Submitted:
23 August 2024
Posted:
26 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
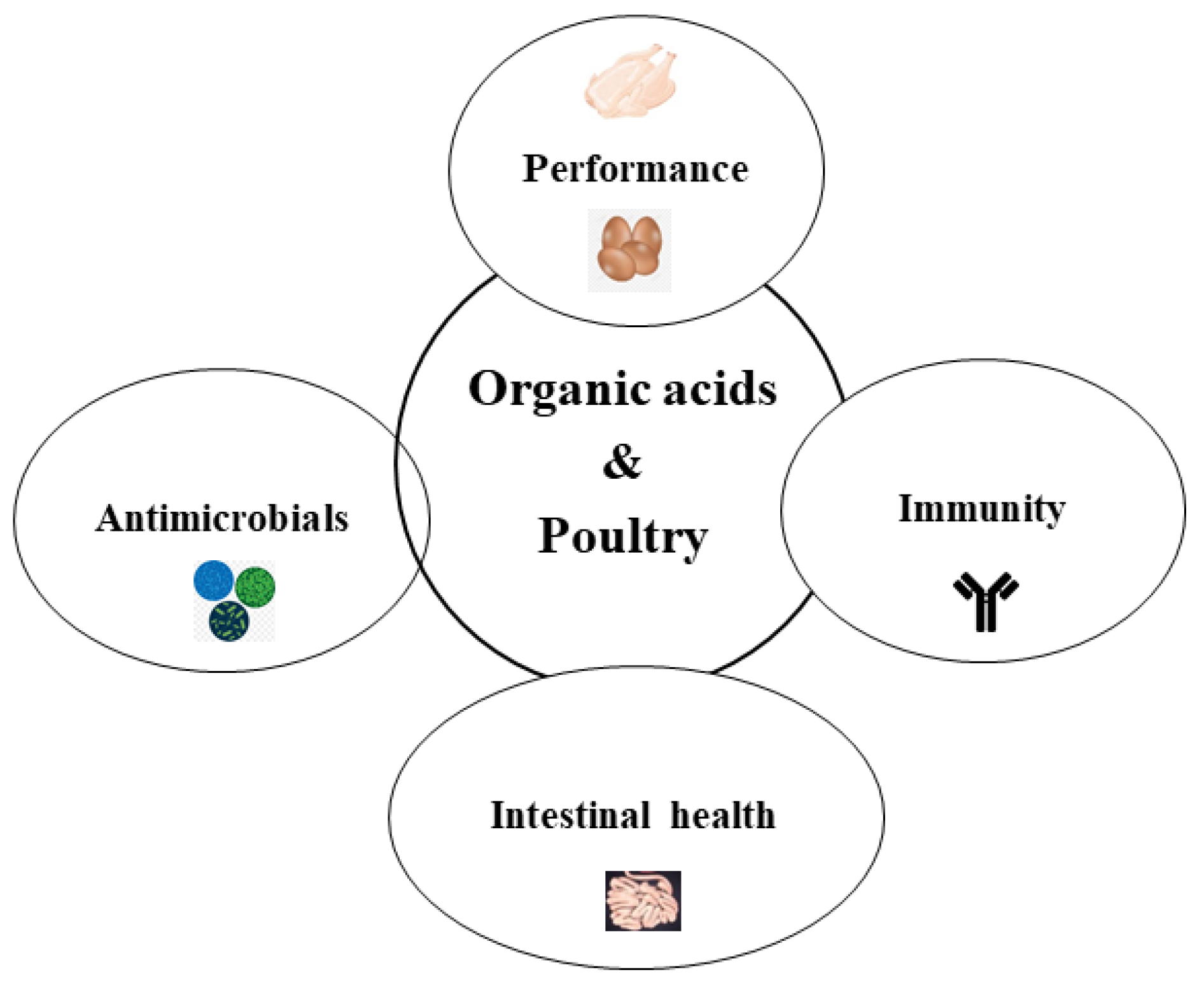
2. The Different Effects of OAs Supplementation for Poultry
2.1. Antimicrobials
2.2. Performance Parameters
2.3. Carcass Traits
2.4. Intestinal Health
2.5. Immune Response
| Organic acid (s) | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Dietary ascorbic acid, malic acid, and tartaric acid | ↑ BWG and feed efficiency | [122] |
| 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 6% of acetic acid, citric acid, lactic acid, malic acid, mandelic acid, propionic acid, or tartaric acid, respectively | ↓ S. typhimurium colonization count | [123] |
| 0.5-1% fumeric acid | Improved metabolizable energy | [124] |
| 0.16% butyric acid | ↓ Salmonella count in caecum | [125] |
| 0.2% butyric acid | ↑ Carcass weight, breast muscles yield, and dressing % ↑ FCR ↓ Abdominal fat |
[91] |
| Dietary citric acid | ↑ FI | [126] |
| 5 and 10 g/kg formic acid | Improved ileal nutrient digestibility | [83] |
| 5000 and 10,000 ppm formic acid | ↑ Growth ↑Apparent ileal digestibility |
[100] |
| 0.05% sodium butyrate | ↓ Lactobacilli and E. coli | [127] |
| Butyric acid 285 mg/kg of feed | ↑ Eggshell strength ↓ Mal-formed eggs |
[128] |
| A combination of acetic acid, citric acid, and lactic acid | ↑ BW | [129] |
| A dietary mixture of formic (70%) and propionic acid (30%) | Improved FI in a quadratic form | [130] |
| Dietary citric acid and phytase | ↑ Specific gravity and eggshell thickness ↓ Egg weight |
[90] |
| 0.5% citric acid or avilamycin, and their combination | ↑ FI, growth, carcass yield, and bone ash ↑ Lactobacillus spp. development ↓ Growth and proliferation of Salmonella and E. coli ↑ Phosphorus utilization in intestine |
[72] |
| 0.09% free or protected sodium butyrate | ↓ S. enteritidis in crop, cecum, and liver | [131] |
| Dietary citric acid | ↑ Lymphocyte number in lymphoid organs | [132] |
| 0.45% of potassium diformate | ↓ Reduced necrotic enteritis-related mortality and the amount of C. perfringens in the jejunum | [133] |
| Dietary 0.4% butyric acid | ↑ BWG and FCR | [134] |
| Dietary 3% citric acid | ↓ Ileal coliform contents | [135] |
| Formic acid in the drinking water | No effect on the counts of total organisms and E. coli in intestine | [136] |
| 3% butyric acid | ↓ Crop pH and caecal coliform count ↑ Intestinal length |
[137] |
| 0.50% formic acid, 0.50% fumaric acid, 0.25% acetic acid, and 2.0% citric acid | ↑ Villus height in duodenum | [30] |
| 250–7,000mg/kg N-butyric acid | ↓ S. Typhimurium or C. perfringens colonization | [138] |
| Dietary 0.15% blend of OAs for broilers | ↑ Antibody titers against ND at 21 days old | [116] |
| 1% a mixture of formic acid (32%), acetic acid (7%), ammonium format (20%), mono- and diglyceride of unsaturated fatty acids, and copper acetate in the drinking water of C. jejuni infected broilers | ↑ FI No effect on the BWG and FCR |
[61] |
| 1% formic acid in feed for 5 days | ↓ Salmonella count | [139] |
| 3% butyric acid, 3% fumaric acid, and 3% lactic acid in the drinking water of broilers | ↑ BW Improved FCR No effect on the cumulative FI |
[140] |
| 0.1% butyric acid | ↓ Salmonella count in caecum | [141] |
| Soft Acid S includes 60% formic acid, 20% propionic acid and 20% soft acid and Soft Acid P consists of 70% propionic acid, 5% citric acid and 25% soft acid (2.5 kg/ton of feed of layer chickens) | ↑ Small intestinal villi ↓ The total bacteria, total yeast-fungi account, and sheep red blood cells levels No effect on the FI, egg production, egg weight, and FCR No effect on the shell stiffness, shape index, shell thickness, albumen index, yolk index, and Haugh Unit |
[142] |
| 0.075% a blend of formic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, and sorbic acid; medium-chain fatty acids combined with ammonium formate; and coconut/palm kernel fatty acid distillate in their water | No growth-promoting effects | [143] |
| 0.4% formic acid, propionic acid | Improved villus height: crypt depth ratio | [144] |
| 1% fumaric acid in diets | ↑ BWG | [145] |
| 1-3 g/kg (0.1–0.3%) of a blend of formic acid, lactic acid, malic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, and orthophosphoric acid in the drinking water | ↑ The apparent metabolizable energies and total phosphorous ileal digestibility ↑ BW, average daily gain, and average daily FI Negative impact on FCR |
[146] |
| 0.05% encapsulated butyrate | ↑ Intestinal weight and epithelial cell area | [74] |
| 2 g/kg organic oil blend | Villus height in ileum | [147] |
| 0.02%, 0.03% and 0.04% protected calcium butyrate | ↑ BWG ↑ Mucosa thickness, villus length, and crypt depth |
[148] |
| 2% citric acid | ↑ Epithelial cell proliferation and villi height of gastrointestinal tract | [149] |
| 5g/kg formic acid | ↑ BWG, dressing % ↓ FCR |
[150] |
| 3 kg/ton a commercial acidifier | ↑ Average daily gain ↓ FCR |
[151] |
| 0.1, 0.02, and 0.04% of formic and propionic acids | ↑ Beneficial intestinal bacterial flora load ↓ E. coli (K:88) ↑ Growth performance parameters ↑ IgG titer to sheep red blood cells and vaccination with infectious bursal disease and infectious bronchitis viruses |
[88] |
| 0.1% and 0.3% formic acid and citric acid for ducklings | ↑ BW, BWG, and FCR | [152] |
| 0.05 or 0.1% Encapsulated sodium butyrate | ↑ Ileal energy digestible coefficient | [72] |
| 2 g/kg OAs combined with 2 g/kg probiotics | ↑ Villus height and crypt depth | [153] |
| 800mg/kg micro encapsulated sodium butyrate | ↑ BW, daily gain, and FCR | [154] |
| 0.1% fermented fatty acids of wheat bran | ↓ Salmonella count | [58] |
| 1% formic acid in water of S. typhimurium infected broilers | ↓ Decreased BW | [155] |
| 0.05 % encapsulated butyric acid | ↑ Lactobacilli and Bifidobacterium ↓ Salmonella and coliform No effect on amylase, protease, and lipase |
