Graphical Abstract
1. Introduction
According to large-scale statistics on domestic dogs in Japan in 2023, 6.84 million dogs are kept as pets and 9.1% of households in Japan share their lives with dogs [
1]. Moreover, it is noteworthy that the total number of human children under the age of 15 was approximately 14.17 million, while the number of domesticated dogs and cats in 2023 was 15.91 million, exceeding the number of human children [
2]. Against this background, domestic dogs and cats are welcomed as family members just like humans and are sometimes raised with love in the same way as human children. Reflecting this trend, despite the recent economic downturn in Japan due to the weak yen and other factors, domestic dogs’ expenses, including medical expenses, have increased year on year [
3], and the number of contracts with pet insurance companies that cover medical expenses has also increased in the same manner [
4]. The above findings indicate that a society is developing in which dogs and cats are respected as much as humans and receive medical care and their welfare is looked after.
The medical care and welfare of domestic dogs lag behind that of humans but are slowly developing day by day and keeping pace with human medical advances. For example, drug treatment options for canine osteoarthritis have evolved over the past decade to keep pace with human medicine [
5]. Advances have also been made in the treatment of various canine cancers, which have improved life expectancy [
6,
7,
8]. While canine medicine has evolved, similar to human medicine, there are very few published papers on the development of testing and treatment methods for dog mitochondrial diseases.
Canine mitochondrial diseases are caused either congenitally or acquired due to mutations or defects in nuclear DNA, which encodes mitochondria-related genes, or in mitochondrial DNA. Mitochondrial damage resulting from such mutations can severely affect organs that are heavily dependent on oxidative metabolism, especially the brain, skeletal and cardiac muscles, sensory organs, and kidneys [
9]. Symptoms of mitochondrial disorders, also known as mitochondrial myopathy, include muscle weakness, gait disturbance, spontaneous pain, and a variety of other symptoms [
9]. In addition, it has been shown that canine cancers are associated with mutations in the mtDNA-encoded genetic and D-loop regions [
9]. Because these mutations in mtDNA present with a wide variety of symptoms including mild to severe symptoms, differential diagnosis is incredibly difficult and requires the development of reliable molecular tests [
9].
As a matter of course, in order to develop a treatment strategy for canine mitochondrial diseases, it is first necessary to establish a test method to aid in making an accurate differential diagnosis. In order to make a diagnosis, it is essential to examine the full-length integrity and mutations of mtDNA. Therefore, we previously established a method for resequencing the full length of mitochondrial DNA from canine oral mucosal DNA using a next-generation sequencer (NGS) to accurately decode sequences and mutations [
10]. This method may be of great help in the differential diagnosis of canine mitochondrial diseases. It could also be applied to identify individual dogs because mammalian mtDNA is maternally inherited.
However, the biological samples that can be collected from dogs are not limited to oral mucosal DNA. Various types of samples can be collected, including blood, skin tissue, urine, hair follicles, residual tissue after surgery, feces, etc. Nevertheless, it is recognized that many dogs show a lack of willingness to have their oral mucosal DNA collected. Therefore, we focused our attention on feces, which can be easily collected in the least invasive manner as a lightweight solid material.
