Submitted:
22 August 2024
Posted:
26 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methodology
Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus
Complications of Diabetes Mellitus
Current Approaches for the Management of T2DM
Plant-Based Diets and Their Role in the Prevention and Management of DM
Plant-Based Diets, Edible Plants, Dietary Adjuncts and their Phytochemicals for the Management of DM and Prevention of DM Complications
| Dietary plants | Plant Parts Used | Traditional uses | Pharmacological actions | Diabetic model | Treatment Dose | Duration of treatment | Phytochemicals | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scientific name | Common name | ||||||||
| 1. Abelmoschus esculentus L. | Okra | Fruit, roots | Chronic kidney disease, T2DM, cardiovascular diseases | Blood glucose↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, VLDL↓, HDL↑, body weight↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓ |
STZ-induced T2DM mice | 200-400 mg/kg/day |
56 days | Oxalic acid, iodine, pectin, flavonoids, saponins, alkaloidsd-galactose, L-rhamnose, D-galacturonic | [143–145,625] |
| 2. Actinidia chinensis | Kiwi | Fruit | Dyspepsia, vomiting, loss of appetite, diabetes | serum microRNA-424↑, Keap1↑, Nrf2↑, IL-6↓, IL-1↓, SOD↑, GSH↑, ALT↓, AST↓, inflammation ↓ | T2DM patients (50-70 years old) | 10mg/kg/day | 270 days | Triterpenoids, polyphenols, β-carotene, lutein, xanthophylls, amino acids | [146–149] |
| 3. Aegle marmelos L. | Stone apple | Fruit | Inflammation, asthma, hyperglycemia, febrifuge, hepatitis, analgesic, antifungal agent, colitis, flatulence, dysentery, fever | Glucose tolerance↑, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities↓, insulin secretion↑, intestinal glucose absorption↓, BMI↓, polydipsia↓, polyphagia↓ | STZ-induced T2DM diabetic rats |
250-500 mg/kg/day |
28 days | Marmelosin, psoralen, limonene, citronellal, citral, marmin, skimmianine, aegelin, fagarine, lupeol, cineol, halfordiol, citronellal, cuminaldehyde, eugenol, marmesinin |
[150–152] |
| 4. Agaricus bisporus | Mushroom | Rhizome | Cold, cough, influenza, asthma, cancer, diabetes, hepatic disorders | Blood glucose↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, insulin secretion↑, glucagon secretion↓ | STZ-induced Sprague-Dawley rats | 200mg/kg/day | 21 days | Lectins, β-glucans, polyphenols, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, protocatechuic acid, gallic acid, cinnamic, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid and catechin | [153–157] |
| 5. Allium cepa | Onion | Fruit | Wound healing, scars, keloids, bee sting inflammation, dysmenorrhea, vertigo, fainting, migraine, bruises, earache, jaundice, pimples, diabetes | Blood glucose↓, FBG↓, TC↓, TG↓ α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓, insulin secretion↑, β-cell protection↑, oxidative stress↓ |
Alloxan- induced diabetic rats |
200-300 mg/kg/day |
42 days | Quercetin, lectin, steroids, catechol, thiocyanate, isoflavones, humulone, quercetin, apigenin, rutin, myricetin, kaempferol, catechin, resveratrol, ajoene, phenolics, phenolic acids and anthocyanins | [158–162] |
| 6. Allium sativum L. | Garlic | Fruit | Cold, fever, headache, abdominal pain, sinus congestion, gout, rheumatism, hemorrhoids, asthma, bronchitis, cancers, cough cardiovascular diseases, arthritis, tuberculosis, rhinitis, malaria, dermatitis, enlarged spleen, fistula, UTI, kidney stone | Blood glucose↓, TC↓, TG↓, GLUT-4 activity↑, β-cell function↑, glucose uptake↑, creatinine↓, uric acid↓, urea↓, AST and ALT↓, insulin sensitivity↑, insulin secretion ↑, insulin production ↑, glucose tolerance↑, | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 100-500 mg/kg/day |
14 days | AJoene, cysteine, allicin, β-resorcylic acid, gallic acid, rutin, protocatechuic acid, quercetin | [163–168] |
| 7. Aloe barbadensis Mill. | Aloe vera | Leaves | Wound healing, constipation, colic, worm infestation, dermatitis, hypertension | FBG ↓, TG↓, TC↓, AGE formation ↓, body weight, diabetic nephropathy↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 300 mg/kg/day | 49 days | Flavonoids, acemannam, flavones, quinone, galactan, pectin, ornanic acids | [169–175,626] |
| 8. Anacardium occidentale L. | Cashew nut | Nut, leaves, bark | Fevers, aches, pains, diarrhea, diabetes, skin irritations, arthritis | Blood glucose↓, SOD↑, IR↓, gluconeogenesis↓, insulin secretion ↑ |
Alloxan- induced Wistar rats | 100-250 mg/kg/ day |
40 hours | Arginine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, arachidic acid, lignoceric acid, gadoleic acid, linolenic acid, cyanidin, peonidin, anacardic acid, cardanol, limonene, lactone, palmitic acid | [176–179] |
| 9. Ananas comosus L. | Pineapple | Fruit, peel, leaves | Pain, skin diseases, edema, wound, indigestion, diabetes and blood clotting | IR↓, insulin sensitivity↑, HDL-c↑, HbA1c↓, body weight↓, LPL activity↑, HMGCoA reductase activity↓ |
Alloxan- induced Wistar rats | 400 mg/kg/ day |
15 days | Bromelain, flavonoids, coumaric acid, ellagic acid, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid | [180–186] |
| 10. Apium graveolens | Celery | Leaves, seeds, roots | Arthritis, spleen dysfunction, diabetes, sleep disturbances, CNS disorders | Blood glucose↓, PPBG↓, plasma insulin↑, GLUT-4 transloaction↑, mitochondrial dysfunction↓, insulin sensitivity↑, inflammation↓ | Elderly diabetic patients above 60 years | 250mg/kg/3 times a day | 12 days | Quercetin, thymoquinone, frocoumarin coumaric acid, gallic acid, flavonoids, alkaloids, steroids, limonene, selinene, glycosides | [187–192,627] |
| 11. Artocarpus heterophyllus | Jackfruit | Fruit, leaves, bark, seeds, roots | Wound healing, cancer, diabetes | PPBG↓, FBG↓, IR↓, HbA1c↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities↓, HDL-c↑, LDL↓ | T2DM patients (18-60) | 30000 mg/kg/day | 84 days | Carotenoids, tannins, volatile acids, sterols, chrysin, silymarin, isoquercetin | [195–199] |
| 12. Asparagus officinalis | Asparagus | Stem | Asthma, liver, rheumatic, kidney, bladder diseases | Blood glucose↓, β-cell function↓, FBG↓, TG↓, serum insulin↑, body weight↓, hepatic glycogen↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 250-500 mg/kg/day |
28 days | Asparagine, tyrosine, arginine, flavonoid, saponin, resin, tannin | [200–204] |
| 13. Avena sativa | Oats | Grains | Dermatitis, cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease | PPBG↓, HbA1c↓, body weight↓, HDL↑, MDA↓, FBG↓, IR↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDquinol-C↓, SOD↑ | T2DM patients (50-70 years) |
1 IU/kg/ day | 28 days | β-glucan, tocopherols, tocotrienols, phenolic acids, sterols, selenium, avenanthramides | [205–209,628] |
| 14. Averrhoa carambola L. | Star fruit | Fruit | Chronic headache, fever, cough, gastroenteritis, diarrhea, diabetes, ringworm infections, skin inflammations hypertension, hyperglycemia | Blood glucose↓, TG↓, TC↓, FFAs↓, serum insulin↑, glucose uptake↑, glycogen synthesis ↑ | STZ-induced Kunming mice | 150-1200 mg/kg/day |
21 days | Catechin, epicatechin, procyanidins, gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, ferulic acid, rutin, isoquercitrin, quercitrin, anthocyanin, anthocyanidin, leucoanthocyanidins, triterpenoids |
[210–214,629] |
| 15. Azadirachta indica | Neem | Leaves, stem, bark, flower, roots, fruit | Fever, skin diseases, infection, inflammation and dental disorders | PPBG↓, FBG↓, HbA1c↓, IR↓, endothelial function↑, oxidative stress ↓, systemic inflammation ↓ | T2DM patients (30-65 years old) | 125-500 mg /kg/twice a day |
84 days | Nimbidin, nimbin, nimbidol, quercetin nimbosteron, saponin, tannin, flavonoids | [215–219] |
| 16. Beta vulgaris | Beetroot | Fruit | Dandruff, loss of libido, stomachaches, diabetes, arthritis, constipation | Blood glucose↓, HbA1c↓, FBG↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, IR↓, HDL↑, ALT↓, AST↓, gluconeogenesis↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓ |
T2DM patients (57±4.5 years) | 100000 mg/kg/ day |
56 days | Betalains, betanin, carotenoids, coumarins, sesquiterpenoids, betagarin, betavulgarin, quercetin, kaempherol, tiliroside, astragalin, rhamnocitrin, rhamnetin, betavulgarosides, betacyanin |
[220–222,630] |
| 17. Brassica juncea | Mustard | Seeds | Arthritis, foot-ache, lumbago, diabetes, rheumatism | Blood glucose↓, FBG↓, TC↓, TG↓, prediabetic IR↓, glucose tolerance↑, insulin secretion↑, intestinal glucose absorption↓ | Fructose- induced Sprague Dawley rats | 100mg/kg/day | 30 days | Chlorogenic acid, sinigrin, р-coumaric acid, vanillic acid, flavonoids, chlorogenic acid, polyphenols, allyl isothiocyanate, cinnamic acid, kaempferol | [223–226] |
| 18. Brassica oleracea var. capitata | Cabbage | Flower | gastritis, peptic ulcers, irritable bowel syndrome, diabetes, idiopathic cephalalgia | FBG↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, HDL↑, insulin sensitivity↑, β-cell function↑ | Alloxan- induced diabetic rabbits. | 500mg/kg/day | 30 days | Myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, apigenin, luteolin, cyanidin daidzein, genistein, glycitein, biochanin A, formononetin | [227–229] |
| 19. Brassica oleracea var. italica | Broccoli | Flower |
Xerophthalmia, hyperlipidemia, fibromyalgia, cancer, diabetes |
Blood glucose↓, lipid peroxidation↓, IL-6↓, TNF-α↓, HbA1c↓, insulin sensitivity↑, β-cell function↑, glucose production ↓. |
T2DM Albino Wistar Rats | 400mg/kg/day | 42 days | Glucosinolates, isothiocyanates, sulforaphane, sinapic acid, gallic acid, vanillic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, apigenin, kaempferol, luteolin, quercetin and myricetin | [230,231,631] |
| 20. Camellia sinensis | Tea | Leaves | Flatulence, indigestion, vomiting, obesity, diarrhea, hyperglycemia, stomach discomfort | Blood glucose↓, IR↓, MDA↓, oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓, insulin release ↑, glycation ↓, glucose tolerance↑ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 100-200 mg/kg/day |
28 days | Caffeine, theanine, proanthocyanidins, myricetin, kaempferol, quercetin, chlorogenic acid, coumarylquinic acid, theogallin, catechins, epicatechin | [232–235,632] |
| 21. Capsicum annuum L. | Red pepper | Seeds | Dyspepsia, ulcer, anorexia, GERD and diabetes. | FBG↓, HbA1c↓, inflammatory cytokines↓, TG↓, TNF-α↓, IL-6↓, plasma insulin↑, gluconeogenesis↓, AMPK↑, FOXO1↑, glucose uptake↑, GLUT-4 translocation↑ | High fat died induced C57BL/KsJ | 200mg/kg/day | 56 days | Lycopene, flavonoids, carotenoids, flavones, apigenin, quercetin, isoquercetin, capsinoids, polyphenols | [236–240] |
| 22. Carica papaya | Papaya | Fruit, seeds, leaves | Hypertension, fever (dengue), obesity, jaundice, UTI, ulcer, constipation, bronchitis, cough, diarrhea, asthma, piles, malaria, wound healing | Blood glucose↓, TG↓, TC↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities↓, oxidative stress ↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 750-3000 mg/100mL/ day |
28 days | Papain, quercetin, kaempferol, p-coumaric acid, carpinine, carpaine, choline, β-carotene, linalool, oleic acid, linolenic acid | [241–244] |
| 23. Carissa carandas | Bengal currant | Fruits | Anorexia, brain disease, cough, asthma, constipation, diarrhea, diabetes, pain, pharyngitis, scabies, leprosy, malaria, myopathic spams, fever, epilepsy, seizures | Blood glucose↓, inflammation↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓ |
Alloxan- induced Swiss albino rats | 400 mg/kg | 1 day | Lignans, flavonoids, steroid, phenolic acids alkaloids | [245–249] |
| 24. Catharanthus roseus L. | Vinca Rosea | Flowers, leaves | Cancer, diabetes, stomach disorders, kidney, liver, cardiovascular disorders | Blood glucose↓, insulin secretion↑, β-cell function↑, TC↓, creatinine↓ |
Alloxan- induced Albino rabbits | 0.5-1mg /kg/day |
24 hours | Gallic acid, rutin, p-coumaric acid, ajmalicine, vindoline, catharanthine, vinblastine, vincristine, caffeic acid, quercetin, kaempferol, syringic acid, chlorogenic acid, ellagic acid, coumarins | [250–254] |
| 25. Centella asiatica | Centella leaves | Leaves | Leprosy, lupus, varicose ulcers, eczema, psoriasis, diarrhea, fever, amenorrhea, female genitourinary tract infections, diabetes, anxiety | Blood glucose↓, insulin sensitivity↑, oxidative stress↓, inflammation↓ |
STZ-induced Sprague-Dawley | 500-1000 mg/kg/day |
14 days | Asiaticoside, madecassic acid, madecassoside, centellase, quercetin, kaempferol, phytosterol | [255–258] |
| 26. Chenopodium quinoa | Quinoa | Grains | Dyslipidemia, diabetes, heart disease | Blood glucose↓, FBG↓, IR↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, α-glucosidase activity↓, lipid accumulation↓, glucose tolerance↑, insulin sensitivity↑ | High fat diet induced C57BL/6J mice | 2000 mg/kg/day | 84 days | Saponins, phytosterols, phytoecdysteroids, phenolics, tocophenols, betalains, tannins, glycine betaine | [259–265] |
| 27. Cicer arietinum | Chickpea | Grains | Digestive diseases, cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes | Blood glucose↓, inflammation↓, organ function↑, intestinal dysbiosis↓, α-amylase, α-glucosidase and DPP4 activity↓, carbohydrate metabolism↑, body weight↓ |
STZ-induced HFF rats | 3000 mg/kg/day | 28 days | Uridine, adenosine, tryptophan, 3-hydroxy-olean-ene, biochanin | [266–271,633] |
| 28. Cinnamomum verum | Cinnamon | Bark | Nausea, vomiting, fever, halitosis, arthritis, coughing, hoarseness, frigidity, cramps, intestinal spasms, bronchitis, asthma, odontalgia, cardiac diseases, diarrhea, vaginitis, neuralgia, rheumatism, piles, urinary disease | Blood glucose↓, GLUT-4 translocation↑, glucose uptake↑, Mitochondrial UCP-1↑, insulin secretion↑, α-glucosidase activity↓, | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 30mg/kg/ Day |
22 days | cinnamaldehyde, cinnamates, cinnamic acid, eugenol, cinnamyl acetate, cubebene, terpinolene, linalool, linalyl acetate, benzyl cinnamate, piperitone, β-sitosterol, flavanol, glucosides, coumarin, protocatechuic acid, vanillic acid, syringic acid | [272–275] |
| 29. Citrullus lanatus L. | Water-melon | Fruit, seeds | Gastrointestinal disorders, urinary disorders, aphrodisiac, fever, laxative, emetic | FBG↓, serum lipid profile↓, glucose-6-phosphatase↓, lipid peroxidation↓, GLUT4↑, GLUT2↑, hexokinase activity↑ | Alloxan- induced Wistar Albino rats | 500-1000 mg/kg/day |
14 days | Stigmasterol, quinic acid, malic acid, epicatechin, caffeic acid, rutin, p-coumaric acid, quercetin, ferulic acid, scopoletin, apigenin, kaempferol, β carotene, citrulline, lycopene, α tocopherol | [276–279] |
| 30. Citrus limon | Lemon | Fruit, peel, leaves | Cough, scurvy, cold, fever, rheumatism, sore throat, diabetes, irregular menstruation | Serum glucose↓, body weight↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL↓, VLDL↓, GSH↑, insulin sensitivity↑, GLUT-4 translocation↑, AGE formation↓, Glucose uptake↑ |
STZ-induced Wistar rats | 200-400 mg/kg/day |
15 days | Limocitrin, hesperidin, diosmin, hesperetin, didymin, naringin, naringenin, tangeretin, rutine, quercetin, β-pinene, γ-terpinene, D-limonene, ferulic acid | [280–287] |
| 31. Citrus maxima | Pomelo | Fruit, peel | Asthma, fever, ulcer, diarrhea, cough, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, insomnia | Blood glucose↓, TG↓, TC↓, HDL↑, LDL↓, α-amylase, α-glucosidase and angiotensin I-converting enzyme activity↓, body weight↓, glucose tolerance ↑ | Alloxan- induced diabetic rats | 200-600 mg/kg/day |
14 days | Terpenoids, sterols, carotenoids, polyphenols, chlorogenic acid, ferulic acid, caffeic acid, gallic acid, ρ-coumaric acid. |
[288–290,634] |
| 32. Citrus reticulata | Orange | Fruit, peel | Alzheimer’s disease, cough, phlegm, diabetes, hepatic steatosis, cancer | mRNA expression ↑, GLUT-4 translocation↑, insulin sensitivity↑, serum fructosamine level ↓, glucose tolerance↑ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 100mg/kg/day | 28 days | Flavonoids hesperidin, quercetin, naringin, nobiletin, tangeretin | [291–295] |
| 33. Cocos nucifera | Coconut | Fruit, husk, water | Diarrhea, diabetes, dermatitis, renal diseases, stomachaches, fever, asthma, abscesses, amenorrhea, gonorrhea, menstrual disorders | Blood glucose↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity ↓, DPPH free radicals↓, IR↓, oxidative stress↓, neuropathy↓, β-cell regeneration ↑ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 250-500 mg/kg/day |
28 days | Chlorogenic, gallic, ferulic, salicylic, coumaric acids, glycosides, rutin, quercetin, vanillin, catechin, epicatechin, neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, lutein | [297–304] |
| 34. Coffea Arabica L. | Coffee | Leaves, fruit, beans | Flu, anemia, edema, asthenia., asthma, backache, cough, jaundice, diarrhea, intestinal pain, migraine, headache, fever, purulent wounds, pharyngitis, diabetes, stomatitis | Blood glucose↓, insulin secretion↑, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓, nephropathy↓, plasma insulin↑, IR↓, TG↓ |
STZ-induced Wistar rats | 1000mg/ kg/day |
90 days | Chlorogenic acids, caffeic, p-coumaric, vanillic, ferulic, protocatechuic acids, flavonoids, alkaloids, caffeine, sitosterol, stigmasterol, coffeasterin, kaempherol, quercetin, sinapic, quinolic, trigonelline, caffeoylquinic, dicaffeoylquinic | [305–307,635] |
| 35. Colocasia esculenta | Taro | Stem, leaves | Rheumatic pain, diabetes, hypertension, pulmonary congestion | Blood glucose↓, HbA1c↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, VLDL↓, HDL↑, body weight↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 405-810 mg/kg/day |
28 days | Tannins, phytates, oxalates, tryptophan, chlorogenic acid, anthraquinone, vitexin, catechins, apigenin, cinnamic acids, isovitexin, orientin, isoorientin, rosmarinic acid | [308–312] |
| 36. Coriandrum sativum | Coriander | Seeds, leaves | Diarrhea, flatulence, colic, indigestion, gastrointestinal diseases, diabetes | Diabetic neuropathy↓, Blood glucose↓, MDA↓, GSH↑, SOD↑, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, AGEs formation↓, lipid peroxidation↓, oxidative stress↓, TNF-α↓ |
STZ-NA induced Wistar rats | 100-400 mg/kg/day |
45 days | Flavonoid, tocopherol, tocotrienol sterol, carotenoids, terpenoids, steroids, saponin, tannin, alkaloids | [313–317] |
| 37. Crocus sativus L. | Saffron | Flower stigma | CNS diseases, diabetes, obesity, cancer, dyslipidemia | Blood glucose↓, MDA↓, NO↓, GSH↑, SOD↑, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓, inflammation↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 10-40mg /kg/day |
28 days | Crocin, β carotenes, crocetin, picrocrocin, zeaxanthene, safranal | [318–323] |
| 38. Cuminum Cyminum L. | Cumin seeds | Seeds | Diarrhea, dyspepsia, epilepsy, toothache, whooping cough, flatulence, indigestion, diabetes, jaundice | Blood glucose↓, AGEs formation↓, HbA1c↓, creatinine↓, blood urea nitrogen↓, serum insulin↑, oxidative stress↓, nephropathy↓ |
STZ-induced Wistar rats | 200-600 mg/kg/day |
28 days | Carvacrol, carvone, α-pinene, limonene, γ-terpinene, linalool, carvenone, p-cymene, cumin aldehyde, limonene, α- and β-pinene, terpinene,s safranal and linalool | [324–326] |
| 39. Cucumis sativus | Cucumber | Fruit, seeds | Sunburn, skin irritation, constipation, thermoplegia, gall bladder stone, hyperdipsia, diabetes | Blood glucose↓ IR↓, body weight↓, insulin sensitivity↑, gluconeogenesis↓, glucagon secretion↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 200-800 mg /kg/day |
9 days | Cucurbitacin, cucumerin, cucumegastigmanes vitexin, orientin, apigenin, isoscoparin | [327–330] |
| 40. Cucurbita pepo L. | Pumpkin | Fruit, seeds | Dermatitis, depression, irritable bladder, intestinal inflammation, prostate enlargement, hyperglycemia | Blood glucose↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, HDL↑, IR↓, ROS↓, SOD↑, GSH↑, MDA↓ | STZ-induced T2DM mice | 400mg/kg/day | 56 days | β-carotene, zeaxanthin, lutein,flavonoids, alkaloids, polysaccharides, polyphenols | [331–335] |
| 41. Curcuma longa L. | Turmeric | Fruit | Cough, diabetes, arthritis, gall bladder stones, dermatitis, cancer, intestinal, stomachic diseases | Blood glucose↓, FBG↓, insulin sensitivity↑, β-cell function↑, IR↓, GLUT-2 activity↑, insulin secretion↑, glucose uptake↑ | STZ-Na induced Wistar rats | 30-60 mg/kg/day |
30 days | Caffeic acid, curdione, coumaric, caffeic acid, casuarinin, curcuminol, isorhamnetin, valoneic acid, eugenol, corymbolone, demethoxycurcumin | [336–340] |
| 42. Daucus carota | Carrot | Fruit | Diarrhea, constipation, intestinal inflammation, weakness, illness, diabetes, rickets | Blood glucose↓ IR↓, Obesity↓, body weight↓, BMI↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓ |
High fructose induced Wistar rats | 50ml/kg/ day | 56 days | Carotenoid, polyacetylenes, ascorbic acid, α and β-carotene, lutein, lycopene, anthocyanins | [341–344,636] |
| 43. Ficus carica | Fig | Fruit, leaves, bark, roots | Dermatitis, leprosy, cancer, anemia, diabetes, paralysis, urinary tract infection, ulcer, liver diseases | FBG↓, PPBG↓, TG↓, HDL↑, LDL↓, VLDL↓, TC↓, pancreatic β-cell apoptosis↓, pancreatic AMPK↑, caspase-3↓, body weight ↓ | STZ-induced C57BL/6 mice |
2000 mg/kg/day | 42 days | Eugenol, anthocyanins, volatile compounds, phenolic acids, flavones, flavanols | [345–350] |
| 44. Fragaria ananassa | Strawberry | Fruit, leaves | Wound healing, platelet aggregation, obesity, diabetes | Blood glucose↓, IR↓, insulin secretion↑, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities↓, plasma creatinine↓, MDA↓, TNF-α↓, IL-6↓, caspase-3↓ | STZ-induced Albino rats | 50-200 mg/kg/day |
30 days | Quercetin, kaempferol, rutin, gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, ellagitannins, octadecatrienoic acid, vitamin C and E, folic acid, carotenoids, anthocyanins, gallotannins | [351–355,637] |
| 45. Glycine max | Soya bean | Seeds, leaves | Osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, diabetes | Blood glucose↓, FBG↓, IR↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, α-glucosidase activity↓, HbA1c↓, HDL↑, body weight↓, glucose uptake↑ | T2DM obese patients (43-51 years) |
2000 mg/kg/day | 84 days | β-conglycinin, phenolic acids, flavonoids, isoflavones, saponins, phytosterols, sphingolipids | [356–360,638] |
| 46. Helianthus annuus | Sunflower | Flowers, seeds | Diabetes, nephrotoxicity, cardiovascular disease, hematologic disorders | Blood glucose↓, nephropathy↓, FBG↓, BMI↓, body weight↓, AGEs formation↓, DPPH↓, NO↓, urea↓ | Alloxan- Induced Albino rats |
150-600 mg/kg/day |
21 days | Flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, tocopherols, carotenoids, saponins, tannins, chlorogenic acid and caffeic acid | [361–364] |
| 47. Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Linn. | China rose | Flowers, leaves | Tumor, hairloss, infertility, diabetes, wounds | Blood glucose↓, insulin secretion↑, β-cell function↑, TC↓, TG↓, hepatic glycogen↓, SOD↑ | STZ-induced Long Evans rats | 250-500 mg/kg/day |
28 days | Quercetin, cyanidin, ascorbic acid, genistic acid, lauric acid, thiamine, niacin, margaric acid, calcium oxalate, hentriacontane | [365–369] |
| 48. Hylocereus undatus | Dragon fruit | Fruit, seeds | Diuretic, healing agent, laxative, gastritis aid | Blood glucose↓, MDA↓, FBG↓, SOD↑, GLUT2↑, oxidative stress↓ | STZ-induced Sprague Dawley rats | 250-500 mg/kg/day |
35 days | Lycopene, β-carotene, betacyanin,oleic acid, octacosane, phthalic acid, eicosane, tetratriacontane, tacosane, campesterol linoleic acid, palmitic acid, gallic acid, syringic acid, protocatechuic acid, p-coumaric acid | [370–372,639] |
| 49. Ipomoea batatas | Sweet potato | Fruit | Aphrodisiac, burns, catarrh, diarrhea, fever, nausea, splenosis, stomach distress, anemia, tumors, hypertension, , prostatitis, asthma, |
Blood glucose↓, IR↓, Insulin sensitivity↑, glucose tolerance↑, insulin secretion↑ | T2DM patients (58±8 years) | 4000 mg/kg/day | 42 days | Anthraquinones, coumarins, flavonoids, saponins, tannins, phenolic acids, quercetin, chlorogenic acid, terpenoids, β-carotene, zeaxanthin, lutein, anthocyanins | [373–377,640] |
| 50. Juglans regia L. | Walnut | Nut, leaves | Curing bacterial infections, stomachaches, thyroid issues, diabetes. cancer, heart conditions, sinusitis | Blood glucose↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓, PTP1B↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 25-100 mg/kg/day |
28 days | tocopherol, gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, catechin, vanillic acid, epicatechin, p-coumaric acid, isoquercitrin, quercetin, luteolin, kaempferol and apigenin | [378–381] |
| 51. Lactuca sativa | Lettuce | Leaves | Hyperglycemia, osteodynia, inflammations | FBG↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, HDL↑, β-cell function↑, SOD↑, GSH↑, glucose production ↑ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 50mg/kg/ day | 28 days | flavonoids, quercetin, flavonols, anthocyanins, hydroxycinnamoyl derivatives | [382–386] |
| 52. Lagenaria siceraria | Bottle gourd | Fruit, leaves, seeds | Jaundice, diabetes, constipation, flatulence, insomnia, ulcer, piles, colitis, insanity, hypertension, congestive cardiac failure, skin diseases, headaches | Blood glucose↓, HbA1c↓, FBG↓, body weight ↓, TC↓, TG↓, insulin production↑, glucose tolerance↑, intestinal glucose absorption↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 400mg/kg/day | 15 days | Isovitexin, isoorientin, saponarin, fucosterol, campesterol, cucurbitacin B, cucurbitacin D, cucurbitacin E, isoquercitrin, kaempferol, gallic acid and protocatechuic acid | [387–390] |
| 53. Laurus nobilis | Bay leaves | Leaves | Stomachaches, phlegm, cold, sore throat, headache, indigestion, flatulence, eructation, epigastric bloating, diabetes | Blood glucose↓, β-cell function↑, α-glucosidase activity↓, Insulin production↑, β-cell regeneration↑ |
STZ-induced Wistar rats | 200mg/kg/day | 28 days | Kaempferol, syringic acid, quercetin, apigenin, luteolin, lauric acid, palmitic acid, linoleic acid, lutein, eugenol | [391–394] |
| 54. Litchi chinensis | Lychee | Fruit, seeds | Cough, ulcer, flatulence, testicular swelling, diabetes, hernia, obesity | Blood glucose↓, FBG↓, renoprotection↑, IR↓, glucose tolerance↑, TG↓, α-glucosidase activity↓ | Alloxan- induced Wistar rats |
2.6 mg/kg/day | 30 days | Flavonoids, triterpenes, sterols, phenolic compounds | [395–397] |
| 55. Luffa acutangula | Ridge gourd | Fruit, seeds | Jaundice, hemorrhoids, dysentery, headache, ringworm infection, insect bite, urinary bladder stone, granular conjunctivitis, constipation, leprosy, diabetes | Blood glucose↓, HbA1c↓, FBG↓, ALT↓, AST↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, VLDL↓, gluconeogenesis↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 200-400 mg/kg/day |
21 days | Luffaculin, luffangulin, apigenin, luteolin, myristic acid, palmitic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, oleanolic acid, machaelinic acid, α-thujene, terpinene | [398,399,641] |
| 56. Malus domestica Borkh | Apple | Fruit, peel | Wound healing, diabetes, asthma, obesity, cardiovascular disease | Blood pressure↓, endothelial function↑, lipid homeostasis↑, insulin resistance ↓ | HFHF-fed ICR mice | 250 mg/kg/ day |
28 days | Procyanidins, flavonoids, chlorogenic acids, hydroxycinnamic acids, anthocyanins, quercetins | [400–409,642] |
| 57. Mangifera indica | Mango | Fruit, peel, bark, seeds | Asthma, tetanus, polyuria, dysentery, anthrax, indigestion, tumor, tympanites, diarrhea, colic | FBG↓, HbA1c↓, serum fructosamine level↓, plasma insulin ↑, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities↓, PPBG ↓ |
STZ-induced Wistar rats | 100-200 mg/kg/day | 60 days | Mangiferins, carotenoids, flavonoids, anthocyanins, gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, chlorogenic acid, ferulic acid | [410–415] |
| 58. Mentha spicata | Mint leaves | Leaves | Cough, cold, asthma, fever, obesity, dementia, hypertension, abdominal pain, headache, menstrual pain, depression, insomnia | FBG↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, VLDL↓ MDA↓, body weight↓, HDL↑, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓ | Alloxan- induced Wistar rats | 300mg/kg/day | 21 days | Carvone, limonene, 1,8-cineole, pulegone, β-bourbonene, β-pinene, dihydrocarveol, α-phellandrene, borneol, linalool, germacrene D and piperitone | [416–418,643] |
| 59. Moringa oleifera Lam. | Moringa | Fruit, leaves | Diabetes, liver disease, cancer, inflammation, hypercholesteremi, hypertension | Blood glucose↓, hepatic functions↑, FBG↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, VLDL↓, HDL↑, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓ |
High fat died induced C57BL/6 mice. | 200mg/kg/day | 21 days | Tannins, βcarotene, vitamin C, quercetin, alkaloids, saponins, steroids, phenolic acids, glucosinolates, flavonoids, terpenes | [419–423] |
| 60. Momordica charantia | Bitter gourd | Fruit, leaves, seeds | T2DM, dyslipidemia, cancer, obesity, malaria, dysentery, hypertension, worm infections | Blood glucose↓, fructosamine↓, IR↓, TC↓, TG↓, insulin secretion↑, HDL↑, MDA↓, GSH↑, glucose uptake↑, β-cell function↑ | STZ-induced Albino rats | 10 mL/kg/ day |
21 days | Saponins, triterpenes, flavonoids, ascorbic acids, steroids, tannins, alkaloids, cardiac glycosides, phlobatinnins anthraquinones | [424–432] |
| 61. Morus alba L. | Mulberry | Fruit, leaves | Insomnia, tinnitus, dizziness, premature aging, diabetes | FBG↓, IR↓, TG↓, HDL↑, LDL↓, TC↓, GLUT-4 translocation↑ | STZ-induced HFF Wistar rats |
400 mg/kg/ day | 49 days | Quercetin, isoquercetin alkaloids, polyphenols, flavonoids, anthocyanins | [434–437] |
| 62. Murraya koenigii L. | Curry leaves | Leaves | Piles, inflammation, itching, fresh cuts, dysentery, bruises, edema, body aches, diabetes, snakebites | Blood glucose↓, MDA↓, GSH↑, IR↓, β-cell regeneration↑ | STZ-NA induced Sprague Dawley rats | 200-400 mg/kg/day |
28 days | Mahanine, mahanimbine, murrayanol, koenimbine, koenigicine, koenigine, murrayone, isomahanine, glycozoline, mukonicine, murrayazolinol, murrayacine, quercetin, apigenin, kaempferol, catechin | [438–441] |
| 63. Myristica fragrans Houtt. | Nutmeg | Fruit, seeds | Skin infection, diarrhea, diabetes, Alzheimer’s diseases, rheumatism, asthma, cold, cough, malaria | Blood glucose↓, serum insulin↑, oxidative stress↓, β-cell function↑, AMPK↑, IL-6↓, TNF-α↓ | Chlorpromazine-induced obese Swiss albino mice | 50-450 mg/kg/day |
7 days | Flavonoids, terpenes, phenylpropanoids, coumarin, lignans, alkanes and indole alkaloids | [442–445] |
| 64. Nigella sativa L. | Black seeds | Seeds | Asthma, dyslipidemia, diabetes, diarrhea | Blood glucose↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓, serum lipids↓ insulin sensitivity↑, gluconeogenesis↓ | STZ-induced Swiss albino mice | 100-700 mg/kg/day |
28 days | Thymoquinone, thymol, limonene, carvacrol, p-cymene, longifolene, α-pinene, linoleic acid, oleic acid, palmitic acid, saponins, flavonoids, alkaloids | [446–450] |
| 65. Ocimum sanctum L. | Holy basil | Leaves, seeds | Anxiety, cough, asthma, diarrhea, fever, dysentery, arthritis, eye diseases, skin diseases, malaria, vomiting, cardiac and genitourinary infection | TC↓, TG↓, LDL↓, VLDL↓, atherogenic index ↓, GSH ↑, Insulin production↑, intestinal glucose absorption↓ |
Alloxan- induced diabetic rabbits | 0.8 mg/kg/ Day |
28 days | Eugenol, euginal, urosolic acid, carvacrol, linalool, caryophyllene, triterpenoids, tannins | [451–454,644] |
| 66. Olea europaea L. | Olive | Fruit, leaves | Diabetes, diarrhea, inflammation, urinary tract infection, intestinal diseases, hemorrhoids, rheumatisms | Blood glucose↓, inflammatory cytokines↓, body weight↓, gluconeogenesis↓, glucose-6-phosphatase enzyme activity↓ |
