1. Introduction
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a formidable challenge in the realm of public health, as it affects hundreds of millions globally, its incidence is increasing, and it has been identified as a risk factor for other chronic conditions [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. This metabolic disorder, characterized by insulin resistance and subsequent hyperglycemia, reflects dramatic shifts in lifestyle and dietary patterns that have been occurring in the last few decades [
6,
7,
8]. The urgency to address the growing T2D epidemic stems from its high prevalence, many serious complications, large cost of management, and a significant role as a nexus in the interplay of other chronic diseases. Obesity, cardiovascular diseases, renal complications, and neurological and neurodegenerative disorders often trail in the wake of T2D, underscoring the systemic impact of this condition [
9,
10,
11,
12].
The hallmark of T2D is hyperglycemia, which results from the combination of insulin dysregulation and consumption of foods that contain digestible carbohydrates [
13]. While low carbohydrate diets can reduce hyperglycemia, they may not be well tolerated, can be difficult to follow for prolonged periods, may remove many essential nutrients from the diet, and may cause increased mortality [
14,
15,
16,
17]. Therefore, the best overall solution to a healthy human physiology may be a data-driven moderate carbohydrate diet whose cumulative postprandial glycemic response is minimized, yet provides all essential nutrients found in carbohydrate-rich foods. We have previously developed machine learned models that predict the postprandial glycemic response based on a metatranscriptomic stool (gut microbiome) test [
18]. We integrated these models into the Viome Precision Nutrition Program (VPNP) and tested it retrospectively in a longitudinal study, which showed reduced T2D molecular signature in a large population (~3,000 participants), and the effect strongly correlated with the adherence to VPNP [
19]. These results gave us confidence to conduct a prospective, blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, whose design, execution, and results are presented in this report. Our hypothesis was that VPNP can reduce HbA1c in adults with prediabetes and diabetes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Approvals.
This was a prospective, decentralized (direct to participant), blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with an intervention lasting ~90 days. The study was registered at
www.clinicaltrials.gov (
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05465616) and approved by a federally registered Institutional Review Board. The participants were blinded in terms of interventional arm assignment.
2.2. Patients and Randomization.
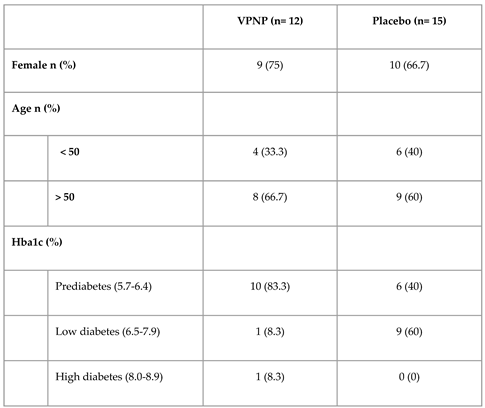
Participants were recruited in the USA via digital advertisements. The inclusion criteria were as follows: signed and dated informed consent form and medical release, ages 18 years or older, able to speak and read English, HbA1c between 5.7-8.9% (inclusive) tested within the past 30 days, willing and able to visit a clinical laboratory, willing and able to follow the trial instructions and dietary recommendations, willing and able to use a smartphone and Viome app. The exclusion criteria were as follows: current or previous use of medications that increase insulin (sulfonylureas, such as glimepiride, glipizide, glyburide, etc.), current or previous use of exogenous insulin (such as Tresiba, Lantus, Toujeo, Levemir, Humalog, Novolog, Apidra, Fiasp, etc.), antibiotic use in the previous month, gestation within the previous six months, on a specific diet (e.g. ketogenic) for the purpose of reducing HbA1c and/or weight within the previous month, allergy to an ingredient in the Viome supplements, currently on an investigational product, significant surgery or medical procedure planned, planned diet or lifestyle change during the trial period (except those appropriate for the trial arm), has previously followed Viome nutritional recommendations (foods and/or supplements). Participants that met the eligibility criteria were enrolled into the trial and randomly assigned to the VPNP group or placebo control group using blocked randomization by age (<50 and >=50), sex, and Hba1c levels (5.7-6.4%, 6.5-7.9%, and 8-8.9%), self reported at this stage. After randomization, final eligibility for each participant was confirmed by sending them to a clinical lab and verifying their HbA1c levels were within the inclusion criteria.
2.3. Trial Endpoints (Outcome Measures)
The primary endpoint was glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c). The secondary endpoints included fasting insulin and fasting glucose. These endpoints were measured at a clinical laboratory before and after the ~90 day intervention.