Feces are a mixture of undigested food residues, intestinal bacteria, cholesterol, and fats [
11]. They also contain cellular debris detached from the intestinal mucosa and dead white blood cells [
11]. In addition, mammalian cell mtDNA copy numbers have been shown to be present in hundreds to thousands of copies per cell, although this depends on the specific tissue [
12,
13]. In other words, canine feces may contain high levels of mitochondrial DNA. In light of the above, it could be hypothesized that the whole mtDNA of dogs can be sequenced and decoded using DNA extracted and purified from feces. Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to establish a method to decode the whole mtDNA sequence using DNA obtained from canine feces.
As a result of the development of our method, the whole mtDNA sequence from the feces samples was successfully decoded with high accuracy. It is anticipated that this method will be utilized for the individual identification of dogs and the differentiation of mitochondrial diseases, which may prove advantageous for the future medical care and welfare of domestic dogs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Ethics
The following study was approved by the Animal Care Committee of Anicom Specialty Medical Institute Inc. (approval numbers: 2020-02, September 28, 2020; 2022-02, March 29, 2022). All owners who participated in the study were informed about the design of the study and their consent was obtained.
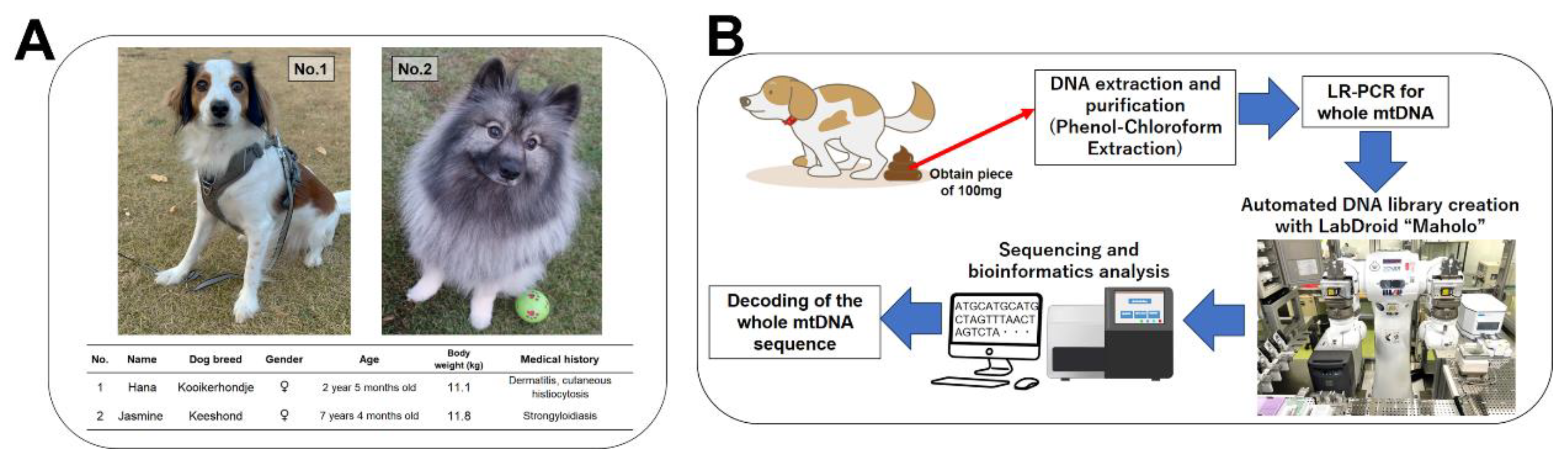
2.2. Subject Dogs and Collected Feces
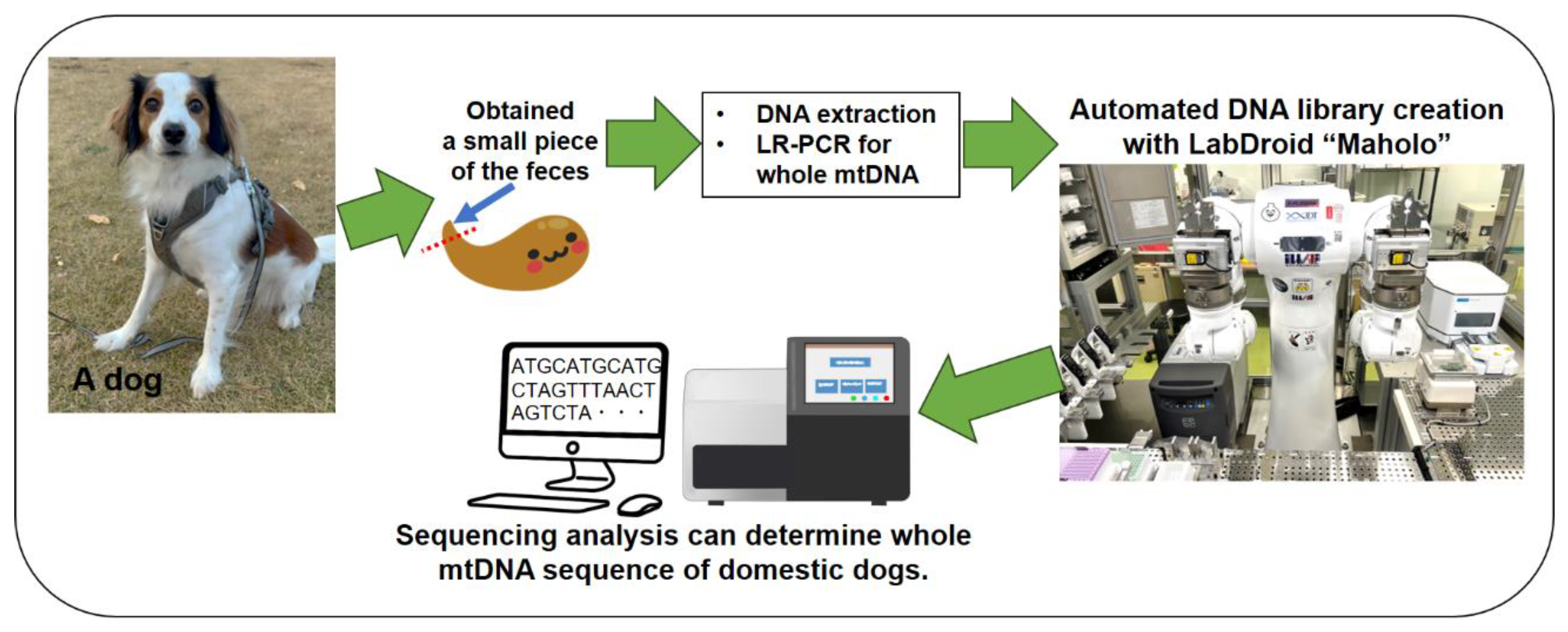
Two Japanese domestic dogs were enrolled in the present study. The breeds were Kooikerhondje and Keeshond. The age, medical history, weight, and other characteristics of the two dogs are shown in
Figure 1A together with photographs showing their appearance. Once each dog had defecated naturally, the feces were sealed in polyethylene bags at natural temperature and transported to our laboratory. Small pieces of feces (approximately 100 mg) were prepared within 1 hour of defecation and used for DNA extraction experiments. An overview of the fecal collection process and subsequent experimental steps is shown as a schematic in
Figure 1B.
2.3. DNA Extraction from the Feces
Fecal DNA was extracted and purified using a method previously reported by our research group [
10]. Approximately 100 mg of feces was homogenized in 500 μl of SNET buffer (10mM Tris, pH 8.0; 100 mM EDTA, pH 8.0; 1% SDS; 100 µg/ml Proteinase K) using crushing beads and bead crusher apparatus. The homogenate was then incubated at 56°C for 1 hour to degrade the protein. Following incubation, 500 μl of phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) solution (Cat# 25970-56; Nacalai Tesque, Nakagyo, Kyoto, Japan) was added and shaken vigorously for 15 seconds. The mixture was allowed to stand at room temperature for 10 minutes. The mixture was centrifuged at 12,000xg for 15 minutes and the supernatant, which is the aqueous layer, was aliquoted at 300 μl into new microtubes. The 300 ul aliquot was added to ribonuclease solution (at a final concentration of 10ug/ml) and then incubated at 37℃ for 10 min. Following this incubation procedure, the solution containing DNA was purified from the mixture using a NucleoSpin Gel and PCR Clean-up kit (Cat#U0609B; Takara Bio, Kusatsu, Shiga, Japan) in accordance with the manufacturer’s manual. Lastly, the DNA was eluted in 50 µL of Tris-HCl buffer (5 mM Tris, pH 8.5).
