crit Care Med 1996, 24, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Keita Å, V.; Phan, V.; McKay, C.M.; Schoultz, I.; Lee, J.; Murphy, M.P.; Fernando, M.; Ronaghan, N.; Balce, D.; et al. Targeting mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species to reduce epithelial barrier dysfunction and colitis. Am J Pathol 2014, 184, 2516–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.; Lutgendorff, F.; Phan, V.; Söderholm, J.D.; Sherman, P.M.; McKay, D.M. Enhanced translocation of bacteria across metabolically stressed epithelia is reduced by butyrate. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2010, 16, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, E.; Hoare, C.; Tanianis-Hughes, J.; Carlson, G.L.; Warhurst, G. Interferon gamma induces translocation of commensal Escherichia coli across gut epithelial cells via a lipid raft-mediated process. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, D.; McKay, C.M.; Gulbransen, B.D.; Phan, V.C.; Wang, A.; McKay, D.M. Interferon-gamma signals via an ERK1/2-ARF6 pathway to promote bacterial internalization by gut epithelia. Cell Microbiol 2012, 14, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.L.; Chen, S.; Wu, H.W.; Lee, T.C.; Lu, Y.Z.; Wu, L.L.; Ni, Y.H.; Sun, C.H.; Yu, W.H.; Buret, A.G.; et al. Persistent gut barrier damage and commensal bacterial influx following eradication of Giardia infection in mice. Gut Pathog 2013, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalischuk, L.D.; Inglis, G.D.; Buret, A.G. Campylobacter jejuni induces transcellular translocation of commensal bacteria via lipid rafts. Gut Pathog 2009, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.L.; Peng, W.H.; Kuo, W.T.; Huang, C.Y.; Ni, Y.H.; Lu, K.S.; Turner, J.R.; Yu, L.C. Commensal bacterial endocytosis in epithelial cells is dependent on myosin light chain kinase-activated brush border fanning by interferon-γ. Am J Pathol 2014, 184, 2260–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosi, T.; Pflug, A.; Discola, K.F.; Neves, D.; Dessen, A. Structural basis of eukaryotic cell targeting by type III secretion system (T3SS) effectors. Res Microbiol 2013, 164, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescigno, M.; Urbano, M.; Valzasina, B.; Francolini, M.; Rotta, G.; Bonasio, R.; Granucci, F.; Kraehenbuhl, J.-P.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Dendritic cells express tight junction proteins and penetrate gut epithelial monolayers to sample bacteria. Nature Immunology 2001, 2, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Torres, A.; Jones-Carson, J.; Bäumler, A.J.; Falkow, S.; Valdivia, R.; Brown, W.; Le, M.; Berggren, R.; Parks, W.T.; Fang, F.C. Extraintestinal dissemination of Salmonella by CD18-expressing phagocytes. Nature 1999, 401, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langa, S. Interactions between lactic acid bacteria, intestinal epithelial cells and immune cells. Development of in vitro models; Complutense University of Madrid: Madrid, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Langa, S.; Maldonado-Barragán, A.; Delgado, S.; Martín, R.; Martín, V.; Jiménez, E.; Ruíz-Barba, J.L.; Mayo, B.; Connor, R.I.; Suárez, J.E.; et al. Characterization of Lactobacillus salivarius CECT 5713, a strain isolated from human milk: from genotype to phenotype. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2012, 94, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescigno, M.; Citterio, S.; Thèry, C.; Rittig, M.; Medaglini, D.; Pozzi, G.; Amigorena, S.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Bacteria-induced neo-biosynthesis, stabilization, and surface expression of functional class I molecules in mouse dendritic cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1998, 95, 5229–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, A.J.; Uhr, T. Induction of protective IgA by intestinal dendritic cells carrying commensal bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1662–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.C.; Bessman, N.J.; Hepworth, M.R.; Kumar, N.; Shibata, N.; Kobuley, D.; Wang, K.; Ziegler, C.G.K.; Goc, J.; Shima, T.; et al. Lymphoid-Tissue-Resident Commensal Bacteria Promote Members of the IL-10 Cytokine Family to Establish Mutualism. Immunity 2016, 44, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roitt, I.M. Essential immunology. 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Martı́n, R.o.; Langa, S.; Reviriego, C.; Jiménez, E.; Marı́n, M.a.L.; Olivares, M.; Boza, J.; Jiménez, J.; Fernández, L.; Xaus, J. The commensal microflora of human milk: new perspectives for food bacteriotherapy and probiotics. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2004, 15, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Bertotto, A.; Gerli, R.; Castellucci, G.; Scalise, F.; Vaccaro, R. Human milk lymphocytes bearing the gamma/delta T-cell receptor are mostly delta TCS1-positive cells. Immunology 1991, 74, 360. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Corrêa-Silva, S.; de Souza, E.C.; Maria Rodrigues, R.; da Fonseca, F.A.M.; Gilio, A.E.; Carneiro-Sampaio, M.; Palmeira, P. Macrophage profile and homing into breast milk in response to ongoing respiratory infections in the nursing infant. Cytokine 2020, 129, 155045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluch, J.; Servant, F.; Païssé, S.; Valle, C.; Valiere, S.; Kuchly, C.; Vilchez, G.; Donnadieu, C.; Courtney, M.; Burcelin, R. The characterization of novel tissue microbiota using an optimized 16S metagenomic sequencing pipeline. PloS one 2015, 10, e0142334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, C.M.; Velasco, C.; Rivas, A.; Andrews, M.; Garman, C.; Jacob, P.B.; Jeffries, M.A. Identification of cartilage microbial DNA signatures and associations with knee and hip osteoarthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatology 2020, 72, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Berthelot, J.-M.; Lioté, F.; Sibilia, J. Tissue microbiota: A’secondary-self’, first target of autoimmunity? 2022, 89, 105337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosang, L.; Canals, R.C.; van der Flier, F.J.; Hollensteiner, J.; Daniel, R.; Flügel, A.; Odoardi, F. The lung microbiome regulates brain autoimmunity. Nature 2022, 603, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immunity to Infection. Primer to the Immune Response 2014, 295–332. [CrossRef]
- Cullin, N.; Antunes, C.A.; Straussman, R.; Stein-Thoeringer, C.K.; Elinav, E. Microbiome and cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1317–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO, I. IARC monographs program on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans-some industrial-chemicals, Lyon, 15-22 February 1994-preamble. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans 1994, 60, 13–33. [Google Scholar]
- Prentice, P.M.; Schoemaker, M.H.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K.; Lambers, T.T.; Van Tol, E.A.; Acerini, C.L.; Olga, L.; Petry, C.J.; Hughes, I.A. Human milk short-chain fatty acid composition is associated with adiposity outcomes in infants. The Journal of nutrition 2019, 149, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, T.; Mikó, E.; Vida, A.; Sebő, É.; Toth, J.; Csonka, T.; Boratkó, A.; Ujlaki, G.; Lente, G.; Kovács, P.; et al. Cadaverine, a metabolite of the microbiome, reduces breast cancer aggressiveness through trace amino acid receptors. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sári, Z.; Mikó, E.; Kovács, T.; Jankó, L.; Csonka, T.; Lente, G.; Sebő, É.; Tóth, J.; Tóth, D.; Árkosy, P.; et al. Indolepropionic Acid, a Metabolite of the Microbiome, Has Cytostatic Properties in Breast Cancer by Activating AHR and PXR Receptors and Inducing Oxidative Stress. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Matuszek, Ż.; Zhang, W.; Xia, Y.; Pan, T.; Sun, J. tRNA Queuosine Modification Enzyme Modulates the Growth and Microbiome Recruitment to Breast Tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Zallot, R.; Grove, T.L.; Payan, D.J.; Martin-Verstraete, I.; Šepić, S.; Balamkundu, S.; Neelakandan, R.; Gadi, V.K.; Liu, C.F.; et al. Discovery of novel bacterial queuine salvage enzymes and pathways in human pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 19126–19135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyles, L.; Jiménez-Pranteda, M.L.; Chilloux, J.; Brial, F.; Myridakis, A.; Aranias, T.; Magnan, C.; Gibson, G.R.; Sanderson, J.D.; Nicholson, J.K.; et al. Metabolic retroconversion of trimethylamine N-oxide and the gut microbiota. Microbiome 2018, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, Q. Awareness of intratumoral bacteria and their potential application in cancer treatment. Discover Oncology 2023, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.; Parida, S.; Lingipilli, B.T.; Krishnan, R.; Podipireddy, D.R.; Muniraj, N. Role of Gut Microbiota in Breast Cancer and Drug Resistance. Pathogens 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Ren, F.; Shang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Association between oral microbiome and breast cancer in the east Asian population: A Mendelian randomization and case–control study. Thoracic Cancer 2024, 15, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, A.D.; Chun, E.; Robertson, L.; Glickman, J.N.; Gallini, C.A.; Michaud, M.; Clancy, T.E.; Chung, D.C.; Lochhead, P.; Hold, G.L.