1. Introduction
In the last few decades, many researchers have become interested in Nanomaterials. Most researchers are investigating the thermophysical properties of these materials for various shapes and sizes while analyzing them at high pressure and temperature. These materials find widespread use in solar panels, wear-resistant coatings, tissue engineering, lithium-ion batteries, cancer treatment, and lightweight armor, among other applications. Materials with at least one dimension reduced to the nanoscale range, known as nanomaterials, have newly evolved features that link bulk and single-molecule materials[
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. The primary focus of nanoscience and nanotechnology study is the unique properties of materials at the nanoscale. Scientists and researchers are drawn to the intriguing behavior of particles at the nanoscale[
6]. The size and shape-dependent characteristics of nanoparticles have sparked great interest in materials research[
7]. Semiconducting nanoparticles, with their configurable band gap and high surface-to-volume ratio, are the most promising of the numerous types of nanoparticles for a range of optoelectronic and photovoltaic applications[
8,
9].
Synthesizing semiconductor nanoparticles with the desired size and shape remains a challenging task. The properties of these nanoparticles are heavily influenced by their size and shape, making it essential to accurately determine their thermal stability for various applications[
1,
10,
11]. Cohesive energy is the amount of energy needed to separate the atoms of a solid into separate atomic species. In semiconductor nanomaterials, cohesive energy is one of the most important physical factors determining a material’s thermal stability, along with melting temperature, vibrational frequency, dielectric properties, electrical conductivity, band gap, melting enthalpy, deby temperature, and Curie temperature. The melting temperature and cohesive energy of nanoparticles with a reasonably free surface are known to decrease with decreasing particle size, both theoretically and empirically[
1,
4,
12,
13]. Using the cohesive energy concept, Srivastava et al. (2023)[
1] reported the melting temperatures of four significant semiconductor nanomaterials: CdSe, CdTe, ZnSe, and ZnS with different sizes and shapes. Although several theoretical models can be used to explain the thermophysical behavior of nanometals, the precise model that can provide a convincing explanation is still lacking[
6]. The thermophysical behavior of materials in various sizes at the nanoscale was found to be beyond the scope of any models now in use. The concept of cohesive energy and melting temperature of the nanomaterial is fundamental to predicting the thermal stability of the nanomaterials.
The bond energy of Qi and Wang has been modified to account for the cohesive energy and melting temperature of semiconductor nanomaterials. The size, packing factor, and shape factor of the semiconductor nanoparticles are taken into account in this improved model. The equation for the size-dependent melting temperature of semiconductor nanoparticles was derived based on the relationship between the cohesive energy and other thermophysical parameters of the nanomaterials. The well-known semiconductor nanomaterials InSb, ZnSe, CdS, and CdSe nanoparticles in various shapes(Nanowire, Spherical, octahedral, hexahedral, and tetrahedral) were the particular focus of this study. A graph presents the comparison between the theoretical results with experimental results, simulation data, previously published data, and other theoretical modeling.
2. Theoretical Models
As Qi and Wang Model[
14], the cohesive energy of nanomaterials
can be expressed as follows:
where
represents the cohesive energy of bulk material,
denotes the number of atoms in nanomaterial, and
denotes the number of surface atoms.
Melting temperature
shows a linear variation with cohesive energy under the relation[
15];
where
is the Boltzmann constant. The relation in Eq. (2) is also done for the nanomaterials as;
where
is the melting temperature of nanomaterial. By rearranging the Eqs. (1-3) we get the relation;
When accounting for variations in particle shape, the shape factor
is determined by comparing the surface area of nanosolids with a spherical shape of diameter(
to the surface area of nanosolids with any shape[
16]. Assuming the atoms that make up the nanoparticles are perfect spheres with a specific diameter
, each surface atom contributes a certain area of
to the total surface area of the particle.Therefore, the shape factor can be mathematically represented as;
where
is the surface area
of the spherical nanoparticle with diameter
,
is the surface area of the nanosolids in any shape whose volume is the same as the spherical nanosolids. From Eq. (5), the surface area of a nanoparticle, regardless of its shape, is determined by;
The total number of surface atoms, denoted by N, can be calculated by dividing the nanoparticle’s surface area by the area of a circle with a diameter equal to the nanoparticle’s diameter
. Thus,
The number of total atoms of nanosolid is the ratio of the particle volume to the atomic volume, which may be written as
Because the volume of the nanosolid is the same as the volume of the atom, the atom is an ideal sphere.
The number of atoms in a nanoparticle cannot be precisely determined without considering the packing factor
, which accounts for the gaps between the constituent crystals[
17]. Thus Eq. (8) becomes;
The packing factor(
) determines the maximum proportion of available space that can be occupied by densely packed hard spheres[
18]:
Combining Eq. (7) and Eq. (9), the ratio of the total number of surface atoms to the number of total atoms within a nanoparticle becomes;
Now, substituting Eq. (11) into Eq. (1), then the Eq. (1) gives the size and shape-dependent cohesive energy of nanosolids with containing the packing factor
;
This also gives the size and shape-dependent melting temperature of nanosolids containing the packing factor
;
The expression in Eq. (13) presents the melting temperature for semiconducting nanomaterials depending on their size and shape.
Equations 12 and 13 describe models that depend on the sizes and shapes of nanoscale solids. These equations establish connections for the cohesive energy and the melting temperature of nanosolids, respectively, considering the crystal’s packing efficiency.
3. Result and Discussion
This research aims to develop a single model that can accurately predict the cohesive energy and melting temperature of various semiconductor nanomaterials, such as ZnSe, InSb, CdSe, and CdS. The model is based on the Qui and Wang cohesive energy formula, which is modified to account for the unique properties of these nanomaterials. The study involves calculating the cohesive energy and melting temperature for different shapes and sizes of these semiconductor nanomaterials using Eqs. 12 and 13. The chosen materials’ atomic diameter (d) and packing factor (
μ) vary based on their crystalline structures, which are listed in
Table 1.
