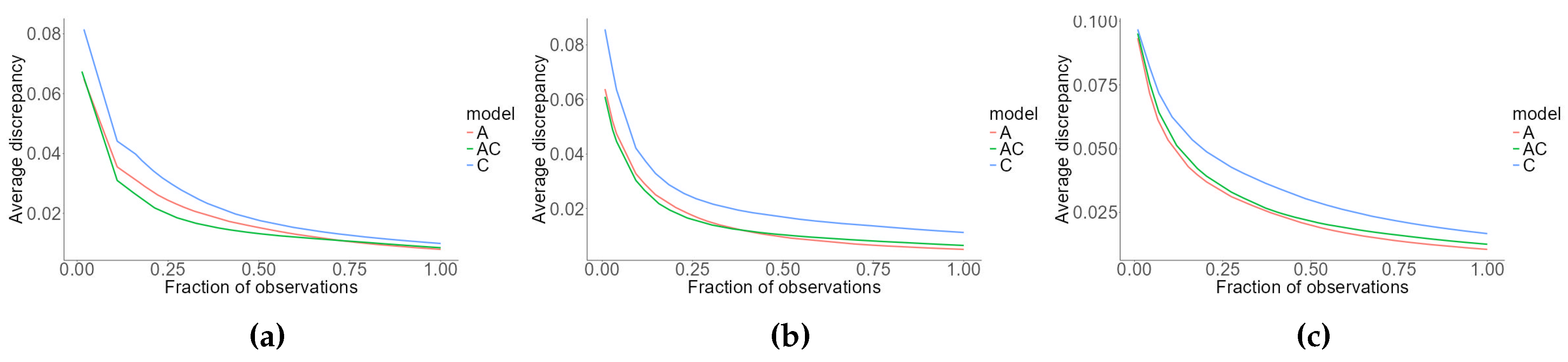
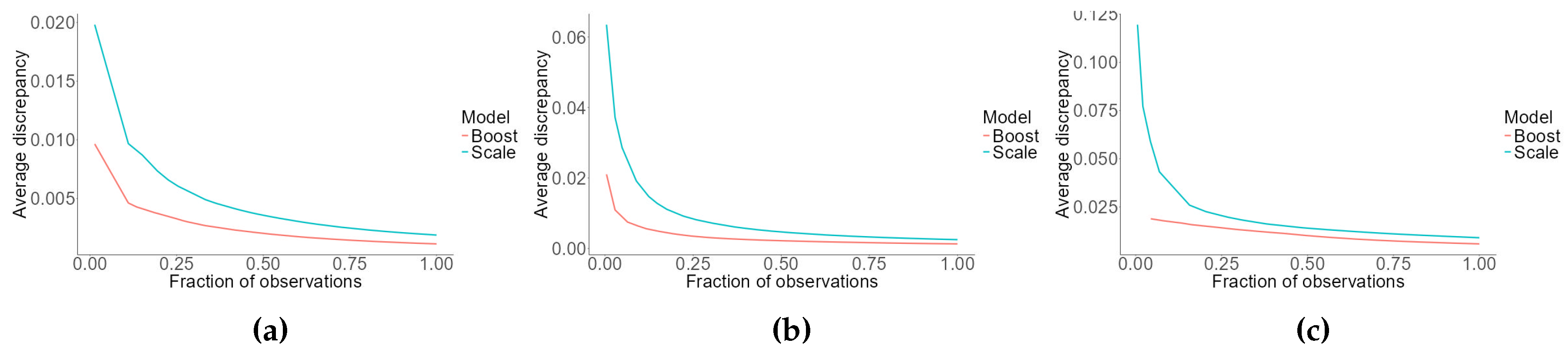
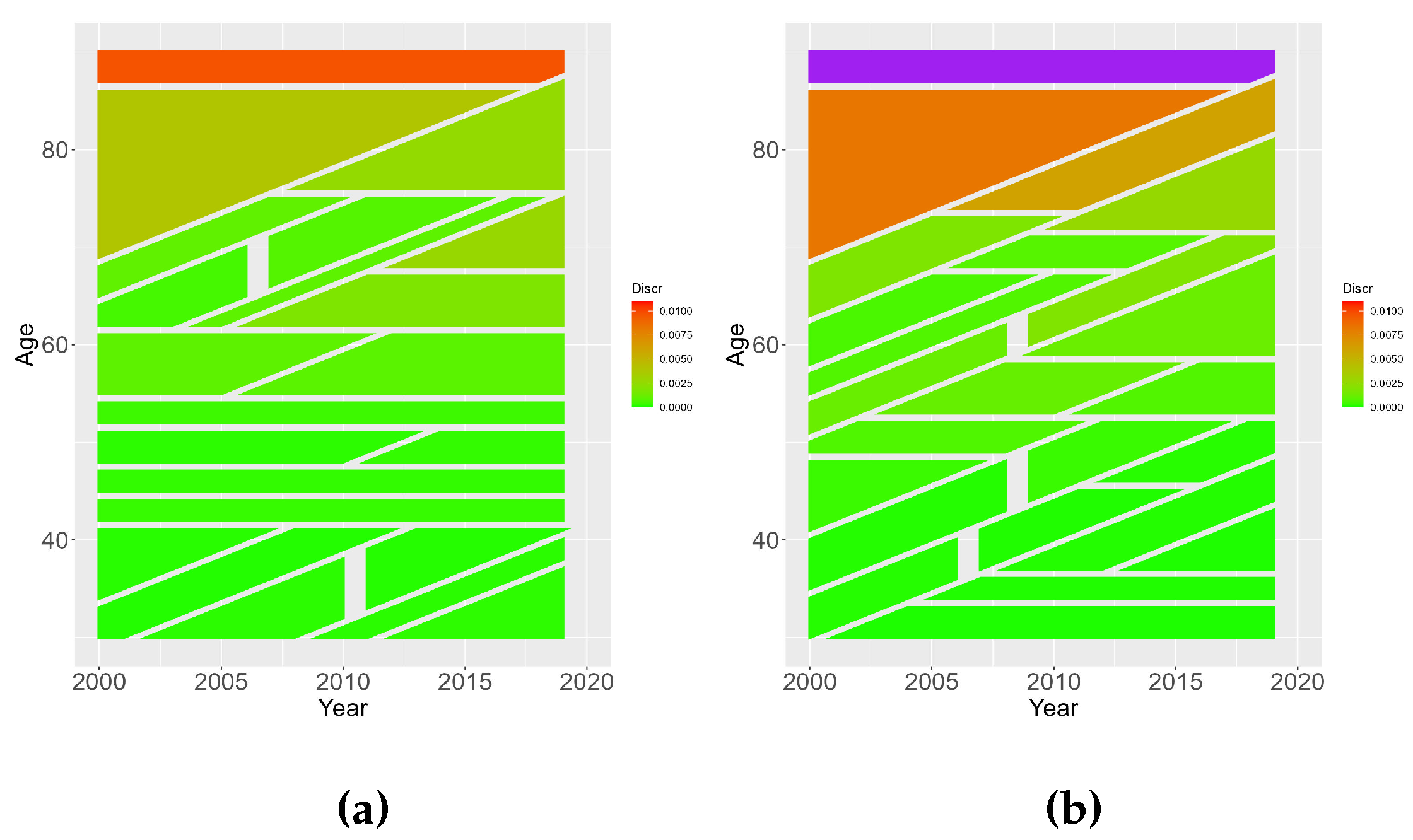
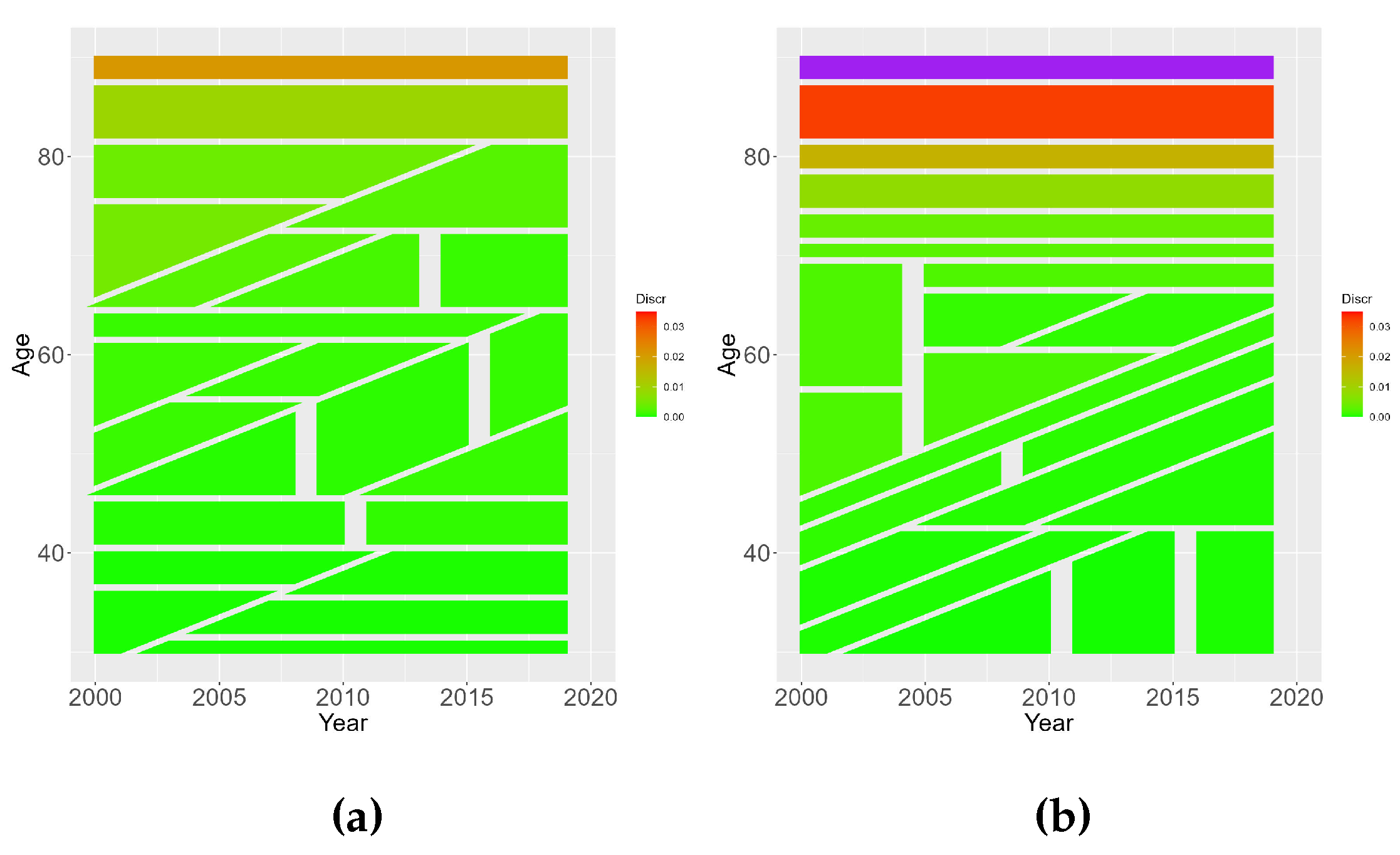
2.1. Contrast Trees and Estimation Boosting
Contrast Trees (CT) are a general methodology that, leveraging tree-based machine learning techniques, allows for assessing differences between two output variables defined on the same input space, be them predictions resulting from different models models or observed outcome data. Specifically, the goal of the Contrast Trees method is to partition the input space to uncover regions presenting higher values of some difference-related quantity between two arbitrary outcome variables ([
16]). Moreover, a boosting procedure making use of CTs can be constructed, in order to reduce differences between the two target variables once differences have been uncovered.
Available data consist of
N observations of the form
, where
is a
P-dimensional vector of observed numerical predictor variables and
and
are the corresponding values of two outcome variables. These can be estimates for a given quantity from different models, or the observed values of a certain quantity of interest. Given a certain sub-region