STZ-induced Wistar rats |
200-400 mg/kg/day |
70 days | Flavonoids, secoiridoids, hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol, cinnamic acid | [455–460] |
| 67. Origanum vulgare | Oregano | Leaves | Acne, cystic fibrosis, diabetes, bacterial infections | Blood glucose↓, glucose uptake↑, GLUT2↑, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓, oxidative stress↓ | STZ-induced Diabetic rats | 20mg/kg/ Day |
15 days | Amburoside, apigenin, luteolin 7-O-glucuronide, rosmarinic acid and lithospheric acid | [461–465,645] |
| 68. Passiflora edulis | Passion fruit | Fruit, peel | Cough, diabetes, dysmenorrhea, dysentery, arthralgia, constipation | Blood glucose↓, TG↓, TC↓, interleukins↓, body weight↓, insulin sensitivity ↑, glucose tolerance ↑ | Cafeteria diet induced C57BL/6 mice | 15% of PEPF (P. edulis peel flour) in CAF diet | 112 days | Piceatannol, flavonoids, triterpenoids, tocopherols, linoleic acid, vitexin, carotenoid, orientin, isoorientin, gallic acid, rutin, quercetin, ascorbic acid | [466–474] |
| 69. Persea americana Mill. | Avocado | Fruit, leaves, seeds, bark | Cardiovascular diseases, diabetes | Blood glucose↓, metabolic state ↑, activation of Akt/Pkb, glucose uptake↑, β-cell regeneration↑, HDL-c↑, LDL↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 150-300 mg /kg/day |
28 days | Flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, tannins, carbohydrates, glycosides | [475–479] |
| 70. Petroselinum crispum | Parsley | Leaves, seeds, roots | Otitis, urinary tract infection, dysmenorrhea, hypertension, diabetes, dermatitis, gastrointestinal disorders | Blood glucose↓, NEG↓, lipid peroxidation↓, body weight↓, GSH↓, insulin sensitivity↑, gluconeogenesis↓ | STZ-induced Swiss albino mice | 200 mg/kg/day | 42 days | Courmarins, phthalides, phenyl propanoids, tocopherols, apigenin, myristicin, apiol | [480–483] |
| 71. Phaseolus vulgaris L. | Kidney bean | Seeds | Wound healing, pharyngitis, fever, unpleasant body odor, obesity, diabetes, vaginal infection | Blood glucose↓, insulin sensitivity↑, TC↓, TG↓, gluconeogenesis↓, α-glucosidase activity↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 150mg/kg/day | 40 days | Protocatechuic acid, p-coumaric acid, procyanidin, myricetin, naringenin, gallic acid, quercetin, catechin, kaempferol, ferulic acid | [484–487] |
| 72. Phoenix dactylifera L. | Date | Fruit, leaves | Fever, inflammation, nervous disorders, loss of consciousness, dementia | Blood glucose↓, serum insulin↑, MDA↓, TNF-α↓, CRP↓ | STZ-induced diabetic rats |
200 mg/kg/ day | 30 days | Ellagic acid, gallic acid, p-coumaric acid, apigenin, naringin, gallic acid, catechin, ferulic acid, sinapic acid, epicatechin, vanillic acid, coumarin, quercetin, rutin, myricetin, luteolin, kaempferol, isorhamnetin, rhamnetin, β-sitosterol, isorhamnetin, procyanidin, protocatechuic acid | [488–491,646] |
| 73.Phyllanthus emblica L. | Amla | Fruit, leaves, bark, roots | Cold, fever, cough, hyperacidity, peptic ulcer, erysipelas, jaundice, diarrhea, dysentery, leprosy, hemorrhages, hematogenesis, anemia, asthma, bronchitis, colic, dyspepsia, hepatopathy, leucorrhea, menorrhagia | Blood glucose↓, TG↓, TC↓, LDL↓, HDL↑, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities↓, AMPK↑ | STZ-induced Wistar rats |
25-75 mg /kg/day | 28 days | Phyllembelic acid, gallic acid, ellagic acid, pectin, quercetin, linolenic, linoleic, oleic, stearic, palmitic, myristic acid, tannins, chebulic, chebulagic, chebulinic acids, alkaloids phyllantidine, phyllantine, lupeol, leucodelphinidin. corilagin, digallic acid, kaempferol and zeatin | [492–495,647] |
| 74. Piper betle L. | Betel leaf | Leaves | Wound healing, bronchitis, diabetes, cough, indigestion in children, headaches, arthritis, | FBG↓, HbA1c↓, IR↓, insulin production↑, glucokinase activity↑ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 75-150mg /kg/day |
30 days | Estragole, linalool, safrol, terpenes, phenols, steroids, saponins, tannins | [496–499] |
| 75. Pisum sativum L. | Pea | Seeds | Blood purifying, wrinkled skin, acne, phlegm, intestinal inflammation, constipation, diabetes | Blood glucose↓, HbA1c↓, NO↓, plasma insulin ↑, glucose homeostasis↑, glucose tolerance↑, polyphagia↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, α-glucosidase activity↓, body weight↓ | STZ-induced ICR mice | 100-400mg /kg/day |
42 days | Flavonoid, quercetin, ellagic acid, coumaric acid, β-sitosterol, β-amyrin, catechin, myricetin, vanillic acid, kaempferol | [500–503] |
| 76. Prunus armeniaca L. | Apricot | Fruit, leaves | Cancer, atherosclerosis, angina, retinopathy, nephropathy, hypertension, diabetes | Blood glucose↓, FBG↓, α-glucosidase activity↓, HbA1c↓, insulin secretion↑, oxidative stress ↓ | Alloxan- induced Swiss mice |
2-8 mg/kg/day | 56 days | Chlorogenic, gallic, ferulic, salicylic, coumaric acids, glycosides, rutin, quercetin, vanillin, catechin, epicatechin, neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, lutein | [504–506] |
| 77. Prunus domestica | Plum | Fruit | Anemia, neurasthenia, leukorrhea, Alzheimer’s disease, irregular menstruation, anxiety, diabetes, constipation | Blood glucose↓, TG↓, TC↓, LDL↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities↓, HMGCoA reductase↓, oxidative stress ↓ | STZ-induced Swiss Albino mice | 50 mg/kg/day | 20 days | Chlorogenic acid, neochlorogenic acid, tocopherols, β-carotenes, quercetin, myricetin, kaempferol, citric acid, malic acid | [507–514] |
| 78. Prunus dulcis | Almonds | Nut | CNS disorders, respiratory disorders, diabetes, urinary tract infections | FBG↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL↓, stomach emptying, time↓, insulin production↑ | T2DM patients (n=58 years) | 60000 mg/kg/ day | 84 days | Oleic acid, linoleic acid, palmitic acid, arachidic acid, anthocyanin, kaempferol, quercetin, isorhamnetin, galactosidase, chlorogenic acid | [515,516] |
| 79. Prunus persica L. | Peach | Fruit, peel, leaves | Enhancing blood circulation, blood clotting, constipation, diabetes | Body weight↓, lipid metabolism↑, lipogenesis↓, fatty acid oxidation↑, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities↓, β-cell regeneration↑ | HFF C57BL/6 male mice | 200-600 mg/kg/day |
56 days | Procyanidin, epicatechin, catechin, prunin, phloridzin, naringenin, neochlorogenic acid, caffeoylquinic acid, chlorogenic acid, quercetin, aucubin, kaempferol, prunitrin | [517–520,648] |
| 80. Punica granatum | Pome-granate | Fruit, peel, seeds | Dysentery, diarrhea, piles, bronchitis, biliousness, diabetes | Blood glucose↓, TG↓, TC↓, HDL↑, LDL↓, intestinal glucose absorption↓, GLUT-4 translocation ↑ | Alloxan- induced Albino eats | 500 mg/kg/ day | 14 days | Ellagic acid, gallotannins, anthocyanins, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin glycosides, punicalin, punicafolin, luteolin, apigenin, anthocyanins, linoleic, oleic, palmitic, stearic, linolenic, arachidic and palmitoleic acids | [521–524] |
| 81. Psidium guajava L. | Guava | Fruit, leaves | Dysentery, diabetes and diarrhea | PPBG↓, FBG↓, HbA1c↓, IR↓, TG↓, TC↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities↓, malondialdehyde↓ | Prediabetes and mild T2DM patients | 190 mg/kg 3 times a day |
84 days | Quercetin, avicularin, apigenin, guaijaverin, kaempferol, hyperin, myricetin, gallic acid, catechin, epicatechin, chlorogenic acid, epigallocatechin gallate, caffeic acid | [525–533] |
| 82. Raphanus sativus L. | Radish | Fruit, leaves | Gallbladder stone, jaundice, flatulence, indigestion, various gastric ailments, piles, constipation, indigestion, colic, dyspepsia, liver enlargement, diabetes | IR↓, intestinal glucose absorption↓, glucose uptake↑, glycoalbumin↓, fructosamine ↓ | STZ-induced T2DM rats | 2.2% of the diet/ day | 21 days | Myricetin, catechin, epicatechin, quercetin, vanillic acid, sinapic acid, p-coumaric acid, β-carotene, camphene, piperitone, carvacrol, linoleic acid, oleic acid, anthocyanin | [534–537] |
| 83. Rosmarinus officinalis L. | Rosemary | Leaves | Mycosis, alopecia, ultraviolet damage, skin cancer, inflammatory diseases, diabetes | FBG↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, GLUT-4 translocation↑, HDL↑, Irs1↓, IR↓, gluconeogenesis↓, glucose uptake↑ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 4000 mg/kg/day | 28 days | Flavonoids, carnosol, carnosoic, rosmarinic, ursolic, oleanolic, micromeric acids | [538–544] |
| 84. Rubus fruticosus | Blackberry | Fruit, leaves | Mouthwash, gum inflammations, mouth ulcers, sore throat, respiratory disorders, anemia, diarrhea, dysentery, cystitis, diabetes, hemorrhoids | Blood glucose↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities↓, oxidative stress↓ | STZ-induced Sprague–Dawley rats | 300 mg/L/day | 35 days | Anthocyanins, malvidin, pelargonidin, cyanidins, kaempferol, quercetin, myricetin, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, rutin, coumarins, gallic acid | [545–548] |
| 85. Salvia hispanica L. | Chia seeds | Seeds | Indigestion, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus | Blood glucose↓, HbA1c↓, FBG↓, macrovascular complications↓, body weight↓, inflammatory cytokines↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓ | T2DM patients (n=42) | 40000 mg/kg/day | 84 days | Myricetin, quercetin, chlorogenic acid, kaempferol and caffeic acid | [549–553] |
| 86. Sesamum indicum | White sesame seeds | Seeds | Wound healing, amenorrhea, ulcer, asthma, hemorrhoids, inflammations, diabetes | Blood glucose↓, HbA1c↓, FBG↓, TC↓, PPBG↓, oxidative stress↓, IR↓ nephropathy↓ |
T2DM patients (18-60 years) | 30 mg/kg/day | 90 days | Sesamin, sesaminol, gamma tocopherol, cephalin, flavonoids, phenolic acids, alkaloids, tannins, saponins, steroids, terpenoids | [554–559] |
| 87. Solanum lycopersicum L. | Tomato | Fruit | Dermatitis, cancer, hypertension, hyperglycemia | Blood glucose↓ IR↓, SOD↑, GSH↑, MDA↓, inflammation↓ | STZ-induced T2DM rats | 30-270mg /kg/day |
56 days | Lycopene, carotenoids, homovanillic acid, chlorogenic acid, tomatine, kaempferol, quercetin, naringenin, p-coumaric acid, caffeic acid | [560–566,649] |
| 88. Solanum melongena | Eggplant | Fruit, leaves | Arthritis, diabetes, dyslipidemia, bronchitis, asthma | Blood glucose↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, VLDL↓, HDL↑, oxidative stress↓, MDA↓, α-glucosidase activity↓, GLUT-4 translocation↑, glucose uptake↑, gluconeogenesis↓ | Alloxan-induced diabetic rats | 100-300 mg/kg/day |
20 days | Solasodine, thiamin, niacin, chlorogenic acid, saponins, delphinidin, anthocyanin, phenols, | [567–571] |
| 89. Spinacia oleracea | Spinach | Leaves | Remedy for bloody stools, diarrhea, stomachaches, obesity, diabetes | Retinopathy↓, MDA↓, inflammation↓, oxidative stress↓, AGEs formation↓, lipid peroxidation↓, IL-6↓, TNF-α↓, IR↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 400mg/kg/day | 84 days | β-carotenoids, lutein, carotenoids, zeaxanthin, vitamins, minerals | [572–577] |
| 90. Syzygium aromaticum | Clove | Flower buds | Flatulence, diarrhea, diabetes, indigestion | Blood glucose↓, PPAR-γ binding↑, aldose reductase↓ | Diabetic KK-Ay mice |
657mg/kg/day | 21 days | Eugenol acetate, eugenol, gallic acid, terpenes, tannins, phenolics, steroids, flavonoids, glycosides and saponins | [578–581,650] |
| 91. Syzygium cumini L. | Java plum | Fruit, seeds, bark | Asthma, bronchitis, sore throat, biliousness, dysentery, diabetes, ulcers | Blood glucose↓, TG↓, TC↓, LDL↓, HDL↑, HMGCoA reductase↓, β cells function ↑, urine glucose↓ | Alloxan- induced diabetic Albino rabbits | 100 mg/kg/day | 15 days | Anthocyanins, glucoside, isoquercetin, ellagic acid, kaemferol, myricetin | [582–584] |
| 92. Tamarindus indica L. | Tamarind | Fruit, leaves, seeds | Inflammation, stomach pain, throat pain, rheumatism, wound, diarrhea, dysentery, fever, malaria, respiratory tract infection, constipation, cell cytotoxicity, gonorrhea, eye diseases | Blood glucose↓, body weight ↓, glucose tolerance ↑, β-cell function↑, glucose tolerance↑, β-cells regeneration↑ | Alloxan- induced Wistar albino rats | 100-250 mg/kg/day |
14 days | Apigenin, anthocyanin, procyanidin, catechin, epicatechin, taxifolin, eriodyctiol, naringenin | [585–589] |
| 93. Theobroma cacao | Cocoa | Fruit, husk, seeds | Measles, malaria, toothache as well as diabetes though improving insulin secretion, GLUT4 translocation, glucose uptake | Blood glucose↓, insulin secretion ↑, ATP↑, GSH↑, Nrf2↑ α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity ↓ |
STZ-induced Sprague Dawley rats | 2.5 mg/mL | 4 hours |
Flavonoids, procyanidins, catechin, epicatechin, theobromine, caffeine | [590–595] |
| 94. Trichosanthes cucumerina L. | Snake gourd | Fruit, leaves, seeds, roots | Bronchitis, headache, cathartic, anthelmintic, stomach disorders, indigestion, bilious fevers, boils, sores, eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis, ulcers, diabetes | FBG↓, IR↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, insulin secretion↑, intestinal glucose absorption ↓ | STZ-induced Albino rats | 750mg/kg/day | 28 days | Gallic acid, neochlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, trans-ferulic acid, catechin hydrate, epicatechin, procyanidin A2, procyanidin B2, rutin, kaempferol, quercetin, ursolic acid, oleanolic acid | [596–598] |
| 95. Trigonella foenum-graecum | Fenugreek seeds | Seeds | Ulcer, sinusitis, hay fever, diarrhea, diabetes, kidney diseases | Blood glucose↓, PPBG↓, FBG↓, glucose uptake↑, glucose tolerance↑, insulin sensitivity↑, intestinal glucose absorption↓ | STZ-induced Long evans rats |
500 mg/kg/ Day |
28 days | Steroids, alkaloids, flavonoids, polyphenols, saponins | [599–602] |
| 97. Vaccinium corymbosum | Blueberry | Fruit, leaves | Cold, inflammation, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, ocular dysfunction | Blood glucose↓, IR↓, insulin secretion↑, retinopathy, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 870 mg leaves/kg/ day and 430 mg leaves +1300 mg fresh fruits /kg/day |
56 days | Anthocyanins, pectin, anthocyanidins, delphinidin, peonidin, malvidin, cyanidin, chlorogenic acid, malic acid, protocatechuic acid, petunidin | [603–605,651] |
| 49. Vigna radiata | Mung bean | Seeds | Heat stroke, gastrointestinal disorders, dermatitis, hyperglycemia, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, melanogenesis | Blood glucose↓, TG↓, LDL↓, NO↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓ | Alloxan-induced Balb/c mice | 200-100mg/kg/day | 10 days | Flavonoids, quercetin, myricetin, kaempferol, catechin, vitexin, isovitexin, coumaric acid luteolin, caffeic and gallic acid | [606–612,652] |
| 98. Vitis vinifera L. | Grapes | Fruit, seeds, peel | Diarrhea, hepatitis, stomachaches, varicose veins, hemorrhoids, atherosclerosis, diabetes, high blood pressure, heavy menstrual bleeding, uterine bleeding, constipation | Blood glucose↓, oxidative stress↓, β-cell regeneration↑, intestinal glucose absorption ↓ | STZ-induced Wistar rats | 250-500 mg/kg/day |
15 days | Triterpenoid acids, oleanolic, betulinic acids, stilbenoid, gallic acid, catechin, epicatechin, gallocatechin, p-coumaric, caffeic and ferulic acids | [613–615] |
| 99. Zea mays | Corn | Grains, husk | Malaria, bladder stone, heart diseases, diabetes | body weight↓, FBG↓, IR↓, TC↓, TG↓, LDL-C↓, HDL↑, MDA↓, SOD↑, oxidative stress↓, α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity↓ |
STZ-induced HFF rats | 300-1200 mg/kg/day |
28 days | Flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, phenols, tannins, phytosterols | [616–621] |
| 100. Zingiber officinale | Ginger | Fruit | Muscular aches, pains, sore throats, cramps, constipation, indigestion, vomiting, arthritis, rheumatism, diabetes, sprains, hypertension, dementia, fever, infectious diseases, helminthiasis | Blood glucose↓, TC↓, TG, β-cell function↑, GLUT-4 activity↑, β-cell function↑, PPAR-γ↑, glucose uptake↑, creatinine↓, body weight↓, urea↓ | STZ-induced Sprague Dawley rats | 500 mg/kg/day | 49 days | β-phellandrene, camphene, cineole, geraniol, curcumene, citral, terpineol, borneol, α-zingiberene, zingiberol, gingerols, shogaols 3-dihydroshogaols, paradols, dihydroparadols, gingerdiols, diarylheptanoids, isogingerol, isoshogaol gingerdiones | [622–624,653] |
| Dietary plants | Plant parts | Phytochemicals | Pharmacological actions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Abelmoschus esculentus L. | Fruit, roots | Flavonoids, pectin, saponins, alkaloids | Lowers blood glucose and lipids, reduces insulin resistance, and enhances GLUT-4 translocation | [143–145] |
| 2. Actinidia chinensis | Fruit | Triterpenoids, flavonoids, phenolic acids | Lowers serum glucose, inflammatory cytokines, blood lipids | [146–149] |
| 3. Aegle marmelos L. | Fruit | Oleic acid, p-cymene, linolenic acid, retinoic acid, myristic acid | Enhances glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, suppresses α-amylase and α-glucosidase, delays intestinal glucose absorption | [150–152,654] |
| 4. Agaricus bisporus | Rhizome | Catechin, lectin, β-glucans, Gallic acid, p-coumaric acid, Ferulic acid, Chlorogenic acid | Regulates insulin and glucagon secretion, reduces body weight and serum glucose | [153–157] |
| 5.. Allium cepa | Fruit | Quercetin, lectin, steroids, catechol, isoflavones, humulone, apigenin, rutin, myricetin, kaempferol, catechin | Decreases α-glucosidase activity, oxidative stress, boosts insulin and adiponectin secretion, protects β-cells | [158–162] |
| 6. Allium sativum L. | Fruit | Allicin, β-resorcylic acid, gallic acid, rutin, protocatechuic acid, quercetin | Enhances insulin production, insulin secretion, glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and GLUT-4 expression | [163–168] |
| 7. Aloe barbadensis Mill. | Leaves | Flavonoids, proanthocyanidins, phenolic acids | Inhibits the glycation process, AGE formation and α-amylase, α-glucosidase enzyme activity | [169–175] |
| 8. Anacardium occidentale L. | Nut, leaves, bark | Kaempferol, anacardic acid, quercetin, linolenic acid, gallic acid, myricetin, catechin, protocatechuic acid, epigallocatechin, naringenin, epicatechin | Inhibits glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase 1 (GFAT1) and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) activity | [176–179,655] |
| 9. Ananas comosus L. | Fruit, peel, leaves | Sinapic acid, daucosterol, coumarin, tannins, flavonoids, benzofuran, stillbenoid | Improves insulin sensitivity and body weight, inhibits HMGCoA reductase activity | [180–186] |
| 10. Apium graveolens | Leaves, seeds, roots | Quercetin, thymoquinone, coumaric acid, gallic acid | Improves insulin sensitivity, GLUT-4 translocation, mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation | [187–192] |
| 11. Artocarpus heterophyllus | Fruit, leaves, bark, seeds, roots | Carotenoid, tannins, sterols, Chysin, isoquercetine | Decreases postprandial glucose, blood lipids, and inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase | [195–199] |
| 12. Asparagus officinalis | Stem | Asparagine, tyrosine, arginine, flavonoid, saponin, resin | Improves insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity, β-cell function and lowers blood glucose | [200–204] |
| 13. Avena sativa | Grains | β-glucan, oleic, linoleic acids, caffeic acids, coumaric acids, gallic acids, avenanthramides | Reduces glycosylated HbA1c, fasting blood glucose, postprandial glucose, insulin resistance | [205–209,656] |
| 14. Averrhoa carambola L. | Fruit | Anthocyanins, rutin, triterpenoids, quercetin, catechin, epicatechin | Elevates insulin secretion, glucose uptake in skeletal muscles and glycogen synthesis | [210–214] |
| 15. Azadirachta indica | Leaves, stem, bark, flower, roots, fruit | Nimbidin, nimbin, nimbidol, quercetin, nimbosterone, ferulic acid, limonene, oleuropeoside | Inhibits α-glucosidase and glucokinase, stimulates insulin secretion | [215–219] |
| 16. Beta vulgaris | Fruit | Lycopene, betalains, betagarin, betavulgarin, quercetin, kaempherol, betanins, carotenoid, coumarin | Inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase, gluconeogenesis, glycogenesis, and reduces serum glucose and lipids | [220–222] |
| 17. Brassica juncea | Seeds | Chlorogenic acid, cinnamic acid, kaempferol, flavonoid, coumaric acid, vanillic acid | Improves blood glucose, glucose tolerance, insulin secretion and inhibits intestinal glucose absorption | [223–226] |
| 18. Brassica oleracea var. capitata | Flower | Myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, apigenin, luteolin, Anthocyanidin | Increases insulin sensitivity, β-cell function and lowers blood glucose | [227–229] |
| 19. Brassica oleracea var. italica | Flower |
Chlorogenic acid, apigenin, kaempferol, luteolin, quercetin and myricetin | Reduces ROS formation and oxidative stress, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase, enhances insulin sensitivity and β-cell function | [230,231] |
| 21. Camellia sinensis | Leaves | Theanine, proanthocyanidins, caffeine, myricetin, kaempferol, quercetin, chlorogenic acid, Catechins, epicatechin | Attenuates insulin resistance and oxidative stress, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase, regulates inflammatory cytokines production | [232–235] |
| 20. Capsicum annuum L. | Seeds | Flavonoids, carotenoids, flavones, apigenin, quercetin and isoquercetin | Activates AMPK, increases GLUT4 translocation, glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and inhibits gluconeogenesis | [236–240] |
| 22. Carica papaya | Fruit, seeds, leaves | Saponins, alkaloids, kaempferol, flavonoids, phenols, terpenoids, steroids, quercetin, caffeic acid |
Decreases α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity, oxidative stress and plasma blood glucose | [241–244] |
| 23. Carissa carandas | Fruits | Lignans, flavonoids, Steroid, phenolic acid | Inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase, pro-inflammatory cytokine release, and lowers blood glucose | [245–249] |
| 24. Catharanthus roseus L. | Flowers, leaves | Gallic acid, rutin, p-coumaric acid, caffeic acid, quercetin, kaempferol, chlorogenic acid, ellagic acid, coumarin | Increases insulin secretion and β-cell function, decreases blood glucose and lipids | [250–254] |
| 25. Centella asiatica | Leaves | Centallase, quercetine, kaempferilm triterpene, ferulic acid | Decreases oxidative and inflammatory stress, body weight, serum glucose and lipids | [255–258] |
| 26. Chenopodium quinoa | Grains | Phytosterols, phytoecdysteroids, phenolics, tocophenols, betalains, tannins, glycine betaines |
Inhibits α-glucosidase, improves insulin sensitivity, lowers postprandial glycemia | [259–265] |
| 27. Cicer arietinum | Grains | Uridine, adenosine, tryptophan, 3-hydroxy-olean-ene, biochanin | Inhibits α-amylase, α-glucosidase and dipeptidyl-4 (DPP4) enzymes | [266–271] |
| 28. Cinnamomum verum | Bark | Cinnamaldehyde, cinnamates, cinnamic acid, eugenol, cinnamyl acetate, linalool | Enhances β-cell function, insulin secretion, GLUT-4 translocation and inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase | [272–275] |
| 29. Citrullus lanatus L. | Fruit, seeds | Lycopene, apigenin, kaempferol, rutin, p-coumaric acid, quercetin, ferulic acid | Inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity, enhances GLUT4 and GLUT2 translocation, and lowers blood glucose | [276–279] |
| 30. Citrus limon | Fruit, peel, leaves | Limocitrin, D-limonene, hesperidin, naringenin, flavonoid | Decreases blood glucose and body weight and enhances GLUT4 translocation | [280–287] |
| 31. Citrus maxima | Fruit, peel | Carotenoids, terpenoids, sterols, alkaloids, phenolics | Facilitates weight loss, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase, increases glucose tolerance and aids diabetic nephropathy | [288–290] |
| 32. Citrus reticulata | Fruit, peel | Hesperidin, quercetin, flavonoids, tannins, anthraquinones | Enhances mRNA expression, GLUT-4 translocation, insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance |
[291–295] |
| 33. Cocos nucifera | Fruit, husk, water | Tannins, resins, flavonoid, alkaloids | Inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity, regenerate β-cells and aids diabetic neuropathy | [297–304] |
| 34. Coffea Arabica L. | Leaves, fruit, beans | Coffeasterin, caffeine, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, vanillic acid, ferulic acid, sitosterol, stigmasterol, kaempherol, quercetin, sinapic acid | Regenerates β-cells, inhibits α-glucosidase and enhances insulin secretion | [305–307] |
| 35. Colocasia esculenta | Stem, leaves | Viexin, isovitexin, orientin, isoorientin, rosmarinic acid, luteolin | Lowers blood glucose levels, oxidative stress and inflammation, inhibits aldose reductase and aids diabetic neuropathy | [308–312,657] |
| 36. Coriandrum sativum | Seeds, leaves | Flavonoids, tocol, carotenoid, saponins | Inhibits TNF-α, IL-6, AGEs formation and aids diabetic neuropathy and nephropathy | [313–317] |
| 37. Crocus sativus L. | Flower stigma | Safranal, β carotenes, crocetin, crocin, picrocrocin, zeaxanthene | Inhibits α-glucosidase and α-amylase, lowers blood glucose, lipids and inflammatory cytokines | [318–323] |
| 38. Cuminum Cyminum L. | Seeds | Cumin aldehyde, safranal, linalool, carvone, carvacrol | Protects β-cells, improves insulin secretion, lowers blood glucose | [324–326] |
| 39. Cucumis sativus | Fruit, seeds | Cucurbitacin, cucumerin A and B, cucumegastigmanes I and II, orientin, apigenin | Reduces glucagon secretion, gluconeogenesis, glycolysis, enhances insulin sensitivity | [327–330] |
| 40. Cucurbita pepo L. | Fruit, seeds | β-carotene, lutein flavonoids, zeaxanthin, alkaloid | Lowers glucose in blood and urine, enhances glucose sensitivity, glutathione, reduces lipid levels | [331–335] |
| 41. Curcuma longa L. | Fruit | Turmerine, turmerone, Cucurmin, curcuminol, demethoxycurcumin, caffeic acid, sinapic acid | Induces glucose uptake, GLUT-2 activity and insulin production, increases insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity, decreases insulin resistance | [336–340,658] |
| 42. Daucus carota | Fruit | α and β-carotene, lutein, lycopene, anthocyanins, ascorbic acid | Regulates hyperglycemia, improves insulin resistance, delays intestinal glucose absorption, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase | [341–344] |
| 43. Ficus carica | Fruit, leaves, bark, roots | Eugenol, anthocyanins, phenolic acids, flavones, flavanols | Reduces postprandial glucose, plasma lipids, body weight, and β-cell apoptosis | [345–350] |
| 44. Fragaria ananassa | Fruit, leaves | Quercetin, kaempferol, p-coumaric acid, p-tyrosol, methyl gallate, rutin | Ameliorates peripheral insulin resistance, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity, increases insulin production | [351–355] |
| 45. Glycine max | Seeds, leaves | β-conglycinin, flavonoids, saponins, phytosterols | Decreases insulin resistance, enhances glucose uptake in skeletal muscles through AMPK activation | [356–360] |
| 46. Helianthus annuus | Flowers, seeds | Flavonoids, tocopherols, carotenoids, saponins, tannins, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid | Reduces body weight, BMI, oxidative stress, AGEs formation and fasting blood glucose | [361–364] |
| 47. Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Linn. | Flowers, leaves | Quercetin, cyanidin, ascorbic acid, genistic acid, lauric acid, thiamine, niacin | Stimulates β-cells, enhances insulin secretion and glycogen accumulation in the liver | [365–369] |
| 48. Hylocereus undatus | Fruit, seeds | Oleic acid, gallic acid, lycopene, p-coumaric acid, linoleic acid, β-carotene | Attenuates plasma glucose, endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, intestinal glucose absorption, and boosts insulin sensitivity | [370–372] |
| 49. Ipomoea batatas | Fruit | Anthraquinones, coumarins, flavonoids, saponins, tannins, quercetin, chlorogenic acid, terpenoids | Mitigates insulin secretion, serum glucose, enhances β-cell function and insulin production | [373–377] |
| 50. Juglans regia L. | Nut, leaves | Gallic acid, caffeoylquinic acid, coumaroylquinic, juglone, quercetin | Increases glucose uptake, inhibits α-glucosidase, α-amylase and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) activity | [378–381,659] |
| 51. Lactuca sativa | Leaves | Flavonoids, quercetin, flavonols, anthocyanins, lutein, β-carotene | Inhibits α-amylase, α-glucosidase and DPP-4, improves postprandial glucose and blood lipids | [382–386] |
| 52. Lagenaria siceraria | Fruit, leaves, seeds | cucurbitacin B, cucurbitacin D, cucurbitacin E, isoquercitrin, kaempferol, gallic acid | Improves glucose tolerance, insulin production, and inhibits intestinal glucose absorption | [387–390] |
| 53. Laurus nobilis | Leaves | Eugenol, kaempferol, syringic acid, quercetin, apigenin, luteolin | Enhances β-cell function, insulin sensitivity and inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase | [391–394] |
| 54. Litchi chinensis | Fruit, seeds | Sterols, triterpenoids, flavonoids, phenolics | Improves insulin resistance, serum triglyceride level, glucose tolerance and inhibits α-glucosidase activity | [395–397] |
| 55. Luffa acutangula | Fruit, seeds | Apigenin, luteolin, myristic acid, α-pinene, carotene, oleanolic acid, β-myrcene, linalool | Enhances insulin secretion, suppresses glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis | [398,399] |
| 56. Malus domestica Borkh | Fruit, peel | Quercetin, pectin, flavonols, flavanols, catechin epicatechin, cyanidin galactoside | Improves endothelial function, lipid homeostasis, insulin resistance, and lowers serum glucose | [400–409] |
| 57. Mangifera indica | Fruit, peel, bark, seeds | Mangiferin, rhamnetin, catechin, epicatechin, gallic acid | Increases insulin sensitivity, lowers postprandial glucose, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase | [410–415] |
| 58. Mentha spicata | Leaves | Limonene, carvone, linalool, piperitone | Suppresses α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity, oxidative stress, and decreases blood glucose and lipids | [416–418] |
| 59. Moringa oleifera Lam. | Fruit, leaves | Anthocyanins, sitogluside, tannin, anthraquinones, β-carotene | Inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase, lowers postprandial glucose and cholesterol, and improves lipid metabolism | [419–423,660] |
| 60. Momordica charantia | Fruit, leaves, seeds | Triterpene, proteid, steroids, flavonoids, ascorbic acid, saponins | Regenerates β-cells, increases glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and suppresses intestinal glucose absorption | [424–432] |
| 61. Morus alba L. | Fruit, leaves | Quercetin, isoquercetin, stillbenoids, flavonoids | Enhances insulin secretion, lowers blood glucose, blood lipids and promotes GLUT-4 translocation | [434–437] |
| 62. Murraya koenigii L. | Leaves | Murrayanol, mahanimbine, kaemferol, catechin, apgenin | Regenerates β-cells, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase, lowers blood glucose | [438–441] |
| 63. Myristica fragrans Houtt. | Fruit, seeds | Lignan, flavonoids, terpenes, coumarin | Inhibits TNF-α and IL-6 release, ameliorates blood glucose, β-cell function, inflammation and obesity | [442–445] |
| 64. Nigella sativa L. | Seeds | Thymoquinone, thymol, limonene, carvacrol, p-cymene, linoleic acid, oleic acid | Inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis, α-amylase and α-glucosidase, increases insulin sensitivity | [446–450] |
| 65. Ocimum sanctum L. | Leaves, seeds | Ursolic acid, eugenol, carvacrol, linalool, caryophyllene | Lowers serum glucose and albumin, increases insulin secretion and lipid metabolism, regenerates β cells | [451–454,661] |