2.4. Analysis of DNA Integrity
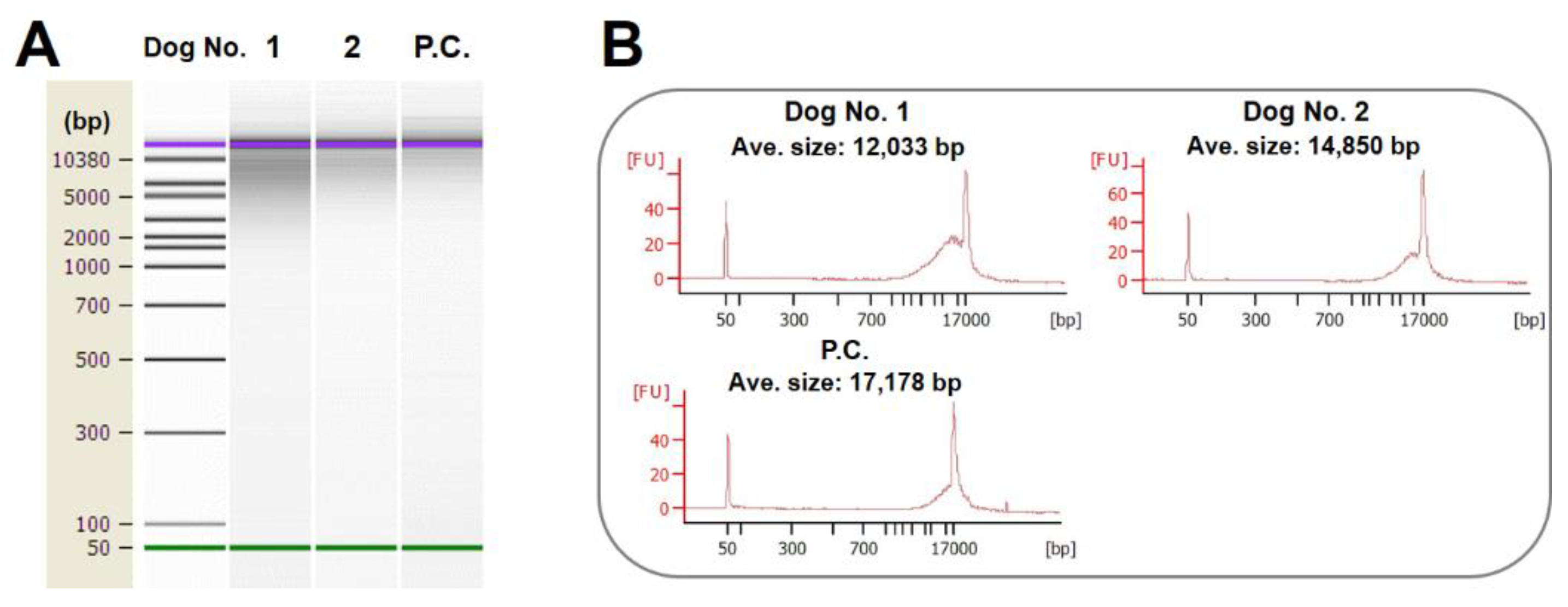
The concentration of the purified DNA was determined using a NanoDrop Lite spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Furthermore, to assess the integrity of the DNA, in particular, to examine any degradation or fragmentation, the purified DNA was analyzed using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) coupled with an Agilent DNA 12,000 Kit (Cat#5067-1508; Agilent Technologies). Moreover, intact mouse liver DNA was used as a positive control (intact DNA) during this analysis [
14].
2.5. LR-PCR for Whole mtDNA
Long-range polymerase chain reaction (LR-PCR) was performed according to our previously reported method [
10]. This LR-PCR, using four primer pairs, can amplify the full length of mtDNA [
10]. A summary of each primer sequence and target location is shown in
supplementary table S1 with sequences of the primer pairs. The information shown in
Table S1 is used with reference to our previous study [
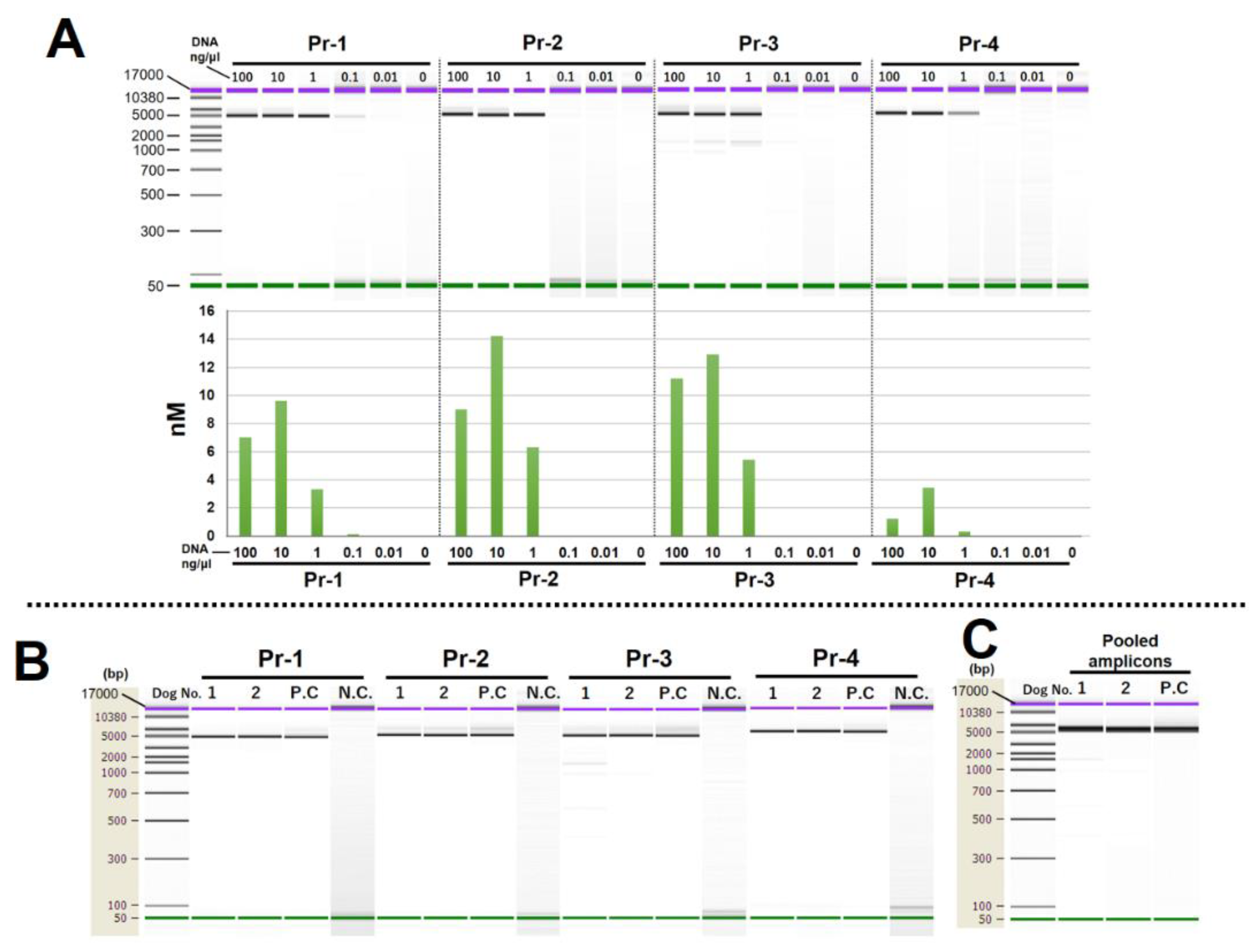
10]. First, to determine the optimal amount of template DNA, DNA from dog No. 1 was used, and serial dilutions of the template DNA were ranged from 0.01 to 100 ng/μl. The LR-PCR was performed using KOD One PCR Master Mix reagent (Cat# KMM-101; TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan), including a high-fidelity PCR enzyme. The template and reagent volume and primer concentrations were 2 and 10 µL and 300 nM, respectively, for a total reaction volume of 20 µL per reaction tube. A positive or negative control sample was also prepared using cell line DNA from the dog (1ng/ul) or Milli-Q water. The conditions for thermal cycling were as follows: 98 °C for 1 min, 5 cycles of 98 °C for 10 s and 74 °C for 30 s, 5 cycles of 98 °C for 10 s and 70 °C for 30 s, 5 cycles of 98 °C for 10 s and 72 °C for 30 s, 30 cycles of 98 °C for 10 s and 68 °C for 30 s, and 4 °C for ∞ [
10]. The size of the amplified products was electrophoresed in the same manner as described in
Section 2.4. to confirm specificity and optimal template concentration. As it was determined that 10 ng/ul was the optimal template DNA concentration in the experiment thus far, LR-PCR was repeated with the DNA concentrations of dogs No.1 and No. 2 (NucleoMag NGS clean-up and Size Select; Takara Bio) set at 10 ng/ul to obtain the desired amplified product. Thereafter, the amplified products were electrophoresed once again, and the concentration (nM) of the amplicon of interest was calculated and pooled so that each of the four amplicons was identical in terms of nM concentration. Following pooling, the amplicons were purified using 0.8 x beads (NucleoMag NGS clean-up and Size Select; Takara Bio) and eluted at 10 ul. The concentration of purified amplicons was measured with a nanodrop, adjusted to 10 ng/ul, and used in the subsequent experiment.
