Introduction
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is the most common form of neurofibromatosis (NF), a group of genetic disorders that cause the development of tumors in the peripheral and central nervous system (Gutmann et al., 2017). Incidence of NF1 is approximately 1 in 3,000 individuals globally with some variations across the globe (Gutmann et al., 2017). Individuals with NF1 experience a wide range of clinical conditions (e.g., benign and/or malignant tumors, café-au-lait macules, skin pigmentation, and bone abnormalities), and they often struggle with cognitive impairment (e.g., poor executive functioning, learning disabilities; Vogel et al., 2017). Increasing evidence suggests that psychosocial problems are frequently found in individuals with NF1 (Domon-Archambault et al., 2018), but this complication is relatively poorly understood. In fact, guidelines for supervision and treatment of NF1 have only recently started to suggest attending to age-appropriate psychosocial needs of individuals with NF1, but noting a lack of consistent evidence to support this recommendation (Carton et al., 2023). This is partly due to the uneven understanding of the variety of psychosocial problems that individuals with NF1 experience. In particular, internalizing and externalizing symptoms are less well understood than the more studied symptoms of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) (Vogel et al., 2017).
Internalizing and externalizing symptoms represent two major categories of mental health problems that are often comorbid and associated with a host of developmental and life outcomes including persistent mental disorders (Hofstra et al., 2002), poor economic status (Vergunst et al., 2023), and elevated mortality risk (Jokela et al., 2009). Internalizing symptoms consist of a group of inwardly-directed emotional symptoms including depressive, anxiety, and somatic symptoms (Vergunst et al., 2023). Externalizing symptoms consist of a group of outwardly-directed behavioral symptoms including aggression and delinquency (Vergunst et al., 2023). Research shows that individuals with NF1 may experience these symptoms more severely than both the general population (Rietman et al., 2018) and individuals with other chronic diseases, including coronary artery disease and cancer (Wang et al., 2012). For individuals with NF1, internalizing and externalizing symptoms will add to other mental, cognitive, and physical challenges they face and further undermine their quality of life (Sanagoo et al., 2019). Thus, it is paramount to improve our understanding of internalizing and externalizing symptoms in the NF1 population to better help them.
To date, the extent to which individuals with NF1 experience internalizing and externalizing symptoms, as compared with the unaffected population, remains unclear. This is mostly due to the limited number of relevant research and discrepancies in findings comparing individuals with versus without NF1. For instance, individuals with NF1 indicated more severe internalizing symptoms (e.g., depressive and anxiety symptoms) than those without NF1 in some studies (Barton & North, 2004; Johnson et al., 1999) but not in others (Biotteau et al., 2020; van der Vaart et al., 2016). Similarly, the discrepancies in externalizing symptoms (e.g., aggression, delinquency) were only found in some studies (Chisholm et al., 2022; Johnson et al., 1999) but not in others (Barton & North, 2004; Klein-Tasman et al., 2014). The inconsistency limits our understanding and holds back the development or refinement of interventions, slowing down our efforts to improve quality of life for individuals with NF1 (Sanagoo et al., 2019). Based on this, a rigorous synthesis of existing findings is critically needed for determining the discrepancies in internalizing and externalizing symptoms between individuals with versus without NF1 as well as for explaining the heterogeneity of findings across studies.
Thus far, three meta-analyses have synthesized existing findings regarding psychosocial problems in individuals with NF1. One meta-analysis focused on quality of life and found a lower mental health score (assessed with quality of life measures) in individuals with NF (both types 1 and 2) than those without (Sanagoo et al., 2019). However, the findings are not informative about how individuals with NF1 experience specific mental health symptoms. To improve mental health status of individuals with NF1, it is crucial to find out how each mental health domain is affected and its potential predictors. Another meta-analysis focused on social functions (Chisholm et al., 2018). The third focused on ADHD symptoms (Hou et al., in press). These studies found more severe ASD and ADHD symptoms in individuals with versus without NF1 and identified some potential predictors of these symptoms. Moving beyond previous meta-analytic studies, the current systematic review and meta-analysis focuses specifically on internalizing and externalizing symptoms as well as their subdimensions.
It is also important to investigate why some studies found greater discrepancies in internalizing and externalizing symptoms between individuals with and without NF1 than others. This will greatly improve interpretations of study findings and help identify subgroups who experience more severe symptoms, to facilitate personalized interventions. Possible factors include sample characteristics, such as sample age (Marçal, 2020), sex composition (Gutman & Codiroli McMaster, 2020; Miner & Clarke-Stewart, 2008), percentage of familial NF1 cases in the sample (Geoffray et al., 2021), severity of intellectual disability (Vogel et al., 2017), and percentage of participants diagnosed with ASD or ADHD (Vogel et al., 2017). A number of methodological factors may also be related. Specifically, the informant of behavioral problems may affect study findings (Rietman et al., 2018, Sharkey et al., 2021). Other potential methodological factors include measures used to assess internalizing and externalizing symptoms (Allison Bender et al., 2008) and the type of the comparison group (i.e., healthy community controls, unaffected siblings, or normative sample), even though each type of comparison group has its own advantages (Bulgheroni et al., 2019).
In sum, this systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted with two aims. Aim 1 was to determine the degree to which individuals with NF1 experience internalizing (i.e., depressive, anxiety, somatic, and total internalizing symptoms) and externalizing (i.e., aggression, delinquency, and total externalizing symptoms) symptoms as compared with an unaffected control group (i.e., healthy community, unaffected siblings, or normative sample). Aim 2 was to test potential moderators of group differences across studies, including sample characteristics (i.e., age, sex, NF1 transmission, intelligence quotient or IQ, ASD diagnosis, and ADHD diagnosis) and methodological factors (i.e., informant, measures, and control group type).
Materials & Methods
This meta-analysis was registered at PROSPERO (CRD42023478258). The completion of this meta-analysis closely followed the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA; see
Table S1) (Tugwell & Tovey, 2021).
Data Sources and Search Strategy
This is one of a series of systematic reviews on neurobehavioral functioning (e.g., socioemotional and behavioral functioning, academic functioning, cognitive functioning) of individuals with NF1. Literature searches were conducted in Scopus, Web of Science, PsycINFO, PubMed, and ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global with a combination of NF1 terms (e.g., neurofibromatosis type 1, NF1) and neurobehavioral functioning terms (e.g., internaliz*, externaliz*, depress*, aggress*, delinquen*). The complete search syntax is in
Table S2. The initial searches were conducted on September 22, 2022, which identified 4,060 records. Additional searches were conducted to identify relevant papers since 2022 using the same search strategies on March 26, 2024. A total of 1,483 records were generated in the supplemental searches.
Study Selection
The inclusion criteria of the larger systematic review project are listed in
Table S3. For the current study, eligible studies must have reported data on internalizing or externalizing problems in individuals with NF1 as well as a normal control group (i.e., healthy community group, unaffected siblings group) or have provided standardized scores (i.e., T scores, standard scores, scaled scores, or
z scores) for the NF1 group (
Table S4). Study titles, abstracts, and full texts were screened by two reviewers independently. A third reviewer resolved conflicts between the two reviewers and finalized the list of studies to be included.
Quality/Certainty Assessment
Five methodological factors, as outlined in the Adapted Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for Cross-Sectional Studies (Moskalewicz & Oremus, 2020), that may bias estimates of group differences in internalizing and externalizing symptoms between individuals with and without NF1 were considered: Representativeness of the sample, sample size, ascertainment of exposure (measurement validity), comparability, and assessment of outcome. For representativeness of the sample, sensitivity analyses were conducted to test whether effect sizes differed before and after removing studies that excluded individuals with a psychiatric disorder (i.e., general psychiatric disorder, depression, anxiety, and ADHD). For sample size, more weight was given to studies with larger samples when synthesizing effect sizes across studies (see
Supplementary Method for details). Regarding measurement validity, whether effect sizes varied across measures of internalizing and externalizing symptoms was tested. For comparability, whether effect sizes varied across three control group types including healthy community, unaffected siblings, and normative data was analyzed. For assessment of outcome, whether effect sizes varied across informants (parent, self, or teacher) was tested. Additionally, meta-regression and subgroup analyses were conducted separately for each type of informant for each outcome. These methodological factors of each included study are reported in
Tables S5-S12.
Data Analysis Plan
Seven sets of meta-analyses were completed for each of the internalizing (i.e., depressive, anxiety, somatic, and total internalizing symptoms) and externalizing (i.e., aggression, delinquency problems, and total externalizing symptoms) variables. The studies included in each set of meta-analysis are listed in
Tables S6-S12. First, group differences in internalizing and externalizing symptoms between the NF1 and the control groups were calculated as Hedges’
g, given its sensitivity to small samples (Cohen, 2013). The magnitude of Hedges’
g was interpreted as small (0.2), medium (0.5), or large (0.8) (Cohen, 2013). Two parameters of heterogeneity were estimated: An overall measure of between-study heterogeneity (τ
2) and the ratio of true heterogeneity to total variance across the observed effect sizes (
I2) (Cohen, 2013). Forest plots were created to present group differences for each variable in each study (one effect size for each study).
Following the calculation of group differences, meta-regression was used to test potential moderators accounting for variance in group differences across studies (Fu et al., 2011). Next, subgroup analyses were conducted for categorical moderators using the ROBUMETA package in R (Fisher & Tipton, 2015), which implements a robust standard error estimation technique that could handle dependent effect sizes (Peng et al., 2018). Finally, publication bias was evaluated. This was completed using meta-regression analyses that examined whether standard errors of effect sizes moderated study effect sizes (Peng et al., 2018). Additional techniques employed included Egger’s tests (Peters et al., 2006) with funnel plot (Amitay & Keinan-Boker, 2015) and trim-and-fill analyses (Shi & Lin, 2019) (using METAFOR in R; Viechtbauer et al., 2015; Viechtbauer & Viechtbauer, 2015). More details of data analysis are in
Supplementary Method.
