Submitted:
26 August 2024
Posted:
26 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MIC Determination by Broth Microdilution and E-Test
2.2. Synergism Test
2.3. Biofilm Test, Biomass, and MTT
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolates
4.2. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
4.3. Synergism Test
4.4. Biofilm Test, Biomass, and MTT
4.5. MBEC
4.6. Estimation of Metabolic Activity by the MTT Reduction Assay
4.7. Biomass
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pedroni, M.A.; Ribeiro, V.S.T.; Cieslinski, J.; Lopes, A.P.A.; Kraft, L.; Suss, P.H.; Tuon, F.F. Different concentrations of vancomycin with gentamicin loaded PMMA to inhibit biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus and their implications. J Orthop Sci 2024, 29, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, J.F.; Ribeiro, V.S.T.; Cieslinski, J.; de Andrade, A.P.; Dantas, L.R.; Pereira, B.Z.; de Almeida, B.; Suss, P.H.; Tuon, F.F. Evaluation of silver nanoparticle-impregnated PMMA loaded with vancomycin or gentamicin against bacterial biofilm formation. Injury 2023, 54 Suppl 6, 110649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telles, J.P.; Cieslinski, J.; Tuon, F.F. Daptomycin to bone and joint infections and prosthesis joint infections: a systematic review. Braz J Infect Dis 2019, 23, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidar, R.; Der Boghossian, A.; Atiyeh, B. Duration of post-surgical antibiotics in chronic osteomyelitis: empiric or evidence-based? Int J Infect Dis 2010, 14, e752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuon, F.F.; Suss, P.H.; Telles, J.P.; Dantas, L.R.; Borges, N.H.; Ribeiro, V.S.T. Antimicrobial Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. Antibiotics (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuon, F.F.; Dantas, L.R.; Suss, P.H.; Tasca Ribeiro, V.S. Pathogenesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm: A Review. Pathogens 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.A.; Pust, T.M.; Cappellini, A.J.; Mandell, J.B.; Ma, D.; Shah, N.B.; Brothers, K.M.; Urish, K.L. Staphylococcus epidermidis Biofilms Have a High Tolerance to Antibiotics in Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Life (Basel) 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, R.; Yuan, Y.; Tarff, A.; Brayton, C.; Gour, N.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Y. Eradication of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Infection by Persister Drug Combination. Antibiotics (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, C.L.; Schmidt-Malan, S.M.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Patel, R. Rifampin-Based Combination Therapy Is Active in Foreign-Body Osteomyelitis after Prior Rifampin Monotherapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandell, J.B.; Orr, S.; Koch, J.; Nourie, B.; Ma, D.; Bonar, D.D.; Shah, N.; Urish, K.L. Large variations in clinical antibiotic activity against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms of periprosthetic joint infection isolates. J Orthop Res 2019, 37, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez-Carmona, M.A.; Mancheno-Losa, M.; Ruiz-Sorribas, A.; Munoz-Gallego, I.; Viedma, E.; Chaves, F.; Van Bambeke, F.; Lora-Tamayo, J. Strain-to-strain variability among Staphylococcus aureus causing prosthetic joint infection drives heterogeneity in response to levofloxacin and rifampicin. J Antimicrob Chemother 2022, 77, 3265–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez-Carmona, M.A.; Munoz-Gallego, I.; Viedma, E.; Lora-Tamayo, J.; Chaves, F. Intraosteoblastic activity of levofloxacin and rifampin alone and in combination against clinical isolates of meticillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus causing prosthetic joint infection. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2019, 54, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lora-Tamayo, J.; Euba, G.; Cobo, J.; Horcajada, J.P.; Soriano, A.; Sandoval, E.; Pigrau, C.; Benito, N.; Falgueras, L.; Palomino, J.; et al. Short- versus long-duration levofloxacin plus rifampicin for acute staphylococcal prosthetic joint infection managed with implant retention: a randomised clinical trial. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2016, 48, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turban, A.; Guerin, F.; Dinh, A.; Cattoir, V. Updated Review on Clinically-Relevant Properties of Delafloxacin. Antibiotics (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Siala, W.; Tulkens, P.M.; Van Bambeke, F. A combined pharmacodynamic quantitative and qualitative model reveals the potent activity of daptomycin and delafloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2013, 57, 2726–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, S.; Tulkens, P.M.; Van Bambeke, F. Contrasting effects of acidic pH on the extracellular and intracellular activities of the anti-gram-positive fluoroquinolones moxifloxacin and delafloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2011, 55, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslinski, J.; Ribeiro, V.S.T.; Kraft, L.; Suss, P.H.; Rosa, E.; Morello, L.G.; Pillonetto, M.; Tuon, F.F. Direct detection of microorganisms in sonicated orthopedic devices after in vitro biofilm production and different processing conditions. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 2021, 31, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha, L.; Ribeiro, V.S.T.; de Andrade, A.P.; Goncalves, G.A.; Kraft, L.; Cieslinski, J.; Suss, P.H.; Tuon, F.F. Evaluation of Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans biofilms adherence to PEEK and titanium-alloy prosthetic spine devices. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 2022, 32, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonca, J.R.; Dantas, L.R.; Tuon, F.F. Activity of multipurpose contact lens solutions against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens and Candida albicans biofilms. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2023, 43, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikdar, R.; Elias, M.H. Evidence for Complex Interplay between Quorum Sensing and Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol Spectr 2022, 10, e0126922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, R.; Farahani, A. Study of genetic diversity, biofilm formation, and detection of Carbapenemase, MBL, ESBL, and tetracycline resistance genes in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from burn wound infections in Iran. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control 2019, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, N.; Oe, K.; Nakamura, T.; Tsuta, K.; Iida, H.; Saito, T. Sonication of Extracted Implants Improves Microbial Detection in Patients With Orthopedic Implant-Associated Infections. J Arthroplasty 2019, 34, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valour, F.; Trouillet-Assant, S.; Riffard, N.; Tasse, J.; Flammier, S.; Rasigade, J.P.; Chidiac, C.; Vandenesch, F.; Ferry, T.; Laurent, F. Antimicrobial activity against intraosteoblastic Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2015, 59, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora-Tamayo, J.; Parra-Ruiz, J.; Rodriguez-Pardo, D.; Barberan, J.; Ribera, A.; Tornero, E.; Pigrau, C.; Mensa, J.; Ariza, J.; Soriano, A. High doses of daptomycin (10 mg/kg/d) plus rifampin for the treatment of staphylococcal prosthetic joint infection managed with implant retention: a comparative study. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2014, 80, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Manso, D.; del Prado, G.; Ortiz-Perez, A.; Manrubia-Cobo, M.; Gomez-Barrena, E.; Cordero-Ampuero, J.; Esteban, J. In vitro susceptibility to antibiotics of staphylococci in biofilms isolated from orthopaedic infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2013, 41, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaton, R.A.; Malizos, K.N.; Viale, P.; Gargalianos-Kakolyris, P.; Santantonio, T.; Petrelli, E.; Pathan, R.; Heep, M.; Chaves, R.L. Daptomycin use in patients with osteomyelitis: a preliminary report from the EU-CORE(SM) database. J Antimicrob Chemother 2013, 68, 1642–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, B.R.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcal biofilm disassembly. Trends Microbiol 2011, 19, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampedro, M.F.; Huddleston, P.M.; Piper, K.E.; Karau, M.J.; Dekutoski, M.B.; Yaszemski, M.J.; Currier, B.L.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Osmon, D.R.; McDowell, A.; et al. A biofilm approach to detect bacteria on removed spinal implants. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010, 35, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, S.C. Formation of biofilms by Staphylococcus aureus on stainless steel and glass surfaces and its resistance to some selected chemical sanitizers. Braz J Microbiol 2007, 38, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.M.; Saini, V.; Ashbaugh, A.G.; Miller, R.J.; Ordonez, A.A.; Ortines, R.V.; Wang, Y.; Sterling, R.S.; Jain, S.K.; Miller, L.S. Oral-Only Linezolid-Rifampin Is Highly Effective Compared with Other Antibiotics for Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Study of a Mouse Model. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2017, 99, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, S.; Sorli, L.; Horcajada, J.P. High-dose daptomycin together with rifampin as salvage therapy for prosthetic joint infections. Med Clin (Barc) 2017, 149, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudjemaa, R.; Briandet, R.; Revest, M.; Jacqueline, C.; Caillon, J.; Fontaine-Aupart, M.P.; Steenkeste, K. New Insight into Daptomycin Bioavailability and Localization in Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms by Dynamic Fluorescence Imaging. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2016, 60, 4983–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C.; Makarewicz, O.; Forstner, C.; Weis, S.; Hagel, S.; Loffler, B.; Pletz, M.W. Should daptomycin-rifampin combinations for MSSA/MRSA isolates be avoided because of antagonism? Infection 2016, 44, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh-Mghir, A.; Muller-Serieys, C.; Dinh, A.; Massias, L.; Cremieux, A.C. Adjunctive rifampin is crucial to optimizing daptomycin efficacy against rabbit prosthetic joint infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2011, 55, 4589–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrest, G.N.; Tamura, K. Rifampin combination therapy for nonmycobacterial infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 2010, 23, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachaki, I.; Vacchelli, M.; Zinzi, D.; Falla, E.; Jiang, Y.; Mantopoulos, T.; Nathwani, D. Comparative efficacy of delafloxacin for complicated and acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections: results from a network meta-analysis. BMC Infect Dis 2021, 21, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravolatz, L.D.; Pawlak, J.M.; Wegner, C. Delafloxacin activity against Staphylococcus aureus with reduced susceptibility or resistance to methicillin, vancomycin, daptomycin or linezolid. J Antimicrob Chemother 2020, 75, 2605–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, J.A.W.; da Cunha, M.; de Moraes, T.P.; Marques, S.; Tuon, F.F.; Gomide, A.L.; de Paula Linhares, G. Brazilian private health system: history, scenarios, and trends. BMC Health Serv Res 2022, 22, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loesch, G.H.; Cruz, J.A.W.; Gasparetto, J.; Oliveira, D.D.S.; Telles, J.P.; Tuon, F.F. Cost minimization analysis of outpatient parenteral/oral antibiotic therapy at a trauma hospital: Public health system. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2021, 42, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coustilleres, F.; Renault, V.; Corvec, S.; Dupieux, C.; Simoes, P.M.; Lartigue, M.F.; Plouzeau-Jayle, C.; Tande, D.; Lamoureux, C.; Lemarie, C.; et al. Clinical, Bacteriological, and Genetic Characterization of Bone and Joint Infections Involving Linezolid-Resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis: a Retrospective Multicenter Study in French Reference Centers. Microbiol Spectr 2023, 11, e0419022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Zorrilla, S.; Sendra, E.; Horcajada, J.P. A profile of delafloxacin in the treatment of adults with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 2022, 15, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.C.; Lin, J.; Yannuzzi, N.A.; Al-Khersan, H.; Patel, N.A.; Maestre-Mesa, J.; Zaidi, M.; Miller, D.; Flynn, H.W., Jr. In vitro Susceptibilities of Methicillin-Susceptible and Resistant Staphylococci to Traditional Antibiotics Compared to a Novel Fluoroquinolone. J Ophthalmic Inflamm Infect 2020, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechmechani, S.; Yammine, J.; Alhuthali, S.; El Mouzawak, M.; Charvourou, G.; Ghasrsallaoui, A.; Chihib, N.E.; Doulgeraki, A.; Karam, L. Study of the Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm, Biofilm-Detached Cells, and Planktonic Cells to Microencapsulated Carvacrol Used Alone or Combined with Low-pH Treatment. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Grajera, M.; Pacha-Olivenza, M.A.; Fernandez-Calderon, M.C.; Gonzalez-Martin, M.L.; Gallardo-Moreno, A.M. Dynamic Adhesive Behavior and Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus aureus on Polylactic Acid Surfaces in Diabetic Environments. Materials (Basel) 2024, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, E.; Perez, M.; Sanz, J.C.; Delgado-Iribarren, A.; Rodriguez-Avial, I. Efficacy of delafloxacin alone and in combination with cefotaxime against cefotaxime non-susceptible invasive isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Rev Esp Quimioter 2024, 37, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siala, W.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.P.; Tulkens, P.M.; Hallin, M.; Denis, O.; Van Bambeke, F. Comparison of the antibiotic activities of Daptomycin, Vancomycin, and the investigational Fluoroquinolone Delafloxacin against biofilms from Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014, 58, 6385–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparetto, J.; Bressianini Jurkonis, L.; Ramos Dantas, L.; Hansen Suss, P.; Francisco Tuon, F. Low-cost antiseptic-impregnated tracheostomy tube for the prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria: In vitro and pilot study in humans. Rev Argent Microbiol 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Clinical Laboratory Standard Insitute - M07 - A10 - Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Suceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically. 2015.