2.6. Preparation for DNA Library and NGS Run
Libraries were created for sequencing via NGS using adjusted and pooled amplicons. The library was created using 50 ng of pooled amplicon DNA. The reagent used to create the library was NEBNext Ultra II FS DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina (Cat# E7805S; New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA). An automatic experiment processing program that conforms to the protocol of this kit was established on LabDroid "Mahoro" (experimental robot; RBI, Koto City, Tokyo, Japan) to automate library creation (
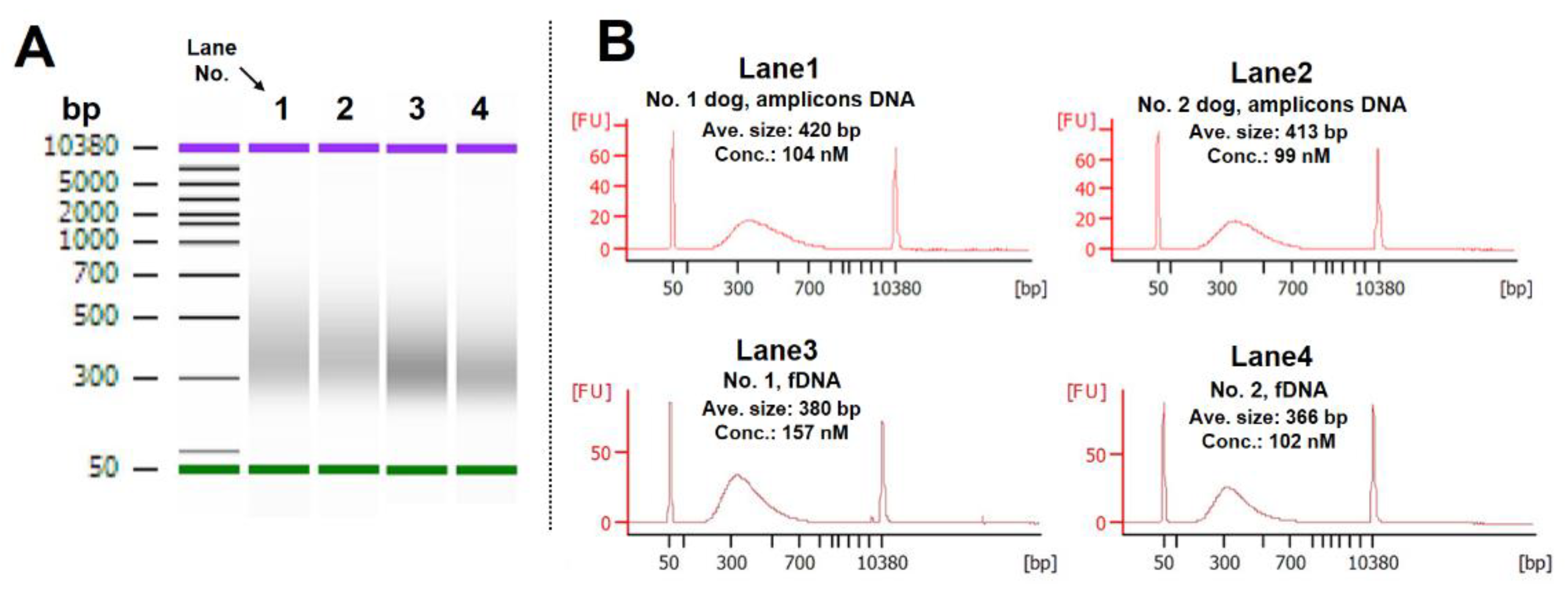
Figure 1B, lower right ). The fragmentation process time was set to 6 minutes in the protocol. In addition, 200 ng of fecal DNA not subjected to LR-PCR was used as a negative control sample, and the libraries were prepared using the same method. The created DNA library was analyzed using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer system (Agilent Technologies) with the Agilent DNA 7500 Kit (Cat#5067-1506; Agilent Technologies). Thereafter, the libraries were adjusted to 10 nM and pooled in an equal volume into one tube.
The pooled libraries were mixed with the PhiX Control v3 Library (final 10%; Cat# FC-110-3001, Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA), diluted to 1 nM, and then subjected to denaturation and neutralization processes. Subsequently, the libraries were diluted further to 1.4 pM and then applied to an NGS run using a MiniSeq Mid Output Kit (300 cycles) (Cat#FC-420-1004; Illumina) in the MiniSeq System (Illumina). Sequencing was performed with the paired-end reads of 150 bases. The cluster density was 264 K/mm2. In addition, the passing filter rate of over Q30 for the clusters was 91.36%, and the data yield was 5.15 G bases with 34.08 M paired-end reads. In addition, the mean quality score was 34.99. Overall, the NGS run was considered capable of obtaining high-quality data. Subsequently, FASTQ files were exported following the performance of further bioinformatics analyses.