of the input space, a discrepancy measure, describing the difference between the outcome variables, is defined as a function of the data points in the sub-region as follows:
The particular choice of discrepancy function depends on the problem at hand. While discrepancies are conceptually similar to loss functions, it must be noted that in the context of Contrast Trees, they are not required to be convex, differentiable nor expressible as sum of terms, each involving a single observation. In the following, we’ll make use of the
mean absolute difference discrepancy :
where
is the number of data points (or, alternatively the sum of weights) relative to region
. A quick review of possible choices for discrepancy functions, and their relation to different estimation problems, can be found in [
16].
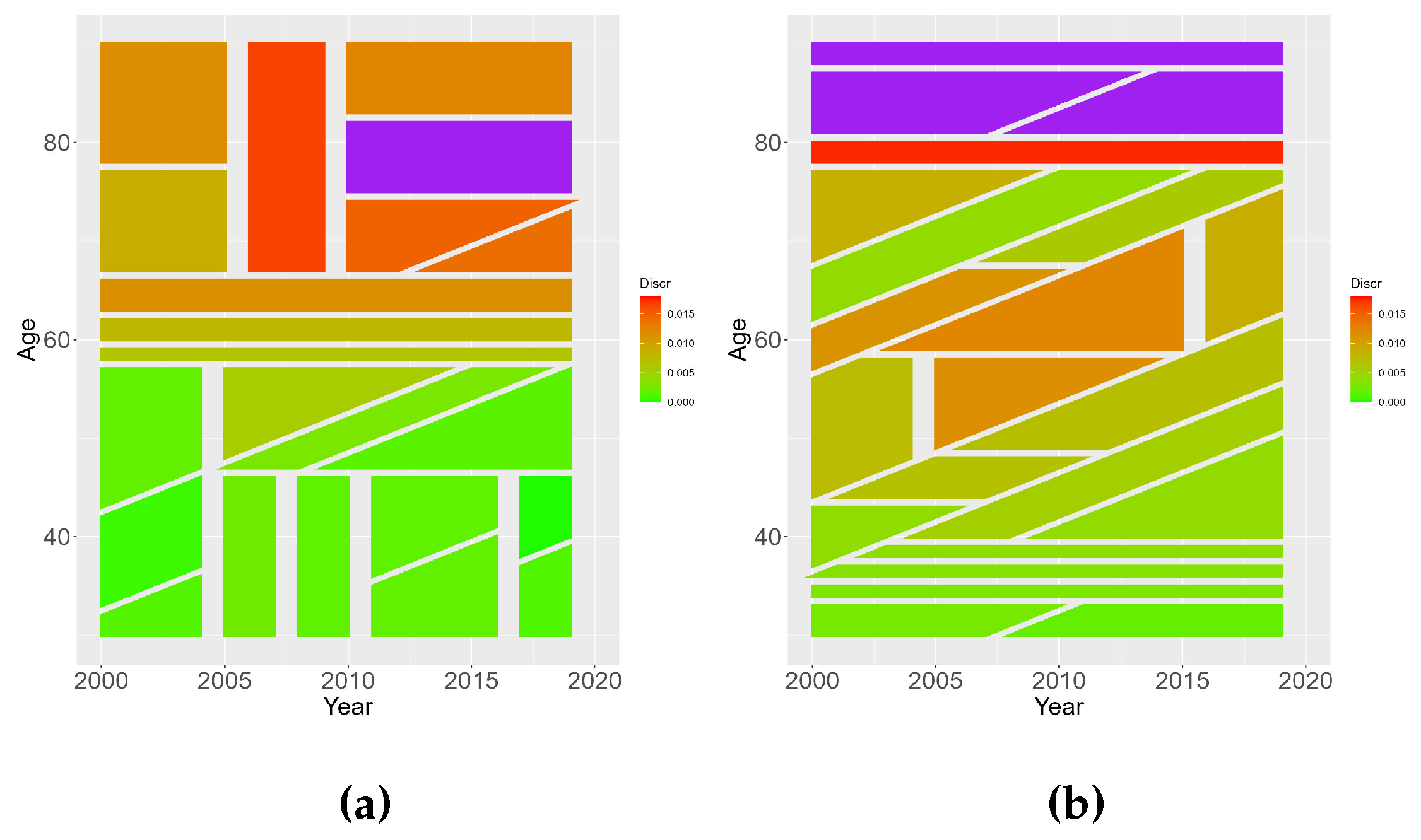
Contrast Trees produce a partition of the input space into
M components, each one with an associated value for discrepancy. Such partition can be analyzed to assess discrepancy patterns, bearing some similarities to residuals analysis in Generalized Linear Models framework. A brief overview of the iterative splitting procedure of the input space is given in Algorithm 1.