| 66. Olea europaea L. | Fruit, leaves | Secoiridoid glycoside, oleuropein, oleanolic acid, flavonoid, cinnamic acid | Enhances glucose tolerance, reduces body weight, inhibits gluconeogenesis and lowers plasma glucose | [455–460] |
| 67. Origanum vulgare | Leaves | Rosmarinic acid, apigenin, luteolin | Increases glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, GLUT-2, decreases blood glucose, oxidative stress,inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase | [461–465] |
| 68. Passiflora edulis | Fruit, peel | Piceatannol, flavonoids, tocopherols, carotenoid, gallic acid, rutin | Improves serum glucose, insulin sensitivity, glucose tolerance, glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, and reduces lipid accumulation and body weight | [466–474] |
| 69. Persea americana Mill. | Fruit, leaves, seeds, bark | Myricetin, luteolin, gallic acid, ascorbic acid | Activates PI3K to facilitate insulin action, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase | [475–479] |
| 70. Petroselinum crispum | Leaves, seeds, roots | Coumarins, tocopherols, apigenin, myristicin | Regulates plasma glucose, body weight, glutathione levels, increases glucose uptake in skeletal muscles and inhibits gluconeogenesis | [480–483] |
| 71. Phaseolus vulgaris L. | Seeds | p-coumaric acid, myricetin, naringenin, gallic acid, quercetin, catechin, kaempferol, ferulic acid | Suppresses α-glucosidase activity, gluconeogenesis, delays the absorption of glucose, increases insulin sensitivity | [484–487] |
| 72. Phoenix dactylifera L. | Fruit, leaves | Flavonoids, oleic acid, linoleic acid, catechin, epicatechin, apigenin, naringenin, anthocyanin | Enhances β-cell function, insulin secretion, decreases blood glucose, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase | [488–491] |
| 73.Phyllanthus emblica L. | Fruit, leaves, bark, roots | Gallic acid, ellagic acid, pectin, quercetin, linoleic, oleic acid, myristic acid, | Inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase, activates AMPK and lowers blood glucose | [492–495] |
| 74. Piper betle L. | Leaves | Eugenol, selinene, hydroxychavicol, cadinene, caryophyllene | Elevates insulin production and glucose usage, activates glucokinase and lowers plasma glucose | [496–499] |
| 75. Pisum sativum L. | Seeds | Uridine, adenosine, tryptophan, 3-hydroxy-olean-ene, biochanin | Inhibits α-amylase, α-glucosidase and dipeptidyl-4 (DPP4) enzymes | [500–503] |
| 76. Prunus armeniaca L. | Fruit, leaves | Quercetin, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid, lutein, catechin, epicatechin | Stimulates insulin secretion, decreases oxidative stress, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase | [504–506] |
| 77. Prunus domestica | Fruit | Catechin, epicatechin, chlorogenic acid, kaempferol, quercetin | Inhibits HMGCoA reductase and α-amylase, lowers blood glucose, lipids, and oxidative stress | [507–514] |
| 78. Prunus dulcis | Nut | Oleic acid, linoleic acid, P-coumaric acid, anthocyanin, kaempferol, quercetin, chlorogenic acid | Increases insulin production and decreases stomach emptying time | [515,516] |
| 79. Prunus persica L. | Fruit, peel, leaves | Naringenin, ferulic acid, Chlorogenic acid, astragalin, carotenoid, anthocyanin, caffeic acid | Ameliorates insulin secretion, pancreatic β-cell regeneration and inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase | [517–520] |
| 80. Punica granatum | Fruit, peel, seeds | Punicalin, punicsfolin, apigenin, quercetin, ellagic acid, gallotannins, anthocyanins, luteolin, kaempferol, lycopene | Enhances insulin sensitivity, insulin production, GLUT-4 translocation, and lowers blood glucose | [521–524] |
| 81. Psidium guajava L. | Fruit, leaves | Quercetin, avicularin, guaijaverin, tannins, triterpenes | Decreases plasma glucose, gluconeogenesis, triglycerides, total cholesterol, and increases glucose uptake in skeletal muscle | [525–533,662] |
| 82. Raphanus sativus L. | Fruit, leaves | Myricetin, catechin, epicatechin, quercetin, vanillic acid, Oleic acid, p-coumaric acid, β-carotene | Inhibits intestinal glucose absorption, increases glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, and lowers blood glucose | [534–537] |
| 83. Rosmarinus officinalis L. | Leaves | Rosmarinic acid, ursolic acid, oleonic acid, carnosol | Enhances insulin sensitivity, GLUT-4 translocation, glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, and inhibits gluconeogenesis | [538–544] |
| 84. Rubus fruticosus | Fruit, leaves | anthocyanins, malvidins, pelargonidin, cyanidins, kaempferol, quercetin | Lowers blood glucose, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase | [545–548] |
| 85. Salvia hispanica L. | Seeds | Omega-3 fatty acid, myricetin, quercetin, chlorogenic acid, kaempferol, caffeic acid | Inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase, reduces body weight, inflammatory cytokines release, blood glucose and lipids | [549–553] |
| 86. Sesamum indicum | Seeds | Sesamin, sesaminol, tocopherol, flavonoids, saponins, steroids, terpenoids | Attenuates postprandial glucose and oxidative stress, improves insulin secretion, glutathione levels and lipid metabolism | [554–559] |
| 87. Solanum lycopersicum L. | Fruit | Lycopene, tomatine, kaempferol, quercetin, chlorogenic acid, β-carotene, naringenin | Attenuates plasma glucose, inflammation, insulin resistance via PI3K/Akt, FOXO1, PPAR-γ regulation | [560–566] |
| 88. Solanum melongena | Fruit, leaves | Thiamin, niacin, flavonoids, saponins, tannins, triterpenoids, anthraquinones | Enhances glucose uptake in skeletal muscles, GLUT-4 translocation, reduces gluconeogenesis, α-amylase, α-glucosidase enzymes and hyperlipidemia | [567–571] |
| 89. Spinacia oleracea | Leaves | β-carotenoids, lutein, carotenoids, zeaxanthin | Reduces serum C-reactive protein, TNF α, IL-6, excess AGEs production, and aids in retinopathy | [572–577] |
| 90. Syzygium aromaticum | Flower buds | Eugenol, gallic acid, ferulic acid, catechin, quercetin | Inhibits α-amylase, α-glucosidase and aldose reductase, lowers blood glucose and activates PPAR-γ | [578–581] |
| 91. Syzygium cumini L. | Fruit, seeds, bark | Anthocyanins, isoquercetin, ellagic acid, kaempferols, myricetin | Regenerates β-cells, improves insulin production and lowers glucose in plasma and urine | [582–584,663] |
| 92. Tamarindus indica L. | Fruit, leaves, seeds | Catechin, anthocyanin, epicatechin, apigenin | Lowers blood glucose, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase, elevates glucose tolerance and regenerate β-cells | [585–589] |
| 93. Theobroma cacao | Fruit, husk, seeds | Catechin, epicatechin, procyanidin, saponins, terpenoids | Protects β-cells, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase, elevates ATP, GSH, Nrf2 and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle | [590–595] |
| 94. Trichosanthes cucumerina L. | Fruit, leaves, seeds, roots | Carotenoids, gallic acid, neochlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, rutin, kaempferol, quercetin, ursolic, oleanolic acids | Simulates insulin secretion, enhances the peripheral use of glucose and prevents intestinal glucose absorption | [596–598] |
| 95. Trigonella foenum-graecum | Seeds | Steroids, alkaloids, flavonoids, polyphenols, saponins | Decreases blood glucose, enhances glucose uptake, insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance | [599–602] |
| 96. Vaccinium corymbosum | Fruit, leaves | Anthocyanins, pectin, anthocyanidins, delphinidin, peonidin, malvidins | Suppresses α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity and aids diabetic retinopathy | [603–605] |
| 97. Vigna radiata | Seeds | quercetin, myricetin, kaempferol, catechin, coumaric acid, luteolin, caffeic, gallic acid | Hinders gluconeogenesis, glycolysis, inhibits α-glucosidase and α-amylase | [606–612] |
| 98. Vitis vinifera L. | Fruit, seeds, peel | Catechin, epicatechin, epicatechin gallate, quercetin, myricetin, resveratrol | Regenerates β-cells, lowers blood glucose, inhibits intestinal glucose absorption and facilitates glycogen synthesis | [613–615,664] |
| 99. Zea mays | Grains, husk | Hirsutrin, flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, phenols, tannins, phytosterols | Ameliorates diabetic complications by suppressing aldose reductase and reducing galactitol formation, inhibits α-amylase and α-glucosidase activity | [616–621] |
| 100. Zingiber officinale | Fruit | Vanilloids, gingerol, paradol, shogaols, zingerone, gingerdiols, | Activates GLUT-4 and PPAR-γ, protects β-cells, facilitate glucose uptake in tissues | [622,623] |
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| AGEs | Advanced Glycation End Products |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| AMPK | AMP-activated Protein Kinase |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| DAGs | Diacylglycerols |
| DM | Diabetes Mellitus |
| DPP-4 | Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 |
| DPPH | 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| ETC | Electron Transport Chain |
| FOXO1 | Forkhead Box O1 |
| GIT | Gastrointestinal Tract |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 |
| GLUT-4 | Glucose Transporter type 4 |
| GLUT2 | Glucose Transporter 2 |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| HbA1c | Glycated Hemoglobin |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| IL-1 | Interleukin-1 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IRS-1 | Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 |
| IRS-2 | Insulin Receptor Substrate 2 |
| IR | Insulin Resistance |
| Keap1 | Kelch-Like ECH-Associated Protein 1 |
| LDL-c | Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| LPL | Lipoprotein Lipase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| PI3K/AKT | Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B Pathway |
| PKB/Akt | Protein Kinase B/Protein Kinase B |
| PKC | Protein Kinase C |
| PPAR-γ | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma |
| PPBG | Postprandial Blood Glucose |
| PPAR-γ | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-gamma |
| PTP1B | Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| SUR | Sulfonylurea Receptors |
| TC | Total Cholesterol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| UCP-1 | Uncoupling Protein 1 |
| VLDL | Very Low-Density Lipoprotein |
References
- Maggio, C. A.; Pi-Sunyer, F. X. Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 32 (4), 805–viii. [CrossRef]
- Harreiter, J.; Roden, M. Diabetes Mellitus – Definition, Klassifikation, Diagnose, Screening und Prävention (Update 2019) [Diabetes Mellitus-Definition, Classification, Diagnosis, Screening and Prevention (Update 2019)]. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2019, 131 (Suppl 1), 6–15. [CrossRef]
- Malone, J. I.; Hansen, B. C. Does Obesity Cause Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM)? Or Is It the Opposite? Pediatr. Diabetes 2019, 20 (1), 5–9. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C. C.; Philipson, L. H. Update on Diabetes Classification. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 99 (1), 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Acharjee, S.; Ghosh, B.; Al-Dhubiab, B.; Nair, A. Understanding Type 1 Diabetes: Etiology and Models. Can. J. Diabetes 2013, 37 (4), 269–276. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M. Type 2 Diabetes. Lancet 2017, 389 (10085), 2239–2251. [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhao, C. Exercise and Type 1 Diabetes. In Physical Exercise For Human Health; 2020; pp 107–121. [CrossRef]
- Vijan, S. Type 2 Diabetes. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162 (5), ITC1–ITC16. [CrossRef]
- IDF Diabetes Atlas Ninth Edition 2019. https://www.idf.org/e-library/epidemiology-research/diabetes-atlas/159-idf-diabetes-atlas-ninth-edition-2019.html (accessed 28th July, 2022).
- Henning, R. Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease. Future Cardiol. 2018, 14 (6), 491–509. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Zhang, W. Risk Factors Contributing to Type 2 Diabetes and Recent Advances in the Treatment and Prevention. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11 (11), 1185–1200. [CrossRef]
- Whiting, D. R.; Guariguata, L.; Weil, C.; Shaw, J. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global Estimates of the Prevalence of Diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 2011, 94 (3), 311–321. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Das, S. Dynamics of Diabetes and Obesity: An Alarming Situation in the Developing Countries in Asia. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16 (15), 1258–1268. [CrossRef]
- Wild, S.; Roglic, G.; Green, A.; Sicree, R.; King, H. Global Prevalence of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27 (5), 1047–1053. [CrossRef]
- Sarker, A. R.; Khanam, M. Socio-economic Inequalities in Diabetes and Prediabetes Among Bangladeshi Adults. Diabetol. Int. 2022, 13, 421–435. [CrossRef]
- Standl, E.; Khunti, K.; Hansen, T. B.; Schnell, O. The Global Epidemics of Diabetes in the 21st Century: Current Situation and Perspectives. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2019, 26 (2_suppl), 7–14. [CrossRef]
- Pulgaron, E.; Delamater, A. Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes in Children: Epidemiology and Treatment. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14 (8). [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R. A.; Ferrannini, E.; Zimmet, P., et al. International Textbook of Diabetes Mellitus, 2 Volume Set, 4th ed.; WileyBlackwell: Hoboken, NJ, 2015.
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Peng, J. Natural Products for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Pharmacology and Mechanisms. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 130, 451–465. [CrossRef]
- Bluestone, J.; Herold, K.; Eisenbarth, G. Genetics, Pathogenesis and Clinical Interventions in Type 1 Diabetes. Nature 2010, 464 (7293), 1293–1300. [CrossRef]
- Bolli, G. B. Insulin treatment in type 1 diabetes. Endocrine Practice 2006, 12, Suppl 1, 105-109. [CrossRef]
- Marín-Peñalver, J. J.; Martín-Timón, I.; Sevillano-Collantes, C.; Del Cañizo-Gómez, F. J. Update on the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. World Journal of Diabetes 2016, 7(17), 354-395. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, A.; Duvoor, C.; Reddy Dendi, V. S.; Kraleti, S.; Chada, A.; Ravilla, R.; Marco, A.; Shekhawat, N. S.; Montales, M. T.; Kuriakose, K.; Sasapu, A.; Beebe, A.; Patil, N.; Musham, C. K.; Lohani, G. P.; Mirza, W. Clinical Review of Antidiabetic Drugs: Implications for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2017, 8, 6. [CrossRef]
- Dey, L.; Attele, A. S.; Yuan, C. S. Alternative therapies for type 2 diabetes. Alternative Medicine Review 2002, 7(1), 45-58.
- Clark, T. A.; Deniset, J. F.; Heyliger, C. E.; Pierce, G. N. Alternative therapies for diabetes and its cardiac complications: role of vanadium. Heart Failure Reviews 2014, 19(1), 123-132. [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Ata, A.; V Anil Kumar, N.; Sharopov, F.; Ramírez-Alarcón, K.; Ruiz-Ortega, A.; Abdulmajid Ayatollahi, S.; Tsouh Fokou, P. V.; Kobarfard, F.; Amiruddin Zakaria, Z.; Iriti, M.; Taheri, Y.; Martorell, M.; Sureda, A.; Setzer, W. N.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Capasso, R.; Ostrander, E. A.; ... Sharifi-Rad, J. Antidiabetic Potential of Medicinal Plants and Their Active Components. Biomolecules 2019, 9(10), 551. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. R.; Leung, W. N.; Cheung, H. Y.; Chan, C. W. Osthole: A Review on Its Bioactivities, Pharmacological Properties, and Potential as Alternative Medicine. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2015, 919616. [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, R. A.; Guthrie, D. W. Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus. Crit. Care Nurs. Q. 2004, 27 (2), 113-125. [CrossRef]
- Skyler, J. S.; Bakris, G. L.; Bonifacio, E.; Darsow, T.; Eckel, R. H.; Groop, L.; Groop, P. H.; Handelsman, Y.; Insel, R. A.; Mathieu, C.; McElvaine, A. T.; Palmer, J. P.; Pugliese, A.; Schatz, D. A.; Sosenko, J. M.; Wilding, J. P.; Ratner, R. E. Differentiation of Diabetes by Pathophysiology, Natural History, and Prognosis. Diabetes 2017, 66 (2), 241-255. [CrossRef]
- Sosenko, J. M.; Skyler, J. S.; Beam, C. A.; Krischer, J. P.; Greenbaum, C. J.; Mahon, J.; Rafkin, L. E.; Matheson, D.; Herold, K. C.; Palmer, J. P.; Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet and Diabetes Prevention Trial–Type 1 Study Groups. Acceleration of the Loss of the First-Phase Insulin Response During the Progression to Type 1 Diabetes in Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 Participants. Diabetes 2013, 62 (12), 4179-4183. [CrossRef]
- Sosenko, J. M.; Palmer, J. P.; Rafkin, L. E.; Krischer, J. P.; Cuthbertson, D.; Greenbaum, C. J.; Eisenbarth, G.; Skyler, J. S.; Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 Study Group. Trends of Earlier and Later Responses of C-Peptide to Oral Glucose Challenges with Progression to Type 1 Diabetes in Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 Participants. Diabetes Care 2010, 33 (3), 620-625. [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Mari, A.; Nofrate, V.; Sosenko, J. M.; Skyler, J. S.; DPT-1 Study Group. Progression to Diabetes in Relatives of Type 1 Diabetic Patients: Mechanisms and Mode of Onset. Diabetes 2010, 59 (3), 679-685. [CrossRef]
- Cerf, M. Beta Cell Dysfunction and Insulin Resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ley, S.; Hu, F. Global Aetiology and Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14 (2), 88-98. [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.; Gannon, M. The Beta Cell in Type 2 Diabetes. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2019, 19 (9). [CrossRef]
- Halban, P. A.; Polonsky, K. S.; Bowden, D. W.; Hawkins, M. A.; Ling, C.; Mather, K. J.; Powers, A. C.; Rhodes, C. J.; Sussel, L.; Weir, G. C. β-cell Failure in Type 2 Diabetes: Postulated Mechanisms and Prospects for Prevention and Treatment. Diabetes Care 2014, 37 (6), 1751–1758. [CrossRef]
- Nowotny, K.; Jung, T.; Höhn, A.; Weber, D.; Grune, T. Advanced Glycation End Products and Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomolecules 2015, 5 (1), 194–222. [CrossRef]
- Singh, V. P.; Bali, A.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A. S. Advanced Glycation End Products and Diabetic Complications. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 18 (1), 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, G. R.; Kemp, B. E. AMPK in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89 (3), 1025–1078. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. W.; Brancati, F. L.; Yeh, H. C. Trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Asians versus whites: results from the United States National Health Interview Survey, 1997-2008. Diabetes Care 2011, 34(2), 353-357. [CrossRef]
- Polak, K.; Czyzyk, A.; Simoncini, T.; Meczekalski, B. New Markers of Insulin Resistance in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2016, 40 (1), 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Handschin, C.; Spiegelman, B. The Role of Exercise and PGC1α in Inflammation and Chronic Disease. Nature 2008, 454 (7203), 463-469. [CrossRef]
- Hee Park, K.; Zaichenko, L.; Brinkoetter, M.; Thakkar, B.; Sahin-Efe, A.; Joung, K.; et al. Circulating Irisin in Relation to Insulin Resistance and the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98 (12), 4899-4907. [CrossRef]
- El-Lebedy, D.; Ibrahim, A.; Ashmawy, I. Novel Adipokines Vaspin and Irisin as Risk Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12 (5), 643-648. [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S. V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375 (24), 2369–2379. [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.; Delgado, V.; Borlaug, B. A.; Bax, J. J. Diabesity: the combined burden of obesity and diabetes on heart disease and the role of imaging. Nature Reviews Cardiology 2021, 18(4), 291-304. [CrossRef]
- Boden, G.; Homko, C.; Barrero, C. A.; Stein, T. P.; Chen, X.; Cheung, P.; Fecchio, C.; Koller, S.; Merali, S. Excessive caloric intake acutely causes oxidative stress, GLUT4 carbonylation, and insulin resistance in healthy men. Science Translational Medicine 2015, 7(304), 304re7. [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A. M.; Pennings, N. Insulin Resistance. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing, 2021.
- Flier, J. S.; Kahn, C. R.; Roth, J. Receptors, antireceptor antibodies and mechanisms of insulin resistance. The New England Journal of Medicine 1979, 300(8), 413-419. [CrossRef]
- Duncan, J. A.; Shah, S. C.; Shulman, D. I.; Siegel, R. L.; Kappy, M. S.; Malone, J. I. Type b insulin resistance in a 15-year-old white youth. The Journal of Pediatrics 1983, 103(3), 421-424. [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity. Frontiers Of Medicine 2013, 7(1), 14-24. [CrossRef]
- Ye, J. Role of Insulin in the Pathogenesis of Free Fatty Acid-Induced Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle. Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders-Drug Targets 2007, 7(1), 65-74. [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.; Donald, C.; Jetha, A.; Covey, S.; Kieffer, T. Hyperinsulinemia Precedes Insulin Resistance in Mice Lacking Pancreatic β-Cell Leptin Signaling. Endocrinology 2010, 151(9), 4178-4186. [CrossRef]
- Minokoshi, Y.; Alquier, T.; Furukawa, N.; Kim, Y. B.; Lee, A.; Xue, B.; Mu, J.; Foufelle, F.; Ferré, P.; Birnbaum, M. J.; Stuck, B. J.; Kahn, B. B. AMP-Kinase Regulates Food Intake by Responding to Hormonal and Nutrient Signals in the Hypothalamus. Nature 2004, 428 (6982), 569–574. [CrossRef]
- Esser, N.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J.; Scheen, A.; Paquot, N. Inflammation as a Link between Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 105 (2), 141-150. [CrossRef]
- Valera Mora, M.; Scarfone, A.; Calvani, M.; Greco, A.; Mingrone, G. Insulin Clearance in Obesity. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2003, 22 (6), 487-493. [CrossRef]
- Michael, M.; Kulkarni, R.; Postic, C.; Previs, S.; Shulman, G.; Magnuson, M.; Kahn, C. Loss of Insulin Signaling in Hepatocytes Leads to Severe Insulin Resistance and Progressive Hepatic Dysfunction. Mol. Cell 2000, 6 (1), 87-97. [CrossRef]
- Farris, W.; Mansourian, S.; Leissring, M.; Eckman, E.; Bertram, L.; Eckman, C. et al. Partial Loss-of-Function Mutations in Insulin-Degrading Enzyme that Induce Diabetes also Impair Degradation of Amyloid β-Protein. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164 (4), 1425-1434. [CrossRef]
- Small, L.; Brandon, A.; Turner, N.; Cooney, G. Modeling insulin resistance in rodents by alterations in diet: what have high-fat and high-calorie diets revealed? American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 2018, 314(3), E251-E265. [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.; Pratipanawatr, T.; Berria, R.; Wang, E.; DeFronzo, R.; Sullards, M.; Mandarino, L. Ceramide Content Is Increased in Skeletal Muscle From Obese Insulin-Resistant Humans. Diabetes 2004, 53(1), 25-31. [CrossRef]
- Bosma, M.; Kersten, S.; Hesselink, M.; Schrauwen, P. Re-evaluating lipotoxic triggers in skeletal muscle: Relating intramyocellular lipid metabolism to insulin sensitivity. Progress In Lipid Research 2012, 51(1), 36-49. [CrossRef]
- Holland, W.; Brozinick, J.; Wang, L.; Hawkins, E.; Sargent, K.; Liu, Y.; et al. Inhibition of Ceramide Synthesis Ameliorates Glucocorticoid-, Saturated-Fat-, and Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance. Cell Metabolism 2007, 5(3), 167-179. [CrossRef]
- Itani, S.; Ruderman, N.; Schmieder, F.; Boden, G. Lipid-Induced Insulin Resistance in Human Muscle Is Associated With Changes in Diacylglycerol, Protein Kinase C, and IκB-α. Diabetes 2002, 51 (7), 2005-2011. [CrossRef]
- Erion, D.; Shulman, G. Diacylglycerol-mediated insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2010, 16 (4), 400-402. [CrossRef]
- El-Lebedy, D.; Ibrahim, A.; Ashmawy, I. Novel Adipokines Vaspin and Irisin as Risk Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12 (5), 643-648. [CrossRef]
- Bunney, P.; Zink, A.; Holm, A.; Billington, C.; Kotz, C. Orexin Activation Counteracts Decrease in Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT) Caused by High-Fat Diet. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 176, 139-148. [CrossRef]
- Boström, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.; et al. A PGC1-α-dependent Myokine that Drives Brown-Fat-Like Development of White Fat and Thermogenesis. Nature 2012. [CrossRef]
- Paradies, G.; Petrosillo, G.; Pistolese, M.; Ruggiero, F. M. Reactive Oxygen Species Affect Mitochondrial Electron Transport Complex I Activity Through Oxidative Cardiolipin Damage. Gene 2002, 286 (1), 135-141. [CrossRef]
- Hurrle, S.; Hsu, W. H. The Etiology of Oxidative Stress in Insulin Resistance. Biomed. J. 2017, 40 (5), 257-262. [CrossRef]
- Mailloux, R. J. An Update on Methods and Approaches for Interrogating Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Production. Redox Biol. 2021, 45, 102044. [CrossRef]
- Burkart, A. M.; Tan, K.; Warren, L.; Iovino, S.; Hughes, K. J.; Kahn, C. R.; Patti, M. E. Insulin Resistance in Human iPS Cells Reduces Mitochondrial Size and Function. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22788. [CrossRef]
- Ceriello, A.; Ihnat, M.; Thorpe, J. The “Metabolic Memory”: Is More Than Just Tight Glucose Control Necessary to Prevent Diabetic Complications? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94 (2), 410-415. [CrossRef]
- Blomen, V.; Boonstra, J. Stable Transmission of Reversible Modifications: Maintenance of Epigenetic Information Through the Cell Cycle. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 68 (1), 27-44. [CrossRef]
- Sircana, A.; Framarin, L.; Leone, N.; Berrutti, M.; Castellino, F.; Parente, R.; De Michieli, F.; Paschetta, E.; Musso, G. Altered Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetes: Just a Coincidence? Curr. Diab. Rep. 2018, 18 (10), 98. [CrossRef]
- Sergi, D.; Naumovski, N.; Heilbronn, L. K.; Abeywardena, M.; O'Callaghan, N.; Lionetti, L.; Luscombe-Marsh, N. Mitochondrial (Dys)function and Insulin Resistance: From Pathophysiological Molecular Mechanisms to the Impact of Diet. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 532. [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D. E.; Wing, R.; Buonocore, C.; Sturis, J.; Polonsky, K.; Fitzsimmons, M. Relative Effects of Calorie Restriction+ and Weight Loss in Noninsulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 77 (5), 1287-1293. [CrossRef]
- Gumbiner, B.; Polonsky, K. S.; Beltz, W. F.; Griver, K.; Wallace, P.; Brechtel, G.; Henry, R. R. Effects of Weight Loss and Reduced Hyperglycemia on the Kinetics of Insulin Secretion in Obese Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1990, 70 (6), 1594-1602. [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J. ’.; O'Brien, P. E. Health Outcomes of Severely Obese Type 2 Diabetic Subjects 1 Year After Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding. Diabetes Care 2002, 25 (2), 358-363. [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Refaat, M.; Mohammedi, K.; Jayyousi, A.; Al Suwaidi, J.; Abi Khalil, C. Macrovascular Complications in Patients with Diabetes and Prediabetes. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7839101. [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J. J.; Deedwania, P.; Acharya, T.; Aguilar, D.; Bhatt, D. L.; Chyun, D. A.; Di Palo, K. E.; Golden, S. H.; Sperling, L. S.; American Heart Association Diabetes Committee of the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health; Council on Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Hypertension. Comprehensive Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors for Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145 (9), e722–e759. [CrossRef]
- Haffner, S.; Lehto, S.; Rönnemaa, T.; Pyörälä, K.; Laakso, M. Mortality from Coronary Heart Disease in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes and in Nondiabetic Subjects with and without Prior Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339 (4), 229-234. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199807233390404.
- Beckman, J.; Creager, M.; Libby, P. Diabetes and Atherosclerosis. JAMA 2002, 287 (19), 2570. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/194930.
- Nesto, R. Correlation between Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes Mellitus: Current Concepts. Am. J. Med. 2004, 116 (5), 11-22. [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, N.; Stenvinkel, P.; Tonelli, M. Associations of Chronic Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, and Severe Obesity With Mortality, Myocardial Infarction, Cancer, and Chronic Pulmonary Disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2 (8), e1910456. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2749271.
- Kenchaiah, S.; Evans, J.; Levy, D.; Wilson, P.; Benjamin, E.; Larson, M.; et al. Obesity and the Risk of Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347 (5), 305-313. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa020245.
- Manson, J.; Colditz, G.; Stampfer, M.; Willett, W.; Rosner, B.; Monson, R.; et al. A Prospective Study of Obesity and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Women. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322 (13), 882-889. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199003293221303.
- Calle, E.; Thun, M.; Petrelli, J.; Rodriguez, C.; Heath, C. Body-Mass Index and Mortality in a Prospective Cohort of U.S. Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341 (15), 1097-1105.
- Unamuno, X.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V. Adipokine Dysregulation and Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Human Obesity. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 48 (9), e12997. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Shi, K.; Guo, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Xia, C.; et al. The Additive Effects of Obesity on Myocardial Microcirculation in Diabetic Individuals: A Cardiac Magnetic Resonance First-Pass Perfusion Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19 (1). [CrossRef]
- Dyck, P.; Kratz, K.; Karnes, J.; Litchy, W.; Klein, R.; Pach, J.; et al. The Prevalence by Staged Severity of Various Types of Diabetic Neuropathy, Retinopathy, and Nephropathy in a Population-Based Cohort: The Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology 1993, 43 (4), 817-817. https://n.neurology.org/content/43/4/817.
- Barrett, A. M.; Lucero, M. A.; Le, T.; Robinson, R. L.; Dworkin, R. H.; Chappell, A. S. Epidemiology, Public Health Burden, and Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain: A Review. Pain Med. 2007, 8 Suppl 2, S50–S62. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Azmi, S.; Yadav, R.; Ferdousi, M.; Kumar, M.; Cuthbertson, D. J.; Lim, J.; Malik, R. A.; Alam, U. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Pharmacotherapy. Clin. Ther. 2018, 40 (6), 828–849. [CrossRef]
- Kaku, M.; Vinik, A.; Simpson, D. M. Pathways in the Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Polyneuropathy. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2015, 15 (6), 609. [CrossRef]
- Bodman, M. A.; Varacallo, M. Peripheral Diabetic Neuropathy. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing 2022. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28723038/.