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeger, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ruf, S.; Meyle, J. Pathogenic Mechanisms of Fusobacterium nucleatum on Oral Epithelial Cells. Front Oral Health 2022, 3, 831607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellarin, M.; Warren, R.L.; Freeman, J.D.; Dreolini, L.; Krzywinski, M.; Strauss, J.; Barnes, R.; Watson, P.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Moore, R.A.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum infection is prevalent in human colorectal carcinoma. Genome Res 2012, 22, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Yamada, M.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Chen, S.G.; Han, Y.W. FadA from Fusobacterium nucleatum Utilizes both Secreted and Nonsecreted Forms for Functional Oligomerization for Attachment and Invasion of Host Cells*. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2007, 282, 25000–25009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Gao, Q.; Mehrazarin, S.; Tangwanichgapong, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Robinson, S.; Liu, Z.; Zangiabadi, A.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum secretes amyloid-like FadA to enhance pathogenicity. EMBO Rep 2021, 22, e52891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.W.; Redline, R.W.; Li, M.; Yin, L.; Hill, G.B.; McCormick, T.S. Fusobacterium nucleatum Induces Premature and Term Stillbirths in Pregnant Mice: Implication of Oral Bacteria in Preterm Birth. Infection and Immunity 2004, 72, 2272–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.W.; Shi, W.; Huang, G.T.J.; Kinder Haake, S.; Park, N.H.; Kuramitsu, H.; Genco, R.J. Interactions between periodontal bacteria and human oral epithelial cells: Fusobacterium nucleatum adheres to and invades epithelial cells. Infection and Immunity 2000, 68, 3140–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engevik, M.A.; Danhof, H.A.; Ruan, W.; Engevik, A.C.; Chang-Graham, A.L.; Engevik, K.A.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Brand, C.K.; Krystofiak, E.S. Fusobacterium nucleatum secretes outer membrane vesicles and promotes intestinal inflammation. MBio 2021, 12, 10–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Nagata, E.; Oho, T. Invasive Streptococcus mutans induces inflammatory cytokine production in human aortic endothelial cells via regulation of intracellular toll-like receptor 2 and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 2. Mol Oral Microbiol 2017, 32, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Maishi, N.; Akahori, E.; Hasebe, A.; Takeda, R.; Matsuda, A.Y.; Hida, Y.; Nam, J.-M.; Onodera, Y.; Kitagawa, Y.; et al. The oral bacterium Streptococcus mutans promotes tumor metastasis by inducing vascular inflammation. Cancer Science 2022, 113, 3980–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, A.I.; Rey, V.S.d.; Zamora, L.; Casamayor, A.; Domínguez, L.; Fernández-Garayzábal, J.F. Streptococcus cuniculi sp. nov., isolated from the respiratory tract of wild rabbits. International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology 2014, 64 Pt 7, 2486–2490. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Zhou, H.; Holden, V.K.; Deepak, J.; Dhilipkannah, P.; Todd, N.W.; Stass, S.A.; Jiang, F. Streptococcus pneumoniae promotes lung cancer development and progression. iScience 2023, 26, 105923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Huang, J.; Xiao, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, X. The Streptococcus virulence protein PepO triggers anti-tumor immune responses by reprograming tumor-associated macrophages in a mouse triple negative breast cancer model. Cell & Bioscience 2023, 13, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Gnanasekar, A.; Lee, A.; Li, W.T.; Haas, M.; Wang-Rodriguez, J.; Chang, E.Y.; Rajasekaran, M.; Ongkeko, W.M. Influence of Intratumor Microbiome on Clinical Outcome and Immune Processes in Prostate Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Martínez, A.F.; González-Fontal, G.R.; Castillo-Mancilla, J.R.; Yang, I.V. Enterobacteriaceae bacteremias among cancer patients: an observational cohort study. Int J Infect Dis 2013, 17, e374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliero, M.; Calvé, A.; Fragoso, G.; Cuisiniere, T.; Hajjar, R.; Dobrindt, U.; Santos, M.M. Oligosaccharides increase the genotoxic effect of colibactin produced by pks+ Escherichia coli strains. BMC cancer 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Aschtgen, M.