[156] |
| Protected or unprotected 0.1% butyrate | No effect on gut weight, retention time, dry matter, organic matter, Nitrogen, and non-protein nitrogen | [157] |
| 0.2% mixture of 32% fumaric acid, 3% formic acid, 13% lactic acid, 3% propionic acid, and 1% citric acid | ↑ The expression of tight junction proteins and performance | [69] |
| 0.1%, 0.15%, and 2% a blend of ortho phosphoric acid, formic acid, and propionic acid in the drinking water | ↓ Growth performance parameters | [158] |
| Dietary 0.30 g/ kg sorbic acid and fumaric acid | ↑ Secretion of trypsin, lipase, and chymotrypsin in the intestine ↑ Spleen index ↑ Ig A in duodenal and ileal mucosa |
[75] |
| 0.06% sodium butyrate | ↑ Lactobacilli ↓ E. coli in Ileum |
[159] |
| A combination of sodium butyrate, citric acid, phosphoric acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, formic acid, and lactic acid | ↑ Growth performance parameters | [160] |
| 3 g/kg organic acid blend in Japanese quails | ↑ Villus height and width in jejunum and dudenum | [161] |
| A blend of OAs (0.1%) in the drinking water of broiler chickens orally challenged with (109 CFU/mL) C. jejuni | ↓ C. jejuni counts | [162] |
| 0.9% formic acid and sodium format | ↓ S. typhimurium colonization ↑ Growth performance parameters |
[163] |
| Dietary fumaric acid | ↑Erythrocyte counts, hemoglobin concentration, and the serum total protein, albumin, globulin, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol | [164] |
| 0.1% (formic acid, acetic acid, and ammonium formate) in drinking water of broilers | ↑ Growth performances ↑ Actinobacteria count ↓ Proteobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, and Cyanobacteria count The relative abundance of the Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, and the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio were not affected |
[165] |
| 0.6 and 1.2g/kg Sodium butyrate | ↑ Average daily gain and FCR | [166] |
| 3% fumaric acid in a diet | ↓ Cholesterol and total lipids | [167] |
| Encapsulated organic acids of formic acid, acetic acid, and butyric acid, besides, essential oils thymol, carvacrol,β-cymene, borneol and myrcene coated with a matrix of triglyceride | ↑ Epithelium thickness and surface area | [105] |
| 0.5 kg/ton feed formic acid with cinnamaldehyde | ↓ Proliferation of C. coli No effect on the cecal and carcass surface loads |
[168] |
| 0.2% butyric acid | No significant effect on dry matter, crude protein, ether extract, calcium, phosphorus, and apparent metabolized energy | [169] |
| 0.2% a mixture of 32% fumaric acid, 3% formic acid, 13% lactic acid, 3% propionic acid, and 1% citric acid | ↓ E. coli population ↑ Lactobacillus spp. and E. coli ratio in the ileum and caecum |
[64] |
| 0.3% a blend of acetic acid, propionic acid, formic acid, and ammonium formate | ↑ Villus height | [4] |
| Dietary supplementation of phosphoric acid (0.1, 0.2, and 0.3/kg) and lactic acid (0.3 g/kg). | ↑ Feed-to-gain ratio ↑ Trypsin, chymotrypsin, and lipase secretion in the duodenum ↑ Breast and thigh muscle pH value ↓ Cooking loss and meat tenderness ↓ Abundance of E. coli and Salmonella ↑ Villus height of the duodenum |
[86] |
| 1 g/kg of diet a mixture of formic acid 40%, formate 40%, and sodium 20% | ↑ Serum glucose level | [170] |
| 0.5-2.5 g/kg feed short and medium chain fatty acids | ↓ C. perfringens shedding in the caecum | [171] |
| A blend of formic acid, acetic acid, and ammonium formate (1.5 ml/L drinking water) + a blend of encapsulated butyrate, encapsulated multi-chain fatty acids, OAs mainly sorbic acid, and phenolic compound) was added to the basal diets at 0.15% and 0.1% in Eimeria spp. challenged broilers | ↑ Average BW, average BWG, and FCR ↑ TNF-γ ↓ Intestinal crypt depth ↑ Villus-height: crypt depth ratio ↑ Intestinal goblet cells ↑ Lactobacillus reuteri, Cyanobacteria |
[31] |
| 0.3% a mixture of 11% formic acid, 13% ammonium formate, 5.1% acetic acid, 10% propionic acid, 4.2% lactic acid, and 2% of other lower levels of OAs (sorbic acid and citric acid) (3000 mg/kg diet) | ↑ Formic acid in cecal contents on day 21 and acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, and the total volatile fatty acids in the cecal content on day 42. ↑ IgA, D-lactate, and IL-10 ↓ pH value in duodenum ↑Amylase activity of the pancreas and the tight junction protein (mainly Claudin-1, Claudin-2, and ZO-1) in duodenum ↑ Villus: crypt ratio in ileum Modulate s microbiota structure ↓ Abundance of E. coli |
[26] |
| Dietary fumaric acid (15 g/kg feed) in Japanese quails | ↑ BW, BWG, and FCR | [27] |
| 0.1% organic acid | ↑ villus height of jejunum | [70] |
| A blend of formic acid (32%), acetic acid (7%), and ammonium formate (20%) | Formic acid improved the physical growth, digestibility, immunity, and antimicrobial activity Acetic acid showed anti-bacteria effect |
[3] |
| 0, 1, 1.5 g/kg feed formic acid | ↑ BW, BWG, and the amount of feed ingested ↓ Glucose, triglycerides, and cholesterol |
[28] |
| A mixture of formic acid (32%), acetic acid (7%), ammonium format (20%), mono- and diglyceride of unsaturated fatty acids, and copper acetate (Under high stocking density) | ↓ Chyme pH value in the proventriculus, gizzard, and duodenum ↑ acetic acid, butyric acid, and isovaleric acid in cecal chyme ↓ Valeric acid in cecal chyme |
[54] |
| A combination of both OAs blend (formic acid, propionic acid, ammonium formate, and ammonium propionate) (200 mg/kg) and essential oils mixture (150mg/kg) | Improve BWG and FCR ↑ Villus height ↓ Growth of C. perfringens, E. coli, and Salmonella ↓ Intestinal lesion score ↓ Serum level of calprotectin and liver enzymes |
[15] |
3. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haulisah, N.A.; Hassan, L.; Bejo, S.K.; Jajere, S.M.; Ahmad, N.I. High levels of antibiotic resistance in isolates from diseased livestock. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 652351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, K.; Becker, S.; Xiao, Y.; Lyu, W.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, G. Differential impact of sub therapeutic antibiotics and ionophores on intestinal microbiota of broilers. Microorganisms. 2019, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.U.; Naz, S.; Raziq, F.; Qudratullah, Q.; Khan, N.A.; Laudadio, V.; Tufarelli, V.; Ragni, M. Prospects of organic acids as safe alternative to antibiotics in broiler chickens diet. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 32594–32604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, D.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, H.J.; Wu, S.G.; Han, Y.M.; Wu, Y.Y.; Qi, G.; Wang, J. Organic acids as alternatives for antibiotic growth promoters alter the intestinal structure and microbiota and improve the growth performance in broilers. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 618144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, A.; Iqbal, S.; Sikandar, A.; Din, S.; Khan, I.; Ashraf, S.; Khan, R.U.; Laudadio, V.; Tufarelli, V. Feeding of phytobiotics and exogenous protease in broilers: comparative effect on nutrient digestibility, bone strength and gut morphology. Agriculture. 2021, 11, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicutella, F.; Mannelli, F.; Daghio, M.; Viti, C.; Buccioni, A. Polyphenols and organic acids as alternatives to antimicrobials in poultry rearing: a review. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021, 10, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, S.; Banday, M.T.; Bhat, G.A., Mir, M.S.; Rehman, M. Effect of dietary supplementation of organic acids on performance, intestinal, histomorphology, and serum biochemistry of broiler chicken. Vet. Med. Int. 2010, 2010, 479485.
- Dittoe, D.K.; Ricke, S.C.; Kiess, A.S. Organic acids and potential for modifying the avian gastrointestinal tract and reducing pathogens and disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, D.; Mun, H.S.; Dilawar, M.A.; Baek, K.S.; Yang, C.J. Time for a paradigm shift in animal nutrition metabolic pathway: Dietary inclusion of organic acids on the production parameters, nutrient digestibility, and meat quality traits of swine and broilers. Life (Basel). 2021, 11, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzóska, F.; Śliwiński, B.; Michalik-Rutkowska, O. Effect of dietary acidifier on growth, mortality, post-slaughter parameters and meat composition of broiler chickens. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2013, 13, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlin, B.V.; Muthuvel, S.; Govidasamy, P.; Villavan, M.; Alagawany, M., Ragab Farag, M., Dhama, K., Gopi, M. Role of acidifiers in livestock nutrition and health: a review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Ber). 2020, 104, 558–569. [CrossRef]
- Vinolya, R.E.; Balakrishnan, U.; Yasi, B.; Chandrasekar, S. Effect of dietary supplementation of acidifiers and essential oils on growth performance and intestinal health of broiler. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2021, 30, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdEl-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Salem, H.M.; El-Tahan, A.M.; Soliman, M.M.; Youssef, G.B.A.; Taha, A.E.; Soliman, S.M.; Ahmed, A.E.; El-kott, A.F.; Al Syaad, K.M; Swelum, A.A. Alternatives to antibiotics for organic poultry production: Types, modes of action and impacts on bird’s health and production. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.H.; Abbas, W.; Huang, J.; He, Q.; Zhen, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z. Effect of blending encapsulated essential oils and organic acids as an antibiotic growth promoter alternative on growth performance and intestinal health in broilers with necrotic enteritis. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Z.; Sultan, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, K.; Jan, A.U.; Aziz, T.; Alharbi, M.; Alshammari, A.; Alasmari, A.F. Effects of an organic acids blend and coated essential oils on broiler growth performance, blood biochemical profile, gut health, and nutrient digestibility. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 23, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawi, M.H.; Abdullah, A.; Ismail, A.; Sarbini, S.R. Manipulation of gut micro biota using acacia gum polysaccharide. ACS Omega. 2021, 6, 17782–17797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeid, T.A.; Al-Homidan, I.H. Organic acids and their potential role for modulating the gastrointestinal tract, antioxidative status, immune response, and performance in poultry: a review. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2022, 78, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricke, S.C. Perspectives on the use of organic acids and short chain fatty acids as antimicrobials. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coban, H.B. Organic acids as antimicrobial food agents: applications and microbial productions. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 43, 569–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, A.A.; Kermanshahi, H.; Golian, A.; Gholizadeh, M.; Gilani, A. Evaluation of varying levels of acid-binding capacity of diets formulated with various acidifiers on physical and histological characteristics of leg bones in broiler chickens. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 23, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, K.; Page, G. Validation of an alternative growth promoter, Presan FY, under research and commercial broiler production conditions in North America. In: Metabolism and Nutrition: Feed Additives I. Poultry Science, United State, 2017; pp. 118.