2.4. Sample Collections and Lab Analyses
In addition to visiting a clinical laboratory for measuring the endpoints, each participant collected stool, blood, and saliva samples at home, both before and after the intervention. Sample collection kits included sample tubes with RNA preservative, collection instructions, and prepaid mailers. For VPNP arm participants, the blood and stool samples collected at baseline were analyzed using clinically validated and licensed RNA sequencing (metatranscriptomic) methods to generate personalized nutritional recommendations, as previously described [
20,
21,
22,
23].
2.5. Interventions
The intervention for all participants lasted ~90 days. The Viome Precision Nutrition Program (VPNP) arm participants received personalized nutritional intervention that consisted of Viome supplements, Viome biotics (prebiotics and probiotics), and food recommendations. The process of converting RNA sequencing data and survey answers into personalized nutritional recommendations was previously described [
19]. The supplements and biotics were physically delivered to each participant, whereas food recommendations were delivered digitally. The foods were grouped into four categories: avoid, minimize, enjoy and superfoods. Avoid foods should not be consumed at all for the duration of the study; minimize foods may be consumed in small amounts totaling less than 20% of daily caloric intake; enjoy foods can be eaten at any frequency and are encouraged to be consumed regularly to add diversity to the diet; superfoods are recommended to be eaten daily and should be included in each meal. VPNP arm participants received different foods under these categories, depending on their sample results and their responses to the surveys. The nutritional recommendations are not one-size-fits-all but are tailored to individual needs and health goals. VPNP does not incorporate any recommendations that would reduce the carbohydrate intake. Instead, it enables the participant to consume foods that are predicted to minimize their postprandial glucose response (PPGR), and minimize or avoid foods that are predicted to spike PPGR, based on previously-developed machine learned algorithms [