- Hébert, H. L.; Veluchamy, A.; Torrance, N.; Smith, B. H. Risk Factors for Neuropathic Pain in Diabetes Mellitus. Pain 2017, 158 (4), 560–568. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K. R.; Cross, J.; Farronay, O.; Ayyar, D. R.; Shebert, R. T.; Bradley, W. G. Demyelinating Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59 (5), 758–765. [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R. Not All Neuropathy in Diabetes Is of Diabetic Etiology: Differential Diagnosis of Diabetic Neuropathy. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2009, 9 (6), 423–431. [CrossRef]
- Pugazhenthi, S.; Qin, L.; Reddy, P. H. Common Neurodegenerative Pathways in Obesity, Diabetes, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863 (5), 1037–1045. [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Tonelli, M.; Bonventre, J.; Coresh, J.; Donner, J. A.; Fogo, A. B.; Fox, C. S.; Gansevoort, R. T.; Heerspink, H.; Jardine, M.; Kasiske, B.; Köttgen, A.; Kretzler, M.; Levey, A. S.; Luyckx, V. A.; Mehta, R.; Moe, O.; Obrador, G.; Pannu, N.; Parikh, C. R.; … ISN Global Kidney Health Summit Participants. Global Kidney Health 2017 and Beyond: A Roadmap for Closing Gaps in Care, Research, and Policy. Lancet 2017, 390 (10105), 1888–1917. [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.; Robinson, B.; Abbott, K. C.; Agodoa, L.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Balkrishnan, R.; Bhave, N.; Dietrich, X.; Ding, Z.; Eggers, P. W.; Gaipov, A.; Gillen, D.; Gipson, D.; Gu, H.; Guro, P.; Haggerty, D.; Han, Y.; He, K.; Herman, W.; Heung, M.; Shahinian, V. US Renal Data System 2018 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73(3 Suppl 1), A7–A8. [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R. Z.; Cox, E. J.; Neumiller, J. J.; Tuttle, K. R. Incretin Drugs in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Biological Mechanisms and Clinical Evidence. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17(4), 227–244. [CrossRef]
- Chatzikyrkou, C.; Menne, J.; Izzo, J.; Viberti, G.; Rabelink, T.; Ruilope, L. M.; Rump, C.; Mertens, P. R.; Haller, H. Predictors for the Development of Microalbuminuria and Interaction with Renal Function. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35(12), 2501–2509. [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.; Campos, E. J.; Martins, J.; Ambrósio, A. F.; Silva, R. Viewing the Choroid: Where We Stand, Challenges and Contradictions in Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Oedema. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95(5), 446–459. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lo, A. Diabetic Retinopathy: Pathophysiology and Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19(6), 1816. [CrossRef]
- Turner, R. C.; Cull, C. A.; Frighi, V.; Holman, R. R. Glycemic Control with Diet, Sulfonylurea, Metformin, or Insulin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Progressive Requirement for Multiple Therapies (UKPDS 49). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. JAMA 1999, 281(21), 2005–2012. [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, S. J.; Niki, I.; Kenna, S.; Weng, L.; Skeer, J.; Coles, B.; Ashcroft, F. M. The Beta-Cell Sulfonylurea Receptor. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1993, 334, 47–61. [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, F. M. Mechanisms of the Glycaemic Effects of Sulfonylureas. Horm. Metab. Res. 1996, 28(9), 456–463. [CrossRef]
- Proks, P.; Reimann, F.; Green, N.; Gribble, F.; Ashcroft, F. Sulfonylurea Stimulation of Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2002, 51(Suppl 3), S368–S376. [CrossRef]
- Sola, D.; Rossi, L.; Schianca, G. P.; Maffioli, P.; Bigliocca, M.; Mella, R.; Corlianò, F.; Fra, G. P.; Bartoli, E.; Derosa, G. Sulfonylureas and Their Use in Clinical Practice. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11(4), 840–848. [CrossRef]
- Douros, A.; Yin, H.; Yu, O.; Filion, K. B.; Azoulay, L.; Suissa, S. Pharmacologic Differences of Sulfonylureas and the Risk of Adverse Cardiovascular and Hypoglycemic Events. Diabetes Care 2017, 40(11), 1506–1513. [CrossRef]
- Melander, A.; Lebovitz, H. E.; Faber, O. K. Sulfonylureas. Why, Which, and How?. Diabetes Care 1990, 13(Suppl 3), 18–25. [CrossRef]
- Owen, M. R.; Doran, E.; Halestrap, A. P. Evidence that Metformin Exerts Its Anti-Diabetic Effects through Inhibition of Complex 1 of the Mitochondrial Respiratory Chain. Biochem. J. 2000, 348(Pt 3), 607–614. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10839993/.
- Milner, Z.; Akhondi, H. Repaglinide. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing, 2022. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32644731/.
- Thornberry, N. A.; Gallwitz, B. Mechanism of Action of Inhibitors of Dipeptidyl-Peptidase-4 (DPP-4). Best Practice & Research. Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2009, 23 (4), 479–486. [CrossRef]
- Hawley, S. A.; Ross, F. A.; Chevtzoff, C.; Green, K. A.; Evans, A.; Fogarty, S.; Towler, M. C.; Brown, L. J.; Ogunbayo, O. A.; Evans, A. M.; Hardie, D. G. Use of Cells Expressing Gamma Subunit Variants to Identify Diverse Mechanisms of AMPK Activation. Cell Metab. 2010, 11(6), 554–565. [CrossRef]
- Vincent, M. F.; Marangos, P. J.; Gruber, H. E.; Van den Berghe, G. Inhibition by AICA Riboside of Gluconeogenesis in Isolated Rat Hepatocytes. Diabetes 1991, 40(10), 1259–1266. [CrossRef]
- Miller, R. A.; Chu, Q.; Xie, J.; Foretz, M.; Viollet, B.; Birnbaum, M. J. Biguanides Suppress Hepatic Glucagon Signalling by Decreasing Production of Cyclic AMP. Nature 2013, 494(7436), 256–260. [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. S.; Hoyte, C. Review of Biguanide (Metformin) Toxicity. J. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 34(11-12), 863–876. [CrossRef]
- Inzucchi, S. E.; Lipska, K. J.; Mayo, H.; Bailey, C. J.; McGuire, D. K. Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. JAMA 2014, 312(24), 2668–2675. [CrossRef]
- Hauner, H. The Mode of Action of Thiazolidinediones. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews 2002, 18 (Suppl 2), S10–S15. [CrossRef]
- Eggleton, J. S.; Jialal, I. Thiazolidinediones. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing, 2022. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31869120/.
- Bischoff, H. The Mechanism of Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibition in the Management of Diabetes. Clinical and Investigative Medicine. Médecine Clinique et Experimentale 1995, 18 (4), 303–311. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8549017/.
- Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P. α-Glucosidase Inhibitors and Their Use in Clinical Practice. Archives of Medical Science : AMS 2012, 8 (5), 899–906. [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G. D.; Verma, S. Mechanisms of Cardiovascular Benefits of Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors: A State-of-the-Art Review. JACC. Basic to Translational Science 2020, 5 (6), 632–644. [CrossRef]
- Halimi, S.; Vergès, B. Adverse Effects and Safety of SGLT-2 Inhibitors. Diabetes & Metabolism 2014, 40 (6 Suppl 1), S28–S34. [CrossRef]
- Black, C.; Donnelly, P.; McIntyre, L.; Royle, P. L.; Shepherd, J. P.; Thomas, S. Meglitinide Analogues for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007, 2007 (2), CD004654. [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.; Bridgeman, M. B. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP-4) Inhibitors in the Management of Diabetes. P & T : A Peer-Reviewed Journal for Formulary Management 2010, 35 (9), 509–513.
- Thota, S.; Akbar, A. Insulin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing, 2021. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32809523/.
- Jensen, M.; De Meyts, P. Molecular Mechanisms of Differential Intracellular Signaling from the Insulin Receptor. Vitamins and Hormones 2009, 80, 51–75. [CrossRef]
- Hay, D. L.; Chen, S.; Lutz, T. A.; Parkes, D. G.; Roth, J. D. Amylin: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Clinical Potential. Pharmacological Reviews 2015, 67 (3), 564–600. [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, O.; Brock, B.; Rungby, J. Amylin Agonists: A Novel Approach in the Treatment of Diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53 (Suppl 3), S233–S238. [CrossRef]
- Adeghate, E.; Kalász, H. Amylin Analogues in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: Medicinal Chemistry and Structural Basis of Its Function. The Open Medicinal Chemistry Journal 2011, 5 (Suppl 2), 78–81. [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M. A.; Quast, D. R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J. J. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes - State-of-the-Art. Molecular Metabolism 2021, 46, 101102. [CrossRef]
- Skov-Jeppesen, K.; Hepp, N.; Oeke, J.; Hansen, M. S.; Jafari, A.; Svane, M. S.; Balenga, N.; Olson, J. A., Jr.; Frost, M.; Kassem, M.; Madsbad, S.; Beck Jensen, J. E.; Holst, J. J.; Rosenkilde, M. M.; Hartmann, B. The Antiresorptive Effect of GIP, But Not GLP-2, Is Preserved in Patients with Hypoparathyroidism - A Randomized Crossover Study. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research : The Official Journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research 2021, 36 (8), 1448–1458. [CrossRef]
- Spranger, J.; Gundert–Remy, U.; Stammschulte, T. GLP-1–Based Therapies: The Dilemma of Uncertainty. Gastroenterology 2011, 141 (1), 20–23. [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M. A.; D’Alessio, D. A. Tirzepatide, a Dual GIP/GLP-1 Receptor Co-Agonist for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes with Unmatched Effectiveness Regrading Glycaemic Control and Body Weight Reduction. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2022, 21 (1), 169. [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Sathyapalan, T.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. Natural Insulin Sensitizers for the Management of Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Possible Molecular Mechanisms. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 2021, 1328, 401–410. [CrossRef]
- Salimifar, M.; Fatehi-Hassanabad, Z.; Fatehi, M. A Review on Natural Products for Controlling Type 2 Diabetes with an Emphasis on Their Mechanisms of Actions. Current Diabetes Reviews 2013, 9 (5), 402–411. [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Lim, Y.; Kim, E. Therapeutic Phytogenic Compounds for Obesity and Diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2014, 15 (11), 21505–21537. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, P.; Samia, J.F.; Khan, J.T.; Rafi, M.R.; Rahman, M.S.; Rahman, A.B.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.A.; Seidel, V. Protective Effects of Medicinal Plant-Based Foods against Diabetes: A Review on Pharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Molecular Mechanisms. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3266. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, P.; Akther, S.; Khan, J.T.; Islam, S.S.; Masud, M.S.R.; Rahman, A.; Seidel, V.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.A. Hyperglycaemia-Linked Diabetic Foot Complications and Their Management Using Conventional and Alternative Therapies. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11777. [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Global Impacts of Western Diet and Its Effects on Metabolism and Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2749. [CrossRef]
- Elkhalifa, A.; Alshammari, E.; Adnan, M.; Alcantara, J. C.; Awadelkareem, A. M.; Eltoum, N. E.; Mehmood, K.; Panda, B. P.; Ashraf, S. A. Okra (Abelmoschus Esculentus) as a Potential Dietary Medicine with Nutraceutical Importance for Sustainable Health Applications. Molecules 2021, 26 (3), 696. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M. T. Phytochemical Information and Pharmacological Activities of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus): A Literature-Based Review. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33 (1), 72–80. [CrossRef]
- Elkhalifa, A.; Al-Shammari, E.; Adnan, M.; Alcantara, J. C.; Mehmood, K.; Eltoum, N. E.; Awadelkareem, A. M.; Khan, M. A.; Ashraf, S. A. Development and Characterization of Novel Biopolymer Derived from Abelmoschus esculentus L. Extract and Its Antidiabetic Potential. Molecules 2021, 26 (12), 3609. [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Hou, J.; Wang, L.; Zheng, M.; Fang, T.; Wang, X.; Xia, J. Actinidia chinensis Planch Root Extract Inhibits Cholesterol Metabolism in Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Upregulation of PCSK9. Oncotarget 2017, 8 (26), 42136–42148. [CrossRef]
- Suksomboon, N.; Poolsup, N.; Lin, W. Effect of Kiwifruit on Metabolic Health in Patients with Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 171–180. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Dai, B.; Tan, W. Actinidia chinensis Planch. Improves the Indices of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammation Status of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Activating Keap1 and Nrf2 via the Upregulation of MicroRNA-424. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 7038789. [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Fang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y.; Huang, L. Actinidia chinensis Planch.: A Review of Chemistry and Pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1236. [CrossRef]
- Venthodika, A.; Chhikara, N.; Mann, S.; Garg, M. K.; Sofi, S. A.; Panghal, A. Bioactive Compounds of Aegle marmelos L., Medicinal Values and Its Food Applications: A Critical Review. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35 (4), 1887–1907. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, P.; Afroz, N.; Jalil, S.; Azad, S. B.; Mustakim, M. G.; Anwar, S.; Haque, S. M.; Hossain, S. M.; Tony, R. R.; Hannan, J. M. Anti-Hyperglycemic Activity of Aegle marmelos (L.) Corr. Is Partly Mediated by Increased Insulin Secretion, α-Amylase Inhibition, and Retardation of Glucose Absorption. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 30 (1), 37–47. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Joshi, T.; Mathpal, S.; Chandra, S.; Tamta, S. In Silico Identification of Antidiabetic Target for Phytochemicals of Aegle marmelos and Mechanistic Insights by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 1–18. [CrossRef]
- Ismaya, W. T.; Tjandrawinata, R. R.; Rachmawati, H. Lectins from the Edible Mushroom Agaricus bisporus and Their Therapeutic Potentials. Molecules 2020, 25 (10), 2368. [CrossRef]
- Yasin, H.; Zahoor, M.; Yousaf, Z.; Aftab, A.; Saleh, N.; Riaz, N.; Shamsheer, B. Ethnopharmacological exploration of medicinal mushroom from Pakistan. Phytomedicine 2019, 54, 43–55. [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Burgos, N.; Barnard, A.; Evans, G.; Preece, J.; Graz, M.; Ruthes, A. C.; Jiménez-Quero, A.; Martínez-Abad, A.; Vilaplana, F.; Ngoc, L. P.; Brouwer, A.; van der Burg, B.; Del Carmen Garrigós, M.; Jiménez, A. Agaricus bisporus and its by-products as a source of valuable extracts and bioactive compounds. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 176–187. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S. C.; Jeong, Y. T.; Yang, B. K.; Islam, R.; Koyyalamudi, S. R.; Pang, G.; Cho, K. Y.; Song, C. H. White button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) lowers blood glucose and cholesterol levels in diabetic and hypercholesterolemic rats. Nutr. Res. (N. Y., N. Y.) 2010, 30 (1), 49–56. [CrossRef]
- Swanston-Flatt, S. K.; Day, C.; Flatt, P. R.; Bailey, C. J. Evaluation of the Antihyperglycemic Properties of Traditional Plant Treatments for Diabetes in Streptozotocin-Diabetic and db/db Mice. Frontiers in Diabetes Research, 1990, 6 (3), 286-293.
- Beigoli, S.; Behrouz, S.; Memarzia, A.; Ghasemi, S.; Boskabady, M.; Marefati, N., et al. Effects of Allium cepa and Its Constituents on Respiratory and Allergic Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Experimental and Clinical Evidence. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 1-22. [CrossRef]
- Akash, M. S.; Rehman, K.; Chen, S. Spice plant Allium cepa: dietary supplement for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrition (Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif.) 2014, 30 (10), 1128–1137. [CrossRef]
- Kianian, F.; Marefati, N.; Boskabady, M.; Ghasemi, S. Z.; Boskabady, M. H. Pharmacological Properties of Allium cepa, Preclinical and Clinical Evidences; A Review. Iranian J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 20 (2), 107–134. [CrossRef]
- Teshika, J. D.; Zakariyyah, A. M.; Zaynab, T.; Zengin, G.; Rengasamy, K. R.; Pandian, S. K.; Fawzi, M. M. Traditional and Modern Uses of Onion Bulb (Allium cepa L.): A Systematic Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59 (sup1), S39–S70. [CrossRef]
- Swanston-Flatt, S. K.; Flatt, P. R. Traditional Dietary Adjuncts for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1991, 50 (3), 641-651.
- Tesfaye, A. Revealing the Therapeutic Uses of Garlic (Allium sativum) and Its Potential for Drug Discovery. Sci. World J. 2021, 2021, 8817288. [CrossRef]
- Eidi, A.; Eidi, M.; Esmaeili, E. Antidiabetic Effect of Garlic (Allium sativum L.) in Normal and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Phytomedicine 2006, 13 (9-10), 624–629. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. T.; Hsu, T. W.; Chen, K. M.; Tan, Y. P.; Lii, C. K.; Sheen, L. Y. The Antidiabetic Effect of Garlic Oil is Associated with Ameliorated Oxidative Stress but Not Ameliorated Level of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines in Skeletal Muscle of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2012, 2 (2), 135–144. [CrossRef]
- Shang, A.; Cao, S. Y.; Xu, X. Y.; Gan, R. Y.; Tang, G. Y.; Corke, H.; Mavumengwana, V.; Li, H. B. Bioactive Compounds and Biological Functions of Garlic (Allium sativum L.). Foods 2019, 8 (7), 246. [CrossRef]
- El-Saber Batiha, G.; Magdy Beshbishy, A.; G Wasef, L.; Elewa, Y.; A Al-Sagan, A.; Abd El-Hack, M. E.; Taha, A. E.; M Abd-Elhakim, Y.; Prasad Devkota, H. Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Garlic (Allium sativum L.): A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12 (3), 872. [CrossRef]
- Swanston-Flatt, S. K.; Day, C.; Bailey, C. J.; Flatt, P. R. Traditional Plant Treatments for Diabetes. Studies in Normal and Streptozotocin Diabetic Mice. Diabetologia 1990, 33 (8), 462-464.
- Ríos, J.; Francini, F.; Schinella, G. Natural Products for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Planta Medica 2015, 81 (12/13), 975–994. [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.; Wachtel-Galor, S., Eds. Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects; 2nd ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, 2011.
- Medina-Cruz, D.; Vernet-Crua, A.; Mostafavi, E.; González, M. U.; Martínez, L.; Kusper, M.; Sotelo, E.; Gao, M.; Geoffrion, L. D.; Shah, V.; Guisbiers, G.; Cholula-Díaz, J. L.; Guillermier, C.; Khanom, F.; Huttel, Y.; García-Martín, J. M.; Webster, T. J. Aloe Vera-Mediated Te Nanostructures: Highly Potent Antibacterial Agents and Moderated Anticancer Effects. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 11 (2), 514. [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Ramirez, A.; Perez, R. M.; Garcia, E.; Garcia, F. E. Antidiabetic Activity of Aloe vera Leaves. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine : eCAM 2020, 2020, 6371201. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, D.; Zhao, T.; Tian, H. Efficacy of Aloe Vera Supplementation on Prediabetes and Early Non-Treated Diabetic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2016, 8 (7), 388. [CrossRef]
- Haghani, F.; Arabnezhad, M. R.; Mohammadi, S.; Ghaffarian-Bahraman, A. Aloe vera and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mellitus. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia : Haseoluoficial da Sociedade Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2022, 32 (2), 174–187. [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-Ramirez, A.; Perez, R. M.; Garcia, E.; Garcia, F. E. Antidiabetic Activity of Aloe vera Leaves. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine : eCAM 2020, 2020, 6371201. [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, Y. S.; Tatke, P. A.; Gabhe, S. Y.; Vaidya, A. B. Antidiabetic activity of extracts of Anacardium occidentale Linn. leaves on n-streptozotocin diabetic rats. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine 2016, 7 (4), 421–427. [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Gültekin-Özgüven, M.; Kırkın, C.; Özçelik, B.; Morais-Braga, M.; Carneiro, J.; Bezerra, C. F.; Silva, T.; Coutinho, H.; Amina, B.; Armstrong, L.; Selamoglu, Z.; Sevindik, M.; Yousaf, Z.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Muddathir, A. M.; Devkota, H. P.; Martorell, M.; Jugran, A. K.; Martins, N.; … Cho, W. C. Anacardium Plants: Chemical, Nutritional Composition and Biotechnological Applications. Biomolecules 2019, 9 (9), 465. [CrossRef]
- Okpashi, V. E.; Bayim, B. P.; Obi-Abang, M. Comparative Effects of Some Medicinal Plants: Anacardium occidentale, Eucalyptus globulus, Psidium guajava, and Xylopia aethiopica Extracts in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Male Wistar Albino Rats. Biochemistry Research International 2014, 2014, 203051. [CrossRef]
- Alexander-Lindo, R. L.; Morrison, E. Y.; Nair, M. G. Hypoglycaemic effect of stigmast-4-en-3-one and its corresponding alcohol from the bark of Anacardium occidentale (cashew). Phytotherapy Research 2004, 18 (5), 403–407. [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Xing, D.; Sun, H.; Wang, W.; Ding, Y.; Du, L. The Effects of Ananas comosus L. Leaves on Diabetic-Dyslipidemic Rats Induced by Alloxan and a High-Fat/High-Cholesterol Diet. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2005, 33 (1), 95–105. [CrossRef]
- Suhrabi, Z.; Taghinejad, H. A Comparative Study on the Efficacy of Ibuprofen and Celecoxib on the Intensity of Perineal Pain Following Episiotomy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2013, 15 (12), e9980. [CrossRef]
- Brown, S. A.; Coimbra, M.; Coberly, D. M.; Chao, J. J.; Rohrich, R. J. Oral Nutritional Supplementation Accelerates Skin Wound Healing: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Arm, Crossover Study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 114 (1), 237–244. [CrossRef]
- Golezar, S. Ananas comosus Effect on Perineal Pain and Wound Healing After Episiotomy: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Iran. Red Crescent Med. J. 2016, 18 (3), e21019. [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, W.; Su, H.; Xing, D.; Cai, G.; Du, L. Hypolipidemic Mechanisms of Ananas comosus L. Leaves in Mice: Different from Fibrates but Similar to Statins. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 103 (3), 267–274. [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wang, W.; Su, H.; Xing, D.; Pan, Y.; Du, L. Effect of Ethanolic Extracts of Ananas comosus L. Leaves on Insulin Sensitivity in Rats and HepG2. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 143 (4), 429–435. [CrossRef]
- Maurer, H. R. Bromelain: Biochemistry, Pharmacology and Medical Use. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58 (9), 1234–1245. [CrossRef]
- Sowbhagya, H. B. Chemistry, Technology, and Nutraceutical Functions of Celery (Apium graveolens L.): An Overview. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54 (3), 389–398. [CrossRef]
- Al-Asmari, A. K.; Athar, M. T.; Kadasah, S. G. An Updated Phytopharmacological Review on Medicinal Plant of Arab Region: Apium graveolens Linn. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2017, 11 (21), 13–18. [CrossRef]
- Rebollo-Hernanz, M.; Zhang, Q.; Aguilera, Y.; Martín-Cabrejas, M. A.; de Mejia, E. G. Cocoa Shell Aqueous Phenolic Extract Preserves Mitochondrial Function and Insulin Sensitivity by Attenuating Inflammation between Macrophages and Adipocytes In Vitro. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63 (10), e1801413. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Huang, X. J.; Chen, G. X. Current Understanding of Glucose Transporter 4 Expression and Functional Mechanisms. World J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 11 (3), 76–98. [CrossRef]
- Panchamoorthy, R.; Mohan, U.; Muniyan, A. Apium graveolens Reduced Phytofabricated Gold Nanoparticles and Their Impacts on the Glucose Utilization Pattern of the Isolated Rat Hemidiaphragm. Heliyon 2022, 8 (1), e08805. [CrossRef]
- Chonpathompikunlert, P.; Boonruamkaew, P.; Sukketsiri, W.; Hutamekalin, P.; Sroyraya, M. The Antioxidant and Neurochemical Activity of Apium graveolens L. and Its Ameliorative Effect on MPTP-Induced Parkinson-like Symptoms in Mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18 (1), 103. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Jain, U. K.; Pathak, A. K. Wound Healing Properties of Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. Ancient Sci. Life 2009, 28 (4), 36–37.
- Fernando, M. R.; Thabrew, M. I.; Karunanayake, E. H. Hypoglycaemic Activity of Some Medicinal Plants in Sri-Lanka. Gen. Pharmacol. 1990, 21 (5), 779–782. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, P.; Akther, S.; Hannan, J.; Seidel, V.; Nujat, N.; Abdel-Wahab, Y. Pharmacologically Active Phytomolecules Isolated from Traditional Antidiabetic Plants and Their Therapeutic Role for the Management of Diabetes Mellitus. Molecules 2022, 27 (13), 4278. [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, B. O.; Ojo, O. A.; Adeyonu, O.; Imiere, O. D.; Fadaka, A. O.; Osukoya, A. O. Ameliorative Activity of Ethanol Extract of Artocarpus heterophyllus Stem Bark on Pancreatic β-Cell Dysfunction in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2017, 22 (4), 538–543. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tu, Z. C.; Xie, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. X.; Sha, X. M.; Lu, Y. Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.) Peel: A Better Source of Antioxidants and α-Glucosidase Inhibitors than Pulp, Flake, and Seed, and Phytochemical Profile by HPLC-QTOF-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2017, 234, 303–313. [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, R.; Maduwanthi, S.; Marapana, R. Nutritional and Health Benefits of Jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.): A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. 2019, 2019, 4327183. [CrossRef]
- Rao, A. G.; Naik, K. S.; Unnikrishnan, A. G.; Joseph, J. Efficacy of Green Jackfruit Flour as a Medical Nutrition Therapy Replacing Rice or Wheat in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutr. Diabetes 2021, 11 (1), 18. [CrossRef]
- Pegiou, E.; Mumm, R.; Acharya, P.; de Vos, R.; Hall, R. D. Green and White Asparagus (Asparagus officinalis): A Source of Developmental, Chemical and Urinary Intrigue. Metabolites 2019, 10 (1), 17. [CrossRef]
- Hafizur, R. M.; Kabir, N.; Chishti, S. Asparagus officinalis Extract Controls Blood Glucose by Improving Insulin Secretion and β-Cell Function in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108 (9), 1586–1595. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, D.; Wang, K.; Wang, R.; Qu, W. The Aqueous Extract of Asparagus officinalis L. By-Product Exerts Hypoglycaemic Activity in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91 (11), 2095–2099. [CrossRef]
- Negi, J. S.; Singh, P.; Joshi, G. P.; Rawat, M. S.; Bisht, V. K. Chemical Constituents of Asparagus. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4 (8), 215–220. [CrossRef]
- Mader, T. L.; Brumm, M. C. Effect of Feeding Sarsaponin in Cattle and Swine Diets. J. Anim. Sci. 1987, 65 (1), 9–15. [CrossRef]
- Paudel, D.; Dhungana, B.; Caffe, M.; Krishnan, P. A Review of Health-Beneficial Properties of Oats. Foods (Basel, Switz.) 2021, 10 (11), 2591. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; De, S.; Belkheir, A. Avena sativa (Oat), a potential neutraceutical and therapeutic agent: an overview. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53 (2), 126–144. [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Cheng, G.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; Tian, H. The Metabolic Effects of Oats Intake in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2015, 7 (12), 10369–10387. [CrossRef]
- Hozlár, P.; Gregusová, V.; Nemeček, P.; Šliková, S.; Havrlentová, M. Study of Dynamic Accumulation in β-D-Glucan in Oat (Avena sativa L.) during Plant Development. Polymers 2022, 14 (13), 2668. [CrossRef]
- Amerizadeh, A.; Ghaheh, H. S.; Vaseghi, G.; Farajzadegan, Z.; Asgary, S. Effect of Oat (Avena sativa L.) Consumption on Lipid Profile With Focus on Triglycerides and High-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C): An Updated Systematic Review. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2022, 101153. Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Yang, D.; Yang, Y.; Xie, H. Carotenoid-Derived Flavor Precursors from Averrhoa carambola Fresh Fruit. Molecules (Basel, Switz.) 2019, 24 (2), 256. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, X. Flavan-3-ols and 2-diglycosyloxybenzoates from the leaves of Averrhoa carambola. Fitoterapia 2020, 140, 104442. [CrossRef]
- Muthu, N.; Lee, S. Y.; Phua, K. K.; Bhore, S. J. Nutritional, Medicinal and Toxicological Attributes of Star-Fruits (Averrhoa carambola L.): A Review. Bioinformation 2016, 12 (12), 420–424. [CrossRef]
- Lakmal, K.; Yasawardene, P.; Jayarajah, U.; Seneviratne, S. L. Nutritional and medicinal properties of Star fruit (Averrhoa carambola): A review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9 (3), 1810–1823. [CrossRef]
- Cazarolli, L. H.; Kappel, V. D.; Pereira, D. F.; Moresco, H. H.; Brighente, I. M.; Pizzolatti, M. G.; Silva, F. R. Anti-hyperglycemic action of apigenin-6-C-β-fucopyranoside from Averrhoa carambola. Fitoterapia 2012, 83 (7), 1176–1183. [CrossRef]
- Subapriya, R.; Nagini, S. Medicinal Properties of Neem Leaves: A Review. Current Medicinal Chemistry. Anti-Cancer Agents 2005, 5 (2). [CrossRef]
- Atangwho, I. J.; Ebong, P. E.; Eyong, E. U.; Asmawi, M. Z.; Ahmad, M. Synergistic Antidiabetic Activity of Vernonia amygdalina and Azadirachta indica: Biochemical Effects and Possible Mechanism. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2012, 141 (3), 878–887. [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Shafique, Z.; Amjad, S. T.; Bin Asad, M. Enzymes Inhibitors from Natural Sources with Antidiabetic Activity: A Review. Phytotherapy Research : PTR 2019, 33 (1), 41–54. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.; Zambad, S.; Ali, M. Effect of Aqueous Extract of Azadirachta indica Leaves on Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Glipizide. Drug Metabolism Letters 2019, 13 (1), 19–24. [CrossRef]
- Pingali, U.; Ali, M. A.; Gundagani, S.; Nutalapati, C. Evaluation of the Effect of an Aqueous Extract of Azadirachta indica (Neem) Leaves and Twigs on Glycemic Control, Endothelial Dysfunction and Systemic Inflammation in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity : Targets and Therapy 2020, 13, 4401–4412. [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, S.; Honarvar, M. Beta vulgaris - A Mini Review of Traditional Uses in Iran, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2019, 16 (1), 74–81. [CrossRef]
- Hadipour, E.; Taleghani, A.; Tayarani-Najaran, N.; Tayarani-Najaran, Z. Biological Effects of Red Beetroot and Betalains: A Review. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34 (8), 1847–1867. [CrossRef]
- Ninfali, P.; Angelino, D. Nutritional and Functional Potential of Beta vulgaris Cicla and Rubra. Fitoterapia 2013, 89, 188–199. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Khatun, A.; Liu, L.; Barkla, B. J. Brassicaceae Mustards: Traditional and Agronomic Uses in Australia and New Zealand. Molecules 2018, 23 (1), 231. [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A. K.; Parmar, N.; Singh, K. H.; Nanjundan, J. Current Achievements and Future Prospects of Genetic Engineering in Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern & Coss.). Planta 2020, 252 (4), 56. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H. Y.; Choi, S. I.; Han, X.; Men, X.; Jang, G. W.; Choi, Y. E.; Lee, O. H. Antiobesity Effect of Brassica juncea Cultivated in Jeongseon with Optimized Sinigrin Content using 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45 (4), e13650. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S. P.; Vats, V.; Ammini, A. C.; Grover, J. K. Brassica juncea (Rai) Significantly Prevented the Development of Insulin Resistance in Rats Fed Fructose-Enriched Diet. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 93 (1), 113–116. [CrossRef]
- Yang, D. K. Cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) Protects Against H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress by Preventing Mitochondrial Dysfunction in H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 2179021. [CrossRef]
- Mageney, V.; Neugart, S.; Albach, D. C. A Guide to the Variability of Flavonoids in Brassica oleracea. Molecules 2017, 22 (2), 252. [CrossRef]
- Assad, T.; Khan, R. A.; Feroz, Z. Evaluation of Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Activity of Methanol Extract of Brassica oleracea. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12 (9), 648–653. [CrossRef]
- Radünz, M.; Mota Camargo, T.; Dos Santos Hackbart, H. C.; Blank, J. P.; Hoffmann, J. F.; Moro Stefanello, F.; da Rosa Zavareze, E. Encapsulation of Broccoli Extract by Electrospraying: Influence of in Vitro Simulated Digestion on Phenolic and Glucosinolate Contents, and on Antioxidant and Antihyperglycemic Activities. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128075. [CrossRef]
- Le, T. N.; Chiu, C. H.; Hsieh, P. C. Bioactive Compounds and Bioactivities of Brassica oleracea L. var. Italica Sprouts and Microgreens: An Updated Overview from a Nutraceutical Perspective. Plants 2020, 9 (8), 946. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S. R.; Rabbee, M. F.; Roy, A.; Chowdhury, R.; Banik, A.; Kubra, K.; Hassan Chowdhury, M. M.; Baek, K. H. Therapeutic Promises of Medicinal Plants in Bangladesh and Their Bioactive Compounds against Ulcers and Inflammatory Diseases. Plants (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 10 (7), 1348. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, P.; Flatt, P. R.; Harriott, P.; Abdel-Wahab, Y. H. A. Anti-Hyperglycaemic and Insulin-Releasing Effects of Camellia Sinensis Leaves and Isolation and Characterisation of Active Compounds. Br J Nutr 2021, 126 (8), 1149–1163. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q. Y.; Li, Q. S.; Lin, X. M.; Qiao, R. Y.; Yang, R.; Li, X. M.; Dong, Z. B.; Xiang, L. P.; Zheng, X. Q.; Lu, J. L.; Yuan, C. B.; Ye, J. H.; Liang, Y. R. Antidiabetic Effects of Tea. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2017, 22 (5), 849. [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, M. I.; Sivamaruthi, B. S.; Chaiyasut, C.; Tencomnao, T. A Review of the Role of Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) in Antiphotoaging, Stress Resistance, Neuroprotection, and Autophagy. Nutrients 2019, 11 (2), 474. [CrossRef]
- Maji, A. K.; Banerji, P. Phytochemistry and Gastrointestinal Benefits of the Medicinal Spice, Capsicum annuum L. (Chilli): A Review. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2016, 13 (2), 97–122. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. K.; Jeong, J.; Kang, E. Y.; Go, G. W. Red Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Seed Extract Improves Glycemic Control by Inhibiting Hepatic Gluconeogenesis via Phosphorylation of FOXO1 and AMPK in Obese Diabetic db/db Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12 (9), 2546. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Cho, K. W.; Jeong, J.; Park, K.; Ryu, Y.; Moyo, K. M.; Kim, H. K.; Go, G. W. Red Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Seed Extract Decreased Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Increased Muscle Glucose Uptake In Vitro. J. Med. Food 2018, 21 (7), 665–671. [CrossRef]
- Sinisgalli, C.; Faraone, I.; Vassallo, A.; Caddeo, C.; Bisaccia, F.; Armentano, M. F.; Milella, L.; Ostuni, A. Phytochemical Profile of Capsicum annuum L. cv Senise, Incorporation into Liposomes, and Evaluation of Cellular Antioxidant Activity. Antioxidants 2020, 9 (5), 428. [CrossRef]
- Silva, L. R.; Azevedo, J.; Pereira, M. J.; Carro, L.; Velazquez, E.; Peix, A.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P. B. Inoculation of the Nonlegume Capsicum annuum (L.) with Rhizobium Strains. 1. Effect on Bioactive Compounds, Antioxidant Activity, and Fruit Ripeness. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62 (3), 557–564. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. P.; Kumar, S.; Mathan, S. V.; Tomar, M. S.; Singh, R. K.; Verma, P. K.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R. P.; Acharya, A. Therapeutic application of Carica papaya leaf extract in the management of human diseases. Daru J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 28 (2), 735–744. [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Talniya, N.; Sahrawat, S.; Kumar, A.; Stashenko, E. Ethnomedicinal Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Carica papaya Plant: A Compendious Review. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2019, 16 (5), 463-480. [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Rojop, I. E.; Díaz-Zagoya, J. C.; Ble-Castillo, J. L.; Miranda-Osorio, P. H.; Castell-Rodríguez, A. E.; Tovilla-Zárate, C. A.; Rodríguez-Hernández, A.; Aguilar-Mariscal, H.; Ramón-Frías, T.; Bermúdez-Ocaña, D. Y. Hypoglycemic Effect of Carica papaya Leaves in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 236. [CrossRef]
- Agada, R.; Usman, W. A.; Shehu, S.; Thagariki, D. In Vitro and In Vivo Inhibitory Effects of Carica papaya Seed on α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Enzymes. Heliyon 2020, 6 (3), e03618. [CrossRef]
- Neimkhum, W.; Anuchapreeda, S.; Lin, W. C.; Lue, S. C.; Lee, K. H.; Chaiyana, W. Effects of Carissa carandas Linn. Fruit, Pulp, Leaf, and Seed on Oxidation, Inflammation, Tyrosinase, Matrix Metalloproteinase, Elastase, and Hyaluronidase Inhibition. Antioxidants 2021, 10 (9), 1345. [CrossRef]
- Itankar, P. R.; Lokhande, S. J.; Verma, P. R.; Arora, S. K.; Sahu, R. A.; Patil, A. T. Antidiabetic potential of unripe Carissa carandas Linn. fruit extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 135 (2), 430–433. [CrossRef]
- Purohit, P.; Palamthodi, S.; Lele, S. S. Effect of karwanda (Carissa congesta Wight) and sugar addition on physicochemical characteristics of ash gourd (Benincasa hispida) and bottle gourd (Lagenaria siceraria) based beverages. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56 (2), 1037–1045. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Bajpai, M.; Mishra, P. Carissa carandas L. - phyto-pharmacological review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72 (12), 1694–1714. [CrossRef]
- El-Desoky, A. H.; Abdel-Rahman, R. F.; Ahmed, O. K.; El-Beltagi, H. S.; Hattori, M. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of naringin isolated from Carissa carandas L.: In vitro and in vivo evidence. Phytomedicine 2018, 42, 126–134. [CrossRef]
- Nammi, S.; Boini, M. K.; Lodagala, S. D.; Behara, R. B. The juice of fresh leaves of Catharanthus roseus Linn. reduces blood glucose in normal and alloxan diabetic rabbits. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2003, 3, 4. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, B.; Singh, R. Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don: A review of its ethnobotany, phytochemistry, ethnopharmacology and toxicities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 284, 114647. [CrossRef]
- Tiong, S. H.; Looi, C. Y.; Hazni, H.; Arya, A.; Paydar, M.; Wong, W. F.; Cheah, S. C.; Mustafa, M. R.; Awang, K. Antidiabetic and antioxidant properties of alkaloids from Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2013, 18 (8), 9770–9784. [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.; Sakoff, J. A.; Vuong, Q. V.; Bowyer, M. C.; Scarlett, C. J. Phytochemical, antioxidant, anti-proliferative and antimicrobial properties of Catharanthus roseus root extract, saponin-enriched and aqueous fractions. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46 (3), 3265–3273. [CrossRef]
- Lee, O. N.; Ak, G.; Zengin, G.; Cziáky, Z.; Jekő, J.; Rengasamy, K.; Park, H. Y.; Kim, D. H.; Sivanesan, I. Phytochemical Composition, Antioxidant Capacity, and Enzyme Inhibitory Activity in Callus, Somaclonal Variant, and Normal Green Shoot Tissues of Catharanthus roseus (L) G. Don. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2020, 25 (21), 4945. [CrossRef]
- Gohil, K. J.; Patel, J. A.; Gajjar, A. K. Pharmacological Review on Centella asiatica: A Potential Herbal Cure-all. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 72 (5), 546–556. [CrossRef]
- Razali, N.; Ng, C. T.; Fong, L. Y. Cardiovascular Protective Effects of Centella asiatica and Its Triterpenes: A Review. Planta Med. 2019, 85 (16), 1203–1215. [CrossRef]
- Oyenihi, A. B.; Langa, S.; Mukaratirwa, S.; Masola, B. Effects of Centella asiatica on Skeletal Muscle Structure and Key Enzymes of Glucose and Glycogen Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108715. [CrossRef]
- Maulidiani, M.; Abas, F.; Khatib, A.; Perumal, V.; Suppaiah, V.; Ismail, A.; Hamid, M.; Shaari, K.; Lajis, N. H. Metabolic Alteration in Obese Diabetes Rats upon Treatment with Centella asiatica Extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 180, 60–69. [CrossRef]
- Angeli, V.; Miguel Silva, P.; Crispim Massuela, D.; Khan, M. W.; Hamar, A.; Khajehei, F.; Graeff-Hönninger, S.; Piatti, C. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): An Overview of the Potentials “f the "Golde” Grain" and Socio-Economic and Environmental Aspects of Its Cultivation and Marketization. Foods (Basel, Switz.) 2020, 9 (2), 216. [CrossRef]
- Vega-Gálvez, A.; Miranda, M.; Vergara, J.; Uribe, E.; Puente, L.; Martínez, E. A. Nutrition facts and functional potential of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa willd.), an ancient Andean grain: a review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90 (15), 2541–2547. [CrossRef]
- Graf, B. L.; Rojas-Silva, P.; Rojo, L. E.; Delatorre-Herrera, J.; Baldeón, M. E.; Raskin, I. Innovations in Health Value and Functional Food Development of Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14 (4), 431–445. [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Liu, J. X.; Yang, X. Y.; Lv, B. H.; Wu, Y. X.; Jiang, G. J. Supplementation of quinoa regulates glycolipid metabolism and endoplasmic reticulum stress in the high-fat diet-induced female obese mice. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18 (1), 95. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, B.; Yan, Y.; Liang, J.; Guan, X. Bound Polyphenols from Red Quinoa Prevailed over Free Polyphenols in Reducing Postprandial Blood Glucose Rises by Inhibiting α-Glucosidase Activity and Starch Digestion. Nutrients 2022, 14 (4), 728. [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Rizzolo, D. A.; Acar-Denizli, N.; Kostov, B.; Roura, E.; Sisó-Almirall, A.; Delicado, P.; Gomis, R. Glycaemia Fluctuations Improvement in Old-Age Prediabetic Subjects Consuming a Quinoa-Based Diet: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2022, 14 (11), 2331. [CrossRef]
- Gabrial, S. G.; Shakib, M. R.; Gabrial, G. N. Effect of Pseudocereal-Based Breakfast Meals on the First and Second Meal Glucose Tolerance in Healthy and Diabetic Subjects. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 4 (4), 565–573. [CrossRef]
- Quintero-Soto, M. F.; Chávez-Ontiveros, J.; Garzón-Tiznado, J. A.; Salazar-Salas, N. Y.; Pineda-Hidalgo, K. V.; Delgado-Vargas, F.; López-Valenzuela, J. A. Characterization of peptides with antioxidant activity and antidiabetic potential obtained from chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) protein hydrolyzates. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86 (7), 2962–2977. [CrossRef]
- Yegrem, L. Nutritional Composition, Antinutritional Factors, and Utilization Trends of Ethiopian Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 5570753. [CrossRef]
- Bhagyawant, S. S.; Narvekar, D. T.; Gupta, N.; Bhadkaria, A.; Gautam, A. K.; Srivastava, N. Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Lectin Exhibit Inhibition of ACE-I, α-amylase and α-glucosidase Activity. Protein Pept. Lett. 2019, 26 (7), 494–501. [CrossRef]
- Jukanti, A. K.; Gaur, P. M.; Gowda, C. L.; Chibbar, R. N. Nutritional quality and health benefits of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): a review. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108 (Suppl 1), S11–S26. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y. X.; Sun, Y. H.; Chen, R. Y. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2007, 32 (16), 1650–1652. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34848240/.