Table 2 provides the shape factor (α) for several popular shapes, including Nanowire, Spherical, Regular octahedral, Regular hexahedral, and Regular tetrahedral, which a low-dimensional solid can also assume.
3.1. Cohesive Energy
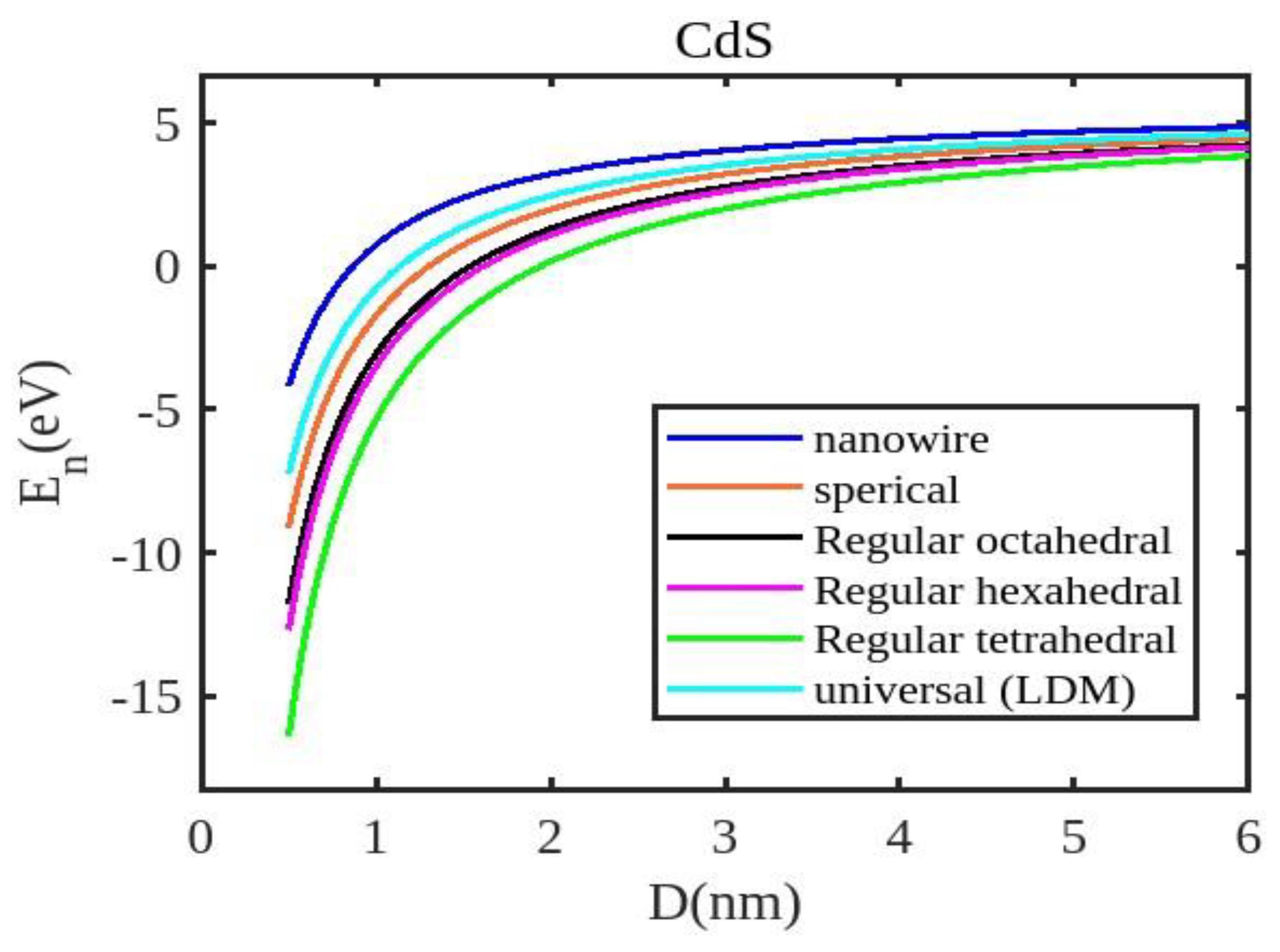
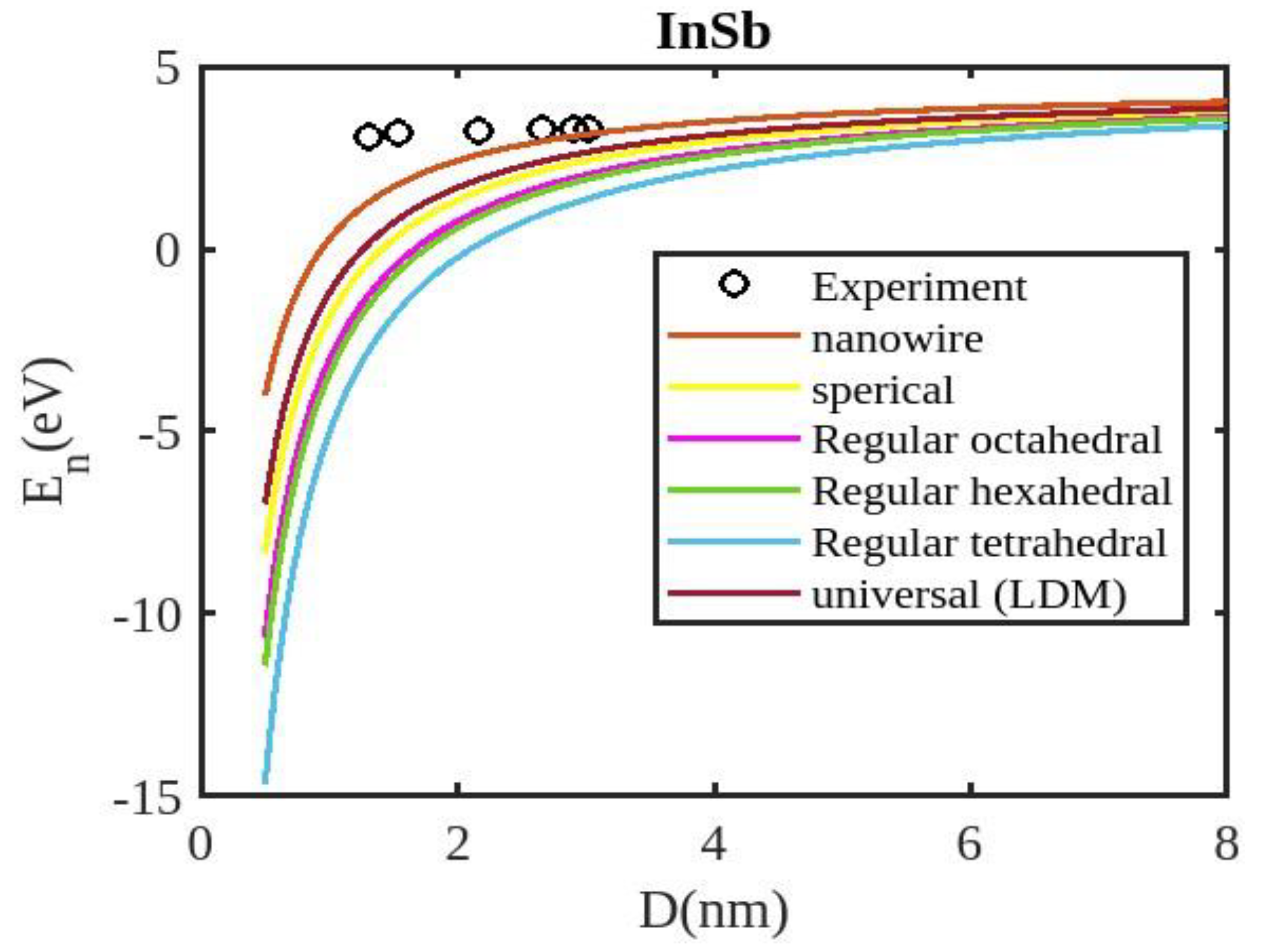
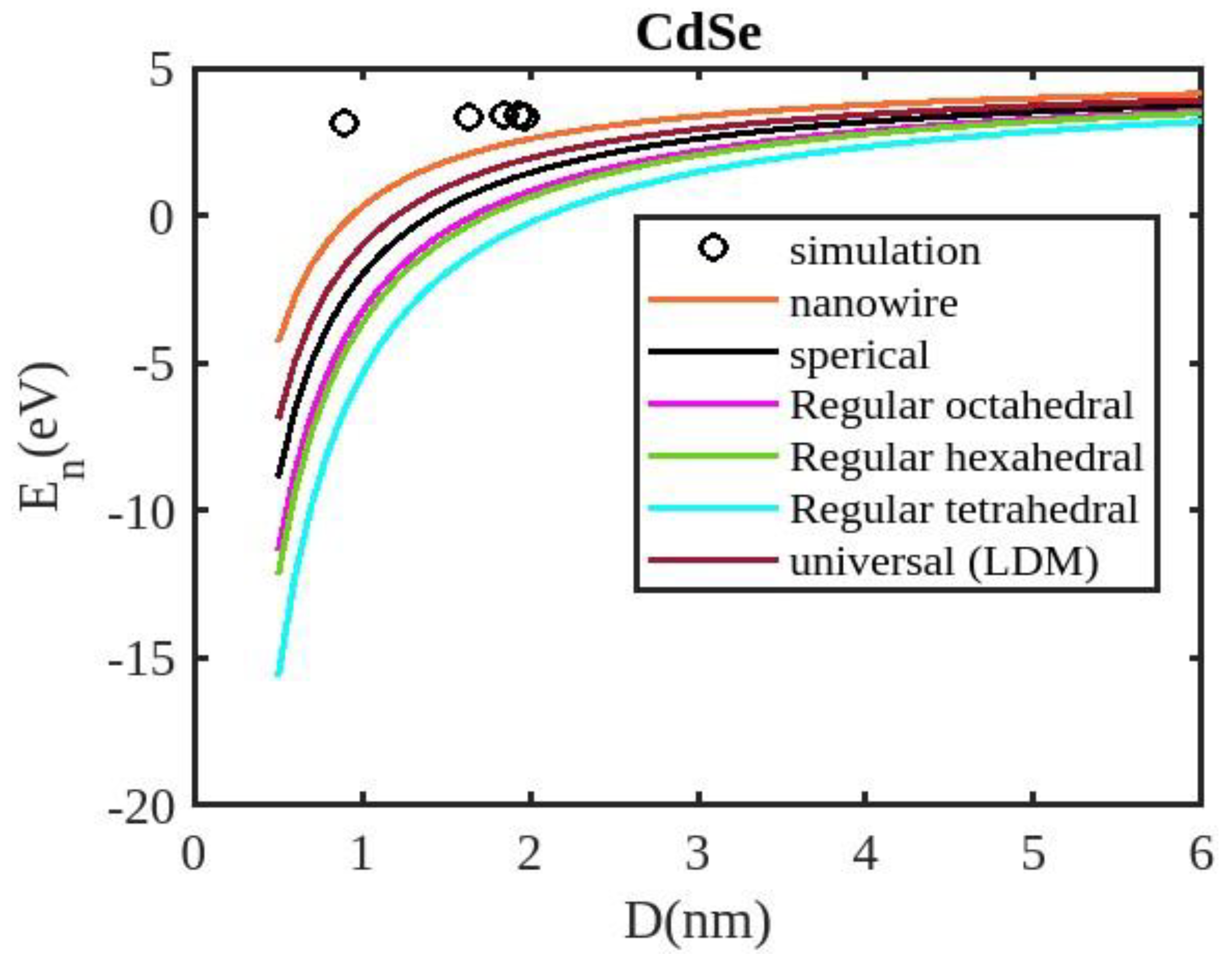
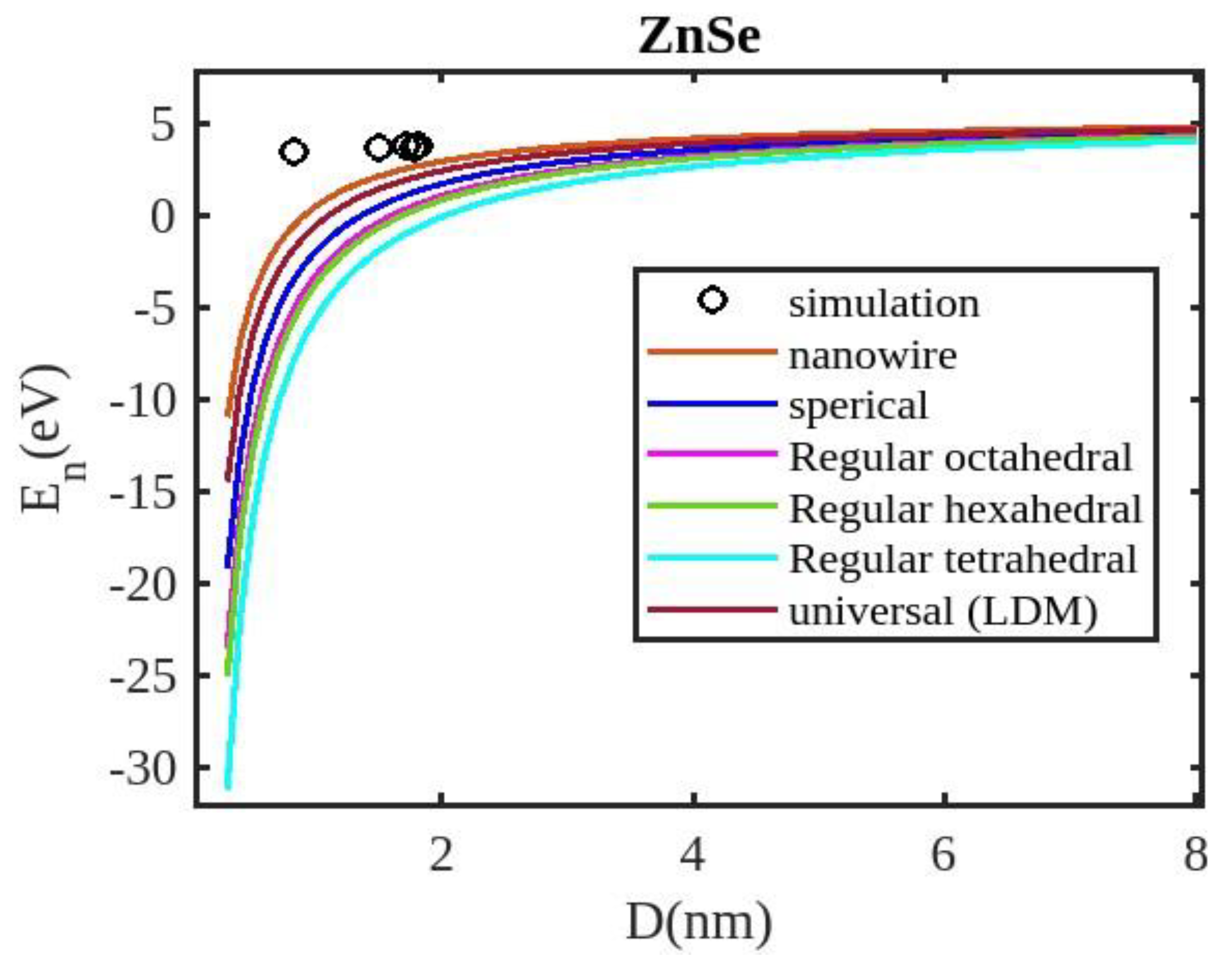
Equation (12) is used to compute the cohesive energy of the semiconducting nanomaterials for the chosen semiconducting materials, ZnSe, InSb, CdSe, and CdS. The input parameters used for calculations are detailed in
Table 1. The computed results are presented in
Figure 1,
Figure 2,
Figure 3 and
Figure 4 visually represent the cohesive energy values for various shapes and semiconductor nanomaterials. For comparison, the theoretical results for the cohesive energy of ZnSe, InSb, CdSe, and CdS nanoparticles are presented in
Figure 1,
Figure 2,
Figure 3 and
