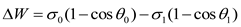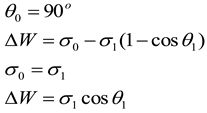1. Introduction
As is well known, oil and gas recovery rate is closely related to reservoir permeability and porosity. For conventional oil reservoirs, the water drive recovery rate can generally reach 30% to 40%.For tight oil reservoirs with a median porosity of 20% and a permeability range of μD to mD, the open flow rate of crude oil can be taken as 5% to 15%.The porosity of shale oil reservoirs is generally less than 15%, and the permeability is less than 1mD, so their recovery rate will be smaller. The recovery rate of shale oil is generally between 1% to 10% (Zhao Wenzhi et al., 2018). In order to improve the crude oil recovery rate of tight and even shale oil reservoirs, it is necessary to further clarify the solid-liquid relationship, improve fluid migration ability, and strengthen the injectability and crude oil utilization ability. Compared to conventional pore throats, nanopore throats exhibit significant nano confinement effects. Fluid and rock walls have strong adsorption properties. The confinement effect places high demands on the wetting effect of the injected fluid. In recent years, nanotechnology has gradually been widely applied in the field of oil and gas. Nano oil displacement agents can solve some engineering problems in the traditional oil and gas reservoir extraction process.Practical problems such as poor reservoir injectability, poor environmental adaptability, and significant reservoir damage. Nanomaterials have small size effects, surface effects, wetting properties, and shear thickening properties.These characteristics have broad application prospects in improving the oil and gas recovery rate of tight reservoirs.The retention and transport of carbon based nanomaterials in porous media have received widespread attention (Bernevig, B.A., 2022).
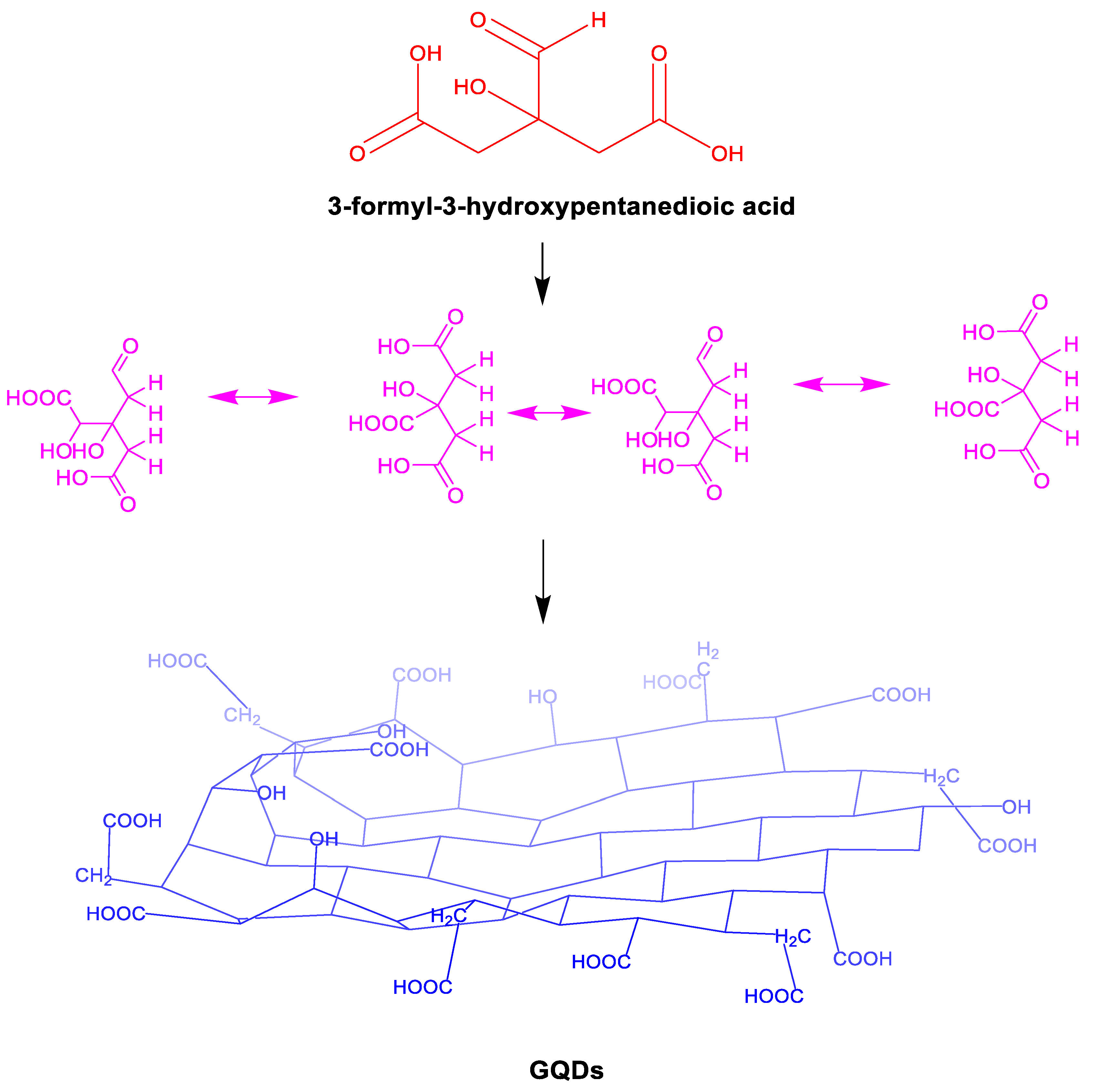
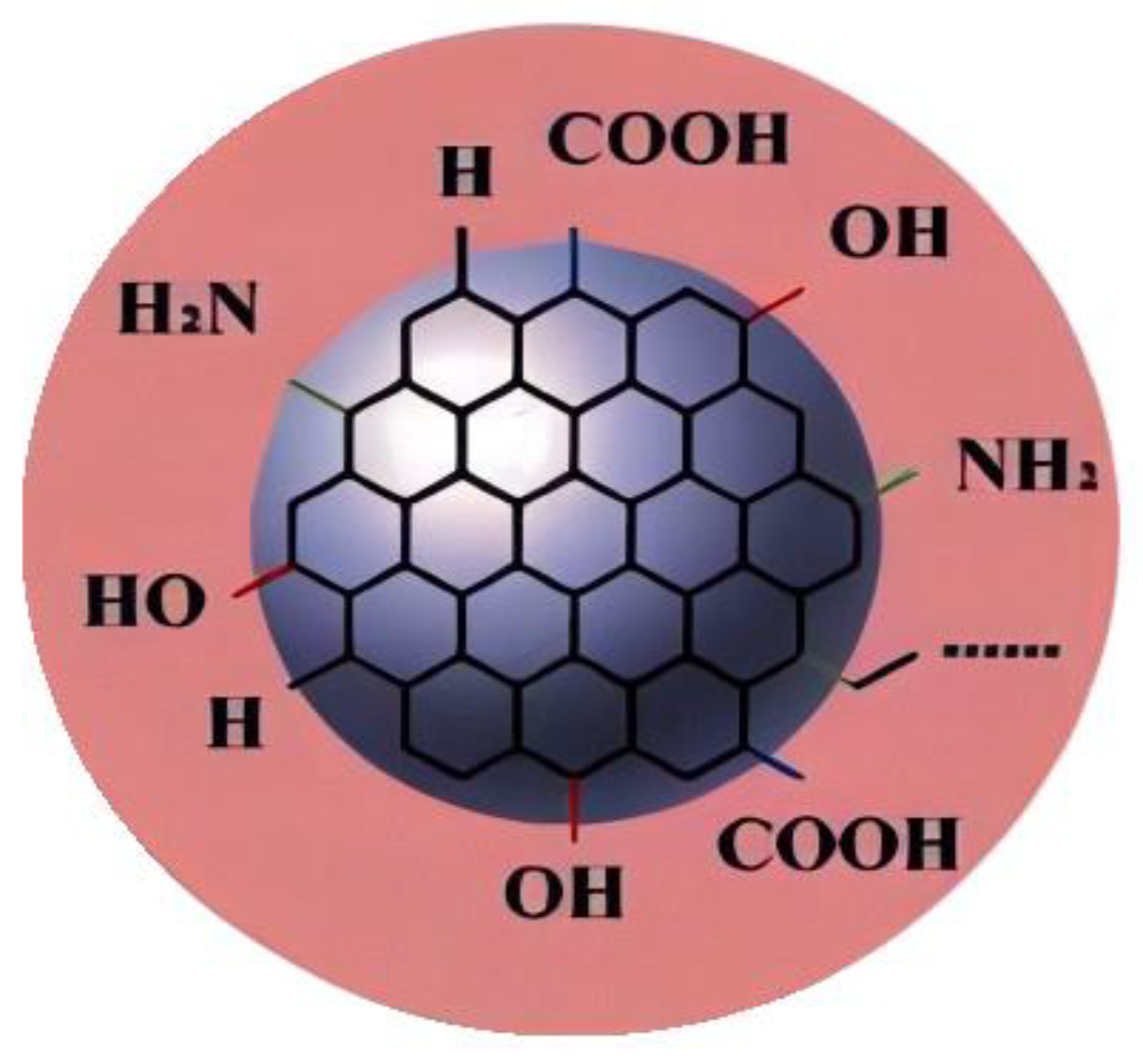
Graphene quantum dots( (GQDs) ) are nanomaterials with a size of less than 10 nm, a nearly spherical structure, and stable luminescence. Graphene quantum dots feature unique fluorescence properties, along with low toxicity and excellent biocompatibility. Consequently, they find a wide range of applications in biological imaging, fluorescence sensing, photocatalysis, and organic photovoltaic devices. This article primarily explores the potential applications of graphene quantum dots in oil and gas field development. GQDs are an emerging particle with rich advantages in oil and gas applications, structural diagram of graphene dots as shown in