- EUCAST. Clinical breakpoint. European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing 2021, Version 11.
- Orhan, G.; Bayram, A.; Zer, Y.; Balci, I. Synergy tests by E test and checkerboard methods of antimicrobial combinations against Brucella melitensis. J Clin Microbiol 2005, 43, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiben, V.; Yamada, C.H.; Telles, J.P.; de Andrade, A.P.; Arend, L.; Ribeiro, V.S.T.; Dantas, L.R.; Suss, P.H.; Tuon, F.F. A carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii outbreak associated with a polymyxin shortage during the COVID pandemic: an in vitro and biofilm analysis of synergy between meropenem, gentamicin and sulbactam. J Antimicrob Chemother 2022, 77, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, E.G.; Shulman, S.T.; Yogev, R. Correlation of antibiotic synergy in vitro and in vivo: use of an animal model of neutropenic gram-negative sepsis. J Infect Dis 1986, 154, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.F.; Henriques, M. Liposomal and Deoxycholate Amphotericin B Formulations: Effectiveness against Biofilm Infections of Candida spp. Pathogens 2017, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traba, C.; Liang, J.F. Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms to reactive discharge gases. Biofouling 2011, 27, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, G.D.; Simpson, W.A.; Younger, J.J.; Baddour, L.M.; Barrett, F.F.; Melton, D.M.; Beachey, E.H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J Clin Microbiol 1985, 22, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
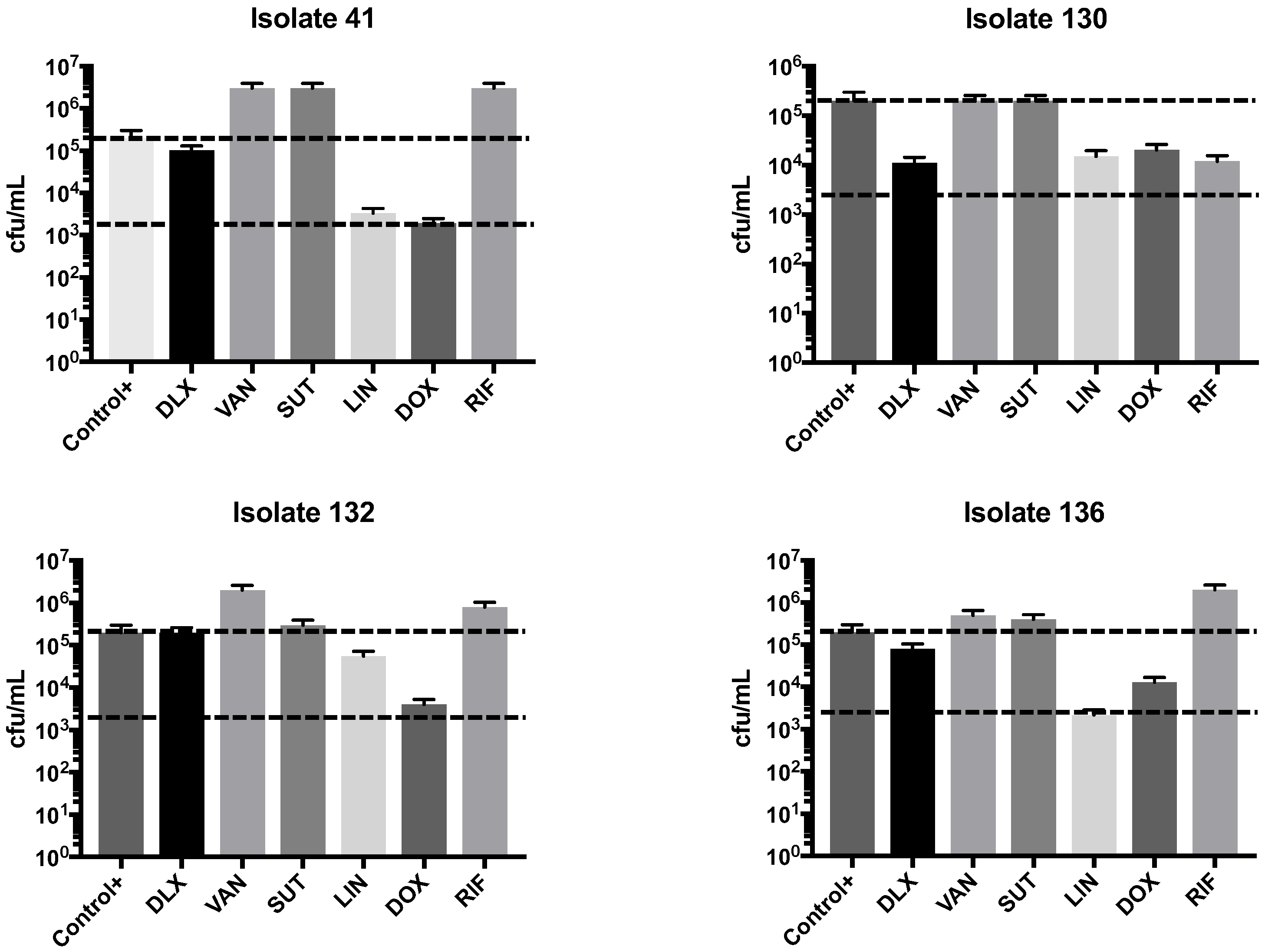
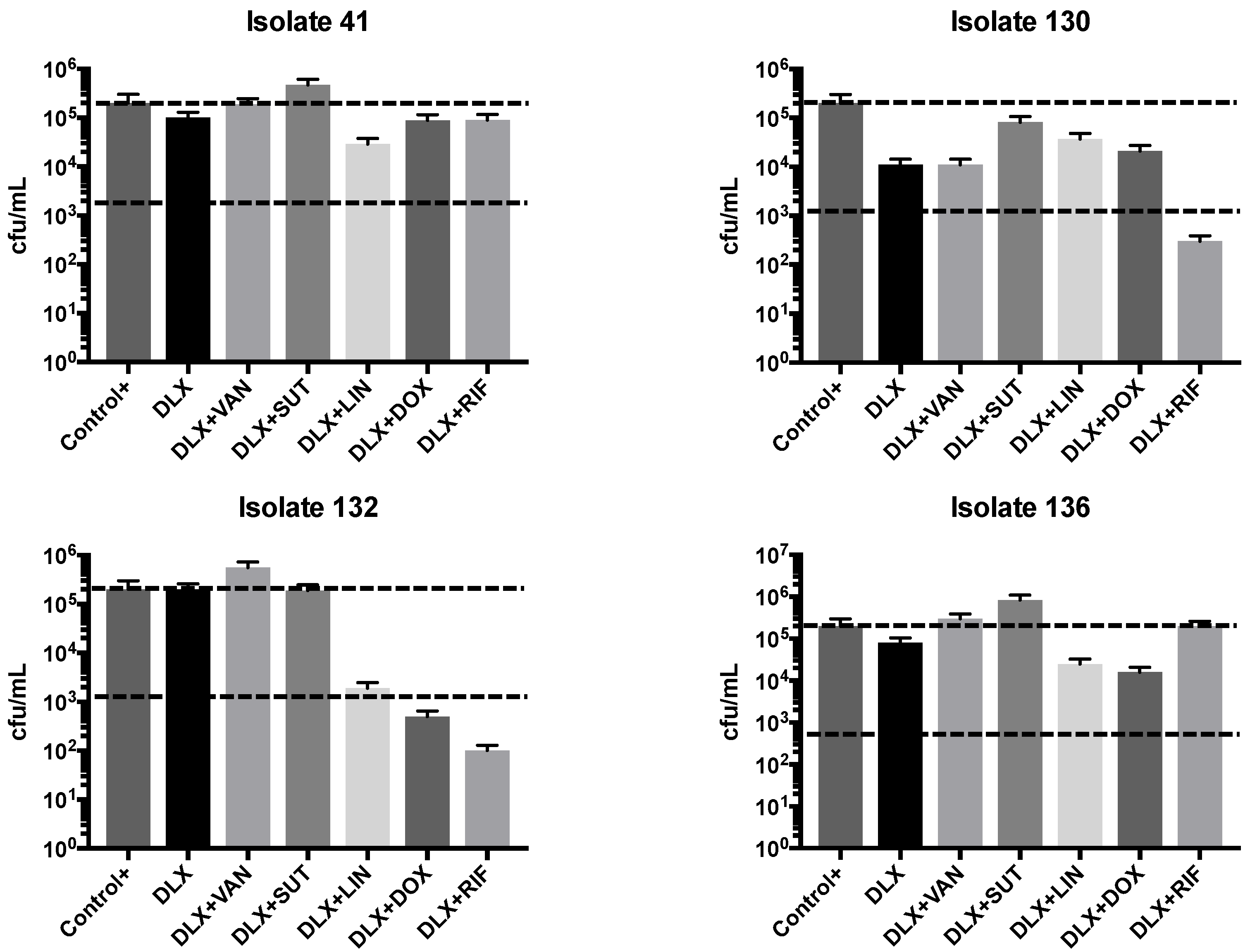
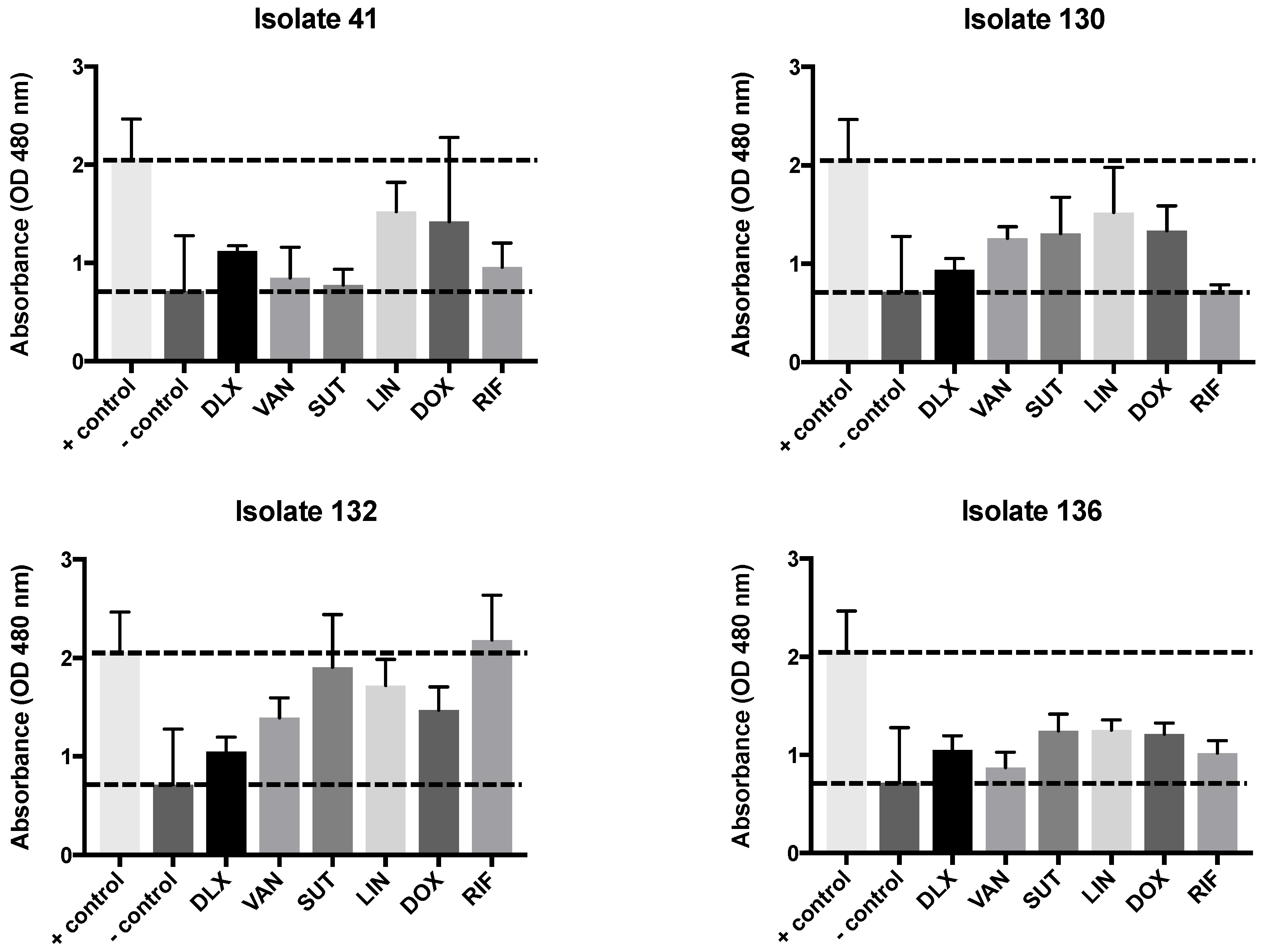

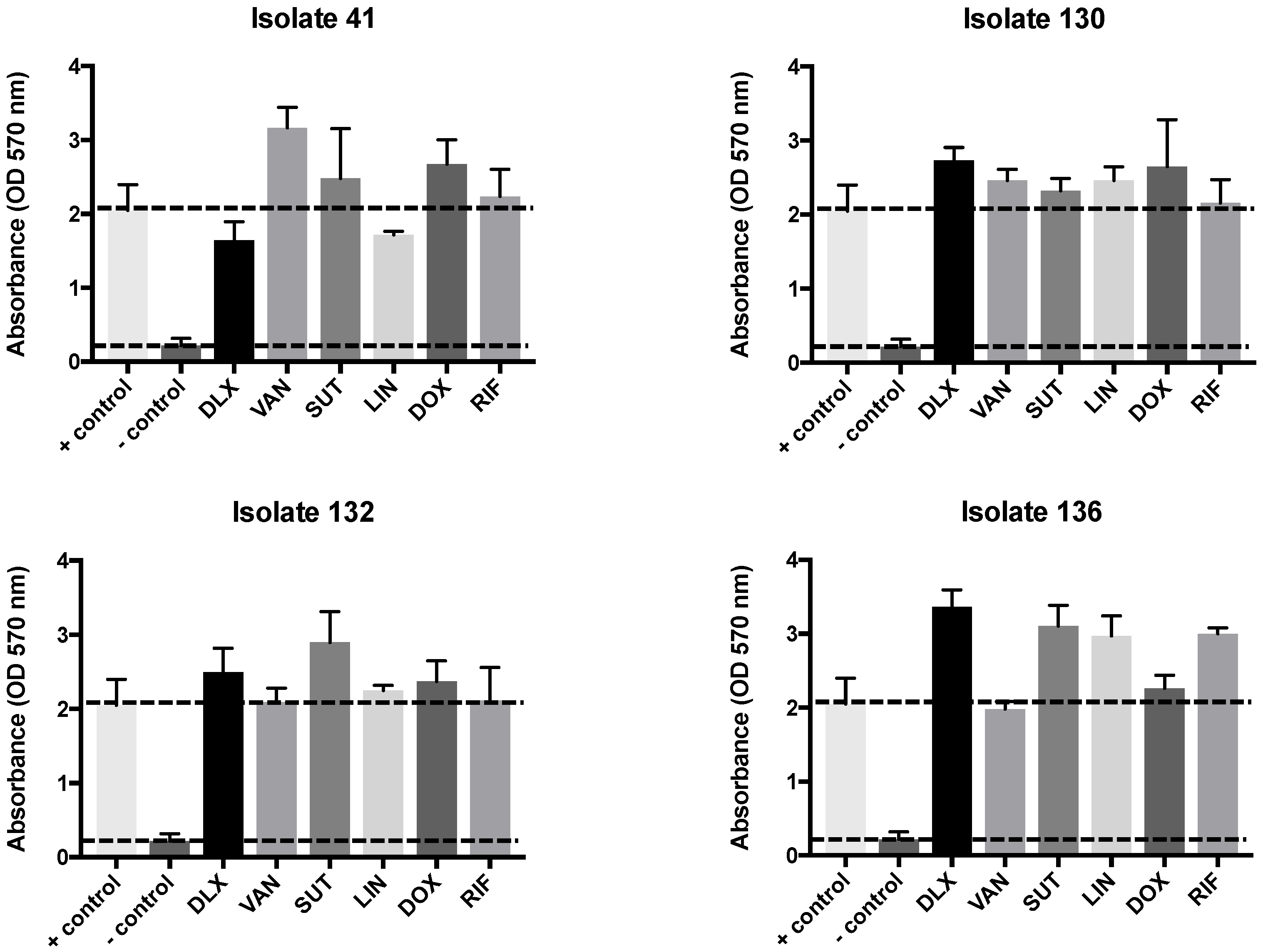