2.7. Bioinformatics Analysis to Determine Whole mtDNA Sequence
The basic information of the NGS run data was confirmed with CLC Genomics Workbench 24.0 software (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany). During quality assessment of the reads, a PHRED score over 20 was confirmed for 99.8% of all reads, indicating the success of the run. The read numbers in the FASTQ files were 7.2 to 9.1 M per sample as paired-end reads. The resequencing analysis for the mtDNA was performed following procedures performed using CLC software. First, because the number of reads obtained on this occasion was predicted to be too high, we used the tool "Subsample Sequence List" to adjust all samples to 1 million reads on the FASTQ data. Thereafter, mapping was performed using the tool “Map Reads to Reference” with the general whole mtDNA sequences of the dogs [
15] to create BAM files. Subsequently, FASTA files including the whole mtDNA sequence were extracted using the tool “Extract Consensus Sequence” with a quality score. In addition, the tool “Alignments and Trees” was used to analyze whether the mtDNA sequence obtained from the feces was an exact match to the mtDNA sequence that we had previously determined from the oral mucosal DNA [
10]. Moreover, to visualize the uniformity of the mapping to the reference sequence, the tool “Create Track List” was used, and the figure included each sample and mitochondrial gene region.
3. Results
3.1. DNA Integrity
The average size of DNA extracted and purified from the feces of the two dogs was 12-14 kbp. In contrast, that of DNA extracted from intact mouse livers was 17 kbp (
Figure 2A, B). Moreover, severe fragmentation was not observed. The above results indicate that the DNA in the dogs’ feces was slightly degraded. However, it was considered of sufficient quality to be used in the subsequent experiment.
3.2. Optimization of LR-PCR
In LR-PCR with serial-diluted fecal DNA, a concentration of 10 ng/ul showed the highest amplification efficiency (
Figure 3A) on all primer pairs. The same LR-PCR procedure was then performed with DNA from the two dogs adjusted to the same concentration (10 ng/ul). In the results, amplified products were obtained with sufficient specificity on all primer pairs (
Figure 3B). The pooled amplicons were purified, and amplicons size was confirmed via electrophoresis, which revealed no issues and confirmed that the amplicons were pooled correctly (
Figure 3C).
3.3. The DNA Libraries Were Accurately Created by the LabDroid “Maholo”
The LabDroid “Maholo” was used to create DNA libraries using pooled amplicon DNA and fecal DNA. As shown in the results, DNA libraries ranging from 366 to 420 bp in average size were obtained, and this size range is considered as fully adaptable for sequencing (
Figure 4A, B). The above result suggested that the LabDroid “Maholo” performed the experimental operation accurately.
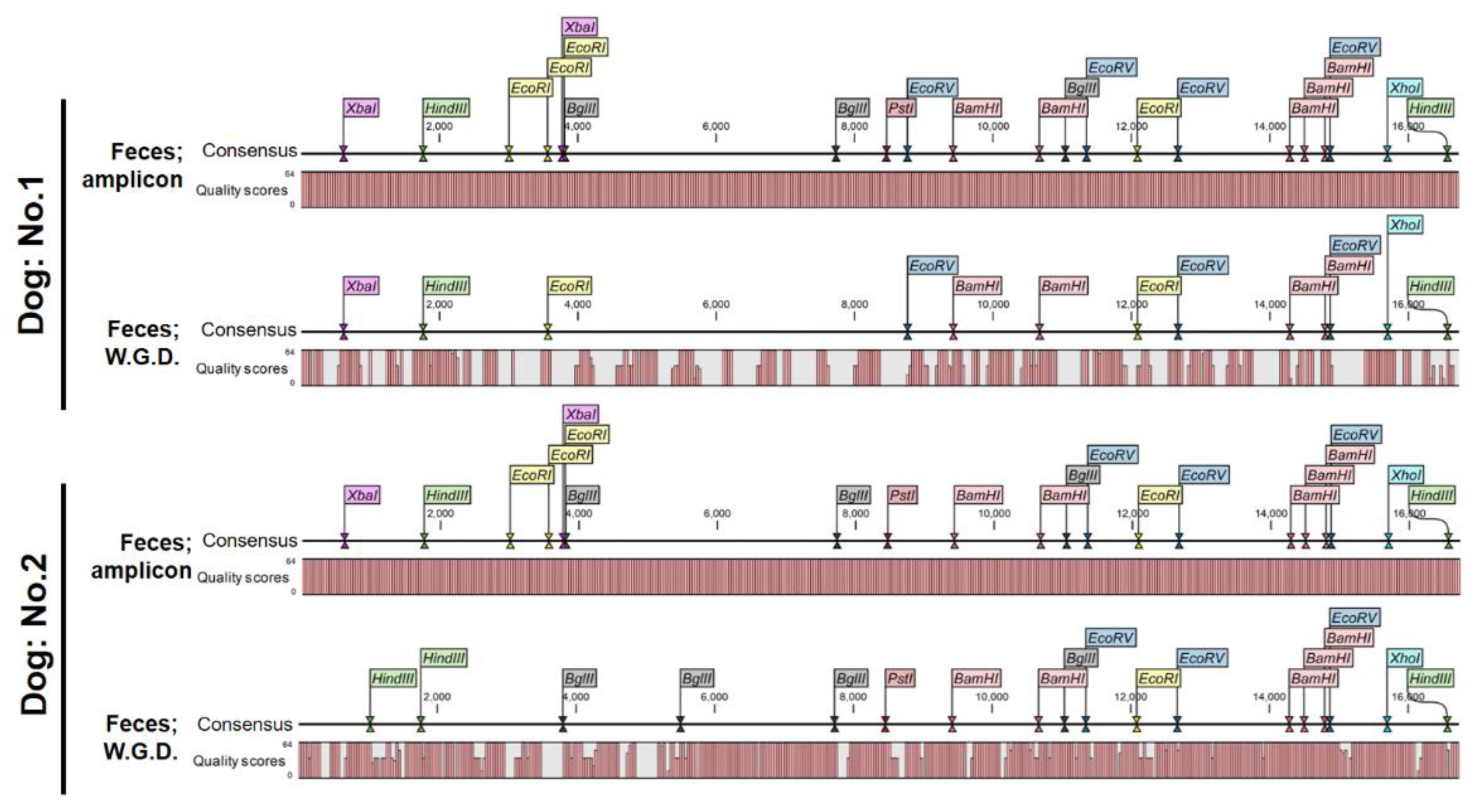
3.4. The Whole mtDNA Sequence of Both Dogs Was Accurately Determined
A consensus sequence was extracted from the BAM file following mapping based on the FASTQ data derived from the amplicons. As a result, the highest quality score of 64 points was observed at all base positions, and the whole mtDNA sequence of the two dogs was accurately determined (
Figure 5). In comparison, mapping using BAM files based on fecal DNA did not yield an accurate mtDNA sequence with a poor-quality score (
Figure 5). The above results indicate that LR-PCR is essential to accurately determine the whole mtDNA sequence.