Figure 4, along with existing experimental data. The theoretical calculations were performed using both the present model and the universal liquid drop model. The liquid drop model describes the size-dependent cohesive energy using the relation
, where
is the cohesive energy of the nanoparticle,
is the bulk cohesive energy,
is the radius of the nanoparticle, and
is the radius of the bulk material[
19].
Our unified model demonstrates that the cohesive energy of nanoparticles decreases as their size diminishes, and its results align more closely with experimental values than the universal liquid drop model of shape factor(. The universal liquid drop model tends to underestimate the cohesive energy, whereas our model provides a more accurate prediction. This suggests that our model is more effective in capturing the cohesive energy of nanoparticles. Additionally, the shape of the nano-particle significantly influences this trend, with nanowire shapes showing the least decrement and regular tetrahedral shapes exhibiting the greatest decrement. Furthermore, the cohesive energy of these nano-particles increases with increasing particle size up to approximately below 2nm. The size-dependent behavior of particles below 4 nm is characterized by significant effects of both size and shape. Within this range, the cohesive energy exhibits a strong dependence on particle size and shape. However, as the particle size is above 4nm, the cohesive energy approaches a constant bulk value, indicating that it becomes less sensitive to size and shape variations. The experimental results for the nanowire of InSb nanoparticles in the 2-4 nm region align closely with our theoretical predictions. This suggests that the particles tend to adopt a nanowire shape within this size range. For nanomaterials, CdSe and ZnSe the calculated result for nanowire shape has consistency with previously reported simulation data within the size range of 1-2nm. This also shows that the predicted shape for these nanoparticles is a nanowire in this size range.