|
Algorithm 1 Iterative splitting procedure - Construction of a Contrast Tree |
|
Require:
|
| ⋄ Choose
|
▹ Maximum number of regions |
| ⋄ Choose
|
▹ Minimum number of data points in a region |
| for do
|
▹ Loop over successive trees |
| ⋄ The input space is partitioned into M disjoint regions ; |
| for do
|
▹ Loop over regions in a tree |
| for do
|
▹ Loop over predictors |
| for all do
|
▹ Loop over values of a predictor |
| ⋄ Define two provisional sub-regions and , with corresponding discrepancies and :
This rule is the same as for ordinary regression trees for numeric variables (see [17] for further details); |
| ⋄ Calculate the quality of the split :
where and are the quota of observations in region falling within each provisional sub-region and is a regulation parameters: as found by [16], results are insensitive to its value; |
| end for
|
| end for
|
| ⋄ The split point for variable , whose value maximizes , with associated discrepancies and is associated to the m-th region; |
| ⋄ Calculate discrepancy improvement for the m-th region:
|
| if then
|
|
| |
▹ Stopping condition (1) |
| ⋄ STOP |
|
| end if
|
|
| end for
|
| ⋄ The region , whose associated split maximizes , is replaced by its associated sub-regions, s.t. the input space is now partitioned into regions |
| if then
|
▹ Stopping condition (2) |
| ⋄ STOP |
|
| end if |
|
| end for
|
|
Results from the CT procedure can be summarized in a so-called lack-of-fit (LOF) curve, which associates to the
m-th region the following coordinates:
Where the abscissa is the quota of data points having discrepancy grater or equal to that of the
m-th region and the ordinate is the average weighted discrepancy in those same regions. Contrast Trees can be applied to assess the goodness-of-fit of a certain model, by choosing as output variables (i.e., "contrasting") predicted values from the model and observed ones. High-discrepancy regions resulting from the procedure can be easily detected and interpreted, without having to formulate distributional hypotheses to define a likelihood: multiple models, of any nature, can be compared estimating a Contrast Tree for each one, contrasting predicted values with out-of-sample observed outcomes. An application of CTs to model diagnostics in the context of mortality models can be found in [
18] .