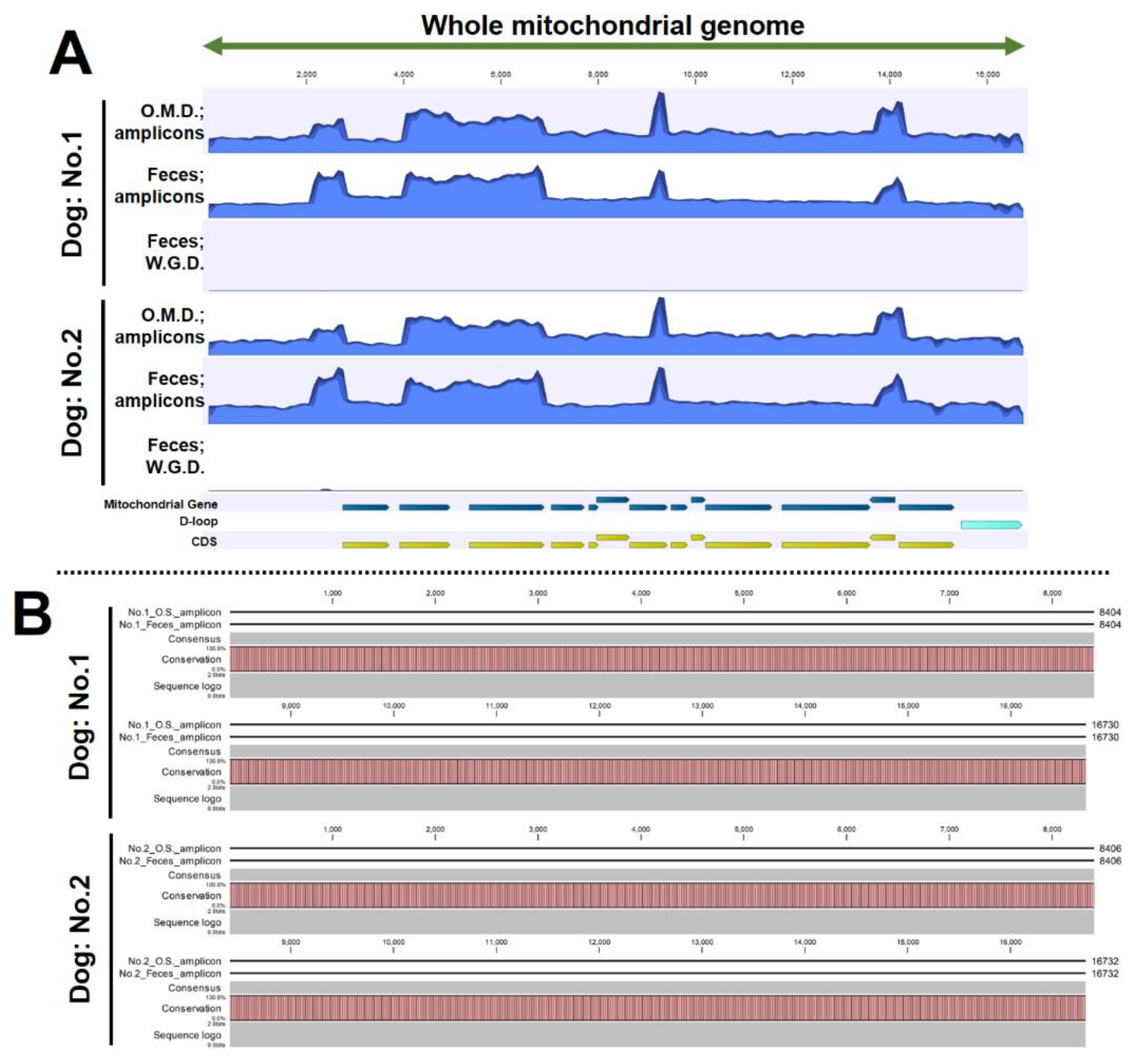
3.5. The Amplicon Sequencing of mtDNA Using Fecal DNA Provides Uniform Coverage and Accurate Sequencing
BAM files derived from the fecal DNA amplicons were visualized on the reference sequence. As a result, uniform coverage was observed in both dogs, including four overlapping locations. (
Figure 6A). Amplicon-derived BAM files of oral mucosal DNA were also visualized [
10], as previously reported by our research team, and similar coverage to that of the fecal DNA amplicons was found (
Figure 6A). However, the BAM file based on fecal DNA not subjected to LR-PCR failed to show a waveform of coverage. In addition, a comparison of sequences obtained from amplicon sequencing of fecal DNA (
Supplementary Data S1 and S2; FASTA files) with those obtained from amplicon sequencing of oral mucosal DNA [
10] showed complete match across all bases in the two dogs (
Figure 6B). The above results suggest that amplicon sequencing using fecal DNA can determine whole mtDNA sequences as accurately as that using oral mucosal DNA.
4. Discussion
The objective of the present study was to develop a method for determining the whole mtDNA sequence of domestic dogs using the least invasive fecal samples available. In addition, we used our previously successful sequencing data of whole mtDNA by using oral mucosal DNA [
10] and compared them to the data from the fecal samples in the present study to confirm their accuracy. As a result, we succeeded in obtaining whole-length mitochondrial DNA amplicons divided into four parts from fecal DNA. Library preparation using the amplicons was automated using an experimental robot, and we were able to obtain a library that can be adapted to next-generation sequencers. Through bioinformatics analysis using the data obtained from sequencing, we were able to accurately determine the mtDNA sequences derived from the feces of the two dogs. Furthermore, this mtDNA sequence was a perfect match to the sequence derived from the oral mucosal DNA. Taken together, these results indicate that the whole mtDNA sequence can be determined from fecal samples using the method established in the study presented herein. Feces represent the least invasive form of sampling and their acquisition does not cause stress to the dog. Therefore, in the future, the use of this method could lead to advancements in the medical care and welfare of dogs.
The use of this method yields four PCR amplicons containing the whole mtDNA sequence (including four duplicated regions), which can be sequenced using a next-generation sequencer. This principle is similar to our previously established method for whole mtDNA sequencing using oral mucosal DNA [
10]. However, we found one difference. In PCR using oral mucosal DNA, the highest amplification efficiency was observed when the template DNA concentration was 1 ng/ul (using 2 ng DNA/PCR reaction) [
10]. Conversely, when fecal DNA was used as a template in the present study, the highest amplification efficiency was achieved at a concentration of 10 ng/ul (using 20 ng DNA/PCR reaction). This difference is likely due to the high mix of DNA from different species in the fecal material, which may comprise food residue and bacteria. Bacteria in fecal solids, excluding water, are estimated to account for 30% of fecal material [
11]. Therefore, depending on the type of specimen, the template concentration should be optimized. In addition, although the two dogs in the present study were healthy on the day of the experiment, if the subject dogs in a study suffer from intestinal conditions/diseases such as diarrhea, constipation, inflammatory diseases, etc., the percentage of intestinal bacteria may vary substantially. If researchers use this method, they would need to first consider the optimal template DNA concentration to adapt to this situation.