- Faridy, J. M.; Stephanie, C. M.; Gabriela, M. O.; Cristian, J. M. Biological Activities of Chickpea in Human Health (Cicer arietinum L.): A Review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75 (2), 142–153. [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Rao, A. S.; Nandal, A.; Kumar, S.; Yadav, S. S.; Ganaie, S. A.; Narasimhan, B. Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review of Cinnamomum verum J. Presl - A Versatile Spice Used in Food and Nutrition. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127773. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Ito, Y.; Muraki, E.; Hosono, T.; Seki, T.; Ariga, T. Verification of the Antidiabetic Effects of Cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum) using Insulin-Uncontrolled Type 1 Diabetic Rats and Cultured Adipocytes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74 (12), 2418–2425. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. H.; Hyun, S. H.; Choung, S. Y. Anti-diabetic Effect of Cinnamon Extract on Blood Glucose in db/db Mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 104 (1-2), 119–123. [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Dey, A.; Koirala, N.; Shaheen, S.; El Omari, N.; Salehi, B.; Goloshvili, T.; Cirone Silva, N. C.; Bouyahya, A.; Vitalini, S.; Varoni, E. M.; Martorell, M.; Abdolshahi, A.; Docea, A. O.; Iriti, M.; Calina, D.; Les, F.; López, V.; Caruntu, C. Cinnamomum Species: Bridging Phytochemistry Knowledge, Pharmacological Properties and Toxicological Safety for Health Benefits. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 600139. [CrossRef]
- Wahid, M.; Saqib, F.; Qamar, M.; Ziora, Z. Antispasmodic Activity of the Ethanol Extract of Citrullus lanatus Seeds: Justifying Ethnomedicinal Use in Pakistan to Treat Asthma and Diarrhea. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 295, 115314. [CrossRef]
- Eke, R.; Ejiofor, E.; Oyedemi, S.; Onoja, S.; Omeh, N. Evaluation of Nutritional Composition of Citrullus lanatus Linn. (Watermelon) Seed and Biochemical Assessment of the Seed Oil in Rats. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45 (6), e13763. [CrossRef]
- Oyenihi, O. R.; Afolabi, B. A.; Oyenihi, A. B.; Ogunmokun, O. J.; Oguntibeju, O. O. Hepato- and Neuro-Protective Effects of Watermelon Juice on Acute Ethanol-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2016, 3, 288–294. [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, B. O.; Shonibare, M. T.; Oyinloye, B. E. Antidiabetic Activity of Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) Juice in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2020, 19 (1), 343–352. [CrossRef]
- Clement, Y. N.; Baksh-Comeau, Y. S.; Seaforth, C. E. An Ethnobotanical Survey of Medicinal Plants in Trinidad. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2015, 11, 67. [CrossRef]
- Balogun, F. O.; Ashafa, A. A Review of Plants Used in South African Traditional Medicine for the Management and Treatment of Hypertension. Planta Med. 2019, 85(4), 312–334. [CrossRef]
- Ali, M. Y.; Zaib, S.; Rahman, M. M.; Jannat, S.; Iqbal, J.; Park, S. K.; Chang, M. S. Didymin, a Dietary Citrus Flavonoid Exhibits Anti-Diabetic Complications and Promotes Glucose Uptake through the Activation of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Insulin-Resistant HepG2 Cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 305, 180–194. [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y. K.; Lee, M. J.; Chen, K.; Lee, Y. C.; Wu, W. S.; Tzeng, Y. M. Insulin-Mimetic Action of Rhoifolin and Cosmosiin Isolated from Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck Leaves: Enhanced Adiponectin Secretion and Insulin Receptor Phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 Cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2011, 624375. [CrossRef]
- Onda, K.; Horike, N.; Suzuki, T.; Hirano, T. Polymethoxyflavonoids Tangeretin and Nobiletin Increase Glucose Uptake in Murine Adipocytes. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27(2), 312–316. [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, G. R.; Vasconcelos, A.; Wu, D. T.; Li, H. B.; Antony, P. J.; Li, H.; Geng, F.; Gurgel, R. Q.; Narain, N.; Gan, R. Y. Citrus Flavonoids as Promising Phytochemicals Targeting Diabetes and Related Complications: A Systematic Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Nutrients 2020, 12(10), 2907. [CrossRef]
- Kundusen, S.; Haldar, P. K.; Gupta, M.; Mazumder, U. K.; Saha, P.; Bala, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Kar, B. Evaluation of Antihyperglycemic Activity of Citrus limetta Fruit Peel in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. ISRN Endocrinol. 2011, 869273. [CrossRef]
- Parhiz, H.; Roohbakhsh, A.; Soltani, F.; Rezaee, R.; Iranshahi, M. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of the Citrus Flavonoids Hesperidin and Hesperetin: An Updated Review of Their Molecular Mechanisms and Experimental Models. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29(3), 323–331. [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, B.; Devkota, H. P.; Poudel, P. Citrus maxima (Brum.) Merr. (Rutaceae): Bioactive Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 8741669. [CrossRef]
- Oboh, G.; Ademosun, A. O. Shaddock peels (Citrus maxima) phenolic extracts inhibit α-amylase, α-glucosidase and angiotensin I-converting enzyme activities: a nutraceutical approach to diabetes management. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2011, 5 (3), 148–152. [CrossRef]
- Somanathan Karthiga, R.; Sukhdeo, S. V.; Madhugiri Lakshminarayan, S.; Mysuru Nanjarajurs, S. Efficacy of Citrus maxima fruit segment supplemented paranthas in STZ induced diabetic rats. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86 (5), 2091–2102. [CrossRef]
- Ho, S. C.; Lin, C. C. Investigation of Heat Treating Conditions for Enhancing the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Citrus Fruit (Citrus reticulata) Peels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56(17), 7976–7982. [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Kamiya, T.; Furukawa, K.; Azumi, M.; Ishizuka, S.; Takayama, S.; Nagase, S.; Arai, H.; Yamakuni, T.; Yaegashi, N. Nobiletin-Rich Citrus reticulata Peels, a Kampo Medicine for Alzheimer's Disease: A Case Series. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2013, 13(1), 236–238. [CrossRef]
- Ali, A. M.; Gabbar, M. A.; Abdel-Twab, S. M.; Fahmy, E. M.; Ebaid, H.; Alhazza, I. M.; Ahmed, O. M. Antidiabetic Potency, Antioxidant Effects, and Mode of Actions of Citrus reticulata Fruit Peel Hydroethanolic Extract, Hesperidin, and Quercetin in Nicotinamide/Streptozotocin-Induced Wistar Diabetic Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longevity 2020, 1730492. [CrossRef]
- Kanaze, F. I.; Termentzi, A.; Gabrieli, C.; Niopas, I.; Georgarakis, M.; Kokkalou, E. The Phytochemical Analysis and Antioxidant Activity Assessment of Orange Peel (Citrus sinensis) Cultivated in Greece-Crete Indicates a New Commercial Source of Hesperidin. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2009, 23(3), 239–249. [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tao, H.; Cao, Y.; Ho, C. T.; Jin, S.; Huang, Q. Prevention of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes with Aged Citrus Peel (Chenpi) Extract. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64(10), 2053–2061. [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, L. Mandarin (Citrus reticulata L.) Essential Oil Incorporated into Chitosan Nanoparticles: Characterization, Anti-Biofilm Properties and Application in Pork Preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 620–628. [CrossRef]
- Lima, E. B.; Sousa, C. N.; Meneses, L. N.; Ximenes, N. C.; Santos Júnior, M. A.; Vasconcelos, G. S.; Lima, N. B.; Patrocínio, M. C.; Macedo, D.; Vasconcelos, S. M. Cocos nucifera (L.) (Arecaceae): A phytochemical and pharmacological review. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 48 (11), 953–964. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S. A.; Ahmad, M. H. A review of medicinal plant research at the University of the West Indies, Jamaica, 1948-2001. West Indian Med. J. 2006, 55 (4), 243–269. [CrossRef]
- Bhandary, M. J.; Chandrashekar, K. R.; Kaveriappa, K. M. Medical ethnobotany of the Siddis of Uttara Kannada district, Karnataka, India. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 47 (3), 149–158. [CrossRef]
- Hope, B. E.; Massey, D. G.; Fournier-Massey, G. Hawaiian materia medica for asthma. Hawaii Med. J. 1993, 52 (6), 160–166.
- Renjith, R. S.; Chikku, A. M.; Rajamohan, T. Cytoprotective, antihyperglycemic and phytochemical properties of Cocos nucifera (L.) inflorescence. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine 2013, 6 (10), 804–810. [CrossRef]
- Bahadoran, Z.; Mirmiran, P.; Azizi, F. Dietary polyphenols as potential nutraceuticals in management of diabetes: a review. Journal of Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders 2013, 12 (1), 43. [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, V. G.; Rajamohan, T. Comparative evaluation of the hypolipidemic effects of coconut water and lovastatin in rats fed fat-cholesterol enriched diet. Food and Chemical Toxicology: An International Journal Published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 2008, 46 (12), 3586–3592. [CrossRef]
- Golbidi, S.; Ebadi, S. A.; Laher, I. Antioxidants in the treatment of diabetes. Current Diabetes Reviews 2011, 7 (2), 106–125. [CrossRef]
- Patay, É. B.; Bencsik, T.; Papp, N. Phytochemical Overview and Medicinal Importance of Coffea Species from the Past until Now. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9 (12), 1127–1135. [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Peng, X.; Dong, D.; Nian, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Hong, D.; Qiu, M. New ent-Kaurane Diterpenes from the Roasted Arabica Coffee Beans and Molecular Docking to α-Glucosidase. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128823. [CrossRef]
- Nemzer, B.; Kalita, D.; Abshiru, N. Quantification of Major Bioactive Constituents, Antioxidant Activity, and Enzyme Inhibitory Effects of Whole Coffee Cherries (Coffea arabica) and Their Extracts. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2021, 26 (14), 4306. [CrossRef]
- Vasant, O. K.; Vijay, B. G.; Virbhadrappa, S. R.; Dilip, N. T.; Ramahari, M. V.; Laxamanrao, B. S. Antihypertensive and Diuretic Effects of the Aqueous Extract of Colocasia esculenta Linn. Leaves in Experimental Paradigms. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11 (2), 621–634.
- Giannoulaki, P.; Kotzakioulafi, E.; Chourdakis, M.; Hatzitolios, A.; Didangelos, T. Impact of Crocus Sativus L. on Metabolic Profile in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus or Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12 (5), 1424. [CrossRef]
- Mitharwal, S.; Kumar, A.; Chauhan, K.; Taneja, N. K. Nutritional, Phytochemical Composition and Potential Health Benefits of Taro (Colocasia esculenta L.) Leaves: A Review. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132406. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Kumar, A.; Tomer, V.; Kumar, V.; Saini, M. Potential of Colocasia Leaves in Human Nutrition: Review on Nutritional and Phytochemical Properties. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43 (7), e12878. [CrossRef]
- Li, H. M.; Hwang, S. H.; Kang, B. G.; Hong, J. S.; Lim, S. S. Inhibitory Effects of Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott Constituents on Aldose Reductase. Molecules 2014, 19 (9), 13212–13224. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Boskabady, M. H.; Khazdair, M. R. Neuroprotective Effects of Coriandrum sativum and its Constituent, Linalool: A Review. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2021, 11 (5), 436–450. [CrossRef]
- Kajal, A.; Singh, R. Coriandrum sativum Seeds Extract Mitigate Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy in Experimental Rats via AGEs Inhibition. PLoS One 2019, 14 (3), e0213147. [CrossRef]
- Kajal, A.; Singh, R. Coriandrum sativum Improve Neuronal Function via Inhibition of Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress and TNF-α in Diabetic Neuropathic Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 112959. [CrossRef]
- Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Coriandrum sativum L.: A Promising Functional Food Toward the Well-being. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 305–323. [CrossRef]
- Wei, J. N.; Liu, Z. H.; Zhao, Y. P.; Zhao, L. L.; Xue, T. K.; Lan, Q. K. Phytochemical and Bioactive Profile of Coriandrum sativum L. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 260–267. [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Zare, V.; Butler, A. E.; Barreto, G. E.; Sahebkar, A. Antidiabetic Potential of Saffron and its Active Constituents. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234 (6), 8610–8617. [CrossRef]
- Singh D. Neuropharmacological Aspects of Crocus sativus L.: A Review of Preclinical Studies and Ongoing Clinical Research. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 14 (7), 880–902. [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Sarwat, M.; Khan, T. H. Mechanism behind the Anti-tumour Potential of Saffron (Crocus sativus L.): The Molecular Perspective. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 115, 27–35. [CrossRef]
- Giannoulaki, P.; Kotzakioulafi, E.; Chourdakis, M.; Hatzitolios, A.; Didangelos, T. Impact of Crocus sativus L. on Metabolic Profile in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus or Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12 (5), 1424. [CrossRef]
- Zengin, G.; Aumeeruddy, M. Z.; Diuzheva, A.; Jekő, J.; Cziáky, Z.; Yıldıztugay, A.; Yıldıztugay, E.; Mahomoodally, M. F. A Comprehensive Appraisal on Crocus chrysanthus (Herb.) Herb. Flower Extracts with HPLC-MS/MS Profiles, Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Properties. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 164, 581–589. [CrossRef]
- Samarghandian, S.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Farkhondeh, T. Immunomodulatory and Antioxidant Effects of Saffron Aqueous Extract (Crocus sativus L.) on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in Rats. Indian Heart J. 2017, 69 (2), 151–159. [CrossRef]
- Allaq, A.; Sidik, N.; Abdul-Aziz, A.; Ahmed, I. Cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.): A Review of Its Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2020, 7 (9), 4016-4021. [CrossRef]
- Johri, R. K. Cuminum cyminum and Carum carvi: An Update. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2011, 5 (9), 63–72. [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, A. G.; Patil, P. B. Antihyperglycemic Activity and Inhibition of Advanced Glycation End Product Formation by Cuminum cyminum in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48 (8-9), 2030–2036. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P. K.; Nema, N. K.; Maity, N.; Sarkar, B. K. Phytochemical and Therapeutic Potential of Cucumber. Fitoterapia 2013, 84, 227–236. [CrossRef]
- Roman-Ramos, R.; Flores-Saenz, J. L.; Alarcon-Aguilar, F. J. Anti-Hyperglycemic Effect of Some Edible Plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 48 (1), 25–32. [CrossRef]
- Atta, A. H.; Saad, S. A.; Atta, S. A.; Mouneir, S. M.; Nasr, S. M.; Desouky, H. M.; Shaker, H. M. Cucumis sativus and Cucurbita maxima Extract Attenuate Diabetes-Induced Hepatic and Pancreatic Injury in a Rat Model. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 71 (4), 10.26402/jpp.2020.4.06. [CrossRef]
- Minaiyan, M.; Zolfaghari, B.; Kamal, A. Effect of Hydroalcoholic and Buthanolic Extract of Cucumis sativus Seeds on Blood Glucose Level of Normal and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2011, 14 (5), 436–442. [CrossRef]
- Balgoon, M. J.; Al-Zahrani, M. H.; Jaouni, S. A.; Ayuob, N. Combined Oral and Topical Application of Pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) Alleviates Contact Dermatitis Associated With Depression Through Downregulation Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 663417. [CrossRef]
- Andolfo, G.; Di Donato, A.; Darrudi, R.; Errico, A.; Aiese Cigliano, R.; Ercolano, M. R. Draft of Zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.) Proteome: A Resource for Genetic and Genomic Studies. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 181. [CrossRef]
- Yoshinari, O.; Sato, H.; Igarashi, K. Anti-Diabetic Effects of Pumpkin and Its Components, Trigonelline and Nicotinic Acid, on Goto-Kakizaki Rats. Biosci., Biotechnol., Biochem. 2009, 73 (5), 1033–1041. [CrossRef]
- Adams, G. G.; Imran, S.; Wang, S.; Mohammad, A.; Kok, M. S.; Gray, D. A.; Channell, G. A.; Harding, S. E. The Hypoglycemic Effect of Pumpkin Seeds, Trigonelline (TRG), Nicotinic Acid (NA), and D-Chiro-Inositol (DCI) in Controlling Glycemic Levels in Diabetes Mellitus. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54 (10), 1322–1329. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qian, L.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Synergistic Hypoglycemic Effects of Pumpkin Polysaccharides and Puerarin on Type II Diabetes Mellitus Mice. Molecules 2019, 24 (5), 955. [CrossRef]
- Ayati, Z.; Ramezani, M.; Amiri, M. S.; Moghadam, A. T.; Rahimi, H.; Abdollahzade, A.; Sahebkar, A.; Emami, S. A. Ethnobotany, Phytochemistry and Traditional Uses of Curcuma spp. and Pharmacological Profile of Two Important Species (C. longa and C. zedoaria): A Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25 (8), 871–935. [CrossRef]
- Sayeli, V. K.; Shenoy, A. K. Antidiabetic Effect of Bio-enhanced Preparation of Turmeric in Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide Induced Type 2 Diabetic Wistar Rats. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2021, 12 (3), 474–479. [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S. M.; Zeb, A.; Mahmood, M.; Abbas, S. R.; Ahmad, Z.; Iqbal, N. Phytochemical Analysis and Biological Activities of Ethanolic Extract of Curcuma longa Rhizome. Braz. J. Biol. 2021, 81 (3), 737–740. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Lateef, E.; Mahmoud, F.; Hammam, O.; El-Ahwany, E.; El-Wakil, E.; Kandil, S.; Abu Taleb, H.; El-Sayed, M.; Hassenein, H. Bioactive Chemical Constituents of Curcuma longa L. Rhizomes Extract Inhibit the Growth of Human Hepatoma Cell Line (HepG2). Acta Pharm. 2016, 66 (3), 387–398. [CrossRef]
- Den Hartogh, D. J.; Gabriel, A.; Tsiani, E. Antidiabetic Properties of Curcumin II: Evidence from In Vivo Studies. Nutrients 2020, 12 (1), 58. [CrossRef]
- Asdaq, S.; Swathi, E.; Dhamanigi, S. S.; Asad, M.; Ali Mohzari, Y.; Alrashed, A. A.; Alotaibi, A. S.; Mohammed Alhassan, B.; Nagaraja, S. Role of Daucus carota in Enhancing Antiulcer Profile of Pantoprazole in Experimental Animals. Molecules 2020, 25 (22), 5287. [CrossRef]
- Esatbeyoglu, T.; Rodríguez-Werner, M.; Schlösser, A.; Liehr, M.; Ipharraguerre, I.; Winterhalter, P.; Rimbach, G. Fractionation of Plant Bioactives from Black Carrots (Daucus carota subspecies sativus varietas atrorubens Alef.) by Adsorptive Membrane Chromatography and Analysis of Their Potential Anti-Diabetic Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64 (29), 5901–5908. [CrossRef]
- Miras-Moreno, B.; Almagro, L.; Pedreño, M. A.; Sabater-Jara, A. B. Effect of Terbinafine on the Biosynthetic Pathway of Isoprenoid Compounds in Carrot Suspension Cultured Cells. Plant Cell Rep. 2018, 37 (7), 1011–1019. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Cawood, M.; Iqbal, Q.; Ariño, A.; Batool, A.; Tariq, R.; Azam, M.; Akhtar, S. Phytochemicals in Daucus carota and Their Health Benefits-Review Article. Foods 2019, 8 (9), 424. [CrossRef]
- Badgujar, S. B.; Patel, V. V.; Bandivdekar, A. H.; Mahajan, R. T. Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Ficus carica: A Review. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52 (11), 1487–1503. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, P.; Chen, J.; Xie, W. Ficus carica Leaves Extract Inhibited Pancreatic β-Cell Apoptosis by Inhibiting AMPK/JNK/Caspase-3 Signaling Pathway and Antioxidation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109689. [CrossRef]
- Ergül, M.; Ergül, M.; Eruygur, N.; Ataş, M.; Uçar, E. In Vitro Evaluation of the Chemical Composition and Various Biological Activities of Ficus carica Leaf Extracts. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 16 (4), 401–409. [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Mishra, A. P.; Nigam, M.; Karazhan, N.; Shukla, I.; Kiełtyka-Dadasiewicz, A.; Sawicka, B.; Głowacka, A.; Abu-Darwish, M. S.; Tarawneh, A. H.; Gadetskaya, A. V.; Cabral, C.; Salgueiro, L.; Victoriano, M.; Martorell, M.; Docea, A. O.; Abdolshahi, A.; Calina, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Ficus Plants: State of the Art from a Phytochemical, Pharmacological, and Toxicological Perspective. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35 (3), 1187–1217. [CrossRef]
- Raafat, K.; Wurglics, M. Phytochemical Analysis of Ficus carica L. Active Compounds Possessing Anticonvulsant Activity. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2018, 9 (4), 263–270. [CrossRef]
- Mawa, S.; Husain, K.; Jantan, I. Ficus carica L. (Moraceae): Phytochemistry, Traditional Uses and Biological Activities. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 974256. [CrossRef]
- El-Hawary, S. S.; Mohammed, R.; El-Din, M. E.; Hassan, H. M.; Ali, Z. Y.; Rateb, M. E.; Bellah El Naggar, E. M.; Othman, E. M.; Abdelmohsen, U. R. Comparative Phytochemical Analysis of Five Egyptian Strawberry Cultivars (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) and Antidiabetic Potential of Festival and Red Merlin Cultivars. RSC Adv. 2021, 11 (27), 16755–16767. [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liang, J.; Xie, H.; Wei, X. Norsesquiterpenoids and Triterpenoids from Strawberry cv. Falandi. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 67–72. [CrossRef]
- da Silva Pinto, M.; Kwon, Y. I.; Apostolidis, E.; Lajolo, F. M.; Genovese, M. I.; Shetty, K. Functionality of Bioactive Compounds in Brazilian Strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch.) Cultivars: Evaluation of Hyperglycemia and Hypertension Potential Using in Vitro Models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56 (12), 4386–4392. [CrossRef]
- Giampieri, F.; Forbes-Hernandez, T. Y.; Gasparrini, M.; Afrin, S.; Cianciosi, D.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Varela-Lopez, A.; Quiles, J. L.; Mezzetti, B.; Battino, M. The Healthy Effects of Strawberry Bioactive Compounds on Molecular Pathways Related to Chronic Diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1398 (1), 62–71. [CrossRef]
- Afrin, S.; Gasparrini, M.; Forbes-Hernandez, T. Y.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Mezzetti, B.; Varela-López, A.; Giampieri, F.; Battino, M. Promising Health Benefits of the Strawberry: A Focus on Clinical Studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64 (22), 4435–4449. [CrossRef]
- Chen, K. I.; Erh, M. H.; Su, N. W.; Liu, W. H.; Chou, C. C.; Cheng, K. C. Soyfoods and soybean products: from traditional use to modern applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96 (1), 9–22. [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Kabir, M. E.; Sarkar, S.; Wann, S. B.; Kalita, J.; Manna, P. Antidiabetic potential of soy protein/peptide: A therapeutic insight. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 194, 276–288. [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, N.; Yamashita, Y.; Nagata, M.; Wanezaki, S.; Ashida, H.; Horio, F.; Kohno, M. Soy β-conglycinin improves glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and ameliorates hepatic insulin resistance in Goto-Kakizaki rats. Nutr. Res. (N. Y., N. Y.) 2014, 34 (2), 160–167. [CrossRef]
- Wanezaki, S.; Tachibana, N.; Nagata, M.; Saito, S.; Nagao, K.; Yanagita, T.; Kohno, M. Soy β-conglycinin improves obesity-induced metabolic abnormalities in a rat model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 9 (2), 168–174. [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Sato, H.; Igarashi, K. Anti-diabetic effects of a kaempferol glycoside-rich fraction from unripe soybean (Edamame, Glycine max L. Me’rill. ’Jindai') leaves on KK-A(y) mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75 (9), 1677–1684. [CrossRef]
- Onoja, S. O.; Udem, S. C.; Anaga, A. O. Ameliorative Effects of Helianthus annuus Against Nephrotoxic, Cardiac, and Haematological Disorders in Alloxan-induced Hyperglycaemia in Albino Rats. J. Vet. Res. 2018, 62 (3), 371–377. [CrossRef]
- Leverrier, A.; Daguet, D.; Calame, W.; Dhoye, P.; Kodimule, S. P. Helianthus annuus Seed Extract Affects Weight and Body Composition of Healthy Obese Adults during 12 Weeks of Consumption: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Study. Nutrients 2019, 11 (5), 1080. [CrossRef]
- Onoja, S. O.; Nnadi, C. O.; Udem, S. C.; Anaga, A. O. Potential antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of a heliangolide sesquiterpene lactone isolated from Helianthus annuus L. leaves. Acta Pharm. (Zagreb, Croat.) 2020, 70 (2), 215–226. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.; Ren, G.; Chen, F. Cynarin-rich sunflower (Helianthus annuus) sprouts possess both antiglycative and antioxidant activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60 (12), 3260–3265. [CrossRef]
- Afiune, L.; Leal-Silva, T.; Sinzato, Y. K.; Moraes-Souza, R. Q.; Soares, T. S.; Campos, K. E.; Fujiwara, R. T.; Herrera, E.; Damasceno, D. C.; Volpato, G. T. Beneficial Effects of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L. Flower Aqueous Extract in Pregnant Rats with Diabetes. PLoS One 2017, 12 (6), e0179785. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Mahdi, F.; Khanna, A. K.; Singh, R.; Chander, R.; Saxena, J. K.; Mahdi, A. A.; Singh, R. K. Antidyslipidemic and Antioxidant Activities of Hibiscus rosa sinensis Root Extract in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 28 (1), 46–50. [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S. S.; Mini, S. Hibiscus rosa sinensis Linn. Petals Modulates Glycogen Metabolism and Glucose Homeostasis Signalling Pathway in Streptozotocin-Induced Experimental Diabetes. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2016, 71 (1), 42–48. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, P.; Azam, S.; Hannan, J.; Flatt, P. R.; Abdel Wahab, Y. Anti-hyperglycaemic Activity of H. rosa-sinensis Leaves Is Partly Mediated by Inhibition of Carbohydrate Digestion and Absorption, and Enhancement of Insulin Secretion. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 253, 112647. [CrossRef]
- Sachdewa, A.; Khemani, L. D. A Preliminary Investigation of the Possible Hypoglycemic Activity of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 1999, 12 (3), 222–226.