- Polycarpo, G.V.; Andretta, I.; Kipper, M,; Cruz-Polycarpo, V.C.; Dadalt, J.C.; Rodrigues, P.H.M.; Albuquerque, R. Meta-analytic study of organic acids as an alternative performance-enhancing feed additive to antibiotics for broiler chickens. Poult. Sci., 2017, 96, 3645–3653. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adewole, D.I.; Oladokun, S.; Santin, E. Effect of organic acids–essential oils blend and oat fiber combination on broiler chicken growth performance, blood parameters, and intestinal health. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banupriya, S.; Kathirvelan, C.; Patric Joshua, P. Significance of feed acidification in poultry feed. Int. J. Sci. Environ. Technol. 2016, 5, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Hamid, H.; Shi, H.Q.; Ma, G.Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, W.X.; Zhao, L.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ji, C.; Ma, Q.G. Influence of acidified drinking water on growth performance and gastrointestinal function of broilers. Poult Sci. 2018, 97, 3601–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Mahfuz, S.; Wang, J.; Piao, X. Effect of dietary supplementation with mixed organic acids on immune function, antioxidative characteristics, digestive enzymes activity, and intestinal health in broiler chickens. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 673316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, F.M.; Ismail, I.E.; Attia, A.I.; Fikry, A.M.; Khalifa, E.; Alagawany, M. Use of fumaric acid as a feed additive in quail's nutrition: its effect on growth rate, carcass, nutrient digestibility, digestive enzymes, blood metabolites, and intestinal microbiota. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaw, A.A.; Hatem, Q.Z.; Kamil, Y.M. Effect of dietary fumaric acid on growth performance and some biochemical parameters in broiler. IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1252, 012120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibner, J.J.; Buttin, P. Use of organic acids as a model to study the digestibility, immune response and intestinal morphology of male broilers fed phosphorus deficient diets supplemented with microbial phytase and organic acids. Livest. Sci. 2002, 157, 506–513. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazalah, A.A.; Atta, A.M.; Elkloub, K.; Mustafa, M.E.L.; Shata, R.F.H. Effect of dietary supplementation of organic acids on performance, nutrients digestibility and health of broiler chicks. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2011, 10, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Bai, S.P.; Zeng, Q.F.; Ding, X.M.; Wang, J.P.; Xuan, Y.; Su, Z.W.; Zhang, K.Y. Effect of organic acids on growth performance, intestinal morphology, and immunity of broiler chickens with and without coccidial challenge. AMB Express. 2021, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauksiene, A.; Ruzauskas, M.; Gruzauskas, R.; Zavistanaviciute, P.; Starkute, V.; Lele, V.; Klupsaite, D.; Klementaviciute, J.; Bartkiene, E. A comparison study of the caecum microbial profiles, productivity and production quality of broiler chickens fed supplements based on medium chain fatty and organic acids. Animals (Basel). 2021, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melaku, M.; Zhong, R.; Han, H.; Wan, F.; Yi, B.; Zhang, H. Butyric and citric acids and their salts in poultry nutrition: Effects on gut health and intestinal microbiota. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Chen, B.; Huang, Y.Q.; Li, P.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, W. Impact of drinking water supplemented 2-hydroxy-4-methylthiobutyric acid in combination with acidifier on performance, intestinal development, and microflora in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidifard, M.; Khalaji, S.; Hedayati, M.; Rajaei sharifabadi, H. Use of condensed fermented corn extractives (liquid steep liquor) as a potential alternative for organic acids and probiotics in broiler ration. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 22, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okey, S.N. Alternative feed additives to antibiotics in improving health and performance in poultry and for the prevention of antimicrobials: A review. Niger. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2023, 6, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hermans, D.; Martel, A.; Van Deun, K.; Verlinden, M.; Van Immerseel, F.; Garmyn, A.; Messens, W.; Heyndrickx, M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F. Intestinal mucus protects Campylobacter jejuni in the ceca of colonized broiler chickens against the bactericidal effects of medium-chain fatty acids. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Guo, A. Biological function of short-chain fatty acids and its regulation on intestinal health of poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 736739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaveerach, P.; Lipman, L.J.A.; van Knapen, F. Antagonistic activities of several bacteria on in vitro growth of 10 strains of campylobacter jejuni/coli. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 90, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Iqbal, J. Recent advances in the role of organic acids in poultry nutrition. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2016, 44, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannenas, I.A.; Papaneophytou, C.P.; Tsalie, E.; Triantafillou, E.; Tontis, D.; Kontopidis, G. A. The effects of benzoic acid and essential oil compounds in combination with protease on the performance of chickens. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2014, 23, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamidi, I.; Paraskeuas, V.; Theodorou, G.; Breitsma, R.; Schatzmayr, G.; Theodoropoulos, G.; Kostas, F.; Mountzouris, K.C. Effects of dietary acidifier supplementation on broiler growth performance, digestive and immune function indices. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2016, 57, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, P.; Parsons, C.M. The effects of several organic acids on growth performance, nutrient digestibilities, and cecal microbial populations in young chicks. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 2581–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, M.; Manafi, M.; Yari, M.; Avara, A. The influence of an acidifier feed additive on biochemical parameters and immune response of broilers. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2014, 4, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, T. The antimicrobial effect of dissociated and un-dissociated sorbic acid at different pH levels. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1983, 54, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajati, H. Application of organic acids in poultry nutrition. Int. J. Avian Wildlife Biol. 2018, 3, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markazi, A.D.; Luoma, A.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Muruge san, R.; Mohnl, M.; Selvaraj, R. Effect of acidifier product supplementation in laying hens challenged with Salmonella. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2019, 28, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanello, C.; Vieira, S.L.; Rios, H.V.; Simoes, C.T.; Ferzola, P.H.; Sorbara, J.O.B.; Cowieson, A.J. Effects of energy, α-amylase, and β-xylanase on growth performance of broiler chickens. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2017, 225, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huyghebaert, G.; Richard, D.; Van Immerseel, F. An update on alternatives to antimicrobial growth promoters for broilers. Vet. J. 2011, 187, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Seok, W.J.; Kim, I.H. Organic acids mixture as a dietary additive for pigs—A review. Animals (Basel). 2020, 10, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.M.D.; Casanova, N.A.; Miyakawa, M.E.F. Microbiota, gut health and chicken productivity: what is the connection? Microorganisms. 2019, 7, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, J.A.; Boy, R.D.; Elrod, C.C. Medium-chain fatty acids and monoglycerides as feed additives for pig production: towards gut health improvement and feed pathogen mitigation. J. Anim. Sci. Bio. 2020, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, G.M.; Aniecevski, E.; Petrolli, T.G.; Da Rosa, G.; Boiago, M.M.; Simões, C.A.; Wagner, R.; Copetti, P.M.; Morsch, V.M.; Araujo, D.N.; Marcon, H.; Pagnussatt, H.; Santos, H.V.; Mendes, R.E.; Loregian, K.E.; Da Silva, A.S. Growth performance and meat quality of broilers fed with micro encapsulated organic acids. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 271, 114706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirshfield, I.N.; Terzulli, S.; O’Byrne, C. Weak organic acids: A panoply of effects on bacteria. Sci. Prog. 2003, 86, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Chen, B.; Dong, Y.; Miao, Z.; Su, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, J. Evaluation of liquid organic acids on the performance, chyme ph, nutrient utilization, and gut microbiota in broilers under high stocking density. Animals (Basel). 2023, 13, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljumaah, M.R.; Alkhulaifi, M.M.; Abudabos, A.M.; Alabdullatifb, A.; El Mubarak, A.H.; Al Suliman, A.R.; Stanley, D. Organic acid blend supplementation increases butyrate and acetate production in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium challenged broilers. PLoS One. 2020, 15, 0232831–0232831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.U.; Chand, N.; Ali, A. Effect of organic acids on the performance of Japanese quails. Pak. J. Zool. 2016, 48, 1799–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, K.; Verspreet, J.; Courtin, C.; Haesebrouck, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Van Immerseel, F. Reduced particle size wheat bran is butyrogenic and lowers Salmonella colonization, when added to poultry feed. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 198, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Dai, D.; Zhang, H.J.; Wu, S.G.; Han, Y.M.; Wu, Y.Y.; Qi, G.H. Organic acids modulate systemic metabolic perturbation caused by Salmonella pullorum challenge in early-stage broilers. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Salem, H.M.; El-Tahan, A.M.; Abd El-Mageed, T.A.; Soliman, S.M.; Khafaga, A.F.; Swelum, A.A.; Ahmed, A.E.; Alshammari, F.A.; Abd El-Hack, M.E. The control of poultry salmonellosis using organic agents: An updated overview. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, K.G.; Rahimi, S.; Khaki, P. Comparison of the effects of probiotic, organic acid and medicinal plant on Campylobacter jejuni challenged broiler chickens. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2012, 14, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, H.M.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Youssef, A.W.; Hassan, E.R. Effect of using organic acids to substitute antibiotic growth promoters on performance and intestinal microflora of broilers. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 23, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, N.K.; Daneshmand, A.; Naeini, S.Z.; Graystone, E.N.; Broom, L.J. Effects of commercial organic acid blends on male broilers challenged with E. coli K88: performance, microbiology, intestinal morphology, and immune response. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 3254–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, S.A.; A-Nasser, A.; Al-Khalaifah, H.S.; AlSadek, D.M.M.; Abdel fattah, D.M.; Roushdy, E.M.; Sherief, W.R.I.A.; Farag, M.F.M.; Altohamy, D.E.; Abdel-Wareth, A.A.A.; Metwally, A.E. Effect of dietary medium-chain-monoglycerides on the growth performance, intestinal histomorphology, amino acid digestibility, and broiler chickens’ blood biochemical parameters. Animals (Basel). 2021, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelli, N.; Pérez, J.F.; Vilarrasa, E.; Cabeza Luna, I.; Melo-Duran, D.; D'Angelo, M.; Solà-Oriol, D. Targeted-release organic acids and essential oils improve performance and digestive function in broilers under a necrotic enteritis challenge. Animals (Basel). 2020, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, A.Y.; Yu, X.G.; Fu, Y.Q.; Wang, M.W.; Qi, N.S.; Xia, M.H.; Kallon, S.; Pan, W.D.; Shi, X.L.; Fang, Y. Effects of dietary supplement of organic acids induced protective immunity against coccidiosis. Iran. J. Appl. Anim. Sci. 2020, 10, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.U.; Naz, S.; Dhama, K.; Kathrik, K.; Tiwari, R.; Abdelrahman, M.M.; Alhidary, I.A.; Zahoor, A. Direct-fed microbial: beneficial applications, modes of action and prospects as a safe tool for enhancing ruminant production and safeguarding health. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 12, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fandos, E.; Martinez-Laorden, A.; Perez-Arnedo, I. Combined effect of organic acids and modified atmosphere packaging on listeria monocytogenes in chicken legs. Animals (Basel). 2020, 10, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodjan, P.; Soisuwan, K.; Thongprajukaew, K.; Theapparat, Y.; Khongthong, S.; Jeenkeawpieam, J., Salaeharae, T. Effect of organic acids or probiotics alone or in combination on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, enzyme activities, intestinal morphology and gut microflora in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Berl). 2018, 102, 931–940. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Kim, I.H. Protected organic acids improved growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and decreased gas emission in broilers. Animals (Basel). 2020, 10, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshkumar, S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, I.H. Effects of the inclusion of dietary organic acid supplementation with anti-coccidium vaccine on growth performance, digestibility, fecal microbial, and chicken fecal noxious gas emissions. Braz. J. Poultry Sci. 2021, 23, eRBCA-2020-1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Islam, K.M.S.; Khan, M.J.; Karim, M.R.; Haque, M.N.; Khatun, M.; Pesti, G.M. Effect of citric acid, avilamycin, and their combination on the performance, tibia ash, and immune status of broilers. Poult, Sci. 2009, 88, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.D.; Bayir, H.O.; Cosby, D.E.; Cox, N.A.; Williams, S.M.; Fowler, J. Evaluation of encapsulated sodium butyrate on growth performance, energy digestibility, gut development, and Salmonella colonization in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 3638–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelqader, A.; Al-Fataftah, A.R. Effect of dietary butyric acid on performance, intestinal morphology, microflora composition and intestinal recovery of heat-stressed broilers. Livest. Sci. 2016, 183, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.I., Mosaad, G.M., Abd Elstar, M. Effect of feeding citric acid on performance of broiler ducks fed different protein levels. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 2016, 6, 18–26.