Figure 1.For example, due to its inherent carbon based composition, these particles do not need to be separated from oil and gas products. It has good water solubility and biocompatibility, which can minimize pollution from environmental transport to the food chain. GQDs are graphite layered structures, which are carbon dots with a large network of sp
2 conjugated island structures. The surface functional groups include hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino, and carbonyl groups. Compared with one-dimensional graphene nanoribbons and two-dimensional graphene nanosheets, zero dimensional GQDs exhibit stronger quantum confinement and boundary effects below 10nm in size, and high concentration nanofluids can also exhibit stronger desorption ability. Stimulation responsive GQDs have advantages such as excellent interfacial activity, temperature and salt resistance, strong desorption, intelligence, and green environmental protection, and have broad application prospects in the field of tight oil and gas development.In order to achieve the dual carbon goal and combine the mechanism of carbon dioxide displacement to improve oil recovery.
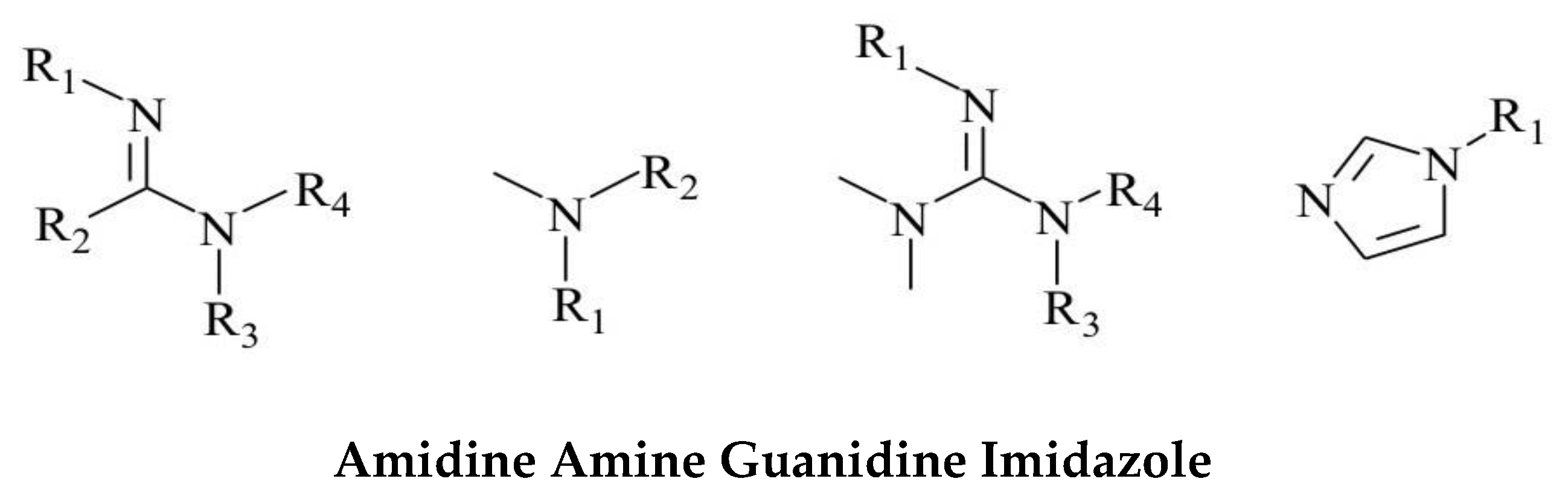
Common carbon dioxide responsive functional groups include tertiary amino groups, amide groups, amidine groups, and phenolic hydroxyl groups. Amino, hydroxyl, and ester groups have lone electron pairs, and these groups have good protonation ability in water dispersed fluids. Under the Lewis acid-base reaction, the hydrophilicity of the hydrophilic head group in the molecule is enhanced. Furthermore, the dispersion of solutes in the solution is altered, resulting in characteristic changes in the physical and chemical properties of the system. Numerous studies have demonstrated the advantage of amidine in binding CO2 because amidine is able to promote the formation of relatively stable carbamate salts. Efficient binding of CO2 by the deprotonation of the hydroxyl group. This article uses tertiary amidine groups to modify the functionality of GQDs. This study prepared graphene quantum dots using a hydrothermal method and synthesized functional graphene quantum dots responsive to carbon dioxide stimulation through the covalent grafting of amidine functional groups. The successful fabrication of the targeted functional graphene quantum dots was confirmed through characterization using infrared FTIR spectroscopy, particle size analysis, transmission electron microscopy, and fluorescence spectrophotometer. Evaluations were conducted to enhance crude oil recovery through tests measuring surface tension, oil-water interfacial tension, adhesion work calculations, wetting reversal experiments, oil sand washing rates, and indoor physical simulation of imbibition. This further assessed the potential application of the prepared carbon dioxide-responsive graphene quantum dots in the development of tight oil and gas fields.