- Liu, J.; Liu, Z. Y.; Zheng, C.; Niu, Y. F. Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Dragon Fruit (Selenicereus undatus (Haw.) D.R.Hunt). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6 (3), 1154–1156. [CrossRef]
- Michelle, C.; Joice, V.; Maria, R. Nutritional Pharmacological and Toxicological Characteristics of Pitaya (Hylocereus undatus): A Review of the Literature. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2017, 11 (27), 300–304. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.; Prabhakar, B. Phytoconstituents and Pharmaco-Therapeutic Benefits of Pitaya: A Wonder Fruit. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44 (7), e13260. [CrossRef]
- Pavithra Bharathi, V.; Ragavendran, C.; Murugan, N.; Natarajan, D. Ipomoea batatas (Convolvulaceae)-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for controlling mosquito vectors of Aedes albopictus, Anopheles stephensi, and Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera). Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45 (8), 1568–1580. [CrossRef]
- Majid, M.; Nasir, B.; Zahra, S. S.; Khan, M. R.; Mirza, B.; Haq, I. U. Ipomoea batatas L. Lam. ameliorates acute and chronic inflammations by suppressing inflammatory mediators, a comprehensive exploration using in vitro and in vivo models. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18 (1), 216. [CrossRef]
- Mohanraj, R.; Sivasankar, S. Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas [L.] Lam)—a valuable medicinal food: a review. J. Med. Food 2014, 17 (7), 733–741. [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Patra, J. K.; Basavegowda, N.; Vishnuprasad, C. N.; Shin, H. S. Comparative study on antidiabetic, cytotoxicity, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using outer peels of two varieties of Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4741–4754. [CrossRef]
- Kusano, S.; Abe, H.; Tamura, H. Isolation of antidiabetic components from white-skinned sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65 (1), 109–114. [CrossRef]
- Croitoru, A.; Ficai, D.; Craciun, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Evaluation and Exploitation of Bioactive Compounds of Walnut, Juglans regia. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25 (2), 119–131. [CrossRef]
- Nasiry, D.; Khalatbary, A. R.; Ahmadvand, H.; Talebpour Amiri, F.; Akbari, E. Protective effects of methanolic extract of Juglans regia L. leaf on streptozotocin-induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2017, 17 (1), 476. [CrossRef]
- Mollica, A.; Zengin, G.; Locatelli, M.; Stefanucci, A.; Macedonio, G.; Bellagamba, G.; Onaolapo, O.; Onaolapo, A.; Azeez, F.; Ayileka, A.; Novellino, E. An assessment of the nutraceutical potential of Juglans regia L. leaf powder in diabetic rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107 (Pt B), 554–564. [CrossRef]
- Rusu, M. E.; Fizesan, I.; Pop, A.; Mocan, A.; Gheldiu, A. M.; Babota, M.; Vodnar, D. C.; Jurj, A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Vlase, L.; Popa, D. S. Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Septum: Assessment of Bioactive Molecules and In Vitro Biological Effects. Molecules 2020, 25 (9), 2187. [CrossRef]
- Sayyah, M.; Hadidi, N.; Kamalinejad, M. Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Lactuca sativa Seed Extract in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 92 (2-3), 325–329. [CrossRef]
- Gopal, S. S.; Lakshmi, M. J.; Sharavana, G.; Sathaiah, G.; Sreerama, Y. N.; Baskaran, V. Lactucaxanthin - a Potential Anti-diabetic Carotenoid from Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) Inhibits α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Activity In Vitro and in Diabetic Rats. Food Funct. 2017, 8 (3), 1124–1131. [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Gillespie, A. L.; Calderwood, D.; Iqbal, H.; Gallagher, C.; Chevallier, O. P.; Elliott, C. T.; Pan, X.; Mirza, B.; Green, B. D. The Health Promoting Bioactivities of Lactuca sativa can be Enhanced by Genetic Modulation of Plant Secondary Metabolites. Metabolites 2019, 9 (5), 97. [CrossRef]
- Farzaei, F.; Morovati, M. R.; Farjadmand, F.; Farzaei, M. H. A Mechanistic Review on Medicinal Plants Used for Diabetes Mellitus in Traditional Persian Medicine. J. Evid.-Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2017, 22 (4), 944–955. [CrossRef]
- Assefa, A. D.; Hur, O. S.; Hahn, B. S.; Kim, B.; Ro, N. Y.; Rhee, J. H. Nutritional Metabolites of Red Pigmented Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) Germplasm and Correlations with Selected Phenotypic Characters. Foods 2021, 10 (10), 2504. [CrossRef]
- Omokhua-Uyi, A. G.; Van Staden, J. Phytomedicinal relevance of South African Cucurbitaceae species and their safety assessment: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112967. [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, R. P.; Kalariya, M.; Parmar, S. K.; Sheth, N. R. Phytochemical and pharmacological review of Lagenaria sicereria. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2010, 1 (4), 266–272. [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, S. F.; Ooi, K. L.; Supriatno. Antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of cucurbit fruit vegetables and identification of active and major constituents from phenolic-rich extracts of Lagenaria siceraria and Sechium edule. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61 (42), 10080–10090. [CrossRef]
- Roopan, S. M.; Devi Rajeswari, V.; Kalpana, V. N.; Elango, G. Biotechnology and pharmacological evaluation of Indian vegetable crop Lagenaria siceraria: an overview. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100 (3), 1153–1162. [CrossRef]
- Batool, S.; Khera, R. A.; Hanif, M. A.; Ayub, M. A. Bay Leaf. Medicinal Plants South Asia 2020, 63–74. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, R. R.; Omer, A. K.; Yener, Z.; Uyar, A.; Ahmed, A. K. Biomedical Effects of Laurus nobilis L. Leaf Extract on Vital Organs in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats: Experimental Research. Ann. Med. Surg. 2020, 61, 188–197. [CrossRef]
- USMANI, Q.; AHMAD, A.; JAMALDEEN, F. Laurus nobilis L., (Habb-ul-Ghar), A Review on Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Ethnomedicinal Uses. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2021, 11 (5), 136–144. [CrossRef]
- Heghes, S. C.; Filip, L.; Vostinaru, O.; Mogosan, C.; Miere, D.; Iuga, C. A.; Moldovan, M. Essential Oil-Bearing Plants From Balkan Peninsula: Promising Sources for New Drug Candidates for the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus and Dyslipidemia. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 989. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S. R.; Mohamed, G. A. Litchi chinensis: Medicinal Uses, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 174, 492–513. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, D.; An, X.; Duan, L.; Duan, Y.; Lian, F. Lychee Seed as a Potential Hypoglycemic Agent, and Exploration of its Underlying Mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 737803. [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Q.; Liao, X. B.; Li, X. H.; Guo, J. W.; Qu, X. L.; Li, L. M. Zhong Yao Cai = Zhongyaocai = Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials 2015, 38 (7), 1466–1471.
- Shendge, P. N.; Belemkar, S. Therapeutic Potential of Luffa acutangula: A Review on Its Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Toxicological Aspects. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1177. [CrossRef]
- Sharmin, R.; Khan, M.; Akhtar, M.; Alim, A.; Islam, M.; Anisuzzaman, A.; Ahmed, M. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Cucumber, White Pumpkin and Ridge Gourd in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Sci. Res. 2012, 5 (1), 161–170. [CrossRef]
- Hammam, W. E.; Gad, A. M.; Gad, M. K.; Kirollos, F. N.; Yassin, N. A.; Tantawi, M.; El Hawary, S. Pyrus communis L. (Pear) and Malus domestica Borkh. (Apple) Leaves Lipoidal Extracts as Sources for Beta-Sitosterol Rich Formulae and Their Wound Healing Evaluation. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Hyson, D. A. A Comprehensive Review of Apples and Apple Components and Their Relationship to Human Health. Adv. Nutr. 2011, 2 (5), 408–420. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Chen, X. Research Progress of Fruit Color Development in Apple (Malus domestica Borkh.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 267–279. [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G. The Role of Polyphenols in Modern Nutrition. Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42 (3), 226–235. [CrossRef]
- Waldbauer, K.; McKinnon, R.; Kopp, B. Apple Pomace as Potential Source of Natural Active Compounds. Planta Med. 2017, 83 (12-13), 994–1010. [CrossRef]
- Boyer, J.; Liu, R. H. Apple Phytochemicals and Their Health Benefits. Nutr. J. 2004, 3, 5. [CrossRef]
- Balasuriya, N.; Rupasinghe, H. P. Antihypertensive Properties of Flavonoid-Rich Apple Peel Extract. Food Chem. 2012, 135 (4), 2320–2325. [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, R. H. Phytochemicals of Apple Peels: Isolation, Structure Elucidation, and Their Antiproliferative and Antioxidant Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56 (21), 9905–9910. [CrossRef]
- Vasile, M.; Bunea, A.; Ioan, C. R.; Ioan, B. C.; Socaci, S.; Viorel, M. Phytochemical Content and Antioxidant Activity of Malus domestica Borkh Peel Extracts. Molecules 2021, 26 (24), 7636. [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, K.; Wu, X.; Liu, R. H. Antioxidant Activity of Apple Peels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51(3), 609–614. [CrossRef]
- Garrido, G.; González, D.; Delporte, C.; Backhouse, N.; Quintero, G.; Núñez-Sellés, A. J.; Morales, M. A. Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Mangifera indica L. Extract (Vimang). Phytother. Res. 2001, 15 (1), 18–21. [CrossRef]
- Gondi, M.; Prasada Rao, U. J. Ethanol Extract of Mango (Mangifera indica L.) Peel Inhibits α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Activities, and Ameliorates Diabetes Related Biochemical Parameters in Streptozotocin (STZ)-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52 (12), 7883–7893. [CrossRef]
- Evans, S. F.; Meister, M.; Mahmood, M.; Eldoumi, H.; Peterson, S.; Perkins-Veazie, P.; Clarke, S. L.; Payton, M.; Smith, B. J.; Lucas, E. A. Mango Supplementation Improves Blood Glucose in Obese Individuals. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2014, 7, 77–84. [CrossRef]
- Roongpisuthipong, C.; Banphotkasem, S.; Komindr, S.; Tanphaichitr, V. Postprandial Glucose and Insulin Responses to Various Tropical Fruits of Equivalent Carbohydrate Content in Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1991, 14 (2), 123–131. [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.T.; Richi, A.E.; Riju, S.A.; Jalal, T.; Orchi, R.J.; Singh, S.; Bhagat, P.; Abdel-Wahab, Y.H.A.; Ansari, P. Evaluation of Antidiabetic Potential of Mangifera indica Leaf in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Rats: Focus on Glycemic Control and Cholesterol Regulation. Endocrines 2024, 5, 137-152. [CrossRef]
- Aderibigbe, A. O.; Emudianughe, T. S.; Lawal, B. A. Evaluation of the Antidiabetic Action of Mangifera indica in Mice. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15 (5), 456–458. [CrossRef]
- Ali-Shtayeh, M. S.; Jamous, R. M.; Abu-Zaitoun, S. Y.; Khasati, A. I.; Kalbouneh, S. R. Biological Properties and Bioactive Components of Mentha spicata L. Essential Oil: Focus on Potential Benefits in the Treatment of Obesity, Alzheimer's Disease, Dermatophytosis, and Drug-Resistant Infections. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2019, 2019, 3834265. [CrossRef]
- Mahboubi, M. Mentha spicata L. Essential Oil, Phytochemistry and Its Effectiveness in Flatulence. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2018, 11 (2), 75–81. [CrossRef]
- El Hassani, F. Z. Characterization, Activities, and Ethnobotanical Uses of Mentha Species in Morocco. Heliyon 2020, 6 (11), e05480. [CrossRef]
- Stohs, S. J.; Hartman, M. J. Review of the Safety and Efficacy of Moringa oleifera. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29 (6), 796–804. [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Jimenez, M.; Almatrafi, M. M.; Fernandez, M. L. Bioactive Components in Moringa Oleifera Leaves Protect against Chronic Disease. Antioxidants 2017, 6 (4), 91. [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Sánchez, K.; Garay-Jaramillo, E.; González-Reyes, R. E. Effects of Moringa oleifera on Glycaemia and Insulin Levels: A Review of Animal and Human Studies. Nutrients 2019, 11 (12), 2907. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Khan, I.; Blundell, R. Moringa oleifera and glycemic control: A review of current evidence and possible mechanisms. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33 (11), 2841–2848. [CrossRef]
- Azad, S. B.; Ansari, P.; Azam, S.; Hossain, S. M.; Shahid, M. I.; Hasan, M.; Hannan, J. Anti-hyperglycaemic activity of Moringa oleifera is partly mediated by carbohydrase inhibition and glucose-fibre binding. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37 (3), BSR20170059. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, P.; Khan, J. T.; Soultana, M.; Hunter, L.; Chowdhury, S.; Priyanka, S. K.; Paul, S. R.; Flatt, P. R.; Abdel-Wahab, Y. H. A. Insulin Secretory Actions of Polyphenols of Momordica Charantia Regulate Glucose Homeostasis in Alloxan-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Rats. RPS Pharmacy and Pharmacology Reports 2024, 3 (1), rqae005. [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Polito, L. Momordica charantia, a Nutraceutical Approach for Inflammatory Related Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 486. [CrossRef]
- Grover, J. K.; Yadav, S. P. Pharmacological actions and potential uses of Momordica charantia: a review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 93 (1), 123–132. [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Maiello, S.; Battelli, M. G.; Bolognesi, A. Plants Producing Ribosome-Inactivating Proteins in Traditional Medicine. Molecules 2016, 21 (11), 1560. [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.; Hsu, C.; Chao, C.; Wein, Y.; Kuo, Y.; Huang, C. Fractionation and identification of 9c, 11t, 13t-conjugated linolenic acid as an activator of PPARα in bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.). J. Biomed. Sci. 2006, 13 (6), 763-772. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M. F.; El Ashry, F. E.; El Maraghy, N. N.; Fahmy, A. Studies on the antidiabetic activities of Momordica charantia fruit juice in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55 (1), 758–765. [CrossRef]
- Chandru, S.; Vishwanath, P.; Devegowda, D.; Ramasamudra, S. N.; Prashant, A.; Hathur, B. Evaluation of Protein Kinase Cβ and PPARγ Activity in Diabetic Rats Supplemented with Momordica charantia. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10 (4), BF01–BF4. [CrossRef]
- Shibib, B. A.; Khan, L. A.; Rahman, R. Hypoglycaemic activity of Coccinia indica and Momordica charantia in diabetic rats: depression of the hepatic gluconeogenic enzymes glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and elevation of both liver and red-cell shunt enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem. J. 1993, 292 (Pt 1), 267–270. [CrossRef]
- Gadang, V.; Gilbert, W.; Hettiararchchy, N.; Horax, R.; Katwa, L.; Devareddy, L. Dietary bitter melon seed increases peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ gene expression in adipose tissue, down-regulates the nuclear factor-κB expression, and alleviates the symptoms associated with metabolic syndrome. J. Med. Food 2011, 14 (1-2), 86–93. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Kong, F.; Wang, S.; Yan, C. Antidiabetic Effects of Morus alba Fruit Polysaccharides on High-Fat Diet- and Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 199, 119–127. [CrossRef]
- Morales Ramos, J. G.; Esteves Pairazamán, A. T.; Mocarro Willis, M.; Collantes Santisteban, S.; Caldas Herrera, E. Medicinal Properties of Morus alba for the Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review. F1000Research 2021, 10, 1022. [CrossRef]
- Chan, E. W.; Lye, P. Y.; Wong, S. K. Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Clinical Trials of Morus alba. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14 (1), 17–30. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Yang, H.; Ke, X. X.; Cui, H. J. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi = China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica 2022, 47 (9), 2373–2391. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, B.; Zeng, G.; Tan, J.; He, X.; Hu, C.; Zhou, Y. Chemical Constituents of Morus alba L. and Their Inhibitory Effect on 3T3-L1 Preadipocyte Proliferation and Differentiation. Fitoterapia 2014, 98, 222–227. [CrossRef]
- Husna, F.; Suyatna, F. D.; Arozal, W.; Poerwaningsih, E. H. Anti-Diabetic Potential of Murraya Koenigii (L.) and its Antioxidant Capacity in Nicotinamide-Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rats. Drug Res. 2018, 68 (11), 631–636. [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, R.; Vijayraja, D.; Jo, S. H.; Ganesan, P.; Su-Kim, I.; Choi, D. K. Medicinal Profile, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Activities of Murraya koenigii and its Primary Bioactive Compounds. Antioxidants (Basel, Switz.) 2020, 9 (2), 101. [CrossRef]
- Arulselvan, P.; Subramanian, S. P. Beneficial Effects of Murraya koenigii Leaves on Antioxidant Defense System and Ultrastructural Changes of Pancreatic Beta-Cells in Experimental Diabetes in Rats. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2007, 165 (2), 155–164. [CrossRef]
- Abeysinghe, D. T.; Alwis, D.; Kumara, K.; Chandrika, U. G. Nutritive Importance and Therapeutics Uses of Three Different Varieties (Murraya koenigii, Micromelum minutum, and Clausena indica) of Curry Leaves: An Updated Review. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 5523252. [CrossRef]
- Barman, R.; Bora, P. K.; Saikia, J.; Kemprai, P.; Saikia, S. P.; Haldar, S.; Banik, D. Nutmegs and Wild Nutmegs: An Update on Ethnomedicines, Phytochemicals, Pharmacology, and Toxicity of the Myristicaceae Species. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35 (9), 4632–4659. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P. H.; Le, T. V.; Kang, H. W.; Chae, J.; Kim, S. K.; Kwon, K. I.; Seo, D. B.; Lee, S. J.; Oh, W. K. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activators from Myristica fragrans (nutmeg) and their anti-obesity effect. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20 (14), 4128–4131. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Song, F.; Hu, D.; Chen, H.; Zhai, Q.; Lu, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Gu, Z.; Wang, G. The Protective Effect of Myristica fragrans Houtt. Extracts Against Obesity and Inflammation by Regulating Free Fatty Acids Metabolism in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12 (9), 2507. [CrossRef]
- Arulmozhi, D.; Kurian, R.; Veeranjaneyulu, A.; Bodhankar, S. Antidiabetic and Antihyperlipidemic Effects of Myristica fragrans in Animal Models. Pharmaceutical Biol. 2007, 45 (1), 64-68. [CrossRef]
- Ali, B. H.; Blunden, G. Pharmacological and Toxicological Properties of Nigella sativa. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17 (4), 299–305. [CrossRef]
- Tiji, S.; Bouhrim, M.; Addi, M.; Drouet, S.; Lorenzo, J. M.; Hano, C.; Bnouham, M.; Mimouni, M. Linking the Phytochemicals and the α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Enzyme Inhibitory Effects of Nigella sativa Seed Extracts. Foods 2021, 10 (8), 1818. [CrossRef]
- Hannan, J. M. A.; Ansari, P.; Haque, A.; Sanju, A.; Huzaifa, A.; Rahman, A.; Ghosh, A.; Azam, S. Nigella Sativa Stimulates Insulin Secretion from Isolated Rat Islets and Inhibits the Digestion and Absorption of (CH2O)n in the Gut. Bioscience Reports 2019, 39 (8), BSR20190723. [CrossRef]
- Kooti, W.; Hasanzadeh-Noohi, Z.; Sharafi-Ahvazi, N.; Asadi-Samani, M.; Ashtary-Larky, D. Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, and Therapeutic Uses of Black Seed (Nigella sativa). Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14 (10), 732–745. [CrossRef]
- Mohebbati, R.; Abbasnezhad, A. Effects of Nigella sativa on Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 252, 112585. [CrossRef]
- Baliga, M. S.; Jimmy, R.; Thilakchand, K. R.; Sunitha, V.; Bhat, N. R.; Saldanha, E.; Rao, S.; Rao, P.; Arora, R.; Palatty, P. L. Ocimum sanctum L (Holy Basil or Tulsi) and Its Phytochemicals in the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Nutrition and Cancer 2013, 65 (Suppl 1), 26–35. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M. M. Tulsi - Ocimum sanctum: A Herb for All Reasons. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine 2014, 5 (4), 251–259. [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, P.; Behera, P.; Das, D.; Panda, S. K. Ocimum sanctum Linn. A Reservoir Plant for Therapeutic Applications: An Overview. Pharmacognosy Reviews 2010, 4 (7), 95–105. [CrossRef]
- P, S.; Zinjarde, S. S.; Bhargava, S. Y.; Kumar, A. R. Potent α-Amylase Inhibitory Activity of Indian Ayurvedic Medicinal Plants. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2011, 11, 5. [CrossRef]
- Bendini, A.; Cerretani, L.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Gómez-Caravaca, A. M.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Lercker, G. Phenolic Molecules in Virgin Olive Oils: A Survey of Their Sensory Properties, Health Effects, Antioxidant Activity and Analytical Methods. An Overview of the Last Decade. Molecules 2007, 12 (8), 1679–1719. [CrossRef]
- Guex, C. G.; Reginato, F. Z.; de Jesus, P. R.; Brondani, J. C.; Lopes, G.; Bauermann, L. F. Antidiabetic Effects of Olea europaea L. Leaves in Diabetic Rats Induced by High-Fat Diet and Low-Dose Streptozotocin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, M. A.; Khan, A.; Hanif, M.; Farooq, U.; Perveen, S. Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology of Olea europaea (Olive). Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 541591. [CrossRef]
- Gouvinhas, I.; Machado, N.; Sobreira, C.; Domínguez-Perles, R.; Gomes, S.; Rosa, E.; Barros, A. Critical Review on the Significance of Olive Phytochemicals in Plant Physiology and Human Health. Molecules 2017, 22 (11), 1986. [CrossRef]
- Samarji, R.; Balbaa, M. Anti-diabetic Activity of Different Oils through Their Effect on Arylsulfatases. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2014, 13 (1), 116. [CrossRef]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Lampousi, A. M.; Portillo, M. P.; Romaguera, D.; Hoffmann, G.; Boeing, H. Olive Oil in the Prevention and Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies and Intervention Trials. Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7 (4), e262. [CrossRef]
- Taleb, M. H.; Abdeltawab, N. F.; Shamma, R. N.; Abdelgayed, S. S.; Mohamed, S. S.; Farag, M. A.; Ramadan, M. A. Origanum vulgare L. Essential Oil as a Potential Anti-Acne Topical Nanoemulsion-In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Molecules (Basel, Switz.) 2018, 23 (9), 2164. [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, G.; Maggini, V.; Maida, I.; Lo Nostro, A.; Calonico, C.; Sassoli, C.; Perrin, E.; Fondi, M.; Mengoni, A.; Chiellini, C.; Vannacci, A.; Gallo, E.; Gori, L.; Bogani, P.; Bilia, A. R.; Campana, S.; Ravenni, N.; Dolce, D.; Firenzuoli, F.; Fani, R. Essential Oil from Origanum vulgare Completely Inhibits the Growth of Multidrug-Resistant Cystic Fibrosis Pathogens. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11 (6), 861–864.
- Yu, H.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Liang, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, Y. Hypoglycemic Activity of Origanum vulgare L. and Its Main Chemical Constituents Identified with HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS. Food Funct. 2021, 12 (6), 2580–2590. [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, B.; Sahoo, N.; Sahoo, S. K. Trends in Diabetes Care with Special Emphasis to Medicinal Plants: Advancement and Treatment. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 33, 102014. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, I.; Silva-Espinoza, B. A.; Ortega-Ramirez, L. A.; Leyva, J. M.; Siddiqui, M. W.; Cruz-Valenzuela, M. R.; Gonzalez-Aguilar, G. A.; Ayala-Zavala, J. F. Oregano Essential Oil as an Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Additive in Food Products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56 (10), 1717–1727. [CrossRef]
- De Faveri, A.; De Faveri, R.; Broering, M. F.; Bousfield, I. T.; Goss, M. J.; Muller, S. P.; Pereira, R. O.; de Oliveira E Silva, A. M.; Machado, I. D.; Quintão, N.; Santin, J. R. Effects of Passion Fruit Peel Flour (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa O. Deg.) in Cafeteria Diet-Induced Metabolic Disorders. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 250, 112482. [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Luan, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Fang, J.; Wang, M.; Zuo, M.; Li, Y. Passiflora edulis: An Insight Into Current Researches on Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 617. [CrossRef]
- De Faveri, A.; De Faveri, R.; Broering, M. F.; Bousfield, I. T.; Goss, M. J.; Muller, S. P.; Pereira, R. O.; de Oliveira E Silva, A. M.; Machado, I. D.; Quintão, N.; Santin, J. R. Effects of Passion Fruit Peel Flour (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa O. Deg.) in Cafeteria Diet-Induced Metabolic Disorders. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 250, 112482. [CrossRef]
- Kitada, M.; Ogura, Y.; Maruki-Uchida, H.; Sai, M.; Suzuki, T.; Kanasaki, K.; Hara, Y.; Seto, H.; Kuroshima, Y.; Monno, I.; Koya, D. The Effect of Piceatannol from Passion Fruit (Passiflora edulis) Seeds on Metabolic Health in Humans. Nutrients 2017, 9 (10), 1142. [CrossRef]
- Uchida-Maruki, H.; Inagaki, H.; Ito, R.; Kurita, I.; Sai, M.; Ito, T. Piceatannol lowers the blood glucose level in diabetic mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38 (4), 629–633. [CrossRef]
- Silva, R. O.; Damasceno, S. R.; Brito, T. V.; Dias, J. M.; Fontenele, A. M.; Braúna, I. S.; Júnior, J. S.; Maciel, J. S.; de Paula, R. C.; Ribeiro, R. A.; Souza, M. H.; Freitas, A. L.; Medeiros, J. V.; Silva, D. C.; Barbosa, A. L. Polysaccharide fraction isolated from Passiflora edulis inhibits the inflammatory response and the oxidative stress in mice. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67 (7), 1017–1027. [CrossRef]
- Dzotam, J. K.; Touani, F. K.; Kuete, V. Antibacterial and antibiotic-modifying activities of three food plants (Xanthosoma mafaffa Lam., Moringa oleifera (L.) Schott and Passiflora edulis Sims) against multidrug-resistant (MDR) Gram-negative bacteria. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 9. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. J.; Zhou, T.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. J.; Zheng, J.; Xu, D. P.; Li, H. B. The Effects of Syzygium samarangense, Passiflora edulis and Solanum muricatum on Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17 (10), 1616. [CrossRef]
- Panelli, M. F.; Pierine, D. T.; de Souza, S.; Ferron, A.; Garcia, J. L.; Santos, K.; Belin, M.; Lima, G.; Borguini, M. G.; Minatel, I. O.; Cicogna, A. C.; Francisqueti, F. V.; Corrêa, C. R. Bark of Passiflora edulis Treatment Stimulates Antioxidant Capacity, and Reduces Dyslipidemia and Body Fat in db/db Mice. Antioxidants (Basel, Switz.) 2018, 7 (9), 120. [CrossRef]
- Dreher, M. L.; Davenport, A. J. Hass Avocado Composition and Potential Health Effects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53 (7), 738–750. [CrossRef]
- Lima, C. R.; Vasconcelos, C. F.; Costa-Silva, J. H.; Maranhão, C. A.; Costa, J.; Batista, T. M.; Carneiro, E. M.; Soares, L. A.; Ferreira, F.; Wanderley, A. G. Anti-Diabetic Activity of Extract from Persea americana Mill. Leaf via the Activation of Protein Kinase B (PKB/Akt) in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141 (1), 517–525. [CrossRef]
- Ojo, O. A.; Amanze, J. C.; Oni, A. I.; Grant, S.; Iyobhebhe, M.; Elebiyo, T. C.; Rotimi, D.; Asogwa, N. T.; Oyinloye, B. E.; Ajiboye, B. O.; Ojo, A. B. Antidiabetic Activity of Avocado Seeds (Persea americana Mill.) in Diabetic Rats via Activation of PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12 (1), 2919. [CrossRef]
- Ezejiofor, A. N.; Okorie, A.; Orisakwe, O. E. Hypoglycaemic and Tissue-Protective Effects of the Aqueous Extract of Persea americana Seeds on Alloxan-Induced Albino Rats. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 20 (5), 31–39. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24643349/.
- Kouamé, N. M.; Koffi, C.; N'Zoué, K. S.; Yao, N.; Doukouré, B.; Kamagaté, M. Comparative Antidiabetic Activity of Aqueous, Ethanol, and Methanol Leaf Extracts of Persea americana and Their Effectiveness in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 5984570. [CrossRef]
- Farzaei, M. H.; Abbasabadi, Z.; Ardekani, M. R.; Rahimi, R.; Farzaei, F. Parsley: A Review of Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry and Biological Activities. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 33 (6), 815–826. [CrossRef]
- Ozsoy-Sacan, O.; Yanardag, R.; Orak, H.; Ozgey, Y.; Yarat, A.; Tunali, T. Effects of Parsley (Petroselinum crispum) Extract versus Glibornuride on the Liver of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 104 (1-2), 175–181. [CrossRef]
- Abou Khalil, N. S.; Abou-Elhamd, A. S.; Wasfy, S. I.; El Mileegy, I. M.; Hamed, M. Y.; Ageely, H. M. Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Impacts of Desert Date (Balanites aegyptiaca) and Parsley (Petroselinum sativum) Aqueous Extracts: Lessons from Experimental Rats. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 8408326. [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.; Hussain, S.; Malik, F. Critique of Medicinal Conspicuousness of Parsley (Petroselinum crispum): A Culinary Herb of Mediterranean Region. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 27 (1), 193–202.