-S.; Fragkoulis, K.; Sanz, G.; Normark, S.; Selivanova, G.; Henriques-Normark, B.; Peuget, S. Enterobacteria impair host p53 tumor suppressor activity through mRNA destabilization. Oncogene 2022, 41, 2173–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallourou, N.; Urbaniak, C.; Puebla-Barragan, S.; Vorkas, P.A.; Swann, J.R.; Reid, G. Characterizing the breast cancer lipidome and its interaction with the tissue microbiota. Communications biology 2021, 4, 1229. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhu, W.; Chen, C.; Yan, B.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Peng, C. The mechanisms of lysophosphatidylcholine in the development of diseases. Life Sciences 2020, 247, 117443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, D.M. The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer 2006, 118, 3030–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xia, H.; Tan, X.; Shi, C.; Ma, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhou, M.; Lv, Z.; Wang, S.; Jin, Y. Intratumoural microbiota: a new frontier in cancer development and therapy. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2024, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, J.S.; Heng, B. Viruses and breast cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2010, 2, 752–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, L.; Gray, E.E.; Brunette, R.L.; Stetson, D.B. DNA tumor virus oncogenes antagonize the cGAS-STING DNA-sensing pathway. Science 2015, 350, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Donnelly, C.R.; Gong, W.; Heath, B.R.; Hao, Y.; Donnelly, L.A.; Moghbeli, T.; Tan, Y.S.; Lin, X.; Bellile, E.; et al. HPV16 drives cancer immune escape via NLRX1-mediated degradation of STING. J Clin Invest 2020, 130, 1635–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.W.; Jiang, S.; Gewurz, B.E. Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1-Mediated Oncogenicity. J Virol 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floor, S.L.; Dumont, J.E.; Maenhaut, C.; Raspe, E. Hallmarks of cancer: of all cancer cells, all the time? Trends Mol Med 2012, 18, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.C.; Brianti, M.T.; Almeida, V.R.; Ortega, M.M.; Fischer, W.; Haas, R.; Matheu, A.; Ribeiro, M.L. Helicobacter pylori infection modulates the expression of miRNAs associated with DNA mismatch repair pathway. Mol Carcinog 2017, 56, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, A.C.; Destefano Shields, C.E.; Wu, S.; Huso, D.L.; Wu, X.; Murray-Stewart, T.R.; Hacker-Prietz, A.; Rabizadeh, S.; Woster, P.M.; Sears, C.L.; et al. Polyamine catabolism contributes to enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis-induced colon tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 15354–15359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Tian, Z.; Kong, X.; Yang, L.; Shan, X.; Dong, B.; Ding, X.; Jing, X.; Jiang, C.; Jiang, N.; et al. FadA promotes DNA damage and progression of Fusobacterium nucleatum-induced colorectal cancer through up-regulation of chk2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2020, 39, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Pan, Y. Fusobacterium nucleatum Caused DNA Damage and Promoted Cell Proliferation by the Ku70/p53 Pathway in Oral Cancer Cells. DNA Cell Biol 2020, 39, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddocks, O.D.; Scanlon, K.M.; Donnenberg, M.S. An Escherichia coli effector protein promotes host mutation via depletion of DNA mismatch repair proteins. mBio 2013, 4, e00152–00113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Jin, Y.H. Intestinal bacterial beta-glucuronidase activity of patients with colon cancer. Arch Pharm Res 2001, 24, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humblot, C.; Murkovic, M.; Rigottier-Gois, L.; Bensaada, M.; Bouclet, A.; Andrieux, C.; Anba, J.; Rabot, S. β-Glucuronidase in human intestinal microbiota is necessary for the colonic genotoxicity of the food-borne carcinogen 2-amino-3-methylimidazo [4, 5-f] quinoline in rats. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 2419–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizumoto, A.; Ohashi, S.; Hirohashi, K.; Amanuma, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Muto, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Acetaldehyde-Mediated Carcinogenesis in Squamous Epithelium. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, I.; Yilmaz, Ö. Possible role of Porphyromonas gingivalis in orodigestive cancers. Journal of oral microbiology 2019, 11, 1563410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Banerjee, P.; Guo, H.F.; Ireland, S.; Pankova, D.; Ahn, Y.H.; Nikolaidis, I.M.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, Y.; et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition drives a pro-metastatic Golgi compaction process through scaffolding protein PAQR11. J Clin Invest 2017, 127, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivant, A.L.; Garmyn, D.; Piveteau, P. Listeria monocytogenes, a down-to-earth pathogen. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2013, 3, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauvau, G.; Vijh, S.; Kong, P.; Horng, T.; Kerksiek, K.; Serbina, N.; Tuma, R.A.; Pamer, E.G. Priming of memory but not effector CD8 T cells by a killed bacterial vaccine. Science 2001, 294, 1735–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhao, J.; Shen, S.; Li, H.; He, K.L.; Shen, G.X.; Mayer, L.; Unkeless, J.; Li, D.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Listeria monocytogenes promotes tumor growth via tumor cell toll-like receptor 2 signaling. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 4346–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Ma, F.; Guo, B.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Rong, Z.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; et al. Listeria monocytogenes promotes breast cancer proliferation and enhances the survival rate of circulating breast cancer cells. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.D.; Mineva, G.M.; Guttman, J.A. Ube2N is present and functions within listeria Actin-rich structures and lamellipodia: A localization and pharmacological inhibition study. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 2023, 306, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Font-Burgada, J.; Palmer, T.; Hamil, A.S.; Biswas, S.K.; Poidinger, M.; Borcherding, N.; Xie, Q.; Ellies, L.G.; et al. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13 controls breast cancer metastasis through a TAK1-p38 MAP kinase cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 13870–13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, M.; Liu, H.; Ziebolz, D.; Schmalz, G.; Jia, B.; Zhao, J. More Than Just a Periodontal Pathogen -the Research Progress on Fusobacterium nucleatum. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022, 12, 815318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, S.; Li, M.; Xu, C.; Jia, D.; Qi, Y.; Hou, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, B. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes colorectal cancer cells adhesion to endothelial cells and facilitates extravasation and metastasis by inducing ALPK1/NF-κB/ICAM1 axis. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2038852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lian, J.; Wu, S.; Luo, D.; Gong, H. Fusobacterium nucleatum-derived small extracellular vesicles facilitate tumor growth and metastasis via TLR4 in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.A.; Buckwold, S.L.; Shin, J.W.; Ascon, M.; Sears, C.L. Mutation of the zinc-binding metalloprotease motif affects Bacteroides fragilis toxin activity but does not affect propeptide processing. Infect Immun 2005, 73, 5273–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradella, D.; Naro, C.; Sette, C.; Ghigna, C. EMT and stemness: flexible processes tuned by alternative splicing in development and cancer progression. Molecular Cancer 2017, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.; Wu, S.; Siddharth, S.; Wang, G.; Muniraj, N.; Nagalingam, A.; Hum, C.; Mistriotis, P.; Hao, H.; Talbot, C.C., Jr.; et al. A Procarcinogenic Colon Microbe Promotes Breast Tumorigenesis and Metastatic Progression and Concomitantly Activates Notch and β-Catenin Axes. Cancer Discov 2021, 11, 1138–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, A.; Yao, B.; Dong, T.; Cai, S. Emerging roles of intratumor microbiota in cancer metastasis. Trends in Cell Biology 2023, 33, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrbeck, A.; Just, I. Cell Entry of C3 Exoenzyme from Clostridium