The establishment of a non-invasive method of sequencing mtDNA from feces has the potential to promote the understanding and management of mitochondrial diseases in domestic dogs. Multiple mitochondrial diseases, such as myopathies, sensory ataxic neuropathy, cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmia, have been reported in domestic dogs and clinical symptoms are heterogeneous, causing difficulties in diagnosis. Many pathogenic mtDNA mutants have been identified in dogs; thus it is possible to diagnose mitochondrial diseases through genetic evaluation [
16]. To date, mitochondrial diseases are rarely found in domestic dogs. However, the significant health impact and frequency of human mitochondrial mutants combined with the genetic similarity between humans and dogs suggest that mitochondrial DNA alterations could also have a significant health impact on domestic dogs and the prevalence of mitochondrial diseases in dogs could be underestimated due to insufficient investigation. Thus, it would be beneficial to perform mitochondrial genetic analyses in veterinary clinics to better understand the genetic causes of diseases, consequently revealing the frequency of mitochondrial diseases. mtDNA genetic tests can also be used to discover genetic defects at an early stage in order to provide appropriate care and facilitate selective breeding programs for domestic dogs. Mitochondrial genetics are inherited entirely from the maternal line; therefore, mtDNA analysis can be performed prior to breeding to ensure the health of descendants.
From another perspective, the application of this method indicates the possibility of analyzing the DNA of other types of dogs using canine fecal samples, and it may be possible to study the epidemiology of stray dogs through fecal DNA analysis. The increase in the number of stray dogs is a public health concern in many countries. This concern emanates from the fact that stray dogs and cats usually carry infectious diseases such as parvovirus, distemper, and rabies, which can be transmitted to humans through human contact [
17,
18]. In parallel with controlling stray dog populations, monitoring the health epidemiology of stray dogs in the community by collecting fecal samples from such dogs and collecting fecal DNA could be a potential measure. Analysis of the diverse DNA present in fecal samples could aid in the identification of the genetic material of viral, bacterial, and parasitic pathogens and identify infections that these animals may have. In this way, zoonotic diseases in stray dogs in public spaces can be monitored and prevention and control measures can be rapidly implemented. Such measures would represent a means of not only protecting human health but also improving the welfare of this venerable friend of man, the animal. Fecal DNA analysis across different geographic regions is also useful for epidemiological surveillance, revealing patterns, trends, and emerging threats and allowing for timely response. Fecal DNA analysis thus has the potential to be part of a comprehensive strategy to protect the health and welfare of both humans and domestic and stray dogs. Therefore, in addition to mtDNA analysis, as employed in the present study, the authors of future studies will be able to reveal in depth the usefulness of fecal samples by employing NGS to quantify the presence and proportion of DNA in samples obtained from various species.
It is recognized that mitochondrial DNA in mammalian cells is inherited from the maternal line [
19]. The complete mitochondrial DNA sequences of a mother and her offspring exhibit a perfect match across their entire length, with the exception of instances where genetic disease is present. This finding was also corroborated in our previous research [
10]. Consequently, the method used in the present study is not only capable of identifying individual dogs but also tracing the blood relatives of dogs over many generations. Moreover, even in the absence of DNA sequence reference data, it is feasible to ascertain the presence of blood relatives if the DNA of the mother or siblings is available. In light of these considerations, it may also be feasible to address challenges at breeding facilities. For instance, at dog breeding facilities, there are instances where the maternal lineage of a puppy is uncertain such as mistaken puppies. In such cases, this method can be employed to ascertain the maternal lineage non-invasively. With such potential applications in mind, the method may prove beneficial in enhancing animal welfare in the future.
There is an interesting report on canine feces testing: In 2024, in Bolzano, northern Italy, the city’s police ordered all local dog owners to have their dogs’ fecal DNA tested in order to tackle the issue of dog feces left on the streets [
20]. This process facilitated the identification and fining of owners who had not picked up their dogs’ feces. The DNA test used in the above study appears to involve the use of a method to detect short tandem repeats (STRs); however, our method of decoding the entire mtDNA may also be applicable. Each test appears to have its advantages and disadvantages. Our method involves the use of NGS, which facilitates the sequencing of the mtDNA of hundreds of dogs at a time and enables high throughput. Furthermore, even if the DNA sequence of the target dog is not registered, it is possible to trace the blood relationship, which may lead to the identification of the owner. However, if the number of samples is small (e.g., less than 10), the cost per sample increases significantly. In addition, advanced skills in NGS and bioinformatics analysis are required. STR-targeted tests are simple and the results can be analyzed at low cost even with a small number of samples; however, they cannot identify dogs if their DNA sequences have not been registered. Thus, although each test has its advantages and disadvantages, using the two tests in different situations would help to obtain accurate evidence and achieve identification of the owner.
Another unique feature of the present study is the successful preparation of automated amplicon DNA libraries. DNA library preparation, when performed by human handlers, requires a high degree of skill and long hours of work. Therefore, there are significant barriers for beginners to perform this experiment. To solve this problem and compile the DNA library with simple operations, we used an experimental robot, LabDroid "Maholo" [
21]. Our study likely represents the first attempt to use LabDroid "Maholo" in veterinary medicine and animal welfare. The above robot was created by a Japanese venture company [
21] and specializes in molecular biology, biochemistry, and cell biology experiments. In recent years, the robot has been able to automatically create pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) [
22]- and iPSC-derived retinal pigment epithelial (iPSC-RPE) cells [
23,
24], and the LabDroid innovation is currently being conducted in Japan. In addition, the robot's user-friendly graphical interface allows researchers to create their own experimental programs from scratch. We successfully used this functionality to create an original amplicon DNA library. Experiments using the robot have also resulted in a significant reduction in operator time and thus a significant reduction in researcher labor. We hope to utilize this robot in the future for veterinary tests that require complex processes, thereby contributing to improvements in veterinary medicine and animal welfare.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, the results of our study show that the whole mtDNA sequence can be determined using fecal DNA from samples from domestic dogs with automated library preparation on the LabDroid " Maholo" and using NGS. Our findings suggest that feces can be adapted for mitochondrial disease and individual identification testing, and their use in testing could aid the future medical care and welfare of domestic dogs.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Table S1: Sequences of the primer pairs and target location; Data S1 and S2: FASTA files of the whole mtDNA sequence determined using fecal DNA obtained from the sample of the two dogs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S.; methodology, T.S., and K.N.; validation, T.S. and, K.N.; formal analysis, T.S., and K.N.; investigation, T.S., and T.T.; writing—original draft preparation, T.S., and K.N.; writing—review and editing, all authors; visualization, T.S., and K.N.; supervision, Y.K. and Y.T.; project administration, T.S and Y.K.; funding acquisition, T.S. and Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The following study was supported by the Research Foundation of Anicom Insurance Inc. (Japan). In addition, the research was partially supported by the academic budget of the Organization for Open Facility Initiatives, University of Tsukuba (academic year 2022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Anicom Specialty Medical Institute Inc. (approval number: 2020-02, date of approval: 28 September 2020; approval number 2022-02, date of approval 29 March 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all dog owners involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and
Supplementary Materials. In addition, the raw data from NGS (FASTQ, BAM, and BCL files) can only be distributed to individual researchers if they are used for research purposes.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Organization for Open Facility Initiatives, University of Tsukuba, for allowing us to use the various analyzers in this study. We would also like to express our gratitude to IWAI Chemicals Company Ltd. and Nikkyo Technos Co., Ltd., for performing the work quickly and accurately.