The figures demonstrate that the cohesive energy predictions from our model for various semiconductor nanoparticles and shapes align with both experimental and simulation results. This suggests that the proposed model, Eq. (12), is likely to be accurate in its predictions. The fraction of surface atoms increases dramatically as materials get smaller until they reach the nanoscale relative to bulk materials. There are many unsaturated ionic charges at the surface because of the high number of surface atoms. According to the model, the cohesive energy is lowest for tetrahedral materials and largest for nanowires. Another surface-dependent phenomenon is the cohesive energy’s shape-dependence. The nanowire has a minimal area, while the tetrahedral shape has a somewhat larger surface area. As a result, the tetrahedral surface’s larger atom count causes greater degradation than the nanowire surface’s. The observed behavior supports the validity of our theoretical model, which incorporates voids within the crystal, dangling surface atoms, and the shape factor. This indicates that the cohesive energy of semiconductor nanomaterials is influenced by the combined effects of their packing factor, size, and shape. To effectively design and optimize semiconductor nanomaterials with specific properties, it is crucial to understand how their cohesive energy changes with size.
3.2. Melting Temperature
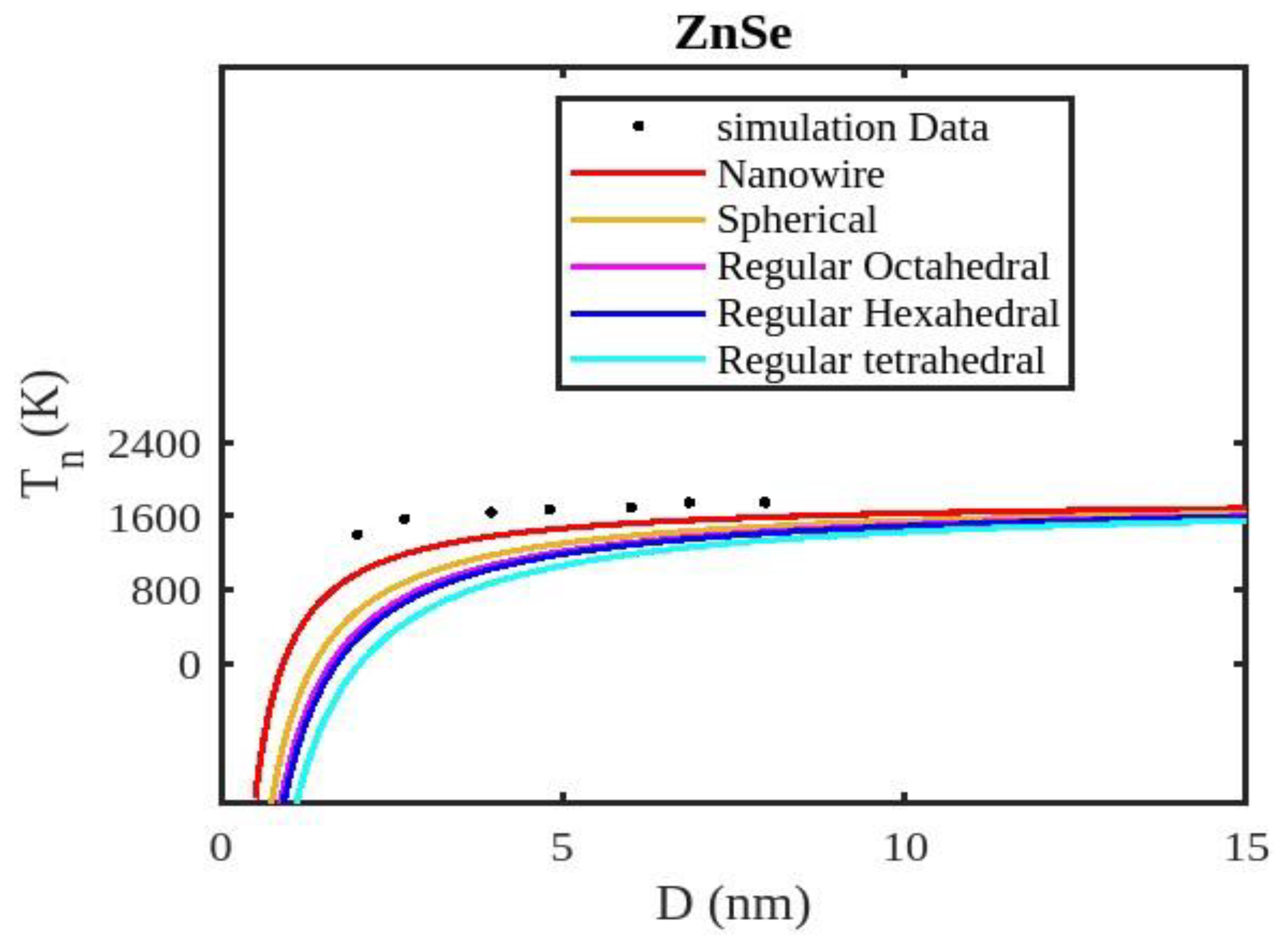
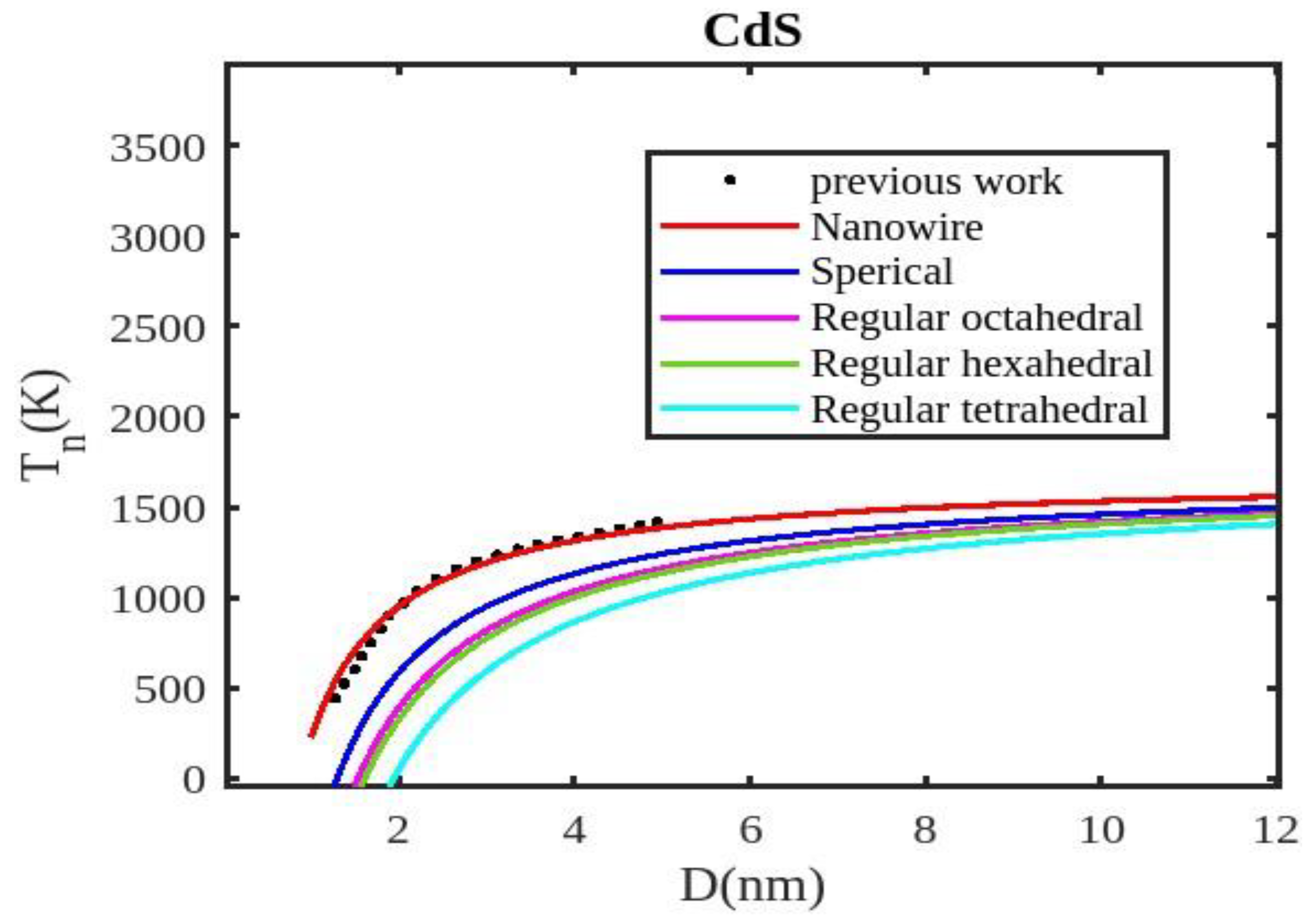
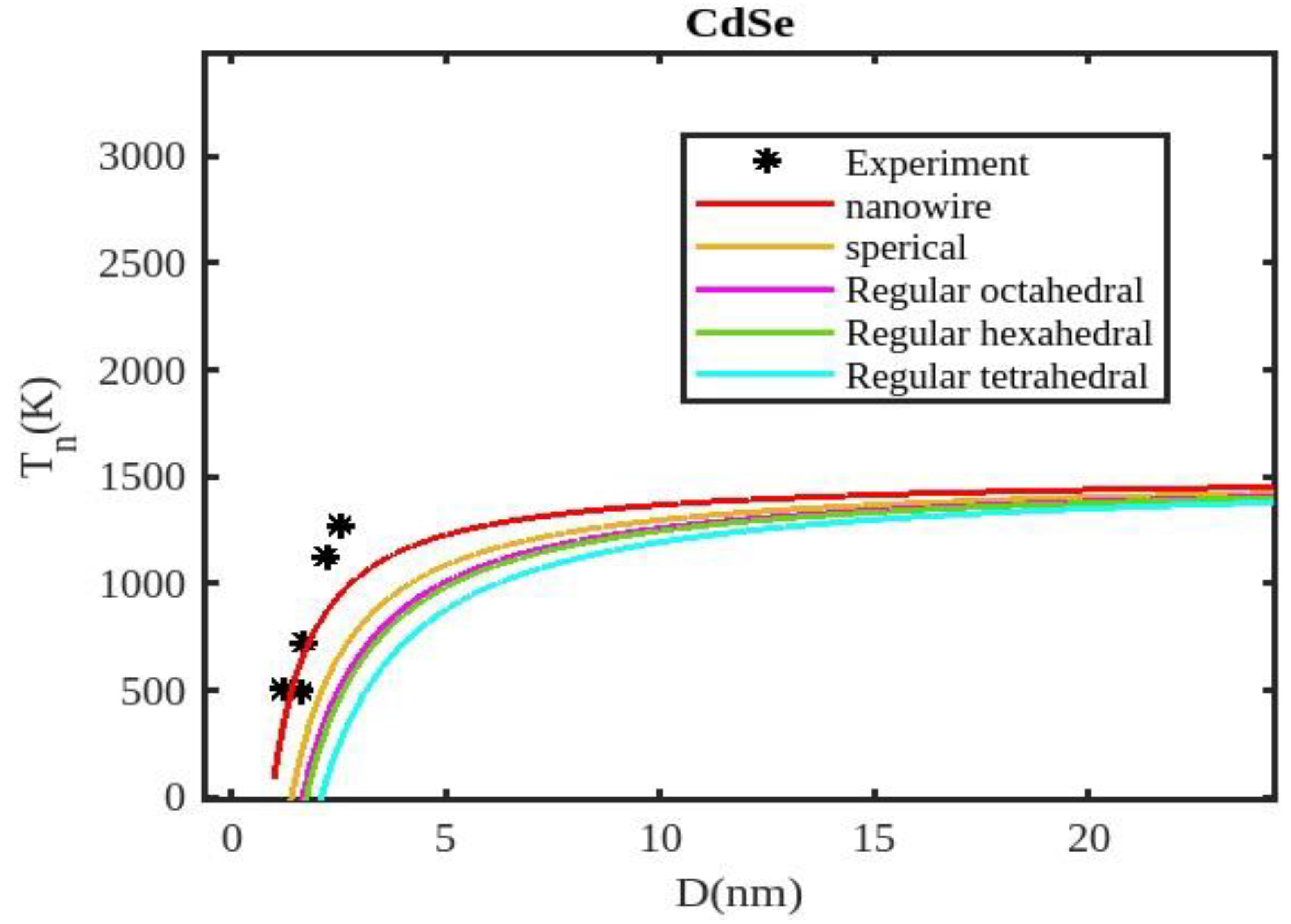
Table 1 lists the bulk material melting temperatures for elements such as ZnSe, CdSe, and CdS. Also, using Equation (13) to calculate the melting temperatures of these materials for various shapes, the results are graphically shown in
Figure 5,
Figure 6 and
Figure 7. The presented figures also include available experimental data, modeling data, and previously published data for comparison. The graphs illustrate that as the size of the nanoparticles decreases, their melting temperature also decreases.