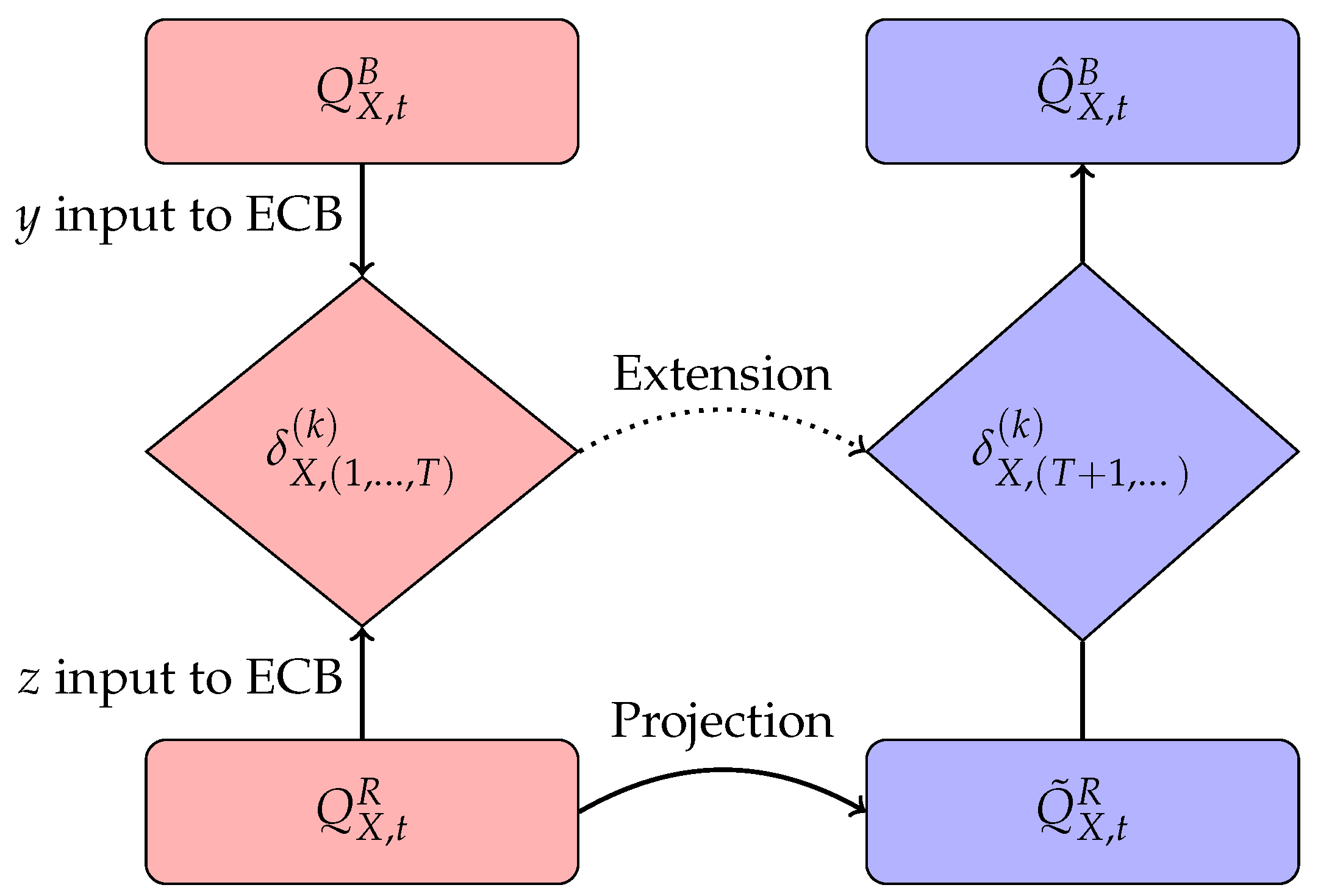
Contrast Trees may also be employed to improve model accuracy, by means of an iterative procedure that reduces uncovered errors and calculates an additive correction to produce more accurate predictions. Estimation Contrast Boosting (ECB) gradually modifies a starting value of z using an additive term, reducing its discrepancy with y, producing, at each step k, a partition of the input space where every element m has an associated update . The resulting prediction for z is then adjusted accordingly, so that an updated estimate is produced.
Please note that in Estimation Contrast Boosting, the two response variables are no longer equivalent: response
y is taken as the reference, while response
z is adjusted. A quick presentation of the boosting procedure is given in Algorithm 2. Since any point
in the input space lies within a single region
of each of the trees resulting from the ECB procedure, each with associated updates
, and given an initial value
, the boosted estimate
is computed as:
More detail about the iterative splitting procedure to produce Contrast Trees or about ECB algorithm can be found in [
16,
18].
|
Algorithm 2 Estimation Contrast Boosting |
|
Require:
|
| ⋄ Choose maximum number of iterations K; |
| ⋄ Choose maximum number of regions M for each iteration; |
| for
do
|
| ⋄ Build a Contrast Tree of versus y using discrepancy in Equation (4), with , thus partitioning input space in M regions ; |
| ⋄ Update as follows:
Where is a learning parameter and the update is found by imposing ; |
| end for |
2.2. Small Population Tables in Relation to Italian Actuarial Practice
In Italian actuarial practice, the assessment of mortality in life insurance companies is heavily influenced from ISVAP Regulation N.22 of 4th April 2008 and its successive modifications
1. Article 23-bis, comma 9 of the regulation states that "The Insurance company conducting life business presents to IVASS the comparison between technical bases, different from interest rates, used for the calculation of technical provisions, and the results of direct experience". This happens trough the filling of table 1/1 of Module 41 contained in the Additional Informations to Financial Statements (
"Informazioni aggiuntive al bilancio d’esercizio").
The module is organized separately by risk type (longevity or mortality), product type, age range and sex: these features define the risk classes to be considered. The underlying idea, common in actuarial mathematics, is to analyze the portfolio separately for groups defined by known risk factors, so that individuals composing these groups can be considered homogeneous from the point of view of probabilistic evaluation. The comparison between direct experience and technical bases consists in reporting the expected number of deaths in the company portfolio, the expected sum of benefit to be paid, the actual number of deaths and the actual paid sum of benefits. Expected number of deaths
and expected sum of benefit to be paid
are defined as follows:
where
is the number of insureds of age
x in risk cluster
C at the beginning of the year,
is the total insured sum for insureds of age
x in cluster
C at the beginning of the year and
is the probability of death between ages
x and
, usually dependent on sex. The table
constitutes part of the prudential technical basis used for pricing purposes. The time period to which all quantities refer is the solar year of the Financial Statements in consideration.