18]. Similar to the nutritional recommendations, the supplements and biotics were also tailored to each participant and consist of prebiotics, probiotics, herbs, amino acids, vitamins, minerals and food extracts. Each VPNP arm participant’s formula for the supplements and biotics was based on the individual’s test results and their responses to the surveys. As a result, each precision supplement formula was unique to the individual. The nutritional intervention for the placebo arm participants consisted of a daily placebo capsule with inert ingredients and a standard healthy diet recommended to Americans by the USDA (Dietary Guidelines for Americans,
https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/). All study participants in the control arm took the same supplement and followed the same nutritional recommendations.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The interim analysis described here was performed when at least 50% of the target enrollment was achieved. Analysis of covariance, with adjustment for sex, age, body mass index (BMI), and the baseline measure (primary or secondary endpoint) was used to compare the differences between the VPNP and the placebo groups. A difference of 0.40 units in Hba1c between the two arms was considered to be clinically significant.
3. Results
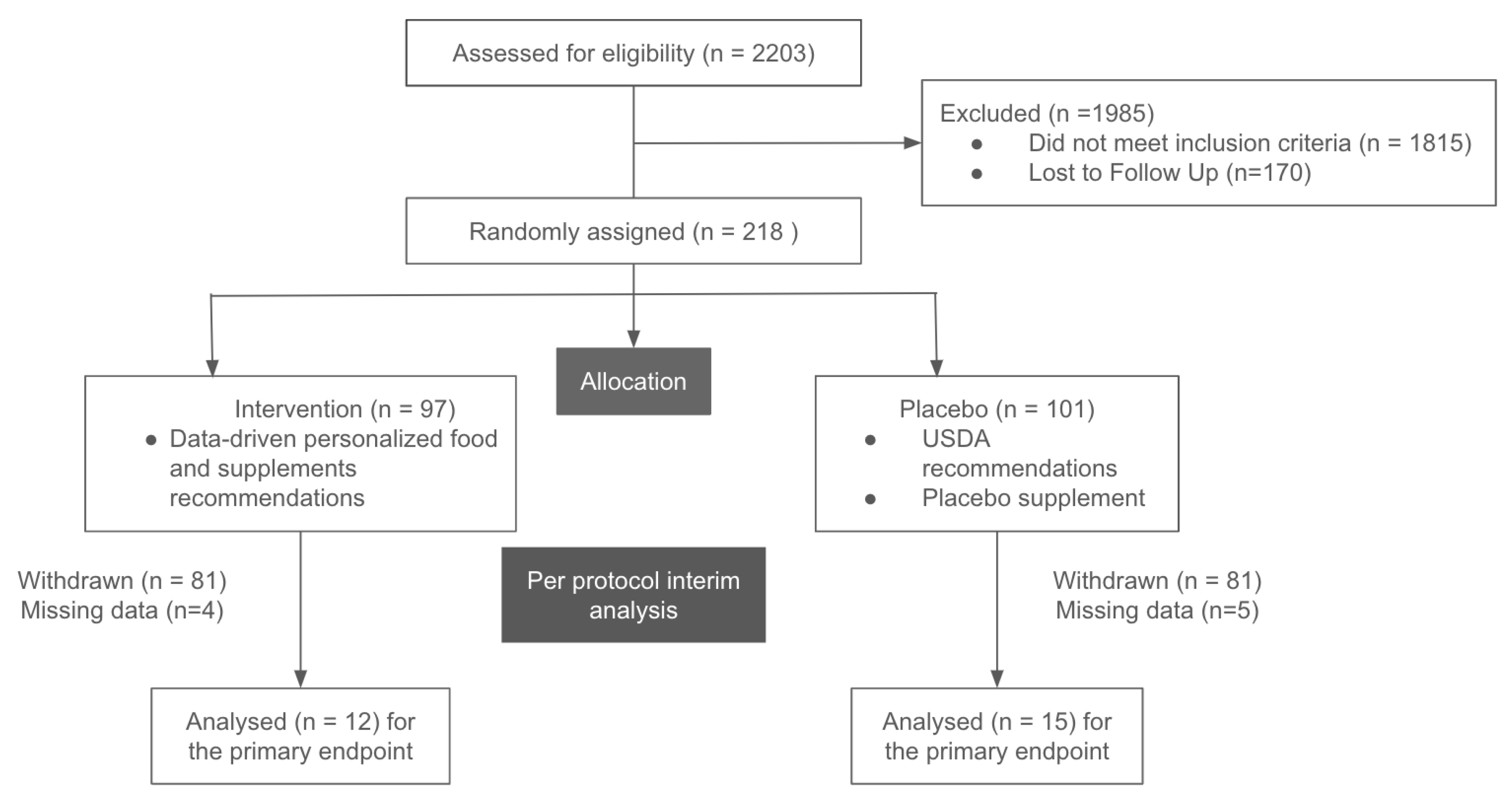
For this interim report from the randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial, we include data from 27 participants with pre-diabetes and diabetes that completed the trial (
Figure 1 and
Table 1). Primary and secondary endpoints were measured prior and post intervention at a nationally recognized clinical laboratory network. The intervention lasted ~90 days, and there were no adverse events reported by any participants in the VPNP arm. HbA1c data were included in the analysis from all 27 participants. Fasting insulin and fasting glucose data were analyzed from a subset of 19 participants, since the clinical lab that performed the tests could not confirm the fasting status for eight participants.
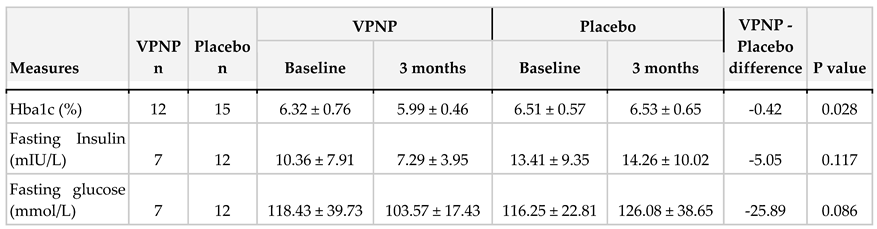
Analysis of covariance, with adjustment for sex, age, BMI, and the baseline HbA1c measure was used to compare the differences between the two trial arms at three months. All three endpoints improved in the VPNP arm relative to the placebo arm (
Table 2).