Furthermore, it is observed that below a diameter of 5nm, the melting temperature decrease is more marked. At the nanoscale, the shape of a nanoparticle becomes a crucial factor in defining its characteristics. For instance, nanowires exhibit a relatively smaller decrease in melting point compared to tetrahedral nanoparticles, which show a more pronounced decrease. Additionally, the melting points of these nanoparticles increase as the particle size increases up to 10 nm. The size and shape effects are evident in the properties of nanomaterials within the range of less than 5 nm. However, beyond a size of 10 nm, the melting temperature approaches the constant bulk value, indicating that it becomes independent of size and shape. The predicted size-dependent melting point behavior of semiconductor nanomaterials aligns well with experimental findings. Also, it is observed that these materials may exhibit a nanowire structure in the size range of less than 5 nm. The graph in
Figure 6 indicates that for CdS nanoparticles with diameters below 6 nm, the melting temperature variation for nanowires is consistent with previously reported data. The graph in
Figure 7 indicates that for CdSe nanoparticles with diameters below 2 nm, the melting temperature variation for nanowires is consistent with experimental findings. The relationship between size, shape, and melting point in nanomaterials is readily explained by the direct link between melting point and cohesive energy.
In nanosolids, the surface area is significantly larger compared to bulk materials, resulting in a substantial increase in the number of surface atoms. This high surface-to-volume ratio leads to a distinct change in the energy state of the surface atoms, which in turn affects the cohesive energy. Consequently, a smaller amount of energy is needed for melting, leading to a predicted decrease in the melting point as the size decreases. There also, it is estimated that the nanowire will have the highest melting point, while the tetrahedral shape will have the lowest melting point. The influence of shape can be further understood by considering the relative surface area of different shapes. The tetrahedral shape, in particular, has a relatively larger surface area, while the nanowire shape has the smallest surface area. This means that the tetrahedral shape, with a higher number of atoms on its surface, experiences a greater decrease in comparison to the nanowire shape, which has fewer atoms on its surface. The definition of the shape factor implies that a larger shape factor corresponds to a greater surface area for a given particle size. Thus, the surface effect on the melting temperature of nanoparticles is intensified when the shape factor is larger. This intensification leads to a significant decrease in the melting temperature across a wide range.