Table 1.
Comparison of functional group performance in response to carbon dioxide stimulation [
16,
17,
18].
Table 1.
Comparison of functional group performance in response to carbon dioxide stimulation [
16,
17,
18].
| Serial Number |
Functional Group |
Advantage |
Boundedness |
| 1 |
Amidine |
Strong sensitivity to carbon dioxide;
A very small amount of carbon dioxide can quickly respond |
The amidine group is alkaline and undergoes a certain degree of hydrolysis in water. But cyclic amidines have the characteristics of simple preparation process and good stability |
| 2 |
Amine |
Weakly alkaline functional group;
Boramine absorbs carbon dioxide at room temperature 2.8 times more than the commonly used reagent ethanolamine, but its response speed is slow;
Tertiary amines are more sensitive to carbon dioxide response than primary amines, with better repeatability and efficiency |
The protonation reaction between the tertiary amino group and carbon dioxide is slow and requires continuous introduction of carbon dioxide for stimulation and regulation. |
| 3 |
Guanidine |
Guanidine and amidine groups have similar properties |
Organic strong base |
| 4 |
Imidazole |
The alkalinity is weak, and the protonated imidazole functional group is more stable compared to the amidine and tertiary amine groups |
High viscosity, with certain biological toxicity |
2. Material and Methods
Preparation of uniformly sized graphene quantum dots using citric acid high-temperature cracking.Efficient binding of CO2 by the deprotonation of the hydroxyl group.This article uses tertiary amidine groups to modify the functionality of GQDs.
Figure 3.
Mechanism of graphene dot synthesis by citric acid pyrolysis.
Figure 3.
Mechanism of graphene dot synthesis by citric acid pyrolysis.
2.1. Experimental Materials
Main Chemical reagents: citric acid(99%), sodium hydroxide(chemical analysis pure), deionized water(Self made in this laboratory).Size and physical property parameters of cores:Three naturally dense core columns, each 5cm in length, 2.5cm in diameter, and with a porosity of 8%. The core permeabilities are 0.39×10-3μm2, 0.45×10-3μm2, and 0.34 ×10-3μm2, respectively.
Experimental instrument: Fourier transform infrared Spectrometer; X-ray diffraction Spectrometer; Laser particle size analyzer; Heated digital display constant temperature magnetic stirrer; Quasi micro electronic balance, Surface thermometer, pH meter and so on. Parameter list representing the main equipment is shown in
Table 2.
2.2. Experimental Procedures
Graphene quantum dots were prepared by citric acid pyrolysis method. The specific preparation process involves placing 2g of citric acid into a 25mL beaker, and then heating the beaker on a digital constant temperature platform (the bottom temperature of the beaker was measured to be 200 ℃).After 3 minutes, citric acid becomes liquid, and within 15 minutes, its color changes from colorless to light yellow, orange, and orange red. Add the liquid obtained from the reaction dropwise into 100mL of 4mg/mL NaOH solution, while vigorously stirring the solution with a magnetic stirrer, and then adjust the pH of the solution with NaOH.
During this process, a series of color changes are accompanied, ultimately resulting in a solution of graphene quantum dots.Synthesize highly dispersed functionalized GQDs through the formation reaction of amide bonds between carboxyl groups and amines in GQDs (F-GQDs).
2.3. Structural Characterization
Infrared Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), particle size analysis, transmission electron microscopy, and fluorescence spectroscopy were used to characterize the structure of the developed functional graphene quantum dots.
2.4. Wetting Reversal Characteristic Experiment
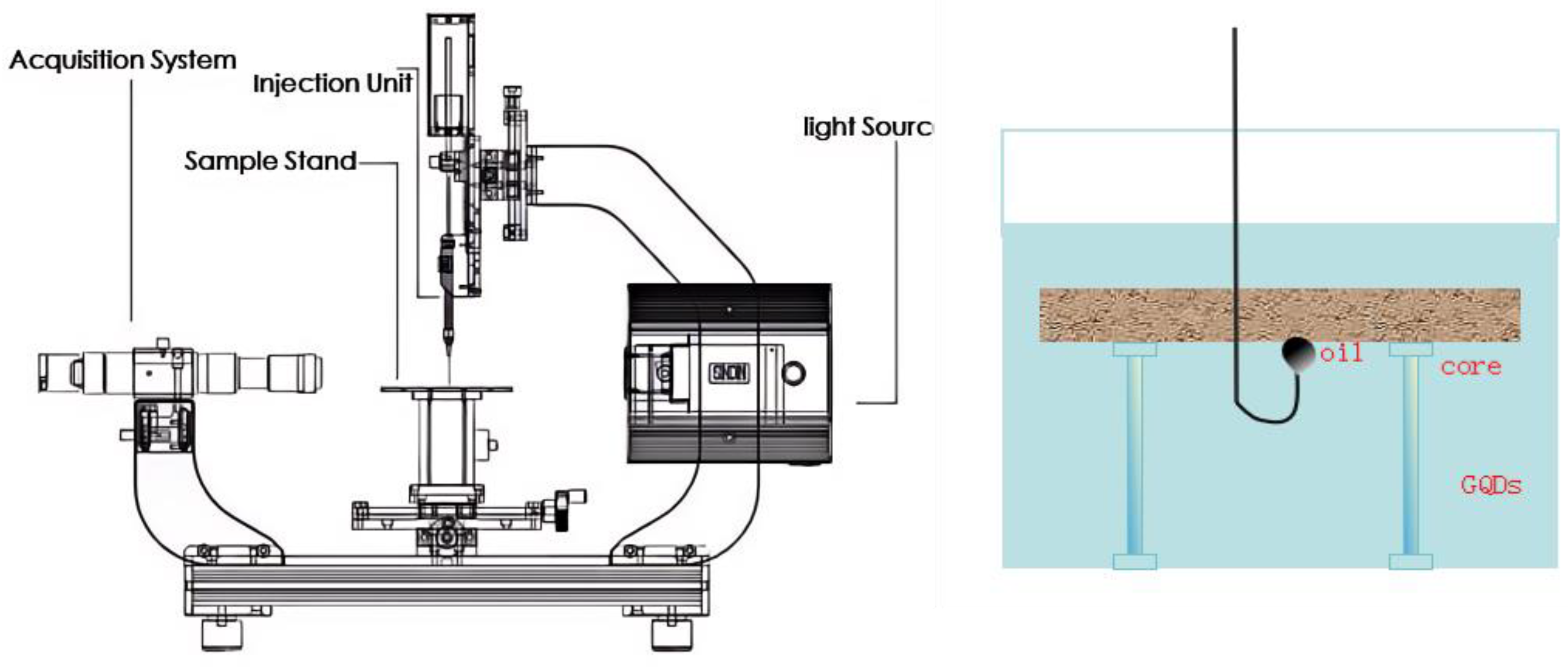
Using dense natural rock core as the experimental physical model, the permeability of the rock core is 0.1 × 10-3 μ m2. Soak the core in water and 0.1wt% F-GQD separately, and use a contact angle tester to add aviation kerosene to the surface of the core in reverse using a three-phase contact method. Monitor the changes of the wetting angle. Experimental conditions: temperature: 20 ℃, pressure: 0.1MPa.