While not required by Solvency II directive, in Italian actuarial practice a very similar approach is adopted in order to produce the mortality hypotheses to be used in the calculation of best estimate liabilities and, more generally, to estimate company mortality tables, especially in the case of products subject to mortality risks. In this case, given a certain risk cluster
C usually described by sex, risk type (mortality, longevity) and product type (e.g., endowment or term life insurance), an adaptation coefficient
is calculated as:
or, using the sum of benefits as a reference:
where
is the observed number of deaths for age
x in cluster
C,
is the sum of benefits paid for insureds dead at age
x in cluster
C and
is the probability of death, distinct by sex, from some reference mortality table, usually a national table of some sort (e.g., SIM2011 table or ISTAT table for people residing in Italy). The table
is a demographic realistic technical base that can be updated over time.
The adapted death rates
or
which will constitute the company death tables are then calculated as follows:
Essentially, this method scales one-year death probabilities in order to reproduce the total number of deaths or the total benefits paid. Data used for the calculation include observations from the last available calendar years. Usually, ten calendar years of data are used: this ensures a sufficiently stable output without having to resort to data from much earlier calendar years, which is often not available and could not reflect the actual, more recent, trends in mortality dynamics. This methodology features ease of implementation, but applies the same adaptation coefficient to all age classes, thus creating a mortality profile which has the same shape as the reference one, while the company underwriting process may affect each age group differently. In the remainder of this work, we will refer to this technique as "table scaling".
To overcome the limitations of table scaling, the ECB algorithm briefly described in
Section 2.1 can be utilized to build mortality tables for small populations, using a machine learning approach for mortality spread calculation and generalising the Italian actuarial practice. At the best of the author’s knowledge, this is the first attempt in applying a machine learning approach to compute mortality spread in a two-population model.
Let
and
be some quantity describing mortality in terms of predictor matrix
X and calendar year
t respectively for reference and book populations, available for observation years
. These can be one-year death probabilities, central mortality rates, mortality odds or, more generally, any quantity describing mortality in a population. The Estimation Boosting algorithm can then be applied to variables
and
, using the quantity relative to reference population as the
z input of Algorithm 2. The ECB procedure then estimates updates
, that can be used to transform the quantity
relative to reference population into the corresponding quantity relative to book population, as per Equation (
6):
A shift in the target of the estimation boosting procedure must be emphasized : while in [
16] the goal was to reduce differences between outcomes
y and
z by producing an updated estimate
and calculate the updates
only as a consequence, now the objective is to obtain the updates themselves, in order to transform the quantity of interest of the reference population into that of the book population. Also note, on the terminological side, that the word "reference" is used in two different meanings in the context, respectively, of two-population models and Estimation Contrast Boosting: in the first case it indicates to the larger population, whose mortality is used as a baseline for mortality spread modelling. In the second case, it designates the
y output variable of the ECB algorithm, in this case
, which in the present application is relative to the
book population.
Now, the quantity
can be projected to calendar years
using some standard mortality projection model, which is feasible for the reference population, thus obtaining estimates
for the quantity of interest in future calendar years. Some assumptions on the updates
must then be made, to extend their range of application from calendar years
, on which they have been estimated, to projection calendar years
. The extended updates
can then be applied to projected estimates in order to obtain boosted estimates
for the book population relative to projection calendar years:
This methodology pertains to two-step models for small population, with the main difference residing in the quantification of mortality spread, which now relies on a machine-learning technique. It must be emphasized that the book population is not requested to be similar to the reference population in terms of geographical, historical or socio-economical features. In such cases, however, a faster estimation boosting convergence and, more generally, a better model performance can be expected. The procedure just described is summarized in
Figure 1, and, in the remainder of this work, we will be referred to as "ECB adaptation".
Before model implementation, some critical issues must be pointed out. First of all, no mechanism for the extension of updates to projection calendar years is straightforwardly provided. So, not having at disposal a tool for update projection, a reduced form of the input design matrix for Estimation Contrast Boosting could be used, adopting as predictors just variables age, cohort, or a combination of the two: this issue will be further addressed in
Section 3.1. Also note that using data from the same calendar years for reference population mortality projection and ECB calibration is not strictly necessary: it could be possible to use a longer time series of data for mortality projection, while making use a shorter time series to calibrate the ECB updates. In fact, not using a mechanism to project the ECB updates means to implicitly assume the the updates themselves, i.e., the transformation function from reference population to book population mortality, do not change with time. This means assuming that relative mortality levels are stable during both ECB calibration and projection time periods, thus suggesting the use of data relative to most recent years.