Results
Participant and Study Characteristics
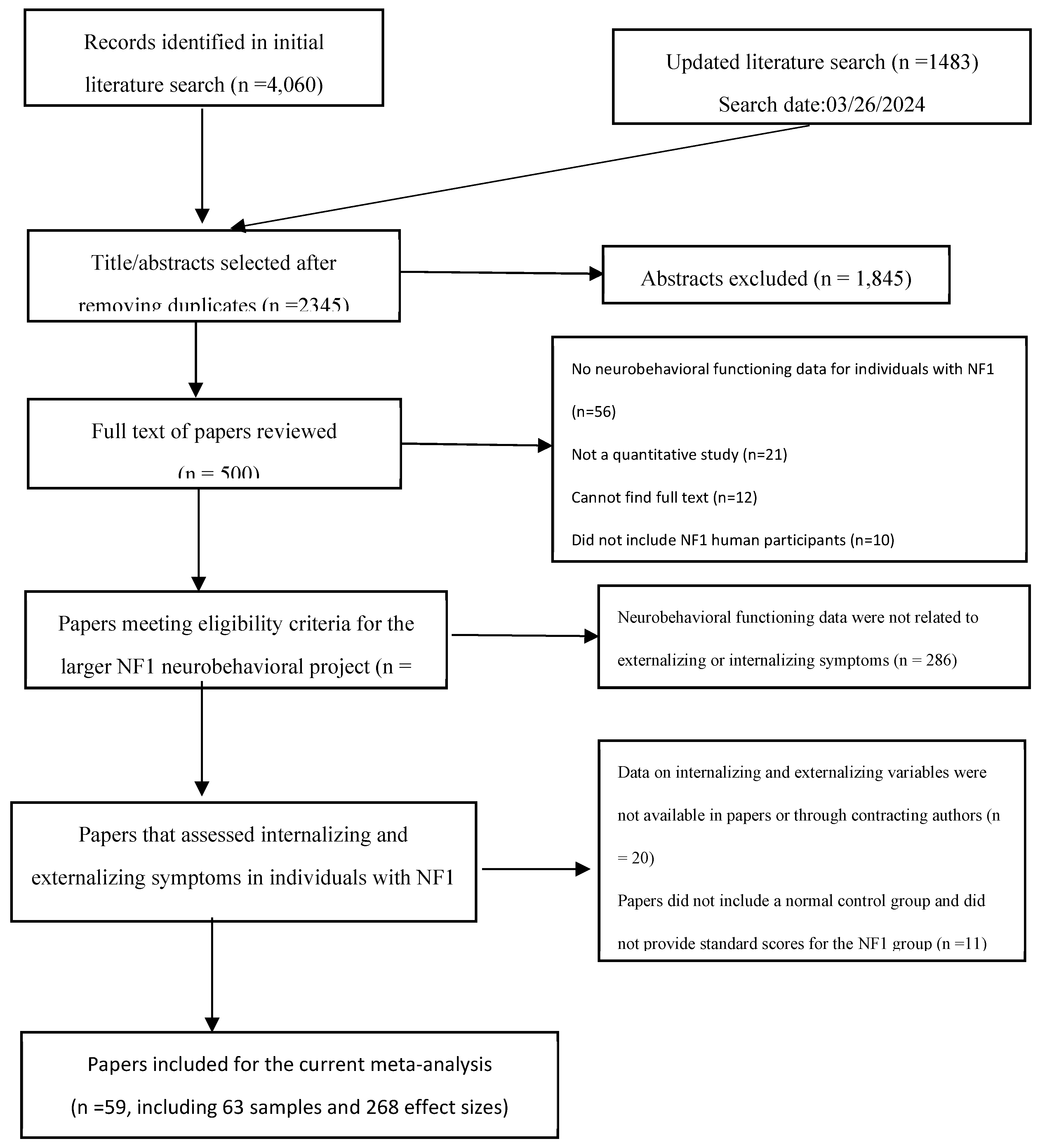
The systematic searches identified 2,345 unique articles, 107 of which examined internalizing and externalizing symptoms in individuals with NF1, and 59 papers had sufficient data to calculate the effect size of group differences in internalizing and externalizing symptoms (
Figure 1). The 59 papers provided 63 unique samples (
N of individuals with NF1 = 3,182,
Table S5). Each unique sample was treated as one study in this meta-analysis (van Geel et al., 2014). The mean age of the included NF1 samples ranged from 2.38 to 46.4 years, the full-scale IQ 83 to 105, the verbal IQ 86 to 112, and the performance IQ 82 to 103. The included NF1 samples had 20-86% females (one sample included males only), 13-58% familial NF1 participants (27 studies reported the data, among which one included familial NF1 cases only and another, sporadic NF1 cases only), 8-77% diagnosed with ADHD (32 studies reported the data, among which five did not include any individuals with ADHD), and 10-71% diagnosed with ASD (12 studies reported the data, among which five did not include any individuals with ASD and two included only individuals with ASD). Due to the small number of studies that reported data on participants’ ASD diagnosis and the highly skewed distribution of the available data, ASD diagnosis data were not included in analysis.
Figure 1. Flow Diagram for the Paper Selection Process in the Current Meta-Analysis
Figure 1.
Flow Diagram for the Paper Selection Process in the Current Meta-Analysis.
Figure 1.
Flow Diagram for the Paper Selection Process in the Current Meta-Analysis.
Among the included studies, 59 (94%) were published journal articles, and four were unpublished dissertations (Gray, 2014; McCurdy, 2019; Potter, 2006; Schrimsher, 2003). Most samples were small in size (Ns = 7–183): 57 (90%) samples had fewer than 100 NF1 participants. Most of the samples were recruited from the United States (n = 20, 32%), followed by Australia (n = 8, 13%), Italy (n = 8, 13%), the Netherlands (n = 6, 10%), and others. Most of the samples included children (aged 0-18 years; n = 54, 86%); 14% of the samples (n =9) included adults only (aged 19 years or older). Among the 268 effect sizes analyzed, the most used measure of internalizing and externalizing symptoms was the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL; k = 168, 63%), followed by the Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC; k = 60, 22%), and others (k =40, 15%). Among the effect sizes, 179 (67%) were based on parent report, 38 (14%) self-report, and 49 (18%) teacher report. For control group type, 77 (29%) were composed of healthy community individuals, 32 (12%) unaffected siblings, and 159 (59%) based on normative data.
Internalizing Symptoms in Individuals with Versus without NF1
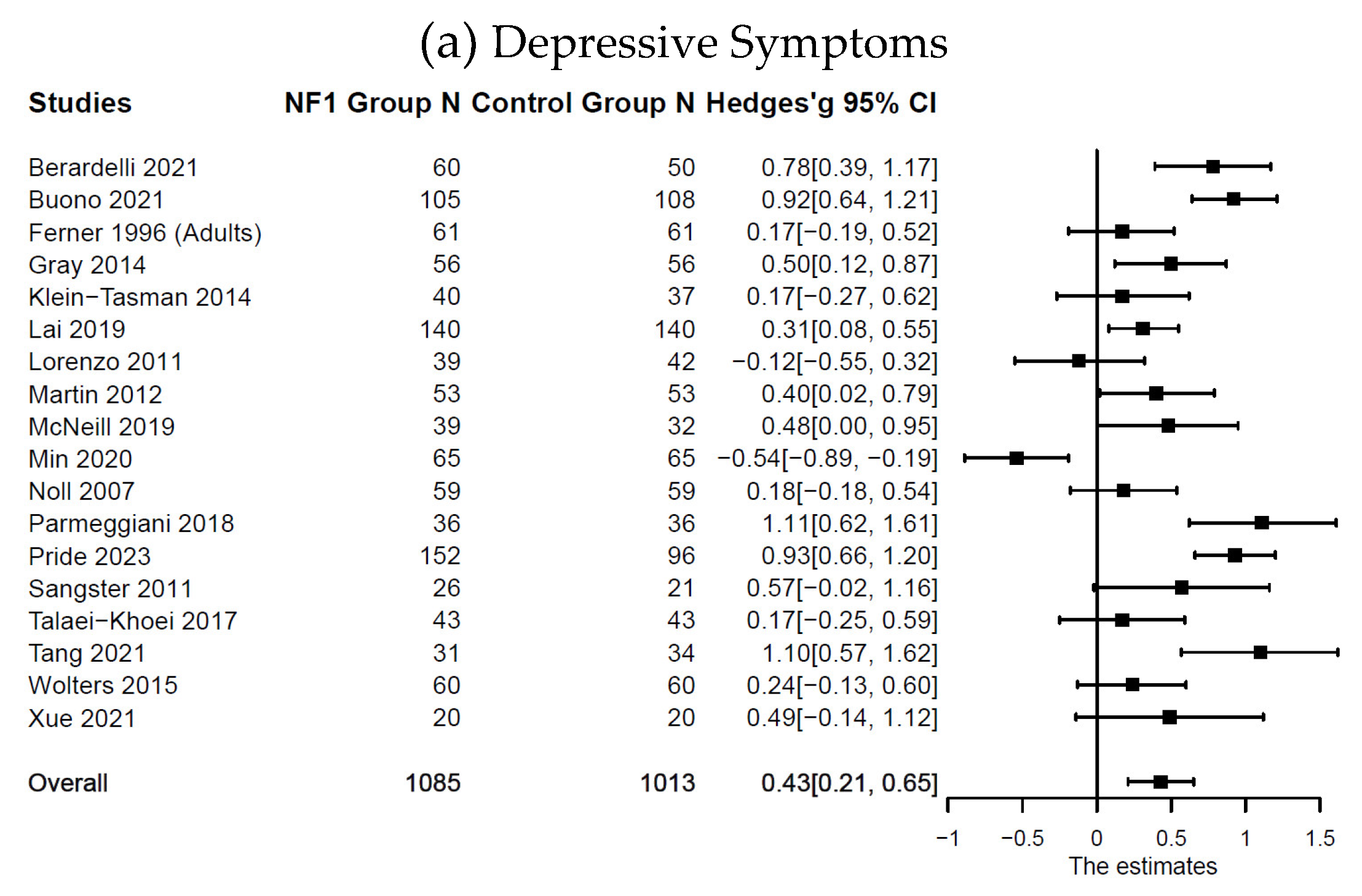
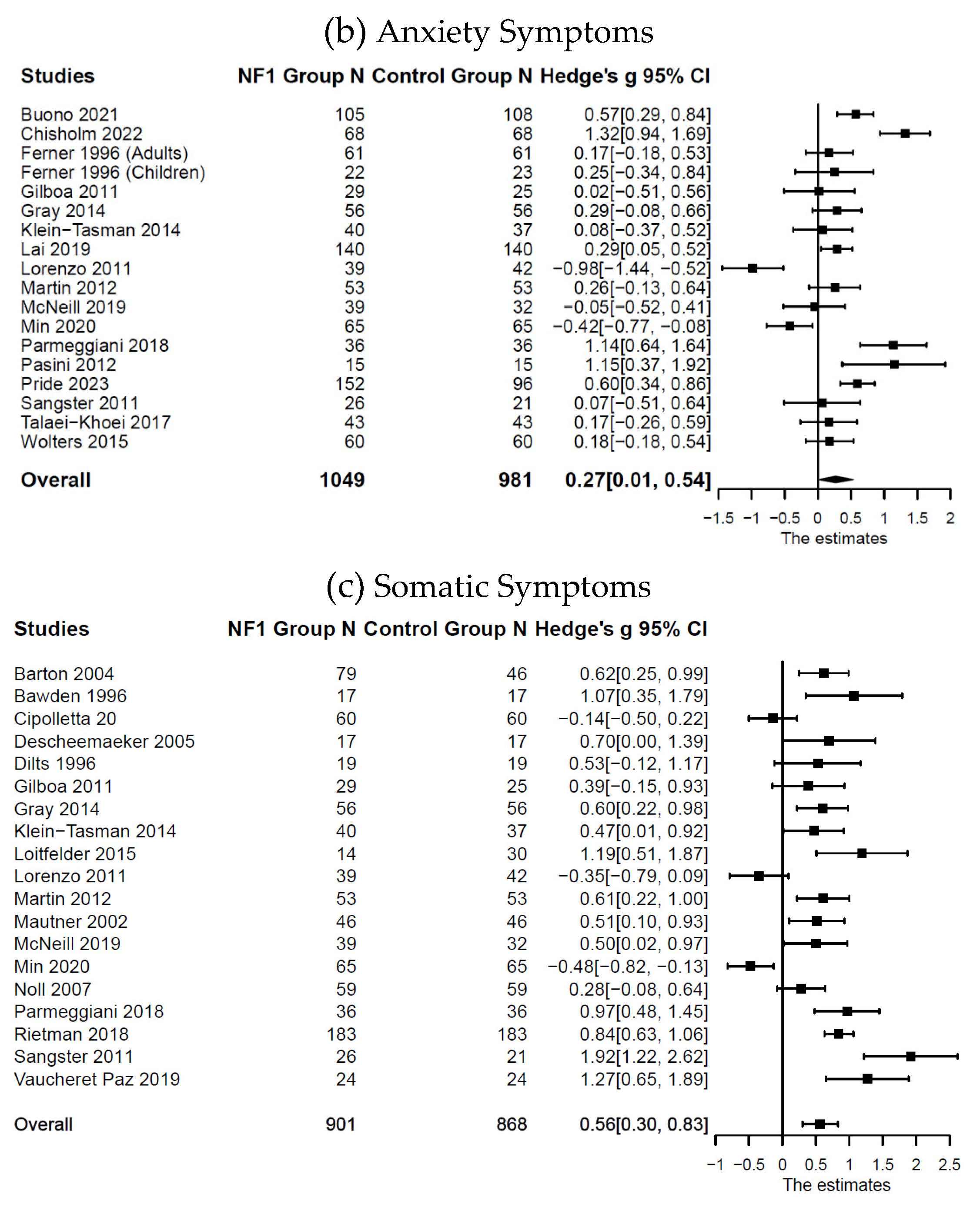
Compared with the control groups (
Table 1), individuals with NF1 showed higher levels of depressive symptoms:
n = 18;
k = 21;
g = 0.43; 95% CI [0.21, 0.65],
p < .001; anxiety symptoms:
n = 18;
k = 24;
g = 0.27; 95% CI [0.01, 0.54],
p = .043; somatic symptoms:
n = 19;
k = 27;
g = 0.56; 95% CI [0.30, 0.83],
p < .001; and total internalizing symptoms:
n = 39;
k = 75;
g = 0.50; 95% CI [0.33, 0.67],
p < .001. Forest plots are presented in
Figure 2 and
Figure 3. Substantial systematic variability was observed in study effect sizes (
I2depressive symptoms = 81%;
I2anxiety symptoms = 84%;
I2somatic symptoms = 83%;
I2total internalizing symptoms = 85%).
Figure 2. Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Depressive, Anxiety, and Somatic Symptoms
Figure 2.
Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Depressive, Anxiety, and Somatic Symptoms. Study labels are composed of first author’s last name and year of publication; for studies that had subgroups of NF1 participants and in which only subgroup data were used in analysis, study labels also include the NF1 subgroup name as labeled in each study.
N = sample size.
CI = confidence interval.
Figure 3. Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Total Internalizing Symptoms
Figure 2.
Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Depressive, Anxiety, and Somatic Symptoms. Study labels are composed of first author’s last name and year of publication; for studies that had subgroups of NF1 participants and in which only subgroup data were used in analysis, study labels also include the NF1 subgroup name as labeled in each study.
N = sample size.
CI = confidence interval.
Figure 3. Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Total Internalizing Symptoms
Figure 3. Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Total Internalizing Symptoms
Figure 3.
Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Total Internalizing Symptoms. Study labels are composed of first author’s last name and year of publication; for studies that had subgroups of NF1 participants and in which only subgroup data were used in analysis, study labels also include the NF1 subgroup name as labeled in each study.
Figure 3.
Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Total Internalizing Symptoms. Study labels are composed of first author’s last name and year of publication; for studies that had subgroups of NF1 participants and in which only subgroup data were used in analysis, study labels also include the NF1 subgroup name as labeled in each study.
Results from moderation analyses are presented in
Table S14 (see
Table S15 for subgroup analyses). Based on the results, the group difference in total internalizing symptoms was greater in studies with participants who had a lower mean verbal IQ (
β = -0.07, 95% CI [-0.14, 0.00],
p = .040). No other moderation effects were found.
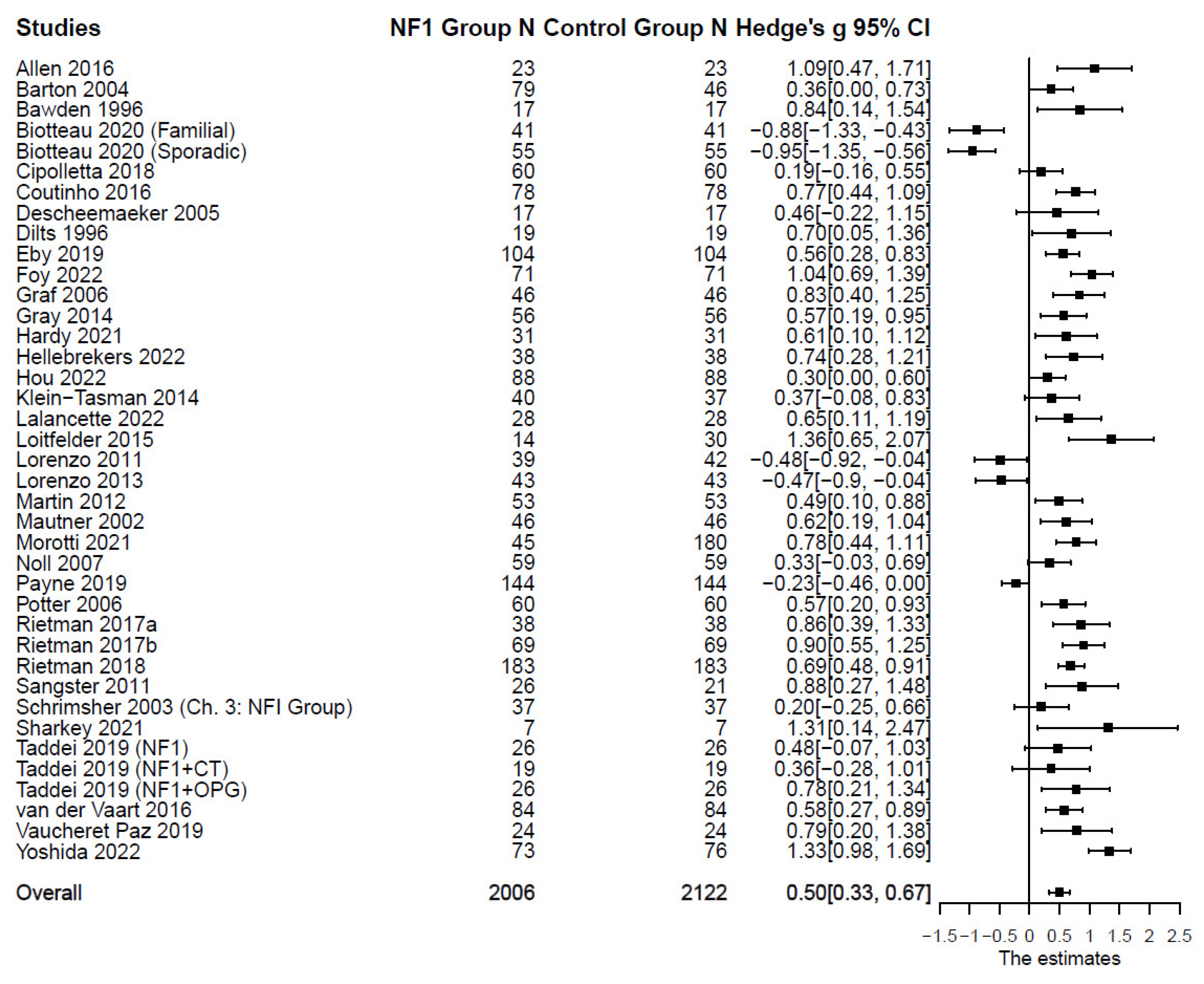
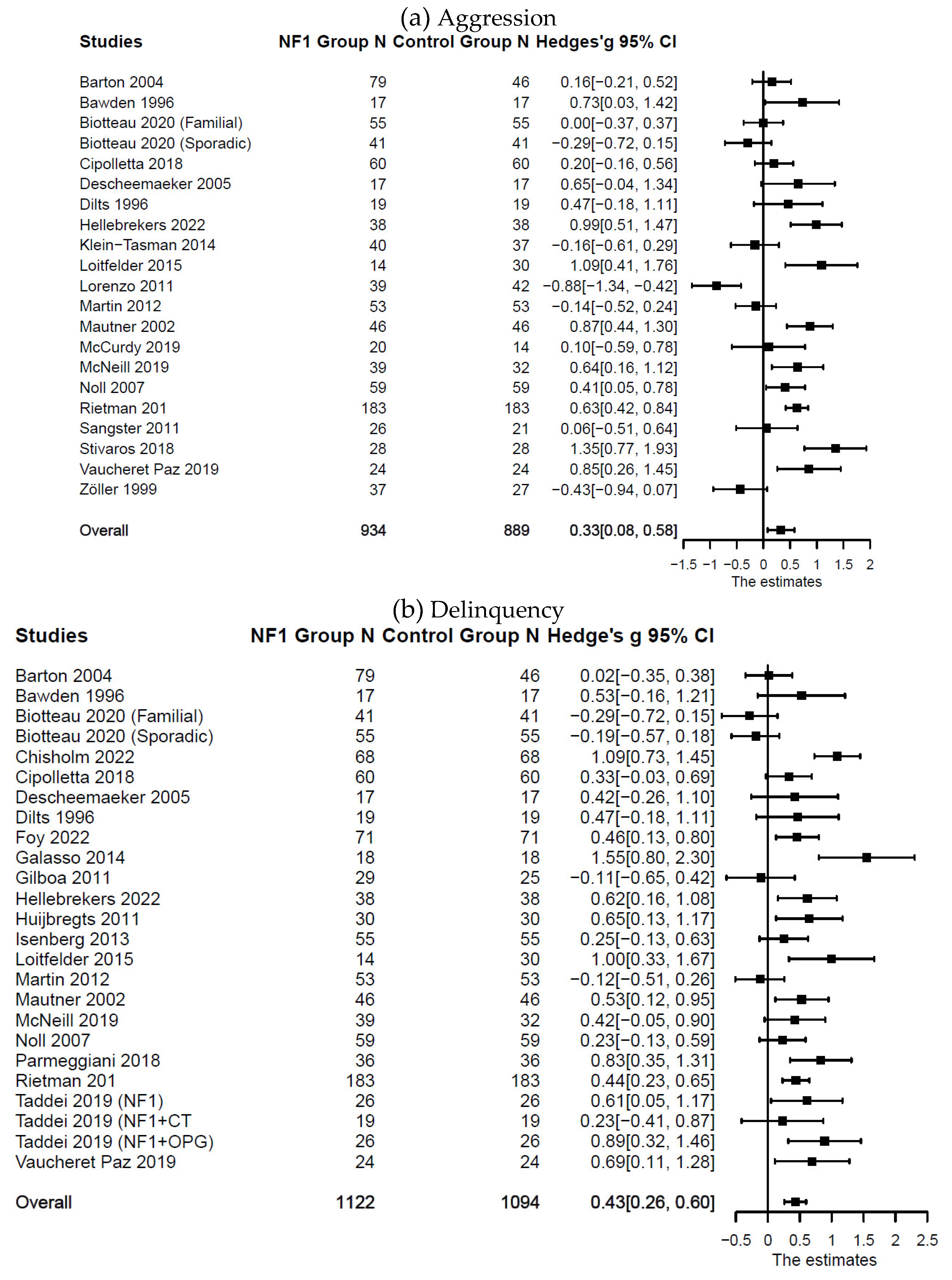
Externalizing Symptoms in Individuals with Versus without NF1
Compared with the control groups (
Table 1), individuals with NF1 also showed higher levels of aggression: (
n = 21;
k = 33;
g = 0.33; 95% CI [0.08, 0.58],
p = .013); delinquency: (
n = 25;
k = 37;
g = 0.43; 95% CI [0.26, 0.60],
p < .001); and total externalizing symptoms: (
n = 33;
k = 47;
g = 0.24; 95% CI [0.13, 0.35],
p < .001). Forest plots are presented in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5. Substantial systematic variability was observed in study effect sizes (
I2aggression = 82%;
I2delinquency = 68%;
I2total externalizing = 53%).
Figure 4. Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Aggression and Delinquency
Figure 4.
Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Aggression and Delinquency. Study labels are composed of first author’s last name and year of publication; for studies that had subgroups of NF1 participants and in which only subgroup data were used in analysis, study labels also include the NF1 subgroup name as labeled in each study.
Figure 4.
Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Aggression and Delinquency. Study labels are composed of first author’s last name and year of publication; for studies that had subgroups of NF1 participants and in which only subgroup data were used in analysis, study labels also include the NF1 subgroup name as labeled in each study.
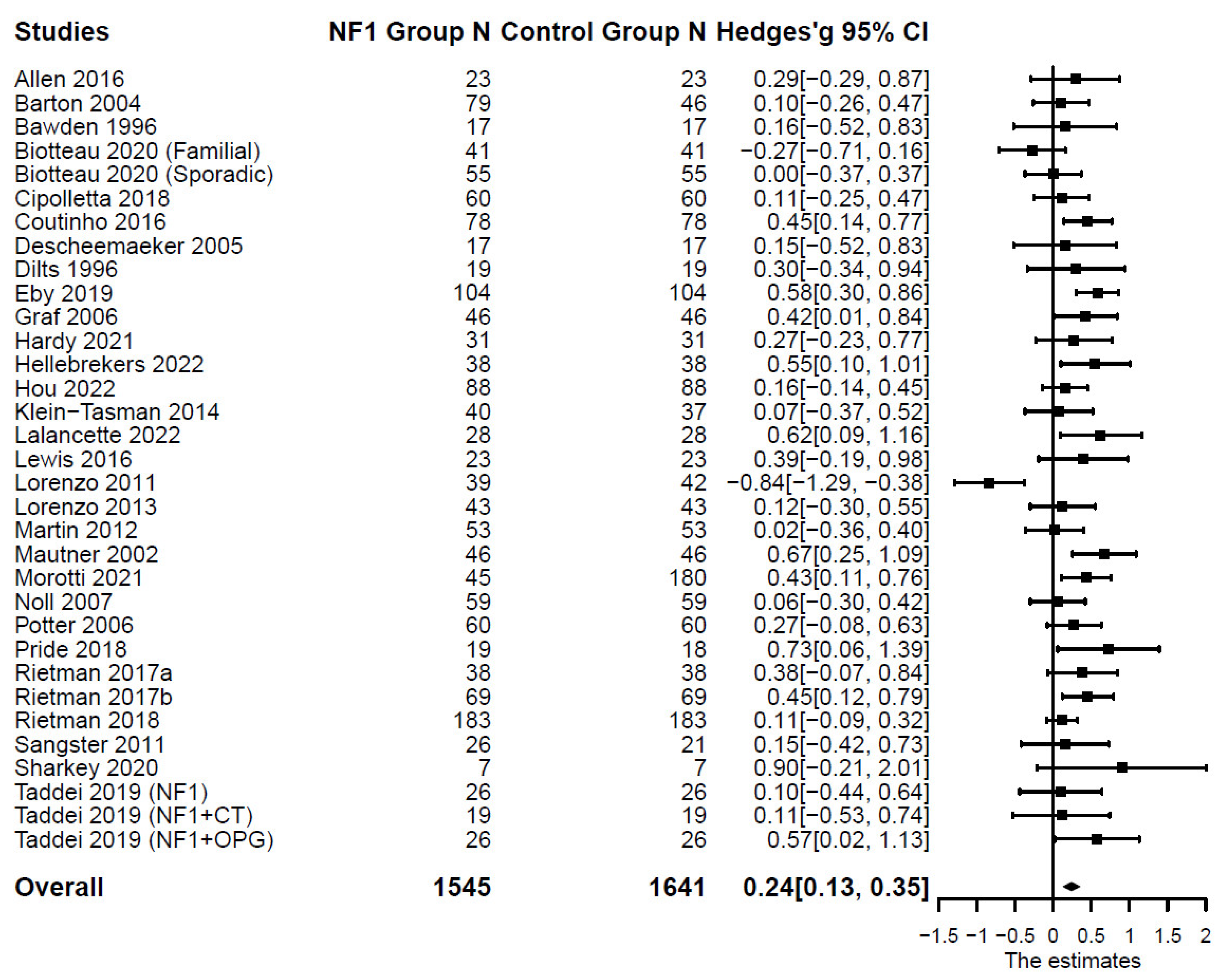
Figure 5. Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Total Externalizing Symptoms