botulinum. In Uptake and Trafficking of Protein Toxins, Barth, H., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2017; pp. 97–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Shang, Q.; Li, W.; Guo, W.; Stojadinovic, A.; Mannion, C.; Man, Y.G.; Chen, T. Antibiotics for cancer treatment: A double-edged sword. J Cancer 2020, 11, 5135–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J.; Shi, W.; Huang, Z.; Xia, W.; Huang, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, S.; Shi, Y.; Bi, X.; et al. Efficacy of Moxifloxacin plus Treatment of Physician’s Choice in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2020, 25, e1439–e1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, J.D.; Ritter, V.; Purington, N.; Andrade, K.; Han, S.; Liu, M.; Liang, S.-Y.; John, E.M.; Gomez, S.L.; Telli, M.L.; et al. Antimicrobial exposure is associated with decreased survival in triple-negative breast cancer. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Normal Breast | Breast Cancer | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microbes | Levels | Functions | Ref. | Microbes | Levels | Functions | Ref. |
| Sphingomonas | Higher | Degrades environmental carcinogens, aromatic hydrocarbons and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons; protective against ER+ breast cancer | [24,28] | Fusobacterium nucleatum | Higher | Promotes breast cancer cell attachment, invasion and colonization during metastasis; impairs immunity and therapy response; activates β-catenin-mediated oncogene transcription and cell proliferation; produces β-lactamase for resistance to β-lactam antibiotics (e.g., penicillin) | [24,29,30,31] |
|
Firmicutes, /Actinobacteria |
Higher | Negatively correlate with stromal fibrosis and breast cancer risk; enriched in breast milk | [32,33,34] | ||||
|
Lactobacillaceae, Acetobacterraceae, Leuconostocaceae Xanthomonadaceae |
Higher | Induce fructose and mannose metabolism and immune-related genes; enriched in breast milk of healthy women | [35,36,37] | Enterobacteriaceae, Staphylococcus | Higher | Induce DNA double-strand break of host cells | [38,39] |
| Ralstonia | Higher | Dysregulates genes involved in the carbohydrate metabolism | [35] | ||||
| Cyanobacteria, | Higher | Produces anti-cancer molecule (e.g, Cryptophycin F) | [40] | Atopobium, Gluconacetobacter, | Higher | Modulate immunological responses | [24,41,42] |
| Proteobacteria, Synergistetes, Tenericutes | Higher | Regulate milk composition and production; | [43,44] | Porphyromonadaceae, Ruminococcaceae, | Higher | Participates in aberrant host metabolism | [40,45,46] |
|
Prevotellaceae Butyricimonas, |
Higher | Produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) propionate and butyrate that exert anti-tumor activities | [40,47,48,49] |
Sutterella, Verrucomicrobiaceae |
Higher | Also found in cecal microbiota | [40,50,51] |
| Acinetobacter, | Higher | Abundant in HR+ and HER2+ breast cancer | [40,52] | ||||
|
Flavobacterium Hydrogenophaga |
Higher | Abundant in metastatic breast cancer | [40,53,54] | ||||
|
Alcaligenaceae, Moraxellaceae, Parabacteroides |
Higher | Enriched in breast milk | [40,55] |
Akkermansia (phylum Verrucomicrobia), Thermia, |
Higher | Abundant in TNBC | [40,56] |
| Cancer types | Microbes | Levels | Protumor mechanisms | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast | Fusobacterium nucleatum | Increased | Suppresses T cell infiltration into tumors; promotes tumor growth and metastatic progression | [29] |
| Anaerococcus, Caulobacter Propionibacterium, Streptococcus, Staphylococcus | Decreased | Positively correlated with oncogenic immune features and T-cell activation-related genes | [81] | |
| Bile duct |
Bifidobacteriaceae, Enterobacteriaceae, Enterococcaceae |
Increased | Increased production of bile acids and ammonia, leading to DNA damage in host cells and carcinogenesis | [84] |
| Cervical | Fusobacterium spp. | Increased | Associated with increased IL-4 and TGF-β1 mRNA in cervical cells | [85] |
|
Anaerotruncus, Anaerostipes, Atopobium, Arthrospira, Bacteroides, Dialister, Peptoniphilus, Porphyromonas, Ruminococcus, Treponema |
Increased | Elevates vaginal pH to weaken host defense against infection and promotes tumor formation | [86] | |
| Colorectal | Bacteroides fragilis | Increased | Increased interleukin-17 in the colon and DNA damage in colonic epithelium that accelerate tumor onset and elevate host mortality | [87] |
| Fusobacterium | Increased | Cancer cell proliferation and distant metastasis | [75] | |