| Clinical Isolates | VAN | LNZ | SMX-TMP | DOX | RIF | DLX pH 7.4 | DLX pH 5.5 | DLX Etest | Dilutions pH 7.4 to 5.5 |
| (µg/mL) | (µg/mL) | (µg/mL) | (µg/mL) | (µg/mL) | (µg/mL) | (µg/mL) | (µg/mL) | ||
| 2 | 0.5 (S) | 2.0 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.125 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 2.0 (R) | 0.5 (R) | 2.0 (R) | 2x |
| 3 | 0.5 (S) | 2.0 (S) | 1.0 (S) | 0.125 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 2.0 (R) | 0.5 (R) | 2.0 (R) | 2x |
| 49 | 0.5 (S) | 2.0 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.125 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 2.0 (R) | 0.5 (R) | 2.0 (R) | 2x |
| 41 | 0.5 (S) | 1.0 (S) | 32 (R) | 4.0 (R) | 2.0 (R) | 0.25 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 0.125 (S) | 3x |
| 57 | 0.5 (S) | 2.0 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.125 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 2.0 (R) | 1.0 (R) | 2.0 (R) | 1x |
| 71 | 0.5 (S) | 4.0 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.125 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 2.0 (R) | 0.5 (R) | 2.0 (R) | 2x |
| 80 | 0.5 (S) | 2.0 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.125 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 2.0 (R) | 0.5 (R) | 2.0 (R) | 2x |
| 102 | 0.5 (S) | 4.0 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.25 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 2.0 (R) | 0.5 (R) | 2.0 (R) | 2x |
| 130 | 0.5 (S) | 4.0 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.125 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 0.004 (S) | 0.004 (S) | 0.002 (S) | 0 |
| 132 | 1.0 (S) | 2.0 (S) | 1.0 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 0.25 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 0.19 (S) | 2x |
| 136 | 0.5 (S) | 2.0 (S) | 32 (R) | 1.0 (S) | 2.0 (R) | 0.25 (S) | 0.015 (S) | 0.125 (S) | 4x |
| 156 | 0.5 (S) | 2.0 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.125 (S) | 0.03 (S) | 2.0 (R) | 0.5 (R) | 2.0 (R) | 2x |
| VAN | LNZ | SMX-TMP | DOX | RIF | |
| Isolate | ∑CIF | ∑CIF | ∑CIF | ∑CIF | ∑CIF |
| 2 | 1.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 0.75 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 49 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 41 | 0.5 | 1.25 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 57 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.4 | 1 |
| 71 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 80 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 102 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 130 | 1.25 | 1 | 2 | 1.5 | 2 |
| 132 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 | 1 |
| 136 | 1.25 | 1 | 1 | 1.5 | 1 |
| 156 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