Figure 4.
Contact angle tester (right: measuring sample).
Figure 4.
Contact angle tester (right: measuring sample).
2.5. Surface Tension and Interfacial Tension Determination Experiments
The surface and interfacial tension of the nanoflooding agent was determined according to the surface and interfacial tension measurement method (SY / T 5370-2018).Experiment condition: temperature is 45℃ and 95℃; pressure: 0.1MPa.Nanoflooding agents (F-GQDs) were prepared according to the stock solution concentration of 0.1%, The experimental oil is aviation kerosene.
2.6. Calculation of Adhesion Work Reduction Value
The adhesion skill reflects the degree of bonding between rocks and crude oil, and is also the work that needs to be overcome to activate the surface of rocks and crude oil. The greater the viscous force of crude oil on the surface of oil wet rocks, the greater the adhesion work. The adhesion work is related to the interfacial tension of the displacement fluid and the interfacial tension of the rock. When chemical agents act on the surface oil of rock cores, the lower the interfacial tension, the smaller the contact angle until the oil is peeled off. The entire process is also a process of decreasing adhesion work.
In theory, reducing the contact angle to 90°is just enough to activate crude oil, and at this point, the adhesion work is the activation adhesion work .In fact, the contact angle that can stably start crude oil should be less than 90°, and the adhesion work is defined as the actual adhesion work.Calculate the adhesion energy of the prepared graphene quantum dots on the target rock core based on the formula for reducing adhesion energy. This part of the study lays a theoretical foundation for the mechanism of graphene quantum dots initiating core oil production.
The calculation formula for the decrease in adhesion energy is shown in 1.1 and 1.2, which is the difference between the theoretical adhesion energy and the actual adhesion energy. In order to simplify the testing process, it is assumed that the interfacial tension remains unchanged before and after the change in contact angle. Calculate using formula 1.3.
2.7. Oil Washing Experiment
To test the oil washing ability of the nanorepellent solution and to characterize the properties of the soluble oil and dissolved organic blockage of the F-GQDs.
Make oil sands and aging: first weigh 7g kerosene and 20 / 40 mesh 42g quartz sand, the oil and quartz sand fully stir evenly. Place the oil sand mixture in a 50℃ water bath for 2h (Consider the temperature loss set 50℃ simulated reservoir 45℃) for aging. After aging, weigh 7g of oil sands and load it into the oil washing test tube with scale, and pour the 0.1% F-GQDs into the test tube with oil sands to observe the oil washing efficiency. Make parallel experiments to observe the effect of washing oil. Under the same experimental conditions, carbon dioxide gas was continuously input into the test tube, and a set of parallel tests were done to observe the experimental effect. As a blank control, water was poured into the oil sands and then fed into carbon dioxide to test the oil washing effect, and two groups of experiments were conducted.
Figure 5.
Instrument diagram of Oil washing effect experiment.
Figure 5.
Instrument diagram of Oil washing effect experiment.
2.8. Imbibition Experiment
The mass method was employed to assess the permeability and absorption efficiency of various fluids acting upon the crude oil within rock cores, with the experiment spanning a total duration of 240 hours. The detailed procedure for the permeability experiment is as follows [
18]: The rock core, saturated with crude oil, is suspended beneath a high-precision balance using copper wire, which allows for real-time recording of the rock’s weight. Concurrently, it is ensured that the core is fully submerged in a beaker of exudate, preventing any contact between the core and the beaker.
By documenting the weight changes of the rock core at various time points, the quantity of oil permeated from the core and its absorption efficiency can be computed. The calculation formulas 1.4are as follows:
R:Imbibition recovery rate; ρo: Oil phase density; ρw: Density of reagent dispersion system
M0:Zero time oil leakage and suction; Mt: t time oil leakage and suction;M: Weight difference before and after core saturation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Graphene Quantum Dots
3.1.1. Morphology and Particle Size of Graphene Quantum Dots
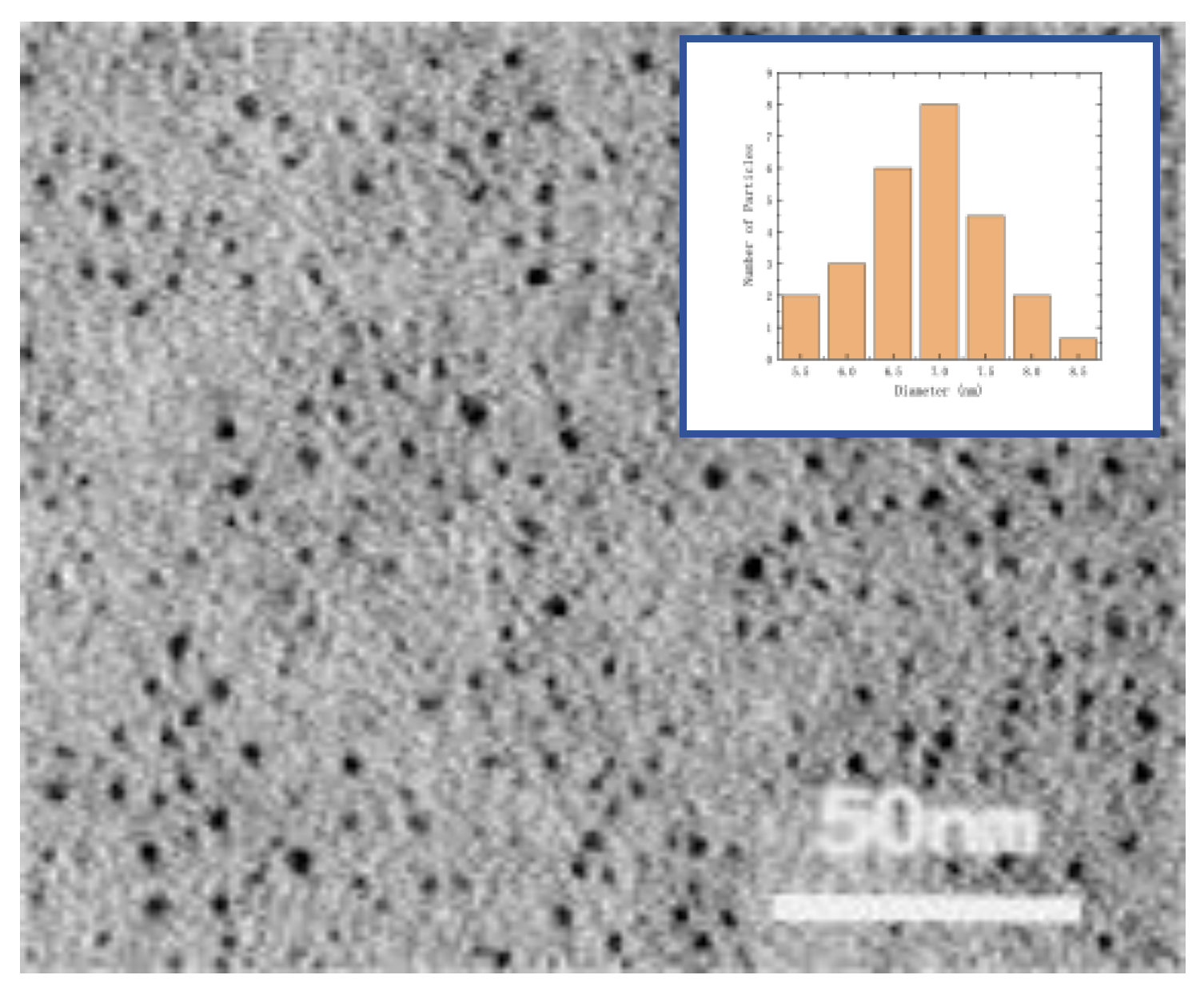
Observe and analyze the prepared F-GQDs using TEM scanning electron microscopy. The result is shown in
Figure 6. TEM imaging shows that the synthesized graphene quantum dots are monodisperse and uniform small spheres with a median particle size of 7nm.