- Yang, X.; Xin, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, X. Impact of essential oils and organic acids on the growth performance, digestive functions and immunity of broiler chickens. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.; Polycarpo, G.; Barbieri, A.; Silva, K.; Ventura, G.; Polycarpo, V.C.C. Performance and economic viability of broiler chickens fed with probiotic and organic acids in an attempt to replace growth-promoting antibiotics. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2019, 21, eRBCA-2018-0912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanello, C.; Rosa, D.P.; Dalmoro, Y.K.; Segatto, A.L.; Vieira, M.S.; Moraes, M.L.; Santin, E. Protected blend of organic acids and essential oils improves growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and intestinal health of broiler chickens undergoing an intestinal challenge. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 6, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristimunha, P.C.; Rosa, A.P.; Boemo, L.S.; Garcez, D.C.; Rosa, D.P.; Londero, A.; Scher, A.; Forgiarini, J. A blend of benzoic acid and essential oil compounds as an alternative to antibiotic growth promoters in broiler diets. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2016, 25, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegani, M.; Korver, D.R. Factors affecting intestinal health in poultry. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 2052–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourya, P.S. Nutrient utilization and growth performance of broilers on dietary supplementation of acidifiers. Ind. J. Anim. Nutr. 2011, 28, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, S.R.; Zulkifli, I.; Davoodi, H.; Zunita, Z.; Ebrahimi, M. Growth performance, intestinal microflora, plasma fatty acid profile in broiler chickens fed herbal plant (Euphorbia hirta) and mix of acidifiers. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2012, 178, 167–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, F.; García, V.; Madrid, J.; Orengo, J.; Catalá, P.; Megías, M.D. Effect of formic acid on performance, digestibility, intestinal histomorphology and plasma metabolite levels of broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2006, 47, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.J.; Zheng, Y.W.; Lai, C.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Zeng, X. Effects of the cooperation of EM and acidifier on digestive enzyme activity, blood biochemical indes and calcium and phosphorus metabolism of broiler. Shandong Poult. 2003, 6, 10–13, [In Chinese)]. [Google Scholar]
- Luckstadt, C.; Mellor, S. The use of organic acids in animal nutrition, with special focus on dietary potassium diformate under European and austral-Asian conditions. Recent Adv. Anim. Nutr. Aus. 2011, 18, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.Q.; Shi, H.Q.; Xie, W.Y.; Zhao, L.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ji, C.; Ma, Q.G. Dietary supplementation with acidifiers improves the growth performance, meat quality and intestinal health of broiler chickens. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudabos, A.M.; Alyemni, A.H.; Dafalla, Y.M.; Khan, R.U. Effect of organic acid blend and Bacillus subtilis alone or in combination on growth traits, blood biochemical and antioxidant status in broilers exposed to Salmonella typhimurium challenge during the starter phase. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2017, 45, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, N.K.; Naeini, S.Z.; Ruiz-Feria, C.A. Growth performance, digestibility, immune response and intestinal morphology of male broilers fed phosphorus deficient diets supplemented with microbial phytase and organic acids. Livest. Sci. 2013, 157, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawale, A. Better eggshell quality with a gut acidifier. Poult. Int. 2005, 44, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Nezhad, Y.E.; Sis, N.M.; Shahryar, H.A.; Dastouri, M.R.; Golshani, A.A.; Tahvildarzadeh, A.; Najafyan, K.A. The effects of combination of citric acid and microbial phytase on the egg quality characteristics in laying hens. Asian J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2008, 3, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeson, S.; Namkung, H.; Antongiovanni, M.; Lee, E.H. Effect of butyric acid on the performance and carcass yield of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 1418–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Jung, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, I.S.; Lee, J.H.; Jo, C. Effect of dietary supplementation of the combination of gallic and linoleic acid in thigh meat of broilers. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 25, 1641–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuoso, B.F.; Dosreis, J.H.; Gebert, R.R.; Barreta, M,; Griss, L.G.; Casagrande, R.A.; De Cristo, T.G.; Santiani, F.; Campigotto, G.; Rampazzo, L.; Stefani, L.M,; Boiago, M.M,; Lopes, L.Q.; Santos, R.C.V,; Baldissera, M.D,; Zanette, R.A,; Tomasi, T.; Da Silva, A.S. Glycerol monolaurate in the diet of broiler chickens replacing conventional antimicrobials: impact on health, performance and meat quality. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 129, 161–167. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X.J.; Gou, Z.Y.; Fan, Q.L.; Ye, J.L.; Jiang, S,Q. Potential effect of acidifier and amylase as substitutes for antibiotic on the growth performance, nutrient digestion and gut microbiota in yellow-feathered broilers. Animals (Basel). 2020, 10, 1858.
- Strous, G.J.; Dekker, J. Mucin-type glycoproteins. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1992, 27, 57–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, M.; Islam, K.M.S.; Howleder, M.A.R.; Haque, M.N.; Chowdhury, R.; Karim, M.R. Effects of dietary citric acid, probiotic and their combination on the performance, tibia ash and non-specific immune status of broiler. Ind. J. Anim. Sci, 2010, 80, 813–816. [Google Scholar]
- Adil, S.; Banday, T.; Bhat, G.A.; Mir, M.S.; Rehman, M. Effect of dietary supplementation of organic acids on performance, intestinal histomorphology, and serum biochemistry of broiler chicken. Vet. Med. Int. 2010, 2010, 479485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagawany, M.; Elnesr, S.S.; Farag, M.R.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Barkat, R.A.; Gabr, A.A.; Foda, M.A.; Noreldin, A.E.; Khafaga, A.F.; El-Sabrout, K.; Elwan, H.A.; Tiwari, R.; Yatoo, M.T.; Michalak, I.; Di Cerbo, A.; Dhama, K. Potential role of important nutraceuticals in poultry performance and health– a comprehensive review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 137, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakir, S.; Midilli, M.; Erol, H.; Simsek, N.; Cinar, M.; Altintas, A.; Alp, H.; Altintas, L.; Cengiz, Ö.; Antalyali, A. Use of combined pro biotic-prebiotic, organic acid and avilamycin in diets of Japanese quails. Rev. Med. Vet. 2008, 159, 565–569. [Google Scholar]
- García, V.; Catalá-Gregori, P.; Hernández, F.; Megías, M.D.; Madrid, J. Effect of formic acid and plant extracts on growth, nutrient digestibility, intestine mucosa morphology, and meat yield of broilers. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2007, 16, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kum, S.; Eren, U.; Önol, A.G.; Sandikci, M. Effects of organic acid supplementation on the intestinal mucosa in broilers. Rev. Med. Vet. 2010, 10, 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Dibner, J.J.; Richards, J.D. Antibiotic growth promoters in agriculture: History and mode of action. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.; Haldar, S.; Ghosh, T.K. Comparative efficacy of an organic acid blend and bacitracin methylene disalicylate as growth promoters in broiler chickens: effects on performance, gut histology, and small intestinal milieu. Vet. Med. Int. 2010, 2010, 645150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Fachi, J.L.; Vieira, A.; Sato, F.T.; Vinolo, M.A.R. Regulation of immune cell function by short-chain fatty acids. Clin. Transl. Immunology. 2016, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matty, H.N.; Hassan, A.A. Effect of supplementation of encapsulated organic acid and essential oil Gallant+® on some physiological parameters of Japanese quails. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 34, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, S.; Banday, T.; Bhat, G.A.; Salahuddin, M.; Raquib, M.; Shanaz, S. Response of broiler chicken to dietary supplementation of organic acids. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2011, 12, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaisrani, S.N.; Van Krimpen, M.M.; Kwakkel, R.P.; Verstegen, M.W.A.; Hendriks, W.H. Diet structure, butyric acid, and fermentable carbo hydrates influence growth performance, gut morphology, and cecal fermentation characteristics in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 2152–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Xiao, Z.; An, W.; Dong, Y., Zhang, B. Dietary sodium butyrate improves intestinal development and function by modulating the microbial community in broilers. PLoS One. 2018; 13, e0197762. [CrossRef]