Figure 5.
Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Total Externalizing Symptoms. Study labels are composed of first author’s last name and year of publication; for studies that had subgroups of NF1 participants and in which only subgroup data were used in analysis, study labels also include the NF1 subgroup name as labeled in each study.
Figure 5.
Forest Plot for Effect Sizes of Total Externalizing Symptoms. Study labels are composed of first author’s last name and year of publication; for studies that had subgroups of NF1 participants and in which only subgroup data were used in analysis, study labels also include the NF1 subgroup name as labeled in each study.
Based on moderation analyses (
Table S14; see
Table S15 for subgroup analyses), the percentage of NF1 participants diagnosed with ADHD moderated differences between the NF1 group and the control group in aggression (
β = 0.02, 95% CI [0.00, 0.01],
p = .017), with studies that had a higher percentage of NF1 participants diagnosed with ADHD reporting a larger group difference. The group difference in aggression was also larger in samples with lower mean verbal IQ (
β = -0.06, 95% CI [-0.11, -0.01],
p = .028) and when the CBCL was used to measure aggression rather than the BASC (
β = 0.57, 95% CI [0.04, 1.10],
p = .039).
Publication Bias
Meta-regression with the Egger’s test indicated no significant publication bias in studies that included depressive, anxiety, total internalizing, aggression, delinquency, and total externalizing symptoms. However, significant publication bias was observed in studies that included somatic symptoms (
Table S13). The funnel plots were largely consistent with these results as the effect sizes were symmetrically distributed around the average effect size for depressive, anxiety, total internalizing, aggression, delinquency, and total externalizing symptoms (
Figures S1-S2). Some asymmetrical distributions were found for somatic symptoms (
Figure S1). The trim-and-fill analyses identified four hypothetical unpublished studies reporting somatic symptoms. After inputting these studies, the mean effect size became smaller but still statistically significant:
g = 0.41; 95% CI [0.12, 0.69],
p = .008.
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analyses were conducted to compare results with and without the four studies that excluded participants with a psychiatric disorder (Biotteau et al., 2020; Hellebrekers et al., 2022; Lewis & Porter, 2016; Tang et al., 2021). The significance level, magnitude of effect sizes, and publication bias evaluation results were largely consistent between the two sets of analyses, except for somatic symptoms. In particular, after removing studies that had potentially biased sample selection (Biotteau et al., 2020; Hellebrekers et al., 2022), the magnitude of the effect size of somatic symptoms changed from weak (Hedges’ g = 0.44) to medium (Hedges’ g = 0.56), and the effect size after adjusting for publication bias changed from Hedges’ g = 0.28 (p = .082) to Hedges’ g = 0.41 (p = .008). Thus, results after removing studies that were potentially biased in sample selection were reported for somatic symptoms, while results based on all eligible studies were reported for other internalizing and externalizing variables. Additional sensitivity analyses were conducted to test if results differed with and without unpublished dissertations (Gray, 2014; McCurdy, 2019; Potter, 2006; Schrimsher, 2003). The results of pooled effect sizes and moderation analyses were consistent with and without the four dissertations. Thus, results from analyses that included the four dissertations were reported, to provide a more thorough synthesis of existing literature.