Conflicts of Interest
Not applicable.
References
- Key Indicator Summary, Survey of Dog and Cat Ownership in Japan, Japan Pet Food Association. Available online: https://petfood.or.jp/data/chart2023/index.html (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Is it true that the number of pets owned has surpassed the number of children born? Available online: https://renove-realcube.com/yomimono/7124/(accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Dog Breeding and Feeding Status and Expenditures, Survey of Dog and Cat Ownership in Japan, Japan Pet Food Association. Available online: https://petfood.or.jp/data/chart2023/index.html (accessed on 17 June 2024).
- Team of “White Paper on Household Animals 2023” project. White Paper on Household Animals 2023, 1st ed; Anicom Holdings, Inc.: Tokyo, Japan, 2024; pp.72.
- Pye, C.; Bruniges, N.; Peffers, M.; Comerford, E. Advances in the Pharmaceutical Treatment Options for Canine Osteoarthritis. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2022, 63, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulkerson, C.M.; Knapp, D.W. Management of Transitional Cell Carcinoma of the Urinary Bladder in Dogs: A Review. Vet. J. 2015, 205, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repasy, A.B.; Selmic, L.E.; Kisseberth, W.C. Canine Apocrine Gland Anal Sac Adenocarcinoma: A Review. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2022, 50, 100682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Nardi, A.B.; dos Santos Horta, R.; Fonseca-Alves, C.E.; de Paiva, F.N.; Linhares, L.C.M.; Firmo, B.F.; Ruiz Sueiro, F.A.; de Oliveira, K.D.; Lourenço, S.V.; De Francisco Strefezzi, R.; et al. Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment of Canine Cutaneous and Subcutaneous Mast Cell Tumors. Cells 2022, 11, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkaczyk-Wlizło, A.; Kowal, K.; Ślaska, B. Mitochondrial DNA Alterations in the Domestic Dog (Canis Lupus Familiaris) and Their Association with Development of Diseases: A Review. Mitochondrion 2022, 63, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugasawa, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Fang, H.; Takemasa, T.; Komine, R.; Tamai, S.; Gu, W.; Tanaka, K.; Kanki, Y.; Takahashi, Y. Establishing a Sequencing Method for the Whole Mitochondrial DNA of Domestic Dogs. Animals (Basel) 2023, 13, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. "feces". Encyclopedia Britannica, 21 May. 2024. https://www.britannica.com/science/feces. (accessed 17 June 2024).
- Kelly, R.D.W.; Mahmud, A.; McKenzie, M.; Trounce, I.A.; St John, J.C. Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number Is Regulated in a Tissue Specific Manner by DNA Methylation of the Nuclear-Encoded DNA Polymerase Gamma A. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 10124–10138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausser, S.; Trumpff, C.; McGill, M.A.; Junker, A.; Wang, W.; Ho, S.-H.; Mitchell, A.; Karan, K.R.; Monk, C.; Segerstrom, S.C.; et al. Mitochondrial Phenotypes in Purified Human Immune Cell Subtypes and Cell Mixtures. bioRxiv 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, N.; Kanki, Y.; Nguyen, K.D.M.; Sugasawa, T. Detection of Gene Doping Using Dried Blood Spots from a Mouse Model with rAAV9 Vector-Mediated Human Erythropoietin Expression as a Pilot Study. Analytica 2024, 5, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canis lupus familiaris Genome Assembly Dog10K_Boxer_Tasha. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/data-hub/genome/GCF_000002285.5/(accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Shelton, G.D.; Mickelson, J.R.; Friedenberg, S.G.; Cullen, J.N.; Mehra, J.M.; Guo, L.T.; Minor, K.M. Multi-Allelic Mitochondrial DNA Deletions in an Adult Dog with Chronic Weakness, Exercise Intolerance and Lactic Acidemia. Animals 2024, 14, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S. Stray Dogs Are a Growing Threat to Public Health. BMJ 2002, 325, 66l–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, G.S.; Singh, B.B.; Dhand, N.K.; Aulakh, R.S.; Ward, M.P.; Brookes, V.J. Stray Dogs and Public Health: Population Estimation in Punjab, India. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, D.C. Why Do We Still Have a Maternally Inherited Mitochondrial DNA? Insights from Evolutionary Medicine. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 781–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Italian province orders all dogs to be DNA tested in poo crackdown, Animals. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2024/jan/17/italian-province-orders-all-dogs-to-be-dna-tested-in-poo-crackdown (accessed on 17 Aug 2024).
- Yachie, N.; Robotic Biology Consortium; Natsume, T. Robotic Crowd Biology with Maholo LabDroids. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 310–312. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasamata, M.; Shimojo, D.; Fuse, H.; Nishi, Y.; Sakurai, H.; Nakahata, T.; Yamagishi, Y.; Sasaki-Iwaoka, H. Establishment of a Robust Platform for Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Research Using Maholo LabDroid. SLAS Technol. 2021, 26, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, M.; Kogawa, Y.; Shibata, Y.; Kitagawa, M.; Kato, S.; Iida, T.; Yorimitsu, T.; Kato, A.; Matsukuma, K.; Maeda, T.; et al. Robotic Cell Processing Facility for Clinical Research of Retinal Cell Therapy. SLAS Technol. 2023, 28, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, G.N.; Tsuzuki, T.; Terada, M.; Sakai, N.; Motozawa, N.; Masuda, T.; Nishida, M.; Watanabe, C.T.; Higashi, T.; Horiguchi, S.A.; et al. Robotic Search for Optimal Cell Culture in Regenerative Medicine. Elife 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).