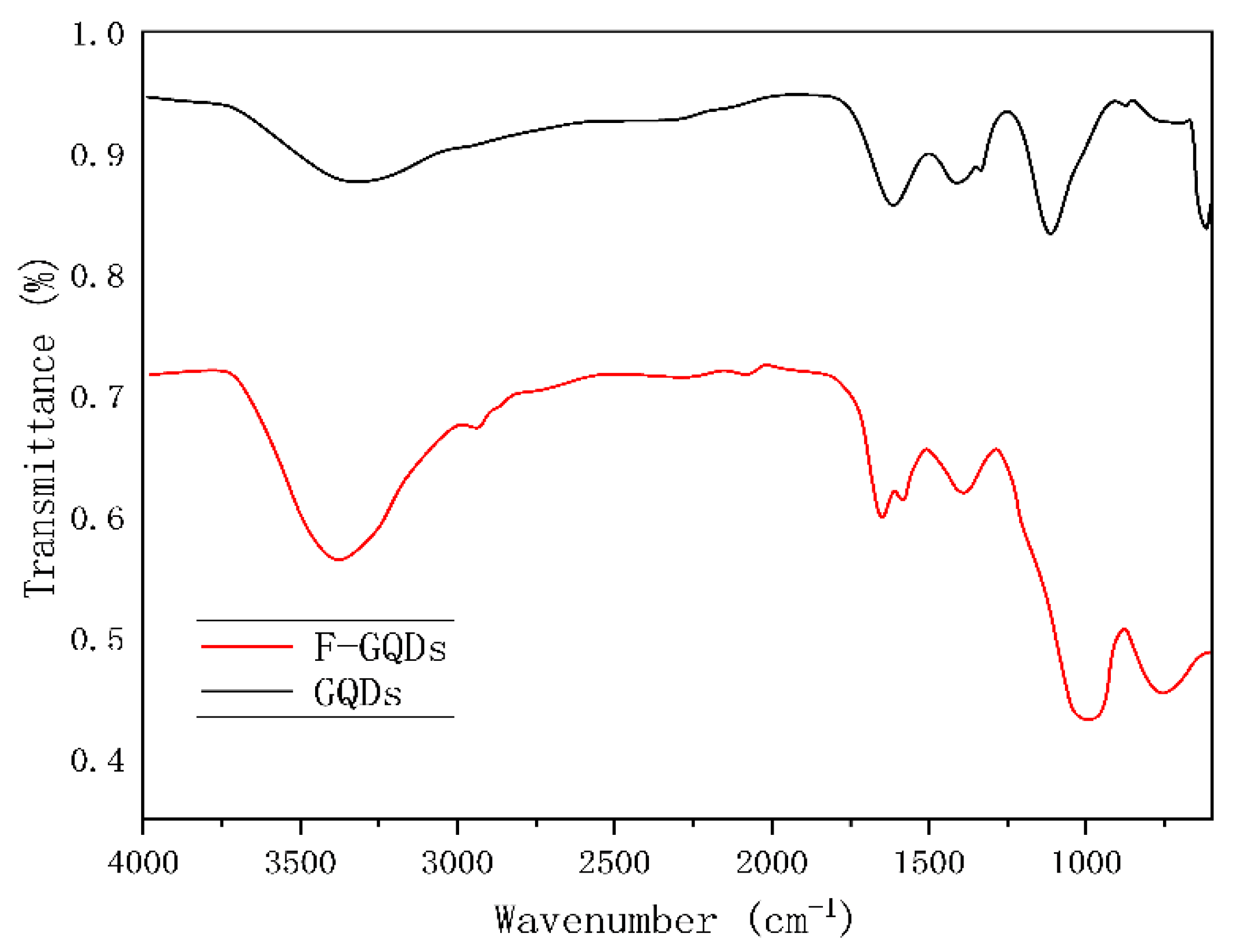
3.1.2. Infrared Spectra of Graphene Quantum Dots
To analyze the surface structure of graphene quantum dots, their infrared spectra were characterized, and the results are shown in
Figure 7.In the infrared spectrum, clear absorption peaks can be observed at 1630cm
-1 and 1359cm
-1, which are considered characteristic peaks of the C=O stretching vibration and the symmetric vibration of carboxylic acid. The peaks at 3438cm
-1 and 1021cm
-1 correspond to the stretching vibration characteristic peaks of hydroxyl -OH and C-O in unsaturated hydroxyl groups. The F-GQDs obtained after functional modification exhibit new characteristic peaks at 1600 cm
-1 to 1300 cm
-1, considering the N-H plane stretching characteristic peak. The appearance of characteristic peaks can confirm the successful preparation of the target product.