- Elnesr, S.S.; Ropy, A.; Abdel-Razik, A.H. Effect of dietary sodium butyrate supplementation on growth, blood biochemistry, haematology and histomorphometry of intestine and immune organs of Japanese quail. Animal. 2019, 13, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.W.; Kessler, J.W.; Fuller, L.; Williams, S.; Mathis, G.F.; Lumpkins, B.; Valdez, F. Effect of feeding an encapsulated source of butyric acid (ButiPEARL) on the performance of male Cobb broilers reared to 42 d of age. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikandar, A.; Zaneb, H.; Younus, M.; Masood, S.; Aslam, A.; Khattak, F.; Ashraf, S.; Yousaf, M.S.; Rehman, H. Effect of sodium butyrate on performance, immune status, microarchitecture of small intestinal mucosa and lymphoid organs in broiler chickens. Asian-Australasian J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, R.Z.; Munawar, S.H.; Manzoor, Z.; Iqbal, Z.; Khan, M.N.; Saleemi, M.K; Zia, M.A.; Yousaf, A. Anticoccidial effects of acetic acid on performance and pathogenic parameters in broiler chickens challenged with Eimeria tenella. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2011, 31, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.; Seddiek, S.A.; Khater, H.F. Effect of butyrate, clopidol and their combination on the performance of broilers infected with Eimeria maxima. Br. Poult. Sci. 2014, 55, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fascina, V.B.; Pasquali, G.A.M.; Carvalho, F.B.; et al. Effects of phytogenic additives and organic acids, alone or in combination, on the performance, intestinal quality and immune responses of broiler chickens. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 2017, 19, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Park, G.H.; Ryu, K.S. Effect of feeding organic acid mixture and yeast culture on performance and egg quality of laying hens. Kor. J. Poult. Sci, 2009, 29, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Houshmand, M.; Azhar, K.; Zulkifli, I.; Bejo, M.H.; Kamyab, A. Effects of non-antibiotic feed additives on performance, immunity and intestinal morphology of broilers fed different levels of protein. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 42, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Khan, S.H.; Rehman, H. Effects of formic acid administration in the drinking water on production performance, egg quality and immune system in layers during hot season. Avian Biol. Res. 2013, 6, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.K.; Bae, S.; Gu, M.J.; You, S.J.; Kim, G.; Park, S.M.; Jeung, W.H.; Ko, K.H.; Cho, K.J.; Kang, J.S.; Yun, C.H. H9N2-specific IgG and CD4+ CD25+ T cells in broilers fed a diet supplemented with organic acids. Poult Sci. 2017, 96, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Q.F.; Gao, F.; Dai, S.F.; Chen, J.; Zhou, G.H. Sodium butyrate maintains growth performance by regulating the immune response in broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 2011, 52, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lecompte, J.C.; Yitbarek, A.; Brady, J.; Sharif, S.; Cavanagh, M.D.; Crow, G.; Guenter, W.; House, J.D.; Camelo-Jaimes, G. The effect of microbial nutrient interaction on the immune system of young chicks after early probiotic and organic acid administration. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Jeong, W.; Jeoung, H.Y. An Avian necrotic enteritis: experimental models, host immunity, pathogenesis, risk factors, and vaccine development Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, H.; Matthes, S.; Harnisch, S. The effect of organic acids in the rations on the performances of broilers and laying hens. Arch. Geflugelkd. 1981, 45, 221–232. [Google Scholar]
- Tamblyn, K.C. , Conner, D.E. Bactericidal activity of organic acids against Salmonella typhimurium attached to broiler chicken skin. J. Food Prot. 1997, 60, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runho, R.C.; Sakomura, N.K.; Kuana, S.; Banzatto, D.; Junqueira, O.M.; Stringhini, J.H. Use of an organic acid (fumaric acid) in broiler rations. Rev. Bras. Zootec. 1997, 26, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Van Immerseel, F.; Fievez, V.; De Buck, J.; Pasmans, F.; Martel, A.; Haesebrouck, F.; Ducatelle, R. Microencapsulated short-chain fatty acids in feed modify colonization and invasion early after infection with Salmonella Enteritidis in young chickens. Poult. Sci. 2004, 83, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, A.N.; Pourreza, J.; Samie, A.H. Effect of different levels of citric acid on calcium and phosphorus efficiencies in broiler chicks. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2006, 9, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Guo, Y. Effects of dietary sodium butyrate supplementation on the intestinal morphological structure, absorptive function and gut flora in chickens. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2007, 132, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengor, E.; Yardimci, M.; Cetingul, S.; Bayram, I.; Sahin, H.; Dogan, I. Short communication effects of short chain fatty acid (SCFA) supplementation on performance and egg characteristics of old breeder hens. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 37, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Fattah, S.A.; El-Sanhoury, M.H.; El-Medany, N.M.; Abdelazeem, F. 2008. Thyroid activity, some blood constituents, organs morphology and performance of broiler chicks fed supplemental organic acids. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2008, 7, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Do Vale, M.; Menten, J.F.M.; Daroz De Morais, S.C.; Brainer, M.M.A. Mixture of formic and propionic acid as additives in broiler feeds. Sci. Agric. (Piracicaba, Braz.). 2004, 61, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Rubio, C.; Ordonez, C.; Abad-González, J.; Garcia-Gallego, A.; Honrubia, M.P.; Mallo, J.J.; Balana-Fouce, R. Butyric acid-based feed additives help protect broiler chickens from Salmonella enteritidis infection. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.N.; Chowdhury, R.; Islam, M.A.; Akbar, M.A. Propionic acid is an alternative to antibiotics in poultry diet. Bangladesh J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 38, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, L.L.; Vidanarachchi, J.K.; Olnood, C.G.; Bao, Y.M.; Selle, P.H.; Choct, M. Effect of potassium diformate on growth performance and gut microbiota in broiler chickens challenged with necrotic enteritis. Br. Poult. Sci. 2009, 50, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.; Rao, S.R.; Raju, M.; Sunder, G.S. Effect of butyric acid on performance, gastrointestinal tract health and carcass characteristics in broiler chickens. Asian-Australs. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 22, 1026–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, A.; Pekel, A.Y.; Issa, G., Demirel, G.; Patterson, P.H. Effect of dietary copper, citric acid, and microbial phytase on digesta pH and ileal and carcass microbiata of broiler chickens fed a low available phosphorus diet. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2010, 19, 422–431. [CrossRef]
- Açikgöz, Z.; Bayraktar, H.; Altan, Ö. Effects of formic acid administration in the drinking water on performance, intestinal microflora and carcass contamination in male broilers under high ambient temperature. Asian-Australs. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 24, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, S.; Banday, M.T.; Bhat, G.A.; Qureshi, S.D.; Wani, S.A. Effect of supplemental organic acids on growth performance and gut microbial population of broiler chicken. Livestock Res. Rural Dev. 2011, 23, 241–149. [Google Scholar]
- Namkung, H.; Yu, H.; Gong, J.; Leeson, S. Antimicrobial activity of butyrate glycerides toward Salmonella typhimurium and Clostridium perfringens. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, S.; Andersson, M.G.; Löfström, C.; Skandamis, P.N.; Gounadaki, A.; Zentek, J.; Häggblom, P. Organic acids for control of Salmonella in different feed materials. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, A.M.; Ragaa, N.M. Effect of dietary supplementation of organic acids on performance and serum biochemistry of broiler chicken. Nat. Sci. 2014, 12, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Cerisuelo, A; Marín, C.; Sánchez-Vizcaino, F.; Gómez, E.A.; De La Fuente, J.M.; Durán, R.; Fernández, C. The impact of a specific blend of essential oil components and sodium butyrate in feed on growth performance and Salmonella counts in experimentally challenged broilers. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 599–606. [CrossRef]