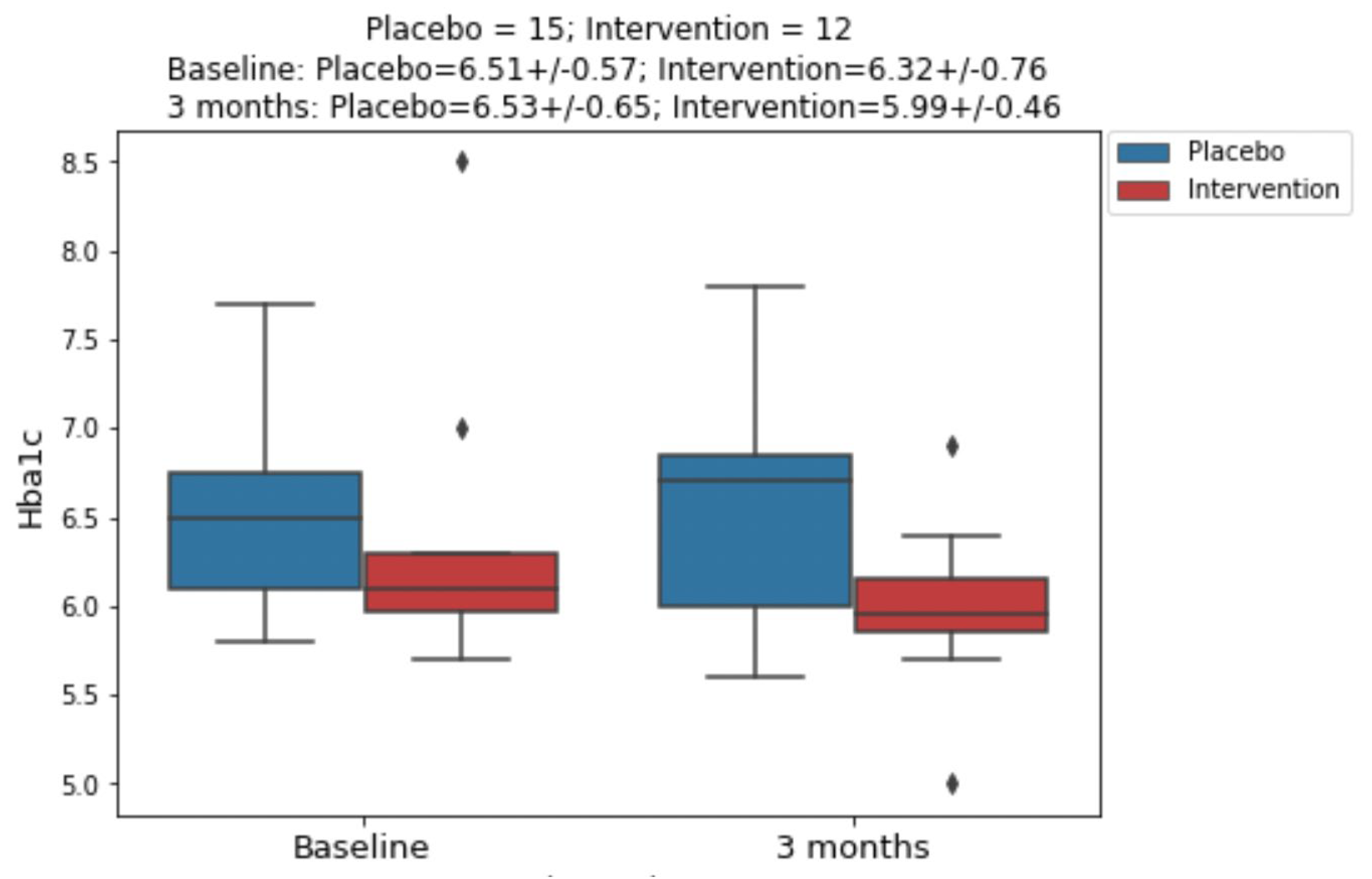
Figure 2.
Hba1c changes from baseline to 3 months post intervention.
Figure 2.
Hba1c changes from baseline to 3 months post intervention.
4. Discussion
The prevalence and incidence of T2D are increasing worldwide, including younger populations. It has become clear that diet plays a significant role in the onset and progression of T2D, starting from insulin resistance to full-blown disease. However, choosing which diet to follow is a very controversial topic. The main reason, we think, is that nutritional studies have focused on the average human, asking if a certain food is good or bad for them. In reality, these findings do not apply to the vast majority of people, as foods need to be personalized, taking into account each person’s microbiome, immune system, genetics, environment, etc. One example is the glycemic index, which applies to the average human. However, as others and we have shown, different people can have very different PPGR to the same foods [
18].
Because we know that different people will have individualized responses to nutritional ingredients, we have developed the Viome Precision Nutrition Program (VPNP), a personalized nutritional intervention whose goal is to maintain or re-establish the healthy homeostasis in the human body by modulating human and microbial physiology using nutritional ingredients [
23]. VPNP is based on the technology platform that uses a person’s biochemical and phenotypic data to compute a highly personalized diet and supplement recommendations. The mathematical algorithms that compute the nutritional recommendations have been trained on very large datasets [
18,
22].
Here, we report the results of a pilot, blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial that tested the efficacy of VPNP on three major metabolic disease endpoints: HbA1c, fasting insulin, and fasting glucose. As shown in table 2 and figure 2, the VPNP improved all three endpoints relative to placebo. These results represent an interim analysis of the trial data, with the trial continuing on. These preliminary results are very encouraging, for several reasons. Not only was the HbA1c improved, which is likely due to the data-driven personalized carbohydrate choices, but the fasting insulin and fasting glucose also improved. This is very important, since elevated fasting insulin and fasting glucose are hallmarks of insulin resistance, which is required for further disease progression into type 2 diabetes (T2D). If we can effectively reverse insulin resistance, it would truly prevent the onset of T2D, and have many positive downstream effects on humanity. Just like all other trials, this study has some limitations. This report includes the results of an interim analysis, and most of the participants fell into the prediabetes category. However, it is very encouraging that we are seeing positive results for HbA1c, even though the average baseline HbA1c was only 6.41%. Despite observing a greater reduction in fasting insulin and fasting glucose in the VPNP group, the sample size was too small to observe a significant difference; for this reason, the trial is continuing.