Discussion
The severity and heterogeneity of internalizing and externalizing symptoms in individuals with NF1 remains unclear given the inconsistent findings across the limited number of studies. This systematic review and meta-analysis synthesized existing findings and tested the extent to which individuals with NF1 experience internalizing and externalizing symptoms compared with those without NF1. Moderators of group differences were also tested to explore potential correlates of internalizing and externalizing symptoms in individuals with NF1. The meta-analyses included 59 studies, 63 unique samples, and 3,182 individuals with NF1. Several important findings emerged.
First and foremost, findings suggest that individuals with NF1 experience more severe internalizing and externalizing symptoms than the unaffected comparison groups. Some variations in sizes of the group differences were also observed across domains of internalizing and externalizing symptoms (Hedges’ gs = 0.24 – 0.50). For instance, the group difference in somatic (Hedge’s g = 0.56) and total internalizing symptoms (Hedge’s g = 0.50) was more than twice the size as in total externalizing symptoms (Hedge’s g = 0.24). This is consistent with previous assessments indicating that internalizing symptoms might be more severe than externalizing symptoms in individuals with NF1 in terms of both prevalence and severity of the symptoms (Domon-Archambault et al., 2018; Hou et al., 2022; Vogel et al., 2017). The observed sizes of group differences are likely smaller than the group differences observed for other more established phenotypes of NF1 including cognitive deficits (Al-Farsi et al., 2022; Crow et al., 2022), ASD (Chisholm et al., 2018), and ADHD (Hou et al., in press; Payne et al., 2021). However, it is critical to recognize and treat internalizing and externalizing symptoms, as they all remained statistically significant even after adjusting for publication bias. NF1 complications are known to increase and worsen over time, while no cure for the disease has been found (Vogel et al., 2017). This often makes individuals with NF1 feel insecure and uncertain about the course of the disease, increasing risks for internalizing and externalizing symptoms (Aghaei et al., 2023). Thus, timely identification and treatment of the problems as well as continued support will benefit individuals with NF1 tremendously.
In addition, the magnitude of group differences varied across study samples, and a number of study characteristics were related. First, the group differences in aggression were larger in studies that included a higher percentage of individuals diagnosed with ADHD in the NF1 group. This is consistent with the available research on individuals with NF1 that found a strong correlation between ADHD symptoms with externalizing symptoms (Coutinho et al., 2016), although the underlying causes remain unclear. In the general population, ADHD symptoms often covary with internalizing and externalizing symptoms (Kuja-Halkola et al., 2015), suggesting potential common underlying genetic and environmental factors. Future research should further test whether the covariations also exist among individuals with NF1 to confirm comorbidity of ADHD with externalizing symptoms in this population.
Second, group differences in total internalizing and aggression symptoms were larger in samples that had a lower verbal IQ. Language skills are frequently found to be linked to internalizing and externalizing symptoms in children without NF1 (Hentges et al., 2021). Abundant evidence shows that language use or skills play an important role in regulating emotions and behaviors (Cole et al., 2010; Salmon et al., 2016; Winsler et al., 2009), which is then associated with the degree of internalizing and externalizing symptoms across developmental periods (Choe et al., 2013; Rhoades et al., 2009). The inability to communicate efficiently and the associated low self-concept and poor social skills might also directly affect individuals’ internalizing symptoms (Winsler et al., 2009). Given the close associations between language skills with internalizing and externalizing symptoms, interventions have targeted language skills in young children to improve their internalizing and externalizing symptoms, and these interventions did produce promising results (Curtis et al., 2018; West et al., 2022). Based on this evidence, intervening in verbal or general language skills of individuals with NF1 might also help decrease their internalizing and externalizing symptoms, a target missing in current interventions that focus primarily on the interactions between the mind and the body (Wei et al., 2021).
Moreover, findings suggest that the levels of externalizing symptoms (i.e., aggression) might be related to the measure used. Specifically, the difference in aggression between individuals with and without NF1 was found to be more prominent when measured by CBCL than BASC, although such a difference was not found for other internalizing or externalizing symptoms. However, our study cannot tell whether this difference was due to the sensitivity of the measures or due to other study or sample characteristics. Perhaps future research with individual-level data, where participants fill out both CBCL and BASC, can better compare the two measures and test how individual characteristics are related to differences in CBCL versus BASC scores.
In general, despite increasing evidence that suggests elevated internalizing and externalizing symptoms in individuals with NF1, there is a lack of research on the predictors. In addition to the factors discussed above, evidence shows that internalizing and externalizing symptoms in individuals with NF1 may be associated with social and demographic variables, such as age and parental education (Hou et al., 2022), as well as NF1-related disease factors, such as visibility and severity of NF1 (Doser et al., 2020; Granström et al., 2012). Preliminary evidence suggests that underlying neuropathological changes associated with NF1 may influence individuals’ psychological conditions (Vogel et al., 2017). Additionally, the multiple neurodevelopmental phenotypes individuals with NF1 experience (e.g., cognitive disability, ADHD and ASD symptoms, motor problems) may provide additive risk for them to develop internalizing symptoms (Rietman et al., 2017b; Vogel et al., 2017). Other possible but understudied factors include insecurity or uncertainty about the course of NF1 and hopelessness over the lack of cure for NF1 (Aghaei et al., 2023), which can be depressing. Fatigue is another understudied factor that is a serious and frequent complication of NF1 (Vassallo et al., 2020) and often found to be related to internalizing symptoms in the general population (ter Wolbeek et al., 2011). Furthermore, internalizing and externalizing symptoms might be jointly affected by biopsychosocial factors (e.g., genetic predisposition, NF1 disease complications, social support, coping strategies) (Nikstat & Riemann, 2020). Much remains to be learned about what factors may contribute to internalizing and externalizing symptoms in individuals with NF1. Future research is critically needed to address this gap to improve our knowledge and inform interventions.
Limitations
Although the current meta-analysis was conducted with robust methods following the most cutting-edge guidelines, several limitations should be considered in interpreting the results. Firstly, out of the 107 studies that focused on internalizing and externalizing symptoms in individuals with NF1, only 59 studies (including 63 independent samples) provided sufficient data for meta-analysis, even after multiple contacts with authors to request missing information. Thus, some moderation tests were potentially underpowered. To address this issue, it will be important for future studies to report study and sample characteristics in more detail. Related to this, the current study only tested a limited number of moderators or potential predictors of internalizing and externalizing symptoms in individuals with NF1, based on findings and data availability of existing research. Thus, factors that were not tested before or prior studies did not provide sufficient data for were not considered, such as fatigue and worry about future health, which should be addressed in future research as well.
Secondly, most of the included studies used a child sample rather than an adult sample (86% vs. 14%). In fact, adults with NF1 may have more pronounced mental health problems, particularly internalizing symptoms (Vogel et al., 2017). Thus, more future research on adults with NF1 is needed for a better understanding of the life-span experience of internalizing and externalizing symptoms among individuals with NF1. Moreover, the current meta-analysis included study-level data instead of individual-level data. Individual-level data will provide better information for testing factors related to internalizing and externalizing symptoms as well as enable the test of covariation among internalizing symptoms, externalizing symptoms, and ADHD symptoms. However, most existing studies with individual-level data have utilized small samples, which have provided limited power for analyses and thus produced unstable results. Future research should make an effort to recruit a larger number of participants or to seek collaborations with other sites to obtain larger samples. Finally, the current meta-analysis did not have sufficient data to test whether the results differed across cultures or socioeconomic groups, an important question that should be addressed in future research.
Conclusions
This systematic review and meta-analysis provides robust evidence that individuals with NF1 experience a wide range of internalizing symptoms (depressive, anxiety, somatic, and total internalizing symptoms) and externalizing symptoms (aggression, delinquency, and total externalizing symptoms) more severely, as compared with the unaffected controls. This evidence supports the inclusion of psychosocial needs in the supervision and treatment of NF1 (Carton et al., 2023) and highlights the importance of early identification as well as continued support and treatment of internalizing and externalizing symptoms in individuals with NF1. This meta-analysis also found that a number of study characteristics (e.g., a higher percentage of participants diagnosed with ADHD, a lower sample mean verbal IQ) were related to worse internalizing and externalizing symptoms (total internalizing symptoms and aggression) observed in some study samples. These findings help to explain the heterogeneity of inconsistent discrepancies in internalizing and externalizing symptoms between individuals with versus without NF1 across studies. Additional research with individual-level data from a larger sample is still needed to better understand predictors of internalizing and externalizing symptoms among individuals with NF1. This research will further enhance our knowledge, inform existing interventions (Wei et al., 2021) and facilitate the development of new interventions or treatments.
Authors Contributions
Conceptualization, D.L. and Y.H.; Data Acquisition, D.L., L.Y., X.W, J.M., B.F.M., E.S.M., A.N., and Y.H.; Methodology, D.L. and L.Y.; Formal Analysis, D.L. and L.Y.; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, D.L.; Writing – Review & Editing, D.L., L.Y., X.W, J.M., B.F.M., E.S.M., A.N., A.B.R., and Y.H.; Supervision, Y.H.; Funding Acquisition, Y.H.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Supplementary Method, Table S1: PRISMA 2020 Checklist, Table S2: Searching Syntax for the Larger NF1 Neurobehavioral Project, Table S3: Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria for the Larger NF1 Neurobehavioral Project, Table S4: Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria for the NF1 Internalizing/Externalizing Study, Table S5: Characteristics of Studies Included in the Meta-Analysis, Table S6: Characteristics of Studies Included in the Meta-Analysis of Depression, Table S7: Characteristics of Studies Included in the Meta-Analysis of Anxiety, Table S8: Characteristics of Studies Included in the Meta-Analysis of Somatic Complaints, Table S9: Characteristics of Studies Included in the Meta-Analysis of Internalizing, Table S10: Characteristics of Studies Included in the Meta-Analysis of Aggression, Table S11: Characteristics of Studies Included in the Meta-Analysis of Delinquency, Table S12: Characteristics of Studies Included in the Meta-Analysis of Externalizing, Table S13: Sensitivity Analysis of Effect Size, Table S14: Results from Moderation Tests, Table S15: Mean Effects for Each Group of Categorical Moderators, Figure S1: Funnel Plots for Effect Sizes of Internalizing Problems, Figure S2: Funnel Plots for Effect Sizes of Externalizing Problems, References.