Aside from these points of attention, this model is quite flexible, leaving considerable freedom in the choice of the quantity of interest, the projection model and the structure of the design matrix used as input in the ECB updates’ estimation.
2.3. Data
HMDHMD
Data used for numerical evaluation have been provided by the Human Mortality Database [
19]. Due to lack of company-specific data, Italian male population has been considered as reference population, while Austria, Slovenia and Lithuania males are considered as book populations. The time period taken into consideration is 1950-2019, for ages comprised between 30 and 90. Calendar years from 2000 to 2019 will be used for mortality projection purposes. Data relative to Slovenia and Lithuania are available, respectively, starting from 1983 and 1959. The first two populations can be considered close, at least in geographical terms, to the reference population. On the contrary, the Lithuanian population has been selected in order to investigate the ECB adaptation procedure behaviour when book and reference populations differ substantially.
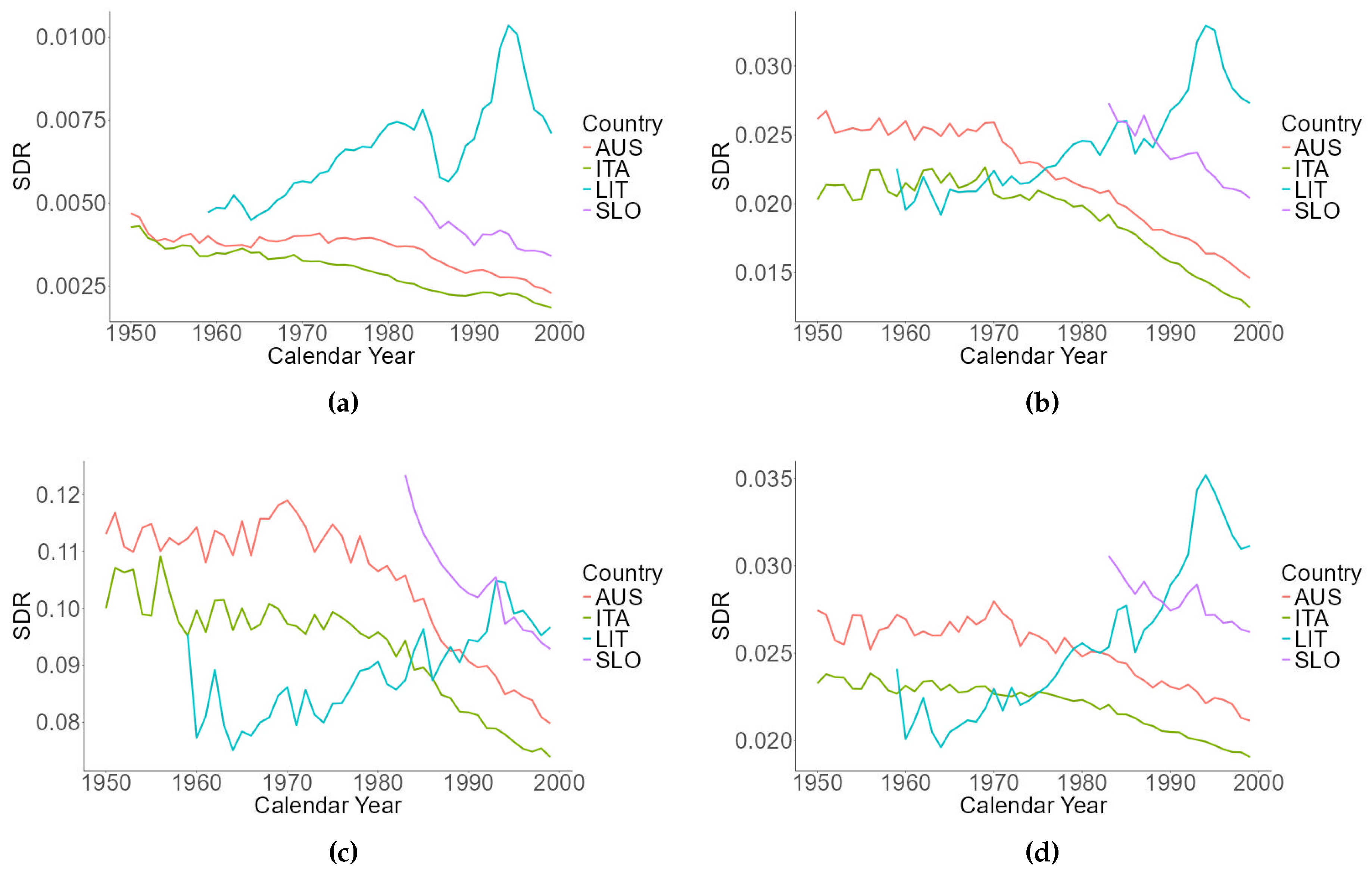
Using the approach proposed by [
20], to have a first qualitative evaluation of similarity between two reference and book populations, Standardized Death Rates (SDR) relative to period 1950-1999 are calculated, separately for age groups 30-50, 50-70, 70-90, and then for the whole age range in consideration. Relative to country
I, ages ranging from
to
, using reference population
R, SDRs are computed as:
where
m denotes the central death rate and
E the central exposure-to-risk. Results are reported in
Figure 2.