5. Conclusions
In this pilot, blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, we measured the effects of data-driven personalized diet and supplements on core metabolic biomarkers: HbA1c, fasting insulin, and fasting glucose. The personalized nutritional intervention lasted approximately 90 days, and compared to placebo, improved all three endpoints. The data-driven personalized nutritional program reduced HbA1c clinically significantly. Further investigations with a larger sample size are needed to observe a significant reduction in fasting insulin and fasting glucose, which are required for further disease progression into T2D.
Data Availability
Supporting data is not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors are employees, contractors, or advisors of Viome Life Sciences, who sponsored the study.
Funding Statement
This trial was funded by Viome Life Sciences.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the Clinical Research, Health Informatics, Computational Systems Biology, Clinical Nutrition, and Data Analytic Solutions team members for their support and advice.
References
- Ye, J. et al. (2023). The global, regional and national burden of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the past, present and future: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Frontiers in Endocrinology. [CrossRef]
- Perng, W. et al. (2023). Youth-Onset Type 2 Diabetes: The Epidemiology of an Awakening Epidemic. Diabetes Care. [CrossRef]
- Reed, J. et al. (2021). A Review of Current Trends with Type 2 Diabetes Epidemiology, Aetiology, Pathogenesis, Treatments and Future Perspectives. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy. [CrossRef]
- Hudspeth, B. (2018). The burden of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes. The American journal of managed care.
- Hamzé, R. et al. (2022). Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Alzheimer’s Disease: Shared Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Common Therapeutic Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. [CrossRef]
- Uusitupa, M. (2002). Lifestyles Matter in the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care.
- Kolb, H. and Martin, S. (2017). Environmental/lifestyle factors in the pathogenesis and prevention of type 2 diabetes. BMC Medicine. [CrossRef]
- Sami, W. et al. (2017). Effect of diet on type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review. International journal of health sciences.
- Hu, F.B. et al. (2001). The Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Mortality From All Causes and Coronary Heart Disease in Women: 20 Years of Follow-up. Archives of Internal Medicine. [CrossRef]
- Azami, M. et al. (2023). The risk of Parkinson’s disease in diabetic people: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Neurologica Belgica. [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, M. et al. (2022). Antidiabetic Drugs in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. [CrossRef]
- (2019). Diabetic neuropathy. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H. and Reaven, G.M. (2008). Insulin Resistance and Hyperinsulinemia. Diabetes Care. [CrossRef]
- Dorans, K.S. et al. (2022). Effects of a Low-Carbohydrate Dietary Intervention on Hemoglobin A1c. JAMA Network Open. [CrossRef]
- Mooradian, A.D. (2020). The Merits and the Pitfalls of Low Carbohydrate Diet: A Concise Review. The Journal of nutrition, health and aging. [CrossRef]
- Seidelmann, S.B. et al. (2018). Dietary carbohydrate intake and mortality: a prospective cohort study and meta-analysis. The Lancet Public Health. [CrossRef]
- Dreher, M.L. (2018). Whole Fruits and Fruit Fiber Emerging Health Effects. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Tily, H. et al. (2022). Gut Microbiome Activity Contributes to Prediction of Individual Variation in Glycemic Response in Adults. Diabetes Therapy. [CrossRef]
- Connell, J. et al. (2023). Data-Driven Precision Nutrition Improves Clinical Outcomes and Risk Scores for IBS, Depression, Anxiety, and T2D. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. [CrossRef]
- Toma, R. et al. (2023). A clinically validated human saliva metatranscriptomic test for global systems biology studies. BioTechniques. [CrossRef]
- Hatch, A. et al. (2019). A Robust Metatranscriptomic Technology for Population-Scale Studies of Diet, Gut Microbiome, and Human Health. International Journal of Genomics. [CrossRef]
- Patridge, E. et al. (2024). Microbial functional pathways based on metatranscriptomic profiling enable effective saliva-based health assessments for precision wellness. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal. [CrossRef]
- Connell, J. et al. (2023). Data-Driven Precision Nutrition Improves Clinical Outcomes and Risk Scores for IBS, Depression, Anxiety, and T2D. American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).