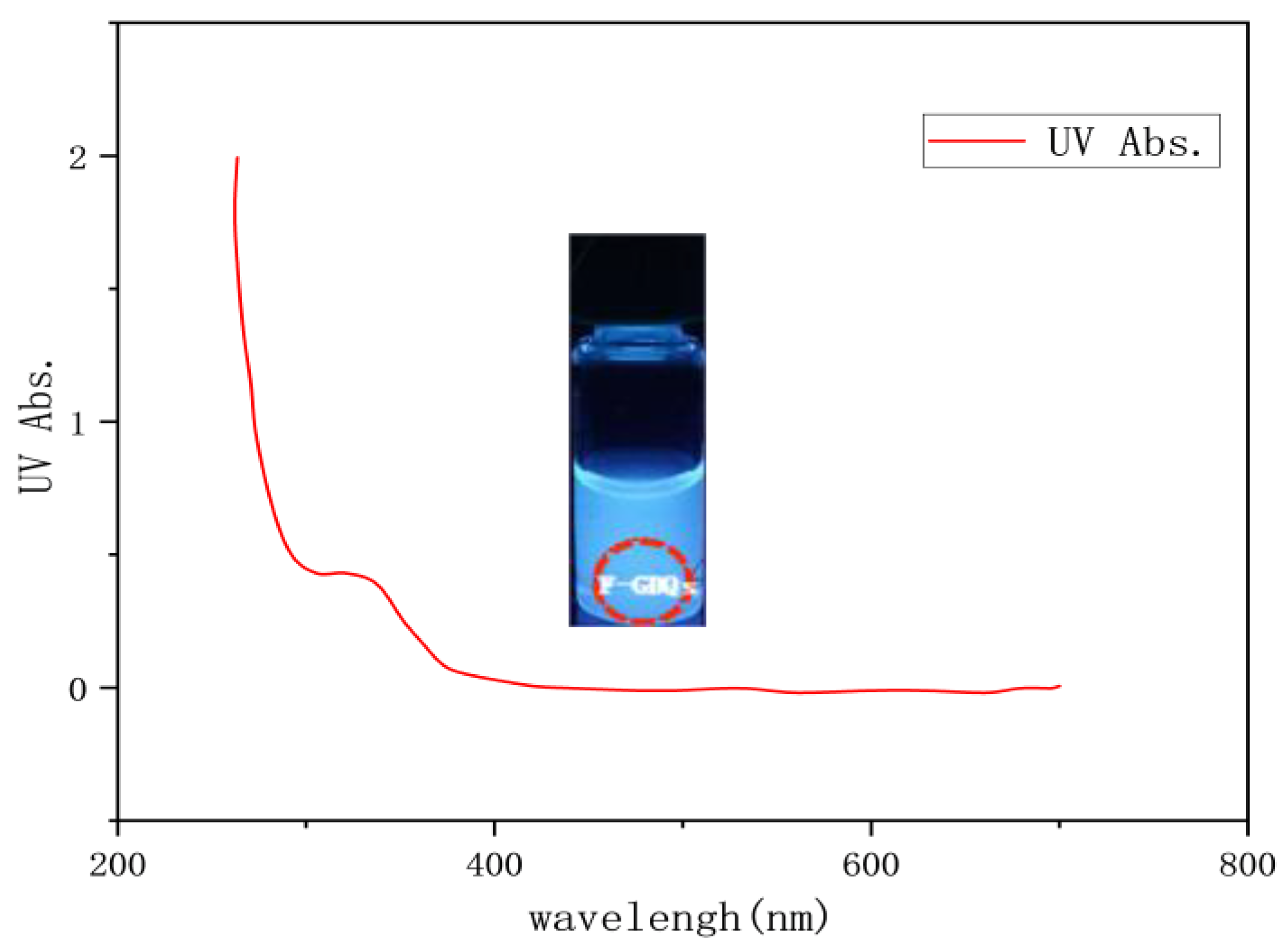
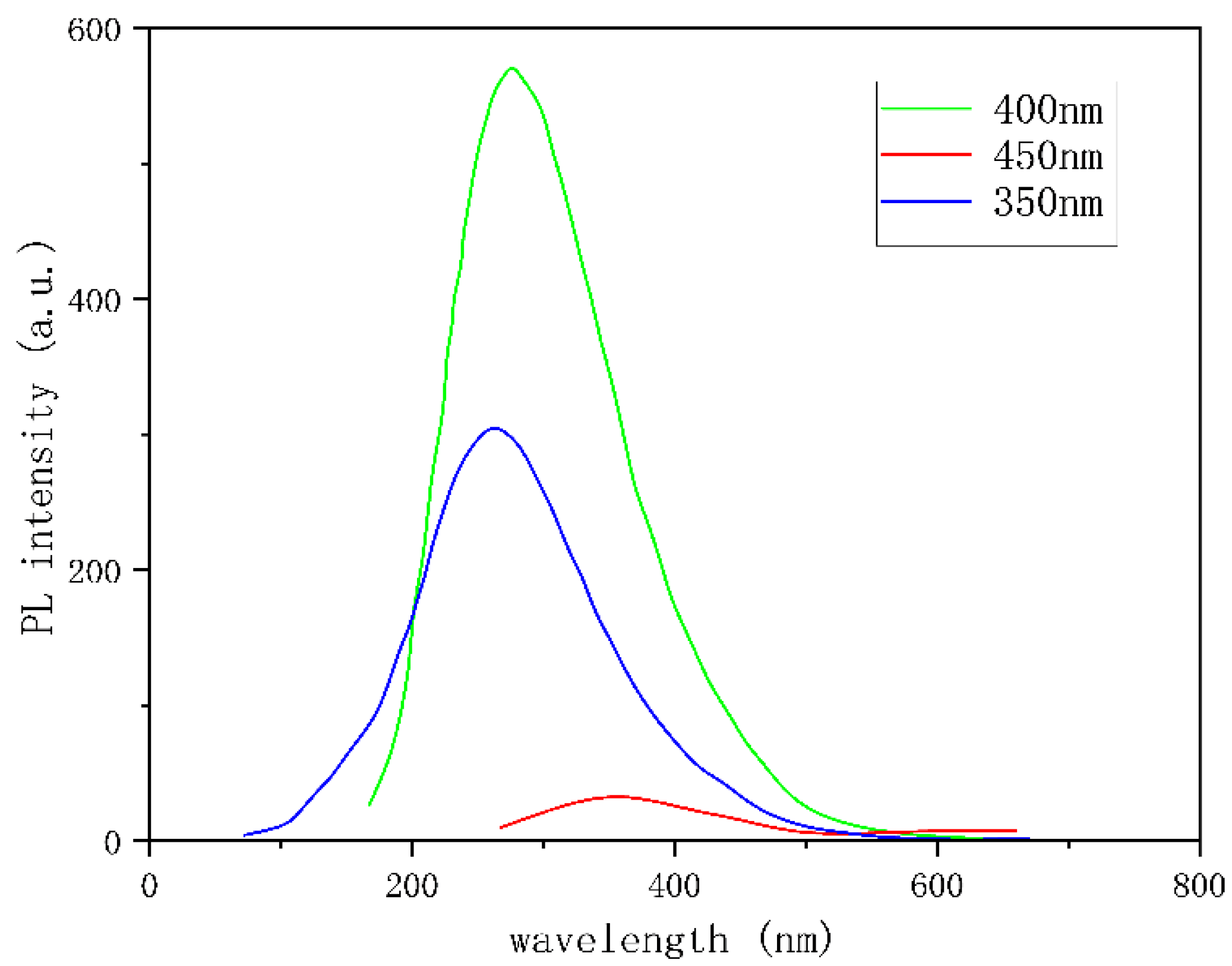
3.1.3. Determination of Fluorescence Intensity of Graphene Quantum Dots
The absorbance and fluorescence intensity were measured by ultraviolet visible absorption spectrometer and fluorescence photometer, respectively. As shown in
Figure 8, an absorption peak within 200 to 250 nm is attributed to the π - π* transition in the sp2 domain of graphene quantum dots. The weak absorption band from 250 to 320 nm is associated with the fluorescence of carbon quantum dots [
19], and the absorption peak within this range approximately aligns with the maximum excitation wavelength of the corresponding fluorescence excitation spectrum. The dispersion system of F-GQDs exhibits a significant red shift in the fluorescence emission peak (400nm) and fluorescence enhancement under UV irradiation at 350 to 450nm.