| Esophageal | Lactobacillus fermentum | Increased | Establishes acidic environment for growth advantage | [88] |
| Helicobacter pylori | Increased | Spread from gastric colonization | [88] | |
| Campylobacter spp. | Increased | Causes inflammation that could contribute to carcinogenesis | [89] | |
| Porphyromonas gingivalis | Increased | Accelerate cell cycle, promotes cellular migration, and metabolism of potentially carcinogenic substances such as ethanol to carcinogenic derivative, acetaldehyde | [90] | |
| Extrahepatic Bile duct |
Helicobacter pylori | Increased | Increases in virulence genes cagA and vacA abundance and promotes tumor formation | [85] |
| Helicobacter bilis | Increased | Induces inflammation to contribute to tumor formation | [91] | |
| Gallbladder | Fusobacterium nucleatum, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp. | Increased | Promotes gallstones development and chronic cholecystitis to contribute to tumor formation | [92] |
| Gastric | Helicobacter pylori | Increased | CagA protein suppresses p53-mediated apoptosis of host cells while increasing cell motility, and metastatic phenotype | [93] |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum | Increased | Induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition | [94] | |
| Liver cancer | Helicobacter bifidus | Increased | Contributes to formation of chronic hepatitis that promotes tumor progression | [95] |
| Lung | Acidovorax spp. | Increased | Associated with carcinomas with p53 mutations | [96] |
| Thermus, Legionella | Increased | Associated with the advanced stage and metastatic cancer | [97] | |
| Oral cancer | Fusobacterium nucleatum | Increased | Induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition | [94] |
| Firmicutes (esp. Streptococcus), Actinobacteria (esp. Rothia) | Increased | Elevated in normal oral tissues | [98] | |
| Ovarian | Mycoplasma | Increased | Prevalent in 60% of tumors | [99] |
| Pancreatic | Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas spp., Mycobacterium avium, Pseudoxanthomonas, Streptomyces, Bacillus cereus | Increased | Contributes to chemotherapy resistance and immune suppression | [100,101] |
| Malassezia globosa | Increased | Induces the complement cascade through the activation of mannose-binding lectin C3 to promote tumorigenesis | [102] | |
| Prostate | Pseudomonas, Escherichia, Immunobacterium, Propionibacterium spp. | Increased | Induces prostatitis and differentiation of prostate basal cells into ductal cells to promote tumor formation | [103] |
| Propionibacterium acnes spp. | Increased | Induces prostatitis and promotes tumor formation | [104] | |
| Staphylococcus | Increased | Induce inflammation of the prostate tissue and promotes tumor formation | [103] | |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum, Streptococcus oligosporus | Increased | Induces chemoresistance by regulating autophagy | [105] |
| Breast cancer Subtypes |
Microbes | Levels | Sample Type | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luminal A | Proteobacteria (Xanthomonadale,) | Increased | Breast tumor | [78] |
| Tenericutes, Proteobacteria, Planctomycetes | Increased | Breast tumor | [106] | |
| Luminal B | Firmicutes (Clostridium) | Increased | Breast tumor | [78] |
| Tenericutes, Proteobacteria, and Planctomycetes | Increased | Breast tumor | [106] | |
| HER2+ | Thermi, Verrucomicrobia (Akkermasia) | Increased | Breast tumor | [78] |
| Firmicutes (Granulicatella:US31),Bacteroidetes (Dyadobacter) | Increased | Breast tumor | [26] | |
| Firmicutes (Filibacter, Anaerostipes), Bacteroides (Cloacibacterium, Alloprevotella), Proteobacteria (PRD01a011B, Stakelama Blastomonas) | Increased | Breast Tumor | [9] | |
| Proteobacteria (Burkholderiales, Helicobacter pylori) | Increased | Breast Tumor | [80] | |
| TNBC | Streptococcaceae, Ruminococcus | Increased | Breast tumor | [78] |
| Actinomycetaceae, Caulobacteriaceae, Sphingobacteriaceae, Enterobacteriaceae, Prevotellaceae, Brucellaceae, Bacillaceae, Peptostreptococcaceae, Flavobacteriaceae | Increased | Breast tumor | [82] | |
| Prevotella, Brevundimonas, Actinomyces, Aerococcus, Arcobacter, Geobacillus, Orientia, Rothia, Streptococcaceae, Ruminococcus, phyla Euryarchaeota | Increased | Breast tumor | [78,82] | |
| Bartonella, Coxiella, Mobiluncus, Mycobacterium, Rickettsia, Sphingomonas,Azomonas, Alkanindiges, Proteus, Brevibacillus, Kocuria, Parasediminibacterium | Increased | Breast tumor | [107] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