Data Availability Statement
Main data genderated in the current study are included in the supplementary document. Additional data can be provided upon request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Sara Yamini, Hossein Dabiriyan Tehrani, Joel Killam, Lauren Morey, Mary-Mac Chown, Devin Guy, Carson Maun, Denny Oliveira, and Taylor Collins for their help with literature search, screening, or data extraction.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aghaei, A., Herran, K., Fanaei, S. A., Khalili, M., & Jayadev, P. (2023). Lived experiences of neurofibromatosis type 1 patients: Social life, stigma, and intervention strategies. Journal of Health Psychology, 0(0), 13591053231208619. [CrossRef]
- Al-Farsi, F. A. H., Al-Alyani, O. B. S., Al-Kumzari, A., & Al-Saadi, T. (2022). Systemic review and meta-analysis of the intellectual integrity of children with neurofibromatosis type 1. World Neurosurgery, 157, 69-74. [CrossRef]
- Allen, T., Willard, V., Anderson, L., Hardy, K., & Bonner, M. (2016). Social functioning and facial expression recognition in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 60(3), 282-293.
- Allison Bender, H., Auciello, D., Morrison, C. E., MacAllister, W. S., & Zaroff, C. M. (2008). Comparing the convergent validity and clinical utility of the Behavior Assessment System for Children-Parent Rating Scales and Child Behavior Checklist in children with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav, 13(1), 237-242. [CrossRef]
- Amitay, E. L., & Keinan-Boker, L. (2015). Breastfeeding and childhood leukemia incidence: A meta-analysis and systematic review. JAMA Pediatrics, 169(6), e151025-e151025. [CrossRef]
- Barton, B., & North, K. (2004). Social skills of children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 46(8), 553-563. [CrossRef]
- Bawden, H., Dooley, J., Buckley, D., Camfield, P., Gordon, K., Riding, M., & Llewellyn, G. (1996). MRI and nonverbal cognitive deficits in children with neurofibromatosis 1. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 18(6), 784-792. [CrossRef]
- Berardelli, I., Maraone, A., Belvisi, D., Pasquini, M., Giustini, S., Miraglia, E., Iacovino, C., Pompili, M., Frascarelli, M., & Fabbrini, G. (2021). The importance of suicide risk assessment in patients affected by neurofibromatosis. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract, 25(4), 350-355. [CrossRef]
- Biotteau, M., Déjean, S., Lelong, S., Iannuzzi, S., Faure-Marie, N., Castelnau, P., Rivier, F., Lauwers-Cancès, V., Baudou, E., & Chaix, Y. (2020). Sporadic and familial variants in NF1: An explanation of the wide variability in neurocognitive phenotype? Front Neurol, 11, 368-368. [CrossRef]
- Bulgheroni, S., Taddei, M., Saletti, V., Esposito, S., Micheli, R., & Riva, D. (2019). Visuoperceptual impairment in children with NF1: From early visual processing to procedural strategies. Behavioural Neurology, 2019, 7146168-7146110. [CrossRef]
- Buono, F. D., Sprong, M. E., Paul, E., Martin, S., Larkin, K., & Garakani, A. (2021). The mediating effects of quality of life, depression, and generalized anxiety on perceived barriers to employment success for people diagnosed with neurofibromatosis type 1. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 16(1), 234. [CrossRef]
- Carton, C., Evans, D. G., Blanco, I., Friedrich, R. E., Ferner, R. E., Farschtschi, S., Salvador, H., Azizi, A. A., Mautner, V., Rohl, C., Peltonen, S., Stivaros, S., Legius, E., Oostenbrink, R., & Group, E. G. N. T. M. G. (2023). ERN GENTURIS tumour surveillance guidelines for individuals with neurofibromatosis type 1. EClinicalMedicine, 56, 101818. [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, A. K., Anderson, V. A., Pride, N. A., Malarbi, S., North, K. N., & Payne, J. M. (2018). Social function and autism spectrum disorder in children and adults with neurofibromatosis type 1: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychology Review, 28(3), 317-340. [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, A. K., Haebich, K. M., Pride, N. A., Walsh, K. S., Lami, F., Ure, A., Maloof, T., Brignell, A., Rouel, M., Granader, Y., Maier, A., Barton, B., Darke, H., Dabscheck, G., Anderson, V. A., Williams, K., North, K. N., & Payne, J. M. (2022). Delineating the autistic phenotype in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Molecular Autism, 13(1), 3-3. [CrossRef]
- Choe, D. E., Olson, S. L., & Sameroff, A. J. (2013). Effects of early maternal distress and parenting on the development of children’s self-regulation and externalizing behavior. Development and Psychopathology, 25(2), 437-453. [CrossRef]
- Cipolletta, S., Spina, G., & Spoto, A. (2018). Psychosocial functioning, self-image, and quality of life in children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1. Child : Care, Health & Development, 44(2), 260-268. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. (2013). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Routledge.
- Cole, P. M., Armstrong, L. M., & Pemberton, C. K. (2010). The role of language in the development of emotion regulation. In S. D. Calkins & M. A. Bell (Eds.), Human brain development. Child development at the intersection of emotion and cognition (pp. 59-77). American Psychological Association. [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, V., Kemlin, I., Dorison, N., Billette de Villemeur, T., Rodriguez, D., & Dellatolas, G. (2016). Neuropsychological evaluation and parental assessment of behavioral and motor difficulties in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Res. Dev. Disabil., 48, 220-230. [CrossRef]
- Crow, A. J. D., Janssen, J. M., Marshall, C., Moffit, A., Brennan, L., Kohler, C. G., Roalf, D. R., & Moberg, P. J. (2022). A systematic review and meta-analysis of intellectual, neuropsychological, and psychoeducational functioning in neurofibromatosis type 1. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 188(8), 2277-2292. [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P. R., Frey, J. R., Watson, C. D., Hampton, L. H., & Roberts, M. Y. (2018). Language disorders and problem behaviors: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics (Evanston), 142(2), 1. [CrossRef]
- Descheemaeker, M. J., Ghesquière, P., Symons, H., Fryns, J. P., & Legius, E. (2005). Behavioural, academic and neuropsychological profile of normally gifted neurofibromatosis type 1 children. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 49(1), 33-46. [CrossRef]
- Dilts, C. V., Carey, J. C., Kircher, J. C., Hoffman, R. O., Creel, D., Ward, K., Clark, E., & Leonard, C. O. (1996). Children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis 1: A behavioral phenotype. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics, 17(4), 229-239.
- Domon-Archambault, V., Gagnon, L., Benoît, A., & Perreault, S. (2018). Psychosocial features of neurofibromatosis type 1 in children and adolescents. Journal of Child Neurology, 33(3), 225-232. [CrossRef]
- Doser, K., Andersen, E. W., Kenborg, L., Dalton, S. O., Jepsen, J. R. M., Kroyer, A., Ostergaard, J., Hove, H., Sorensen, S. A., Johansen, C., Mulvihill, J., Winther, J. F., & Bidstrup, P. E. (2020). Clinical characteristics and quality of life, depression, and anxiety in adults with neurofibromatosis type 1: A nationwide study. Am J Med Genet A, 182(7), 1704-1715. [CrossRef]
- Eby, N. S., Griffith, J. L., Gutmann, D. H., & Morris, S. M. (2019). Adaptive functioning in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Relationship to cognition, behavior, and magnetic resonance imaging. Dev Med Child Neurol 61(8), 972-978. [CrossRef]
- Ferner, R. E., Hughes, R. A., & Weinman, J. (1996). Intellectual impairment in neurofibromatosis 1. J Neurol Sci, 138(1-2), 125-133. [CrossRef]
- Fisher, Z., & Tipton, E. (2015). robumeta: An R-package for robust variance estimation in meta-analysis. arXiv.org. [CrossRef]
- Foy, A. M. H., Hudock, R. L., Shanley, R., & Pierpont, E. I. (2022). Social behavior in RASopathies and idiopathic autism. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 14(1), 5-5. [CrossRef]
- Fu, R., Gartlehner, G., Grant, M., Shamliyan, T., Sedrakyan, A., Wilt, T. J., Griffith, L., Oremus, M., Raina, P., Ismaila, A., Santaguida, P., Lau, J., & Trikalinos, T. A. (2011). Conducting quantitative synthesis when comparing medical interventions: AHRQ and the Effective Health Care Program. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 64(11), 1187-1197. [CrossRef]
- Galasso, C., Lo-Castro, A., Di Carlo, L., Pitzianti, M. B., D’Agati, E., Curatolo, P., & Pasini, A. (2014). Planning deficit in children with neurofibromatosis type 1:A neurocognitive trait independent from attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)? Journal of Child Neurology, 29(10), 1320-1326. [CrossRef]
- Geoffray, M.-M., Robinson, L., Ramamurthy, K., Manderson, L., O’Flaherty, J., Lehtonen, A., Tordjman, S., Green, J., Vassallo, G., & Garg, S. (2021). Predictors of cognitive, behavioural and academic difficulties in NF1. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 140, 545-550. [CrossRef]
- Gilboa, Y., Rosenblum, S., Fattal-Valevski, A., Toledano-Alhadef, H., Rizzo, A. S., & Josman, N. (2011). Using a Virtual Classroom environment to describe the attention deficits profile of children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Res Dev Disabil, 32(6), 2608-2613. [CrossRef]
- Graf, A., Landolt, M. A., Mori, A. C., & Boltshauser, E. (2006). Quality of life and psychological adjustment in children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1. The Journal of Pediatrics, 149(3), 348-353. [CrossRef]
- Granström, S., Langenbruch, A., Augustin, M., & Mautner, V.-F. (2012). Psychological burden in adult neurofibromatosis type 1 patients: impact of disease visibility on body image. Dermatology (Basel), 224(2), 160-167. [CrossRef]
- Gray, L. S. (2014). Family functioning and coping: Mediators and moderators between severity and internalizing disorders for children with nf1 (Publication Number 3635151) [Doctoral Dissertation, The George Washington University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