3.2. Wetting Reversal Characteristic
The oil-treated core was placed in tap water and nano repellent (F-GQDs) liquid phase pool respectively, and the contact angle change of clean water and nano repellent on the core surface was determined.Studies show that F-GQDs have good wetting inversion ability. The results are shown in
Figure 8,after soaking in F-GQDs liquid, the oil drop on the surface of the core were changed from oily to hydrophilic.
Figure 10.
Contact angle determination results.
Figure 10.
Contact angle determination results.
3.3. Surface Tension and Interfacial Tension Determination
The nano repellent (F-GQDs) was prepared according to the concentration of 0.1%, and the results of the interface tension are shown in
Table 1. According to the experimental data, it can be found that F-GQDs have strong interface activity, and the interfacial tension of oil and water can reach the medium-high temperature range of 10
-3mN/m.
Table 1.
Interface tension of F-GQDs.
Table 1.
Interface tension of F-GQDs.
| Number |
T/℃ |
Detection index/
mN/m |
Results/
mN/m |
| 1 |
45 |
surface tension |
25.58 |
| interfacial tension |
0.92×10-2
|
| 2 |
90 |
surface tension |
20.35 |
| interfacial tension |
0.11×10-2
|
3.4. Calculation of Adhesion Reduction Value
Combined with the interfacial tension test and wetting angle data, the adhesion work value was calculated, and the ability of F-GQDs nanofluiding to start core crude oil was further evaluated. The experimental data are shown in
Table 2.The study proves that when the surface wetting of the core changes from oily wetting to water wetting, the adhesion work is greatly reduced, the interface tension is reduced, the theoretical adhesion work is reduced, and the adhesion work is reduced to increased. The calculated value of adhesion work indicates that the F-GQDs have a good ability to start crude oil.
Table 2.
Data table of calculation of theoretical adhesion and actual adhesion.
Table 2.
Data table of calculation of theoretical adhesion and actual adhesion.
| No. |
IFT
(10-2mN/m) |
contact angle θ (°) |
cosθ |
W0(10-2mN/m) |
W1(10-2mN/m) |
wettability |
| 1 |
0.92 |
121.51 |
-0.52 |
0.92 |
1.40 |
lipophilicity |
| 2 |
0.92 |
58.53 |
0.52 |
0.92 |
0.44 |
hydrophily |
| 3 |
0.11 |
121.51 |
-0.52 |
0.11 |
0.17 |
lipophilicity |
| 4 |
0.11 |
58.53 |
0.52 |
0.11 |
0.05 |
hydrophily |
3.5. Oil Washing Experiment Analysis
The experimental results are shown in
Table 3, which was 86%, and the average oil washing rate of F-GQDs was 97%. In the blank control test, carbon dioxide was used in the water, and the average oil washing efficiency was 4.80%.The oil washing efficiency of CO
2 + F-GQDs is significantly greater than the washing efficiency of a single mode. Considering the carbon dioxide stimulation responsiveness of the surface functional groups of F-GQDs improves the mixing ability of crude oil, which then greatly improves the oil washing efficiency.
Table 3.
Effect results of F-GQDs (20℃).
Table 3.
Effect results of F-GQDs (20℃).
| Number |
Sample |
Oil sand contains oil volume(ml) |
Wash oil volume(ml) |
Oil washing rate(%) |
Average value(%) |
| 1 |
F-GQDs |
1.25 |
1.10 |
88.00 |
86.00 |
| 2 |
F-GQDs |
1.25 |
1.05 |
84.00 |
| 3 |
CO2+F-GQDs |
1.25 |
1.20 |
96.00 |
97.00 |
| 4 |
CO2+F-GQDs |
1.25 |
1.22 |
98.00 |
| 5 |
CO2+Water |
1.25 |
0.05 |
4.00 |
4.80 |
| 6 |
CO2+Water |
1.25 |
0.07 |
5.60 |
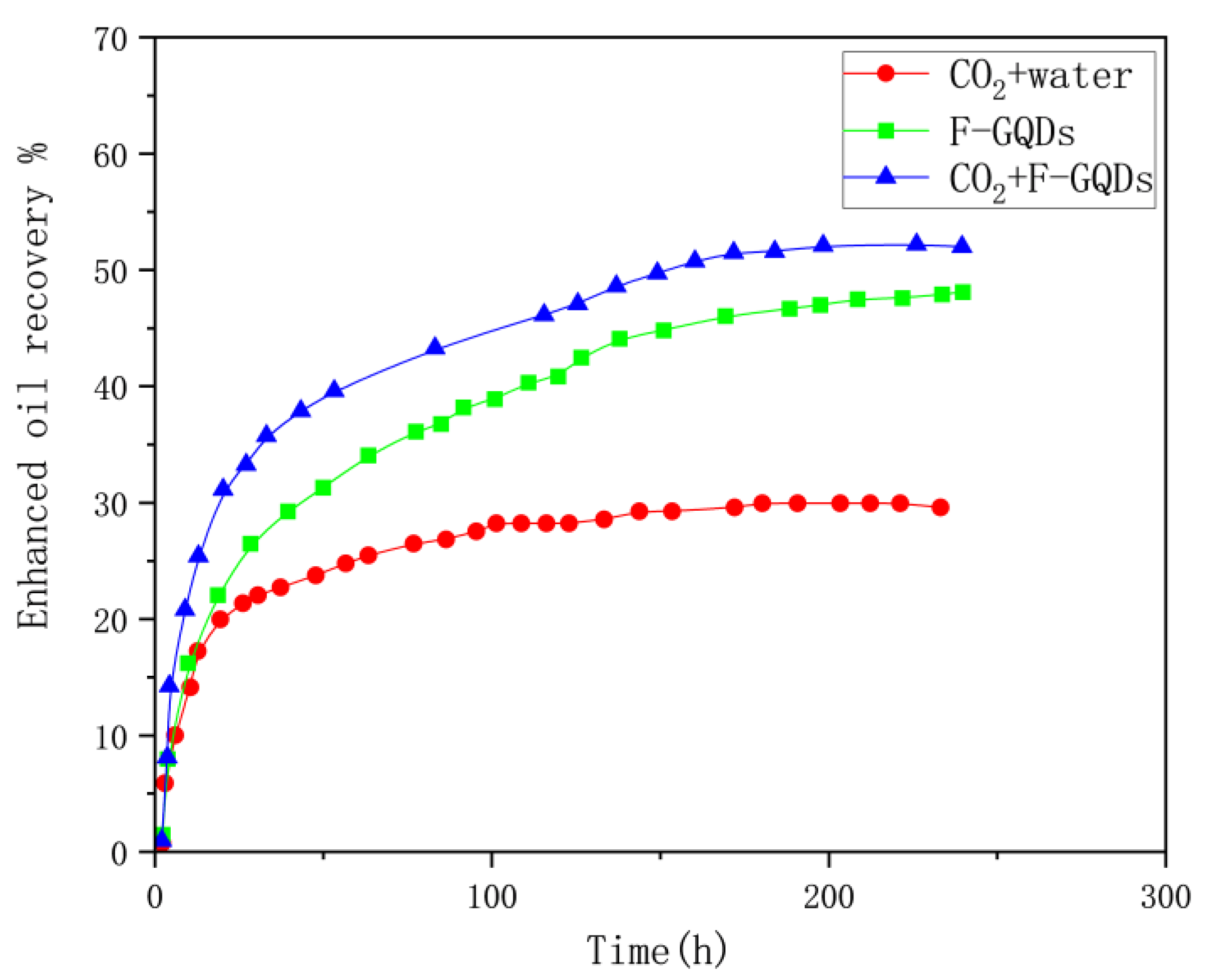
3.6. Imbibition Experiment Analysis
The imbibition experimental curves of the three dispersion systems (CO
2+Water,0.1wt% F-GQDs and CO
2 +0.1wt% F-GQDs) are shown in
Figure 11.