Moreover, it has been observed that the impact of particle shape is more pronounced in smaller particles compared to larger ones. Our observation confirms the validity of our model, which considers voids within the crystal, dangling surface atoms, and shape factors simultaneously. Therefore, the thermal stability of a semiconductor nanomaterial is influenced by its packing factor, size, and shape. To effectively design and optimize semiconductor nanomaterials with specific properties, it is crucial to understand how their thermal stability changes with size.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, the bond energy model has been expanded comprehensively to include size, shape, and packing efficiency, providing a general approach to investigating thermophysical properties such as cohesive energy and melting point in semiconductor nanoparticles. Our research demonstrates that reducing the size of a material to the nanoscale significantly affects its properties. Furthermore, we observed that the shape of the particle becomes increasingly important for smaller nanoparticles. These changes in behavior are attributed to the dominant influence of surface effects at the nanoscale. Our model’s predictions align well with experimental data, simulations, and existing literature, confirming that the size, shape, surface atom relaxation, and packing efficiency of the crystalline structure influence the physical properties of nanosolids. This consistency demonstrates the model’s ability to predict the thermal stability of semiconductor nanomaterials exactly. The differences between predicted and experimental values can potentially be explained by examining several factors, such as quantum effects, defects, disorders, impurities, and strain. By incorporating these aspects into a comprehensive model, it becomes possible to analyze the thermophysical charact eristics of different-shaped semiconductor nanoparticles across a range of sizes that have not been previously explored. Gaining insight into how size and shape influence thermophysical properties is vital for efficiently designing and optimizing semiconductor nanomaterials with desired properties.