- Almuaigel, M. F.; Seif, M. A.; Albuali, H. W.; Alharbi, O.; Alhawash, A. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of aqueous extract of Phaseolus vulgaris pods in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 742–746. [CrossRef]
- Sutedja, A. M.; Yanase, E.; Batubara, I.; Fardiaz, D.; Lioe, H. N. Antidiabetic components from the hexane extract of red kidney beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): isolation and structure determination. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2020, 84 (3), 598–605. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Leng, X.; Duan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, Z.; Min, S.; Wei, D.; Wang, X. Functional component isolated from Phaseolus vulgaris lectin exerts in vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity through potentiation of apoptosis and immunomodulation. Molecules 2021, 26 (2), 498. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Teng, C.; Yao, Y.; Ren, G.; Richel, A. Anti-obesity effects of α-amylase inhibitor enriched-extract from white common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) associated with the modulation of gut microbiota composition in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Food Funct. 2020, 11 (2), 1624–1634. [CrossRef]
- Alhaider, I. A.; Mohamed, M. E.; Ahmed, K.; Kumar, A. Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera) Fruits as a Potential Cardioprotective Agent: The Role of Circulating Progenitor Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 592. [CrossRef]
- Mia, M. A.; Mosaib, M. G.; Khalil, M. I.; Islam, M. A.; Gan, S. H. Potentials and Safety of Date Palm Fruit against Diabetes: A Critical Review. Foods 2020, 9 (11), 1557. [CrossRef]
- El Abed, H.; Chakroun, M.; Fendri, I.; Makni, M.; Bouaziz, M.; Drira, N.; Mejdoub, H.; Khemakhem, B. Extraction Optimization and In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Postprandial Hyperglycemia Effects of Inhibitor from Phoenix dactylifera L. Parthenocarpic Fruit. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 835–843. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z. X.; Shi, L. E.; Aleid, S. M. Date Fruit: Chemical Composition, Nutritional and Medicinal Values, Products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93 (10), 2351–2361. [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Sharma, N.; Oladeji, O. S.; Sourirajan, A.; Dev, K.; Zengin, G.; El-Shazly, M.; Kumar, V. Traditional Uses, Bioactive Composition, Pharmacology, and Toxicology of Phyllanthus emblica Fruits: A Comprehensive Review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114570. [CrossRef]
- Gaire, B.; Subedi, L. Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Medicinal Properties of Phyllanthus emblica Linn. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Krishnaveni, M.; Mirunalini, S. Therapeutic Potential of Phyllanthus emblica (Amla): The Ayurvedic Wonder. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 21 (1), 93–105. [CrossRef]
- Huang, H. Z.; Qiu, M.; Lin, J. Z.; Li, M. Q.; Ma, X. T.; Ran, F.; Luo, C. H.; Wei, X. C.; Xu, R. C.; Tan, P.; Fan, S. H.; Yang, M.; Han, L.; Zhang, D. K. Potential Effect of Tropical Fruits Phyllanthus emblica L. for the Prevention and Management of Type 2 Diabetic Complications: A Systematic Review of Recent Advances. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60 (7), 3525–3542. [CrossRef]
- Fazal, F.; Mane, P. P.; Rai, M. P.; Thilakchand, K. R.; Bhat, H. P.; Kamble, P. S.; Palatty, P. L.; Baliga, M. S. The Phytochemistry, Traditional Uses and Pharmacology of Piper Betel Linn (Betel Leaf): A Pan-Asiatic Medicinal Plant. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 2014, Advance online publication. [CrossRef]
- Santhakumari, P.; Prakasam, A.; Pugalendi, K. V. Antihyperglycemic Activity of Piper betle Leaf on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Journal of Medicinal Food 2006, 9 (1), 108–112. [CrossRef]
- Nayaka, N.; Sasadara, M.; Sanjaya, D. A.; Yuda, P.; Dewi, N.; Cahyaningsih, E.; Hartati, R. Piper betle (L): Recent Review of Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties, Safety Profiles, and Commercial Applications. Molecules 2021, 26(8), 2321. [CrossRef]
- Arambewela, L. S.; Arawwawala, L. D.; Ratnasooriya, W. D. Antidiabetic Activities of Aqueous and Ethanolic Extracts of Piper betle Leaves in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 102(2), 239–245. [CrossRef]
- Zilani, M. N.; Sultana, T.; Asabur Rahman, S. M.; Anisuzzman, M.; Islam, M. A.; Shilpi, J. A.; Hossain, M. G. Chemical composition and pharmacological activities of Pisum sativum. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17 (1), 171. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Sharma, A. K.; Dobhal, M. P.; Sharma, M. C.; Gupta, R. S. Antidiabetic and antioxidant potential of β-sitosterol in streptozotocin-induced experimental hyperglycemia. J. Diabetes 2011, 3 (1), 29–37. [CrossRef]
- Fatima, N.; Hafizur, R. M.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S.; Nisar, M.; Kabir, N. Ellagic acid in Emblica officinalis exerts anti-diabetic activity through the action on β-cells of pancreas. Eur. J. Nutr. 2016, 56 (2), 591–601. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. P.; Qian, Y. F.; Qin, G. Y.; Zhao, L. Y.; Chen, G. T. Antidiabetic activities of glycoprotein from pea (Pisum sativum L.) in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12 (11), 5087–5095. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Chhajed, M.; Arora, S.; Thakur, G.; Gupta, R. Medicinal Value of Apricot: A Review. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 80 (5). [CrossRef]
- Al-Soufi, M.; Alshwyeh, H.; Alqahtani, H.; Al-Zuwaid, S.; Al-Ahmed, F.; Al-Abdulaziz, F. et al. A Review with Updated Perspectives on Nutritional and Therapeutic Benefits of Apricot and the Industrial Application of Its Underutilized Parts. Molecules 2022, 27 (15), 5016. [CrossRef]
- Raafat, K.; El-Darra, N.; Saleh, F. A.; Rajha, H. N.; Maroun, R. G.; Louka, N. Infrared-Assisted Extraction and HPLC-Analysis of Prunus armeniaca L. Pomace and Detoxified-Kernel and Their Antidiabetic Effects. Phytochem. Anal. 2018, 29 (2), 156–167. [CrossRef]
- Egbekun, M. K.; Akowe, J. I.; Ede, R. J. Physico-Chemical and Sensory Properties of Formulated Syrup from Black Plum (Vitex doniana) Fruit. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1996, 49 (4), 301–306. [CrossRef]
- Lombardi-Boccia, G.; Lucarini, M.; Lanzi, S.; Aguzzi, A.; Cappelloni, M. Nutrients and Antioxidant Molecules in Yellow Plums (Prunus domestica L.) from Conventional and Organic Productions: A Comparative Study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52 (1), 90–94. [CrossRef]
- Bouayed, J.; Rammal, H.; Dicko, A.; Younos, C.; Soulimani, R. Chlorogenic Acid, a Polyphenol from Prunus domestica (Mirabelle), with Coupled Anxiolytic and Antioxidant Effects. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 262 (1-2), 77–84. [CrossRef]
- Tinker, L. F.; Schneeman, B. O.; Davis, P. A.; Gallaher, D. D.; Waggoner, C. R. Consumption of Prunes as a Source of Dietary Fiber in Men with Mild Hypercholesterolemia. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53 (5), 1259–1265. [CrossRef]
- Birari, R. B.; Bhutani, K. K. Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors from Natural Sources: Unexplored Potential. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12 (19-20), 879–889. [CrossRef]
- Youssef, F. S.; Ashour, M. L.; El-Beshbishy, H. A.; Ahmed Hamza, A.; Singab, A.; Wink, M. Pinoresinol-4-O-β-D-Glucopyranoside: A Lignan from Prunes (Prunus domestica) Attenuates Oxidative Stress, Hyperglycemia and Hepatic Toxicity In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72 (12), 1830–1839. [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. H.; Huang, K. J.; Weng, C. F.; Shiuan, D. Exploration of Natural Product Ingredients as Inhibitors of Human HMG-CoA Reductase through Structure-Based Virtual Screening. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 3313–3324. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Sommella, E.; Santarcangelo’, C.; D'Avino, D.; Rossi, A.; Dacrema, M.; Minno, A. D.; Di Matteo, G.; Mannina, L.; Campiglia, P.; Magni, P.; Daglia, M. Hydroethanolic Extract of Prunus domestica L.: Metabolite Profiling and In Vitro Modulation of Molecular Mechanisms Associated to Cardiometabolic Diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14 (2), 340. [CrossRef]
- Karimi, Z.; Firouzi, M.; Dadmehr, M.; Javad-Mousavi, S. A.; Bagheriani, N.; Sadeghpour, O. Almond as a nutraceutical and therapeutic agent in Persian medicine and modern phytotherapy: A narrative review. Phytotherapy Research 2021, 35 (6), 2997–3012. [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Vo, P.; Furuyashiki, T.; Kamasaka, H.; Kuriki, T. Co-ingestion of whole almonds and almond oil with carbohydrate suppresses postprandial glycaemia in mice in an insulin-dependent and insulin-independent manner. J. Nutr. Sci. 2019, 8, e25. [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Kim, K. W.; Lee, S.; Jo, C.; Lee, K.; Ham, I.; Choi, H. Y. Endothelium-Dependent Vasorelaxant Effect of Prunus persica Branch on Isolated Rat Thoracic Aorta. Nutrients 2019, 11 (8), 1816. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Qi, Y.; Kim, R.; Song, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, H. Y.; Jang, D. S.; Kang, K. S. Methyl Caffeate Isolated from the Flowers of Prunus persica (L.) Batsch Enhances Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion. Biomolecules 2021, 11 (2), 279. [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, P.; Wojdyło, A.; Laskowski, P. Inhibitory Potential against Digestive Enzymes Linked to Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes and Content of Bioactive Compounds in 20 Cultivars of the Peach Fruit Grown in Poland. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2018, 73 (4), 314–320. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Su, M.; Du, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Ye, Z. Comparison of Phytochemical Differences of the Pulp of Different Peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] Cultivars with Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity Variations in China Using UPLC-Q-TOF/MS. Molecules 2019, 24 (10), 1968. [CrossRef]
- Bagri, P.; Ali, M.; Aeri, V.; Bhowmik, M.; Sultana, S. Antidiabetic effect of Punica granatum flowers: effect on hyperlipidemia, pancreatic cells lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in experimental diabetes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47 (1), 50–54. [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Barman, S. Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic effects of ethanolic extract of leaves of Punica granatum in alloxan-induced non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus albino rats. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2012, 44 (2), 219–224. [CrossRef]
- Fourati, M.; Smaoui, S.; Hlima, H. B.; Elhadef, K.; Braïek, O. B.; Ennouri, K.; Mtibaa, A. C.; Mellouli, L. Bioactive Compounds and Pharmacological Potential of Pomegranate (Punica granatum)–Seeds - A Review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2020, 75 (4), 477–486. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Thanh, H.; Thi Huyen, N.; Van Khanh, N.; Kim Thu, D.; Thanh Tung, B. Phytochemicals and antidiabetic activity of the aqueous extract of the Punica granatum fruit in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 30 (4), 10.1515/jbcpp-2019-0061. [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, R. M.; Mitchell, S.; Solis, R. V. Psidium guajava: A Review of Its Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117 (1), 1–27. [CrossRef]
- Paoli, P.; Cirri, P.; Caselli, A.; Ranaldi, F.; Bruschi, G.; Santi, A.; Camici, G. The Insulin-Mimetic Effect of Morin: A Promising Molecule in Diabetes Treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830 (4), 3102–3111. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, C.; Torres, N.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J. A.; Noriega, L. G.; Torre-Villalvazo, I.; Leal-Díaz, A. M.; Antunes-Ricardo, M.; Márquez-Mota, C.; Ordaz, G.; Chavez-Santoscoy, R. A.; Serna-Saldivar, S. O.; Tovar, A. R. The Effect of Isorhamnetin Glycosides Extracted from Opuntia ficus-indica in a Mouse Model of Diet-Induced Obesity. Food Funct. 2015, 6 (3), 805–815. [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, Y.; Miyazaki, K. Anti-Hyperglycemic and Anti-Hyperlipidemic Effects of Guava Leaf Extract. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 7, 9. [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Xie, L.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, W.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, F. Aqueous Extract of Guava (Psidium guajava L.) Leaf Ameliorates Hyperglycemia by Promoting Hepatic Glycogen Synthesis and Modulating Gut Microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 907702. [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Peng, B.; Wei, W.; Tian, X.; Wu, Z. Antioxidant and Anti-Diabetic Activities of Polysaccharides from Guava Leaves. Molecules 2019, 24 (7), 1343. [CrossRef]
- Morais-Braga, M. F.; Carneiro, J. N.; Machado, A. J.; Dos Santos, A. T.; Sales, D. L.; Lima, L. F.; Figueredo, F. G.; Coutinho, H. D. Psidium guajava L., from Ethnobiology to Scientific Evaluation: Elucidating Bioactivity against Pathogenic Microorganisms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 1140–1152. [CrossRef]
- Díaz-de-Cerio, E.; Verardo, V.; Gómez-Caravaca, A. M.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Health Effects of Psidium guajava L. Leaves: An Overview of the Last Decade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18 (4), 897. [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Garbanzo, C.; Zimmermann, B. F.; Schulze-Kaysers, N.; Schieber, A. Characterization of Phenolic and Other Polar Compounds in Peel and Flesh of Pink Guava (Psidium guajava ‘Criolla’) by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array and Mass Spectrometric Detection. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100 (Pt 3), 445–453. [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Chatterji, S.; Mehta, S.; Rai, P. K.; Singh, R. K.; Yadav, D. K.; Watal, G. Antidiabetic Effect of Raphanus sativus Root Juice. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49 (1), 32–37. [CrossRef]
- Banihani, S. A. Radish (Raphanus sativus) and Diabetes. Nutrients 2017, 9 (9), 1014. [CrossRef]
- Gamba, M.; Asllanaj, E.; Raguindin, P.; Glisic, M.; Franco, O.; Minder, B.; et al. Nutritional and Phytochemical Characterization of Radish (Raphanus sativus): A Systematic Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 205–218. [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, P. R.; Barnes, D. M. Phytochemical Composition and Biological Activity of 8 Varieties of Radish (Raphanus sativus L.) Sprouts and Mature Taproots. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76 (1), C185–C192. [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, J. P.; Johnson, J. J. Rosemary (Salvia rosmarinus): Health-Promoting Benefits and Food Preservative Properties. Int. J. Nutr. 2021, 6 (4), 1–10.
- de Macedo, L. M.; Santos, É.; Militão, L.; Tundisi, L. L.; Ataide, J. A.; Souto, E. B.; Mazzola, P. G. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L., syn Salvia rosmarinus Spenn.) and Its Topical Applications: A Review. Plants (Basel, Switz.) 2020, 9 (5), 651. [CrossRef]
- Bao, T. Q.; Li, Y.; Qu, C.; Zheng, Z. G.; Yang, H.; Li, P. Antidiabetic Effects and Mechanisms of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and Its Phenolic Components. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48 (6), 1353–1368. [CrossRef]
- Jayanthy, G.; Roshana Devi, V.; Ilango, K.; Subramanian, S. P. Rosmarinic Acid Mediates Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Insulin Resistant Skeletal Muscle Through Activation of AMPK. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118 (7), 1839–1848. [CrossRef]
- Naimi, M.; Vlavcheski, F.; Shamshoum, H.; Tsiani, E. Rosemary Extract as a Potential Anti-Hyperglycemic Agent: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Nutrients 2017, 9 (9), 968. [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, J. P.; Johnson, J. J. Rosemary (Salvia rosmarinus): Health-promoting benefits and food preservative properties. Int. J. Nutr. 2021, 6 (4), 1–10.
- Altinier, G.; Sosa, S.; Aquino, R. P.; Mencherini, T.; Della Loggia, R.; Tubaro, A. Characterization of Topical Antiinflammatory Compounds in Rosmarinus officinalis L. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55 (5), 1718–1723. [CrossRef]
- Kaume, L.; Howard, L. R.; Devareddy, L. The Blackberry Fruit: A Review on Its Composition and Chemistry, Metabolism and Bioavailability, and Health Benefits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60 (23), 5716–5727. [CrossRef]
- Gowd, V.; Bao, T.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zheng, X.; Cui, S.; Chen, W. Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activity of Blackberry after Gastrointestinal Digestion and Human Gut Microbiota Fermentation. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 618–627. [CrossRef]
- Rambaran, T. F.; Nembhard, N.; Bowen-Forbes, C. S.; Alexander-Lindo, R. L. Hypoglycemic Effect of the Fruit Extracts of Two Varieties of Rubus rosifolius. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44 (9), e13365. [CrossRef]
- Stefănuţ, M. N.; Căta, A.; Pop, R.; Tănasie, C.; Boc, D.; Ienaşcu, I.; Ordodi, V. Anti-Hyperglycemic Effect of Bilberry, Blackberry and Mulberry Ultrasonic Extracts on Diabetic Rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2013, 68 (4), 378–384. [CrossRef]
- Knez Hrnčič, M.; Ivanovski, M.; Cör, D.; Knez, Ž. Chia Seeds (Salvia hispanica L.): An Overview-Phytochemical Profile, Isolation Methods, and Application. Molecules 2019, 25 (1), 11. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Nadeem, M.; Khalique, A.; Imran, M.; Mehmood, S.; Javid, A.; Hussain, J. Nutritional and Therapeutic Perspectives of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.): A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53 (4), 1750–1758. [CrossRef]
- Alwosais, E.; Al-Ozairi, E.; Zafar, T. A.; Alkandari, S. Chia Seed (Salvia hispanica L.) Supplementation to the Diet of Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Improved Systolic Blood Pressure: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutr. Health 2021, 27 (2), 181–189. [CrossRef]
- Sosa Crespo, I.; Laviada Molina, H.; Chel Guerrero, L.; Ortiz Andrade, R.; Betancur Ancona, D. Efecto Inhibitorio de Fracciones Peptídicas Derivadas de la Hidrólisis de Semillas de Chía (Salvia hispanica) sobre las Enzimas α-Amilasa y α-Glucosidasa [Inhibitory Effect of Peptide Fractions Derivatives from Chia (Salvia hispanica) Hydrolysis Against α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Enzymes]. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35 (4), 928–935. [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Nadeem, M.; Khalique, A.; Imran, M.; Mehmood, S.; Javid, A.; Hussain, J. Nutritional and Therapeutic Perspectives of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.): A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53 (4), 1750–1758. [CrossRef]
- Mili, A.; Das, S.; Nandakumar, K.; Lobo, R. A Comprehensive Review on Sesamum indicum L.: Botanical, Ethnopharmacological, Phytochemical, and Pharmacological Aspects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 281, 114503. [CrossRef]
- Sankar, D.; Ali, A.; Sambandam, G.; Rao, R. Sesame Oil Exhibits Synergistic Effect with Anti-diabetic Medication in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30 (3), 351–358. [CrossRef]
- Jeng, K.; Hou, R. Sesamin and Sesamolin: Natures Therapeutic Lignans. Curr. Enzyme Inhib. 2005, 1 (1), 11-20. [CrossRef]
- Yargholi, A.; Najafi, M. H.; Zareian, M. A.; Hawkins, J.; Shirbeigi, L.; Ayati, M. H. The Effects of Sesame Consumption on Glycemic Control in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trial. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 2873534. [CrossRef]
- Aslam, F.; Iqbal, S.; Nasir, M.; Anjum, A. A. White Sesame Seed Oil Mitigates Blood Glucose Level, Reduces Oxidative Stress, and Improves Biomarkers of Hepatic and Renal Function in Participants with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38 (3), 235–246. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y. C.; Thùy, T. D.; Wang, S. Y.; Huang, P. L. Type 1 diabetes, cardiovascular complications and sesame (zhī má). J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2014, 4 (1), 36–41. [CrossRef]
- Blum, A.; Monir, M.; Wirsansky, I.; Ben-Arzi, S. The Beneficial Effects of Tomatoes. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 16 (6), 402–404. [CrossRef]
- Fukushi, Y.; Mariya, Y.; Yamada, K.; Yoshida, K.; Sasa, A.; Saito, H.; Hirai, A.; Suzuki, S.; Aizawa, K.; Suganuma, H.; Itaki, C. Tomato Juice Consumption Could Improve Breast Skin Adverse Effects of Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients. In Vivo 2020, 34 (5), 3013–3021. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Chen, B.; Bai, Y.; Miao, T.; Rui, L.; Zhang, H.; Xia, B.; Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Wang, X. D.; Zhang, D. Lycopene in Protection Against Obesity and Diabetes: A Mechanistic Review. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104966. [CrossRef]
- Ali, M. Y.; Sina, A. A.; Khandker, S. S.; Neesa, L.; Tanvir, E. M.; Kabir, A.; Khalil, M. I.; Gan, S. H. Nutritional Composition and Bioactive Compounds in Tomatoes and Their Impact on Human Health and Disease: A Review. Foods 2020, 10 (1), 45. [CrossRef]
- Ford, E. S.; Will, J. C.; Bowman, B. A.; Narayan, K. M. Diabetes Mellitus and Serum Carotenoids: Findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 149 (2), 168–176. [CrossRef]
- Toor, R. K.; Lister, C. E.; Savage, G. P. Antioxidant Activities of New Zealand-Grown Tomatoes. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 56 (8), 597–605. [CrossRef]
- Collins, E. J.; Bowyer, C.; Tsouza, A.; Chopra, M. Tomatoes: An Extensive Review of the Associated Health Impacts of Tomatoes and Factors That Can Affect Their Cultivation. Biology 2022, 11 (2), 239. [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, P. R.; Galvão, A. M.; Batista, C. M.; Azevedo, G. S.; Oliveira, R. D.; Lamounier, R. P.; Freire, N.; Barros, A. M.; Sakurai, E.; Oliveira, J. P.; Vieira, E. C.; Alvarez-Leite, J. I. Eggplant (Solanum melongena) Infusion Has a Modest and Transitory Effect on Hypercholesterolemic Subjects. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2000, 33 (9), 1027–1036. [CrossRef]
- Yarmohammadi, F.; Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Effect of Eggplant (Solanum melongena) on the Metabolic Syndrome: A Review. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 24 (4), 420–427. [CrossRef]
- Gürbüz, N.; Uluişik, S.; Frary, A.; Frary, A.; Doğanlar, S. Health Benefits and Bioactive Compounds of Eggplant. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 602–610. [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Koyama, M.; Tian, S.; Watanabe, M.; Takahashi, A.; Miyatake, K.; Nakamura, K. Antihypertensive Effects of Orally Administered Eggplant (Solanum melongena) Rich in Acetylcholine on Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 376–382. [CrossRef]
- Das, J.; Lahan, J. P.; Srivastava, R. B. Solanum melongena: A Potential Source of Antifungal Agent. Indian J. Microbiol. 2010, 50 (Suppl 1), 62–69. [CrossRef]
- Otari, K. V.; Gaikwad, P. S.; Shete, R. V.; Upasani, C. D. Protective Effect of Aqueous Extract of Spinacia oleracea Leaves in Experimental Paradigms of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflammopharmacology 2012, 20 (5), 277–287. [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Pérez, R.; Cano-Martínez, A.; Gutiérrez-Velázquez, E.; Martínez-Rosas, M.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, R. M.; Jiménez-Gómez, F.; Flores-Estrada, J. Spinach Methanolic Extract Attenuates the Retinal Degeneration in Diabetic Rats. Antioxidants 2021, 10 (5), 717. [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yang, X. Effects of Spinach Nitrate on Insulin Resistance, Endothelial Dysfunction Markers and Inflammation in Mice with High-Fat and High-Fructose Consumption. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 32010. [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J. L.; Moreau, R. Functional Properties of Spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) Phytochemicals and Bioactives. Food Funct. 2016, 7 (8), 3337–3353. [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, R.; Velazquez, E. G.; Carrera, S. Spinacia oleracea Linn Considered as One of the Most Perfect Foods: A Pharmacological and Phytochemical Review. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19 (20), 1666–1680. [CrossRef]
- Nemzer, B.; Al-Taher, F.; Abshiru, N. Extraction and Natural Bioactive Molecules Characterization in Spinach, Kale and Purslane: A Comparative Study. Molecules 2021, 26 (9), 2515. [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G. E.; Alkazmi, L. M.; Wasef, L. G.; Beshbishy, A. M.; Nadwa, E. H.; Rashwan, E. K. Syzygium aromaticum L. (Myrtaceae): Traditional Uses, Bioactive Chemical Constituents, Pharmacological and Toxicological Activities. Biomolecules 2020, 10 (2), 202. [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Rojas, D. F.; de Souza, C. R.; Oliveira, W. P. Clove (Syzygium aromaticum): A Precious Spice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4 (2), 90–96. [CrossRef]
- Irahal, I. N.; Guenaou, I.; Lahlou, F. A.; Hmimid, F.; Bourhim, N. Syzygium aromaticum Bud (Clove) Essential Oil is a Novel and Safe Aldose Reductase Inhibitor: In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Evidence. Hormones 2022, 21 (2), 229–240. [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Moss-Pierce, T.; Ford, P.; Jiang, T. A. Syzygium aromaticum L. (Clove) Extract Regulates Energy Metabolism in Myocytes. J. Med. Food 2014, 17 (9), 1003–1010. [CrossRef]
- Ayyanar, M.; Subash-Babu, P. Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels: A Review of Its Phytochemical Constituents and Traditional Uses. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2 (3), 240–246. [CrossRef]
- Ayyanar, M.; Subash-Babu, P.; Ignacimuthu, S. Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels., a Novel Therapeutic Agent for Diabetes: Folk Medicinal and Pharmacological Evidences. Complement. Ther. Med. 2013, 21 (3), 232–243. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S. B.; Nasir, A.; Prabhu, K. M.; Murthy, P. S.; Dev, G. Hypoglycaemic and Hypolipidemic Effect of Ethanolic Extract of Seeds of Eugenia jambolana in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rabbits. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 85 (2-3), 201–206. [CrossRef]
- Komakech, R.; Kim, Y. G.; Matsabisa, G. M.; Kang, Y. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic potential of Tamarindus indica Linn. (Fabaceae): a narrative review. Integr. Med. Res. 2019, 8 (3), 181–186. [CrossRef]
- Maiti, R.; Jana, D.; Das, U. K.; Ghosh, D. Antidiabetic effect of aqueous extract of seed of Tamarindus indica in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 92 (1), 85–91. [CrossRef]
- Krishna, R. N.; Anitha, R.; Ezhilarasan, D. Aqueous extract of Tamarindus indica fruit pulp exhibits antihyperglycaemic activity. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2020, 10 (5), 440–447.
- Bhadoriya, S. S.; Ganeshpurkar, A.; Bhadoriya, R.; Sahu, S. K.; Patel, J. R. Antidiabetic potential of polyphenolic-rich fraction of Tamarindus indica seed coat in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 29 (1), 37–45. [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, S. R.; Joseph, J. A.; Anandakumar, S.; Venkatesan, V.; Madhavan, C. N.; Agarwal, A. Ameliorative potential of Tamarindus indica on high fat diet induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Sci. World J. 2014, 507197. [CrossRef]
- Rusconi, M.; Conti, A. Theobroma cacao L., the Food of the Gods: a scientific approach beyond myths and claims. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61 (1), 5–13. [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.; Martín, M. A.; Goya, L. Effects of Cocoa Antioxidants in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Antioxidants 2017, 6 (4), 84. [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Okabe, M.; Natsume, M.; Ashida, H. Cacao liquor procyanidin extract improves glucose tolerance by enhancing GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. J. Nutr. Sci. 2012, 1, e2. [CrossRef]
- Rowley, T. J., 4th; Bitner, B. F.; Ray, J. D.; Lathen, D. R.; Smithson, A. T.; Dallon, B. W.; Plowman, C. J.; Bikman, B. T.; Hansen, J. M.; Dorenkott, M. R.; Goodrich, K. M.; Ye’, L.; O'Keefe, S. F.; Neilson, A. P.; Tessem, J. S. Monomeric cocoa catechins enhance β-cell function by increasing mitochondrial respiration. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 49, 30–41. [CrossRef]
- Martín, M. Á.; Fernández-Millán, E.; Ramos, S.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L. Cocoa flavonoid epicatechin protects pancreatic beta cell viability and function against oxidative stress. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58 (3), 447–456. [CrossRef]
- Martín, M. A.; Ramos, S.; Cordero-Herrero, I.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L. Cocoa phenolic extract protects pancreatic beta cells against oxidative stress. Nutrients 2013, 5 (8), 2955–2968. [CrossRef]
- Arawwawala, M.; Thabrew, I.; Arambewela, L. Antidiabetic activity of Trichosanthes cucumerina in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2009, 3 (2). [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, R.; Thabrew, M. I.; Thammitiyagodage, G. M.; Galhena, B. P.; Arawwawala, L. M. The gastroprotective effect of ethyl acetate fraction of hot water extract of Trichosanthes cucumerina Linn and its underlying mechanisms. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17 (1), 312. [CrossRef]
- Busuioc, A. C.; Botezatu, A. D.; Furdui, B.; Vinatoru, C.; Maggi, F.; Caprioli, G.; Dinica, R. M. Comparative Study of the Chemical Compositions and Antioxidant Activities of Fresh Juices from Romanian Cucurbitaceae Varieties. Molecules 2020, 25 (22), 5468. [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Gupta, N.; Chatterjee, S. Investigating Therapeutic Potential of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. as Our Defense Mechanism against Several Human Diseases. J. Toxicol. 2016, 2016, 1250387. [CrossRef]
- Hannan, J. M.; Ali, L.; Rokeya, B.; Khaleque, J.; Akhter, M.; Flatt, P. R.; Abdel-Wahab, Y. H. Soluble Dietary Fibre Fraction of Trigonella foenum-graecum (Fenugreek) Seed Improves Glucose Homeostasis in Animal Models of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes by Delaying Carbohydrate Digestion and Absorption, and Enhancing Insulin Action. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 97 (3), 514–521. [CrossRef]
- Neelakantan, N.; Narayanan, M.; de Souza, R. J.; van Dam, R. M. Effect of Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) Intake on Glycemia: A Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 7. [CrossRef]
- Nagulapalli Venkata, K. C.; Swaroop, A.; Bagchi, D.; Bishayee, A. A Small Plant with Big Benefits: Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum Linn.) for Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61 (6), 10.1002/mnfr.201600950. [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Sun, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, M.; Yang, J. Molecular Mechanism and Health Role of Functional Ingredients in Blueberry for Chronic Disease in Human Beings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19 (9), 2785. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Abdullah; Zhao, M.; Tang, J.; Deng, L.; Feng, F. Probiotics-Fermented Blueberry Juices as Potential Antidiabetic Product: Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Antidiabetic Potentials. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101 (10), 4420–4427. [CrossRef]
- Ferlemi, A.; Lamari, F. Berry Leaves: An Alternative Source of Bioactive Natural Products of Nutritional and Medicinal Value. Antioxidants 2016, 5 (2), 17. [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Dong, Y.; Ren, H.; Li, L.; He, C. A review of phytochemistry, metabolite changes, and medicinal uses of the common food mung bean and its sprouts (Vigna radiata). Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8 (1), 4. [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Yousaf, L.; Xue, Y.; Hu, J.; Wu, J.; Hu, X.; Feng, N.; Shen, Q. Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L.): Bioactive Polyphenols, Polysaccharides, Peptides, and Health Benefits. Nutrients 2019, 11 (6), 1238. [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Yang, X.; Tian, J.; Liu, C.; Cheng, X.; Ren, G. Antioxidant and antidiabetic activities of black mung bean (Vigna radiata L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61 (34), 8104–8109. [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Cai, W.; Wu, T.; Xu, B. Phytochemical distribution in hull and cotyledon of adzuki bean (Vigna angularis L.) and mung bean (Vigna radiate L.), and their contribution to antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic activities. Food Chem. 2016, 201, 350–360. [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J. P.; Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A. Bioactive constituents in pulses and their health benefits. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54 (4), 858–870. [CrossRef]
- Ali, N. M.; Mohd Yusof, H.; Yeap, S. K.; Ho, W. Y.; Beh, B. K.; Long, K.; Koh, S. P.; Abdullah, M. P.; Alitheen, N. B. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of untreated, germinated, and fermented mung bean aqueous extract. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 350507. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Srivastava, N.; Bhagyawant, S. S. Vicilin-A major storage protein of mungbean exhibits antioxidative potential, antiproliferative effects and ACE inhibitory activity. PLoS One 2018, 13 (2), e0191265. [CrossRef]
- Mansour, R.; Haouas, N.; Ben Kahla-Nakbi, A.; Hammami, S.; Mighri, Z.; Mhenni, F.; Babba, H. The Effect of Vitis vinifera L. Leaves Extract on Leishmania infantum. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12 (3), 349–355.
- Orhan, N.; Aslan, M.; Orhan, D. D.; Ergun, F.; Yeşilada, E. In-vivo Assessment of Antidiabetic and Antioxidant Activities of Grapevine Leaves (Vitis vinifera) in Diabetic Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 108 (2), 280–286. [CrossRef]
- Nassiri-Asl, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Review of the Pharmacological Effects of Vitis vinifera (Grape) and its Bioactive Constituents: An Update. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30 (9), 1392–1403. [CrossRef]
- Lao, F.; Sigurdson, G. T.; Giusti, M. M. Health Benefits of Purple Corn (Zea mays L.) Phenolic Compounds. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16 (2), 234–246. [CrossRef]
- Rahmatullah, M.; Ferdausi, D.; Mollik, A. H.; Jahan, R.; Chowdhury, M. H.; Haque, W. M. A survey of medicinal plants used by Kavirajes of Chalna area, Khulna district, Bangladesh. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2009, 7 (2), 91–97. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Chen, Q.; Di, L.; Li, N. Evaluation of Anti-Diabetic Potential of Corn Silk in High-Fat Diet/ Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mice Model. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21 (1), 131–138. [CrossRef]
- Kim, T. H.; Kim, J. K.; Kang, Y. H.; Lee, J. Y.; Kang, I. J.; Lim, S. S. Aldose reductase inhibitory activity of compounds from Zea mays L. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 727143. [CrossRef]
- Sabiu, S.; O'Neill, F. H.; Ashafa, A. Kinetics of α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitory potential of Zea mays Linnaeus (Poaceae), Stigma maydis aqueous extract: An in vitro assessment. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 183, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. J.; Zhao, J. L. Corn silk (Zea mays L.), a source of natural antioxidants with α-amylase, α-glucosidase, advanced glycation and diabetic nephropathy inhibitory activities. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 510–517. [CrossRef]
- Ali, B. H.; Blunden, G.; Tanira, M. O.; Nemmar, A. Some Phytochemical, Pharmacological and Toxicological Properties of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe): A Review of Recent Research. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46 (2), 409–420. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Song, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, Z. Effects of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Components of the Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 5692962. [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q. Q.; Xu, X. Y.; Cao, S. Y.; Gan, R. Y.; Corke, H.; Beta, T.; Li, H. B. Bioactive Compounds and Bioactivities of Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Foods 2019, 8 (6), 185. [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Yan, T.; Xu, F.; Xiao, F.; Wu, B.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y. Polysaccharide from Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) Improves Antioxidant Capacity via PI3K/AKT Pathways and Nrf2 Translocation in a Type 2 Diabetes Model. Molecules 2019, 24 (10), 1906. [CrossRef]
- Arora, M. K.; Sarup, Y.; Tomar, R.; Singh, M.; Kumar, P. Amelioration of Diabetes-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy by Aloe vera: Implication of Oxidative Stress and Hyperlipidemia. J. Diet. Suppl. 2019, 16 (2), 227–244. [CrossRef]
- Yusni, Y.; Zufry, H.; Meutia, F.; Sucipto, K. W. The effects of celery leaf (Apium graveolens L.) treatment on blood glucose and insulin levels in elderly pre-diabetics. Saudi Med. J. 2018, 39 (2), 154–160. [CrossRef]
- Lammert, A.; Kratzsch, J.; Selhorst, J.; Humpert, P. M.; Bierhaus, A.; Birck, R.; Kusterer, K.; Hammes, H. P. Clinical benefit of a short term dietary oatmeal intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes and severe insulin resistance: a pilot study. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2008, 116 (2), 132–134. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liang, T.; Wen, Q.; Lin, X.; Tang, J.; Zuo, Q.; Tao, L.; Xuan, F.; Huang, R. Protective effects of total extracts of Averrhoa carambola L. (Oxalidaceae) roots on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33 (5), 1272–1282. [CrossRef]
- Aliahmadi, M.; Amiri, F.; Bahrami, L. S.; Hosseini, A. F.; Abiri, B.; Vafa, M. Effects of raw red beetroot consumption on metabolic markers and cognitive function in type 2 diabetes patients. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2021, 20 (1), 673–682. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Burman, S.; Nair, A. B.; Chauhan, S.; Sircar, D.; Roy, P.; Dhanwat, M.; Lahiri, D.; Mehta, D.; Das, R.; Khalil, H. E. Brassica oleracea Extracts Prevent Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 27 (1), 50–62. [CrossRef]
- Haidari, F.; Omidian, K.; Rafiei, H.; Zarei, M.; Mohamad Shahi, M. Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) Supplementation to Diabetic Rats Improves Serum and Hepatic Oxidative Stress Markers. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12 (1), 109–114.