Italian and Austrian mortality present a similar trend, with quite a regular behaviour, both on separate and joint age groups. Slovenian mortality data, while available only since 1983, displays a similar, albeit more irregular, pattern. This is expected since Slovenian population is the least numerous of the three countries. On the other hand, Lithuanian mortality exhibits a completely different pattern, being smaller than the Italian one until year 1975, then steadily increasing until year 1995 and eventually decreasing again.
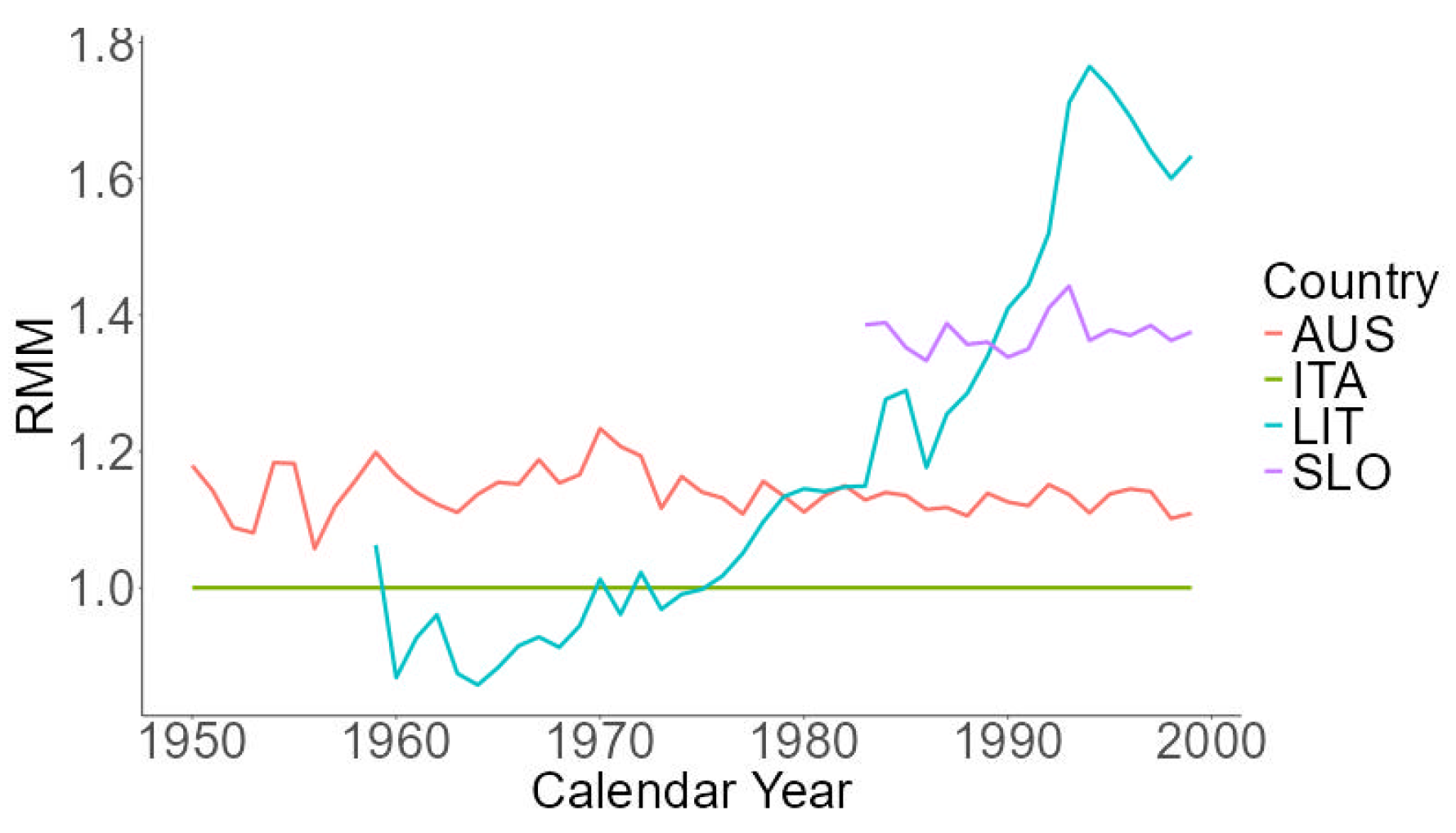
Following [
12], a relative Measure of Mortality (RMM) il aslo computed as:
The nearer RRM value is to 1, the closer the book and reference population are on average in terms of mortality. As it can be seen from
Figure 3, the mortality of reference population tends to be the lowest, in contrast to what would presumably happen using, say, a group of annuitants as book population.
Again, we can clearly see that Italian, Austrian and Slovenian mortality evolve similarly. Lithuanian relative mortality dynamics behaves differently: while initially lower in respect to reference population, it gets higher and higher from the mid-sixties to the mid-nineties, then decreases. This suggests caution in the choice of the time frame per ECB mortality boosting calibration.