- Gutman, L. M., & Codiroli McMaster, N. (2020). Gendered pathways of internalizing problems from early childhood to adolescence and associated adolescent outcomes. J Abnorm Child Psychol, 48(5), 703-718. [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, D. H., Ferner, R. E., Listernick, R. H., Korf, B. R., Wolters, P. L., & Johnson, K. J. (2017). Neurofibromatosis type 1. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers, 3(1), 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Hardy, K. K., Berger, C., Griffin, D., Walsh, K. S., Sharkey, C. M., Weisman, H., Gioia, A., Packer, R. J., & Acosta, M. T. (2021). Computerized working memory training for children with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1): A pilot study. J Child Neurol, 36(12), 1078-1085. [CrossRef]
- Hellebrekers, D. M. J., van Abeelen, S. A. M., Catsman, C. E., van Kuijk, S. M. J., Laridon, A. M., Klinkenberg, S., Hendriksen, J. G. M., & Vles, J. S. H. (2022). Cognitive and behavioral functioning in two neurogenetic disorders; how different are these aspects in Duchenne muscular dystrophy and neurofibromatosis type 1? PloS one, 17(10), e0275803. [CrossRef]
- Hentges, R. F., Devereux, C., Graham, S. A., & Madigan, S. (2021). Child language difficulties and internalizing and externalizing symptoms: A meta-analysis. Child Development, 92(4), e691-e715. [CrossRef]
- Hofstra, M. B., van der Ende, J., & Verhulst, F. C. (2002). Child and adolescent problems predict DSM-IV disorders in adulthood: A 14-year follow-up of a Dutch epidemiological sample. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry, 41(2), 182-189. [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y., Wu, X., Liu, D., Martin, S., Toledo-Tamula, M. A., Allen, T., Baldwin, A., Gillespie, A., Goodwin, A., Widemann, B. C., & Wolters, P. L. (2022). Demographic and disease-related predictors of socioemotional development in children with neurofibromatosis type 1 and plexiform neurofibromas: An exploratory study. Cancers, 14(23), 5956. [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y., Yu, L., Liu, D., Wilson-Lemoine, E., Wu, X., Moreira, J., Mujica, B., Mukhopadhyay, E., Novotney, A., & Payne, J.M. (in press). Systematic review and meta-analysis: Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
- Huijbregts, S. C., & de Sonneville, L. M. (2011). Does cognitive impairment explain behavioral and social problems of children with neurofibromatosis type 1? Behav Genet, 41(3), 430-436. [CrossRef]
- Isenberg, J. C., Templer, A., Gao, F., Titus, J. B., & Gutmann, D. H. (2013). Attention skills in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. J Child Neurol, 28(1), 45-49. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N. S., Saal, H. M., Lovell, A. M., & Schorry, E. K. (1999). Social and emotional problems in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Evidence and proposed interventions. J Pediatr, 134(6), 767-772. [CrossRef]
- Jokela, M., Ferrie, J., & Kivimaki, M. (2009). Childhood problem behaviors and death by midlife: The British National Child Development Study. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry, 48(1), 19-24. [CrossRef]
- Klein-Tasman, B. P., Janke, K. M., Luo, W., Casnar, C. L., Hunter, S. J., Tonsgard, J., Trapane, P., van der Fluit, F., & Kais, L. A. (2014). Cognitive and psychosocial phenotype of young children with neurofibromatosis-1. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 20(1), 88-98. [CrossRef]
- Kuja-Halkola, R., Lichtenstein, P., D’Onofrio, B. M., & Larsson, H. (2015). Codevelopment of ADHD and externalizing behavior from childhood to adulthood. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 56(6), 640-647. [CrossRef]
- Lai, J. S., Jensen, S. E., Charrow, J., & Listernick, R. (2019). Patient reported outcomes measurement information system and quality of life in neurological disorders measurement system to evaluate quality of life for children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1 associated plexiform neurofibroma. J Pediatr, 206, 190-196. [CrossRef]
- Lalancette, E., Charlebois-Poirier, A. R., Agbogba, K., Knoth, I. S., Jones, E. J. H., Mason, L., Perreault, S., & Lippe, S. (2022). Steady-state visual evoked potentials in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Associations with behavioral rating scales and impact of psychostimulant medication. J Neurodev Disord, 14(1), 42. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A. K., & Porter, M. A. (2016). Social competence in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Relationships with psychopathology and cognitive ability. Journal of Childhood & Developmental Disorders, 02(02). [CrossRef]
- Loitfelder, M., Huijbregts, S. C., Veer, I. M., Swaab, H. S., Van Buchem, M. A., Schmidt, R., & Rombouts, S. A. (2015). Functional connectivity changes and executive and social problems in neurofibromatosis type I. Brain Connect, 5(5), 312-320. [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J., Barton, B., Acosta, M. T., & North, K. (2011). Mental, motor, and language development of toddlers with neurofibromatosis type 1. The Journal of Pediatrics, 158(4), 660-665. [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J., Barton, B., Arnold, S. S., & North, K. N. (2013). Cognitive features that distinguish preschool-age children with neurofibromatosis type 1 from their peers: A matched case-control study. The Journal of Pediatrics, 163(5), 1479-1483.e1471. [CrossRef]
- Marçal, K. E. (2020). Demographic and socioeconomic predictors of behavioral trajectories from age 3 to 15: A longitudinal mixed effects approach. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 29(7), 1818-1832. [CrossRef]
- Martin, S., Wolters, P., Baldwin, A., Gillespie, A., Dombi, E., Walker, K., & Widemann, B. (2012). Social-emotional functioning of children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1 and plexiform neurofibromas: Relationships with cognitive, disease, and environmental variables. J Pediatr Psychol, 37(7), 713-724. [CrossRef]
- Mautner, V.-F., Kluwe, L., Thakker, S. D., & Leark, R. A. (2002). Treatment of ADHD in neurofibromatosis type 1. Dev Med Child Neurol 44(3), 164-170.
- McCurdy, M. D. (2019). Social competence in youth with neurofibromatosis type 1 (Publication Number 13903256) [Doctoral Disseration, Drexel University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
- McNeill, A. M., Hudock, R. L., Foy, A. M. H., Shanley, R., Semrud-Clikeman, M., Pierpont, M. E., Berry, S. A., Sommer, K., Moertel, C. L., & Pierpont, E. I. (2019). Emotional functioning among children with neurofibromatosis type 1 or Noonan syndrome. Am J Med Genet A, 179(12), 2433-2446. [CrossRef]
- Min, K., Hong, D. W., Kim, E. K., & Lee, B. H. (2020). Psychological characteristics of adult neurofibromatosis type 1 patients seeking elective surgery. Archives of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 26(4), 150-156. [CrossRef]
- Miner, J. L., & Clarke-Stewart, K. A. (2008). Trajectories of externalizing behavior from age 2 to age 9: relations with gender, temperament, ethnicity, parenting, and rater. Dev Psychol, 44(3), 771-786. [CrossRef]
- Morotti, H., Mastel, S., Keller, K., Barnard, R. A., Hall, T., O’Roak, B. J., & Fombonne, E. (2021). Autism and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorders and symptoms in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Dev Med Child Neurol 63(2), 226-232. [CrossRef]
- Moskalewicz, A., & Oremus, M. (2020). No clear choice between Newcastle–Ottawa Scale and Appraisal Tool for Cross-Sectional Studies to assess methodological quality in cross-sectional studies of health-related quality of life and breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 120, 94-103. [CrossRef]
- Nikstat, A., & Riemann, R. (2020). On the etiology of internalizing and externalizing problem behavior: A twin-family study. PloS one, 15(3), e0230626. [CrossRef]
- Noll, R. B., Reiter-Purtill, J., Moore, B. D., Schorry, E. K., Lovell, A. M., Vannatta, K., & Gerhardt, C. A. (2007). Social, emotional, and behavioral functioning of children with NF1. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A, 143A(19), 2261-2273. [CrossRef]
- Parmeggiani, A., Boiani, F., Capponi, S., Duca, M., Angotti, M., Pignataro, V., Sacrato, L., Spinardi, L., Vara, G., Maltoni, L., Cecconi, I., Pastore Trossello, M., & Franzoni, E. (2018). Neuropsychological profile in Italian children with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) and their relationships with neuroradiological data: Preliminary results. Eur J Paediatr Neurol, 22(5), 822-830. [CrossRef]
- Pasini, A., Lo-Castro, A., Di Carlo, L., Pitzianti, M., Siracusano, M., Rosa, C., & Galasso, C. (2012). Detecting anxiety symptoms in children and youths with neurofibromatosis type I. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet, 159B(7), 869-873. [CrossRef]
- Payne, J. M., Haebich, K. M., MacKenzie, R., Walsh, K. S., Hearps, S. J. C., Coghill, D., Barton, B., Pride, N. A., Ullrich, N. J., Tonsgard, J. H., Viskochil, D., Schorry, E. K., Klesse, L., Fisher, M. J., Gutmann, D. H., Rosser, T., Packer, R. J., Korf, B., Acosta, M. T.,... North, K. N. (2021). Cognition, ADHD symptoms, and functional impairment in children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1. J. Atten. Disord., 25(8), 1177-1186. [CrossRef]
- Payne, J. M., Hearps, S. J. C., Walsh, K. S., Paltin, I., Barton, B., Ullrich, N. J., Haebich, K. M., Coghill, D., Gioia, G. A., Cantor, A., Cutter, G., Tonsgard, J. H., Viskochil, D., Rey-Casserly, C., Schorry, E. K., Ackerson, J. D., Klesse, L., Fisher, M. J., Gutmann, D. H.,... Consortium, N. F. C. T. (2019). Reproducibility of cognitive endpoints in clinical trials: Lessons from neurofibromatosis type 1. Ann Clin Transl Neurol, 6(12), 2555-2565. [CrossRef]
- Peng, P., Barnes, M., Wang, C., Wang, W., Li, S., Swanson, H. L., Dardick, W., & Tao, S. (2018). A meta-analysis on the relation between reading and working memory. Psychological Bulletin, 144(1), 48-76. [CrossRef]