- Li, P.; Lu, B.; Gong, J.; Li, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Tian, X.; Han, B.; Guo, Y.; Xie, Z.; Liao, Q. Chickpea Extract Ameliorates Metabolic Syndrome Symptoms via Restoring Intestinal Ecology and Metabolic Profile in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65 (13), e2100007. [CrossRef]
- Ani, P. N.; Ochu, K. E. Anti-diabetic, anti-hyperlipidemic and hepatoprotective potential of shaddock (Citrus maxima) peel extract. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2020, 19 (3), 271–278. [CrossRef]
- Boonphang, O.; Ontawong, A.; Pasachan, T.; Phatsara, M.; Duangjai, A.; Amornlerdpison, D.; Jinakote, M.; Srimaroeng, C. Antidiabetic and Renoprotective Effects of Coffea arabica Pulp Aqueous Extract through Preserving Organic Cation Transport System Mediated Oxidative Stress Pathway in Experimental Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Molecules 2021, 26 (7), 1907. [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, M.; Pandey, H.; Raja Gopal Reddy, M.; Prabhakaran Sobhana, P.; Korrapati, D.; Uday Kumar, P.; Vajreswari, A.; Jeyakumar, S. M. Carrot Juice Consumption Reduces High Fructose-Induced Adiposity in Rats and Body Weight and BMI in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2021, 14, 11786388211014917. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, D. S.; Abd El-Maksoud, M. A. Effect of strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) leaf extract on diabetic nephropathy in rats. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 96 (2), 87–93. [CrossRef]
- Choi, M. S.; Ryu, R.; Seo, Y. R.; Jeong, T. S.; Shin, D. H.; Park, Y. B.; Kim, S. R.; Jung, U. J. The beneficial effect of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) leaf extracts in adults with prediabetes: a randomized placebo controlled trial. Food Funct. 2014, 5 (7), 1621–1630. [CrossRef]
- Anand Swarup, K. R.; Sattar, M. A.; Abdullah, N. A.; Abdulla, M. H.; Salman, I. M.; Rathore, H. A.; Johns, E. J. Effect of dragon fruit extract on oxidative stress and aortic stiffness in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Pharmacogn. Res. 2010, 2 (1), 31–35. [CrossRef]
- Ludvik, B.; Waldhäusl, W.; Prager, R.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Pacini, G. Mode of action of Ipomoea batatas (Caiapo) in type 2 diabetic patients. Metabolism 2003, 52 (7), 875–880. [CrossRef]
- Omokhua-Uyi, A.; Van Staden, J. Phytomedicinal relevance of South African Cucurbitaceae species and their safety assessment: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112967. [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Y. Comparative study on the effects of apple peel polyphenols and apple flesh polyphenols on cardiovascular risk factors in mice. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2018, 40 (1), 65–72. [CrossRef]
- Bayani, M.; Ahmadi-Hamedani, M.; Jebelli Javan, A. Study of Hypoglycemic, Hypocholesterolemic and Antioxidant Activities of Iranian Mentha spicata Leaves Aqueous Extract in Diabetic Rats. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16 (Suppl), 75–82.
- Gupta, S.; Mediratta, P. K.; Singh, S.; Sharma, K. K.; Shukla, R. Antidiabetic, antihypercholesterolaemic and antioxidant effect of Ocimum sanctum (Linn) seed oil. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 44 (4), 300–304.
- Lemhadri, A.; Zeggwagh, N. A.; Maghrani, M.; Jouad, H.; Eddouks, M. Anti-hyperglycaemic activity of the aqueous extract of Origanum vulgare growing wild in Tafilalet region. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 92 (2-3), 251–256. [CrossRef]
- Saddi, A. A.; Mohamed, A. M.; Shaikh, A. M. Prophylactic mechanisms of Cucumis melo var. flexuosus and Phoenix dactylifera fruit extracts against diabetic cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 31 (2, Suppl.), 699–707.
- Srinivasan, P.; Vijayakumar, S.; Kothandaraman, S.; Palani, M. Anti-diabetic activity of quercetin extracted from Phyllanthus emblica L. fruit: In silico and in vivo approaches. J. Pharm. Anal. 2018, 8 (2), 109–118. [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kim, Y. S.; Kim, L.; Park, H. J.; Lee, D.; Kim, H. Anti-Obesity Effects of the Flower of Prunus persica in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11 (9), 2176. [CrossRef]
- Kermani, J.; Goodarzi, N.; Bakhtiari, M. An Experimental Study to Evaluate the Protective Effects of Solanum lycopersicum Seed Essential Oil on Diabetes-Induced Testicular Injuries. Medicina 2019, 55 (8), 499. [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, M.; Mimaki, Y.; Ohtomo, T.; Yamada, J.; Nishiyama, T.; Mae, T.; Kishida, H.; Kawada, T. Hypoglycemic effects of clove (Syzygium aromaticum flower buds) on genetically diabetic KK-Ay mice and identification of the active ingredients. J. Nat. Med. 2012, 66 (2), 394–399. [CrossRef]
- Ștefănescu Braic, R.; Vari, C.; Imre, S.; Huțanu, A.; Fogarasi, E.; Todea, T.; Groșan, A.; Eșianu, S.; Laczkó-Zöld, E.; Dogaru, M. Vaccinium Extracts as Modulators in Experimental Type 1 Diabetes. J. Med. Food 2018, 21 (11), 1106–1112. [CrossRef]
- Yeap, S. K.; Mohd Ali, N.; Mohd Yusof, H.; Alitheen, N. B.; Beh, B. K.; Ho, W. Y.; Koh, S. P.; Long, K. Antihyperglycemic effects of fermented and nonfermented mung bean extracts on alloxan-induced-diabetic mice. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 285430. [CrossRef]
- Al-Amin, Z. M.; Thomson, M.; Al-Qattan, K. K.; Peltonen-Shalaby, R.; Ali, M. Anti-diabetic and hypolipidaemic properties of ginger (Zingiber officinale) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 96 (4), 660–666. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Amir, M.; Ahmad, A.; Ali, A.; Ali, A.; Wahab, S.; Barkat, H. A.; Ansari, M. A.; Sarafroz, M.; Ahmad, A.; Barkat, M. A.; Alam, P. Aegle marmelos Leaf Extract Phytochemical Analysis, Cytotoxicity, In Vitro Antioxidant and Antidiabetic Activities. Plants 2021, 10 (12), 2573. [CrossRef]
- Méril-Mamert, V.; Ponce-Mora, A.; Sylvestre, M.; Lawrence, G.; Bejarano, E.; Cebrián-Torrejón, G. Antidiabetic Potential of Plants from the Caribbean Basin. Plants 2022, 11 (10), 1360. [CrossRef]
- Kim, I. S.; Hwang, C. W.; Yang, W. S.; Kim, C. H. Multiple Antioxidative and Bioactive Molecules of Oats (Avena sativa L.) in Human Health. Antioxidants 2021, 10 (9), 1454. [CrossRef]
- Chalk, C.; Benstead, T. J.; Moore, F. Aldose reductase inhibitors for the treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, 2007 (4), CD004572. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D. W.; Fu, M.; Gao, S. H.; Liu, J. L. Curcumin and diabetes: a systematic review. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 636053. [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Huseini, H. F.; Larijani, B.; Mohammad, K.; Najmizadeh, A.; Nourijelyani, K.; Jamshidi, L. The hypoglycemic effect of Juglans regia leaves aqueous extract in diabetic patients: A first human trial. Daru J. Fac. Pharm., Tehran Univ. Med. Sci. 2014, 22 (1), 19. [CrossRef]
- Zainab, B.; Ayaz, Z.; Alwahibi, M. S.; Khan, S.; Rizwana, H.; Soliman, D. W.; Alawaad, A.; Mehmood Abbasi, A. In-silico elucidation of Moringa oleifera phytochemicals against diabetes mellitus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27 (9), 2299–2307. [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, S.; Balamurugan, S.; Christapher, P. V.; Petchi, R. R.; Yeng, W. Y.; Sujithra, J.; Vijaya, C. Evaluation of Antidiabetic and Antihyperlipidemic Effects of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Leaves of Ocimum tenuiflorum (Lamiaceae) and Prediction of Biological Activity of its Phytoconstituents. Pharmacognosy Res. 2015, 7 (2), 156–165. [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Banu, H.; Ramya Bai, R.; Shanmugavalli, R. Biochemical evaluation of antihyperglycemic and antioxidant nature of Psidium guajava leaves extract in streptozotocin-induced experimental diabetes in rats. Pharm. Biol. 2009, 47 (4), 298-303. [CrossRef]
- Gajera, H. P.; Gevariya, S. N.; Hirpara, D. G.; Patel, S. V.; Golakiya, B. A. Antidiabetic and antioxidant functionality associated with phenolic constituents from fruit parts of indigenous black jamun (Syzygium cumini L.) landraces. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54 (10), 3180–3191. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.; Rizvi, S. Role of red grape polyphenols as antidiabetic agents. Integr. Med. Res. 2014, 3 (3), 119-125. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, P.; Hannon-Fletcher, M. P.; Flatt, P. R.; Abdel-Wahab, Y. H. A. Effects of 22 Traditional Anti-Diabetic Medicinal Plants on DPP-IV Enzyme Activity and Glucose Homeostasis in High-Fat Fed Obese Diabetic Rats. Biosci Rep 2021, 41 (1), BSR20203824. [CrossRef]
- Life, 1: 12(8), 1146. [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Boas, A.A.; Pintado, M.; Oliveira, A.L.S. Natural Bioactive Compounds from Food Waste: Toxicity and Safety Concerns. Foods 2021, 10, 1564. [CrossRef]
- Ioniță-Mîndrican, C.-B.; Ziani, K.; Mititelu, M.; Oprea, E.; Neacșu, S.M.; Moroșan, E.; Dumitrescu, D.-E.; Roșca, A.C.; Drăgănescu, D.; Negrei, C. Therapeutic Benefits and Dietary Restrictions of Fiber Intake: A State of the Art Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2641. [CrossRef]
- Chandel, V.; Biswas, D.; Roy, S.; Vaidya, D.; Verma, A.; Gupta, A. Current Advancements in Pectin: Extraction, Properties and Multifunctional Applications. Foods 2022, 11, 2683. [CrossRef]
- Hannan, J.; Nipa, N.; Toma, F. T.; Talukder, A.; Ansari, P. Acute Anti-Hyperglycaemic Activity of Five Traditional Medicinal Plants in High Fat Diet Induced Obese Rats. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2023, 15 (2), 5. [CrossRef]
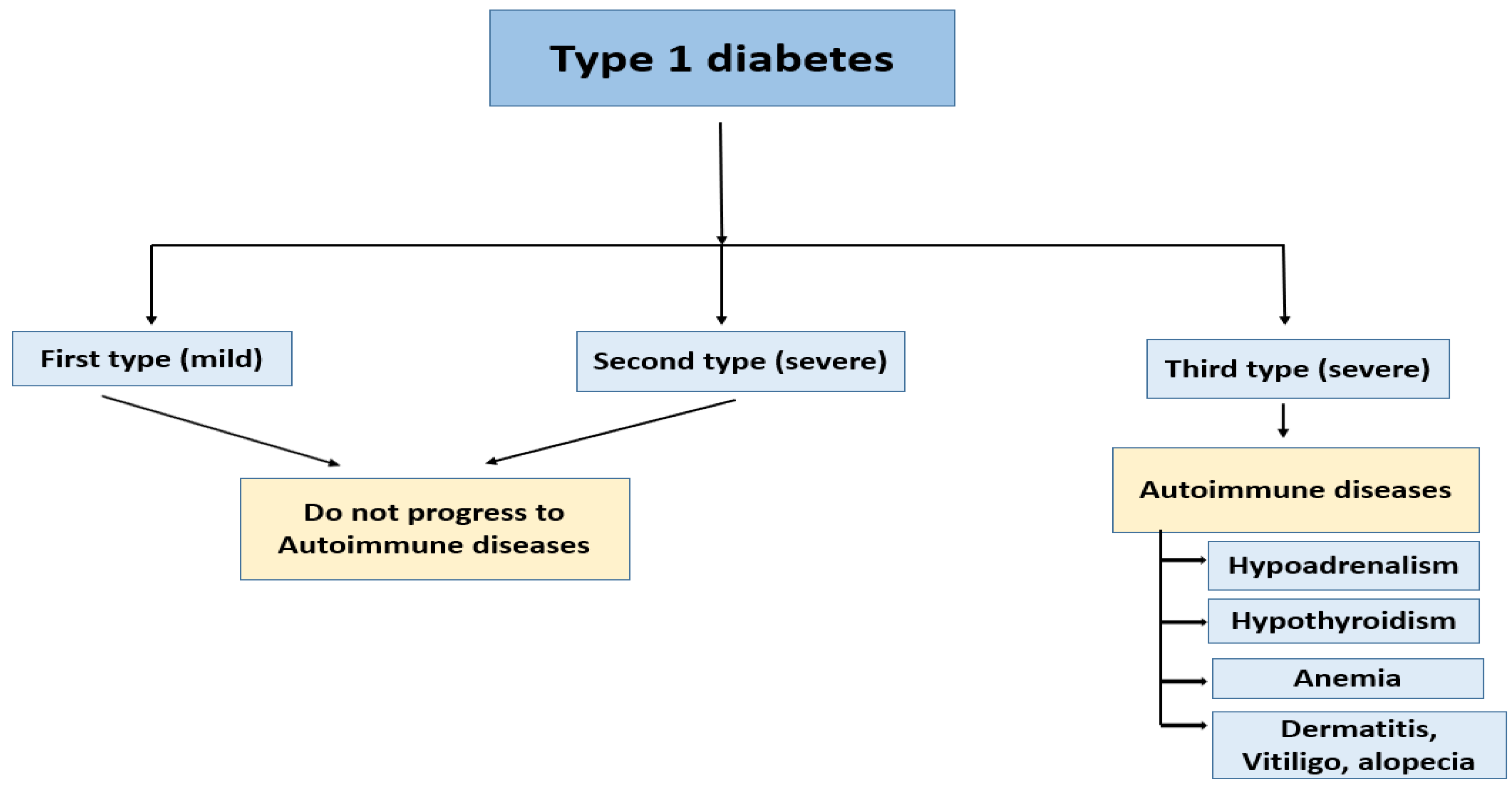
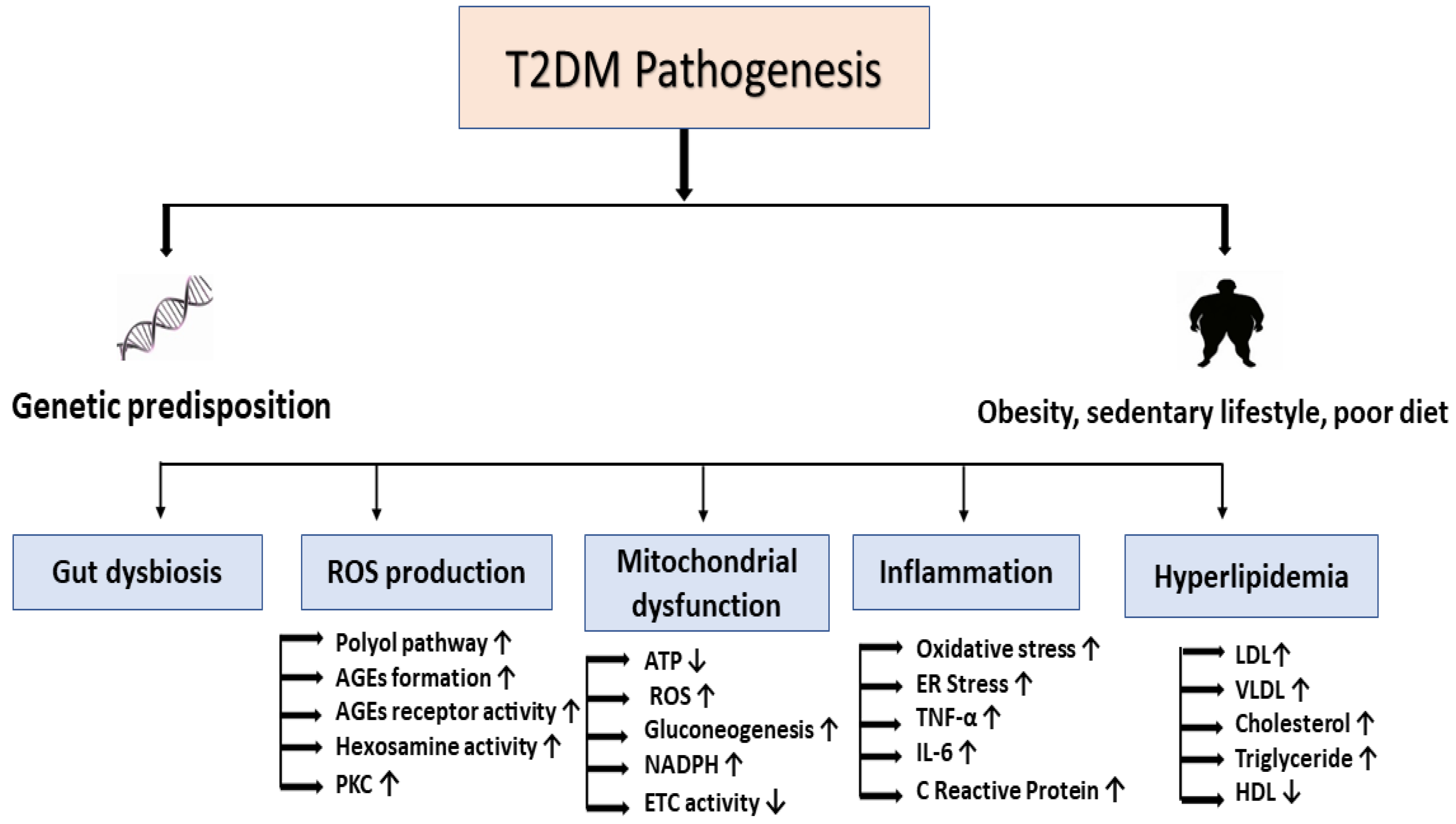
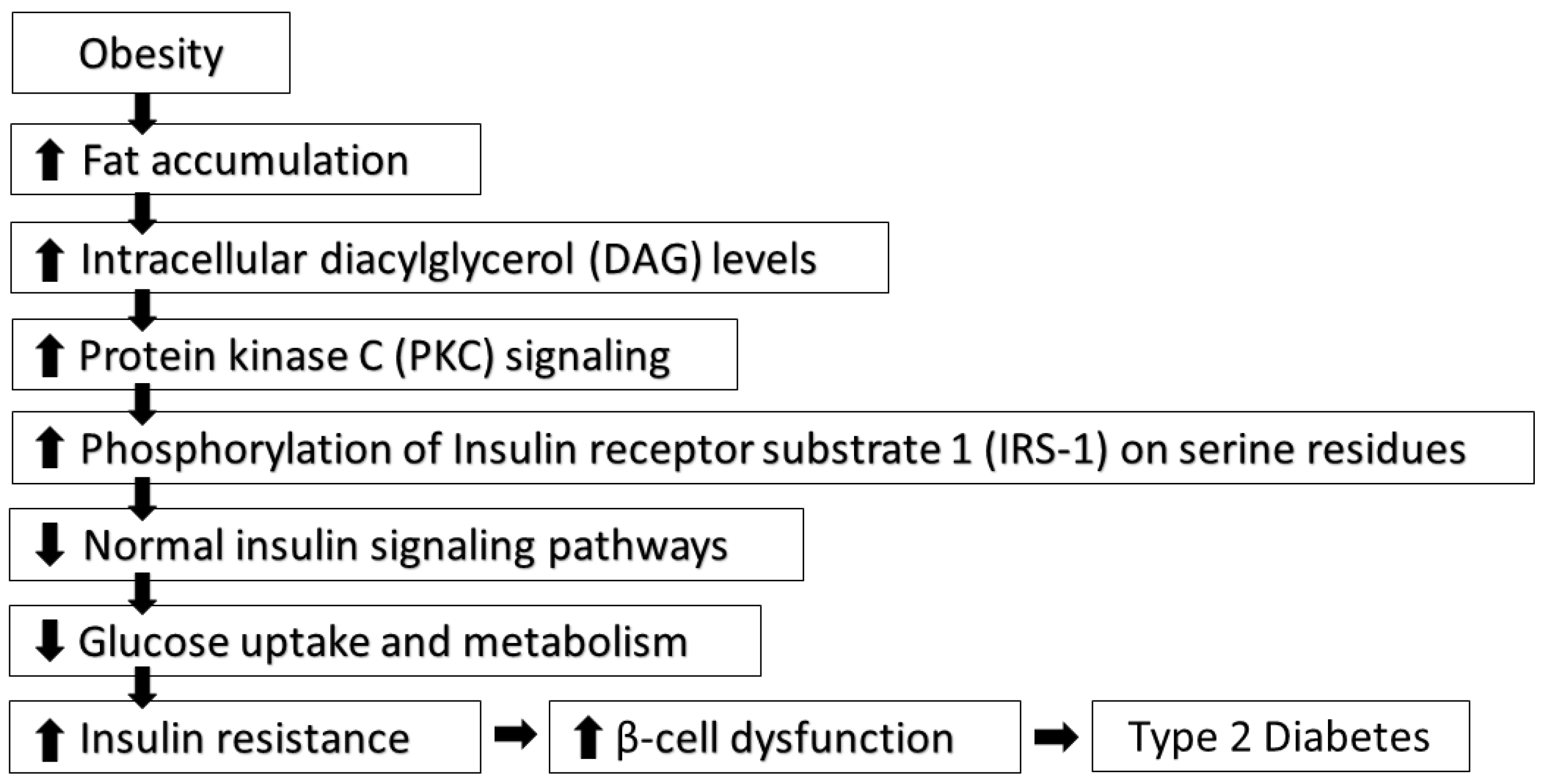
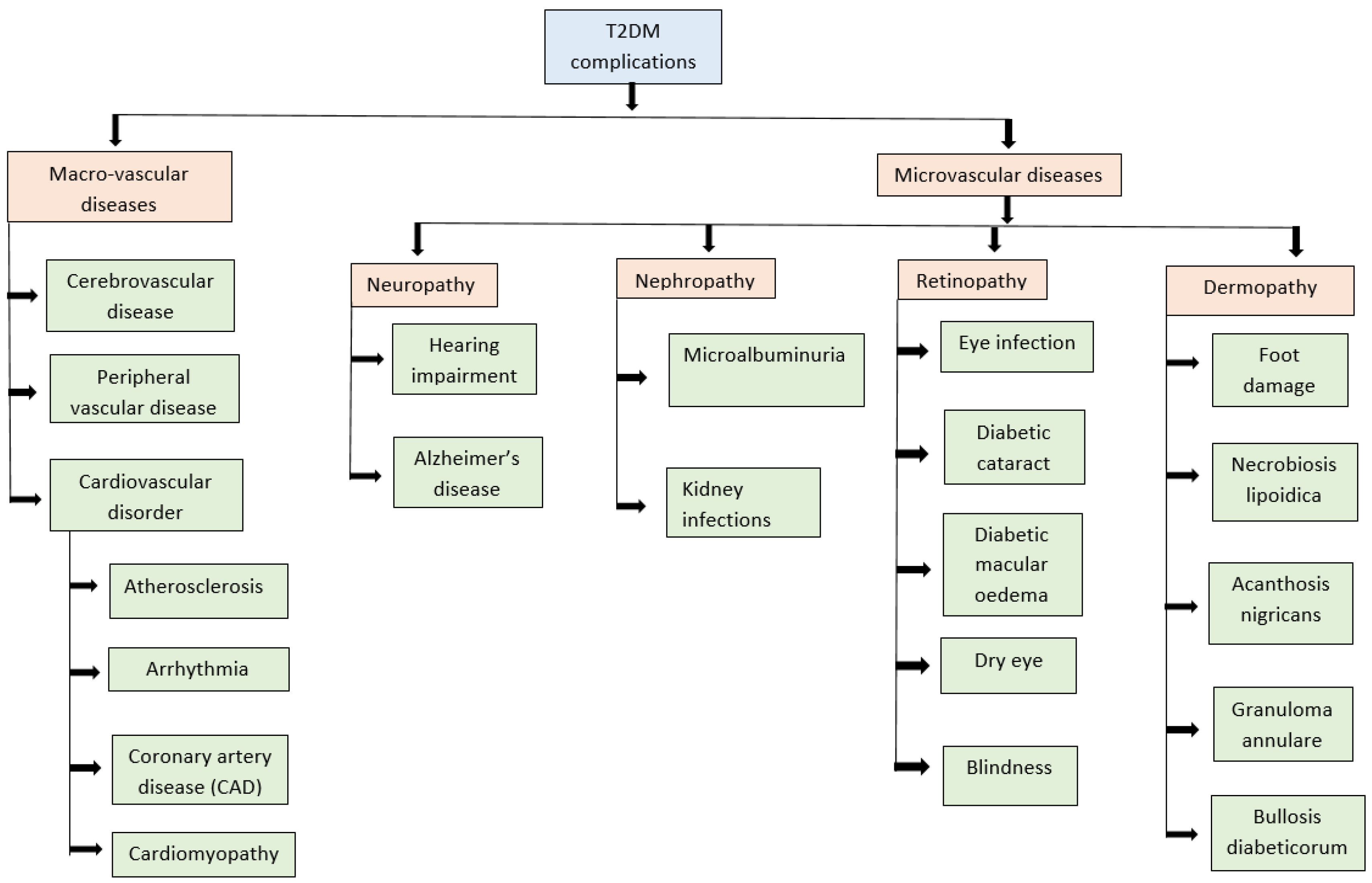
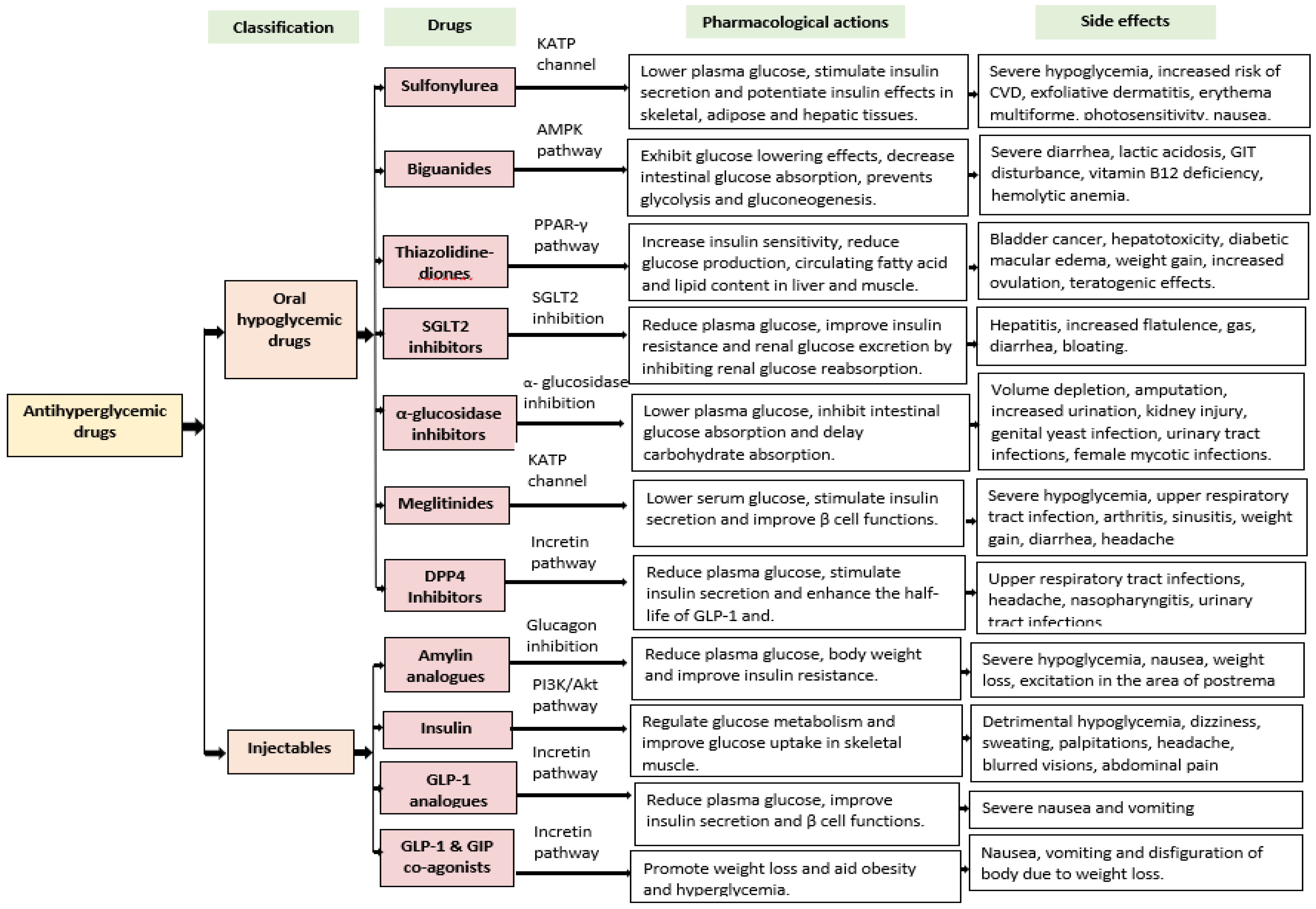
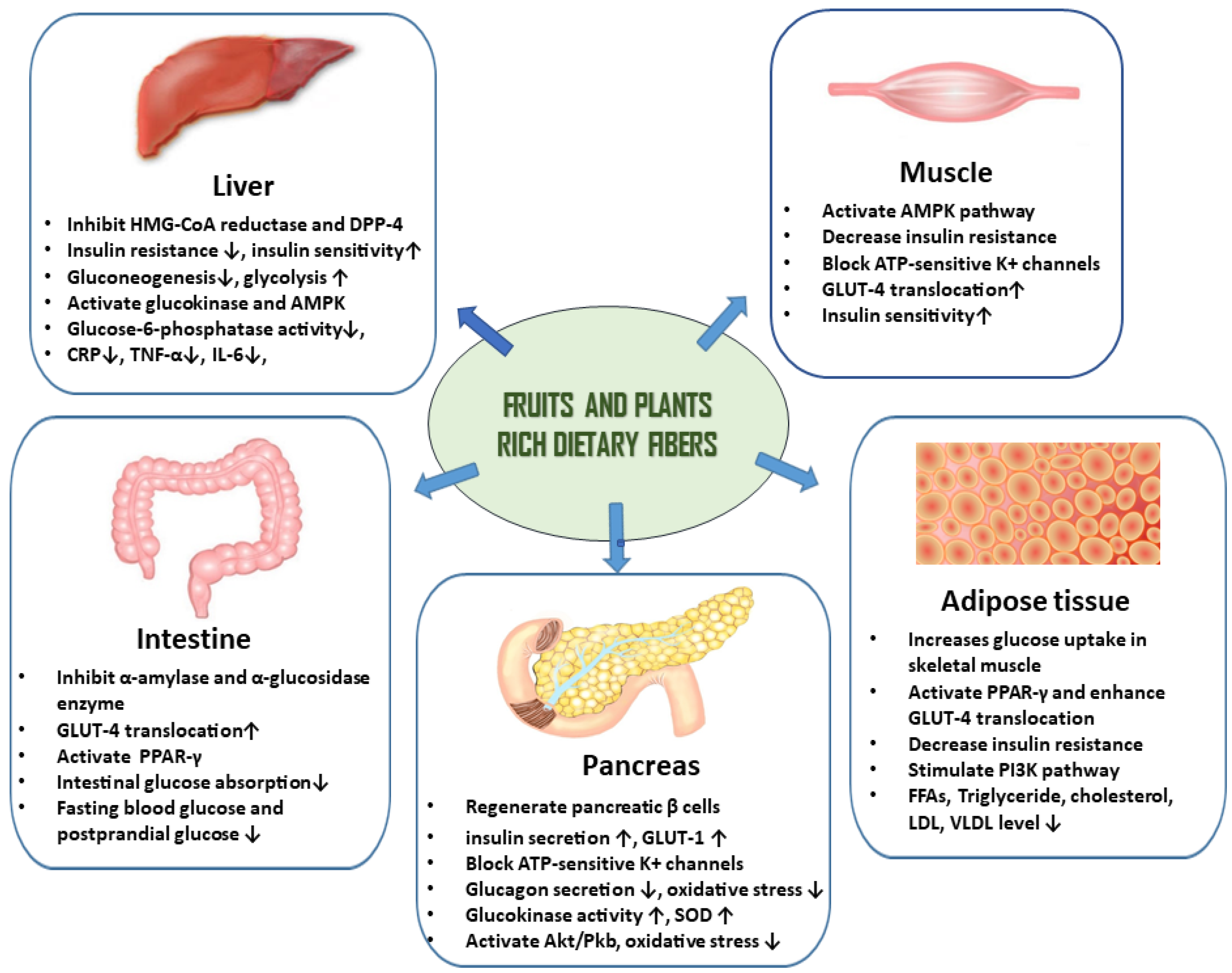
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