The imbibition experiment demonstrates that the F-GQDs system exhibits effective oil washing capabilities, achieving a crude oil recovery rate of 45% after 240 hours. When combined with carbon dioxide, the system’s oil recovery rate accelerates under the same conditions, further increasing the recovery rate to over 50%. The recovery rate of the carbon dioxide and water system serving as the blank control is approximately 20%. The comprehensive experimental data reveals that the F-GQDs system shows promising application potential for enhancing oil recovery from tight reservoirs.
4. Conclusions
The nanofluid oil displacement method has great potential for application, but the structure-activity relationship between nanomaterials and enhanced energy recovery in dense reservoirs is still unclear. Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) are quasi zero dimensional nanomaterials with graphene structures. Compared with one-dimensional graphene nanoribbons and two-dimensional graphene nanosheets, zero dimensional GQDs exhibit stronger quantum confinement and boundary effects below 10nm in size, and high concentration nanofluids can also exhibit stronger desorption ability.Carbon dioxide responsive GQDs have advantages such as excellent interfacial activity, temperature and salt resistance, strong desorption, intelligence, and green environmental protection.It has broad application prospects in the field of tight oil and gas development.
(1)In this paper, a carbon dioxide stimulus-responsive graphene quantum dots (F-GQDs) was developed, and it was confirmed that the target product was prepared smoothly.
(2)The prepared nanofluids are circular and highly dispersed liquid with a median particle size of 7nm.
(3)0.1wt%F-GQDs evaluate the interfacial tension, surface tension, and the adhesion, studies show that F-GQDs have strong interfacial activity and wetting reversal ability.
(4)The calculated value of adhesion work indicates that the F-GQDs have a good ability to start crude oil.
(5)The oil sands experiment shows that the F-GQDs has a good oil washing effect of more than 86%.After the introduction of carbon dioxide, the efficiency of F-GQDs washing oil can reach 97%.
(6)The F-GQDs system has good oil washing ability, and the oil recovery rate reaches 45% in 240h. The oil recovery rate increases after being combined with carbon dioxide, and the oil recovery rate is further improved to more than 50%. F-GQDs system has good application potential for tight reservoir recovery.
Based on the above research data, the prepared F-GQDs have good potential to improve crude oil recovery and have excellent performance. After composite carbon dioxide, the oil washing capacity is greatly improved, and the comprehensive performance and flooding effect of F-GQDs in porous media will be studied in the future.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, P.Y.and F.S.; funding acquisition, F.S.; data curation,Y.Y., P.Y.and B.Z; investigation, P.Y.and F.S.; methodology, M.L. and J.W.; project administration, J.W. and C.Z.; resources, M.L. ;software, P.Y.All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, Project number: 52304026
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dordanihaghighi, S.; Allahbakhsh, A.; Kuur, C.; Arjmand, M.Synthesis, Applications, and Prospects of Graphene Quantum Dots:A Comprehensive Review. Small 2021, 18, 2102683.
- Konstantatos, G.; Badioli, M.; Gaudreau, L.; Osmond, J.;Bernechea, M.; de Arquer, F. P. G.; Gatti, F.; Koppens, F. H. L.Hybrid graphene-quantum dot phototransistors with ultrahigh gain.Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 363−368. [CrossRef]
- Tetsuka, H.; Asahi, R.; Nagoya, A.; Okamoto, K.; Tajima, I.;Ohta, R.; Okamoto, A. Optically Tunable Amino-Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5333−5338. [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.-F.; Teng, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-J.; Teng, H. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots as Photocatalysts for Overall WaterSplitting under Visible Light Illumination. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26,3297−3303. [CrossRef]
- Dinda, D.; Park, H.; Lee, H.-J.; Oh, S.; Park, S. Y. Graphene Quantum Dot with Covalently Linked Rhodamine Dye: A High Efficiency Photocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution. Carbon 2020, 167,760−769. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Miao, H.; Jing, J.; Zhu, Y.; Choi, W. Photocatalytic activity enhancement of PDI supermolecular via π-π action and energy level adjusting with graphene quantum dots. Appl. Catal., B 2021, 281, 119547. [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Revia, R. A.; Zhang, M. Graphene Quantum Dots and Their Applications in Bioimaging, Biosensing, and Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 1904362.
- Gao, W.; Gou, W.; Zhou, X.; Ho, J. C.; Ma, Y.; Qu, Y. AmineModulated/Engineered Interfaces of NiMo Electrocatalysts for Improved Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Solutions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1728−1733. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Tien, H. N.; Dong, Q.; Xu, W. L.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Yu, M. Ultrathin, Ethylenediamine-Functionalized Graphene Oxide Membranes on Hollow Fibers for CO2 Capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 184−191. [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical Photolysis of Water at a Semiconductor Electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37−38. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, S.; Guo, L.; Mao, S. S. Semiconductor-Based Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6503−6570. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Niu, S.; Han, D.; Liu, T.; Wang, G.; Li, Y. Progress in Developing Metal Oxide Nanomaterials for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700555.
- Guo, Y.; Park, T.; Yi, J. W.; Henzie, J.; Kim, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Bando, Y.; Sugahara, Y.; Tang, J.; Yamauchi, Y. Nanoarchitectonics for Transition-Metal-Sulfide-Based Electrocatalysts for Water Splitting. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807134.
- Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Cai, M.; Liu, C.; You, Y.; Wang, R.; Channa, A. I.; Lin, F.; Huo, D.; Xu, G.; Tong, X.; Wang, Z. M. Role of Copper Doping in Heavy Metal-Free InP/ZnSe Core/Shell Quantum Dots for Highly Efficient and Stable Photoelectrochemical Cell. Adv. EnergyMater. 2021, 11, 2101230. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. Z.; Davey, K.; Qiao, S.-Z. Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Containing Metal-Free Photocatalysts for Hydrogen Production: Progress and Challenges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6,1305−1322. [CrossRef]
- Endo T,Nagai D,Monma T,et al.A novel construction of a reversible eixation-release system of carbon dioxide by amidines and their polymers[J]..Macromolecules,2004,37(6):2007-2009.
- Lu H,Jiang J,Huang Z,et al.A water-soluble CO2-triggered viscosity-responsive copolymer of N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate and acrylamide[J].Appl Polym Sci,2014,131(19):2.
- Bates E D,Mayton R,Ntai I,Davis J H,Jr,CO2 capture by a task-specific ionic liquid[J].Journal of American Chemical Society,2002,124(6):926-927.
- Pan D Y, Zhang J C, Li Z, et al. Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv Mater, 2010, 22 (6): 734-738.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).