References
- S. Srivastava, P. Singh, A. K. Pandey, and C. K. Dixit, “Melting Temperature of Semiconducting Nanomaterials at different Shape and Size,” Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects, vol. 36, p. 101067, 2023.
- R. L. Jaiswal, B. K. Pandey, D. Mishra, and H. Fatma, “Thermo-physical Behavior of Nanomaterials with the Change in Size and Shape,” Int. J. Thermodyn., vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 1–7, 2021.
- P. Gharbani, A. Mehrizad, and S. A. Mosavi, “Optimization, kinetics and thermodynamics studies for photocatalytic degradation of Methylene Blue using cadmium selenide nanoparticles,” npj Clean Water, vol. 5, no. 1, p. 34, 2022.
- K. Pandey, S. Srivastava, C. K. Dixit, P. Singh, and S. Tripathi, “Shape and size dependent thermophysical properties of nanomaterials,” Iran. J. Sci., pp. 1–15, 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Pandey, C. K. Dixit, and S. Srivastava, “Theoretical model for the prediction of lattice energy of diatomic metal halides,” J. Math. Chem., pp. 1–6, 2023.
- T. Kumari, B. K. Pandey, J. Gupta, R. L. Jaiswal, and S. Shukla, “Unified model for the prediction of thermophysical properties of nanometals,” Solid State Commun., vol. 371, p. 115254, 2023.
- K. Pandey and R. L. Jaiswal, “Dimensional effect on cohesive energy, melting temperature and Debye temperature of metallic nanoparticles,” Phys. B Condens. Matter, vol. 651, p. 414602, 2023.
- Y. Wei, X.-P. Liu, C. Mao, H.-L. Niu, J.-M. Song, and B.-K. Jin, “Highly sensitive electrochemical biosensor for streptavidin detection based on CdSe quantum dots,” Biosens. Bioelectron., vol. 103, pp. 99–103, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. Ye, H. Zhen, and X. Liu, “Improved performance in green light-emitting diodes made with CdSe-conjugated polymer composite,” Synth. Met., vol. 158, no. 21–24, pp. 879–882, 2008.
- G. Nedelcu, “The heating study of two types of colloids with magnetite nanoparticles for tumours therapy,” Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 99–102, 2008.
- D. Dukes III, C. D. Pitts, A. B. Kapingidza, D. E. Gardner, and R. C. Layland, “Comparison of the observed size-dependent melting point of CdSe nanocrystals to theoretical predictions,” Eur. J. Chem., vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 39–43, 2018. [CrossRef]
- T. Bachels, H.-J. Güntherodt, and R. Schäfer, “Melting of isolated tin nanoparticles,” Phys. Rev. Lett., vol. 85, no. 6, p. 1250, 2000.
- H. K. Kim, S. H. Huh, J. W. Park, J. W. Jeong, and G. H. Lee, “The cluster size dependence of thermal stabilities of both molybdenum and tungsten nanoclusters,” Chem. Phys. Lett., vol. 354, no. 1–2, pp. 165–172, 2002.
- W. H. Qi and M. P. Wang, “Size and shape dependent melting temperature of metallic nanoparticles,” Mater. Chem. Phys., vol. 88, no. 2–3, pp. 280–284, 2004.
- J. Shanker and M. Kumar, “Studies on melting of alkali halides,” Phys. status solidi, vol. 158, no. 1, pp. 11–49, 1990.
- W. H. Qi, M. P. Wang, and G. Y. Xu, “Comment on ‘Size effect on the lattice parameters of nanoparticles,’” J. Mater. Sci. Lett., vol. 22, pp. 1333–1334, 2003.
- S. Mishra, B. K. S. Mishra, B. K. Pandey, R. L. Jaiswal, and J. Gupta, “Unified model for the studies of band gap of nanosolids with their varying shape and size,” Chem. Phys. Lett., p. 141177, 2024.
- Kittel and, P. McEuen, Introduction to solid state physics. John Wiley & Sons, 2018.
- S. C. Vanithakumari and K. K. Nanda, “A universal relation for the cohesive energy of nanoparticles,” Phys. Lett. A, vol. 372, no. 46, pp. 6930–6934, 2008.
- P. Poole and F. J. Owens, “Introduction to nanotechnology,” 2003.
- T. Vogel et al., “Ag-assisted CBE growth of ordered InSb nanowire arrays,” Nanotechnology, vol. 22, no. 1, p. 15605, 2010. [CrossRef]
- J. Lockwood, G. Yu, and N. L. Rowell, “Optical phonon frequencies and damping in AlAs, GaP, GaAs, InP, InAs and InSb studied by oblique incidence infrared spectroscopy,” Solid State Commun., vol. 136, no. 7, pp. 404–409, 2005.
- M. Singh and T. D. Phantsi, “Bond theory model to study cohesive energy, thermal expansion coefficient and specific heat of nanosolids,” Chinese J. Phys., vol. 56, no. 6, pp. 2948–2957, 2018.
- H. D. Berry and Q. Zhang, “Theoretical investigation of size and shape dependent melting temperature of transition metal clusters,” Solid State Commun., vol. 376, p. 115357, 2023.
- Y. Zhang, L.-M. Tang, F. Ning, D. Wang, and K.-Q. Chen, “Structural stability and electronic properties of InSb nanowires: A first-principles study,” J. Appl. Phys., vol. 117, no. 12, 2015.
- L. I. Ovsiannikova, “Atomic structure and cohesion energy of ZnSe and CdSe clusters,” Phys. Solid State, vol. 61, pp. 673–679, 2019.
- S. Sengul and S. S. Dalgic, “Size dependence of melting process of ZnSe nanowires: molecular dynamics simulations,” J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater., vol. 13, no. November-December 2011, pp. 1542–1547, 2011.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).