- Gül, M.; Ali Tunç, M.; Seyda Cengiz; Yildiz, A. Effect of organic acids in diet on laying hens’ performance, egg quality indices, intestinal microflora, and small intestinal villi height. Europ. Poult. Sci., 2014, 78, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Jansen, W.; Reich, F.; Klein, G. Large-scale feasibility of organic acids as a permanent preharvest intervention in drinking water of broilers and their effect on foodborne Campylobacter spp. before processing. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboola, A.F.; Omidiwura, B.R.O.; Odu, O.; Popoola, I.O.; Iyayi, E.A. Effects of organic acid and probiotic on performance and gut morphology in broiler chickens. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 45, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banday, M.T.; Adil, S.; Khan, A.A.; Untoo, M. A study on efficacy of fumaric acid supplementation in diet of broiler chicken. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2015, 14, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khooshechin, F.; Hosseini, S.M.; Nourmohammadi, R. Effect of dietary acidification in broiler chickens: 1. Growth performance and nutrients ileal digestibility. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 14, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basmaciolu-Malayoglu, H.; Ozdemir, P.; Bagriyanik, H.A. Influence of an organic acid blend and essential oil blend, individually or in combination, on growth performance, carcass parameters, apparent digestibility, intestinal microflora and intestinal morphology of broilers. Br. Poult. Sci. 2016, 57, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, S.A.; Barri, A.; Hejdysz, M.; Rutkowski, A. Effect of different doses of coated butyric acid on growth performance and energy utilization in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadagheri, N.; Najafi, R.; Najafi, G. Effects of dietary supplementation of organic acids and phytase on performance and intestinal histomorphology of broilers. Vet. Res. Forum. 2016, 7, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Naela, M.; Korany, R.M. Studying the effect of formic acid and potassium deformity on performance, immunity and gut health of broiler chickens. Anim. Nutr. 2016, 2, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yang, C.W.; Yang, Z.B.; Yang, W.R.; Jiang, S.Z.; Yi Wen, K.E. Effects of feed acidifiers on growth performance, caecum micro flora and nutrient and energy utilisation in broilers. Eur. Poult. Sci. 2017, 81, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaggar, A.S.; Abo El-Maaty, H.M.A. Impact of using organic acids on growth performance, blood biochemical and hematological traits and immune response of ducks (Cairina moschata). Egypt. Poult. Sci. J. 2017, 37, 907–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodjan, P.; Soisuwan, K.; Thongprajukaew, K.; Theapparat, Y.; Khongthong, S.; Jeenkeawpieam, J.; Salaeharae, T. Effect of organic acids or probiotics alone or in combination on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, enzyme activities, intestinal morphology and gut microflora in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutri (Berl). 2017, 102, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhen, W.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Z.; Guo, Y. Effect of microencapsulated sodium butyrate dietary supplementation on growth performance and intestinal barrier function of broiler chickens infected with necrotic enteritis. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 232, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourassa, D.V.; Wilson, K.M.; Ritz, C.R.; Kiepper, B.K.; Buhr, R.J. Evaluation of the addition of organic acids in the feed and/or water for broilers and the subsequent recovery of Salmonella typhimurium from litter and ceca. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazi, V.; Foroozandeh, A.D.; Toghyani, M.; Dastar, B.; Koochaksaraie, R.R. Effects of Pediococcus acidilactici, mannan-oligosaccharide, butyric acid and their combination on growth performance and intestinal health in young broiler chickens challenged with Salmonella typhimurium. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2034–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moquet, P.C.A.; Salami, S.A.; Onrust, L.; Hendriks, W.H.; Kwakkel, R.P. Butyrate presence in distinct gastrointestinal tract segments modifies differentially digestive processes and amino acid bioavailability in young broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, S.; Chand, N.; Khan, M.S.; Maris, H. Effect of organic acid blend on carcass yield, nutrient digestibility and tibia ash during starter phase of broiler chicks. Pak. J. Zool. 2018, 50, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makled MN, Abouelezz KFM, Gad-Elkareem AEG and Sayed AM (2019) Comparative influence of dietary probiotic, yoghurt, and sodium butyrate on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, blood hematology, and immune response of meat-type chickens. Tropical Animal Health and Production 51, 2333–2342.
- Sabour, S.; Tabeidian, S.A.; Sadeghi, G. Dietary organic acid and fiber sources affect performance, intestinal morphology, immune responses and gut microflora in broilers. Anim. Nutr. 2019, 5, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustundag, O.A.; Ozdogan, M. Effects of bacteriocin and organic acid on growth performance, small intestine histomorphology, and microbiology in Japanese quails (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 2187–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Yu, H.M.; Xie, J.J.; Cui, H.; Gao, X.H. Effect of pectin oligosaccharides and zinc chelate on growth performance, zinc status, antioxidant ability, intestinal morphology and short-chain fatty acids in broilers. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Berl). 2019, 103, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, P.; Yadav, S.; Cosby, D.E.; Cox, N.A.; Jendza, J.A.; Kim, W.K. Research Note: Effect of organic acid mixture on growth performance and Salmonella typhimurium colonization in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 2645–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; He, S.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, D.; Dai, S.; Hu, H. Effects of dietary supplementation of fumaric acid on growth performance, blood hematological and biochemical profile of broiler chickens exposed to chronic heat stress. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2020, 22, eRBCA-2019-1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, L.; Shao, D.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Han, Y.; Shi, S. Selectived and reshaped early dominant microbial community in the cecum with similar proportions and better homogenization and species diversity due to organic acids as AGP alternatives mediate their effects on broilers growth. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.X.; Li, S.Q.; Zhao, Z.; An, L. Sodium butyrate as an effective feed additive to improve growth performance and gastrointestinal development in broilers. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 6, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, H.; Afiffy, O.; Mahrous, M. Effect of using formic acid on growth performance and some blood parameter of broiler chicken. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2020, 66, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortada, M.; Cosby, D.E.; Shanmugasundaram, R.; Selvaraj, R.K. In vivo and in vitro assessment of commercial probiotic andorganic acid feed additives in broilers challenged with Campylobacter coli. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2020, 29, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nari, N.; Ghasemi, H.A. Growth performance, nutrient digestibility, bone mineralization, and hormone profile in broilers fed with phosphorus deficient diets supplemented with butyric acid and Saccharomyces boulardii. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- qbal, H.; Rahman, A.; Khanum,S.; Arshad, M.; Badar, I.H.; Asif, A.R.; Hayat, Z.; Iqbal, M.A. Effect of essential oil and organic acid on performance, gut health, bacterial count and serological parameters in broiler. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2021, 23, eRBCA-2021-1443. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Toghyani, M.; Kheravii, S.K.; Pineda, L.; Han, Y.; Swick, R.A. , Wu, S.B. Organic acid blends improve intestinal integrity, modulate short-chain fatty acids profiles and alter microbiota of broilers under necrotic enteritis challenge. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 8, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