- Peters, J. L., Sutton, A. J., Jones, D. R., Abrams, K. R., & Rushton, L. (2006). Comparison of two methods to detect publication bias in meta-analysis. JAMA : The Journal of the American Medical Association, 295(6), 676-680. [CrossRef]
- Potter, B. S. (2006). Evaluating everyday executive functions and psychosocial behavior in children with neurofibromatosis type I (Publication Number 3220711) [Doctoral Dissertation, Antioch University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
- Pride, N. A., Haebich, K. M., Walsh, K. S., Lami, F., Rouel, M., Maier, A., Chisholm, A. K., Lorenzo, J., Hearps, S. J. C., North, K. N., & Payne, J. M. (2023). Sensory Processing in Children and Adolescents with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Cancers (Basel), 15(14). [CrossRef]
- Pride, N. A., Korgaonkar, M. S., North, K. N., & Payne, J. M. (2018). Impaired engagement of the ventral attention system in neurofibromatosis type 1. Brain Imaging Behav, 12(2), 499-508. [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, B. L., Greenberg, M. T., & Domitrovich, C. E. (2009). The contribution of inhibitory control to preschoolers’ social–emotional competence. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 30(3), 310-32. [CrossRef]
- Rietman, A. B., Oostenbrink, R., Bongers, S., Gaukema, E., van Abeelen, S., Hendriksen, J. G., Looman, C. W. N., de Nijs, P. F. A., & de Wit, M. C. (2017b). Motor problems in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. J Neurodev Disord, 9, 19. [CrossRef]
- Rietman, A. B., Oostenbrink, R., van Noort, K., Franken, M.-C., Catsman - Berrevoets, C., Aarsen, F., Heniksen, J. G., & de Nijs, P. (2017a). Development of emotional and behavioral problems in neurofibromatosis type 1 during young childhood. Am J Med Genet A, 173(9), 2373-2380. [CrossRef]
- Rietman, A. B., Vaart, T., Plasschaert, E., Nicholson, B. A., Oostenbrink, R., Krab, L. C., Descheemaeker, M. J., de Wit, M. C., Moll, H., Legius, E., & de Nijs, P. (2018). Emotional and behavioral problems in children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1. American journal of medical genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric genetics, 177(3), 319-328. [CrossRef]
- Salmon, K., O’Kearney, R., Reese, E., & Fortune, C.-A. (2016). The role of language skill in child psychopathology: implications for intervention in the early years. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 19(4), 352-367. [CrossRef]
- Sanagoo, A., Jouybari, L., Koohi, F., & Sayehmiri, F. (2019). Evaluation of QoL in neurofibromatosis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis study. BMC neurology, 19(1), 123-123. [CrossRef]
- Sangster, J., Shores, E. A., Watt, S., & North, K. N. (2011). The cognitive profile of preschool-aged children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Child Neuropsychol, 17(1), 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Schrimsher, G. W. (2003). Neuroanatomical and visual -spatial/motor performance correlates of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder symptomatology in children with neurofibromatosis type-I and normal children (Publication Number 3089791) [Doctoral Dissertation, University of Houston]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
- Sharkey, C. M., Mullins, L. L., Clawson, A. H., Gioia, A., Hawkins, M. A. W., Chaney, J. M., Walsh, K. S., & Hardy, K. K. (2021). Assessing neuropsychological phenotypes of pediatric brain tumor survivors. Psychooncology, 30(8), 1366-1374. [CrossRef]
- Shi, L., & Lin, L. (2019). The trim-and-fill method for publication bias: Practical guidelines and recommendations based on a large database of meta-analyses. Medicine (Baltimore), 98(23), e15987-e15987. [CrossRef]
- Stivaros, S., Garg, S., Tziraki, M., Cai, Y., Thomas, O., Mellor, J., Morris, A. A., Jim, C., Szumanska-Ryt, K., Parkes, L. M., Haroon, H. A., Montaldi, D., Webb, N., Keane, J., Castellanos, F. X., Silva, A. J., Huson, S., Williams, S., Gareth Evans, D.,... Consortium, S. (2018). Randomised controlled trial of simvastatin treatment for autism in young children with neurofibromatosis type 1 (SANTA). Mol Autism, 9, 12. [CrossRef]
- Taddei, M., Erbetta, A., Esposito, S., Saletti, V., Bulgheroni, S., & Riva, D. (2019). Brain tumors in NF1 children: Influence on neurocognitive and behavioral outcome. Cancers, 11(11), 1772. [CrossRef]
- Talaei-Khoei, M., Riklin, E., Merker, V. L., Sheridan, M. R., Jordan, J. T., Plotkin, S. R., & Vranceanu, A. M. (2017). First use of patient reported outcomes measurement information system (PROMIS) measures in adults with neurofibromatosis. J Neurooncol, 131(2), 413-419. [CrossRef]
- Tang, H., Wu, Q., Li, S., Fang, Y., Yang, Z., Wang, B., Wang, X., & Liu, P. (2021). Visuospatial but not verbal working memory deficits in adult patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 751384. [CrossRef]
- ter Wolbeek, M., van Doornen, L. J., Kavelaars, A., Tersteeg-Kamperman, M. D., & Heijnen, C. J. (2011). Fatigue, depressive symptoms, and anxiety from adolescence up to young adulthood: A longitudinal study. Brain Behav Immun, 25(6), 1249-1255. [CrossRef]
- Tugwell, P., & Tovey, D. (2021). PRISMA 2020. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 134, A5-A6. [CrossRef]
- van der Vaart, T., Rietman, A. B., Plasschaert, E., Legius, E., Elgersma, Y., Moll, H. A., & Group, N.-S. S. (2016). Behavioral and cognitive outcomes for clinical trials in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Neurology, 86(2), 154-160.
- van Geel, M., Vedder, P., & Tanilon, J. (2014). Bullying and weapon carrying: A meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatrics, 168(8), 714-720. [CrossRef]
- Vassallo, G., Mughal, Z., Robinson, L., Weisberg, D., Roberts, S. A., Hupton, E., Eelloo, J., Burkitt Wright, E. M., Garg, S., Lewis, L., Evans, D. G., & Stivaros, S. M. (2020). Perceived fatigue in children and young adults with neurofibromatosis type 1. J Paediatr Child Health, 56(6), 878-883. [CrossRef]
- Vaucheret Paz, E., López Ballent, A., Puga, C., García Basalo, M. J., Baliarda, F., Ekonen, C., Ilari, R., & Agosta, G. (2019). Cognitive profile and disorders affecting higher brain functions in paediatric patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. Neurología (English Edition), 34(6), 353-359. [CrossRef]
- Vergunst, F., Commisso, M., Geoffroy, M. C., Temcheff, C., Poirier, M., Park, J., Vitaro, F., Tremblay, R., Cote, S., & Orri, M. (2023). Association of childhood externalizing, internalizing, and comorbid symptoms with long-term economic and social outcomes. JAMA Netw Open, 6(1), e2249568. [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W., López-López, J. A., Sánchez-Meca, J., & Marín-Martínez, F. (2015). A comparison of procedures to test for moderators in mixed-effects meta-regression models. Psychological Methods, 20(3), 360-374. [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W., & Viechtbauer, M. W. (2015). Package ‘metafor’. The Comprehensive R Archive Network. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/metafor/metafor.pdf.
- Vogel, A. C., Gutmann, D. H., & Morris, S. M. (2017). Neurodevelopmental disorders in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Dev Med Child Neurol, 59(11), 1112-1116. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. L., Smith, K. B., Esparza, S., Leigh, F. A., Muzikansky, A., Park, E. R., & Plotkin, S. R. (2012). Emotional functioning of patients with neurofibromatosis tumor suppressor syndrome. Genet Med, 14(12), 977-982. [CrossRef]
- Wei, G., Farooq, J., & Kumar, A. (2021). Impact of mind-body treatment interventions on quality of life in neurofibromatosis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dermatol Ther, 34(1), e14613. [CrossRef]
- West, G., Lervåg, A., Snowling, M. J., Buchanan-Worster, E., Duta, M., & Hulme, C. (2022). Early language intervention improves behavioral adjustment in school: Evidence from a cluster randomized trial. Journal of School Psychology, 92, 334-345. [CrossRef]
- Winsler, A., Fernyhough, C., & Montero, I. (2009). Private speech, executive functioning, and the development of verbal self-regulation. Cambridge University Press.
- Wolters, P. L., Burns, K. M., Martin, S., Baldwin, A., Dombi, E., Toledo-Tamula, M. A., Dudley, W. N., Gillespie, A., & Widemann, B. C. (2015). Pain interference in youth with neurofibromatosis type 1 and plexiform neurofibromas and relation to disease severity, social-emotional functioning, and quality of life. Am J Med Genet A, 167(9), 2103-2113. [CrossRef]
- Xue, H., Wu, Q., Yang, Z., Wang, B., Wang, X., & Liu, P. (2021). Dissociated deficits between explicit and implicit empathetic pain perception in neurofibromatosis type 1. Brain Sci, 11(12). [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y., Ehara, Y., Koga, M., & Imafuku, S. (2022). Health-related quality of life in patients with neurofibromatosis 1 in Japan: A questionnaire survey using EQ-5D-5L. J Dermatol, 49(12), 1228-1232. [CrossRef]
- Zöller, M. E., & Rembeck, B. (1999). A psychiatric 12-year follow-up of adult patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. J Psychiatr Res, 33(1), 63-68. [CrossRef]
Table 1.
Summary of Mean Effect Sizes across Studies .
Table 1.
Summary of Mean Effect Sizes across Studies .
| |
Hedges’ g
|
LL |
UL |
SE |
df |
p-value |
n |
k |
Tao2
|
I2 (%) |
| Depressive Symptoms |
0.43 |
0.21 |
0.65 |
0.10 |
16.80 |
<0.001 |
18 |
21 |
0.16 |
80.96 |
| Anxiety Symptoms |
0.27 |
0.01 |
0.54 |
0.13 |
16.77 |
0.043 |
18 |
24 |
0.20 |
83.93 |
| Somatic Symptoms |
0.56 |
0.30 |
0.83 |
0.13 |
17.72 |
<0.001 |
19 |
27 |
0.23 |
82.51 |
| Total Internalizing Symptoms |
0.50 |
0.33 |
0.67 |
0.08 |
37.34 |
<0.001 |
39 |
75 |
0.24 |
85.12 |
| Aggression |
0.33 |
0.08 |
0.58 |
0.12 |
19.74 |
0.013 |
21 |
33 |
0.23 |
82.02 |
| Delinquency |
0.43 |
0.26 |
0.60 |
0.08 |
23.05 |
<0.001 |
25 |
37 |
0.10 |
67.86 |
| Total Externalizing Symptoms |
0.24 |
0.13 |
0.35 |
0.05 |
29.23 |
<0.001 |
33 |
47 |
0.05 |
52.50 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).